Investigation of Key Components in Class A Foam for Synergistic Wetting and Adhesion: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Case
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental and Methods
2.1. Materials
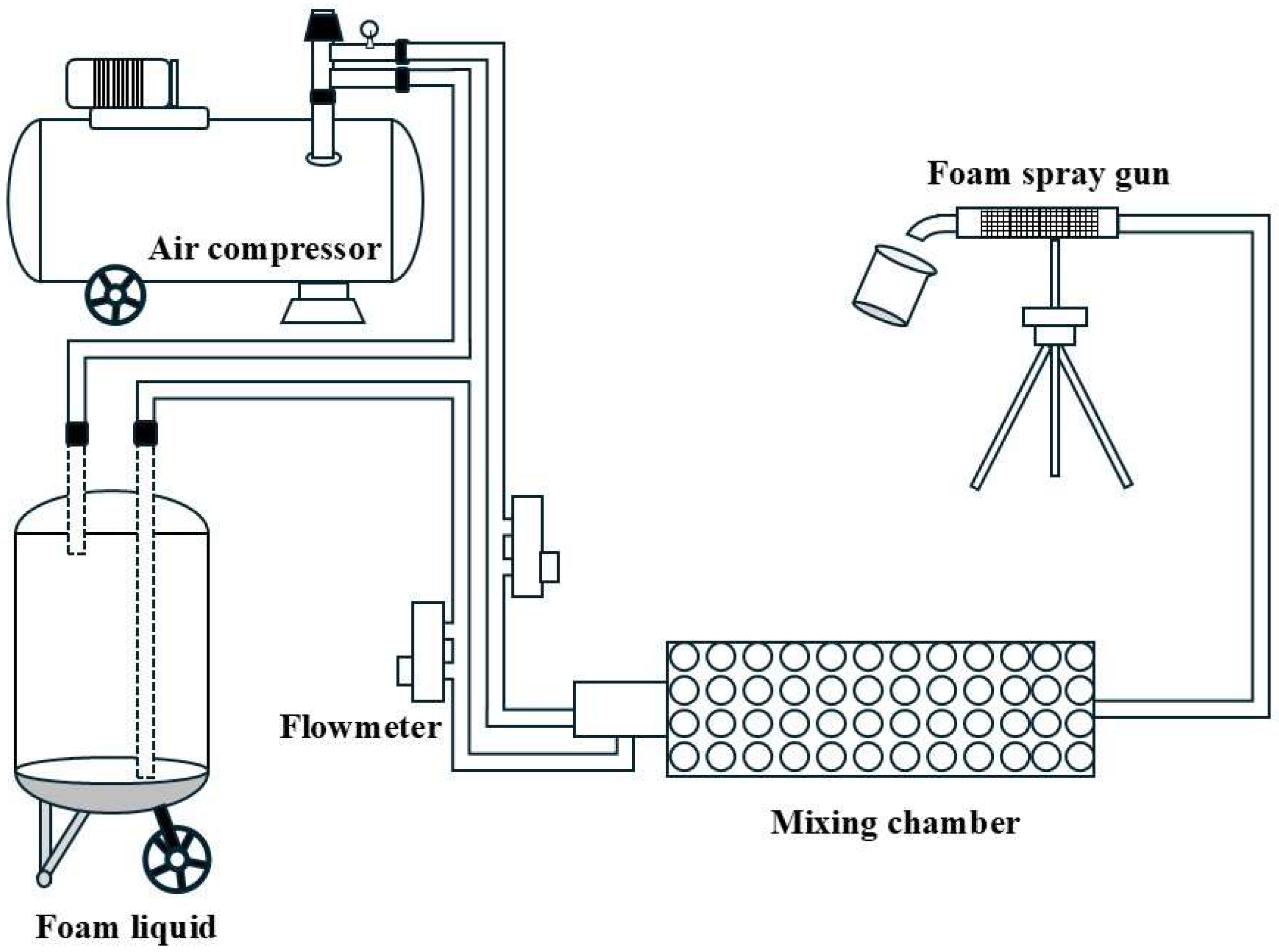
2.2. Formulation of Foam Concentrate
2.3. Surface Tension
2.4. Viscosity
2.5. Wetting Time
2.6. Foam Multiplier
2.7. MD Simulation Details
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Selection of Critical Foam Components Guided by Physicochemical Parameters
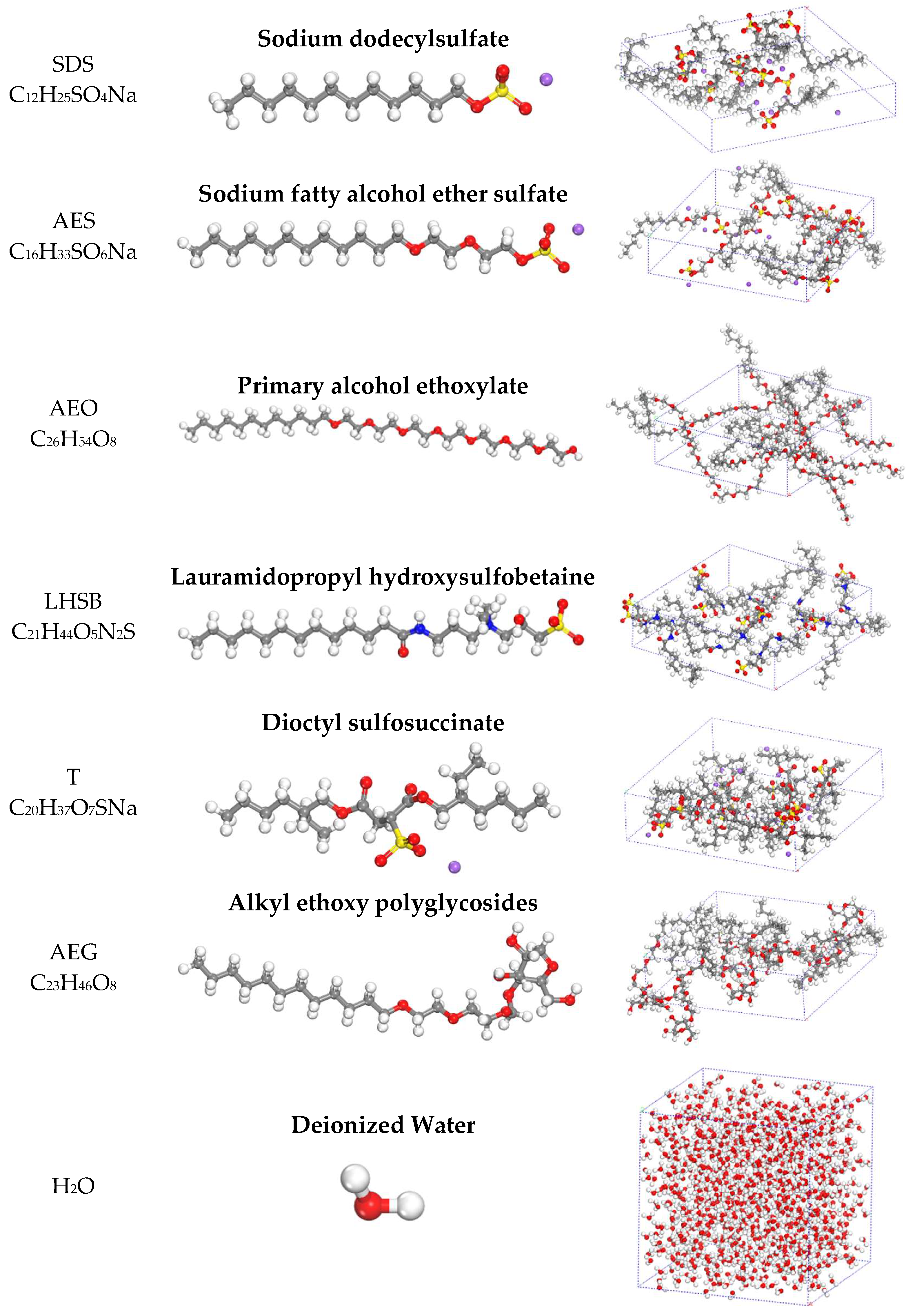
3.2. Molecular Modeling of Key Components in Foam Formulations
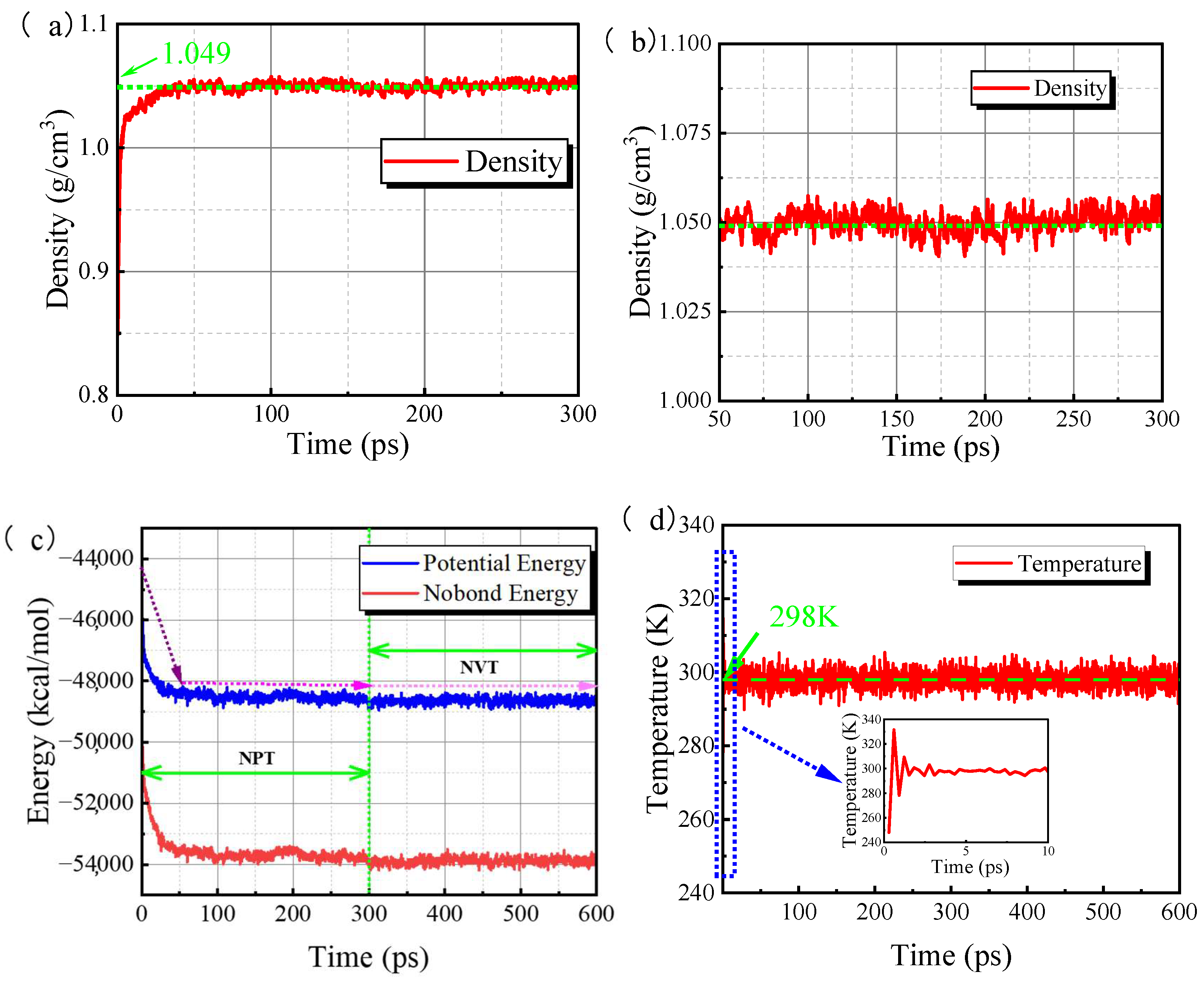
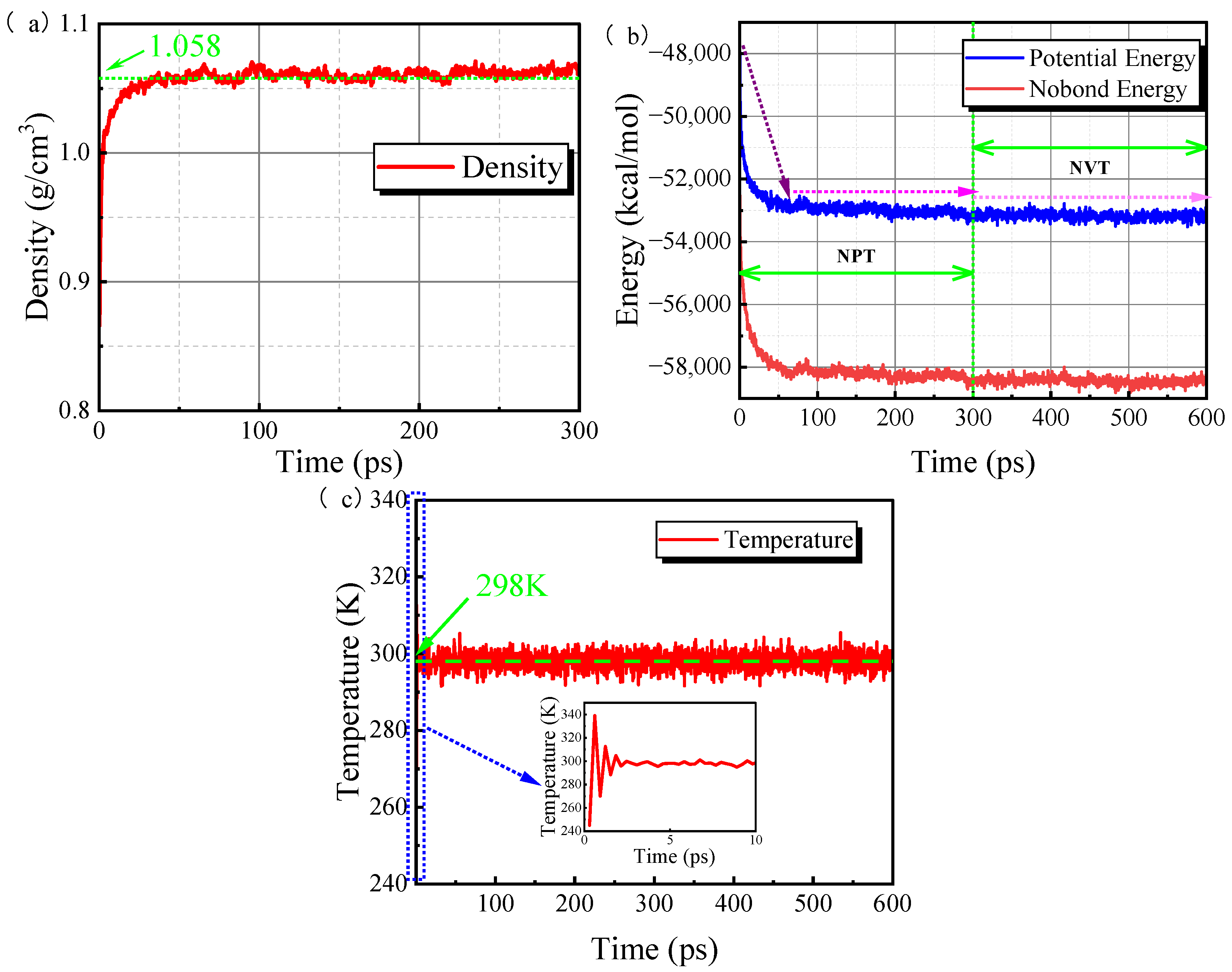
3.3. System Equilibrium Processes
3.4. Radial Distribution Function
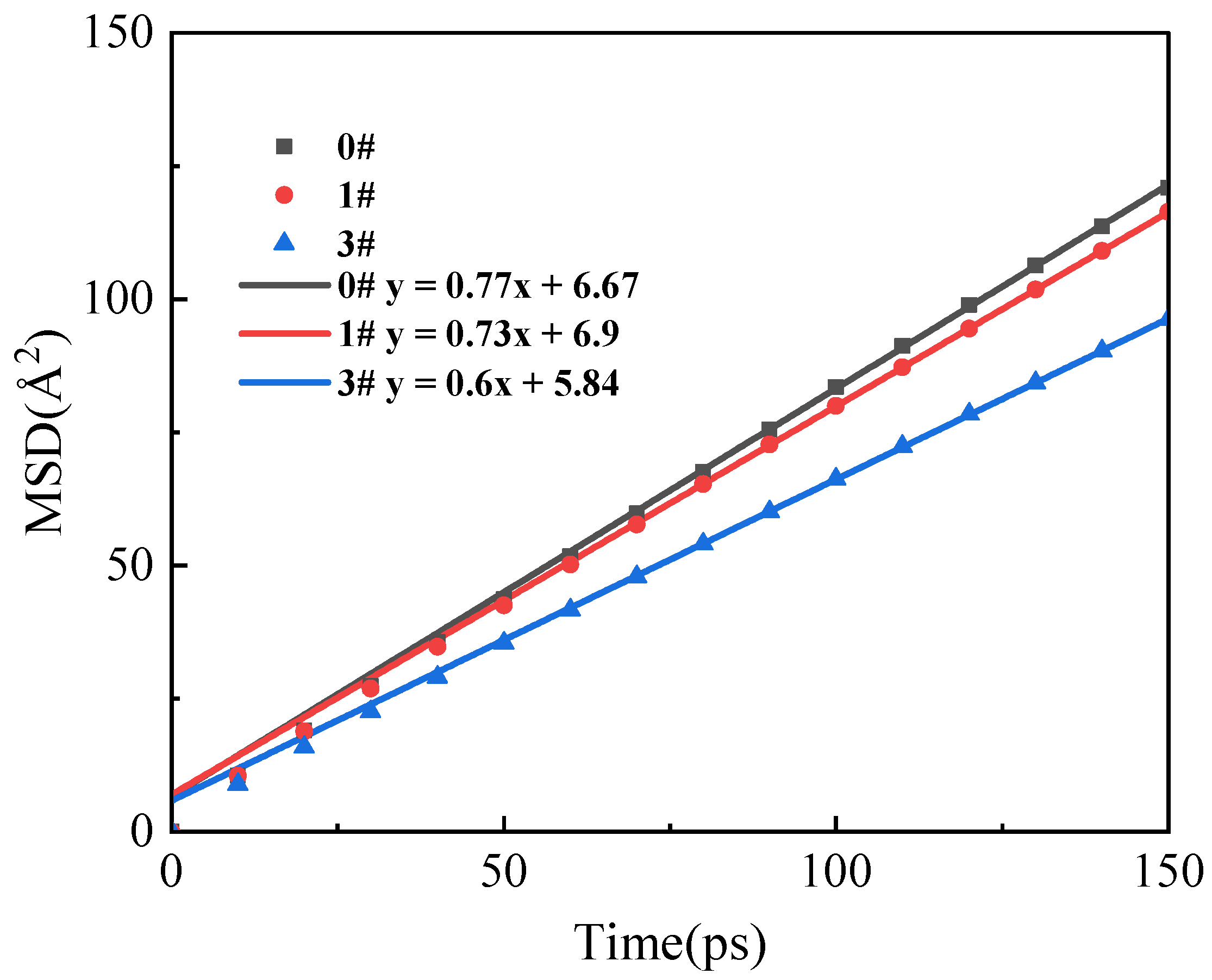
3.5. Mean Square Displacement
3.6. Hydrogen Bond
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Fameau, A.-L.; Salonen, A. Effect of particles and aggregated structures on the foam stability and aging. Comptes Rendus Phys. 2014, 15, 748–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannis, I.; Innocente, M.S.; Davies, J.D.; Ryan, J.L.; Gkanas, E.I. Investigating the impact of iron oxide nanoparticles on the stability of class A foam for wildfire suppression. Fire Saf. J. 2024, 150, 104282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linteris, G.T. Clean Agent Suppression of Energized Electrical Equipment Fires. Fire Technol. 2011, 47, 1–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Chen, N.; Jiao, Z.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, W.; Pan, R. Analysis of ternary foam of hydrocarbon/silicone/low carbon alcohol and the inhibition effect on coal spontaneous combustion. Huagong Xuebao/CIESC J. 2022, 73, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdankus, T.; Gylys, M.; Paukstaitis, L.; Jonynas, R. Experimental investigation of heat transfer from a horizontal flat surface to aqueous foam flow. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 123, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Xue, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.; Ma, L.; Ding, X.; Liu, X. Aggregation behavior and foam properties of the mixture of hydrocarbon and fluorocarbon surfactants with addition of nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 323, 115070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.L.; Belmonte, J.M.; Graner, F.; Glazier, J.A.; de Almeida, R.M.C. 3D simulations of wet foam coarsening evidence a self similar growth regime. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 473, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Gao, P.; Jiang, K.; Kong, D.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; Shang, F.; Zhang, J. Comparative study on the enhancement of the stability of siloxane-based Gemini/sodium alpha-alkenyl sulfonate mixed dispersions using xanthan gum, carboxymethyl cellulose, and gelatin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 292, 139378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Zhu, G.; Liu, C.; Hu, X.; Zhong, F.; He, L.; Liu, T.; Peng, M. Preparation and properties of a fluorine-free aerogel foam extinguishing agent. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 707, 135826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Jiao, J.; Wu, J.; Lang, X.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y.; Cui, P.; Shang, Z.; Mu, X.; Mu, S.; et al. Environmentally friendly fluorine-free fire extinguishing agent based on the synergistic effect of silicone, hydrocarbon surfactants and foam stabilizers. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 694, 134216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, P.; Li, B.; Chen, J.; He, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Kong, D. Effect of temperature on stability and film thinning behavior of aqueous film forming foam. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 370, 120978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Kuai, D.; Wang, G.; Li, S. Preparation of a fluorine-free foam for the prevention and control of spontaneous combustion of coal and its flame-retardant properties. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 196, 106886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Guan, J.; Wang, N.; Wei, Z.; Xu, Z.; Niu, G. Design of fluorine-free foam extinguishing agent with high surface activity, foam stability and pool fire suppression by optimization of surfactant composition and foam system. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 693, 134094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Qi, L.; Wu, J.; Lang, X.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, G.; Cui, P.; Shang, Z.; Mu, X.; Mu, S.; et al. Synthesis of Carboxyl Modified Polyether Polysiloxane Surfactant for the Biodegradable Foam Fire Extinguishing Agents. Molecules 2023, 28, 3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Wu, X.; Lu, S.; Li, C. Experimental Study on Foam Properties of Mixed Systems of Silicone and Hydrocarbon Surfactants. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2016, 19, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, T.H.; Dlugogorski, B.Z.; Kennedy, E.M. Sealability properties of fluorine-free fire-fighting foams (FfreeF). Fire Technol. 2008, 44, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.-H.; Yang, W.-J.; Lv, S.-H.; Zhu, T.-T.; Sharif, H.M.A.; Yang, C.; Du, J.; Lin, H. Is HFPO-DA (GenX) a suitable substitute for PFOA? A comprehensive degradation comparison of PFOA and GenX via electrooxidation. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 111995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Qiu, K.; Li, H.; Miao, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Lu, S. Interfacial and rheological properties of long-lived foams stabilized by rice proteins complexed to transition metal ions in the presence of alkyl polyglycoside. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 630, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Min, R.; Wang, G.; Wu, Q.; Qu, A.; Zhuo, C.; Wang, Q.; Ruan, X. Evaluation of interfacial, micellar, and foaming properties of the solutions comprising fluorocarbon surfactant, cocamidopropyl betaine, and Gleditsia saponin as fire-extinguishing agents. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2023, 272, 118590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.L.; Zeng, J.X.; Zou, Q.; Zheng, L.G.; Pan, R.K. Fluorine-free foaming extinguishing agent: Design route, fire extinguishing performance, foam stability mechanism. Arab. J. Chem. 2024, 17, 105712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.N.; Jing, M.J.; Hou, S.Y.; Gong, Y.W.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, J.C.; Zhang, B. Preparation and Fire-Retardant Mechanism of Self-Hardening Silica Foam for Wood Fire Prevention. Silicon 2022, 14, 12633–12644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ge, J.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Cao, G.; Zhang, G.; Dai, M. Synergistic effect of long and short carbon chain betaine type foaming agent. Chem. Eng. Oil Gas 2022, 51, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Hanamertani, A.S.; Saraji, S.; Piri, M. A comparative investigation of the effect of gas type on foam strength and flow behavior in tight carbonates. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2023, 276, 118798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, G. Experimental Study on the Effects of New Foam on the Improvement of Sandy Soil for Earth Pressure Balance Shield. Buildings 2023, 13, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, X.; Tao, W.; Ji, B. Study on effect of coal dust particle size on wettability of surfactant compounding solution. China Saf. Sci. J. (CSSJ) 2023, 33, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Zhdanova, A.O.; Islamova, A.G.; Kopylov, N.P. Interaction of Drops of Fire-Extinguishing Compositions with Fragments of Combustible Materials. Bull. Tomsk. Polytech. Univ.-Geo Assets Eng. 2022, 333, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, K.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Wang, J. Study on preparation and characteristics of CMC/ZrCit/GDL fire-fighting gel foam. Coal Sci. Technol. 2023, 51, 122–129. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Li, F.; Fang, H.; Miao, X.; Wang, J.; Zong, R.; Lu, S. Foaming behavior of fluorocarbon surfactant used in fire-fighting: The importance of viscosity and self-assembly structure. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 327, 114811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenckhan, W.; Saint-Jalmes, A. The science of foaming. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 222, 228–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qu, Z.; Yin, Y.; Bai, J.; Yu, B. Review of Molecular Simulation Method for Gas Adsorption/desorption and Diffusion in Shale Matrix. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 28, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.A.; Criscenti, L.J. Molecular-level understanding of gibbsite particle aggregation in water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 600, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Xu, G.; Yuan, S.; Chen, Y.; Yan, H. Molecular Dynamics Study of Alkyl Benzene Sulfonate at Air/Water Interface: Effect of Inorganic Salts. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 5025–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Song, J.; Sun, Y.; Xu, M.; Wen, X.; Wei, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, B.; Lv, K.; Liu, D. Molecular insight into the effect of the number of introduced ethoxy groups on the calcium resistance of anionic-nonionic surfactants at the oil/water interface. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 667, 131382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Li, T.; Zhang, G.; Xiong, J.; Lang, X.; Quan, X.; Cheng, Y.; Wei, Y. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of the Short-Chain Fluorocarbon Surfactant PFHXA and the Anionic Surfactant SDS at the Air/Water Interface. Molecules 2024, 29, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, B.; Liu, T.; Wang, D.; Tang, L.; Zhou, L.; Gou, S. Another Possible Rationale for Foam Stability: The Quantity and Strength of Hydrogen Bonds at the Gas-Liquid Interface. J. Phys. Chem. B 2025, 129, 3083–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Ge, S.; Jing, D.; Liu, S.; Chen, X. Wetting Mechanism and Experimental Study of Synergistic Wetting of Bituminous Coal with SDS and APG1214. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, P.; Chen, Z. Molecular simulation study of the influence of different surfactants on the wetting characteristics of anthracite. Arab. J. Chem. 2024, 17, 105637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Yan, K. Adsorption of collectors on model surface of Wiser bituminous coal: A molecular dynamics simulation study. Miner. Eng. 2015, 79, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivai, M.; Hambali, E.; Suryani, A.; Fitria, R.; Firmansyah, S.; Pramuhadi, G. Formulation and performance test of palm-based foaming agent concentrate for fire extinguisher application. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Biomass (ICB)—Toward Sustainable Biomass Utilization for Industrial and Energy Applications, Bogor, Indonesia, 24–25 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, P.; Chen, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Effects of surfactant types on anthracite dust wettability: Experimental and molecular simulations. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 403, 124901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Li, B. Effects of hydrophilic groups of nonionic surfactants on the wettability of lignite surface: Molecular dynamics simulation and experimental study. Fuel 2018, 231, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Material | Molecular Formula | Source | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) | C12H25NaO4S | Tianjin Yongda Chemical Co. | Primary foaming agent |
| Sodium lauryl ether sulfate (AES) | C16H33SO6Na | Shandong Yusuo Chemical Technology | Auxiliary blowing agent |
| Lauryl glucoside (APG1214) | C16H32O6 | Shandong Yusuo Chemical Technology | Auxiliary blowing agent |
| Lauryl hydroxy sulfobetaine (LHSB) | C17H37NO4S | Shandong Yusuo Chemical Technology | Foam stabilizing agent |
| Cocamidopropyl betaine (CAB-35) | C19H38N2O3 | Shandong Yusuo Chemical Technology | Foam stabilizing agent |
| Fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether glucoside (AEG050) | (C6H11O5)m (C2H4O)nO C12H25 | Shandong Yusuo Chemical Technology | Foam stabilizing agent |
| Disodium lauryl citrate sulfosuccinate (PEG-5) | C42H76O23S2Na | Shandong Yusuo Chemical Technology | Foam stabilizing agent |
| Alcohol ethoxylate (AEO) | C26H54O8 | Shandong Yusuo Chemical Technology | Wetting agent |
| Sodium bis(2-ethylhexyl) sulfosuccinate (AOT) | C20H37O7SNa | Jiangsu Haian Petrochemical Plant | Wetting agent |
| Sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate (LAS) | C18H29NaO3S | Tianjin Yongda Chemical Co. | Wetting agent |
| Sodium dioctyl sulfosuccinate (T) | C20H37O7SNa | Shandong Yusuo Chemical Technology | Wetting agent |
| Ethylene glycol monobutyl ether (BCS) | C6H14O2 | Zhengzhou Yinfeng Reagent | cosolvent |
| Diethylene glycol monobutyl ether (DEBCS) | C8H18O3 | Zhengzhou Yinfeng Reagent | cosolvent |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proportion/% | Primary Foaming Agent (15) | Auxiliary Foaming Agent (5) | Wetting Agent (4) | Foam Stabilizing Agent (5) | Cosolvent (20) | Deionized Water (51) |
| 1# | SDS | AES | AEO | LHSB | BCS | / |
| 2# | SDS | APG12 | AOT | CAB35 | DEBCS | / |
| 3# | SDS | AES | T | AEG | BCS | / |
| 4# | SDS | APG12 | LAS | PEG | DEBCS | / |
| 5# | SDS | AES | AOT | AEG | DEBCS | / |
| 6# | SDS | APG12 | AEO | PEG | BCS | / |
| 7# | SDS | AES | LAS | LHSB | DEBCS | / |
| 8# | SDS | APG12 | T | CAB35 | BCS | / |
| 9# | SDS | AES | T | PEG | DEBCS | / |
| 10# | SDS | APG12 | LAS | AEG | BCS | / |
| 11# | SDS | AES | AEO | CAB35 | DEBCS | / |
| 12# | SDS | APG12 | AOT | LHSB | BCS | / |
| 13# | SDS | AES | LAS | CAB35 | BCS | / |
| 14# | SDS | APG12 | T | LHSB | DEBCS | / |
| 15# | SDS | AES | AOT | PEG | BCS | / |
| 16# | SDS | APG12 | AEO | AEG | DEBCS | / |
| Group | Foaming Multiplicity | Surface Tension (mN/m) | Viscosity (mPa·s) | Wetting Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFFF | 2.1 | 19.81 | 0.99 | / |
| 1# | 8.4 | 29.33 | 1.5 | 7.8 |
| 2# | 4.8 | 28.37 | 1.6 | 14.44 |
| 3# | 7.3 | 29.47 | 1.4 | 6.62 |
| 4# | 5.35 | 31.9 | 2 | 9.44 |
| 5# | 5.6 | 31.8 | 1.8 | 4.97 |
| 6# | 5.5 | 32.17 | 1.6 | 9.94 |
| 7# | 5.1 | 32.2 | 1.8 | 6.16 |
| 8# | 4.74 | 30.63 | 1.3 | 6.62 |
| 9# | 5.33 | 32.1 | 2 | 4.53 |
| 10# | 4.6 | 32.27 | 1.7 | 11.97 |
| 11# | 7.01 | 31.1 | 1.8 | 9.73 |
| 12# | 4.92 | 29.73 | 1.5 | 5.18 |
| 13# | 4.3 | 31.17 | 1.7 | 7.06 |
| 14# | 4.96 | 30.9 | 1.86 | 4.25 |
| 15# | 5.95 | 31.17 | 1.6 | 8.50 |
| 16# | 7.8 | 31.7 | 1.69 | 6.69 |
| Average | 5.73 | 31 | 1.68 | 7.74 |
| Group | Molecules Bonded to H2O | Average Number |
|---|---|---|
| 0# | H2O | 9271 |
| SDS | 960 | |
| 1# | H2O | 8863 |
| SDS | 942 | |
| AES | 178 | |
| AEO | 138 | |
| LHSB | 169 | |
| 3# | H2O | 8951 |
| SDS | 933 | |
| AES | 185 | |
| T | 150 | |
| AEG | 145 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, H.; Zhao, A.; Zhang, L.; Wang, F.; Cheng, L.; Ma, L. Investigation of Key Components in Class A Foam for Synergistic Wetting and Adhesion: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Case. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9888. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189888
Ma H, Zhao A, Zhang L, Wang F, Cheng L, Ma L. Investigation of Key Components in Class A Foam for Synergistic Wetting and Adhesion: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Case. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(18):9888. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189888
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Huizhong, Ao Zhao, Lan Zhang, Fei Wang, Liang Cheng, and Liyang Ma. 2025. "Investigation of Key Components in Class A Foam for Synergistic Wetting and Adhesion: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Case" Applied Sciences 15, no. 18: 9888. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189888
APA StyleMa, H., Zhao, A., Zhang, L., Wang, F., Cheng, L., & Ma, L. (2025). Investigation of Key Components in Class A Foam for Synergistic Wetting and Adhesion: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Case. Applied Sciences, 15(18), 9888. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189888






