Research on Control Strategy of Semi-Active Suspension System Based on Fuzzy Adaptive PID-MPC
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Establishment of Semi-Active Suspension System Model
2.1. Half-Car Semi-Active Suspension System Model
2.2. Construction of Random Road Excitation Model
3. Fuzzy Adaptive PID-MPC Strategy
3.1. MPC Principles
3.2. Predictive Model
3.3. Selection of the Cost Function J
3.4. Constraints for Semi-Active Suspension System Control
3.5. PID Controller
3.6. Fuzzy Adaptive PID Controller
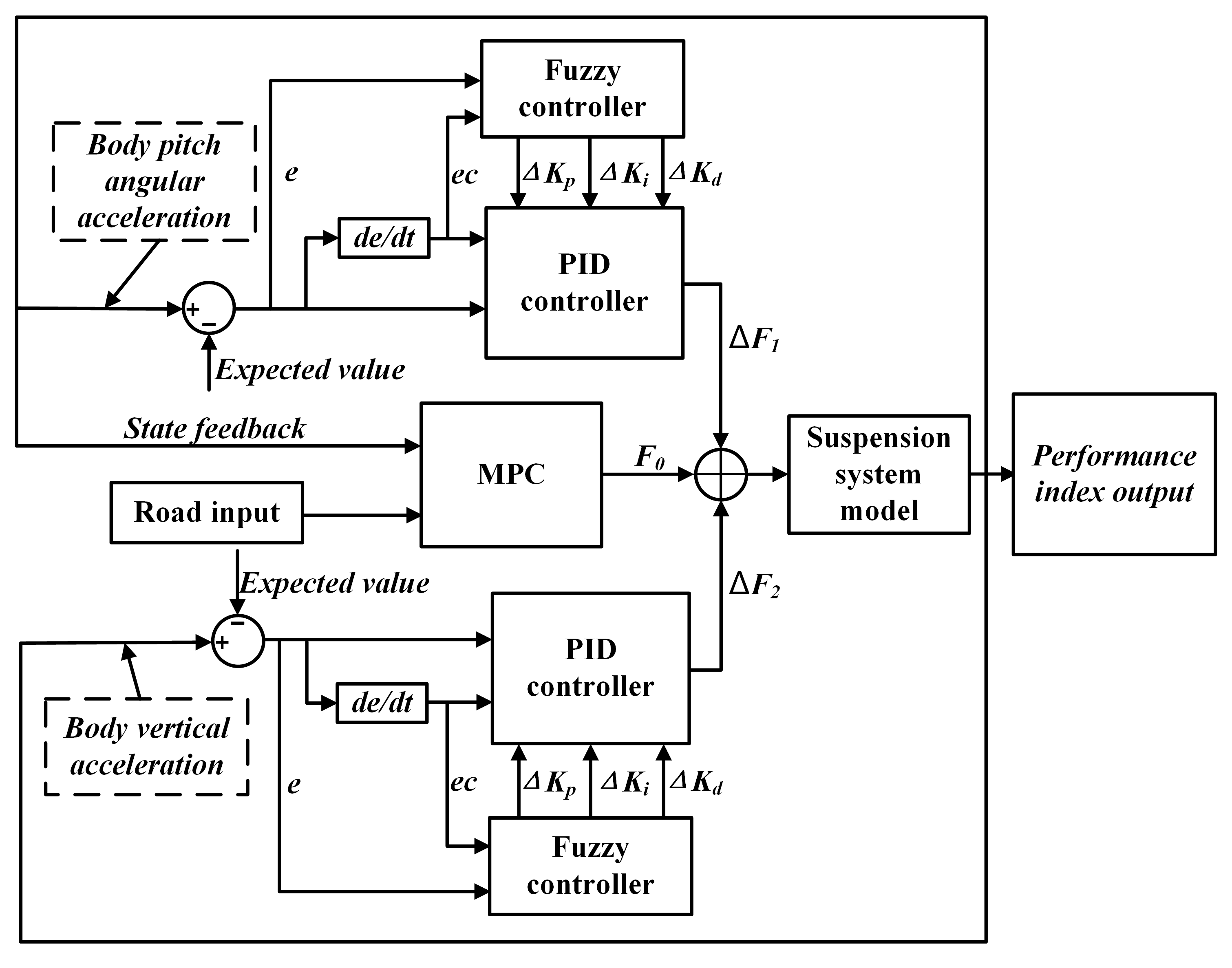
3.7. Fuzzy Adaptive PID-MPC Controller
4. Simulation Results Analysis
4.1. Simulation Analysis of Speed Bump Road Surface
4.2. Simulation Analysis of Class B Road Surface
4.3. Simulation Analysis of Class C Road Surface
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PID | Proportional–integral–derivative |
| MPC | Model predictive control |
| PID-MPC | Proportional–integral–derivative model predictive control |
| VSL-MPC | Variable step-size model predictive control |
| MR | Magnetorheological |
| EMPC | Explicit model predictive control |
| PSD | Power spectral density |
| NL | Negative large |
| NM | Negative medium |
| NS | Negative small |
| ZO | Zero |
| PS | Positive small |
| PM | Positive medium |
| PL | Positive large |
| RMS | Root mean square |
| ABS | Antilock braking system |
| TCS | Traction control system |
References
- Li, G.; Gu, R.H.; Xu, R.X.; Hu, G.L.; Ou, Y.N.; Xu, M. Study on Fuzzy LQG Control Strategy for Semi-active Vehicle Suspensions with Magnetorheological Dampers. Noise Vib. Control 2021, 41, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raković, S.V.; Zhang, S. Model Predictive Control with Implicit Terminal Ingredients. Automatica 2023, 151, 110942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carron, A.; Arcari, E.; Wermelinger, M.; Hewing, L.; Hutter, M.; Zeilinger, M.N. Data-Driven Model Predictive Control for Trajectory Tracking with a Robotic Arm. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 3758–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.S.; Lo, J.N.; Yin, J.; Yu, F. Model Predictive Controller Design of Active Suspension for Vehicle Driven by Hub-Motor. Mach. Des. Res. 2023, 39, 180–184+192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Chen, B.; Wu, C.Q. Model Predictive Control of Semi-active Suspension for Hub-motor Electric Vehicle. J. Chongqing Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 2022, 36, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Manzoor, T.; Pei, H.; Xia, Y.; Sun, Z.; Ali, Y. Compound Learning-Based Model Predictive Control Approach for Ducted-Fan Aerial Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2025, 36, 9395–9407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bououden, S.; Chadli, M.; Zhang, L.; Yang, T. Constrained Model Predictive Control for Time-Varying Delay Systems: Application to an Active Car Suspension. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2016, 14, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjellberg, F.; Sundell, S. Real-Time Nonlinear Model Predictive Control for Semi-Active Suspension with Road Preview. Master’s Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Theunissen, J.; Sorniotti, A.; Gruber, P.; Fallah, S.; Ricco, M.; Kvasnica, M.; Dhaens, M. Regionless Explicit Model Predictive Control of Active Suspension Systems with Preview. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 4877–4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Li, Z.Y.; Liu, C.L. Vertical Vibration of Hub Motor Driven Electric vehicle Based on EMPC. J. Vib. Shock 2022, 41, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.K.; Zeng, M.K.; Liu, X.; Jiang, A. Research on Preview Control of Semi-Active Suspension Based on VSL-MPC. Automot. Eng. 2022, 44, 1537–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, A.S. Preview Model Predictive Control Controller for Magnetorheological Damper of Semi-Active Suspension to Improve Both Ride and Handling. SAE Int. J. Veh. Dyn. Stab. NVH 2020, 4, 305–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, T.; Kim, C.-J.; Yi, K. Model Predictive Control of a Semi-Active Suspension with a Shift Delay Compensation Using Preview Road Information. Control Eng. Pract. 2023, 137, 105584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Huang, H.P.; Wang, X.K.; Yu, L. Transition Mode Flight Control Method of TRUAVs Based on Hybrid Control of Model Calibration MPC and PID. Robot 2025, 47, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, L.; Feng, Y.B.; Li, S.Z.; He, Z.X.; Han, X.X. Design of Dynamic Inverse Active Disturbance Rejection Controller for Semi-active MR Suspension System of Heavy Vehicles. J. Vib. Shock 2024, 43, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Z.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.J. Vehicle Speed Decoupling Road Identification Method Based on Least Squares. J. Jilin Univ. (Eng. Technol. Ed.) 2024, 54, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S. Research on Ride Comfort Control of Air Suspension Based on Genetic Algorithm Optimized Fuzzy PID. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.P.; Chen, W.W.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, M.F. Modeling and Simulation on Stochastic Road Surface Irregularity Based on Matlab/Simulink. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2010, 41, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- GB 7031-2005; Mechanical Vibration-Road Surface Profiles-Reporting of Measured Data. China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 1987.
- Qin, S.J.; Badgwell, T.A. A Survey of Industrial Model Predictive Control Technology. Control Eng. Pract. 2003, 11, 733–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morari, M.; Barić, M. Recent Developments in the Control of Constrained Hybrid Systems. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2006, 30, 1619–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, R.G.; Li, D.W.; Lin, S. Model Predictive Control-Status and Challenges. Acta Autom. Sin. 2013, 39, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Liu, T.R.; Yang, Z. Current Status and Future Prospects of Shield Tunneling Attitude Control Technology. Tunn. Constr. 2024, 44, 1154–1164. [Google Scholar]
- Banharkou, I.; Gherbi, S.; Mehennaoui, L. A Robust LQR-Based Fuzzy-Immune PID Applied for a Greenhouse Temperature Networked Control. Eur. J. Electr. Eng. 2022, 24, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chang, X.; Gu, Y.; Wang, P.; Shang, S. Design of Dynamic Deep Sowing System for Peanut Planter with Double-Loop Feedback Fuzzy PID Control. Agriculture 2025, 15, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Xu, C.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Ye, F. Trajectory Tracking Method of Four-Wheeled Independent Drive and Steering AGV Based on LSTM-MPC and Fuzzy PID Cooperative Control. Electronics 2025, 14, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Chai, T.Y. An Optimal Tuning Method of PID Controller Parameters. Acta Autom. Sin. 2023, 49, 2272–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.P.; Wang, Z.R. Graphene Preparation Control System Based on Adaptive Fuzzy PID. J. Appl. Sci. 2022, 40, 876–886. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, M.J. Model Predictive Control of Active Suspension Based on Road Information Recognition. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
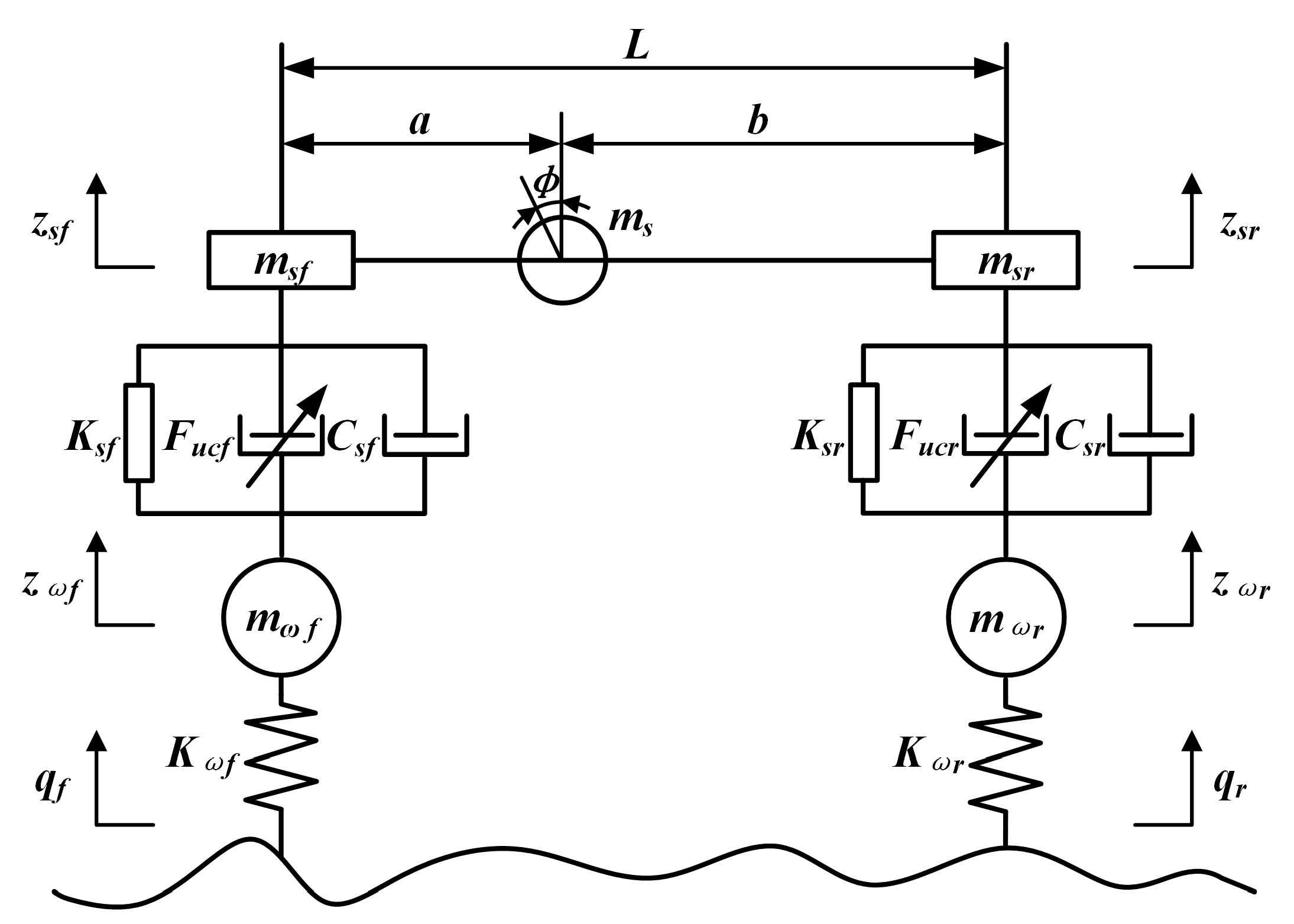


















| Parameter | Notation | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Sprung mass | ms/kg | 1270 |
| Unsprung mass | mω/kg | 88.6 |
| Rotational inertia | I/kg·m2 | 1536.7 |
| Wheelbase | L/m | 2.91 |
| Distance from CG to front axle | a/m | 1.015 |
| Distance from CG to rear axle | b/m | 1.895 |
| Suspension damping | Cs/N·s·m−1 | 6000 |
| Suspension stiffness | Ks/N·m−1 | 27,000 |
| Tire stiffness | Kω/N·m−1 | 268,000 |
| Road Grade | Lower Limit (×10−6 m3) | Geometric Mean (×10−6 m3) | Upper Limit (×10−6 m3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 8 | 16 | 32 |
| B | 32 | 64 | 128 |
| C | 128 | 256 | 512 |
| D | 512 | 1024 | 2048 |
| B | 2048 | 4096 | 8192 |
| ΔKp | ec | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NL | NM | NS | ZO | PS | PM | PL | ||
| NL | PL | PL | PL | PL | PM | PS | ZO | |
| NM | PL | PL | PL | PL | PM | ZO | ZO | |
| NS | PM | PM | PM | PM | ZO | NS | NS | |
| ZO | PM | PM | PS | ZO | NS | NS | NM | |
| PS | PS | PS | ZO | NS | NM | NM | NM | |
| PM | PS | ZO | NS | NM | NM | NM | NL | |
| PL | ZO | ZO | NM | NM | NM | NL | NL | |
| ΔKi | ec | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NL | NM | NS | ZO | PS | PM | PL | ||
| NL | NL | NL | NM | NM | NS | ZO | ZO | |
| NM | NL | NL | NM | NS | NS | ZO | ZO | |
| NS | NL | NM | NS | NS | ZO | PS | PS | |
| ZO | NM | NM | NS | ZO | PS | PM | PM | |
| PS | NM | NS | ZO | PS | PS | PM | PL | |
| PM | ZO | ZO | PS | NM | PM | PL | PL | |
| PL | ZO | ZO | PS | PM | PM | PL | PL | |
| ΔKd | ec | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NL | NM | NS | ZO | PS | PM | PL | ||
| NL | PS | NS | NL | NL | NL | NM | PS | |
| NM | PS | NS | NL | NM | NM | NS | ZO | |
| NS | ZO | NS | NM | NM | NS | NS | ZO | |
| ZO | ZO | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | ZO | |
| PS | ZO | ZO | ZO | ZO | ZO | ZO | ZO | |
| PM | PL | PS | PS | PS | PS | PS | PL | |
| PL | PL | PM | PM | PM | PS | PS | PL | |
| RMS | Passive Suspension | MPC | PID-MPC | Fuzzy Adaptive PID-MPC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle vertical acceleration (m·s−2) | 0.5853 | 0.4922 | 0.4167 | 0.3740 |
| Vehicle pitch angle acceleration (rad·s−2) | 0.1315 | 0.1123 | 0.0955 | 0.0872 |
| RMS | Passive Suspension | MPC | PID-MPC | Fuzzy Adaptive PID-MPC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle vertical acceleration (m·s−2) | 0.5664 | 0.4580 | 0.3943 | 0.3501 |
| Vehicle pitch angle acceleration (rad·s−2) | 0.1297 | 0.1057 | 0.0883 | 0.0811 |
| Front suspension dynamic deflection (m) | 0.0073 | 0.0080 | 0.0081 | 0.0081 |
| Rear suspension dynamic deflection (m) | 0.0034 | 0.0036 | 0.0038 | 0.0039 |
| Front wheel dynamic load (N) | 1152.1 | 1240.9 | 1294.9 | 1264.8 |
| Rear wheel dynamic load (N) | 635.7 | 701.5 | 721.0 | 735.5 |
| RMS | Passive Suspension | MPC | PID-MPC | Fuzzy Adaptive PID-MPC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle vertical acceleration (m·s−2) | 1.1309 | 0.9159 | 0.7886 | 0.7037 |
| Vehicle pitch angle acceleration (rad·s−2) | 0.2538 | 0.2101 | 0.1810 | 0.1642 |
| Front suspension dynamic deflection (m) | 0.0145 | 0.0160 | 0.0163 | 0.0162 |
| Rear suspension dynamic deflection (m) | 0.0067 | 0.0072 | 0.0075 | 0.0080 |
| Front wheel dynamic load (N) | 2304.2 | 2552.6 | 2663.7 | 2601.8 |
| Rear wheel dynamic load (N) | 1271.3 | 1429.0 | 1468.9 | 1504.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, C.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, R.; Li, Z. Research on Control Strategy of Semi-Active Suspension System Based on Fuzzy Adaptive PID-MPC. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9768. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179768
Cai C, Wang G, Wang Z, Li R, Li Z. Research on Control Strategy of Semi-Active Suspension System Based on Fuzzy Adaptive PID-MPC. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9768. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179768
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Cheng, Guiyong Wang, Zhigang Wang, Raoqiang Li, and Zhiwei Li. 2025. "Research on Control Strategy of Semi-Active Suspension System Based on Fuzzy Adaptive PID-MPC" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9768. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179768
APA StyleCai, C., Wang, G., Wang, Z., Li, R., & Li, Z. (2025). Research on Control Strategy of Semi-Active Suspension System Based on Fuzzy Adaptive PID-MPC. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9768. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179768





