Parametric and Correlation Study of Effusion Cooling Applied to Gas Turbine Blades
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Setup
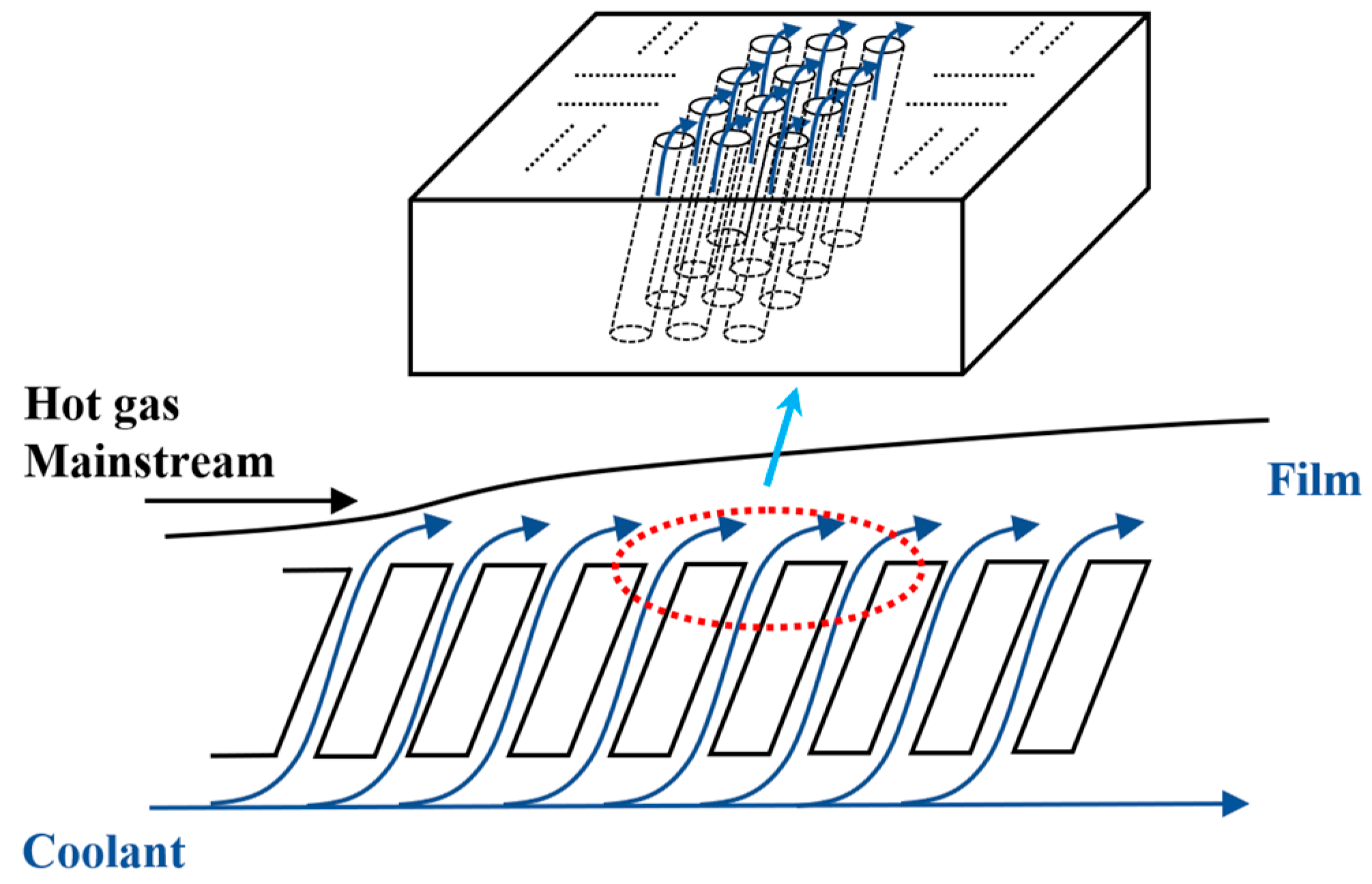
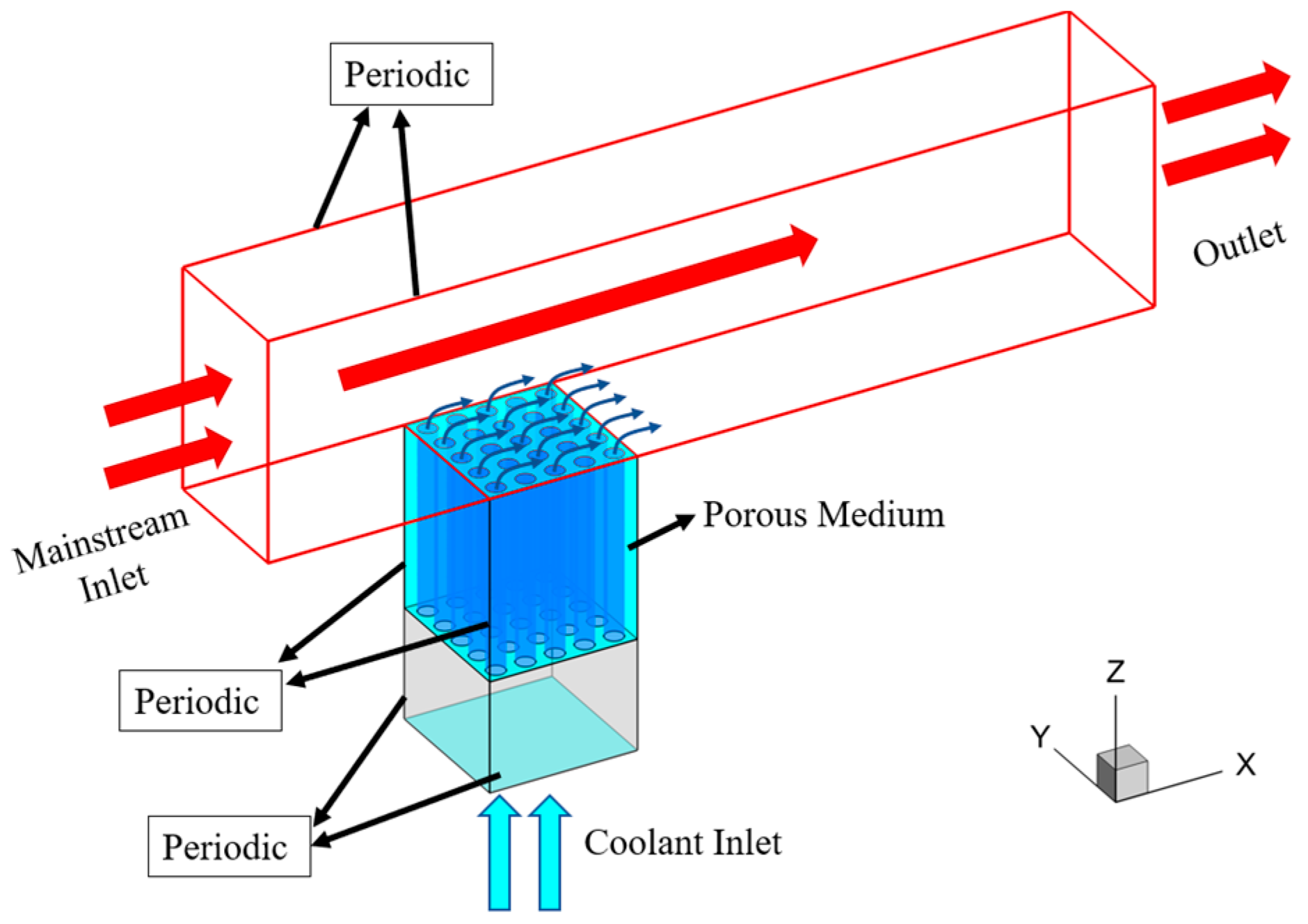
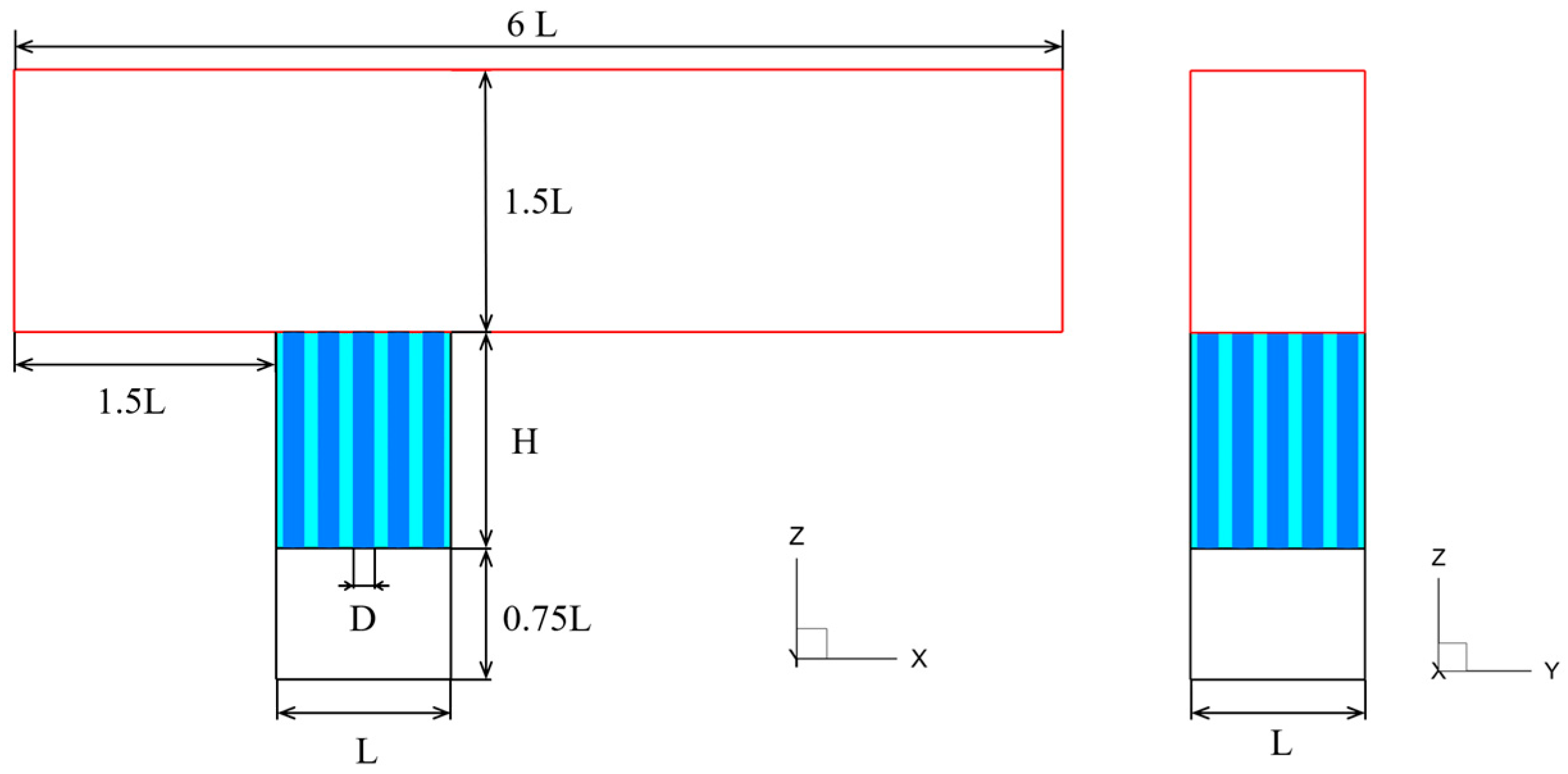
2.1. Geometric Model
2.2. Boundary Conditions
2.3. Numerical Method
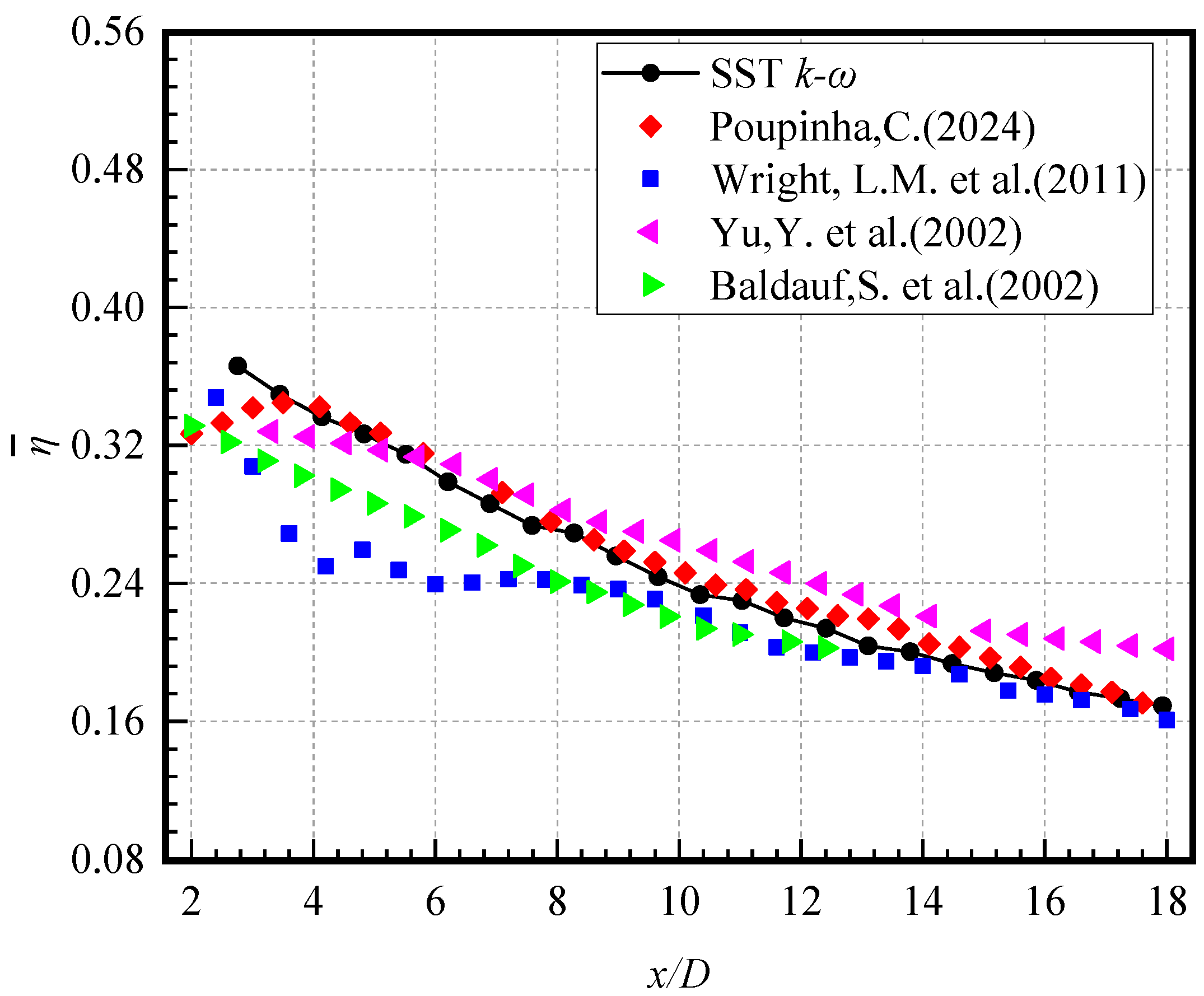
2.4. Turbulence Model Verification
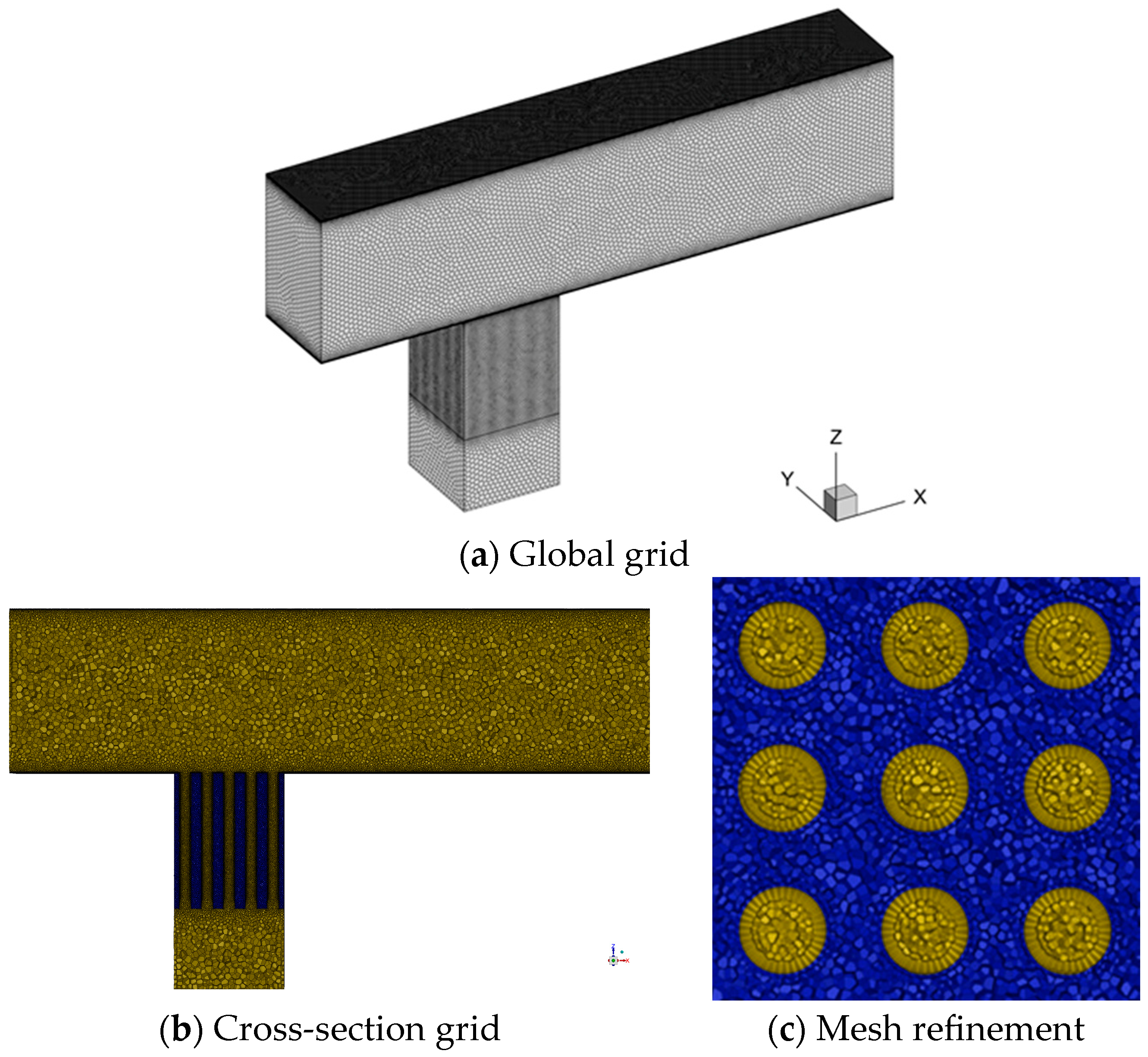
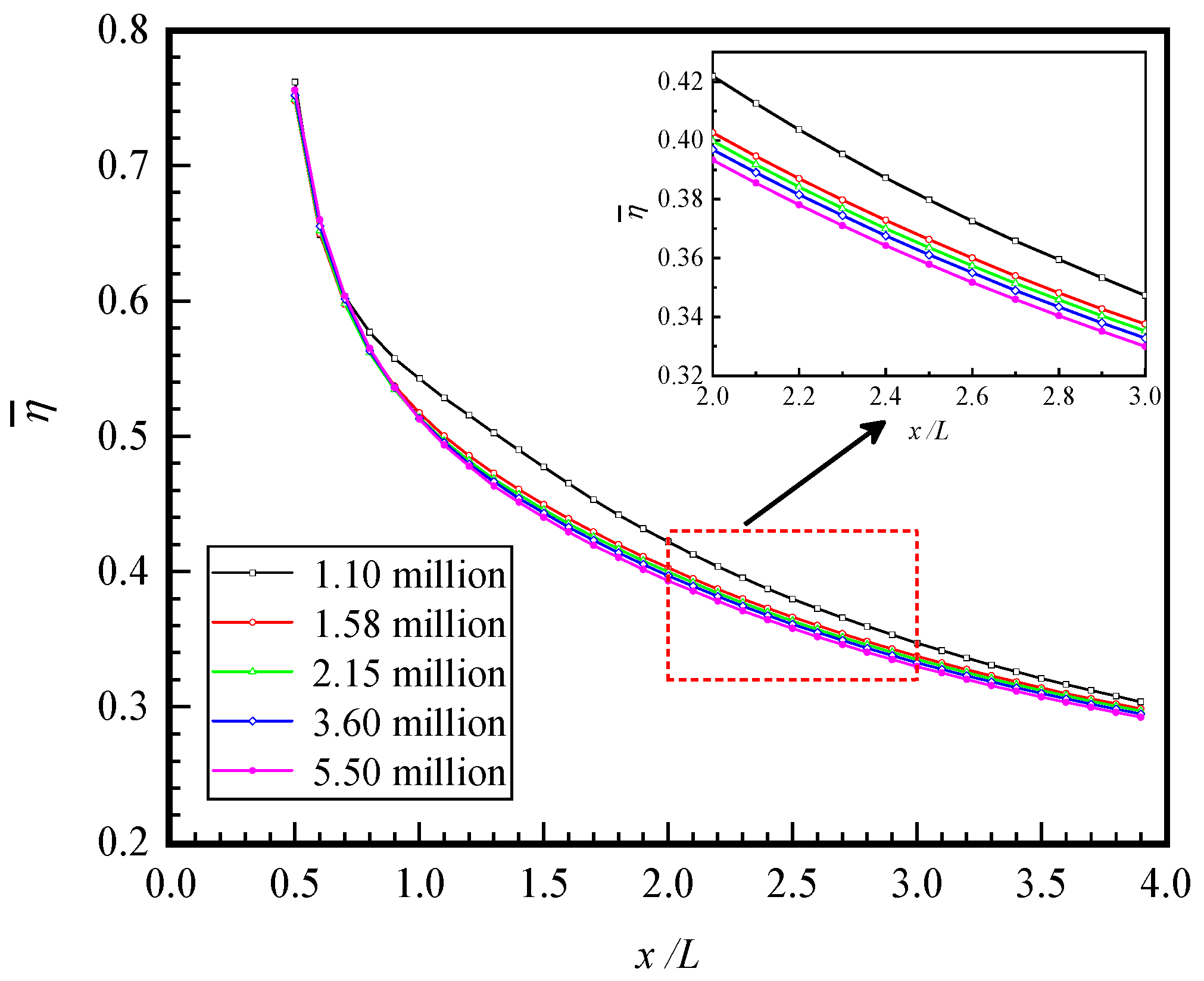
2.5. Grid Independence Verification
3. Results and Discussion
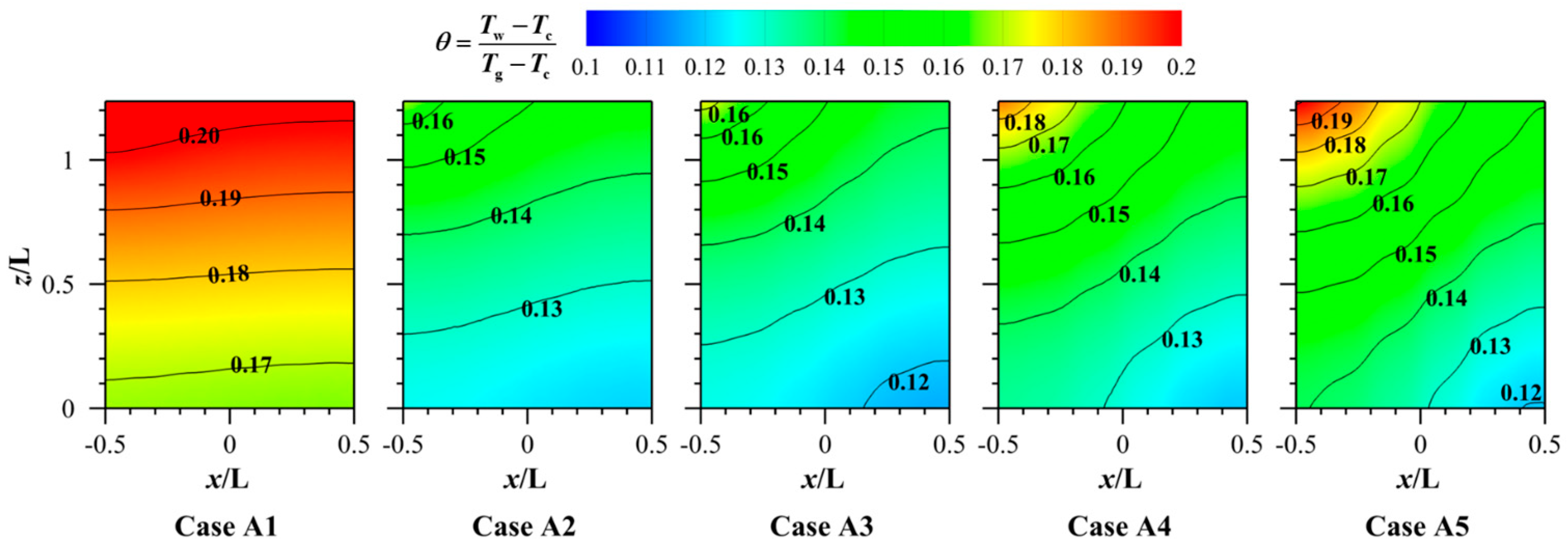
3.1. Effect of Different Porosities
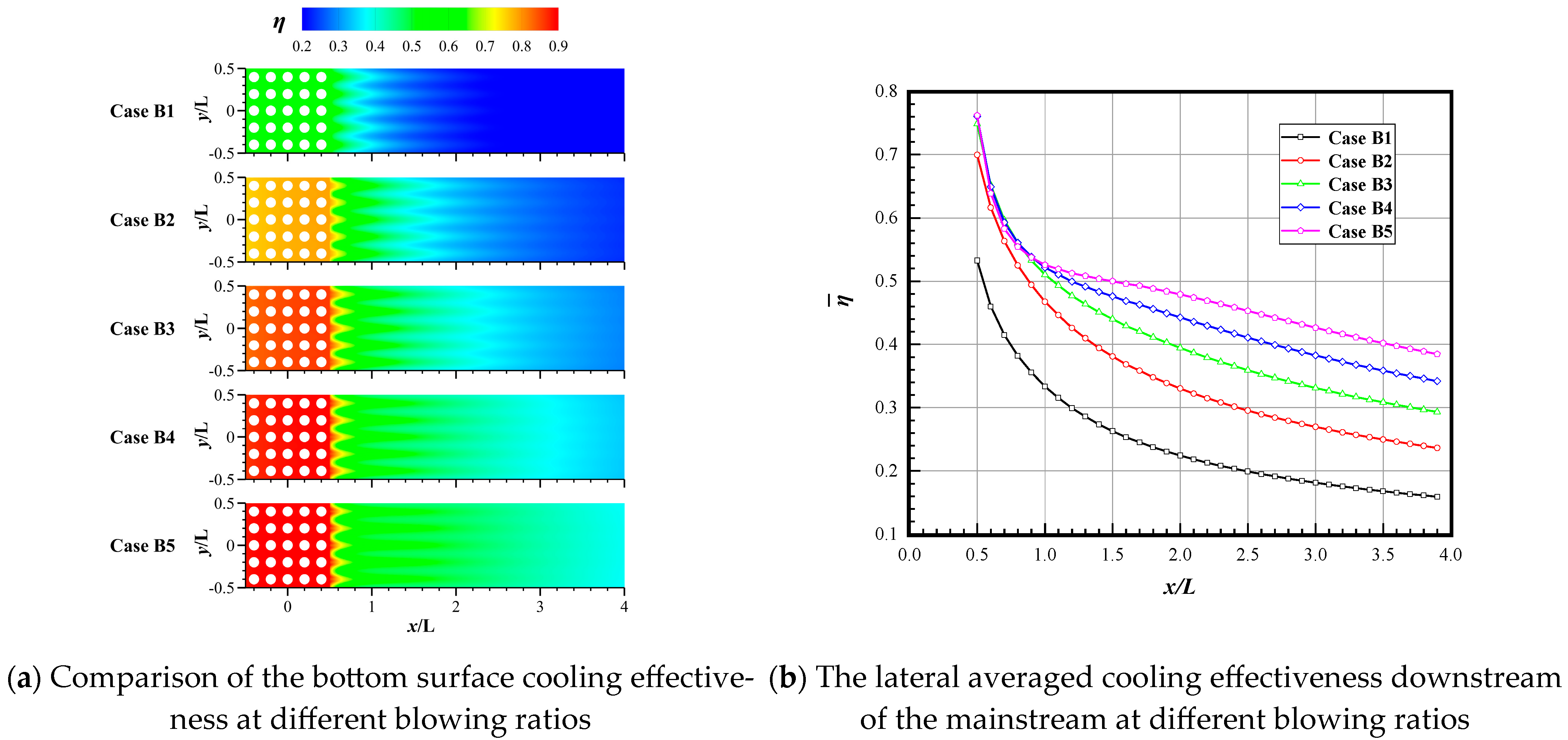
3.2. Effect of Different Blowing Ratios
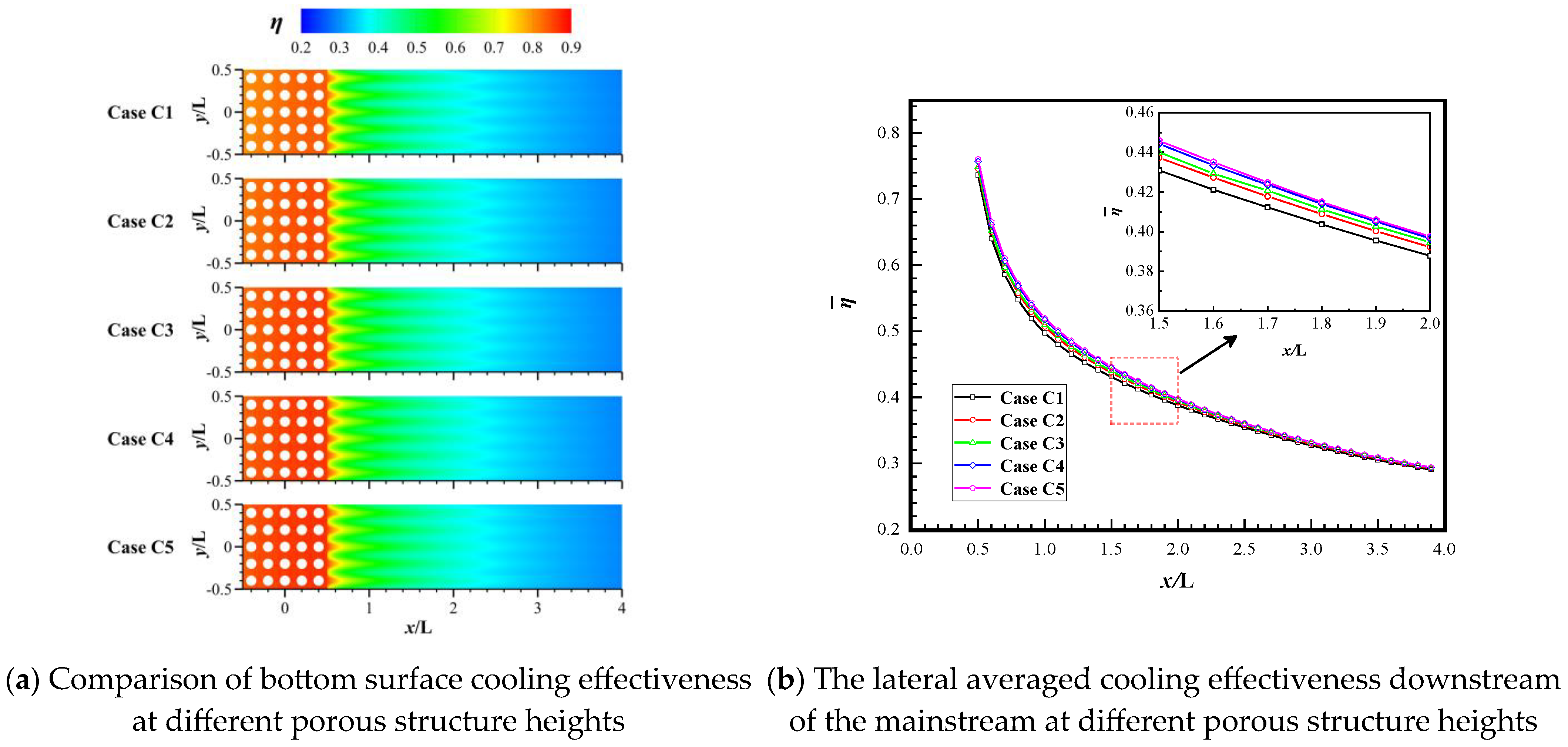
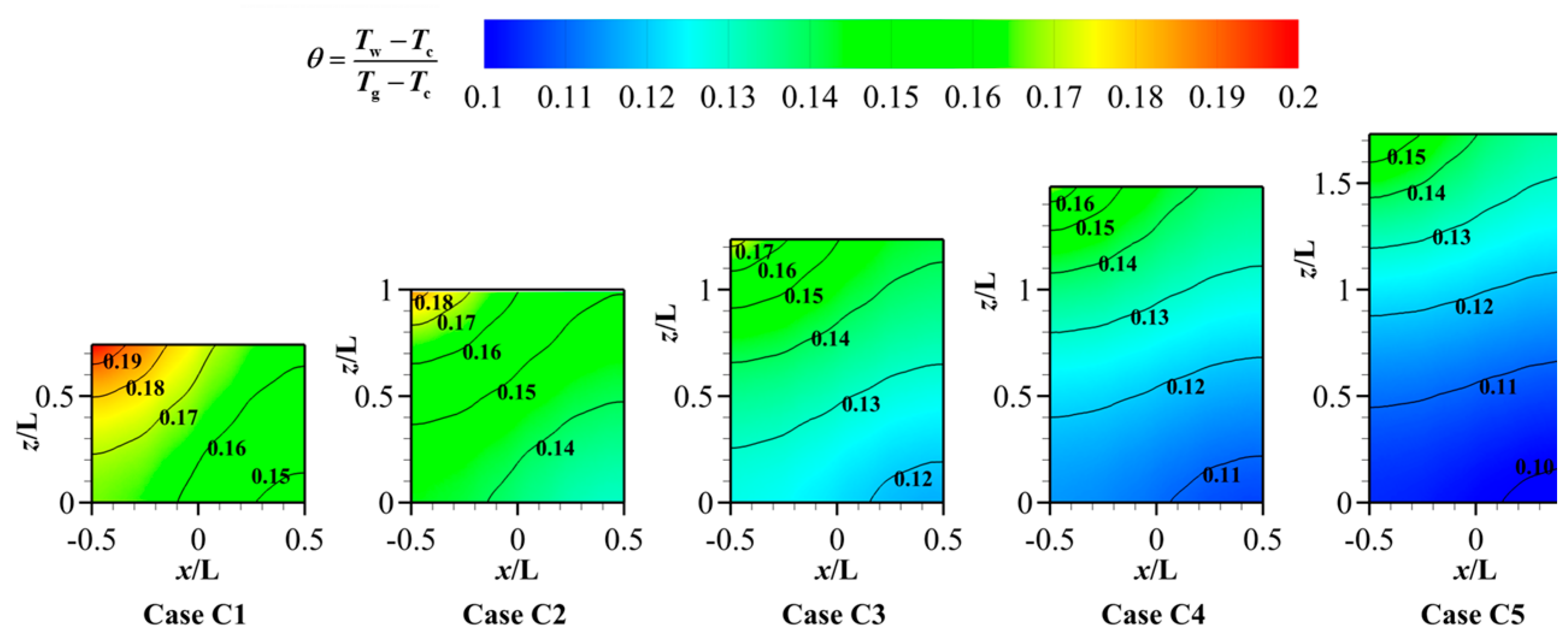
3.3. Effect of Different Porous Structure Heights (H)
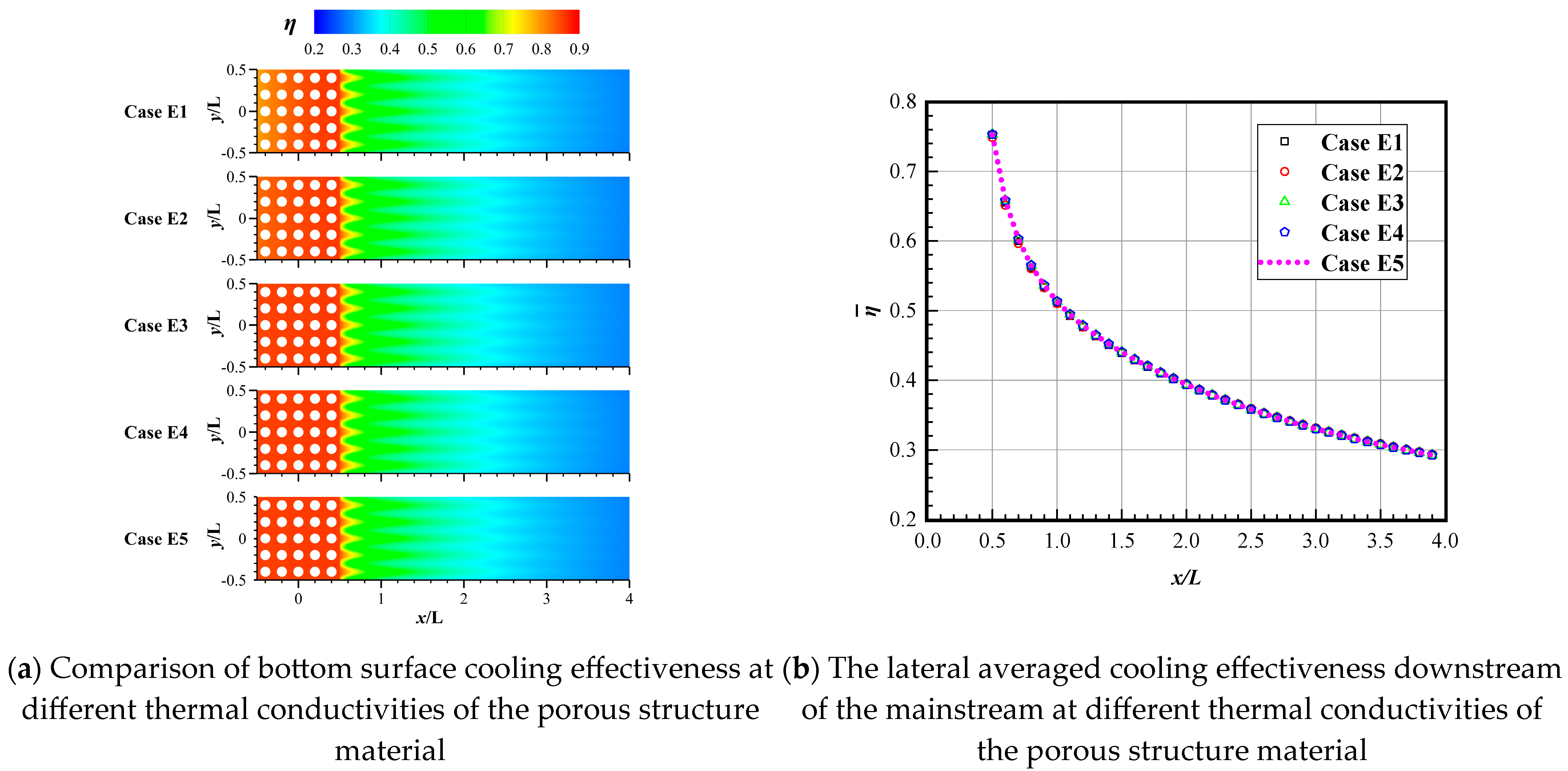
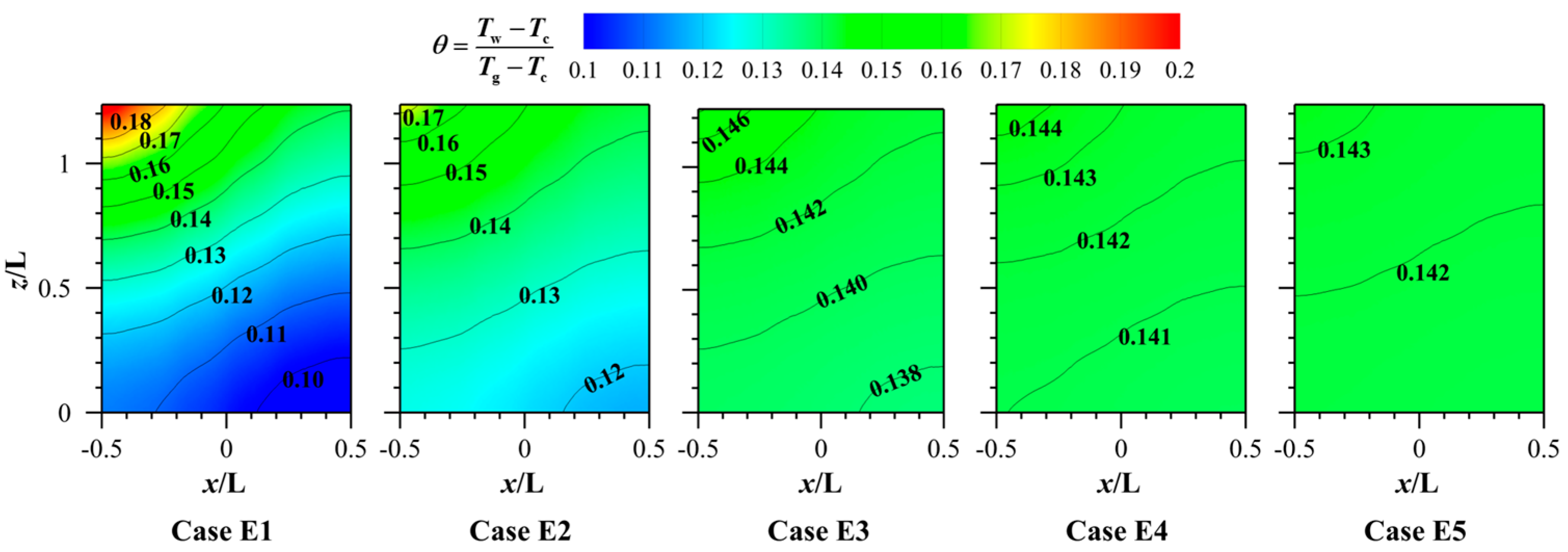
3.4. Effect of Different Thermal Conductivities (λ) of the Porous Structure Material
3.5. Effects of Different Temperature Ratios
4. Correlations
5. Conclusions
- Porosity markedly affects cooling effectiveness. As porosity rises, the η of the porous structure surface first improves and then declines, whereas the averaged downstream η gradually increases. Higher porosity reduces the temperature on the outer surface of the porous structure yet produces a non-uniform temperature distribution.
- The blowing ratio and η are positively correlated. In general, as the blowing ratio increases, η also improves.
- Surprisingly, the height of the porous structure and the thermal conductivity of the material exert minimal influence on the cooling effectiveness of both the porous surface and the downstream region. This is because as the ventilation time increases, the temperature of the porous material will eventually reach equilibrium. The height of the porous structure and the material’s thermal conductivity mainly affect the heat conduction performance. In this coupling of convective heat transfer and thermal conduction, the effect of convective heat transfer is more intense, while the influence of thermal conduction is reduced. However, a larger height of the porous structure and a smaller thermal conductivity coefficient can lead to a non-uniform temperature distribution on the outer surface of the porous structure.
- Although the cooling effectiveness is a relative formula, different temperature ratios between the mainstream inlet and the coolant inlet make the cooling effectiveness change, and a similar coolant coverage pattern is formed.
- The formula fitted for the cooling effectiveness of the porous surface demonstrates high precision and all errors remain below 2%. The formula is capable of accurately predicting the cooling effectiveness of such surfaces. Future research can conduct correlation fitting between downstream cooling effectiveness and related parameters to predict their cooling effectiveness, providing references and options for design and optimization.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Vh | Volume of Holes |
| Vs | Volume of Solid |
| L | Width of Inlet |
| D | Diameter of Holes |
| T | Temperature |
| TM | Temperature of Mainstream |
| TC | Temperature of Coolant |
| TW | Temperature of Wall |
| φ | Porosity |
| Br | Blowing Ratio |
| λ | Thermal Conductivity |
| H | Height of Porous Structure |
| Rt | Ratio of Temperature |
| η | Cooling Effectiveness |
| Lateral Averaged Cooling Effectiveness | |
| Averaged Cooling Effectiveness | |
| θ | Wall Temperature Distribution Coefficient |
References
- Han, J.C.; Dutta, S. Gas Turbine Heat Transfer and Cooling Technology, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis: Oxfordshire, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Facchini, B.; Tarchi, L. Adiabatic and overall effectiveness measurements of an effusion cooling array for turbine endwall application. J. Turbomach.-Trans. Asme 2010, 132, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, K.M.B.; Johansson, T.G. An experimental study of surface temperature distribution on effusion-cooled plates. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power-Trans. Asme 2001, 123, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krewinkel, R. A review of gas turbine effusion cooling studies. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 66, 706–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulmer, G.; Ligrani, P. Effects of blowing ratio on surface heat transfer characteristics of a transonic turbine squealer blade tip with a double plenum film cooling supply arrangement. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 221, 125043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Cheng, H.C. Effects of side hole position and blowing ratio on sister hole film cooling performance in a flat plate. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 93, 718–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.W.; Han, F. Experimental investigations of the effects of the injection angle and blowing ratio on the leading-edge film cooling of a rotating twisted turbine blade. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 127, 856–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wei, H. Experimental study on the conjugate heat transfer of double-wall turbine blade components with/without pins. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2018, 8, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K. Investigations of film cooling and heat transfer on a turbine blade squealer tip. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 110, 630–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.H.; Liu, X. Experimental investigation on heat transfer characteristics of film cooling using parallel-inlet holes. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2012, 60, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; He, L. Influence of inhomogeneous porosity on effusion cooling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 144, 118675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Mao, J.K. Numerical investigation on transpiration cooling performance with different porosities and mainstream pressure gradients. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2023, 184, 107991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimacombe, B.J.; Scobie, J.A. Effect of porosity and injection ratio on the performance of transpiration cooling through gyroids. Int. J. Turbomach. Propuls. Power 2023, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.F.; Sun, H.O. Numerical investigation on transpiration cooling performance of turbine blades with non-uniform porosity. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 235, 121394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Liu, Y.Y. Multiple-jet impingement heat transfer in double-wall cooling structures with pin fins and effusion holes. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2018, 133, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tian, K. Effect of hole configurations on film cooling performance. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A-Appl. 2019, 75, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.F.; Wang, X.J. Influences of effusion hole diameter on impingement/effusion cooling performance at turbine blade leading edge. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 134, 1101–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.P.; Chen, Y.J. Effects of blowing ratio and film hole arrangement on cavity blade tip cooling. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 075108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.W.; Zhang, D.W. Numerical investigation of the effects of the hole inclination angle and blowing ratio on the characteristics of cooling and stress in an impingement/effusion cooling system. Energies 2023, 16, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.N.; Liu, C.L. Investigation on the film cooling performance of diffuser shaped holes with different inclination angles. Int. J. Turbo Jet-Engines 2017, 34, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Song, B. Investigation of film cooling effectiveness of full-coverage inclined multihole walls with different hole arrangements. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2003, Collocated with the 2003 International Joint Power Generation Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–19 June 2003; pp. 651–660. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, K.Y. Film-cooling performance of converged-inlet hole shapes. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2018, 124, 196–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishal, V.; Sriraam, J. Studies on effusion cooling: Impact of geometric parameters on cooling effectiveness and coolant consumption. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.H.; Zhang, J.Z. Improvement on film cooling effectiveness by a combined slot-effusion scheme. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 126, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.B.; Ge, B. Conjugate heat transfer characteristics of effusion cooling under realistic swirl flow in a three-sector gas turbine model combustor. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 213, 118735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjun, C.K.; Jayakumar, J.S. Experimental and numerical investigation of effusion cooling effectiveness of combustion chamber liner plates. J. Heat Transf.-Trans. Asme 2018, 140, 082201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Jiang, Y.T. Flow and heat transfer analysis on impingement/effusion cooling configuration including jet orifices with conformal pins. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 076122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.J.; Liu, Y.Y. Numerical investigation on conjugate heat transfer of impingement/effusion double-wall cooling with different crossflow schemes. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 155, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahr, D.W. Gas turbine combustion—Alternative fuels and emissions. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2010, 132, 116501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadia, A. Advanced combustor liner cooling technology for gas turbines. Def. Sci. J. 1988, 38, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulli, S.; Maddalena, L. Variable transpiration cooling for the thermal management of reusable hypersonic vehicles. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, S.; Nicoud, F. Adiabatic homogeneous model for flow around a multiperforated plate. AIAA J. 2008, 46, 2623–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Min, Z. Transpiration cooling for additive manufactured porous plates with partition walls. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 124, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Xie, H. Numerical study of flow and heat transfer characteristics of impingement/effusion cooling. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2009, 22, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguntade, H.I.; Andrews, G.E. Impingement/effusion cooling with low coolant mass flow. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2017: Turbomachinery Technical Conference and Exposition, Charlotte, NC, USA, 26–30 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, H.H.; Rhee, D.H. Local heat/mass transfer measurement on the effusion plate in impingement/effusion cooling systems. J. Turbomach.-Trans. Asme 2001, 123, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.M.; Zhang, J.Z. Experimental investigation on impingement/effusion cooling with short normal injection holes. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 69, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Liu, C.L. Effects of impingement gap and hole arrangement on overall cooling effectiveness for impingement/effusion cooling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 152, 119449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poupinha, C.; Kozlowska, S. Experimental study on transpiration cooling through additively manufactured porous structures. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 227, 125532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, L.M.; McClain, S.T. Effect of density ratio on flat plate film cooling with shaped holes using psp. J. Turbomach.-Trans. Asme 2011, 133, 041011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yen, C.H. Film cooling effectiveness and heat transfer coefficient distributions around diffusion shaped holes. J. Heat Transf.-Trans. Asme 2002, 124, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldauf, S.; Scheurlen, M. Heat flux reduction from film cooling and correlation of heat transfer coefficients from thermographic measurements at enginelike conditions. J. Turbomach.-Trans. Asme 2002, 124, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Case Name | φ | Br | H | Material, λ | Rt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 10% | 0.3% | 10D | Steel, 16.27 W/(m·K) | 1.3 |
| A2 | 20% | ||||
| A3 | 30% | ||||
| A4 | 40% | ||||
| A5 | 50% | ||||
| B1 | 30% | 0.1% | 10D | Steel, 16.27 W/(m·K) | 1.3 |
| B2 | 0.2% | ||||
| B3 | 0.3% | ||||
| B4 | 0.4% | ||||
| B5 | 0.5% | ||||
| C1 | 30% | 0.3% | 6D | Steel, 16.27 W/(m·K) | 1.3 |
| C2 | 8D | ||||
| C3 | 10D | ||||
| C4 | 12D | ||||
| C5 | 14D | ||||
| E1 | 30% | 0.3% | 10D | Titanium, 7.44 W/(m·K) | 1.3 |
| E2 | Steel, 16.27 W/(m·K) | ||||
| E3 | Nickel, 91.74 W/(m·K) | ||||
| E4 | Aluminum, 202.4 W/(m·K) | ||||
| E5 | Copper, 387.6 W/(m·K) | ||||
| F1 | φ = 30% | 0.3% | 10D | Steel, 16.27 W/(m·K) | 1.3 |
| F2 | 2 | ||||
| F3 | 3 | ||||
| F4 | 4 | ||||
| F5 | 5 |
| Case | φ | Br | H | Material, λ | Rt | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 10% | 0.3% | 10D | Steel, 16.27 W/(m·K) | 1.3 | 0.7948708 |
| A2 | 20% | 0.8473646 | ||||
| A3 | 30% | 0.8472585 | ||||
| A4 | 40% | 0.8370339 | ||||
| A5 | 50% | 0.8281744 | ||||
| B1 | 30% | 0.1% | 10D | Steel, 16.27 W/(m·K) | 1.3 | 0.6036934 |
| B2 | 0.2% | 0.7765922 | ||||
| B3 | 0.3% | 0.8472585 | ||||
| B4 | 0.4% | 0.8831263 | ||||
| B5 | 0.5% | 0.9037894 | ||||
| C1 | 30% | 0.3% | 6D | Steel, 16.27 W/(m·K) | 1.3 | 0.8241882 |
| C2 | 8D | 0.8377439 | ||||
| C3 | 10D | 0.8472585 | ||||
| C4 | 12D | 0.8528423 | ||||
| C5 | 14D | 0.8573566 | ||||
| E1 | 30% | 0.3% | 10D | Ti, 7.44 W/(m·K) | 1.3 | 0.8363346 |
| E2 | Steel, 16.27 W/(m·K) | 0.8472585 | ||||
| E3 | Ni, 91.74 W/(m·K) | 0.8557141 | ||||
| E4 | Al, 202.4 W/(m·K) | 0.8567652 | ||||
| E5 | Cu, 387.6 W/(m·K) | 0.8571849 | ||||
| F1 | 30% | 0.3% | 10D | Steel, 16.27 W/(m·K) | 1.3 | 0.8472585 |
| F2 | 2 | 0.82963384 | ||||
| F3 | 3 | 0.81644962 | ||||
| F4 | 4 | 0.80892233 | ||||
| F5 | 5 | 0.80399101 |
| Case | φ | Br | H | λ, W/(m·K) | Rt | Formula (7) | Error | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 0.25 | 0.015 | 16 | 16.27 | 3.33 | 0.69320353 | 0.690964779 | 0.323% |
| G2 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 16 | 297.73 | 4.67 | 0.8742778 | 0.864400342 | 1.13% |
| G3 | 0.25 | 0.035 | 9 | 297.73 | 2.67 | 0.8496429 | 0.844428195 | 0.614% |
| G4 | 0.3 | 0.015 | 10 | 297.73 | 1.67 | 0.70758362 | 0.70601803 | 0.221% |
| G5 | 0.45 | 0.03 | 16 | 16.27 | 5 | 0.8107224 | 0.797001194 | 1.69% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Zhao, J.; Liu, R.; Xi, W. Parametric and Correlation Study of Effusion Cooling Applied to Gas Turbine Blades. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9778. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179778
Liu J, Zhao J, Liu R, Xi W. Parametric and Correlation Study of Effusion Cooling Applied to Gas Turbine Blades. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9778. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179778
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jian, Jiancheng Zhao, Renshuo Liu, and Wenxiong Xi. 2025. "Parametric and Correlation Study of Effusion Cooling Applied to Gas Turbine Blades" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9778. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179778
APA StyleLiu, J., Zhao, J., Liu, R., & Xi, W. (2025). Parametric and Correlation Study of Effusion Cooling Applied to Gas Turbine Blades. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9778. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179778







