Holoscopic 3D Imaging Systems: A Review of History, Recent Advances and Future Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Holoscopic 3D Imaging System Principle and Development
2.1. From Stereoscopic Vision to Integral Photography
2.2. Experimental Refinements and Optical Principles
| Year | Milestone | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1838s | Charles Wheatstone | Invention of the stereoscope, based on the theory of binocular disparity [15]. |
| 1908s | Gabriel Lippmann | Proposal of integral photography using a microlens array to capture 3D scenes [1]. |
| 1930s | Eugène Estanave | Extended Lippmann’s concept using pinhole arrays and multi-lens configurations [2]. |
| 1960s | Anaglyph, Polarized, Stereo Film | Commercial adoption of stereoscopic display technologies in cinema and media [17,18,19]. |
| 1990s | Digital Holoscopic Prototypes | Emergence of digital systems combining CCD sensors with microlens arrays [22,23,24]. |
| 2010s | Light Field and Holoscopic | Rise of computational light field imaging and holoscopic displays with AI [37,38,39]. |
| 2020s | AI + Holoscopic | Integration of deep learning with holoscopic systems for applications [35,36,40]. |
2.3. Holoscopic 3D Imaging vs. Light Field Imaging vs. Stereoscopic Imaging
3. Holoscopic 3D Imaging System Architecture
3.1. Capture System: Microlens Array-Based Single Aperture Acquisition of 3D Information
3.2. Display System: Image Reconstruction, MLA Integration, and Spatial Parallax
4. Recent Advances and Technical Innovations
4.1. High-Precision Sensing and Recognition in Holoscopic 3D Capture Systems
4.2. Synthetic Holoscopic Data Generation
5. Applications and Comparative Evaluation of Holoscopic 3D Imaging Systems
- (a)
- Human–Machine Interaction and Gesture Recognition
- (b)
- Autonomous Driving and Spatial Perception
- (c)
- Medical Imaging and Surgical Assistance
- (d)
- Cultural Heritage and 3D Documentation
6. Discussion
6.1. Technical Challenges
- (1)
- Spatial–Angular Resolution Trade-off
- (2)
- Parallax Aliasing and Angular Artifacts
- (3)
- Dataset Scarcity and Benchmarking Difficulties
6.2. Emerging Trends and Opportunities
- (1)
- Neural Rendering and Learning-Based Depth Estimation
- (2)
- Cross-Modal Sensing Fusion
- (3)
- Miniaturization and Device-Level Integration
- (4)
- Commercial Viability, Practical Barriers and Economic Considerations
6.3. Implications for the Broader 3D Imaging Landscape
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| H3D | Holoscopic 3D |
| MLA | microlens array |
| VPIs | viewpoint images |
| EI | elemental image |
| CNNs | convolutional neural networks |
| RNNs | recurrent neural networks |
| GANs | generative adversarial networks |
| CCD | charge-coupled device |
| CMOS | complementary metal oxide semiconductor |
| LFI | Light Field Imaging |
| ToF | Time of Flight |
| HMDs | head-mounted displays |
| IP | intellectual property |
| OEM | Original Equipment Manufacturer |
| DSPM | Distributed pixel mapping |
References
- Lippmann, G. La photographie intégrale. Comptes-Rendus l’Acad. Sci. 1908, 146, 446–451. [Google Scholar]
- Estanave, E. Le stéréophotographie et la photographie intégrale. C. R. Acad. Sci. 1930, 190. [Google Scholar]
- Steurer, J.; Pesch, M.; Hahne, C.; Kauff, P. 3D Holoscopic Video Imaging System. Proc. SPIE 2012, 8291, 829109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggoun, A.; Tsekleves, E.; Zarpalas, D.; Dimou, A.; Daras, P.; Nunes, P.; Ducla Soares, L. Immersive 3D Holoscopic Video System. IEEE Multimed. 2013, 20, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makanjuola, J.K.; Aggoun, A.; Swash, M.; Grange, P.C.R.; Challacombe, B.; Dasgupta, P. 3D-Holoscopic Imaging: A New Dimension to Enhance Imaging in Minimally Invasive Therapy in Urologic Oncology. J. Endourol. 2013, 27, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Swash, M.R.; Meng, H. Semantic 3D Scene Classification Based on Holoscopic 3D Camera for Autonomous Vehicles. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Natural Computation, Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery, Xi′an, China, 1–3 August 2020; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 897–904. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Peng, M.; Swash, M.R.; Chen, T.; Qin, R.; Meng, H. Holoscopic 3D Microgesture Recognition by Deep Neural Network Model Based on Viewpoint Images and Decision Fusion. IEEE Trans. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 2021, 51, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnaim, N.; Abbod, M.; Swash, R. Recognition of Holoscopic 3D Video Hand Gesture Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Technologies 2020, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MarketsandMarkets. 3D Imaging Market by Component (Hardware, Software, Services), Deployment Mode, Organization Size, Application Area (Healthcare, Entertainment & Media, Automotive, Industrial) and Region—Global Forecast to 2028; MarketsandMarkets: Maharashtra, India, 2023; Available online: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/3d-imaging-market-998.html (accessed on 18 June 2025).
- IMARC Group. 3D Display Market: Global Industry Trends, Share, Size, Growth, Opportunity and Forecast 2024–2033. Available online: https://www.imarcgroup.com/3d-display-market (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Fact.MR. Autostereoscopic 3D Display Market Forecast 2023–2033. Available online: https://www.factmr.com (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Verified Market Reports. Naked Eye 3D LED Display Market Size and Forecast 2024–2033. Available online: https://www.verifiedmarketreports.com (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Data Insights Market Research. Global Autostereoscopic Display Market Report. Available online: https://www.datainsightsmarket.com (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Wheatstone, C. Contributions to the Physiology of Vision.—Part the First. On Some Remarkable, and Hitherto Unobserved, Phenomena of Binocular Vision. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1838, 128, 371–394. [Google Scholar]
- Rollmann, W. Zwei neue stereoskopische Methoden. Ann. Phys. 1853, 165, 186–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Hong, J.; Park, G.; Hong, K.; Min, S.W.; Lee, B. A Full-Color Anaglyph Three-Dimensional Display System Using Active Color Filter Glasses. J. Inf. Disp. 2011, 12, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, T.L.; Hellbaum, R.F. LC shutter glasses provide 3-D display for simulated flight. Inf. Disp. 1986, 2, 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Javidi, B.; Okano, F. Three-Dimensional Imaging, Visualization, and Display. In Three-Dimensional Imaging, Visualization, and Display; Son, J.Y., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 14, pp. 281–299. [Google Scholar]
- Okoshi, T. Three-Dimensional Imaging Techniques; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, D.E. History of Lenticular and Related Autostereoscopic Methods; Leap Technologies: Hillsboro, OR, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Swash, M.R.; Aggoun, A.; Abdulfatah, O.; Li, B.; Fernández, J.C.; Tsekleves, E. Holoscopic 3D Image Rendering for Autostereoscopic Multiview 3D Display. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Broadband Multimedia Systems and Broadcasting (BMSB), London, UK, 5–7 June 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatrouk, B.; Meng, H.; Swash, M.R. Holoscopic Elemental-Image-Based Disparity Estimation Using Multi-Scale, Multi-Window Semi-Global Block Matching. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swash, M. Holoscopic 3D Imaging and Display Technology: Camera/Processing/Display. Ph.D. Thesis, Brunel University London, Uxbridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Swash, M.R.; Aggoun, A.; Abdulfatah, O.; Li, B.; Fernández, J.C.; Alazawi, E.; Tsekleves, E. Pre-Processing of Holoscopic 3D Image for Autostereoscopic 3D Displays. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on 3D Imaging, Palo Alto, CA, USA, 3–5 December 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Swash, M.R.; Aggoun, A.; Abdulfatah, O.; Fernandez, J.C.; Alazawi, E.; Tsekleves, E. Distributed pixel mapping for refining dark area in parallax barriers based holoscopic 3D Display. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on 3D Imaging, Seattle, WA, USA, 29 June–1 July 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Swash, M.R.; Lei, T.; Li, K.; Xiong, N.; Wang, L. Implementation and Evaluation of Innovative 3D Pixel Mapping Method for LED Holoscopic 3D Wall Display. In Advances in Natural Computation, Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery. ICNC-FSKD 2020; Lecture Notes on Data Engineering and Communications Technologies; Springer: Cham, Switzerland; Volume 88, pp. 104–117. [CrossRef]
- Alazawi, E.; Swash, M.R.; Abbod, M. 3D Depth Measurement for Holoscopic 3D Imaging System. J. Comput. Commun. 2016, 4, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fernández, J.C.J. Capturing of 3D Content Using a Single Aperture Camera. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bedfordshire, Luton, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Aggoun, A.; McCormick, M.; Spilsbury, M.; Velisavljevic, V.; Reid, D.; Davies, P. Immersive 3D Holoscopic Video System. IEEE MultiMedia 2013, 20, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhi, A.; Bouras, A.; Alfaqheri, T.; Aondoakaa, A.S.; Sadka, A.H. Investigating 3D Holoscopic Visual Content Upsampling Using Super-Resolution for Cultural Heritage Digitization. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2019, 75, 188–198. [Google Scholar]
- Alazawi, E.; Aggoun, A.; Abbod, M.; Swash, M.R.; Fatah, O.A.; Fernandez, J. Scene Depth Extraction from Holoscopic Imaging Technology. In Proceedings of the 2013 3DTV-Conference: Vision Beyond Depth (3DTV-CON), Aberdeen, UK, 7–9 October 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatrouk, B.; Swash, M.R.; Sadka, A.H. Innovative 3D depth map generation from a holoscopic 3D image based on graph cut technique. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.04217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Meng, H.; Swash, M.R.; Gaus, Y.F.A.; Qin, R. Holoscopic 3D Micro-Gesture Database for Wearable Device Interaction. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), Xi′an, China, 15–19 May 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Shao, J. Classification of Holoscopic 3D Micro-Gesture Images and Videos. In Proceedings of the 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), Xi′an, China, 15–19 May 2018; pp. 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L. Plenoptic Imaging and Processing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; ISBN 978-981-97-6914-8. eBook ISBN: 978-981-97-6915-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaqheri, T.; Aondoakaa, A.S.; Swash, M.R.; Sadka, A.H. Low-delay single holoscopic 3D computer-generated image to multiview images. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2020, 17, 2015–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Jia, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Su, X.; Liu, S. Holoscopic 3D Micro-Gesture Recognition Based on Fast Preprocessing and Deep Learning Techniques. In Proceedings of the 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), Xi′an, China, 15–19 May 2018; pp. 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Jyoti, S.; Dhall, A. Hybrid Neural Networks Based Approach for Holoscopic Micro-Gesture Recognition in Images and Videos. In Proceedings of the 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), Xi′an, China, 15–19 May 2018; pp. 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Meng, H.; Swash, M.R.; Shan, S. A Novel Pseudo Viewpoint Based Holoscopic 3D Micro-Gesture Recognition. In Proceedings of the Companion Publication of the 2020 International Conference on Multimodal Interaction (ICMI ′20 Companion), Virtual, 25–29 October 2020; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Wang, C.; Chen, T. Attention-based Residual Network for Micro-Gesture Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), Xi′an, China, 15–19 May 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatah, O.A.; Aggoun, A.; Swash, M.R.; Alazawi, E.; Fernandez, J. Generating Stereoscopic 3D from Holoscopic 3D. In Proceedings of the 2013 3DTV-Conference: Vision Beyond Depth (3DTV-CON), Aberdeen, UK, 6–8 October 2013; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swash, M.R.; Aggoun, A.; Abdulfatah, O.; Li, B.; Fernández, J.C.; Tsekleves, E. Omnidirectional Holoscopic 3D Content Generation Using Dual Orthographic Projection. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Broadband Multimedia Systems and Broadcasting (BMSB), London, UK, 5–7 June 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazawi, E.; Abbod, M.; Aggoun, A.; Swash, M.R.; Fatah, O.A.; Fernandez, J. Super Depth-Map Rendering by Converting Holoscopic Viewpoint to Perspective Projection. In Proceedings of the 2014 3DTV-Conference: The True Vision—Capture, Transmission and Display of 3D Video (3DTV-CON), Budapest, Hungary, 2–4 July 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatrouk, B.; Meng, H.; Swash, M.R. Disparity Estimation from Holoscopic Elemental Images. In Advances in Natural Computation, Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery. ICNC-FSKD 2020; Lecture Notes on Data Engineering and Communications Technologies; Meng, H., Lei, T., Li, M., Li, K., Xiong, N., Wang, L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Swash, M.R.; Sadka, A.H. Real-Time Holoscopic 3D Video Interlacing. In Proceedings of the 2020 7th International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN), Noida, India, 27–28 February 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatrouk, B.; Meng, H.; Swash, R. Elemental Images Labelling and Grouping to Minimise Disparity Error in Texture-less Regions of Holoscopic Images. In Proceedings of the 2023 8th International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC), Dalian, China, 27–30 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Swash, M.R.; Meng, H. Reliable Holoscopic 3D Face Recognition. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN), Noida, India, 27–28 February 2020; pp. 696–701. [Google Scholar]
- Aondoakaa, A.S.; Swash, M.R.; Sadka, A. 3D Depth Estimation from a Holoscopic 3D Image. In Imaging and Applied Optics 2017 (3D, AIO, COSI, IS, MATH, pcAOP); Paper DW1F.5; OSA Technical Digest (online); Optica Publishing Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Jeong, M.; Lee, M.; Kim, J.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, S.S.; Jeon, H.G.; Shin, J. The path-tracing simulation of light-field camera system: SurfCam/GrainCams for lunar surface exploration. Adv. Space Res. 2025, 75, 4050–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Fessler, J.A.; Norris, T.B. Focal stack camera: Depth estimation performance comparison and design exploration. Opt. Contin. 2022, 1, 2030–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Yu, Z. (Eds.) Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C.; Jeon, H.-G.; Yoon, Y.; Kweon, I.S.; Kim, S.J. EPINET: A fully-convolutional neural network using epipolar geometry for depth from light-field images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2018), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 4748–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatrouk, B.; Meng, H.; Aondoakaa, A.; Swash, R. A New Raw Holoscopic Image Simulator and Data Generation. In Proceedings of the 2023 8th International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC), Dalian, China, 14–16 July 2023; pp. 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Yu, Z. A Fast Automatic Holoscopic 3D Micro-Gesture Recognition System for Immersive Applications. In Advances in Natural Computation, Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery, ICNC-FSKD 2019; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, S.; Swash, M.R.; Sadka, A. Immersive 360 Holoscopic 3D Imaging System Design. In Imaging and Applied Optics 2017 (3D, AIO, COSI, IS, MATH, pcAOP); Paper DW1F.4; OSA Technical Digest (online); Optica Publishing Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starks, M. Stereoscopic Imaging Technology; 3DTV Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Available online: http://www.3dmagic.com/articles/sit.html (accessed on 10 June 2025).


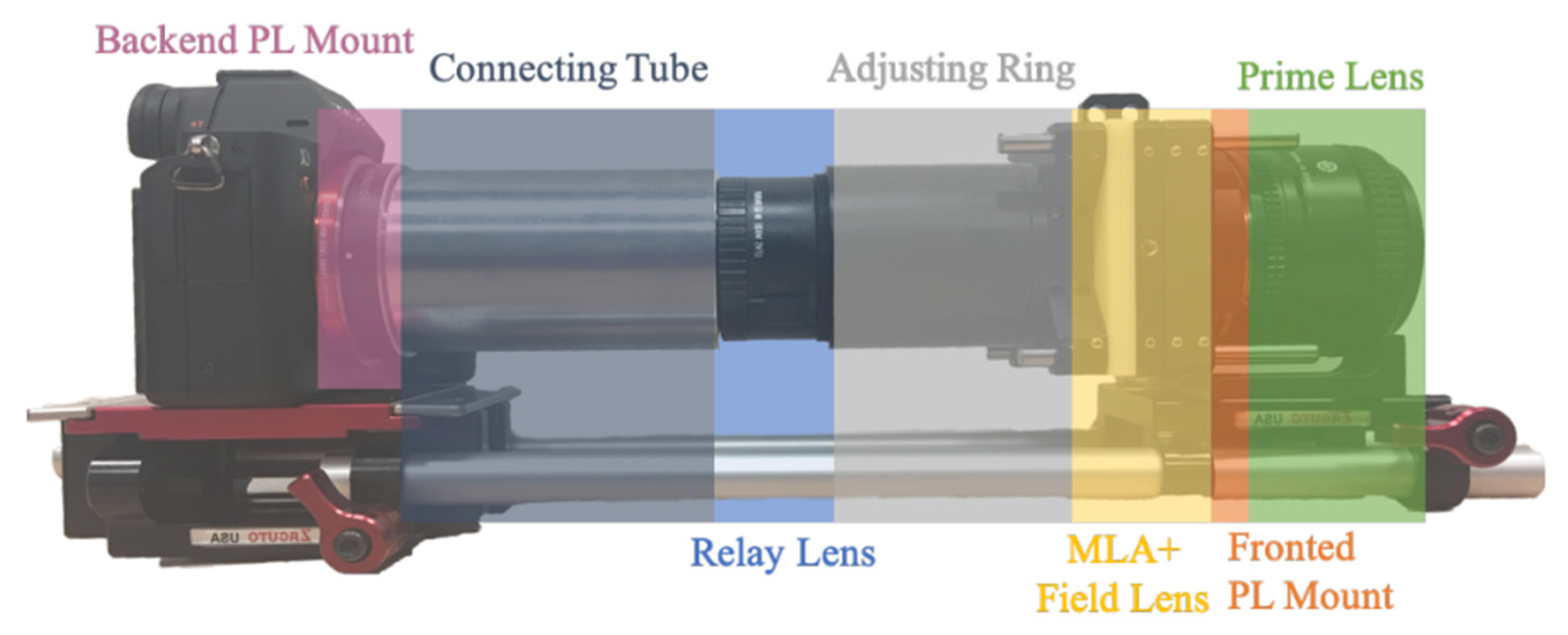
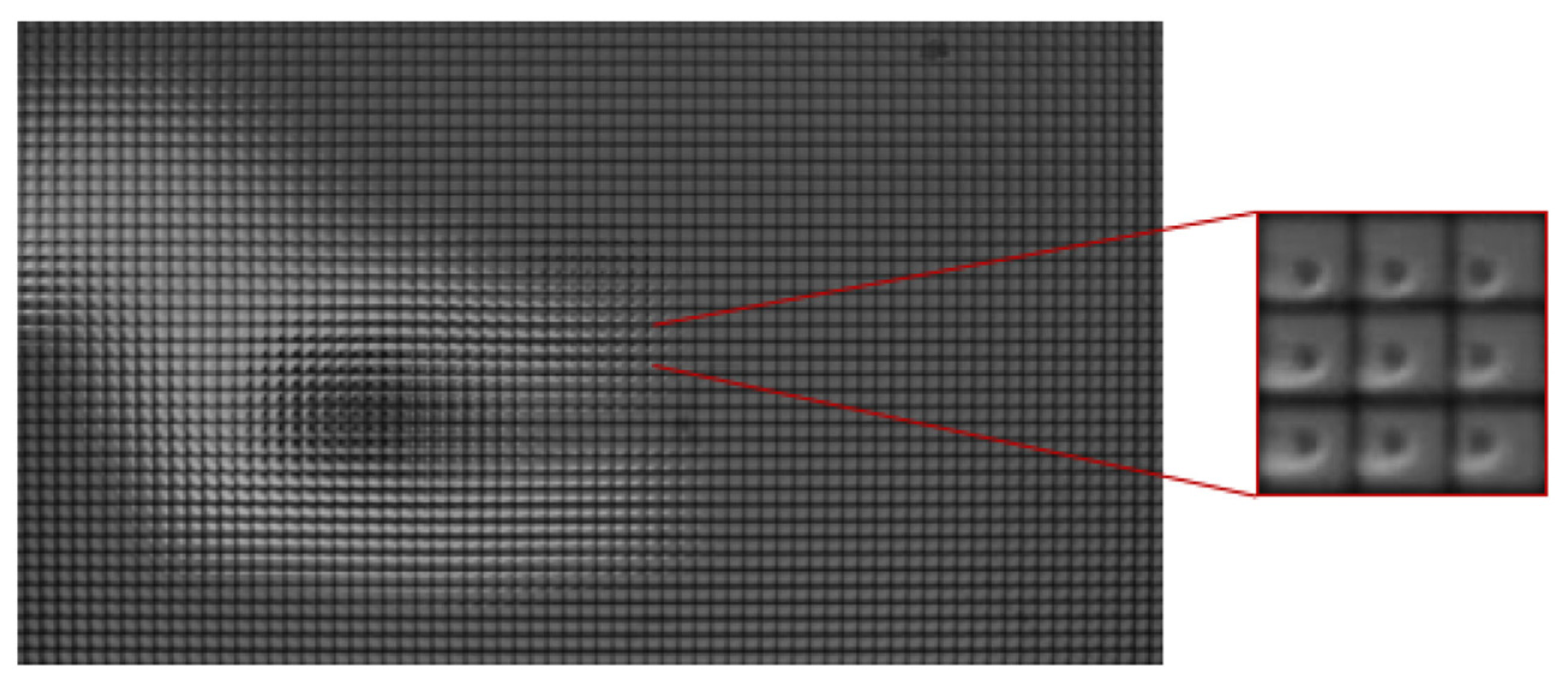



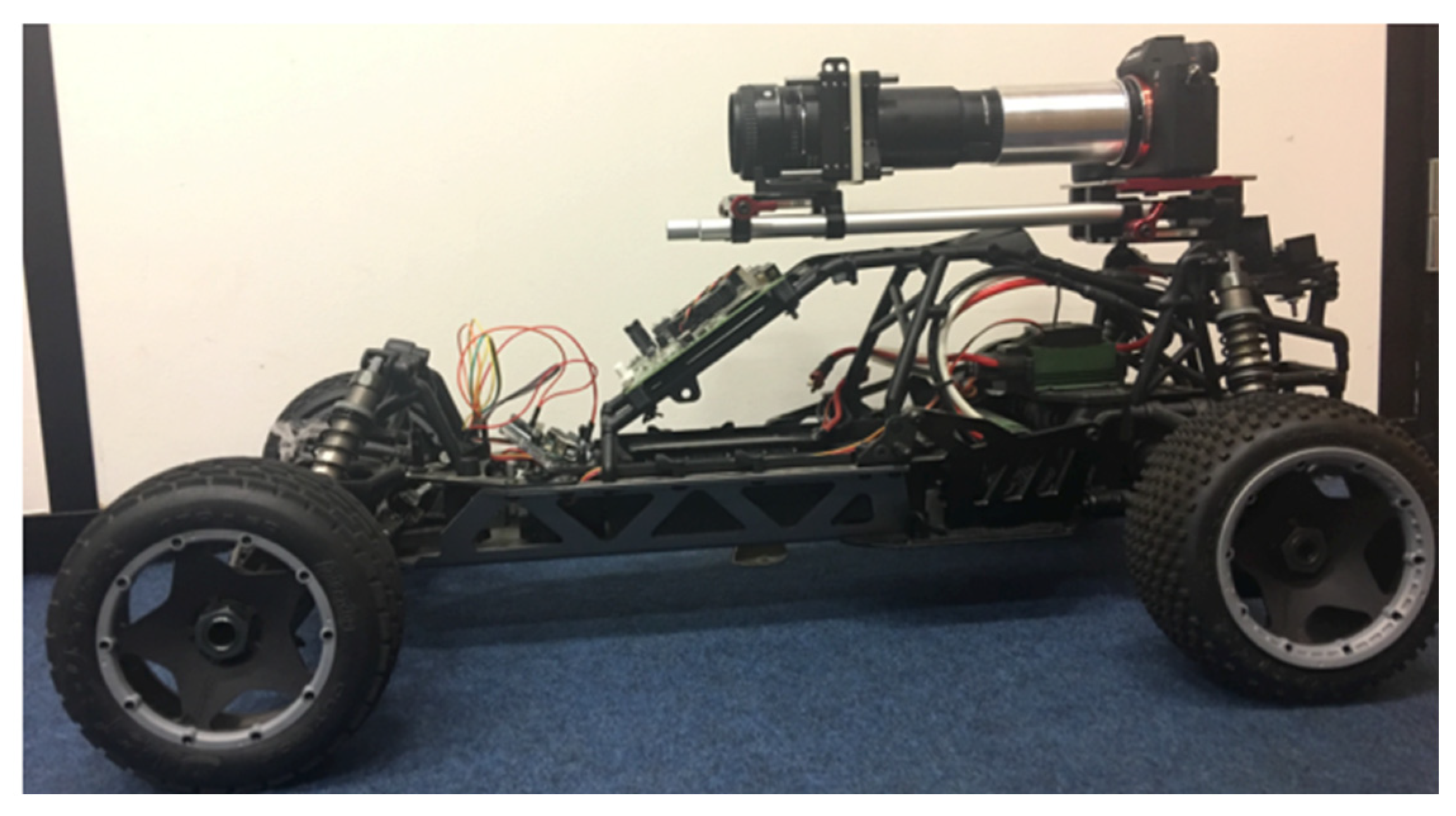
| Category | H3D | LFI | Stereoscopic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capture Method | Holoscopic 3D camera | Plenoptic camera/ | Dual-camera/ |
| Single sensor + MLA | MLA-based camera/ | Dual-view capture | |
| Elemental image array | Camera arrays | ||
| Parallax | Full (horizontal + vertical) | Horizontal only | Horizontal only |
| Depth Reconstruction | Embedded in EI View synthesis Optical replay | Computed from plenoptic function using disparity or rendering | Derived from binocular disparity |
| Display Mode | Glasses-free autostereoscopic with MLA display | Computationally rendered or specialized display | Requires glasses or headgear |
| Computation Overhead | Moderate | High | Low |
| decoding and rendering algorithms | refocusing and dense depth processing | Simple stereo matching | |
| Advantages | Real-time 3D Compact/immersive No eyewear needed | Refocusing ability Digital zoom Multiple-view synthesis | Mature tech Cost-effective Widespread |
| Limitations | Spatial-angular resolution trade-off Calibration needed | Resolution limits Heavy computation Bulky hardware | Visual fatigue Lack of vertical parallax Limited realism |
| Applications | AR/VR Gesture/facial recognition Medical imaging | Computational photography scientific imaging VR | 3D cinema gaming entertainment |
| Metric | H3D | LFI | Stereoscopic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spatial Resolution (MP effective) | ~2–5 MP per view (35 MP sensor divided by MLA) [48] | ~4 MP per view (40 MP Lytro sensor; space–angle trade-off) [49] | 2–8 MP per view (Full HD–4K per eye) |
| Depth Accuracy | mm–cm level via disparity/graph-cut depth estimation [33] | mm-level RMSE reported in recent algorithms [50] | ~1% of distance at near; up to ~9% at far |
| Depth Reconstruction | Moderate; near real-time possible with optimized algorithms [33] | GPU accelerated; some deep networks achieve near real-time [51,52] | Real-time feasible (low computational load) |
| Hardware Cost | Moderate: single sensor + MLA [48] | High: custom MLA or multi-camera arrays | Low: consumer stereo or depth modules |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Meng, H.; Swash, M.R.; Huang, Y.; Yan, C. Holoscopic 3D Imaging Systems: A Review of History, Recent Advances and Future Directions. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10284. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810284
Liu Y, Meng H, Swash MR, Huang Y, Yan C. Holoscopic 3D Imaging Systems: A Review of History, Recent Advances and Future Directions. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(18):10284. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810284
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yi, Hongying Meng, Mohammad Rafiq Swash, Yiyuan Huang, and Chen Yan. 2025. "Holoscopic 3D Imaging Systems: A Review of History, Recent Advances and Future Directions" Applied Sciences 15, no. 18: 10284. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810284
APA StyleLiu, Y., Meng, H., Swash, M. R., Huang, Y., & Yan, C. (2025). Holoscopic 3D Imaging Systems: A Review of History, Recent Advances and Future Directions. Applied Sciences, 15(18), 10284. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810284







