Mathematical Modelling of Throughput in Peer-Assisted Symbiotic 6G with SIC and Relays
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Related Works
1.2. Motivations and Contributions
- Joint time-domain framework: this is the first unified time-domain allocation framework that jointly allocates the TDMA backscatter window and the PD–NOMA duration under time normalization, energy-causality, and QoS, while consistently treating both perfect and imperfect SIC in multi-cluster SRNs with mandatory relaying.
- Imperfect SIC (practical suitability): a parametric residual-interference factor is embedded into the SINR and QoS expressions of both phases, quantifying the performance degradation under imperfect cancellation and the gain under perfect SIC, thereby enhancing the practical suitability and realism of the model.
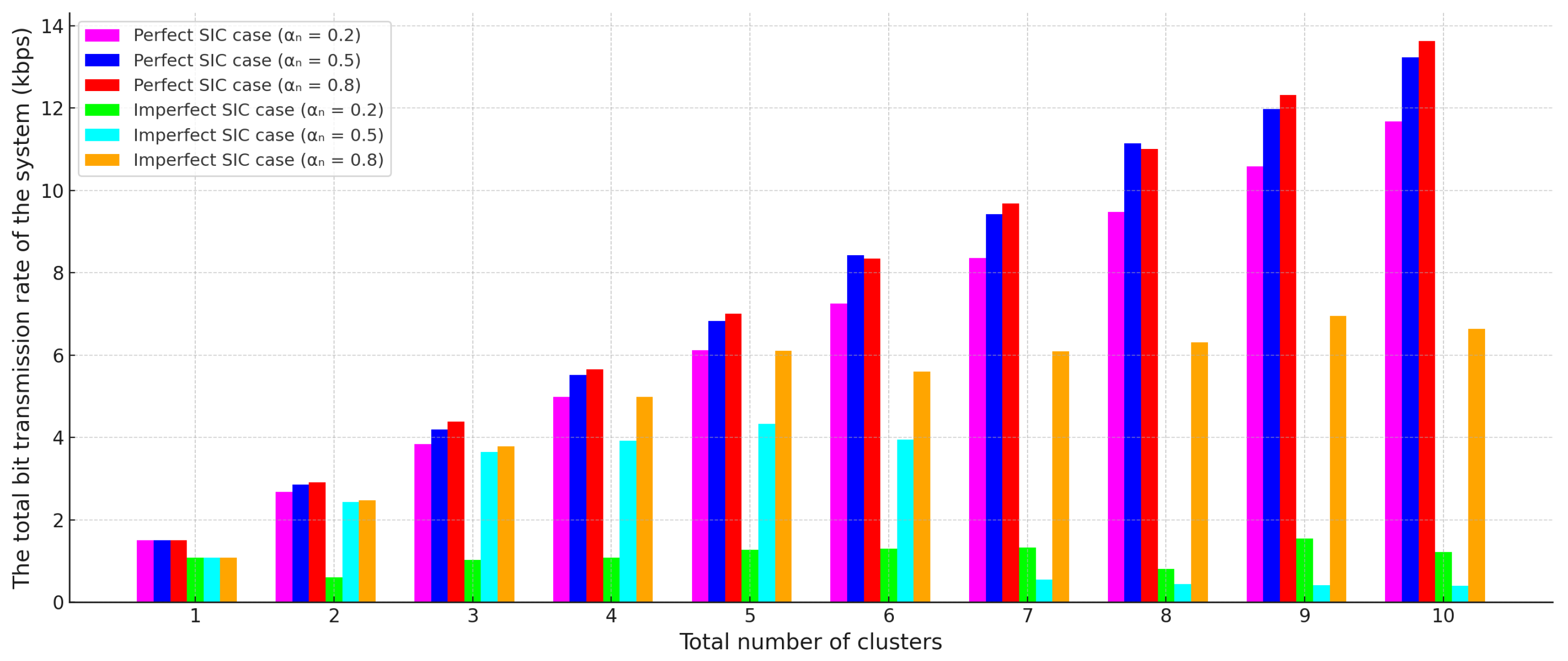
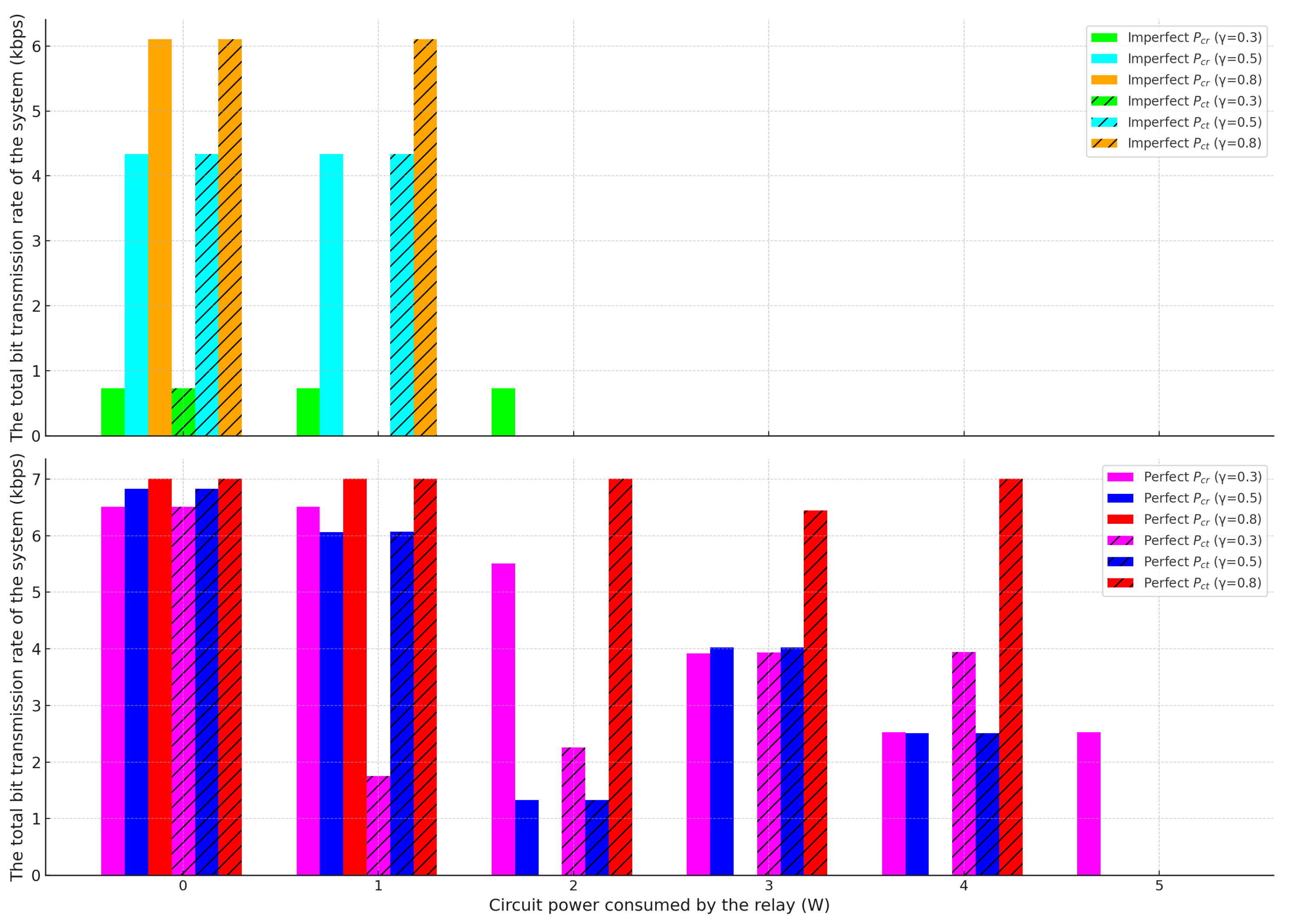
- Capacity determinants: it is shown that network capacity is determined by the triad of base station power, channel noise, and SIC accuracy; the proposed scheme performs near the global optimum in this domain.
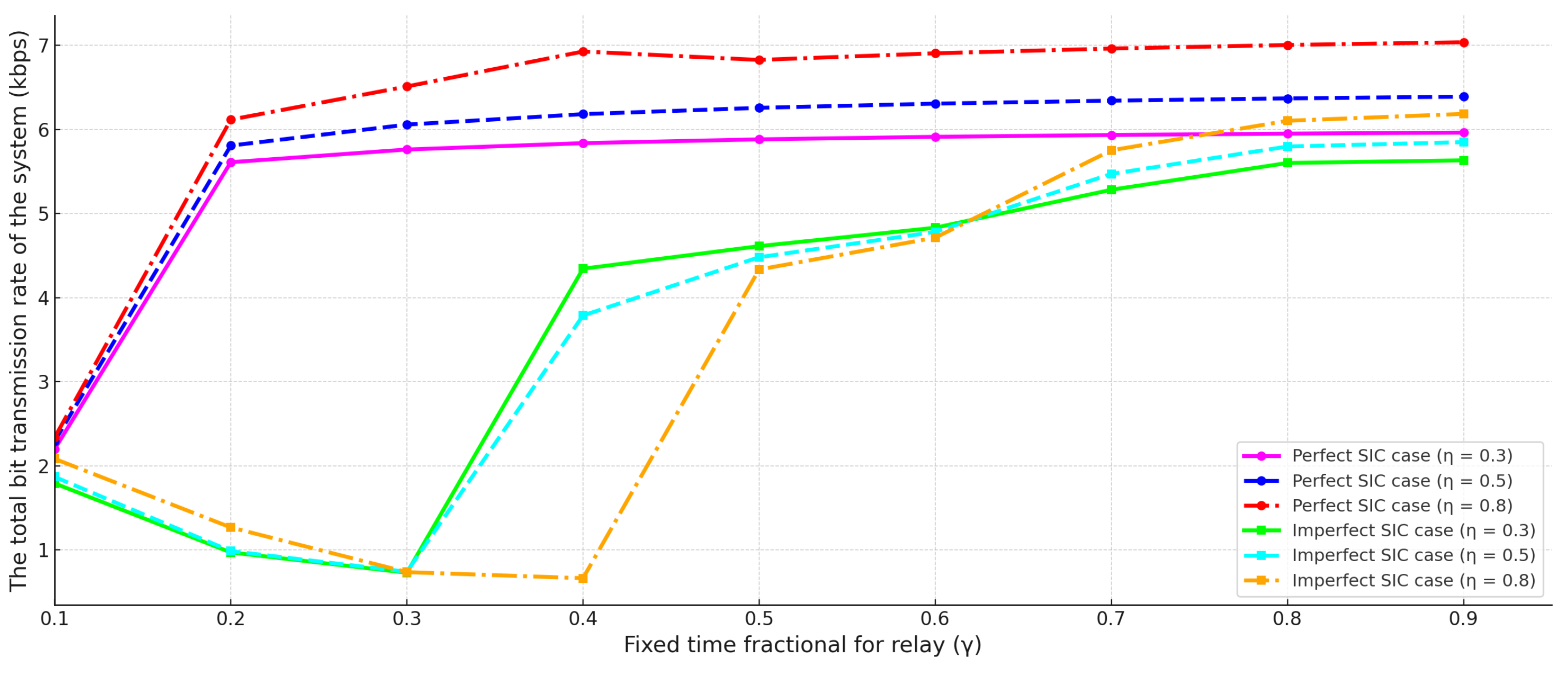
- Actionable design rules: increasing fixed time fractional for relay is shown to rapidly close the perfect–imperfect SIC performance gap, providing clear design guidelines for 6G applications.
1.3. Paper Organization
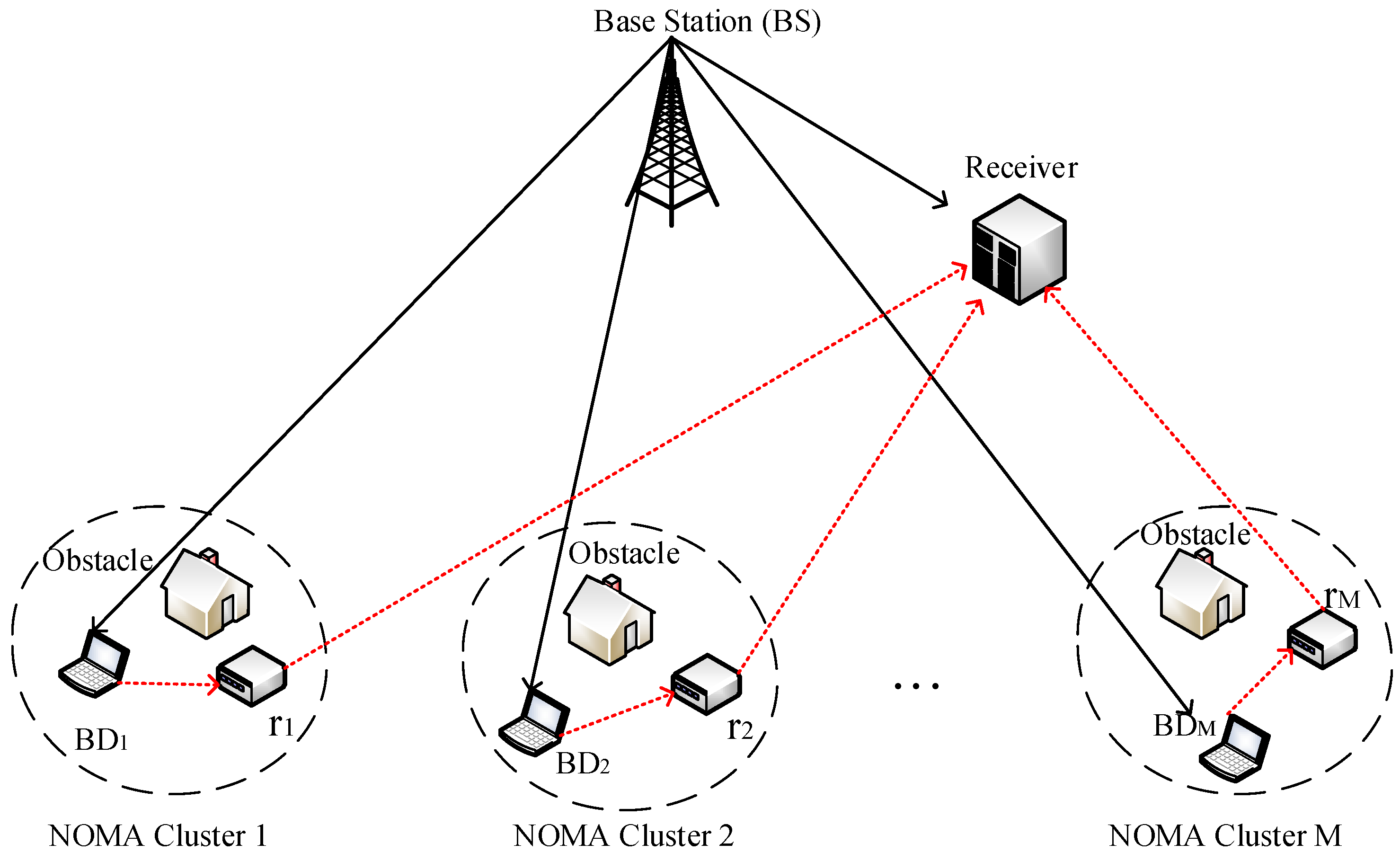
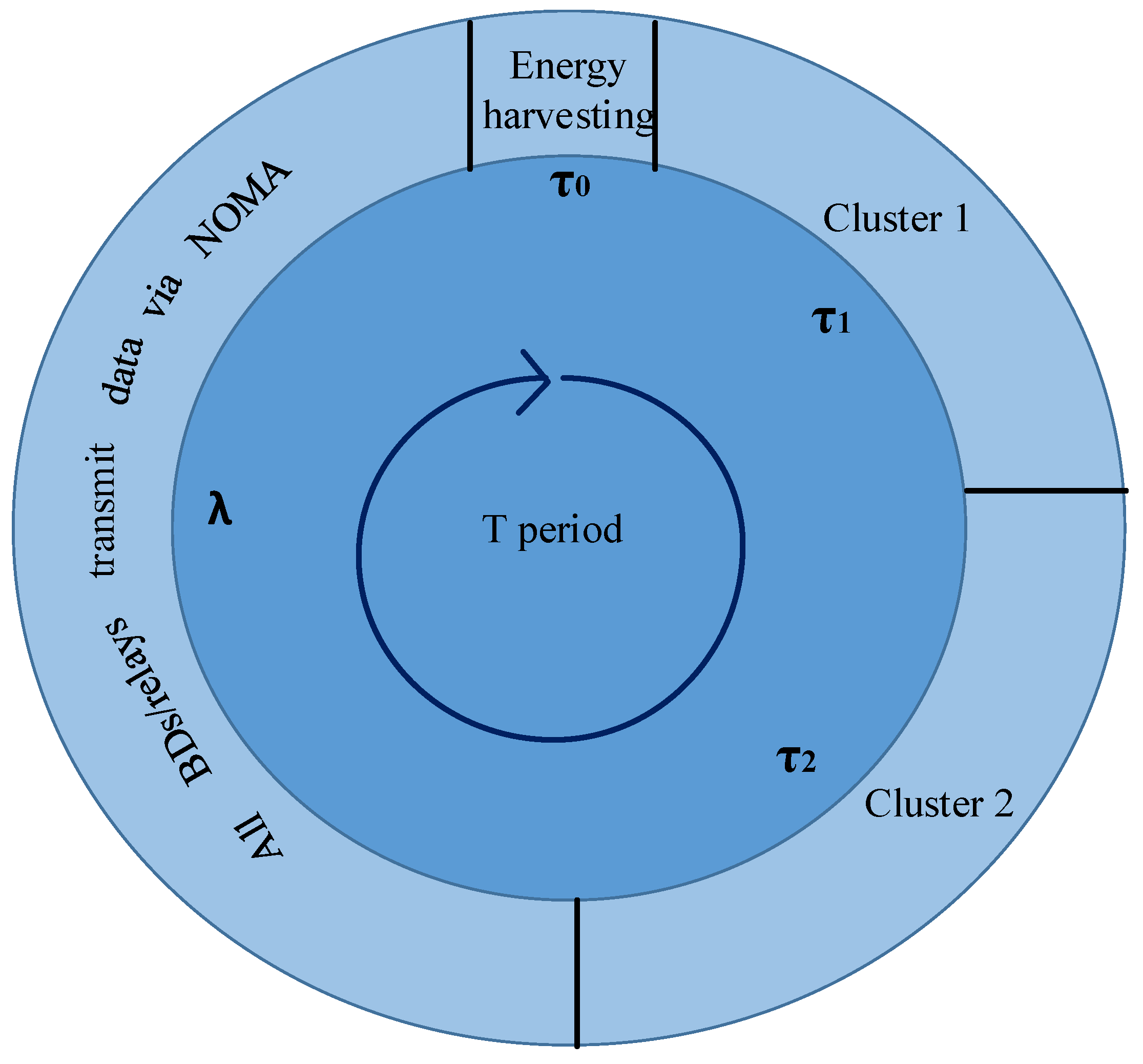
2. System Model
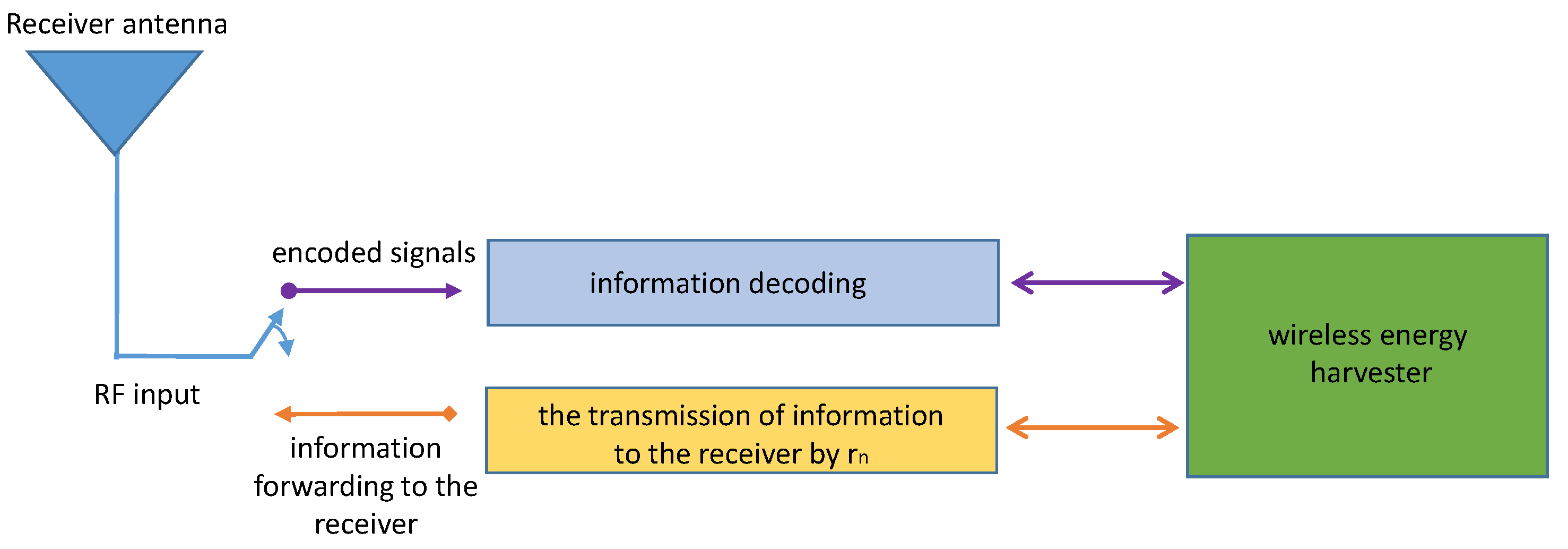
Downlink, Backscatter, and Relay Signal Models
3. Mathematical Modeling
3.1. Perfect SIC Case
3.1.1. Base Station-Plus-Peer-Assisted-Based Energy Harvesting Method for the Perfect SIC Case
3.1.2. Capacity and Throughput Analysis Under Perfect SIC
3.2. Imperfect SIC Case
3.3. Solution Methodology and Computational Complexity
Computational Complexity
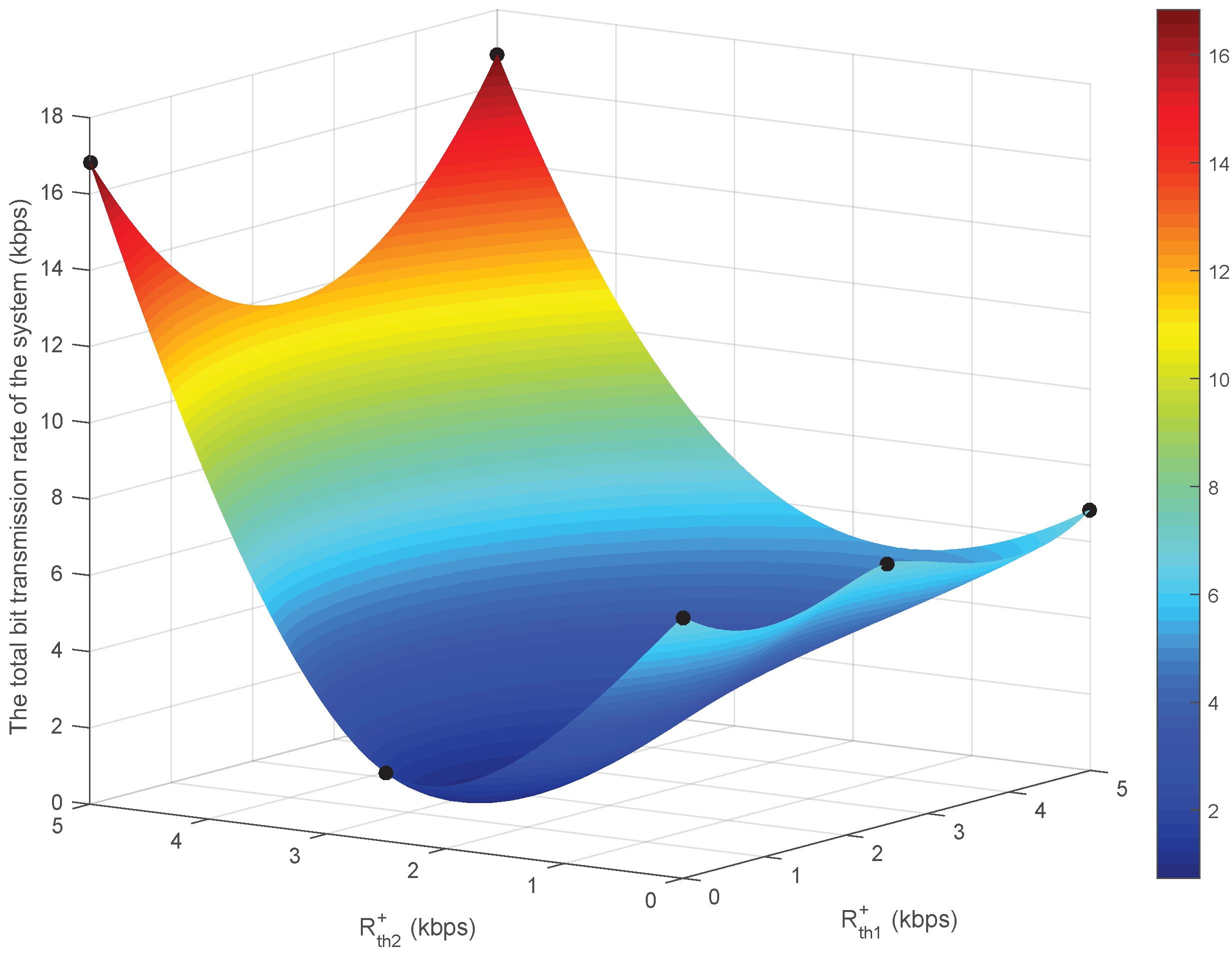
4. Numerical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jawad, A.T.; Maaloul, R.; Chaari, L. A Comprehensive Survey on 6G and Beyond: Enabling Technologies, Opportunities of Machine Learning and Challenges. Comput. Netw. 2023, 237, 110085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrag, M.A.; Friha, O.; Kantarci, B.; Tihanyi, N.; Cordeiro, L.; Debbah, M.; Hamouda, D.; Al-Hawawreh, M.; Choo, K.K.R. Edge Learning for 6G-Enabled Internet of Things: A Comprehensive Survey of Vulnerabilities, Datasets, and Defenses. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2023, 25, 2654–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordani, M.; Polese, M.; Mezzavilla, M.; Rangan, S.; Zorzi, M. Toward 6G Networks: Use Cases and Technologies. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2020, 58, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennanen, H.; Hänninen, T.; Tervo, O.; Tölli, A.; Latva-Aho, M. 6G: The Intelligent Network of Everything. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 1319–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onay, M.Y.; Ertug, O. Ambient Backscatter Communication Based Cooperative Relaying for Heterogeneous Cognitive Radio Networks. Radioengineering 2023, 32, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onay, M.Y.; Dulek, B. Performance Analysis of TV, FM and WiFi Signals in Backscatter Communication Networks. In Proceedings of the 27th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), Sivas, Turkey, 24–26 April 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.; Liang, Y.-C.; Guo, H.; Yang, G.; Zhang, R. Symbiotic Radio: A New Communication Paradigm for Passive Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 1350–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onay, M.Y.; Dokmetas, B. 3D Printed Microstrip Antenna for Symbiotic Communication: WiFi Backscatter and Bit Rate Evaluation for IoT. Internet Things 2025, 32, 101643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsabah, M.; Naser, M.A.; Mahmmod, B.M.; Abdulhussain, S.H.; Eissa, M.R.; Al-Baidhani, A.; Noordin, N.K.; Sait, S.M.; Al-Utaibi, K.A.; Hashim, F. 6G Wireless Communications Networks: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 148191–148243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Kim, G.; Shim, S.; Jang, S.; Song, J.; Lee, B. Key Technologies for 6G-Enabled Smart Sustainable City. Electronics 2024, 13, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Kang, X.; Liang, Y.-C. Minimum Throughput Maximization for Peer-Assisted NOMA-Plus-TDMA Symbiotic Radio Networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 1847–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D. Backscatter Communication via Harvest-Then-Transmit Relaying. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 6843–6847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Huang, Y.; Yu, F.R.; Si, P.; Zhang, H. Ambient Backscatter Communication-Assisted Intelligent Resource Management for Green Industrial IoT. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2025, 32, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Shen, S.; Tsang, D.H.K.; Murch, R. MIMO Ambient Backscatter Communications: Capacity Maximization and Beamforming Optimization. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 15829–15843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-J.; Xu, K.; Yan, Y.; Chen, L. Relay Selection-Based Cooperative Backscatter Transmission With Energy Harvesting: Throughput Maximization. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2022, 11, 1533–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Peng, M.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, T. Distributed MIMO Assisted Battery-Free Backscatter Communications for Ambient Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things Mag. 2025, 8, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Shen, S. Beamforming Design for Multi-Antenna Multi-Tag Symbiotic Radio Backscatter Systems. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2023, 170, 154820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, D.; Zhu, H. Cooperative Resource Allocation for Hybrid NOMA-OMA-Based Wireless Powered MC-IoT Systems with Hybrid Relays. Electronics 2024, 13, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Ihsan, A.; Khan, W.U.; Ranjha, A.; Zhang, S.; Wu, S.X. Energy-Efficient Beamforming and Resource Optimization for AmBSC-Assisted Cooperative NOMA IoT Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 12434–12448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Ding, Z. Backscatter-Assisted Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access Network for Next Generation Communication. IET Signal Process. 2023, e12211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Khan, W.U.; Ihsan, A.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Tsiftsis, T.A. Backscatter Sensors Communication for 6G Low-Powered NOMA-Enabled IoT Networks Under Imperfect SIC. IEEE Syst. J. 2022, 16, 5883–5893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhawatrah, M. Energy-Harvesting Cooperative NOMA in IoT Networks. Model. Simul. Eng. 2024, 1043973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khavari-Moghaddam, S.; Farahmand, S.; Razavizadeh, S.M.; Lee, I. Optimum Solutions for Weighted Sum-Rate of NOMA and TDMA in Wireless-Powered IoT Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 3302–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, D.; De, C.K.; Chandra, A. Performance Analysis of NOMA Based Hybrid Cognitive Radio Network Assist by Full-Duplex Relay. Telecommun. Syst. 2025, 88, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özduran, V.; Nomikos, N.; Nasab, E.S.; Ansari, I.S.; Trakadas, P. Relay-Aided Uplink NOMA Under Non-Orthogonal CCI and Imperfect SIC in 6G Networks. IEEE Open J. Veh. Technol. 2024, 5, 658–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liang, Y.-C.; Kam, P.-Y. Backscatter-NOMA: A Symbiotic System of Cellular and Internet-of-Things Networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 20000–20013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhu, J.; Yang, B.; She, X.; Wang, G.; Tellambura, C. Outage Analysis of Hybrid Backscatter Communication Systems With Opportunistic SIC. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2023, 12, 2163–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Alouini, M.-S.; Xin, K.; Li, H.; Xu, S. Symbiotic Ambient Backscatter Systems: Outage Behavior and Ergodic Capacity. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 23670–23690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ding, H.; Elkashlan, M.; Li, H.; Xin, K. A Novel Symbiotic Backscatter-NOMA System. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 11006–11011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onay, M.Y. Dynamic Time Allocation Based Physical Layer Security for Jammer-Aided Symbiotic Radio Networks. Radioengineering 2024, 33, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onay, M.Y. Secrecy Rate Maximization for Symbiotic Radio Network with Relay-Obstacle. Int. J. Comput. Exp. Sci. Eng. 2024, 10, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onay, M.Y. Secrecy Rate Performance Analysis of Jammer-Aided Symbiotic Radio with Sensing Errors for Fifth Generation Wireless Networks. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeganeh, R.S.; Omidi, M.J.; Ghavami, M. Multi-BD Symbiotic Radio-Aided 6G IoT Network: Energy Consumption Optimization with QoS Constraint Approach. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2023, 7, 2067–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.-C.; Zhang, Q.; Larsson, E.G.; Li, G.Y. Symbiotic Radio: Cognitive Backscattering Communications for Future Wireless Networks. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2020, 6, 1242–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Sun, Q.; Chen, X.; Dang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wong, K.-K. Rate-Splitting Assisted Cell-Free Symbiotic Radio: Channel Estimation and Transmission Scheme. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2025, 73, 5313–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisen, S.; Jose, J.; Ding, Z.; Choi, K.; Bhatia, V. On Performance of Backscatter-NOMA Systems: Symbiotic Communication for IoT Devices. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 15854–15859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Ni, W.; Wang, X.; Hossain, E. Beamforming Design for Novel Relay-Assisted Multi-User Multi-Tag Symbiotic Radios. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2023, 12, 2253–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, N.; Yang, G.; Liang, Y.C.; Fu, S.; Chen, X. Joint Beamforming and Backscatter Communication Design for Symbiotic Radio Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 19441–19453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nahari, A.; Jäntti, R.; Zheng, G.; Mishra, D.; Nie, M. Ergodic Secrecy Rate Analysis and Optimal Power Allocation for Symbiotic Radio Networks. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 82327–82337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Wen, S.; Ng, S.X.; Zhang, J. Utility-Based Cooperative Resource Sharing in Symbiotic-Radio-Aided Internet of Things Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 10, 19368–19384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ding, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, Y.C. Multiple Access Design for Symbiotic Radios: Facilitating Massive IoT Connections with Cellular Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2023, 23, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, G.; Xu, R.; He, R.; Wei, X.; Tellambura, C. Capacity Analysis for Wireless Symbiotic Communication Systems with BPSK Tags Under Sensitivity Constraint. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2022, 26, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, R.; Ai, B.; Lian, Z.; Zeng, L.; Niyato, D.; Peng, Y. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Energy Efficiency Maximization in RSMA-IRS-Assisted ISAC System. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2025, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ai, B.; Niu, Y.; Han, Z.; Wang, N.; Ma, Z.; Xiong, L. STAR-RIS Assisted Train-to-Ground Communications in Space-Air-Ground Integrated Networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2025, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, E.; Lian, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Ling, L.; Luo, C. Double-IRS Auxiliary Communications: Models and Performance Prediction. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2024, 13, 2571–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, B.; Yang, Z.; Gui, G.; Sari, H. Optimal Time Allocation in Backscatter Assisted Wireless Powered Communication Networks. Sensors 2017, 17, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
| TDMA phase duration; . | |
| PD–NOMA data-phase duration; . | |
| T | Frame duration; . |
| jth time slot within (). | |
| Time slot vector within : . | |
| Time duration of . | |
| M | Number of clusters/relays/BDs. |
| n | Cluster/relay/BD index (). |
| Energy-harvesting efficiency. | |
| Fixed time fractional. | |
| Power reflection coefficient of . | |
| Imperfect-SIC coefficient (residual-interference factor). | |
| BS transmit power. | |
| Relay receiver/transmitter circuit powers. | |
| Initial energy/total energy consumed by the relay. | |
| Noise power. | |
| B | Bandwidth. |
| BS → receiver channel gain. | |
| BS → relay n () channel gain. | |
| Relay receiver channel gain. | |
| BS channel gain. | |
| channel gain. | |
| Performance gap factor. | |
| The channel gain between and . | |
| Minimum bit target over (QoS). | |
| Per-BD QoS threshold. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Onay, M.Y. Mathematical Modelling of Throughput in Peer-Assisted Symbiotic 6G with SIC and Relays. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9504. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179504
Onay MY. Mathematical Modelling of Throughput in Peer-Assisted Symbiotic 6G with SIC and Relays. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9504. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179504
Chicago/Turabian StyleOnay, Muhammed Yusuf. 2025. "Mathematical Modelling of Throughput in Peer-Assisted Symbiotic 6G with SIC and Relays" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9504. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179504
APA StyleOnay, M. Y. (2025). Mathematical Modelling of Throughput in Peer-Assisted Symbiotic 6G with SIC and Relays. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9504. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179504






