Abstract
To address the limitations of existing optimization-based 3D style transfer methods in terms of visual quality, 3D consistency, and real-time rendering performance, we propose a novel 3D Gaussian scene style transfer method based on 2D priors and iterative optimization. Our approach introduces a progressive training pipeline that alternates between fine-tuning the 3D Gaussian field and updating a set of supervised stylized images. By gradually injecting style information into the 3D scene through iterative refinement, the method effectively preserves the geometric structure and spatial coherence across viewpoints. Furthermore, we incorporated a pre-trained stable diffusion model as a 2D prior to guide the style adaptation of the 3D Gaussian representation. The combination of diffusion priors and differentiable 3D Gaussian rendering enables high-fidelity style transfer while maintaining real-time rendering capability. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method significantly improves the visual quality and multi-view consistency of 3D stylized scenes, offering an effective and efficient solution for real-time 3D scene stylization.
1. Introduction
The task of transferring artistic styles to three-dimensional (3D) scenes has attracted increasing attention in recent years, particularly with the growing demands of immersive applications such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), film production, and digital content creation. Compared to traditional two-dimensional (2D) style transfer [1,2,3], 3D style transfer [4] faces additional challenges in ensuring multi-view consistency, preserving geometric structure, and achieving real-time rendering capabilities. A successful 3D style transfer method must not only render visually compelling results from arbitrary viewpoints but also maintain coherent structural and semantic information throughout the entire 3D scene.
Among the most advanced approaches in this domain are neural radiance field (NeRF) [5]-based optimization methods that utilize high-resolution image-level style loss. These methods typically optimize a radiance field by comparing rendered views with a target style image, thereby enabling the transfer of 2D artistic features—such as texture, color palette, and brush strokes—into a 3D volumetric scene. This category of methods has shown great potential in generating stylized 3D environments by extending the power of 2D neural style transfer to the 3D domain.
However, despite recent progress, optimization-based 3D style transfer methods are still confronted with several critical limitations that hinder their applicability in real-world scenarios. First, and foremost, is the difficulty in maintaining 3D structural consistency during style transfer. As the style is applied across different views, artifacts often emerge due to the lack of explicit constraints enforcing geometric and semantic coherence. This is particularly problematic under novel viewpoints where supervision is sparse or non-existent. Additionally, these methods often rely on computationally intensive volumetric rendering, which severely impacts their real-time performance, making them unsuitable for interactive applications like gaming or virtual prototyping.
To overcome these challenges, recent advancements in explicit 3D scene representation particularly 3D Gaussian Splatting, have introduced a new paradigm for fast and expressive radiance field modeling. Unlike implicit neural field approaches that learn a continuous mapping from 3D coordinates to color and density via neural networks, 3D Gaussian representations describe a scene as a set of spatially distributed, anisotropic Gaussians. Each Gaussian acts as a volumetric primitive with attributes such as color, opacity, and orientation. With a differentiable rasterization pipeline, this representation achieves significantly faster rendering speed while maintaining high visual quality. It provides a promising alternative for real-time, high-fidelity 3D content generation.
Building upon this powerful representation, our work explores the potential of 3D Gaussian fields for style transfer. However, stylizing explicit radiance fields also presents unique challenges. Directly optimizing Gaussians to match the global statistics of a style image can lead to spatial inconsistencies and loss of structural details. To address this, we draw inspiration from the success of 2D style transfer models and pre-trained diffusion models, which have shown exceptional capabilities in generating visually coherent and semantically rich images. By integrating these 2D priors into the 3D optimization process, we aim to inject stylistic features in a controlled and gradual manner, ensuring consistency across viewpoints and preserving the underlying structure of the scene. Specifically, we propose a novel 3D Gaussian Style Transfer method based on 2D Priors and Iterative Optimization. Our approach consists of two key components: (1) leveraging the explicit and efficient rendering pipeline of 3D Gaussians to enable real-time stylized rendering, and (2) integrating 2D style networks and diffusion priors to guide the stylization process, ensuring that the transferred style is coherent and spatially consistent across views. The training pipeline is formulated as an iterative optimization process, where multi-view rendered images are compared against style exemplars using a combination of perceptual, style, and diffusion-based losses. The model is gradually refined with supervisory feedback, allowing the target style to be incorporated into the scene while preserving geometric fidelity. Our method offers the following contributions:
- Real-time 3D style transfer via 3D Gaussian representation: We adopt 3D Gaussians as the base representation for stylization, achieving fast rendering and interactive feedback that meets the demands of real-time applications.
- Cross-domain guidance using 2D style models and diffusion priors: By incorporating 2D neural style transfer models and stable diffusion guidance, we provide strong priors that enhance visual fidelity and stylistic coherence throughout the 3D scene.
- An iterative optimization framework for gradual and consistent stylization: We introduce a multi-stage training strategy that allows for progressive style injection under multi-view constraints, leading to improved 3D consistency and perceptual quality.
- A new direction for 3D stylization research: Our framework demonstrates that 2D priors and diffusion models can be effectively leveraged to enhance 3D scene stylization, opening new possibilities for integrating generative models with graphics pipelines.
2. Related Works
2.1. Two-Dimensional Image Style Transfer
Image style transfer aims to generate a new image that preserves the content of a source image while adopting the artistic style of a reference image. The seminal work by Gatys et al. [1] introduced Neural Style Transfer (NST), which utilized feature statistics from a pre-trained CNN [6,7] to model artistic style, laying the foundation for subsequent research. Due to the high computational cost of optimization-based methods, Johnson et al. [2] proposed a feed-forward network using perceptual loss to enable real-time style transfer. To improve multi-style flexibility, Chen et al. proposed the Whitening and Coloring Transform (WCT) [8], enabling a single model to transfer multiple styles. AdaIN [9] further enhanced efficiency by matching feature statistics for zero-shot style transfer. With the recent rise in diffusion models, style transfer has seen significant advancements. InST [10] leverages CLIP [11] to perform text-guided style transfer, while StyleDiffusion [12] introduces a content-style disentanglement framework, achieving controllable and high-quality style generation. Despite the significant progress made in 2D image style transfer, applying these methods to 3D scenes with arbitrary viewpoints remains challenging. Traditional 2D techniques often lack spatial consistency constraints and are unable to effectively perceive or model the geometric properties of 3D environments. As a result, it is difficult to maintain cross-view consistency during 3D scene stylization, leading to noticeable discrepancies across different viewpoints. Previous studies [13] have shown that simply combining 3D novel view synthesis with 2D style transfer frequently results in inconsistent multi-view outputs. This is mainly due to the inability of 2D methods to account for the geometric constraints and depth information inherent in 3D scenes, which causes unnatural artifacts in novel view synthesis. Therefore, achieving high-quality 3D scene style transfer requires a joint optimization of both novel view synthesis and style transfer to ensure stylistic coherence and spatial consistency.
2.2. Three-Dimensional Gaussian Scene Style Transfer
Native 3D generation has progressed significantly with corerepresentations such as meshes [14] and point clouds [15]. Meshes enable continuous surface modeling, while pointclouds allow flexible spatial detail. This field now includes singleview 3D generation for full reconstructions from minimal input and multi-view methods that ensure crossview consistency. For 3D stylization, methods like [13] embed styles directly into 3D structures, while StyleRF [16] offers zero-shot stylization by transforming radiance field features but lacks adaptability and control.
Recent advances in 3D stylization have explored various techniques to embed artistic styles into 3D content, with reference-based methods like [17] for controlled stylization and arbitrary reference techniques for flexible style transfer.
Since the introduction of the 3D Gaussian model, several researchers have proposed style transfer algorithms based on 3D Gaussian distributions, aiming to overcome the computational limitations of neural radiance fields. StyleGaussian [18] achieves real-time style transfer through three steps: embedding, transformation, and decoding. This method first embeds scene features extracted by a VGG encoder into the reconstructed 3D Gaussians, then transforms the embedded features according to a reference style image to achieve the desired style effect, and finally decodes the transformed features into stylized RGB colors, producing rendered images with specific artistic styles. Although StyleGaussian improves the efficiency of style transfer, decoding stylized features directly into RGB colors compromises the consistency of the 3D Gaussian rasterization rendering process.
SGSST [19] proposes a Simultaneously Optimized Scales loss to enable ultra-high-resolution 3D stylization. StyleSplat [20] is an optimization-based method that segments individual 3D objects within the scene for separate processing, then fine-tunes the Gaussian distributions of the selected objects via nearest neighbor feature matching loss to obtain stylized results, while this method achieves style transfer for 3D Gaussian scenes, the segmentation process may cause unclear boundaries between objects, negatively impacting the final stylization quality. Additionally, its high computational complexity may lead to long training times when handling large-scale 3D scenes.
In this work, contemporaneous with StyleGaussian and StyleSplat, differs from these 3D Gaussian-based style transfer methods. We approach the 3D Gaussian style transfer task from a different perspective and conduct more in-depth research and experiments.
3. Method
3.1. Overview
As illustrated in Figure 1, this study proposes an optimization-based stylization method for 3D Gaussian scenes, aiming to transfer the artistic style of a given reference image onto a reconstructed 3D scene. The inputs to this method include a single style image, a reconstructed 3D scene represented by 3D Gaussians, and a set of source supervision images used for scene reconstruction. The style image—an artistic painting or a reference photograph—defines the target esthetic and texture characteristics, providing clear visual guidance for scene stylization. The input 3D Gaussian scene, reconstructed from captured image data, encodes dense geometric and textural information, serving as a robust foundation for subsequent style transfer optimization. The source supervision image set typically consists of a multi-view image sequence captured from different perspectives, along with corresponding camera poses and calibration parameters. The multi-view image sequence supplies the necessary input for reconstructing the 3D Gaussian scene. The camera poses specify the position and orientation of each captured image, ensuring accurate scene reconstruction and rendering, while the camera calibration parameters include intrinsic (e.g., focal length, principal point offsets) and extrinsic (e.g., pose matrices) parameters for precise 3D scene recovery. Given these inputs, the algorithm outputs a stylized 3D Gaussian scene that preserves the original scene’s geometric structure and content consistency, while effectively incorporating the artistic features and style of the input reference image. Based on the design of loss functions, our method comprises two core modules: 3D Gaussian optimization guided by the supervision image set and 3D Gaussian optimization based on diffusion priors. The first module enables consistent style integration from 2D images to the 3D scene, while the second leverages a diffusion model [21] to introduce global image priors, further enhancing style expression in fine details and unseen regions. Together, these two modules accomplish the complete pipeline of 3D Gaussian scene style transfer and optimization. The following sections provide a detailed explanation of each component.
3.2. Optimization of Three-Dimensional Gaussians
The optimization of 3D Gaussians via iterative supervised image set updates is a cyclic and progressive process. It involves iteratively fine-tuning the reconstructed 3D Gaussian scene by updating the supervision image set. This process alternates between the following two steps: Step 1 applies a 2D style transfer model to stylize rendered images from the 3D Gaussian scene. The stylized renderings inherit artistic attributes from the input style image, including color, texture, and brushstroke patterns. These stylized images are then used to replace the corresponding views in the supervision image set, resulting in an updated set of supervision images. Step 2 leverages the updated supervision image set to fine-tune the reconstructed 3D Gaussian model. In each training iteration, the stylized supervision images serve as targets. The algorithm computes the difference between the rendered outputs of the current 3D Gaussian model and the updated supervision images, and backpropagates the error to update the parameters of the 3D Gaussians. This process progressively integrates the style characteristics of the supervision images into the 3D Gaussian scene.
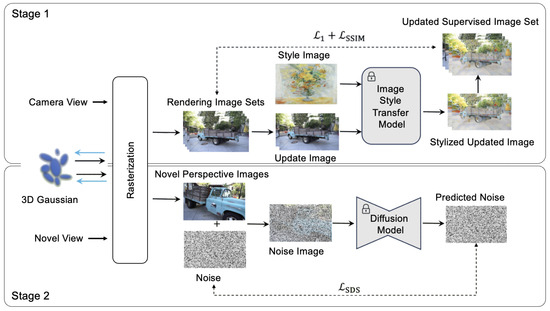
Figure 1.
Flowchart of three-dimensional Gaussian style transfer algorithm based on 2D prior and iterative optimization.
The style transfer process for rendered images is illustrated in Figure 2. To stylize the supervision image corresponding to a given viewpoint , the method first renders the 3D Gaussian model from , producing a rendered image that serves as the content image for 2D style transfer. The style image and the content image are then fed into an encoder to extract style and content feature vectors. Adaptive instance normalization [9] is applied to compute stylized features, which are subsequently decoded into the stylized image .
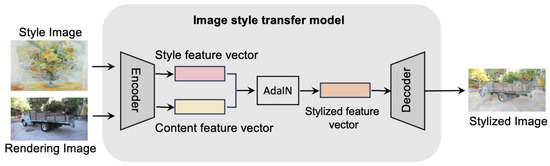
Figure 2.
Stylized flowchart of rendered images.
The original image set consists of images captured from a series of viewpoints. Before the first iteration, the viewpoints in the original image sets are randomly shuffled to generate an index list, which determines the update order in subsequent iterations. In each training round, a subset of n viewpoints is selected to render n content images, which are then stylized to obtain the stylized image set . These stylized images replace the original images from the same viewpoints in , yielding the updated supervision dataset . Let m be the total number of images in the source dataset (i.e., number of camera viewpoints), and define the dataset update ratio as . After the first round of supervision image set updates, the updated set is used to train the 3D Gaussian model through supervised learning, producing a partially stylized 3D Gaussian scene. At the end of each round, the process repeats—updating the supervision set and refining the 3D Gaussians. As iterations continue, the original images in the supervision set are gradually replaced, and the style information is increasingly embedded into the model.
The core of this method is an alternating optimization process: the supervision image set is iteratively updated using adaptive instance normalization, and the 3D Gaussian scene is fine-tuned based on the updated supervision data. In each iteration, the supervision set contains a mixture of newly replaced stylized images, previously replaced stylized images from earlier rounds, and yet-to-be-replaced original images. Therefore, during each fine-tuning stage, the supervision signal is a hybrid of pixel information from different stages of the style integration process. In the early training stages, replacing part of the original supervision images with stylized ones may cause abrupt changes in the supervision signal, potentially destabilizing the 3D Gaussian training and leading to inconsistencies in the reconstructed 3D scene. However, as the iterations progress, all training images used for 3D Gaussian updates will be successively re-rendered and stylized. Under the guidance of the updated supervision set, the 3D Gaussian model gradually converges toward a globally coherent stylized scene. This progressive style infusion ensures training stability while allowing the target style to gradually permeate and integrate into a globally consistent 3D representation. In each iteration of the 3D Gaussian scene stylization, the backpropagated gradients aggregate a random mixture of ray-based information from multiple viewpoints. This enhances training stability and effectively transfers the learned style into the 3D scene, resulting in a three-dimensionally consistent stylized 3D Gaussian scene.
3.3. Diffusion Prior-Based 3D Gaussian Optimization
During the 3D scene stylization process, insufficient viewpoint coverage in the supervision image set may lead to a loss of detail in certain regions of the reconstructed scene, ultimately impairing the overall 3D representation. Such coverage limitations can result in incompleteness and visual inconsistencies in the stylized output, thereby degrading the quality of the stylized 3D Gaussian scene. To address this challenge and ensure a comprehensive and consistent 3D representation in the stylized scene, this study introduces a diffusion prior based on a pre-trained Stable Diffusion model into the fine-tuning process of style transfer. Inspired by the SparseGS algorithm [22], we propose a novel optimization strategy that incorporates diffusion priors to mitigate the issue of incomplete viewpoint coverage. Specifically, for regions insufficiently covered by the camera poses in the supervision set, we render these areas and optimize them using a pre-trained Stable Diffusion model [21]. The diffusion model serves to enhance local details during the denoising process by leveraging its learned image priors, allowing the recovery of visual information that would otherwise be lost due to limited supervision, thus improving the overall visual fidelity of the 3D scene.
As illustrated in Figure 3, the proposed approach first generates a set of new camera poses in the world coordinate system, which do not exist in the original supervision set. Using these newly sampled poses, the 3D Gaussian scene is rendered to produce a set of novel-view rendered images . Gaussian noise is then added to these images, and the noisy images are passed through the diffusion model to obtain predicted noise . The optimization loss is computed by comparing the ground-truth noise with the predicted noise , and the resulting gradients are used to update the parameters of the 3D Gaussian model. This encourages the model to produce renderings from novel views that not only align with the target style but also exhibit rich and consistent details. This diffusion-prior-guided optimization process takes full advantage of the strong generative prior provided by the diffusion model. As the Stable Diffusion model is trained on large-scale datasets, it provides reliable pixel-level information that can be used to interpolate missing details in the stylized 3D Gaussian scene. Integrating this loss into the optimization enables the recovery of fine-grained details from viewpoints that are not sufficiently covered in the supervision set. Therefore, we embed the Stable Diffusion model into the 3D stylization framework and iteratively refine the scene representation through repeated optimization. This strategy effectively leverages the robust prior knowledge encapsulated in diffusion models to fill in the gaps left by sparse supervision, ensuring that even under limited viewpoint coverage, the stylized 3D scene retains a high degree of detail, consistency, and realism. The resulting stylized 3D Gaussian scene thus achieves visually coherent and realistic representations across the entire scene.
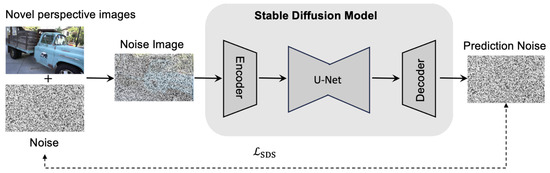
Figure 3.
Flowchart of three-dimensional Gaussian optimization based on diffusion prior.
3.4. Loss Function
The training process of the proposed algorithm is divided into two modules: 3D Gaussian optimization based on iterative updates from the supervision image set and 3D Gaussian optimization guided by diffusion priors. These two modules adopt different forms of loss functions according to their respective optimization strategies.
For the 3D Gaussian optimization based on the supervision image set, we introduce the loss and the Structural Similarity Index (SSIM) loss [23]. For the 3D Gaussian optimization guided by diffusion priors, we employ the Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) loss [24].
loss quantifies model accuracy via the mean absolute error between predicted and ground-truth values. In image generation tasks, loss can effectively reduce the lost of details and enhance photorealism.In our training pipeline, we leverage loss to strictly penalize the absolute deviation between the 3D Gaussian rendering and the stylized 2D supervision, thereby transferring the reference style into the 3D Gaussian representation and producing a stylized 3D Gaussian scene. The loss is calculated as the absolute difference between pixel values of two images, and is formulated as follows:
where denotes the pixel values from the supervision image, and represents the pixel values from the rendered image. Minimizing the loss ensures that the absolute error between the rendered 3D Gaussian image and the stylized 2D supervision image is minimized, thereby transferring the style from the supervision image into the 3D Gaussian model and producing a stylized 3D Gaussian scene.
The Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM) loss is a metric used to evaluate the similarity between two images, focusing primarily on luminance, contrast, and structural fidelity. Unlike traditional metrics such as Mean Squared Error (MSE) or Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR), SSIM is a structure-based loss function that assesses similarity by comparing local statistics within corresponding regions of the two images. The core idea is that if two images are similar in terms of brightness, contrast, and structural patterns, they can be considered visually similar. The SSIM loss is more robust to variations in lighting and small-scale noise. Its computation is defined as follows:
Here, and denote the mean pixel values of the supervision image and the rendered image, respectively, while and represent their corresponding standard deviations. and are small constants introduced to avoid division by zero. In this study, the structural similarity loss is incorporated into the training process to ensure that minimizing the loss maximizes the structural similarity between the rendered 3D Gaussian image and the stylized 2D supervision image, resulting in outputs that better align with the characteristics of the human visual system.
The 3D Gaussian optimization based on iterative updates from the supervision image set employs both loss and structural similarity loss between the rendered image set and the supervision image set to optimize the 3D Gaussian scene. The loss function is defined as follows:
where denotes the loss between the rendered images and the supervision images, represents the structural similarity loss, and is a weighting hyperparameter set within the range [0.2, 0.8].
The diffusion prior-based 3D Gaussian optimization leverages the Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) loss to optimize the 3D Gaussian scene. SDS loss is a type of loss function commonly used in generative models, where the core idea is to utilize a large-scale pre-trained model (the teacher model) to guide the training of a smaller model (the student model), thereby enabling high-quality generation with fewer optimization steps. In this study, the pre-trained diffusion model serves as the teacher to guide the optimization of the 3D Gaussian model. The SDS loss is formally defined as follows:
Here, G denotes the parameters of the stylized 3D Gaussian model, represents the expectation, denotes the predicted noise computed by the diffusion model, denotes the noisy image obtained by adding noise to the rendered image under the novel viewpoint, t denotes the diffusion timestep, and denotes the injected random noise. The Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) loss leverages the powerful prior knowledge embedded in the diffusion model and optimizes the 3D Gaussian scene via gradient backpropagation. By incorporating SDS loss, the 3D Gaussian optimization process can effectively recover missing details in the stylized 3D Gaussian scene from novel viewpoints.
4. Experiment
4.1. Datasets
We evaluate our method on three widely used 3D reconstruction datasets to ensure comprehensive performance analysis. LLFF [25] contains high-resolution images of real-world scenes with relatively simple geometry and limited camera viewpoints. It is used to test stylization under high resolution and narrow view ranges. Tanks and Temples [26] includes large-scale indoor and outdoor scenes captured with industrial laser scanners. It provides low-resolution images with wide camera baselines, and is used to evaluate performance on complex, real-world environments. MipNeRF 360 [27] is a dataset for 360° view synthesis with complex geometry and full view coverage. It is used to test stylization in scenes with dense viewpoints and challenging structures. We use COLMAP [28,29] to preprocess the image data and generate sparse point clouds as initialization for training the 3D Gaussian fields. Each scene is trained for 20,000 iterations. For style images, we use the WikiArt dataset, a large-scale collection of artistic paintings from various styles and artists, commonly used for image generation and style transfer tasks.
4.2. Implementation Details
Our 3D Gaussian style transfer method based on 2D priors and iterative optimization does not separate training and inference. The input includes a reconstructed 3D Gaussian, multi-view supervision images, and a style image. Training consists of two stages:
Stage 1:
- Randomize camera view order for supervision image replacement.
- Render the 3D Gaussian from the selected views, perform style transfer on rendered images using the style image.
- Replace corresponding supervision images with stylized ones.
- Compute loss between rendered and supervision images to optimize the 3D Gaussian via backpropagation.
Training uses the Adam optimizer [30] with a warm-up and exponential decay schedule. The learning rate starts from 1 × 10−8, increases to 1.6 × 10−4, and decays to 1.6 × 10−6. A minimum value of 1 × 10−15 is set for stability. The loss weight is 0.8, and the total training steps are 5000.
Stage 2:
- Generate new camera poses and render new views using the optimized 3D Gaussian.
- Add noise to these images and use a pre-trained diffusion model to predict noise. The difference between predicted and added noise is used to further refine the 3D Gaussian.
Stage 2 also uses the Adam optimizer with an initial learning rate of 1.6 × 10−6.
4.3. Qualitative Comparison
To objectively evaluate the effectiveness of our style transfer method, we compare it with several recent open-source approaches in 3D scene stylization, including ARF [31], StyleRF [16], LSNV [13], StylizedNeRF [32], and StyleGaussian [18], under the same experimental conditions. For LSNV, StyleRF, and StyleGaussian, we utilize available pretrained models when provided, and follow the authors’ official hyperparameter settings otherwise. In the LLFF dataset Figure 4 and Figure 5, ARF produces noisy, jagged outputs; StylizedNeRF transfers style but results in overly blurred images; StyleRF introduces severe artifacts and destroys scene structure. In contrast, our method yields stylized renderings with richer textures and better integration between style and content, preserving the overall scene structure and details. In the flower scene, StylizedNeRF fails to retain the original structure, and StyleRF exhibits style mismatch and a yellowish tone, while our method effectively transfers style while preserving high-resolution features like petals and stamens. In the Tanks and Temples dataset, Figure 6 and Figure 7, StylizedNeRF is excluded due to lack of support. For the train scene, ARF outputs are noisy, LSNV distorts geometry, and StyleGaussian introduces color artifacts inconsistent with the target style, whereas our method achieves faithful style transfer with natural texture fusion and preserved structural integrity. Similarly, in the truck scene, ARF and StyleRF suffer from noise and poor generalization, LSNV and StyleGaussian blur or deform structural details, while our method consistently maintains the scene’s content and structure during stylization.
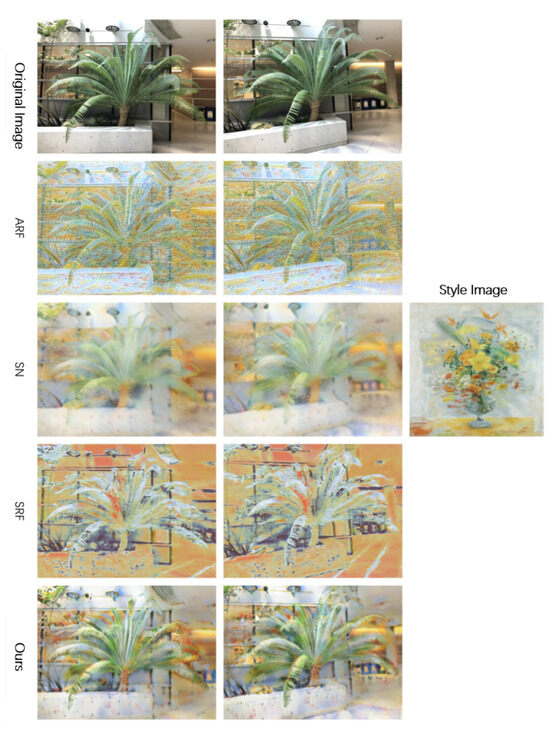
Figure 4.
Comparative experimental results on the LLFF dataset.
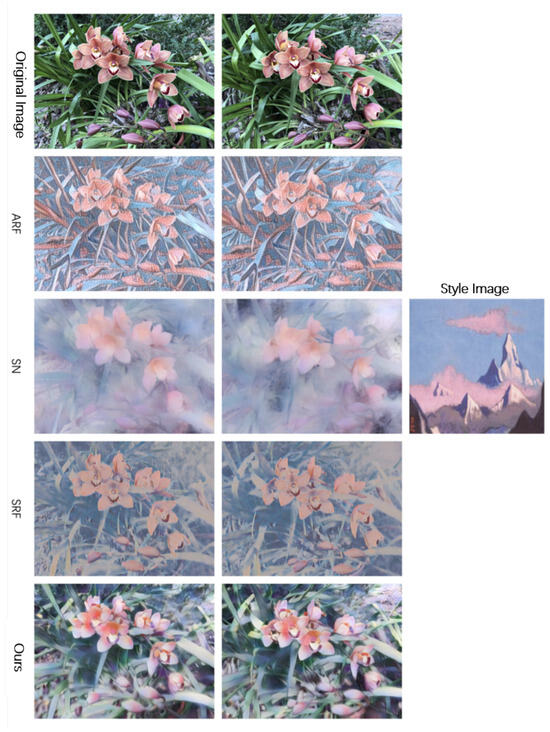

Figure 5.
Comparative experimental results on the LLFF dataset.

Figure 6.
Comparative experimental results on the Tanks and Temples dataset.

Figure 7.
Comparative experimental results on the Tanks and Temples dataset.
4.4. Quantitative Comparison
We evaluate short-range and long-range consistency under both nearby and distant viewpoints, using these metrics to compare four algorithms on the LLFF dataset (Table 1). Lower scores indicate better 3D consistency, and the best results per row are bolded. Our method achieves the best consistency scores among all methods except StylizedNeRF, whose higher scores are likely due to its overly blurred outputs—visual detail is lost, but this uniformity improves consistency metrics. Despite this, StylizedNeRF performs poorly in visual quality, making our method superior overall. On the Tanks and Temples dataset (Table 2), our method outperforms others in all metrics except LSNV’s long-range consistency. Similarly to StylizedNeRF, LSNV’s strong consistency score likely stems from its blurred, structure-less outputs. Nonetheless, considering both visual and quantitative results, our method achieves better stylization quality and 3D consistency. Additionally, average rendering speed results (Table 3) show that our method is the fastest, enabling real-time stylization.

Table 1.
Evaluation indicators of different algorithms on the LLFF dataset. The best value in bold.

Table 2.
Evaluation indicators of different algorithms on the Tanks and Temples dataset. The best value in bold.

Table 3.
Average rendering speed of different algorithms. The best value in bold.
4.5. User Study
To further validate the visual quality of our method, we conducted a simple user study on the results generated by different methods. We reuse the images in the quantitative comparisons and randomly sample 10 groups. Each group consists of the original image, a style image, the results of our method, and several recent open-source approaches in 3D scene stylization. A total of 17 participants were given a series of images, and we compared our method against each baseline separately. We then ask participants to choose the better one by jointly considering the following three aspects: content preservation, stylization effect, and overall preference. As shown in Table 4, our method is preferred in both categories, indicating that our method can perform competitive results.

Table 4.
User study. Users show a clear preference for our method against recent open-source approaches in three-dimensional scene stylization.
4.6. Ablation Study
To evaluate the impact of the iterative training strategy and dataset update ratio on stylization quality, we conducted ablation studies using different update ratios (0.1–0.9). Results show that smaller ratios (0.1–0.3) yield better stylization, preserving scene structure while injecting style. Larger ratios introduce unstable supervision, causing blur and artifacts. Smaller ratios enable gradual style integration, improving 3D consistency. Quantitative results in Table 5 show that a 0.3 ratio achieves the best short-range consistency, while 0.1 performs best in long-range consistency. This is because moderate updates balance new and old information, enhancing local detail, while lower ratios help maintain stable global features.

Table 5.
Evaluation indicators of different dataset update ratios on the MipNeRF 360 dataset. The best value in bold.
5. Conclusions
This work introduces a novel style transfer method that combines 2D image priors with iterative optimization for 3D Gaussian scenes, offering a new approach for 3D scene stylization. Compared to existing methods, it achieves better multi-view consistency, high visual quality, and real-time rendering. The key innovation lies in using 2D priors to guide the stylization of 3D Gaussians, progressively transferring style information while maintaining structural integrity. With diffusion priors, the method ensures consistent and high-quality appearance across all views. Overall, it expands the potential of style transfer in graphics and provides an efficient solution for 3D content generation and rendering.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.Z., L.Z. and H.Y.; methodology, W.Z., H.Y.; software, X.W. and H.Y.; validation, L.Z. and L.C.; formal analysis, W.X.; investigation, X.W.; resources, L.Z. and W.X.; data curation, W.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, W.Z., H.Y.; writing—review and editing, W.Z., L.Z.; visualization, X.W.; supervision, H.L.; project administration, W.Z., X.W. and H.Y.; funding acquisition, L.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by Zhejiang Province Program (2025C01068, 2024C03263, LZ25F020006), Zhejiang Provincial Cultural Relics Protection Science and Technology Project (2024009), the National Program of China (62172365), Macau project: Key technology research and display system development for new personalized controllable dressing dynamic display, and Ningbo Science and Technology Plan Project (2025Z052, 2025Z062, 2022Z167, 2023Z137).
Data Availability Statement
The data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gatys, L.A.; Ecker, A.S.; Bethge, M. Image style transfer using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2414–2423. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.; Alahi, A.; Li, F.-F. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 694–711. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.Y.; Lee, K.H. Arbitrary Style Transfer With Style-Attentional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5873–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xing, W.; Sun, J.; Chu, T.; Huang, Y.; Ji, B.; Zhao, L.; Lin, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z. PNeSM: Arbitrary 3D scene stylization via prompt-based neural style mapping. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 1091–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Mildenhall, B.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Tancik, M.; Barron, J.T.; Ramamoorthi, R.; Ng, R. Nerf: Representing scenes as neural radiance fields for view synthesis. Commun. ACM 2021, 65, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 26th Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; Volume 25. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Fang, C.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Lu, X.; Yang, M.H. Universal style transfer via feature transforms. In Proceedings of the 30th Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Belongie, S. Arbitrary style transfer in real-time with adaptive instance normalization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1501–1510. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, N.; Tang, F.; Huang, H.; Ma, C.; Dong, W.; Xu, C. Inversion-based style transfer with diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 10146–10156. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; PmLR: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Xing, W. Stylediffusion: Controllable disentangled style transfer via diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 7677–7689. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.P.; Tseng, H.Y.; Saini, S.; Singh, M.; Yang, M.H. Learning to stylize novel views. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 13869–13878. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Pang, A.; Zeng, X.; Cheng, W.; Fu, Y.; Yin, F.; Wang, B.; Yu, J.; Yu, G.; et al. Meshxl: Neural coordinate field for generative 3d foundation models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 97141–97166. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Huang, X.; Hao, Z.; Liu, M.Y.; Belongie, S.; Hariharan, B. Pointflow: 3D point cloud generation with continuous normalizing flows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 4541–4550. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Zhan, F.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Y.; El Saddik, A.; Lu, S.; Xing, E.P. Stylerf: Zero-shot 3D style transfer of neural radiance fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 8338–8348. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; He, Z.; Xing, J.; Yao, X.; Jia, J. Ref-npr: Reference-based non-photorealistic radiance fields for controllable scene stylization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 4242–4251. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Zhan, F.; Xu, M.; Theobalt, C.; Shao, L.; Lu, S. Stylegaussian: Instant 3D style transfer with gaussian splatting. In Proceedings of the SIGGRAPH Asia 2024 Technical Communications, Tokyo, Japan, 3–6 December 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Galerne, B.; Wang, J.; Raad, L.; Morel, J.M. SGSST: Scaling Gaussian Splatting Style Transfer. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference, Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 June 2025; pp. 26535–26544. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.; Kuthiala, A.; Sethi, P.S.; Saxena, P. Stylesplat: 3d object style transfer with gaussian splatting. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.09473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 June 2022; pp. 10684–10695. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, H. SparseGS: Real-Time 360° Sparse View Synthesis Using Gaussian Splatting; University of California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, B.; Jain, A.; Barron, J.T.; Mildenhall, B. Dreamfusion: Text-to-3D using 2D diffusion. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.14988. [Google Scholar]
- Mildenhall, B.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Ortiz-Cayon, R.; Kalantari, N.K.; Ramamoorthi, R.; Ng, R.; Kar, A. Local light field fusion: Practical view synthesis with prescriptive sampling guidelines. ACM Trans. Graph. (ToG) 2019, 38, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapitsch, A.; Park, J.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Koltun, V. Tanks and temples: Benchmarking large-scale scene reconstruction. ACM Trans. Graph. (ToG) 2017, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, J.T.; Mildenhall, B.; Verbin, D.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Hedman, P. Mip-nerf 360: Unbounded anti-aliased neural radiance fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5470–5479. [Google Scholar]
- Schönberger, J.L.; Zheng, E.; Frahm, J.M.; Pollefeys, M. Pixelwise view selection for unstructured multi-view stereo. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part III 14. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 501–518. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.; Long, X.; Yang, K.; Yao, Y.; Yin, W.; Ma, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, X. Gaussianpro: 3D gaussian splatting with progressive propagation. In Proceedings of the Forty-First International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 21–27 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Kolkin, N.; Bi, S.; Luan, F.; Xu, Z.; Shechtman, E.; Snavely, N. Arf: Artistic radiance fields. In Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 717–733. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.H.; He, Y.; Yuan, Y.J.; Lai, Y.K.; Gao, L. Stylizednerf: Consistent 3D scene stylization as stylized nerf via 2D-3D mutual learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 18342–18352. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).