Investigation of an Innovative Blade with an Internal Channel and Tangential Slots for Enhanced Thrust Generation Using the Coanda Effect
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
CFD Simulation Setup
3. Results
3.1. Visualization and Analysis of Results
3.2. Design Evaluation and Simulation Sensitivity
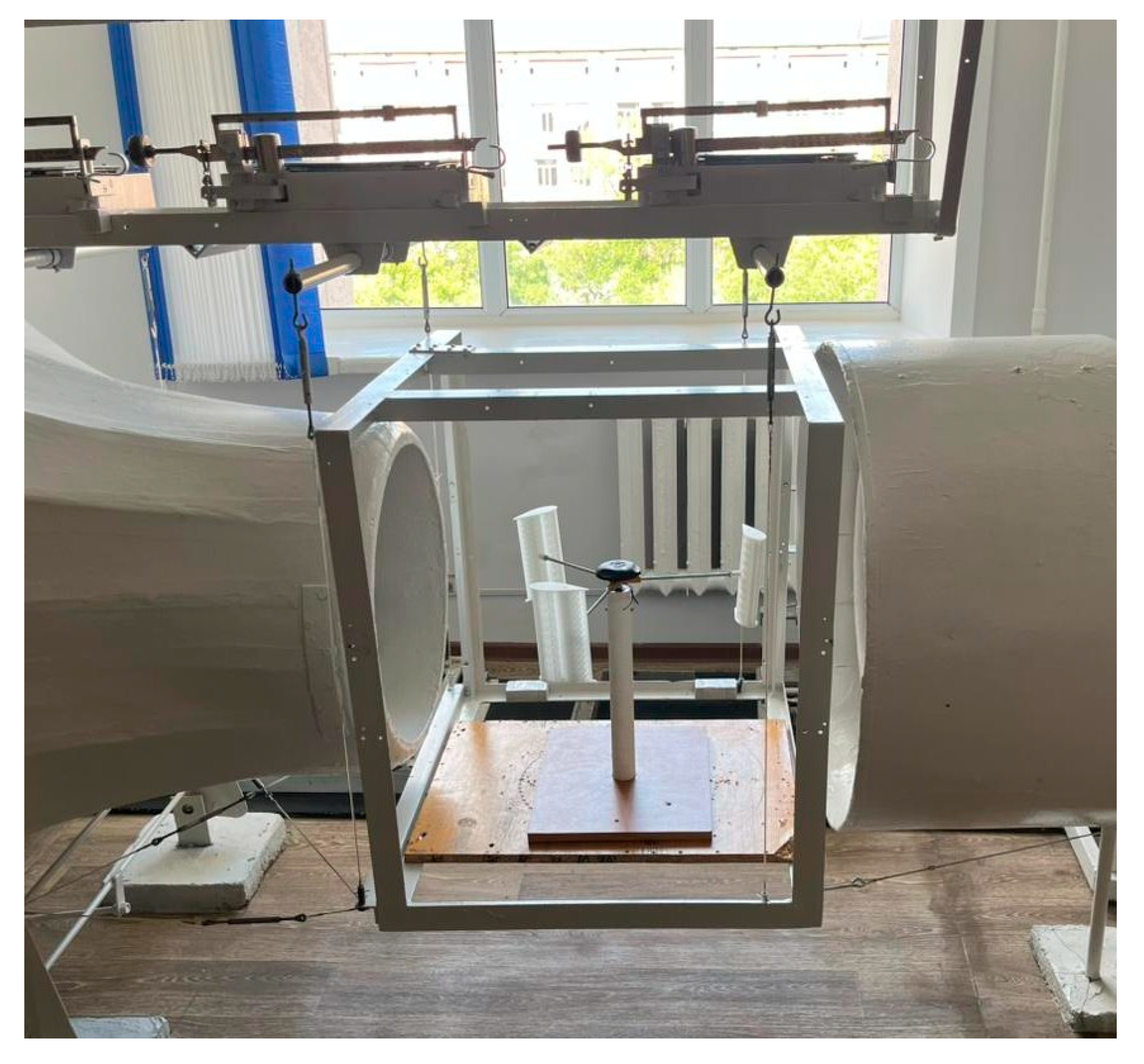
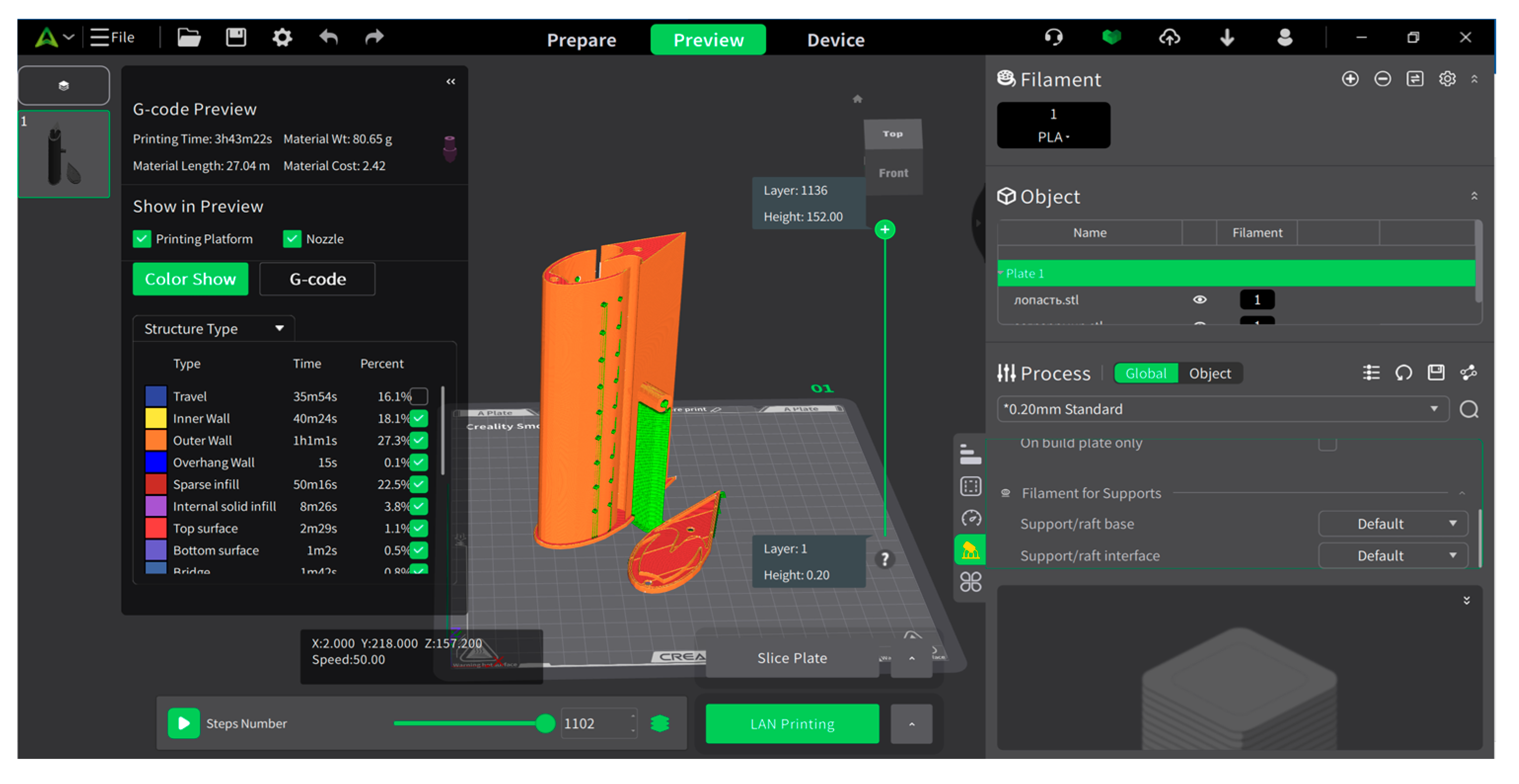
3.3. Development of the Laboratory Model
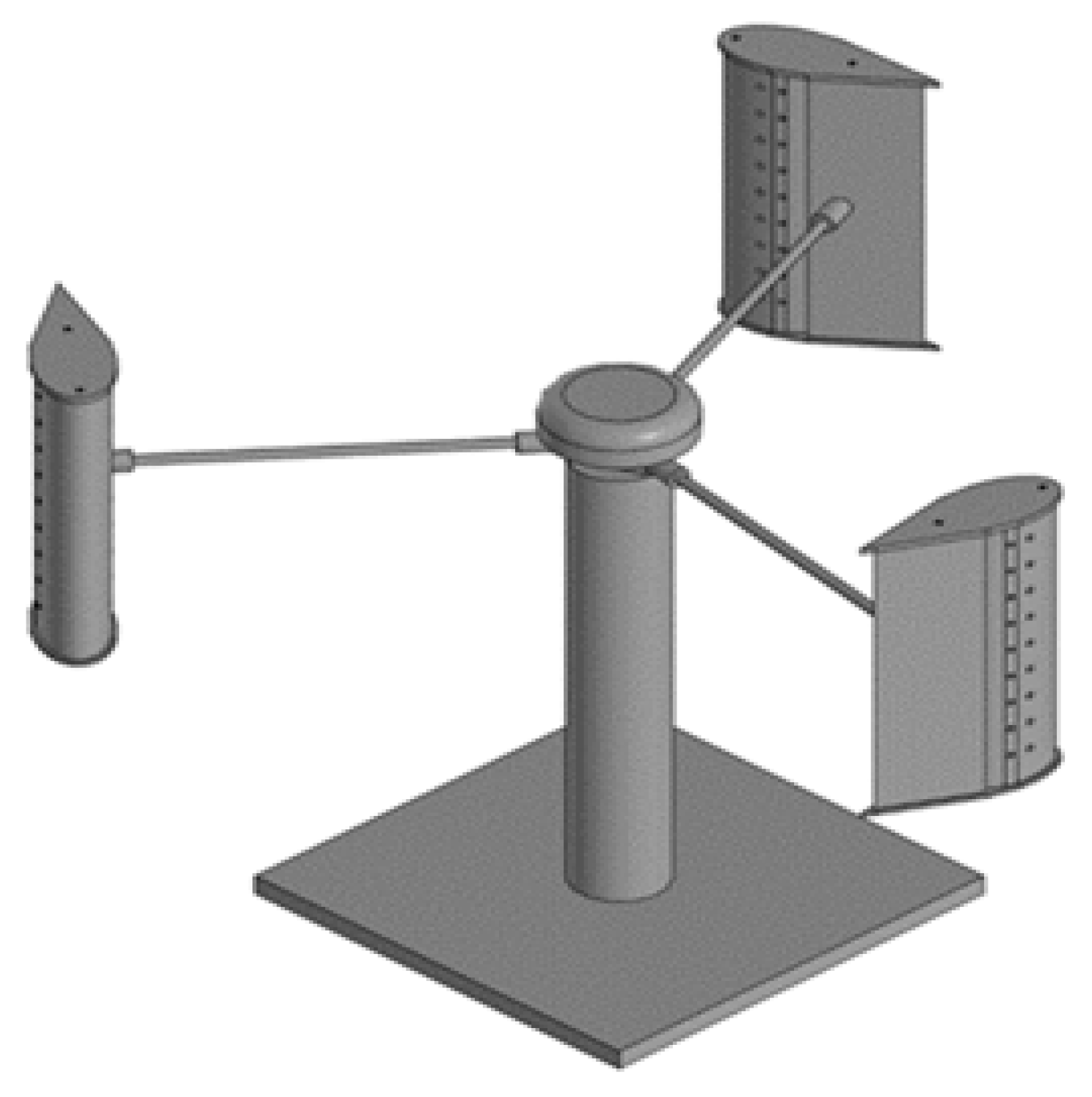
3.4. Characteristics of the Laboratory Model and 3D Design
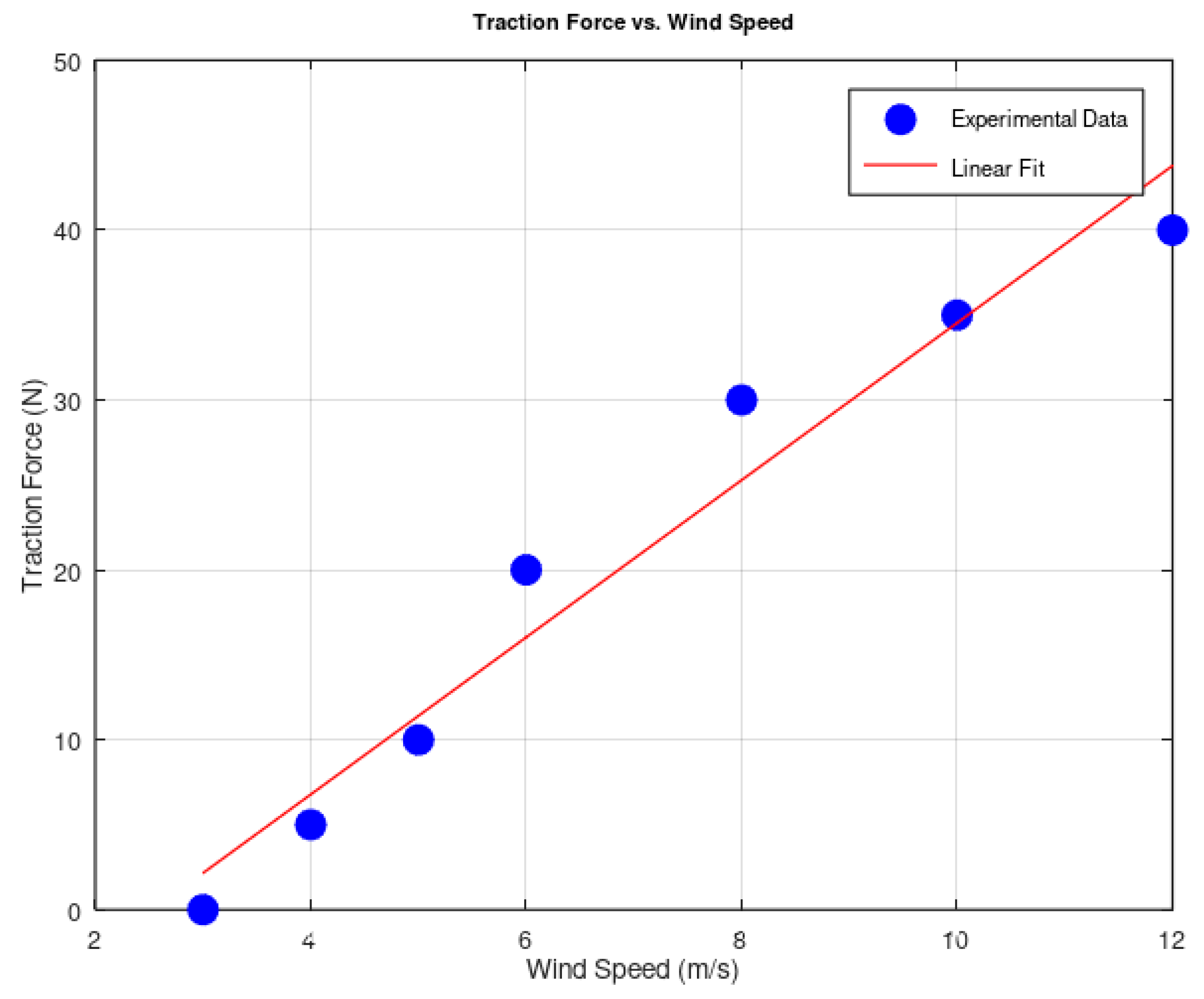
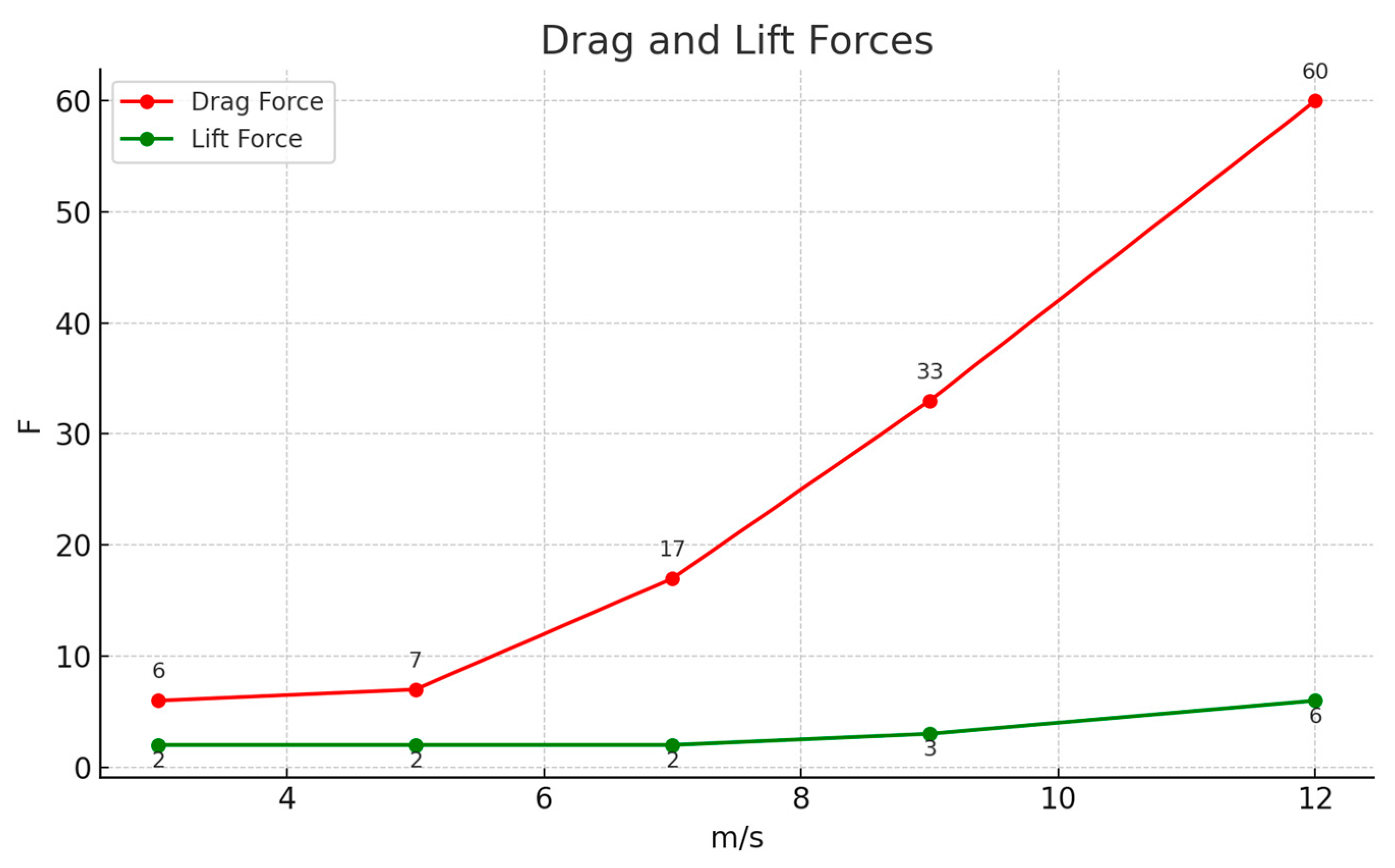
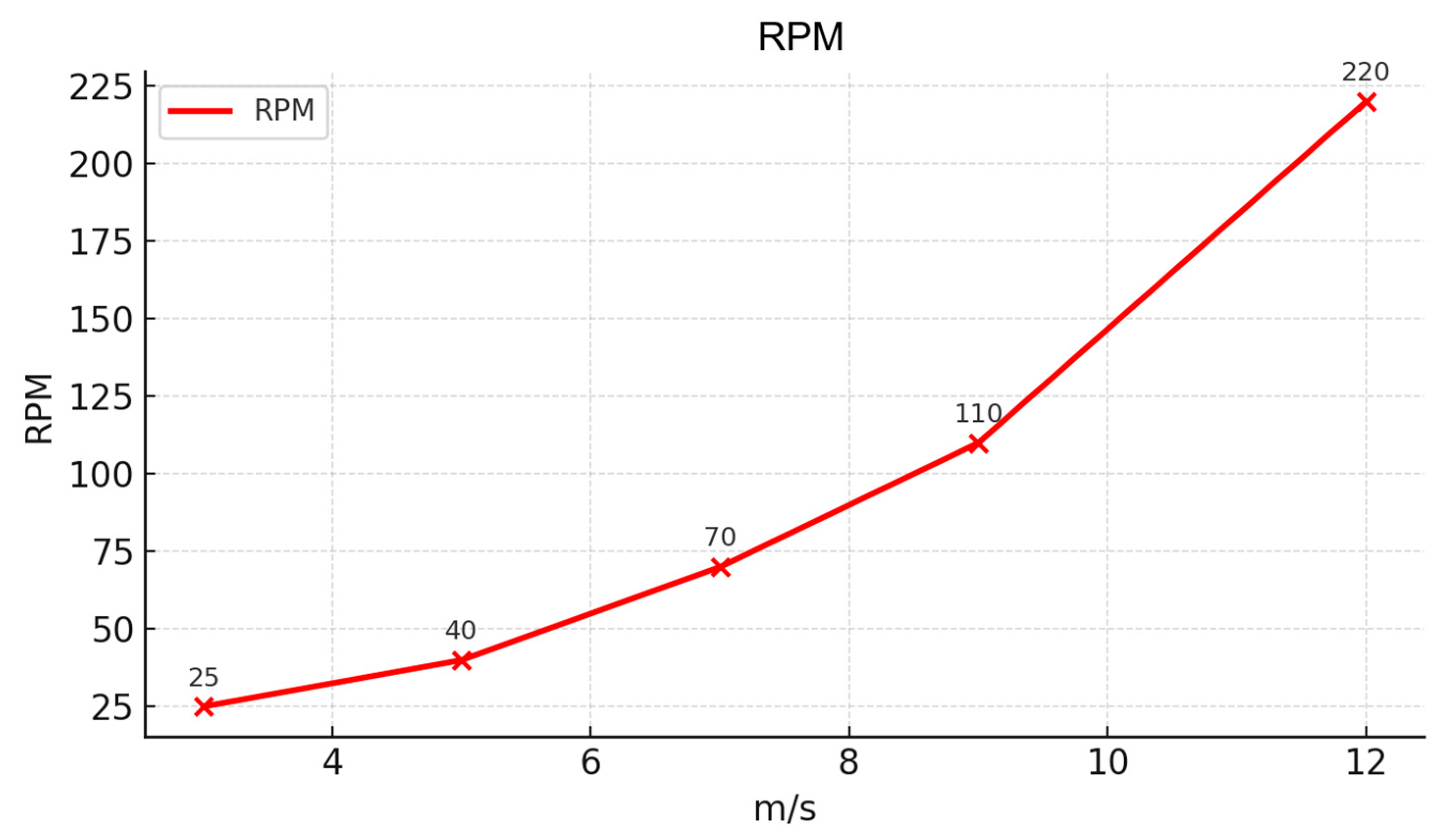
3.5. Experimental Results and TheirAnalysis
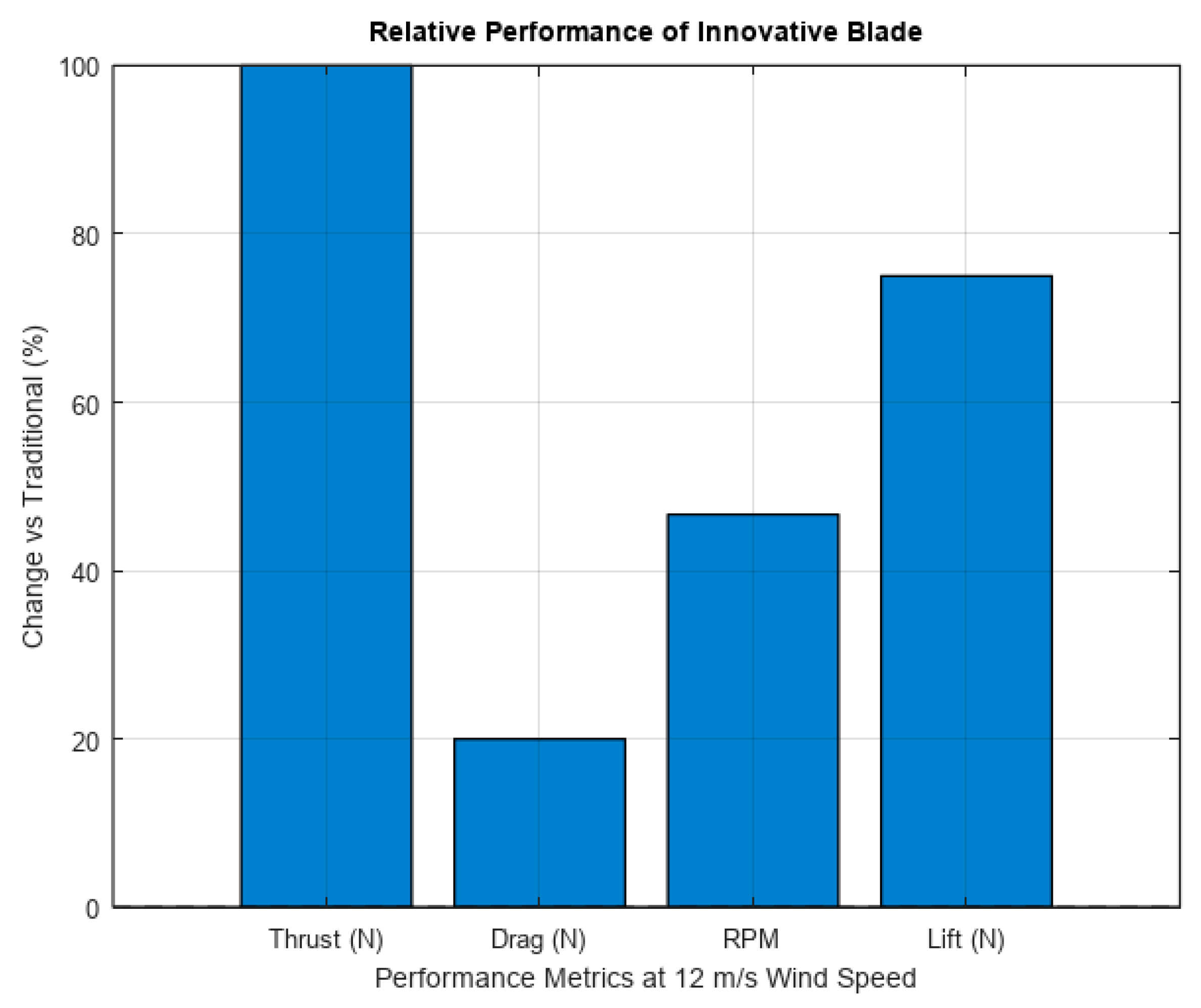
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CFD | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
| PETG | Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol |
| ANSYS | Analysis System Software |
References
- Shires, A.; Kourkoulis, V. Application of Circulation Controlled Blades for VAWTs. Energies 2013, 6, 3744–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, J.P.; Nix, A.C.; Panther, C.C.; Huebsch, W.W.; Smith, J.E. Dynamic Circulation Control for a VAWT using Virtual Solidity Matching. Smart Grid Renew. Energy 2017, 8, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wilhelm, J.P.; Panther, C.C.; Pertl, F.A.; Smith, J.E. Vortex Analytical Model of a CC-VAWT. In Proceedings of the ASME 2009 3rd International Conference on Energy Sustainability, San Francisco, CA, USA, 19–23 July 2009. ASME ES2009-90348. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Wilhelm, J.P.; Nawrocki, A.; Hard, S.; Smith, J.E. Controller Design Methodology for a CC-VAWT. (Cited Within Wilhelm 2017). In Proceedings of the 28th AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 28 June–1 July 2010. AIAA 2010-4405. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Larion, I.; Lemu, H.G. Study of Coanda Effect Applied to Vertical Wind Turbine Blades. In Proceedings of the ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–20 November 2014. ASME IMECE (Draft Proceedings). [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Gu, J.; Hu, K.; Zhu, H.; Miao, J.; Li, X.; Ma, D.; Mi, Y.; Wang, Z. Influences of trailing edge split flap on the aerodynamic performance of VAWT. Energy Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.D. Fundamentals of Aerodynamics, 6th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, X. Numerical simulation of airflow dynamics in turbine blades using ANSYS. Int. J. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 2022, 36, 321–335. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, M.; Lee, H.S. 3D printing technologies in renewable energy applications. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 58, 456–467. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, M.O.L. Aerodynamics of Wind Turbines, 3rd ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, P.D.; Kuznetsov, A.V. Mathematical modeling of aerodynamic structures in wind turbine blades. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2023, 75, 041001. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, L.K.; Patel, R. Aerodynamic optimization of wind turbine blades using the Coanda effect. Wind. Energy Sci. 2021, 6, 89–102. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.J.; Park, J.H. Structural analysis of composite materials in wind turbine applications. Compos. Struct. 2023, 295, 115789. [Google Scholar]
- Michna, J.; Śledziewski, M.; Rogowski, K. The Harmonic Pitching NACA 0018 Airfoil in Low Reynolds Number Flow. Energies 2025, 18, 2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, K.; Schmidt, H. Optimization of 3D printing parameters for PETG in engineering applications. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 32, 101045. [Google Scholar]
- Panaitescu, M.; Panaitescu, F.-V.; Panait, P.-G.; Scupi, A. Considerations Regarding Oiling System for Offshore Wind Turbines. TransNav 2023, 17, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristea, M.; Popa, A.; Scurtu, I.C. Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulation Approach for Scrubber Wash Water pH Modelling. Energies 2022, 15, 5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scupi, A.; Panait, P.-G.; Panaitescu, F.-V. Some aspects regarding the optimization of the wind turbine’s vibration systems. J. Mar. Technol. Environ. 2022, 2, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simsek, S.; Dogan, F. Comparison of the efficiency of wind power plants from renewable energy types to reduce atmosphere pollution in Marmara region. Therm. Sci. 2023, 27, 3171–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stan, L.; Calimanescu, I.; Popa, V. Computer fluid dynamics (CFD) study of new innovative backflow marine propeller. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 400, 082019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulus, A.; Moldovan, S.I. Optimization of Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Systems to Capture Vehicle-Induced Highway Winds. Energies 2025, 18, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilotijević, V.; Svorcan, J.M.; Šekularac, M.B.; Vušanović, I.; Hondžo, M. Aerodynamic analysis of field wind turbine: A comparative study of computational methods with experimental validation. Therm. Sci. 2025, 29, 1607–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, F.M. Fluid Mechanics, 9th ed.; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hand, B.P.; Kelly, G.; Cashman, A. Aerodynamic design and performance parameters of a lift-type vertical-axis wind turbine: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 139, 110699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.D.; Nguyen, T. Experimental methods in wind tunnel testing for turbine blades. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2021, 125, 110387. [Google Scholar]
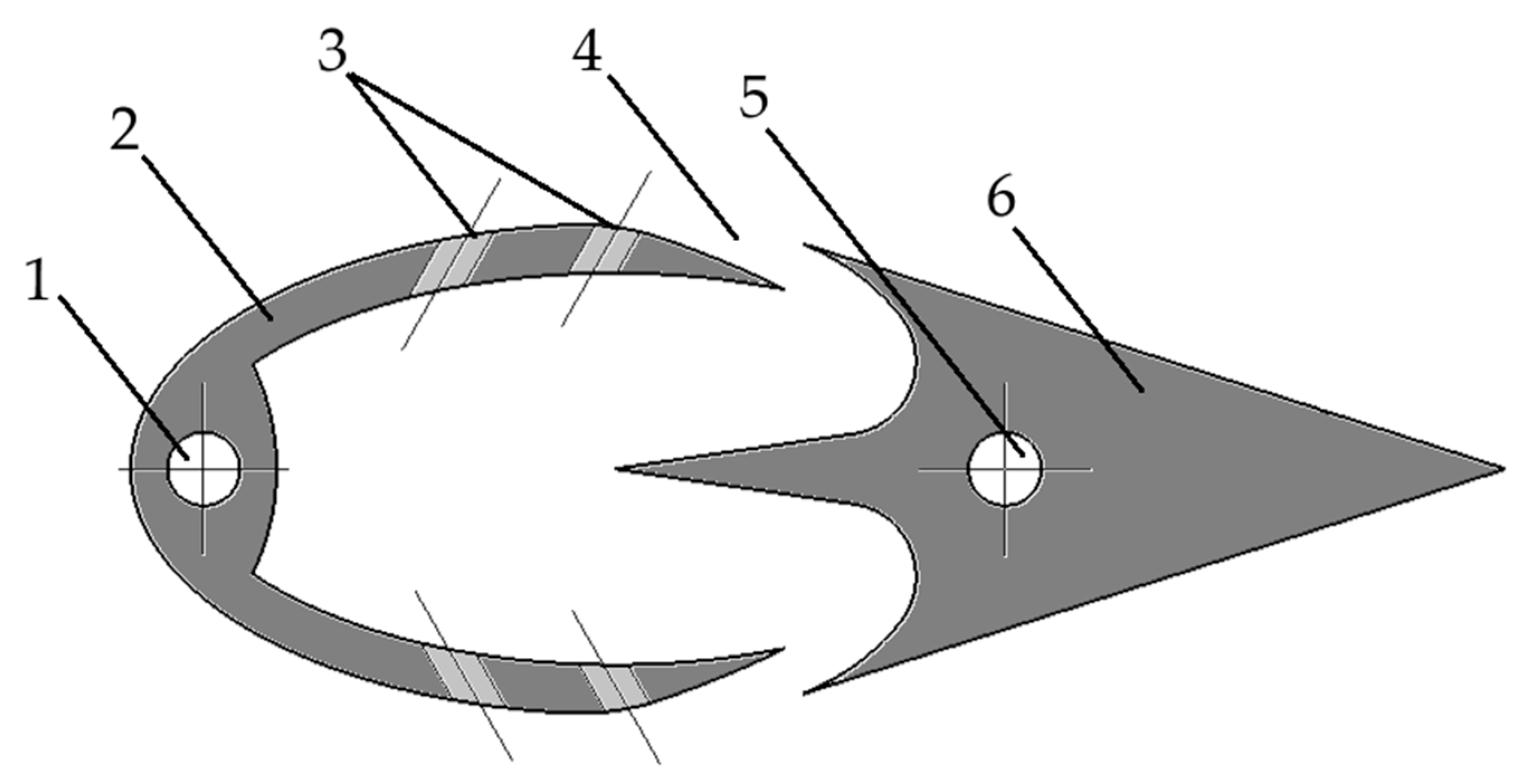
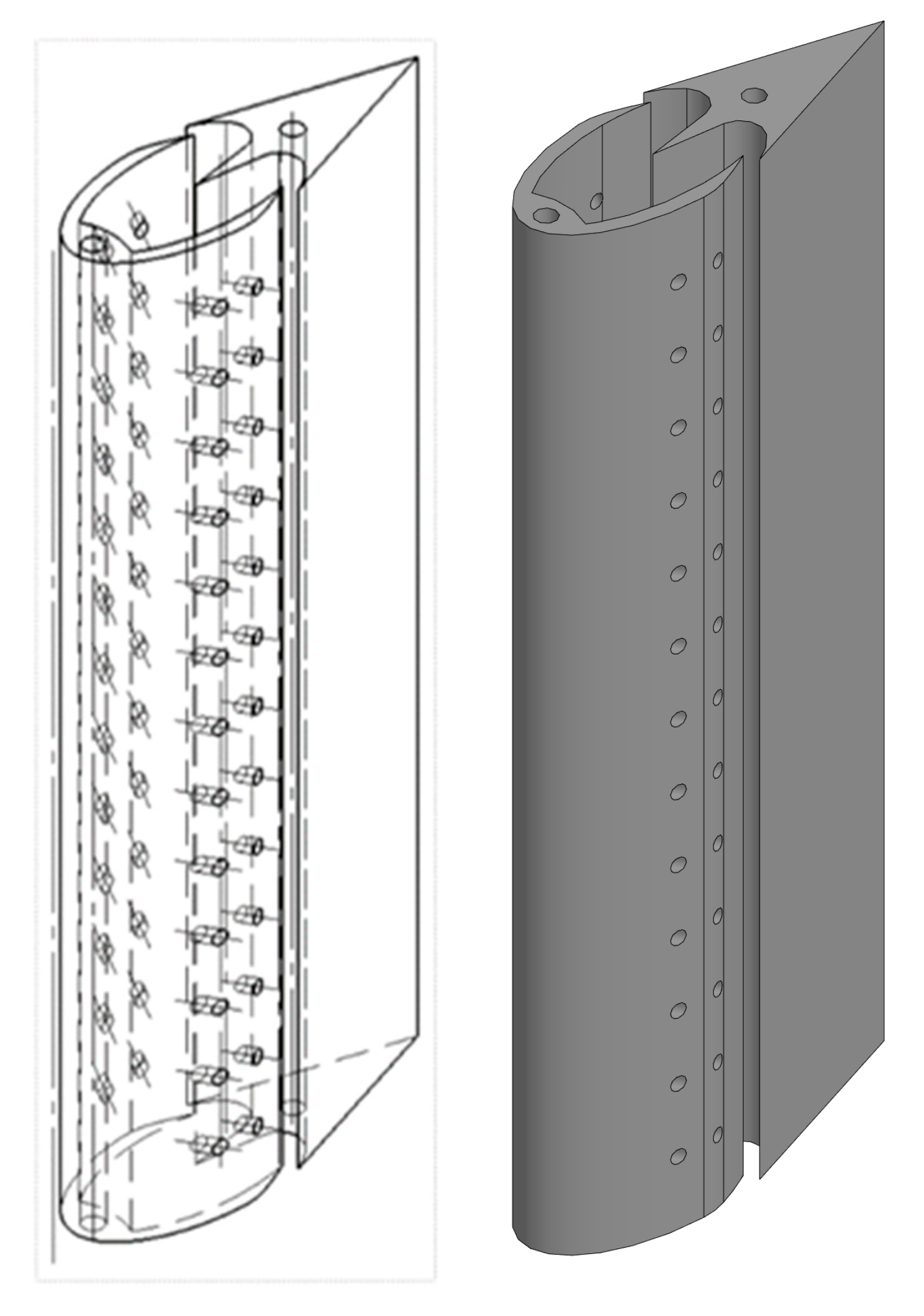

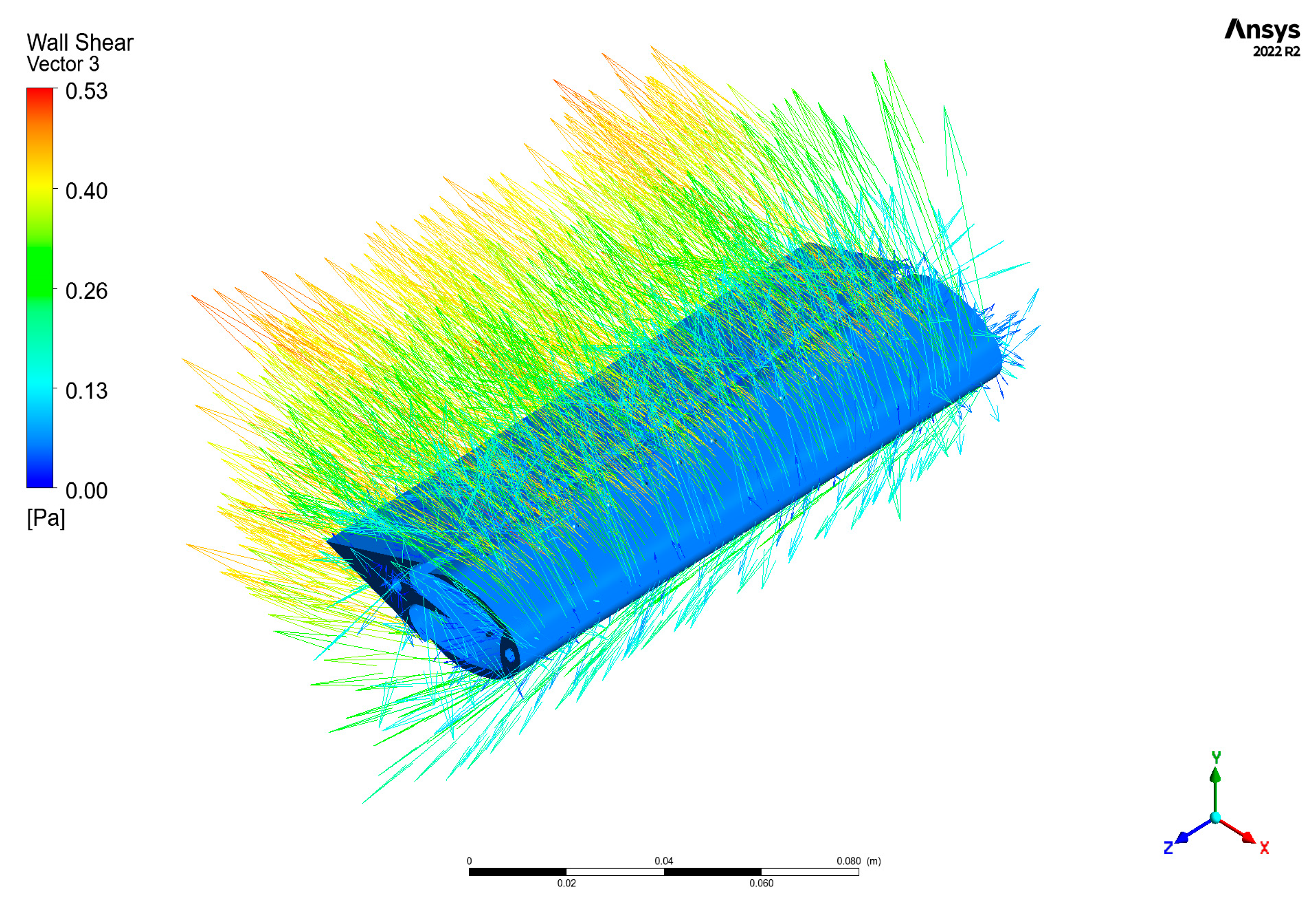
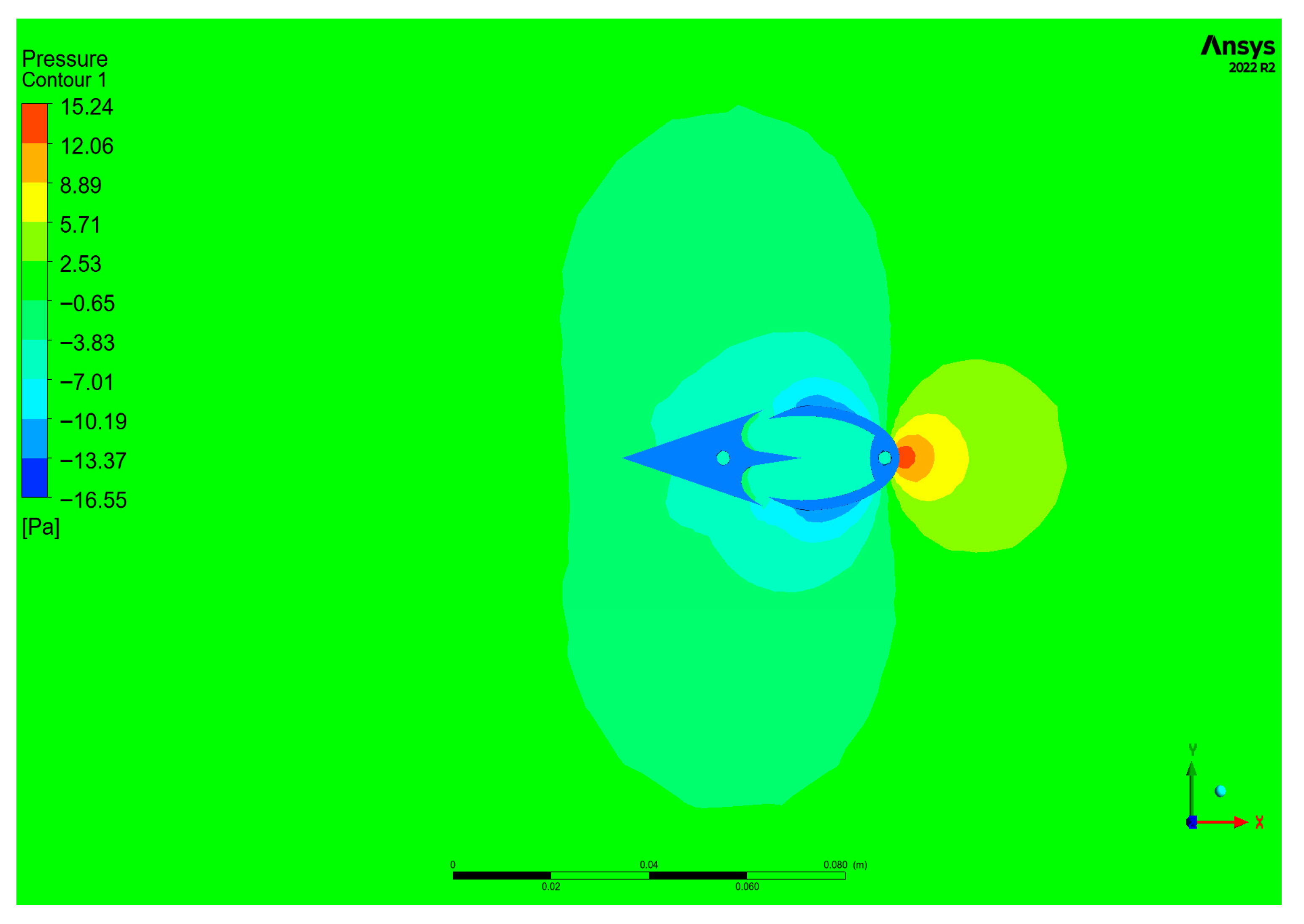
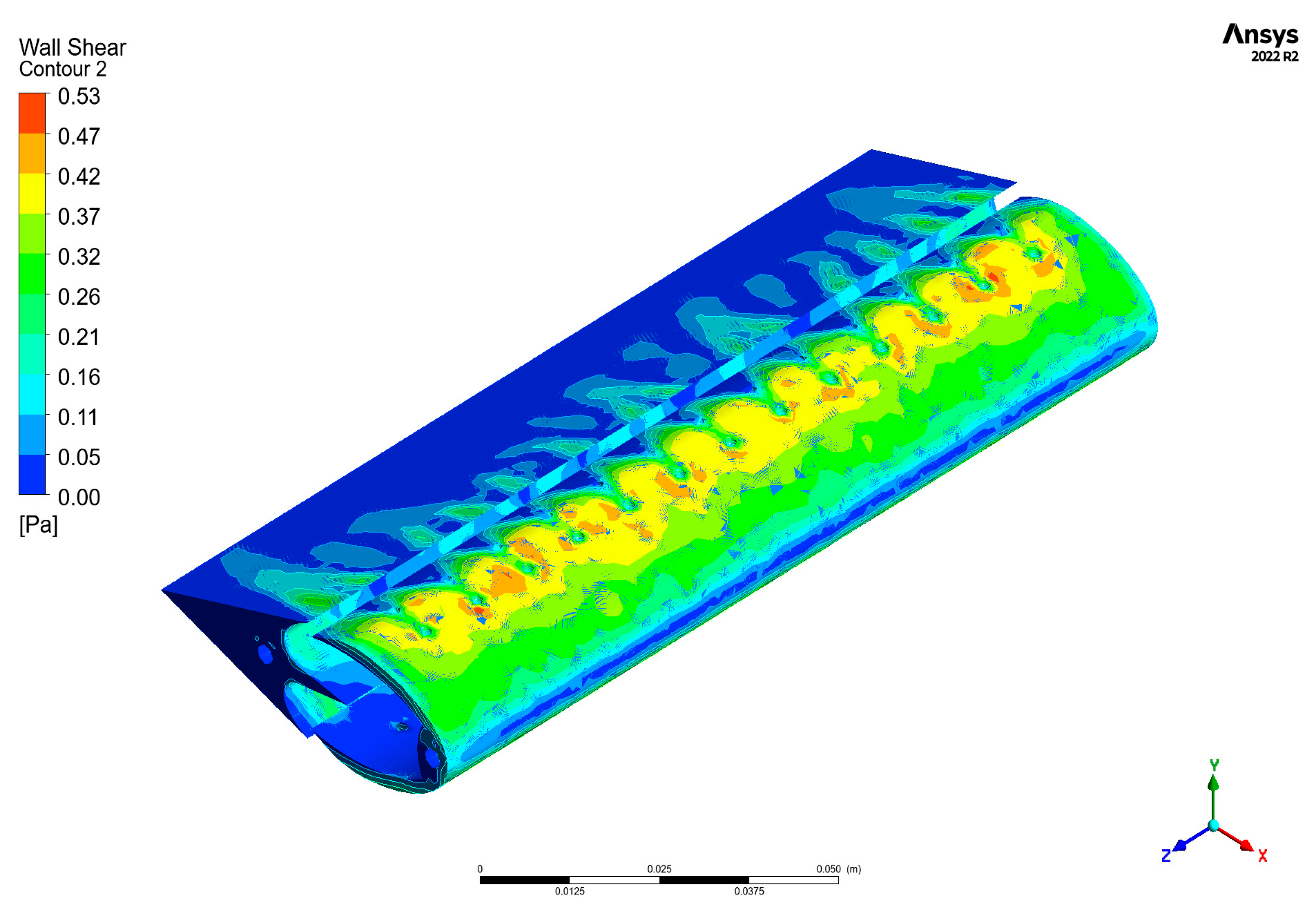
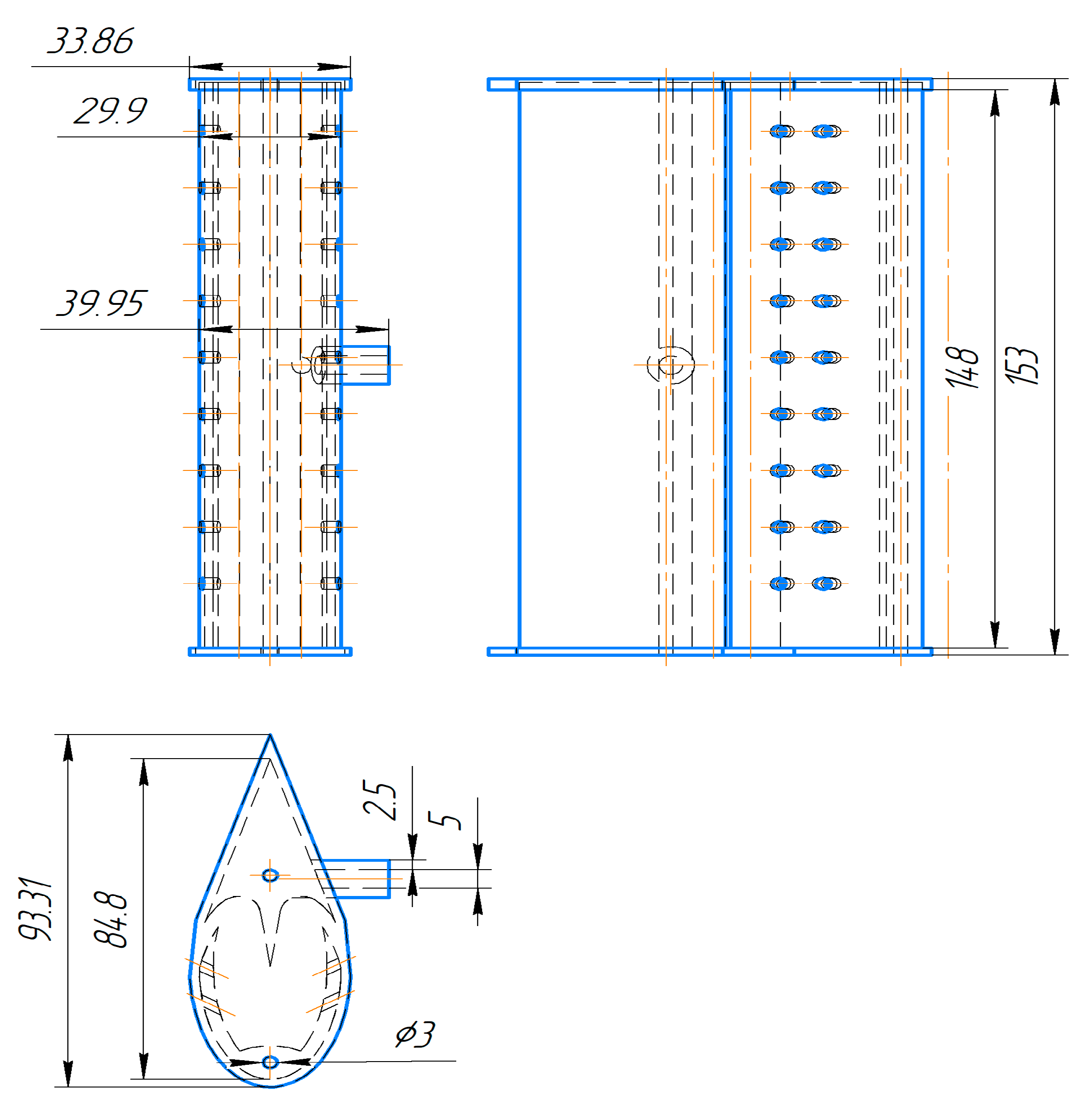
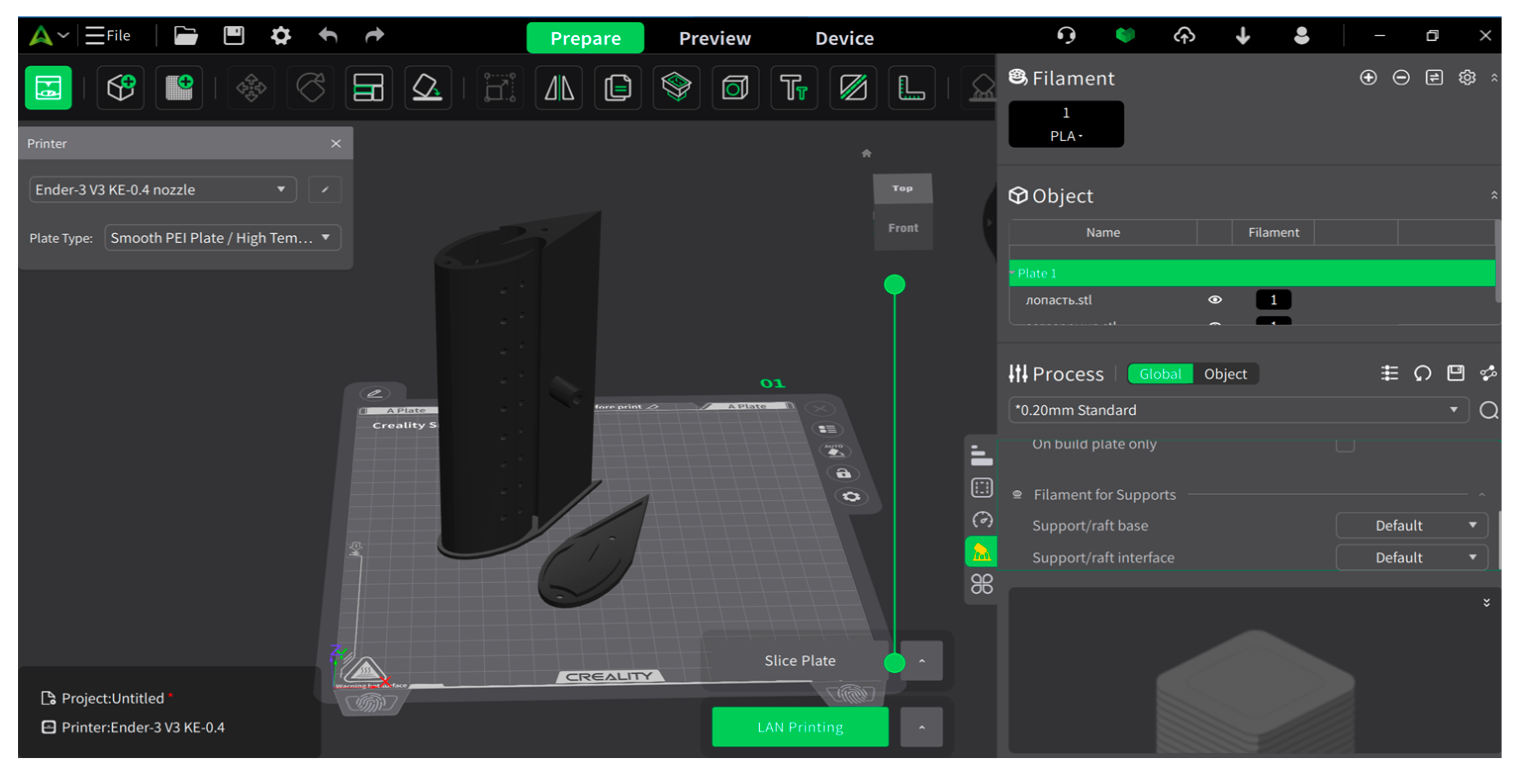
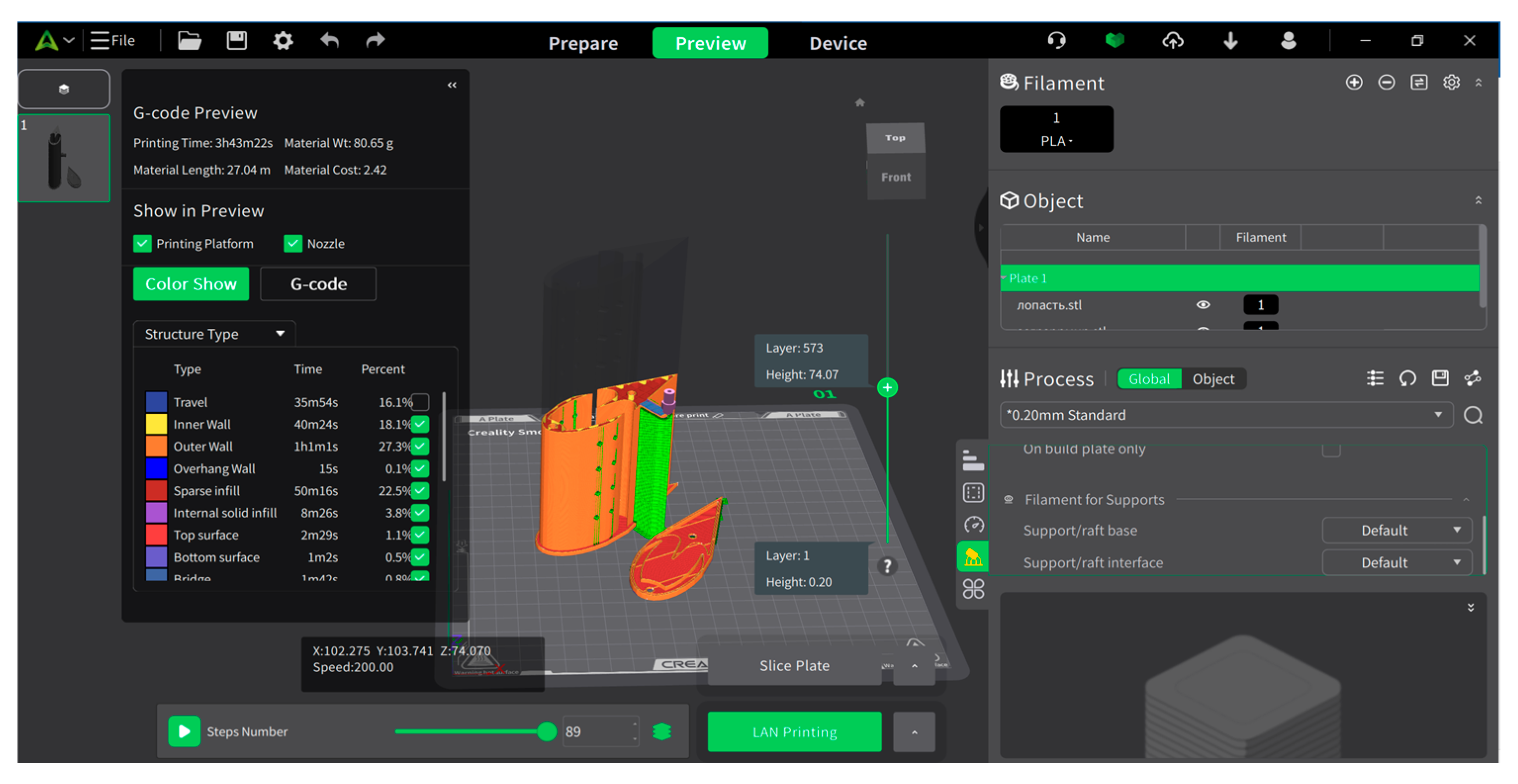

| Mesh Case | Max Element Length Throughout Domain | Max Element Length in the Interest Area | Nodes | Elements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial mesh | 0.1 m | 0.04 m | 97,266 | 118,883 |
| Rougher mesh | 0.1 m | 0.02 m | 122,362 | 620,681 |
| Refined mesh | 0.1 m | 0.01 m | 168,459 | 925,743 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scheaua, F.D.; Ramazanuly, A.M.; Scurtu, I.C. Investigation of an Innovative Blade with an Internal Channel and Tangential Slots for Enhanced Thrust Generation Using the Coanda Effect. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10117. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810117
Scheaua FD, Ramazanuly AM, Scurtu IC. Investigation of an Innovative Blade with an Internal Channel and Tangential Slots for Enhanced Thrust Generation Using the Coanda Effect. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(18):10117. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810117
Chicago/Turabian StyleScheaua, Fanel Dorel, Almat Mukhamedrahim Ramazanuly, and Ionut Cristian Scurtu. 2025. "Investigation of an Innovative Blade with an Internal Channel and Tangential Slots for Enhanced Thrust Generation Using the Coanda Effect" Applied Sciences 15, no. 18: 10117. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810117
APA StyleScheaua, F. D., Ramazanuly, A. M., & Scurtu, I. C. (2025). Investigation of an Innovative Blade with an Internal Channel and Tangential Slots for Enhanced Thrust Generation Using the Coanda Effect. Applied Sciences, 15(18), 10117. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810117








