Nano Zero-Valent Iron—Rubber Seed Shell Biochar (nZVI-RSSB) Enhances Removal of Cadmium from Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Biochar
2.3. Characterization of Biochar
2.4. Batch Adsorption Experiment
2.4.1. Adsorption Kinetics
2.4.2. Adsorption Isotherm
2.4.3. Removal of Heavy Metals by Biochar in the Actual Water
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Characterization of Biochar
3.2. Factors Influencing Cd (II) Adsorption of Biochar
3.2.1. Effect of Time on Cd (II) Adsorption of RSSB and nZVI-RSSB
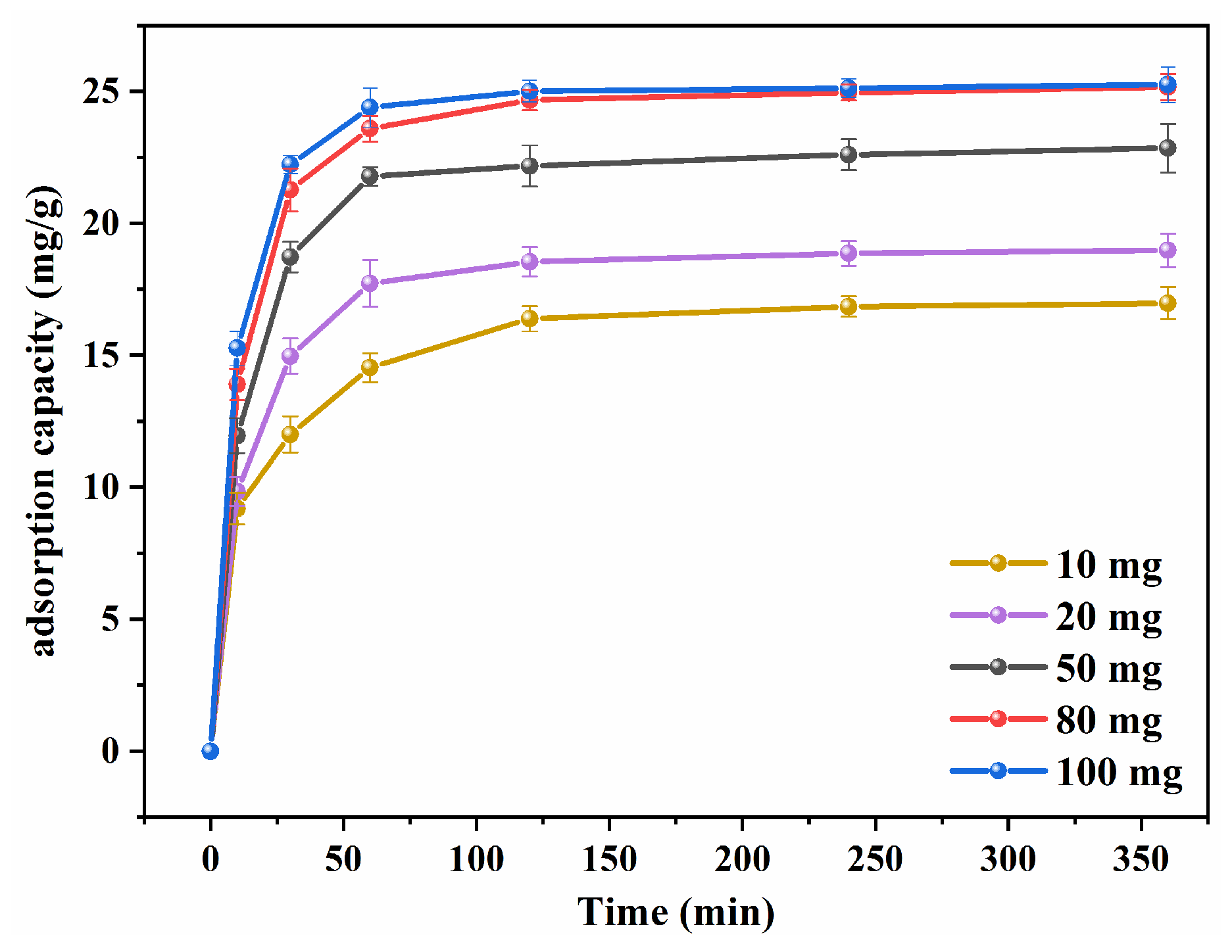
3.2.2. Effect of Dosages on Cd (II) Adsorption of nZVI-RSSB450
3.2.3. Effect of Initial Cd (II) Concentration on Cd (II) Adsorption of nZVI-RSSB
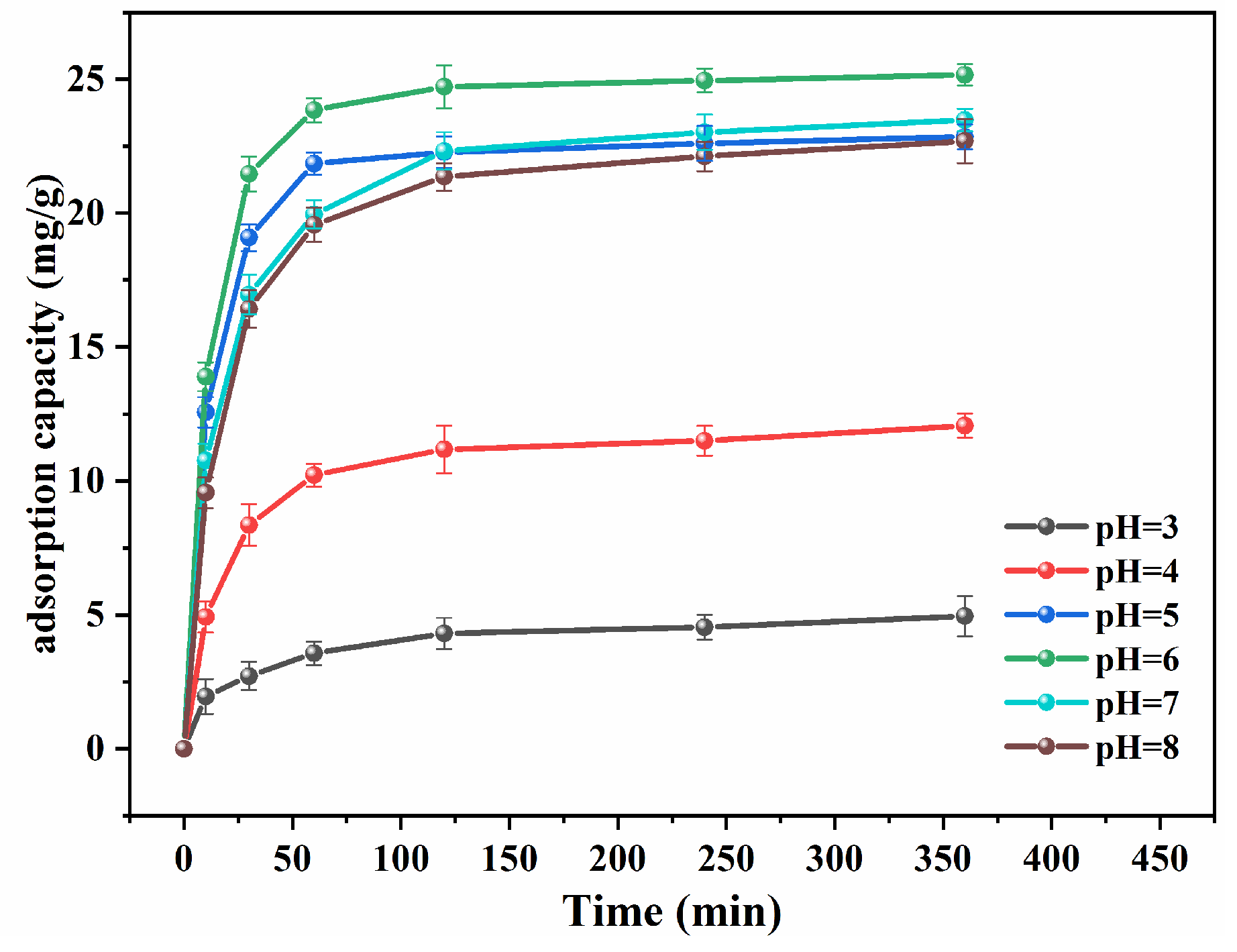
3.2.4. Effect of pH on Cd (II) Adsorption of nZVI-RSSB
3.2.5. Effects of Temperature on Cd (II) Adsorption of nZVI-RSSB450
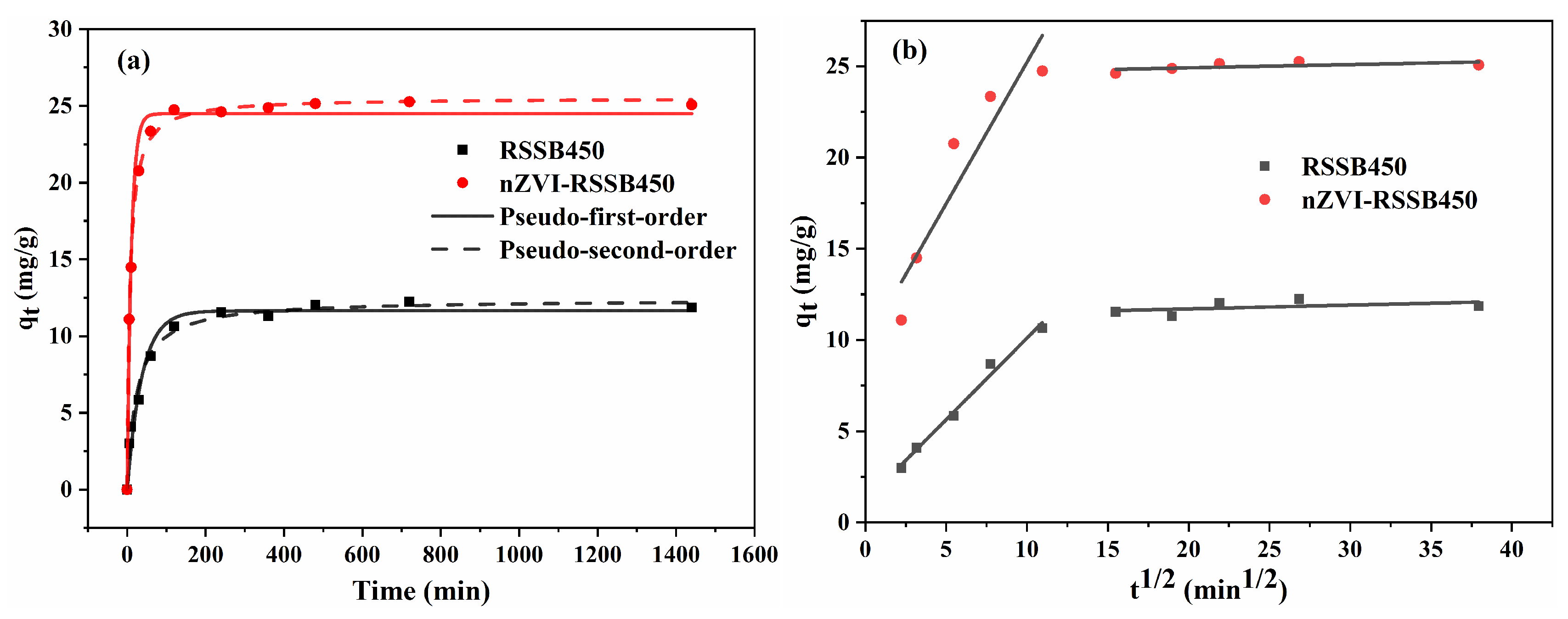
3.3. Cd (II) Adsorption Kinetics of RSSB450 and nZVI-RSSB450
3.4. Cd (II) Adsorption Isotherm of RSSB450 and nZVI-RSSB450
3.5. Removal of Metals by Biochar in the Actual Water
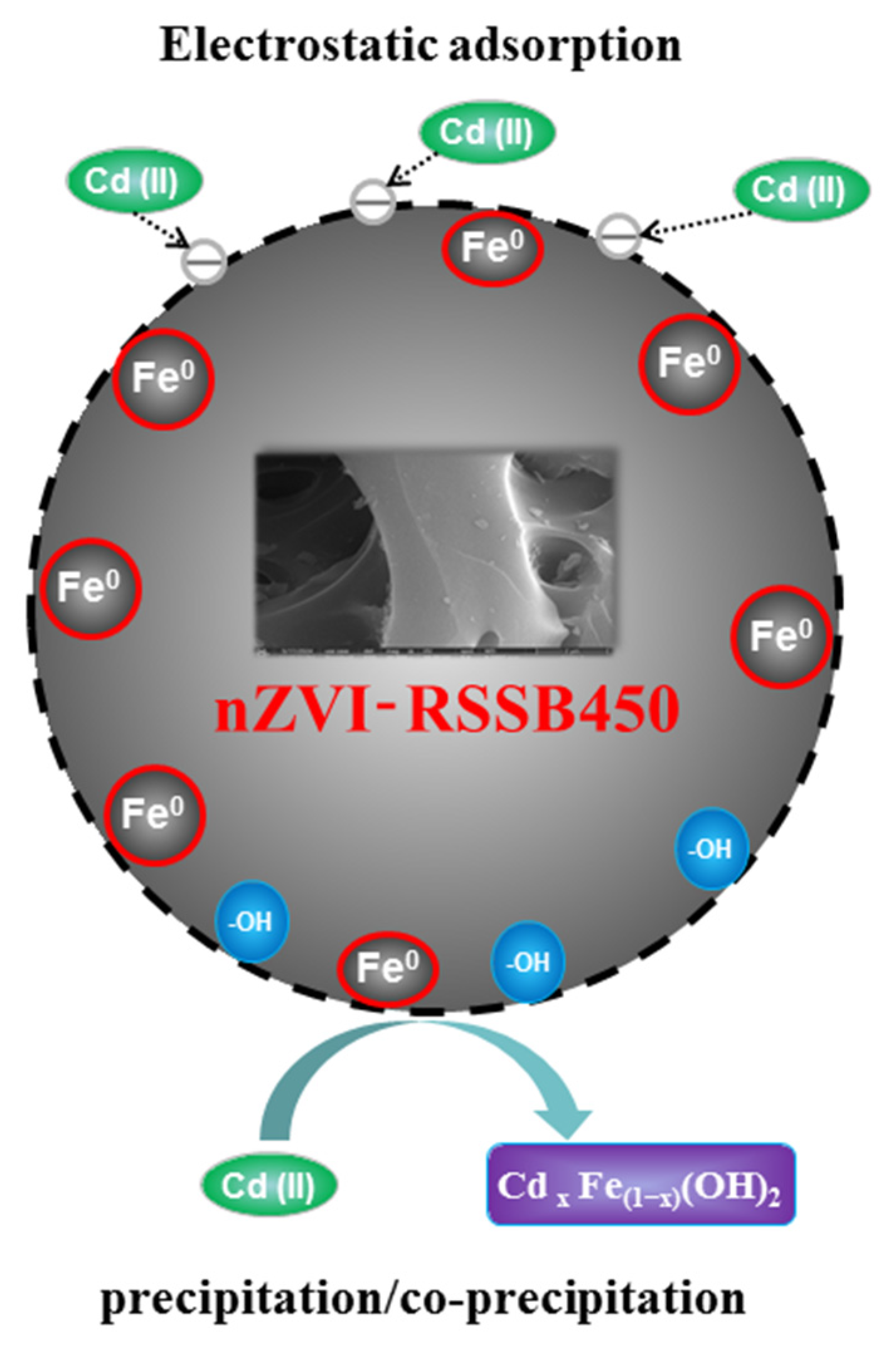
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shrestha, R.; Ban, S.; Devkota, S.; Sharma, S.; Joshi, R.; Tiwari, A.P.; Kim, H.Y.; Joshi, M.K. Technological trends in heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; DesMarais, T.; Costa, M. Metals and mechanisms of carcinogenesis. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 59, 537–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Tao, Y. Pollution status of heavy metals and metalloids in Chinese lakes: Distribution, bioaccumulation and risk assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 248, 114293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Luo, C.; Yan, F.; Yang, Y.; Guo, B.; Wang, L.; Xu, S.; Wu, F.; Ji, P. Remediation of Pb (II) and Cd (II) in polluted waters with calcium thioglycolate–modified straw biochar. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 338, 122638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Kan, Y.; Xu, X. Stability and regeneration of metal catalytic sites with different sizes in Fenton-like system. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 108278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Li, X.; Xing, J.; Xu, G. Adsorption of potentially toxic elements in water by modified biochar: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zheng, L.; Wang, S.L.; Wu, Z.; Wu, W.; Niazi, N.K.; Shaheen, S.M.; Rinklebe, J.; Bolan, N.; Yong, S.; et al. Sorption mechanisms of lead on silicon-rich biochar in aqueous solution: Spectroscopic investigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, C.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y. Novel carbon-based sorbents for elemental mercury removal from gas streams: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, P.; Liang, D.; Yang, L.; Shi, H.; Xiong, Z.; Ding, L.; Zhang, K.; Luo, X. Evaluating the adsorptivity of organo-functionalized silica nanoparticles towards heavy metals: Quantitative comparison and mechanistic insight. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhang, N.; Chen, T.; Ding, Z. Sorption of Pb (II) and Cu (II) on the colloid of black soil, red soil and fine powder kaolinite: Effects of pH, ionic strength and organic matter. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2019, 31, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Chen, T.; Huang, Q.; Wang, J.; Lu, S.; Yan, J. Enhanced adsorption for Pb (II) and Cd (II) of magnetic rice husk biochar by KMnO4 modification. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 8902–8913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Duan, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Qiu, P.; He, Y.; Shang, P. Selective adsorption and recovery of silver from acidic solution using biomass-derived sulfur-doped porous carbon. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 40088–40099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; He, F.; Yu, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, H.; Yong, S.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, B. Surface functional groups of carbon-based adsorbents and their roles in the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 366, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, R.; Pant, D.; Malaviya, P. Engineered algal biochar for contaminant remediation and electrochemical applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrees, M.; Batool, S.; Kalsoom, T.; Yasmeen, S.; Kalsoom, A.; Raina, S.; Zhuang, Q.; Kong, J. Animal manure-derived biochars produced via fast pyrolysis for the removal of divalent copper from aqueous media. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 213, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Xiao, G.; Liang, J.; Kong, L.; Yao, X.; Diao, Z. A novel pigeon waste based biochar composite for the removal of heavy metal and organic compound: Performance, products and mechanism. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 666, 131277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Lai, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Han, W.; Zhang, M.; Ji, H. Synthesis and environmental applications of biochar-supported nano-zero-valent iron composites: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024, 22, 1345–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, G.; Usman, M.; Ahmed, Z.; Hyder, S.; Alwahibi, M.S.; Rizwana, H.; Iqbal, J.; Ali, B.; Iqbal, R.; Ahmad, S.; et al. Improving wheat physio-biochemical attributes in ciprofloxacin-polluted saline soil using nZVI-modified biochar. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 286, 117202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, R.; Xiao, R.; Zhang, Z. Effects and mechanisms of nano zero-valent iron-modified biochar on Cd (II) stabilization in contaminated soils. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2022, 41, 2478–2487. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, C.; Ren, J.; Tao, L.; Ren, H.; Wang, M.; Wang, B. Study of the remediation effect and mechanism of biochar-loaded nZVI on heavy metal contaminated soil. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Tufail, S.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.; Shang, J. Green sustainable and highly efficient hematite nanoparticles modified biochar-clay granular composite for Cr (VI) removal and related mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 123009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Yousef, S.; Ali, S.; Sriubas, M.; Varnagiris, S.; Tuckute, S.; Abdelnaby, M.; Kamel, B.M. Highly efficient visible light photodegradation of Cr (VI) using electrospun MWCNTs-Fe3O4@ PES nanofibers. Catalysts 2021, 11, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Kaur, M.; Ubhi, M.K.; Kaur, N.; Greneche, J.M. Composition optimization of activated carbon-iron oxide nanocomposite for effective removal of Cr (VI) ions. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 258, 124002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eljamal, O.; Eljamal, R.; Maamoun, I.; Khalil, A.M.; Shubair, T.; Falyouna, O.; Sugihara, Y. Efficient treatment of ammonia-nitrogen contaminated waters by nano zero-valent iron/zeolite composite. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 131990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, M.E.; Mohamed, A.K.; Salam, M.A. Self-decoration of N-doped graphene oxide 3-D hydrogel onto magnetic shrimp shell biochar for enhanced removal of hexavalent chromium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Ye, J.; Zeng, S.; Yang, C. Research and development status of rubber seed resources. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2019, 24, 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Onyekwere, O.S.; Odiakaose, C.; Uyanga, K.A. Multi response optimization of the functional properties of rubber seed-shear butter based core oil using d-optimal mixture design. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2017, 17, 207–223.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Preparation, Detoxification Process and Stability of Rubber Seed Emulsion. Master’s Thesis, Hainan University, Haikou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tao, L.; Bi, B.; Niu, G.; Han, X.; Deng, L. Study on the potential development and utilization value of rubber seed resources. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2015, 30, 642–647. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Shi, Z.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, J. Study on preparation of activated carbon by microwave irradiation of rubber seed shell zinc chloride. Sichuan For. Sci. Technol. 2007, 28, 82–84. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, T.; Deng, X.; Dai, W. Study on preparation of rubber seed shell activated carbon by steam method. For. Chem. Ind. 2006, 26, 41–43. [Google Scholar]
- Diao, Z.; Qian, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, J.; Chen, Z.; Guo, P.; Dong, F.; Yan, L.; Kong, L.; Chu, W. Removals of Cr (VI) and Cd (II) by a novel nanoscale zero valent iron/peroxydisulfate process and its Fenton-like oxidation of pesticide atrazine: Coexisting effect, products and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 397, 125382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Tang, X.; He, M.; Yang, S.; Liu, X.; Xu, J. Simultaneous adsorption of Cd (II) and As (III) by a novel biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron in aqueous systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Gao, J.; Chen, X.; Ouyang, X.; Weng, L.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y. Stability and interaction of biochar and iron mineral nanoparticles: Effect of pH, ionic strength, and dissolved organic matter. Biochar 2022, 4, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Yang, L.; Ouyang, D.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, W.; Gu, M.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; Huang, L.; Qian, L. Enhanced removal of 1, 2, 4-trichlorobenzene by modified biochar supported nanoscale zero-valent iron and palladium. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Guo, J.; Ren, J.; Zhou, F. Efficient removal of lead from aqueous solution by urea-functionalized magnetic biochar: Preparation, characterization and mechanism study. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 91, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villabona-Ortíz, A.; Tejada-Tovar, C.N.; Ortega-Toro, R. Modelling of the adsorption kinetics of chromium (VI) using waste biomaterials. Rev. Mex. De Ing. Química 2020, 19, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Zhao, B.; Diao, J. Adsorption characteristics of wheat straw biochar on Cd (II)2+ in water. China Environ. Sci. 2017, 37, 551–559. [Google Scholar]
- Maamoun, I.; Eljamal, R.; Falyouna, O.; Bensaida, K.; Sugihara, Y.; Eljamal, O. Insights into kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamics of phosphorus sorption onto nanoscale zero-valent iron. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 328, 115402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, M.B.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Abbas, F.; Bibi, I.; Riaz, M.; Khalil, U.; Niazi, N.K.; Rinklebe, J. A review of biochar-based sorbents for separation of heavy metals from water. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2020, 22, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Fang, Z.; Tsang, P.E.; Fang, J.; Zhao, D. Stabilisation of nanoscale zero-valent iron with biochar for enhanced transport and in-situ remediation of hexavalent chromium in soil. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Ouyang, D.; Yan, J.; Qian, L.; Han, L.; Chen, M.; Li, J.; Gu, M. Mechanistic insights into adsorptive and oxidative removal of monochlorobenzene in biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron/persulfate system. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Shi, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, F.; Chen, Z.; Pang, W.; Yang, D. Adsorption characteristics and mechanism of nano zero-valent iron modified biochar on ammonia nitrogen in water. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 3270–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Huang, M.; Huang, C. Specific chemical adsorption of selected divalent heavy metal ions onto hydrous γ-Fe2O3-biochar from dilute aqueous solutions with pH as a master variable. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Xu, L.; Li, N.; Wang, K.; Qu, Y.; Xu, Y. Enhanced arsenic migration in tailings soil with the addition of humic acid, fulvic acid and thiol-modified humic acid. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razmi, B.; Ghasemi-Fasaei, R.; Ronaghi, A.; Mostowfizadeh-Ghalamfarsa, R. Application of Taguchi optimization for evaluating the capability of hydrochar, biochar, and activated carbon prepared from different wastes in multi-elements bioadsorption. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 347, 131292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Zhang, W.; Yan, J.; Han, L.; Chen, Y.; Ouyang, D.; Chen, M. Nanoscale zero-valent iron supported by biochars produced at different temperatures: Synthesis mechanism and effect on Cr (VI) removal. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Xu, S.; Ma, Z.; Mou, Y. Trivalent antimony removal using carbonaceous nanomaterial loaded with zero-valent bimetal (iron/copper) and their effect on seed growth. Chemosphere 2022, 296, 134047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, U.K.; Ji, W.; Liang, Y.; Ma, H.; Pu, S. Mechanism enhanced active biochar support magnetic nano zero-valent iron for efficient removal of Cr (VI) from simulated polluted water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Y.; Cheng, K.; Li, J.; Tsang, D.C. Fabrication and characterization of hydrophilic corn stalk biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron composites for efficient metal removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Ye, Z.; Xie, W.; Chen, Q.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.; Yao, M. Rapid magnetic removal of aqueous heavy metals and their relevant mechanisms using nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI) particles. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4050–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Alam, M.S.; Konhauser, K.O.; Alessi, D.S.; Xu, S.; Tian, W.; Liu, Y. Influence of pyrolysis temperature on production of digested sludge biochar and its application for ammonium removal from municipal wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhuo, H.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Peng, X.; Zhong, L. Using FeCl3 as a solvent, template, and activator to prepare B, N co-doping porous carbon with excellent supercapacitance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 15983–15994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhong, D.; Xu, Y.; Chang, H.; Shen, H.; Xu, C.; Mou, J.; Zhong, N. Enhanced removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution by nano-zero-valent iron supported by KOH activated sludge-based biochar. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 651, 129697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, A.; Sheng, D.; Sun, K.; Si, Y.; Azeem, M.; Abbas, A.; Bilal, M. Remediation of heavy metals polluted environment using Fe-based nanoparticles: Mechanisms, influencing factors, and environmental implications. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Cai, C.; Chi, H.; Reid, B.J.; Coulon, F.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Y. Remediation of cadmium and lead polluted soil using thiol-modified biochar. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 122037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Qu, B.; Yuan, H.; Song, J.; Li, W. Heavy metal mobility in contaminated sediments under seawater acidification. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 192, 115062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Yuan, F.; Zeng, G.; Li, X.; Gu, Y.; Shi, L.; Liu, W.; Shi, Y. Influence of pH on heavy metal speciation and removal from wastewater using micellar-enhanced ultrafiltration. Chemosphere 2017, 173, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, H.; Yan, F.; Li, S.; Guo, B.; Luo, C.; Huang, X.; Ji, P. Utilization of KOH-modified fly ash for elimination from aqueous solutions of potentially toxic metal ions. Environ. Res. 2023, 223, 115396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Meng, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, F.; Brookes, P. Zeolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron: New findings on simultaneous adsorption of Cd (II), Pb (II), and As (III) in aqueous solution and soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, D.H.K.; Lee, S.M. Magnetic biochar composite: Facile synthesis, characterization, and application for heavy metal removal. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 454, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.T.; Zhou, H.; Tang, S.F.; Zeng, P.; Gu, J.F.; Liao, B.H. Enhancing Cd (II) adsorption on rice straw biochar by modification of iron and manganese oxides. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 300, 118899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Rao, D.; Zou, L.; Teng, Y.; Yu, H. Capacity and potential mechanisms of Cd (II) adsorption from aqueous solution by blue algae-derived biochars. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 145447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, A.L.; Rusmirovic, J.D.; Velickovic, Z.; Kovacevic, T.; Jovanovic, A.; Cvijetic, I.; Marinkovic, A.D. Kinetics and column adsorption study of diclofenac and heavy-metal ions removal by amino-functionalized lignin microspheres. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 93, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W. Recycling spent lithium-ion battery as adsorbents to remove aqueous heavy metals: Adsorption kinetics, isotherms, and regeneration assessment. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 156, 104688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.M.; Yoo, S.; Choi, Y.K.; Park, S.; Kan, E. Adsorption isotherm, kinetic modeling and mechanism of tetracycline on Pinus taeda-derived activated biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 259, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Zhang, T.; Xiao, S.; He, H.; Yang, J.; Qin, Z. Preparation and adsorption performance of functionalization cellulose-based composite aerogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 211, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Sun, Y.; Liang, C.; Yang, T.; Mi, S.; Dai, Y.; Yu, M.; Yao, Q. Adsorption characteristics and mechanisms of Cd (II)2+ from aqueous solution by biochar derived from corn stover. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17714. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; He, J.; Sun, J.; Pei, Z.; Wu, Q.; Yu, R. Capacity and mechanisms of Pb (II) and Cd (II) (II) sorption on five plant-based biochars. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, G.; Liu, R.; Xu, J.; Si, W.; Wang, G. Efficient flocculation of multiple heavy metals by iron-based modified-carbonate biochar: Adsorption mechanism and practical application. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, F.; Wei, Y.; Li, G.; Shen, K.; He, H.J. High cadmium adsorption on nanoscale zero-valent iron coated Eichhornia crassipes biochar. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wu, Q.; Huang, C.; Wang, P.; Cheng, H.; Sun, C.; Zhu, J.; Xu, H.; Ouyang, K.; Guo, J.; et al. Synergistic effect and mechanism of Cd (II) (II) and As (III) adsorption by biochar supported sulfide nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

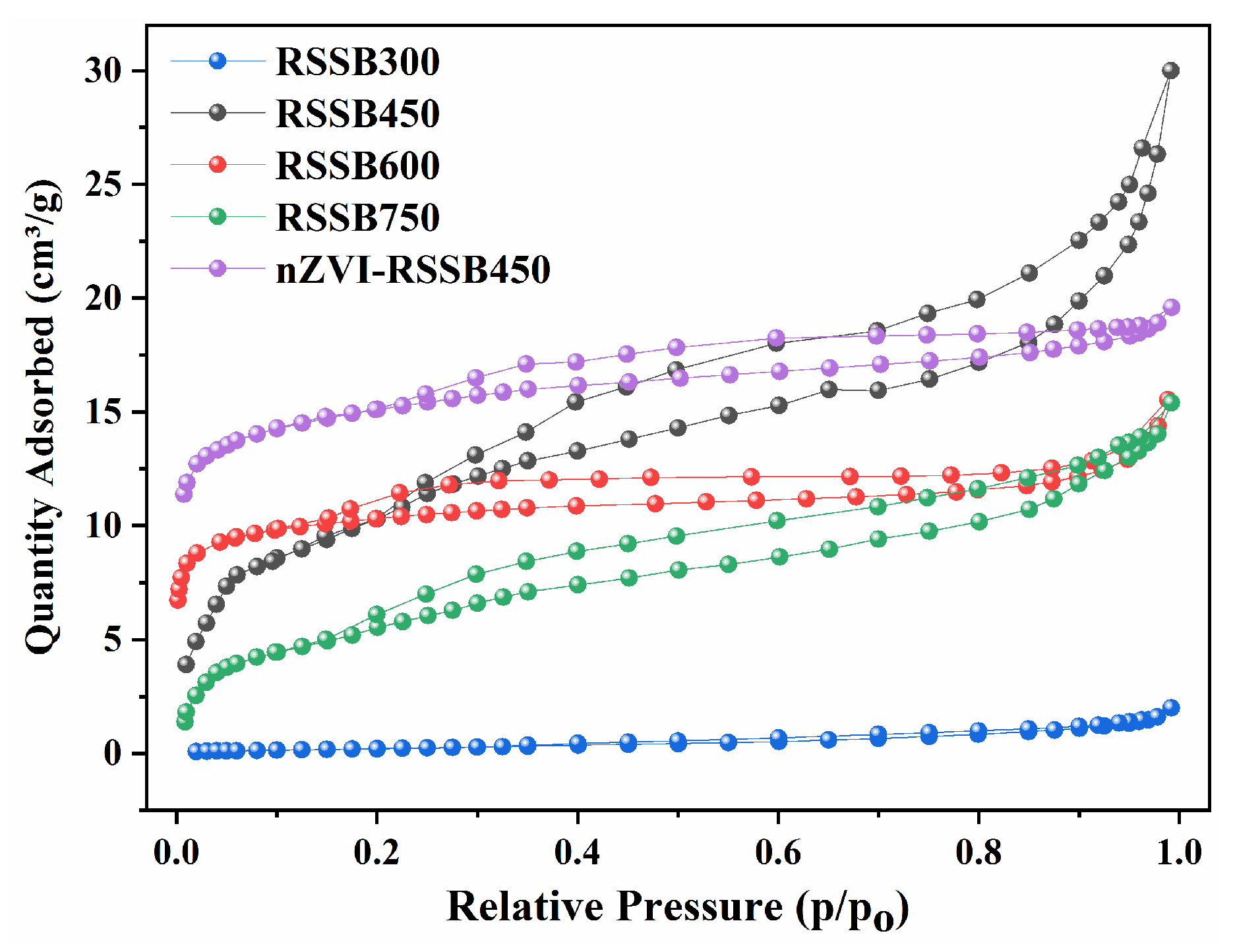
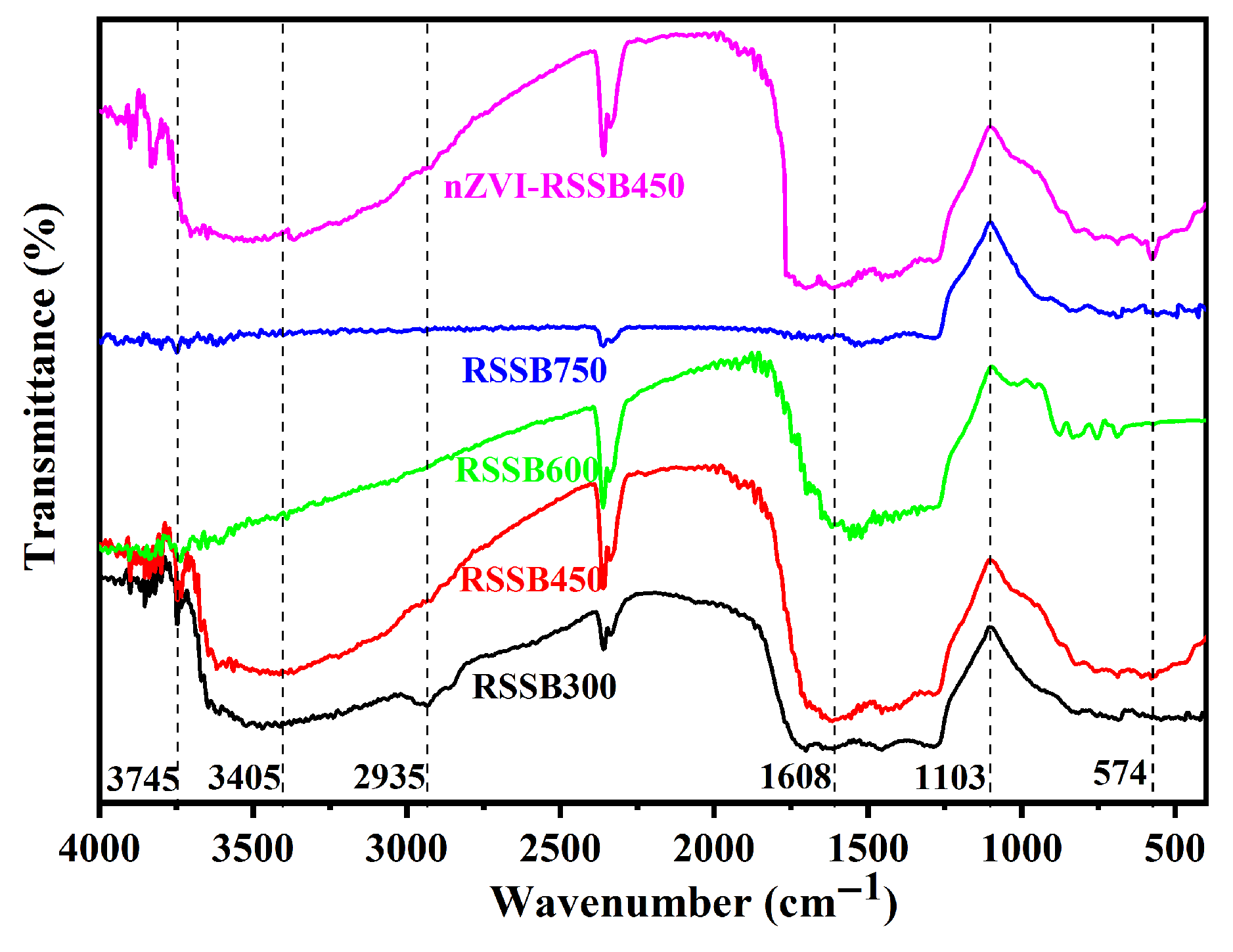
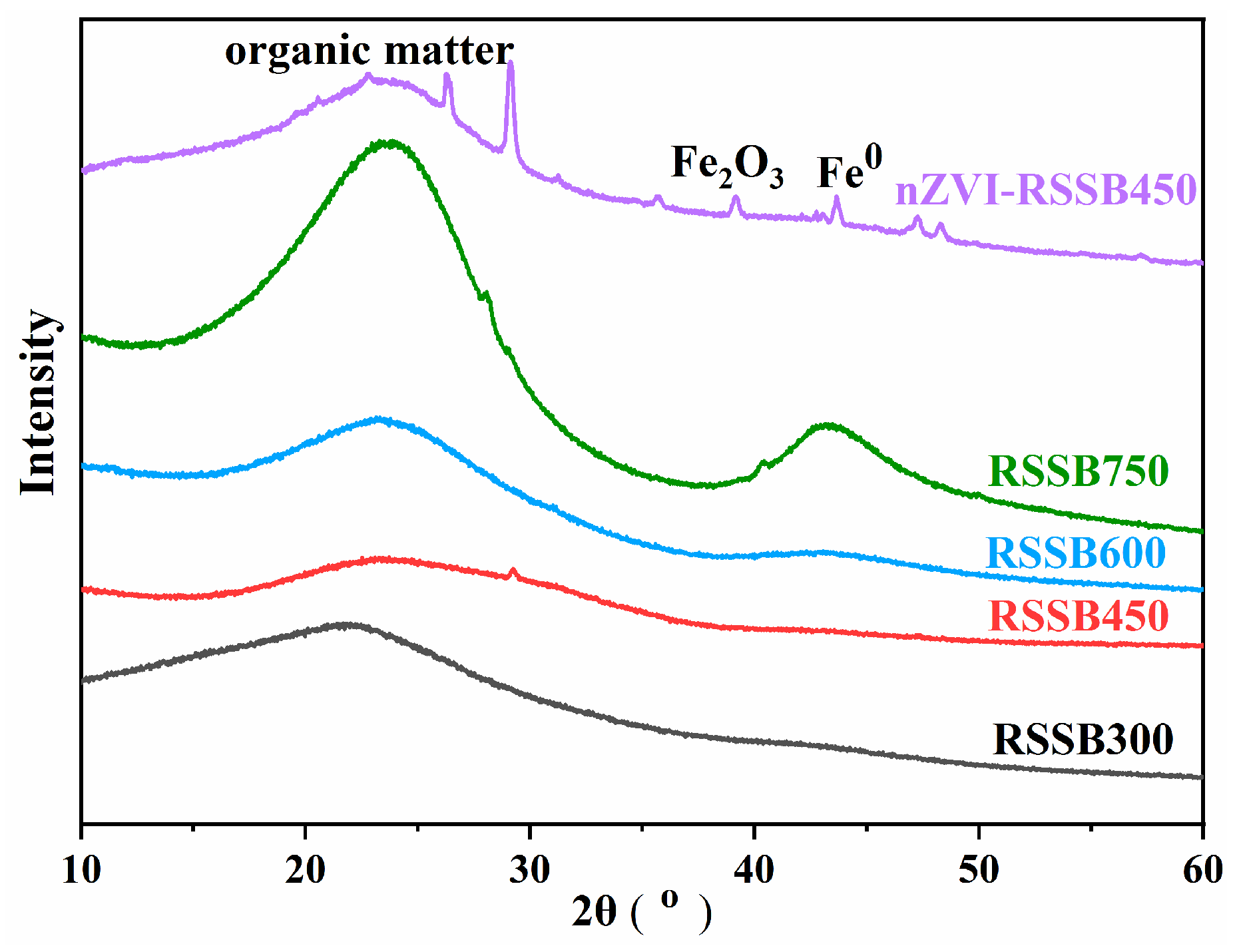
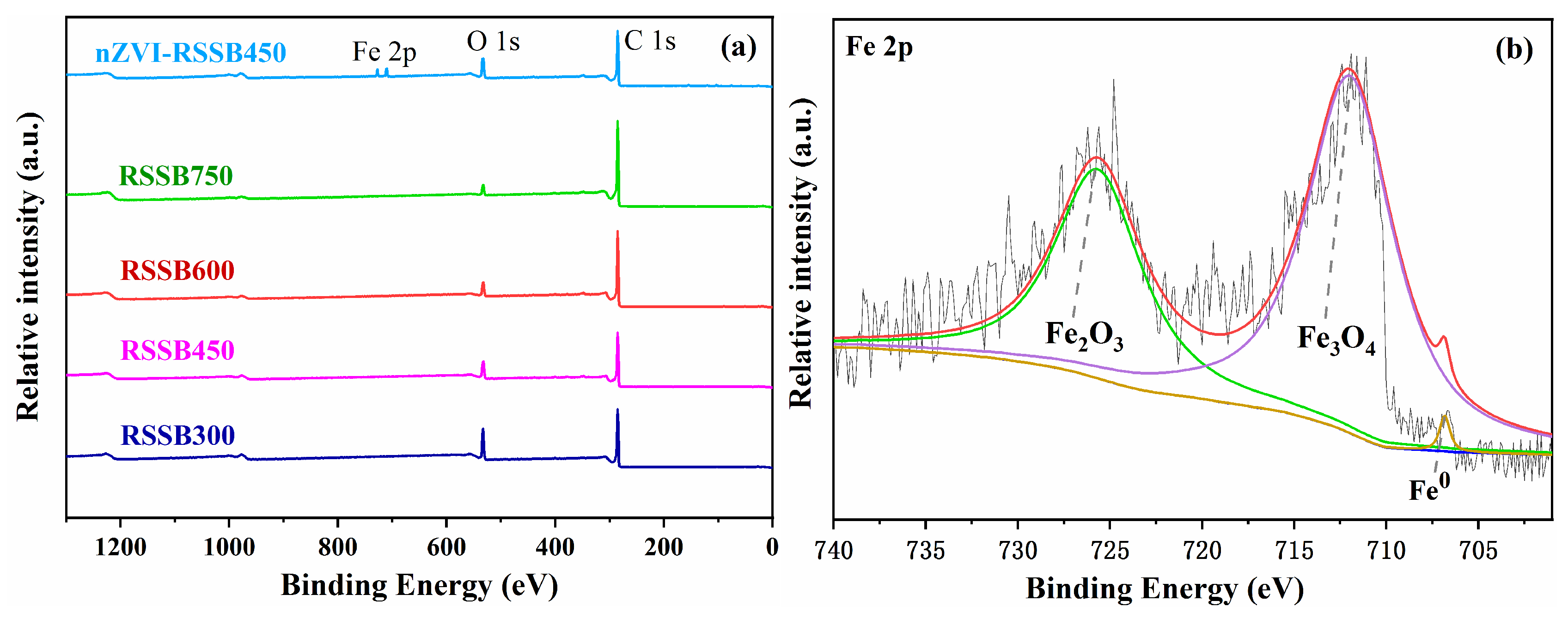





| Material | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Total Pore Volume (m3/g) | Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RSSB300 | 1.249 | 0.00308 | 9.844 |
| RSSB450 | 57.298 | 0.0303 | 3.944 |
| RSSB600 | 13.027 | 0.0148 | 5.076 |
| RSSB750 | 20.922 | 0.0239 | 4.824 |
| nZVI-RSSB450 | 39.416 | 0.0240 | 6.466 |
| Material | Pseudo-First-Order Kinetic Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe/(mg/g) | k1/min−1 | R2 | qe/(mg/g) | K2/g/mg·min−1 | R2 | |
| RSSB450 | 11.653 | 0.0266 | 0.9652 | 12.394 | 0.0034 | 0.9850 |
| nZVI-RSSB450 | 24.501 | 0.0940 | 0.9806 | 25.536 | 0.0057 | 0.9979 |
| Material | Intraparticle Diffusion Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | kip1/mg·min−0.5/g | R2 | C2 | kip2/mg·min−0.5/g | R2 | |
| RSSB450 | 1.1762 | 0.8932 | 0.9864 | 11.300 | 0.0207 | 0.4844 |
| nZVI-RSSB450 | 9.7210 | 1.5509 | 0.8739 | 24.568 | 0.0178 | 0.6098 |
| Material | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm/(mg/g) | KL/(L/mg) | R2 | KF/[(mg/g)(L/mg)1/n] | n | R2 | |
| RSSB450 | 13.977 | 0.1184 | 0.9862 | 3.6286 | 0.2757 | 0.9157 |
| nZVI-RSSB450 | 29.251 | 0.3754 | 0.9875 | 10.549 | 0.2337 | 0.9360 |
| Parameter | pH | Cd (II) (μg/L) | Pb (μg/L) | Cr(VI)(μg/L) | As (μg/L) | Hg (μg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial concentration | 6.04 ± 0.01 | 4.73 ± 0.12 | 38 ± 1.5 | 32 ± 2.2 | 17 ± 1.2 | 0.8 ± 0.04 |
| Final concentration (RSSB450) | 6.72 ± 0.02 | ND | 2.2 ± 0.11 | 6.1 ± 0.24 | 4.9 ± 0.3 | ND |
| Final concentration (nZVI-RSSB450) | 7.52 ± 0.02 | ND | 0.8 + 0.02 | ND | ND | ND |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhan, G.; Zhang, Z. Nano Zero-Valent Iron—Rubber Seed Shell Biochar (nZVI-RSSB) Enhances Removal of Cadmium from Water. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9807. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179807
Zhan G, Zhang Z. Nano Zero-Valent Iron—Rubber Seed Shell Biochar (nZVI-RSSB) Enhances Removal of Cadmium from Water. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9807. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179807
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhan, Guoyan, and Zhenhua Zhang. 2025. "Nano Zero-Valent Iron—Rubber Seed Shell Biochar (nZVI-RSSB) Enhances Removal of Cadmium from Water" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9807. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179807
APA StyleZhan, G., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Nano Zero-Valent Iron—Rubber Seed Shell Biochar (nZVI-RSSB) Enhances Removal of Cadmium from Water. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9807. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179807








