Emotion Recognition in Autistic Children Through Facial Expressions Using Advanced Deep Learning Architectures
Abstract
1. Introduction
- It compares CNN and transformer-based architectures for emotion classification in autistic children, evaluating their strengths and limitations in capturing subtle facial cues.
- It assesses the role of dataset composition and transfer learning in optimizing model accuracy and generalizability across diverse ASD expressions.
- It demonstrates the potential for scalable, real-time, and objective emotion-aware systems that can augment therapeutic interventions, social skills training, and assistive communication technologies.
2. Related Works
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Preprocessing and Experimental Setup
3.2. CNN and Transfer Learning for Emotion Classification
| Algorithm 1: CNN with Transfer Learning |
| 1. function EmotionRecognition_CNN (Input_Images, Pretrained_Model) 2. Input: 3. Input_Images: Set of training images with emotion labels 4. Pretrained_Model: A CNN model pre-trained on ImageNet 5. Output: Trained_CNN_Model 6. Preprocess Input_Images (resize, normalize, augment) 7. Load Pretrained_Model without top classification layers 8. Freeze early layers of Pretrained_Model to retain learned features 9. Add custom classification layers: 10. Dense layer with ReLU activation 11. Dropout for regularization 12. Final Dense layer with Softmax activation for emotion classes 13. Compile model using Adam optimizer and cross-entropy loss 14. Train model on Input_Images with validation split 15. Evaluate model performance on test set 16. return Trained_CNN_Model 17. end function |
3.3. Transformer-Based Approach for Emotion Classification
| Algorithm 2: Transformer-Based Emotion Classification |
| 1. function EmotionRecognition_Transformer(Input_Images, Transformer_Model) 2. Input: 3. Input_Images: Set of facial images labeled with emotions 4. Transformer_Model: Pretrained model for emotion analysis 5. Output: Trained_Transformer_Model 6. Preprocess Input_Images: 7. Convert grayscale to RGB if necessary 8. Normalize pixel values and apply standard augmentation 9. Use Transformer_Model to extract deep features from Input_Images 10. Store extracted features and corresponding labels 11. Define custom classifier head: 12. Dense layer with ReLU activation 13. Dropout for regularization 14. Final Dense layer with Softmax activation 15. Compile model with suitable optimizer and loss function 16. Train classifier head using extracted features and labels 17. Evaluate model using accuracy, F1-score, and AUC 18. return Trained_Transformer_Model 19. end function |
3.4. Performance Assessment
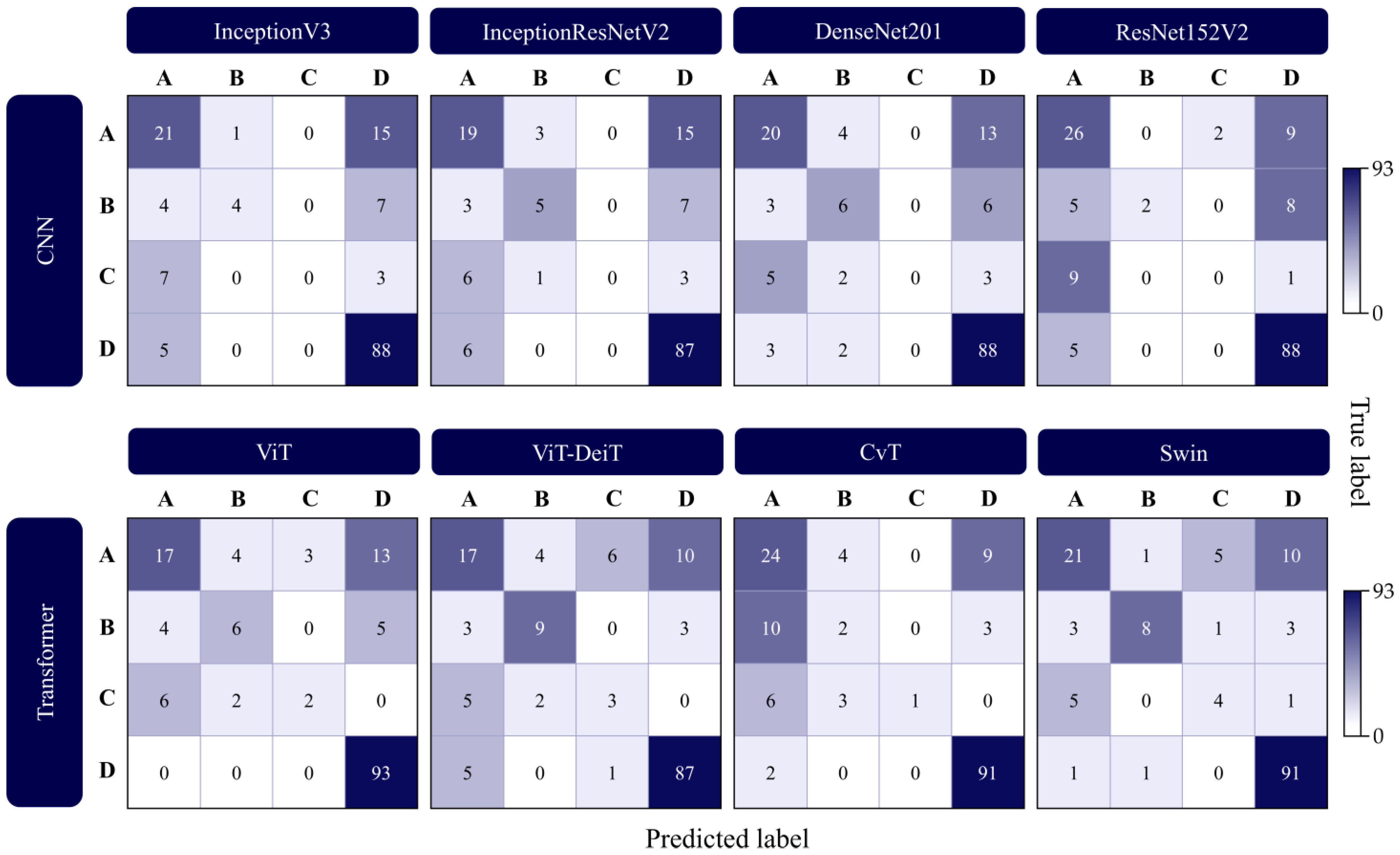
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sauer, A.K.; Stanton, J.E.; Hans, S.; Grabrucker, A.M. Autism Spectrum Disorders: Etiology and Pathology. In Autism Spectrum Disorders; Grabrucker, A.M., Ed.; Exon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2021; ISBN 978-0-645-00178-5. [Google Scholar]
- Hirota, T.; King, B.H. Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Review. JAMA 2023, 329, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.; Bhushan, B. Facial Expression Databases and Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Scoping Review. Autism Res. Off. J. Int. Soc. Autism Res. 2025, 18, 1314–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, V.G.; Kohli, M.; Kohli, S.; Prathosh, A.P.; Wadhera, T.; Das, D.; Panigrahi, D.; Kommu, J.V.S. Computer Vision-Based Assessment of Autistic Children: Analyzing Interactions, Emotions, Human Pose, and Life Skills. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 47907–47929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElMahalawy, J.; ElSwaify, Y.A.; Elliboudy, D.; Abbas, O.M.; Moustafa, N.; Wael, N. AI-Powered Human-Computer Interaction Assisting Early Identification of Emotional and Facial Symptoms of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children: “A Deep Learning-Based Enhanced Facial Feature Recognition System. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Machine Intelligence and Smart Innovation (ICMISI), Alexandria, Egypt, 12–14 May 2024; pp. 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Nefaie, A.H.; Aldhyani, T.H.H.; Ahmad, S.; Alzahrani, E.M. Application of Artificial Intelligence in Modern Healthcare for Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1569464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altered Interactive Dynamics of Gaze Behavior During Face-to-Face Interaction in Autistic Individuals: A Dual Eye-Tracking Study|Molecular Autism|Full Text. Available online: https://molecularautism.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13229-025-00645-5 (accessed on 31 July 2025).
- Hedger, N.; Chakrabarti, B. Autistic Differences in the Temporal Dynamics of Social Attention. Autism Int. J. Res. Pract. 2021, 25, 1615–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, K.; White, S.; Dziwisz, M.; Agarwal, P.; Moss, J. Visual Attention Patterns during a Gaze Following Task in Neurogenetic Syndromes Associated with Unique Profiles of Autistic Traits: Fragile X and Cornelia de Lange Syndromes. Cortex 2024, 174, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, M.K. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Facial Emotion Recognition in Autism Spectrum Disorder: The Specificity of Deficits and the Role of Task Characteristics. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 133, 104518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, M.H.; Chen, N.T.M.; Iyer, K.K.; Lipp, O.V.; Bölte, S.; Falkmer, M.; Tan, T.; Girdler, S. Mechanisms of Facial Emotion Recognition in Autism Spectrum Disorders: Insights from Eye Tracking and Electroencephalography. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 80, 488–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, N.M.; Al-Allaf, A.F. Facial Expression Recognition (FER) of Autism Children Using Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 4th International Iraqi Conference on Engineering Technology and Their Applications (IICETA), Najaf, Iraq, 21–22 September 2021; pp. 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Syed, A.J.; Durrani, D.J.; Shahid, N.; Khan, W.; Muhammad, A. Expression Detection of Autistic Children Using CNN Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2023 Global Conference on Wireless and Optical Technologies (GCWOT), Malaga, Spain, 24–27 January 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Jaffar, S.S.; Abdulbaqi, H.A. Facial Expression Recognition in Static Images for Autism Children Using CNN Approaches. In Proceedings of the 2022 Fifth College of Science International Conference of Recent Trends in Information Technology (CSCTIT), Baghdad, Iraq, 15–16 November 2022; pp. 202–207. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Chattopadhyay, P.; Wang, L. Vision Transformers for Image Classification: A Comparative Survey. Technologies 2025, 13, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elharrouss, O.; Himeur, Y.; Mahmood, Y.; Alrabaee, S.; Ouamane, A.; Bensaali, F.; Bechqito, Y.; Chouchane, A. ViTs as Backbones: Leveraging Vision Transformers for Feature Extraction. Inf. Fusion 2025, 118, 102951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, T. Deep Learning Approach to Predict Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Psychiatry 2024, 24, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, F.; Choi, S.; Kang, Y.H.; Cheon, K.-A.; Lee, S.W. Exploring the Structural and Strategic Bases of Autism Spectrum Disorders with Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 153341–153352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, T.; Akram, S.; Rashid, M.; Jaffar, A.; Bhatti, S.M.; Iqbal, M.A. A Deep Learning-Based Ensemble for Autism Spectrum Disorder Diagnosis Using Facial Images. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0321697. Available online: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0321697 (accessed on 31 July 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer-Lindenberg, H.; Moessnang, C.; Oakley, B.; Ahmad, J.; Mason, L.; Jones, E.J.H.; Hayward, H.L.; Cooke, J.; Crawley, D.; Holt, R.; et al. Facial Expression Recognition Is Linked to Clinical and Neurofunctional Differences in Autism. Mol. Autism 2022, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corluka, N.; Laycock, R. The Influence of Dynamism and Expression Intensity on Face Emotion Recognition in Individuals with Autistic Traits. Cogn. Emot. 2024, 38, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dia, M.; Khodabandelou, G.; Sabri, A.Q.M.; Othmani, A. Video-Based Continuous Affect Recognition of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder Using Deep Learning. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2024, 89, 105712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, S.W.H.; Md Sabri, A.Q.; Othmani, A. Autism Classification and Monitoring from Predicted Categorical and Dimensional Emotions of Video Features. Signal Image Video Process. 2024, 18, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milling, M.; Baird, A.; Bartl-Pokorny, K.D.; Liu, S.; Alcorn, A.M.; Shen, J.; Tavassoli, T.; Ainger, E.; Pellicano, E.; Pantic, M.; et al. Evaluating the Impact of Voice Activity Detection on Speech Emotion Recognition for Autistic Children. Front. Comput. Sci. 2022, 4, 837269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FERAC Dataset. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/rajasreechaiti/ferac-dataset (accessed on 31 July 2025).
- Islam, M.M. The Impact of Transfer Learning on AI Performance Across Domains. J. Artif. Intell. Gen. Sci. 2024, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanaja, D.S.; Arockia Raj, J. AI-Enhanced IoT Tool for Emotional and Social Development in Children with Autism. Int. J. High Speed Electron. Syst. 2025, 2540148. Available online: https://www.worldscientific.com/doi/10.1142/S0129156425401482?srsltid=AfmBOoo_5VRFMRuybfFDxDhc_GbQ7OIjmyYw3DjMyYXbhyeUOi9abV1M (accessed on 31 July 2025). [CrossRef]
- Talaat, F.M. Real-Time Facial Emotion Recognition System among Children with Autism Based on Deep Learning and IoT. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 12717–12728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, F.; Pollak, S.; Albert, P.; Luz, S. Emotion Recognition in Low-Resource Settings: An Evaluation of Automatic Feature Selection Methods. Comput. Speech Lang. 2021, 65, 101119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, W.-C.; Song, P.-H. A Face Image Classification Method of Autistic Children Based on the Two-Phase Transfer Learning. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1226470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthukkumar, R. Enhancing the Identification of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Facial Expressions Using DenseResNet-Based Transfer Learning Approach. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2025, 103, 107433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, T.; Ali, M.H.; Khan, M.I.; Satu, M.S.; Uddin, M.J.; Alyami, S.A.; Ali, S.; Azad, A.; Moni, M.A. Improved Transfer-Learning-Based Facial Recognition Framework to Detect Autistic Children at an Early Stage. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrin, M.; Hoque, K.E.; Chaiti, R.D. Emotion Recognition of Autistic Children from Facial Images Using Hybrid Model. In Proceedings of the 2024 15th International Conference on Computing Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Kamand, India, 24–28 June 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sandeep, P.V.K.; Kumar, N.S. Pain Detection through Facial Expressions in Children with Autism Using Deep Learning. Soft Comput. 2024, 28, 4621–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, K.; Shao, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, X. Applying a Convolutional Vision Transformer for Emotion Recognition in Children with Autism: Fusion of Facial Expressions and Speech Features. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzubaidi, L.; Zhang, J.; Humaidi, A.J.; Al-Dujaili, A.; Duan, Y.; Al-Shamma, O.; Santamaría, J.; Fadhel, M.A.; Al-Amidie, M.; Farhan, L. Review of Deep Learning: Concepts, CNN Architectures, Challenges, Applications, Future Directions. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pávez, R.; Díaz, J.; Arango-López, J.; Ahumada, D.; Méndez, C.; Moreira, F. Emotion Recognition in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder Using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Trends and Applications in Information Systems and Technologies; Rocha, Á., Adeli, H., Dzemyda, G., Moreira, F., Ramalho Correia, A.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 585–595. [Google Scholar]
- Alamgir, F.M.; Zaman, T.; Hassan, M.M.; Jonayed, M.R.; Alam, M.S. Classification Model for Autism Spectrum Disorder Individuals: Utilizing Facial Grid-Wise Emotion Features and Dual-Branch Visual Transformation. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Power, Electrical, Electronics and Industrial Applications (PEEIACON), Rajshahi, Bangladesh, 12–13 September 2024; pp. 864–869. [Google Scholar]
- Indra Devi, K.B.; Durai Raj Vincent, P.M. The Emergence of Artificial Intelligence in Autism Spectrum Disorder Research: A Review of Neuro Imaging and Behavioral Applications. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2025, 56, 100718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharthi, A.G.; Alzahrani, S.M. Do It the Transformer Way: A Comprehensive Review of Brain and Vision Transformers for Autism Spectrum Disorder Diagnosis and Classification. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 167, 107667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Yamaguchi, Y. Visualization Comparison of Vision Transformers and Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 2327–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Rauf, Z.; Sohail, A.; Khan, A.R.; Asif, H.; Asif, A.; Farooq, U. A Survey of the Vision Transformers and Their CNN-Transformer Based Variants. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 2917–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Sun, B.; Li, S. Facial Expression Recognition with Visual Transformers and Attentional Selective Fusion. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2023, 14, 1236–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.; Mendes, C.; Ribeiro, J.; Ribeiro, R.; Miragaia, R.; Rodrigues, N.; Costa, N.; Pereira, A. Systematic Review of Emotion Detection with Computer Vision and Deep Learning. Sensors 2024, 24, 3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwooi, S.K.W.; Othmani, A.; Sabri, A.Q.M. Deep Learning-Based Approach for Continuous Affect Prediction from Facial Expression Images in Valence-Arousal Space. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 96053–96065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadiar, A.; Melinda, M.; Muthiah, Z.; Zainal, Z.; Rizky, M.M. Thermal Image Classification of Autistic Children Using Res-Net Architecture. Indones. J. Electron. Electromed. Eng. Med. Inform. 2025, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagmatova, Z.; Umirzakova, S.; Kutlimuratov, A.; Abdusalomov, A.; Im Cho, Y. A Hyper-Attentive Multimodal Transformer for Real-Time and Robust Facial Expression Recognition. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
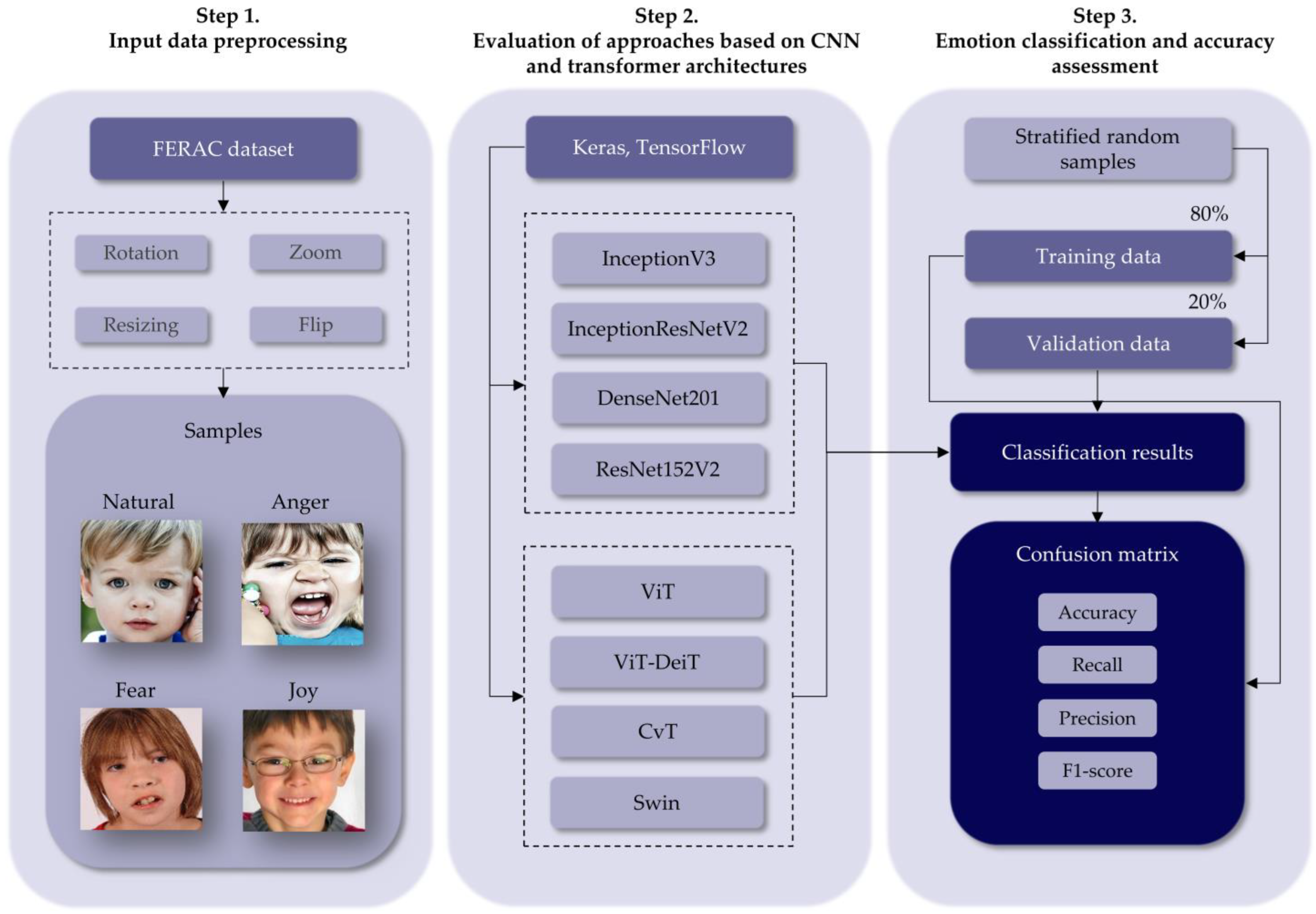

| Category | Total Images | Training Images | Validation Images |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural | 184 | 147 | 37 |
| Anger | 74 | 59 | 15 |
| Fear | 49 | 39 | 10 |
| Joy | 463 | 370 | 93 |
| Total | 770 | 615 | 155 |
| Deep Learning Approach | Model | Accuracy | F1-Score | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | InceptionV3 | 0.7290 | 0.6868 | 0.6802 | 0.7290 |
| InceptionResNetV2 | 0.7161 | 0.6774 | 0.6532 | 0.7161 | |
| DenseNet201 | 0.7355 | 0.7007 | 0.6755 | 0.7355 | |
| ResNet152V2 | 0.7484 | 0.7048 | 0.7328 | 0.7484 | |
| Transformer | ViT | 0.7613 | 0.7341 | 0.7272 | 0.7613 |
| ViT-DeiT | 0.7484 | 0.7395 | 0.7347 | 0.7484 | |
| CvT | 0.7613 | 0.7300 | 0.7525 | 0.7613 | |
| Swin | 0.8000 | 0.7889 | 0.7903 | 0.8000 |
| Deep Learning Approach | Model | Natural | Anger | Fear | Joy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | InceptionV3 | 0.5676 | 0.4000 | 0.0000 | 0.8544 |
| InceptionResNetV2 | 0.5352 | 0.4167 | 0.0000 | 0.8488 | |
| DenseNet201 | 0.5882 | 0.4138 | 0.0000 | 0.8670 | |
| ResNet152V2 | 0.6341 | 0.2353 | 0.0000 | 0.8844 | |
| Transformer | ViT | 0.5312 | 0.4444 | 0.2667 | 0.9118 |
| ViT-DeiT | 0.5075 | 0.6000 | 0.3000 | 0.9016 | |
| CvT | 0.6076 | 0.1667 | 0.1818 | 0.9286 | |
| Swin | 0.6269 | 0.6400 | 0.4000 | 0.9192 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radočaj, P.; Martinović, G. Emotion Recognition in Autistic Children Through Facial Expressions Using Advanced Deep Learning Architectures. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9555. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179555
Radočaj P, Martinović G. Emotion Recognition in Autistic Children Through Facial Expressions Using Advanced Deep Learning Architectures. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9555. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179555
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadočaj, Petra, and Goran Martinović. 2025. "Emotion Recognition in Autistic Children Through Facial Expressions Using Advanced Deep Learning Architectures" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9555. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179555
APA StyleRadočaj, P., & Martinović, G. (2025). Emotion Recognition in Autistic Children Through Facial Expressions Using Advanced Deep Learning Architectures. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9555. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179555






