The Study on the Relation Between Rock Indentation Crater Morphology and Rock Mechanical Index Based on Indentation Experiments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Rock Samples
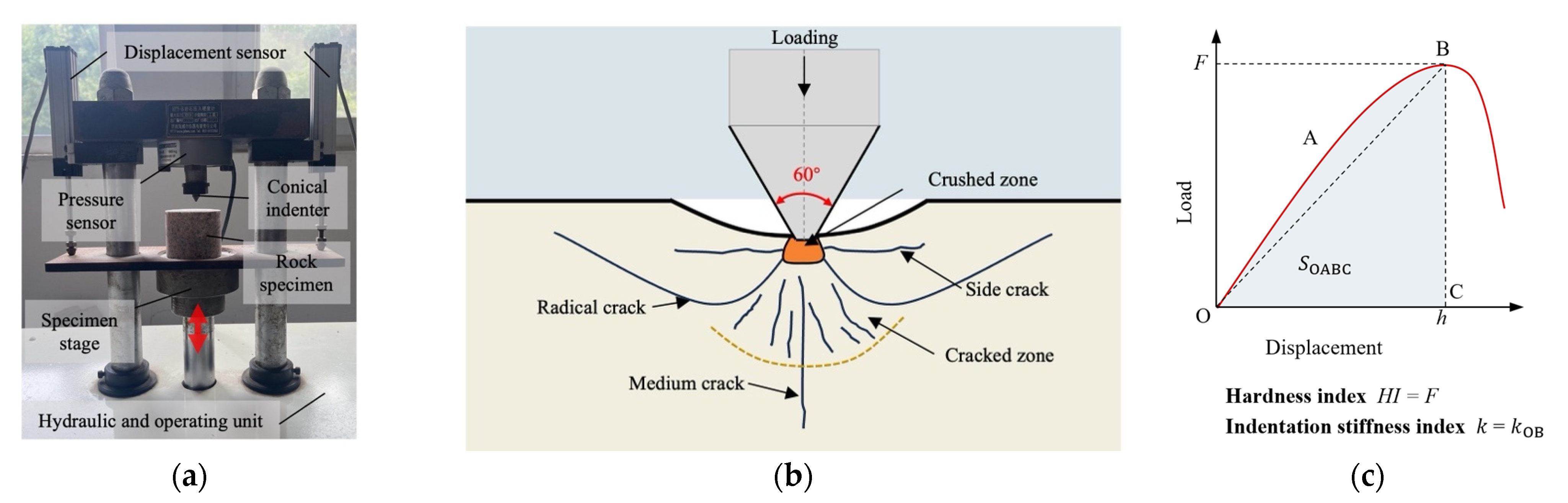
2.2. Indentation Test
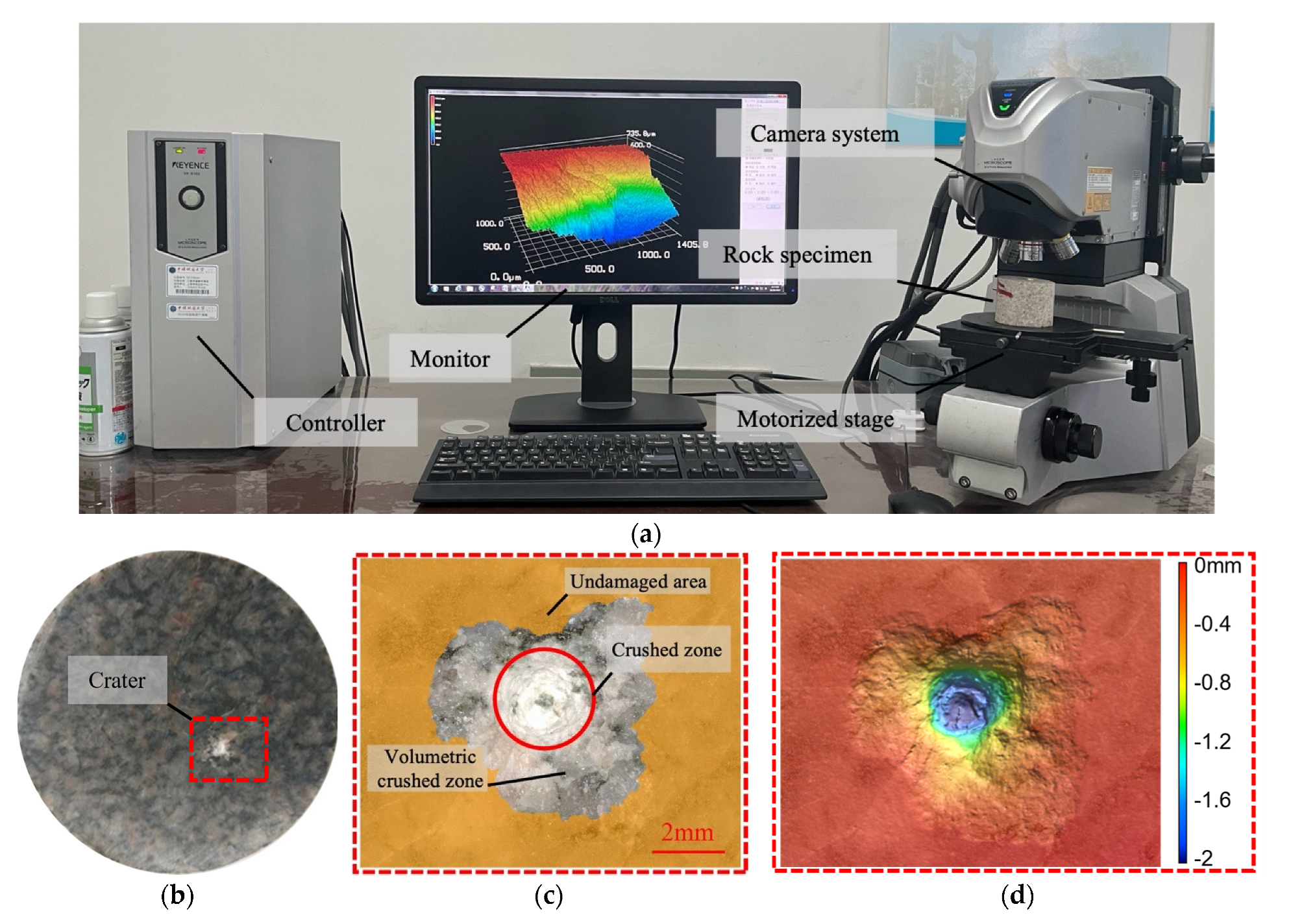
2.3. 3D Topography Measurement
3. Results & Discussion
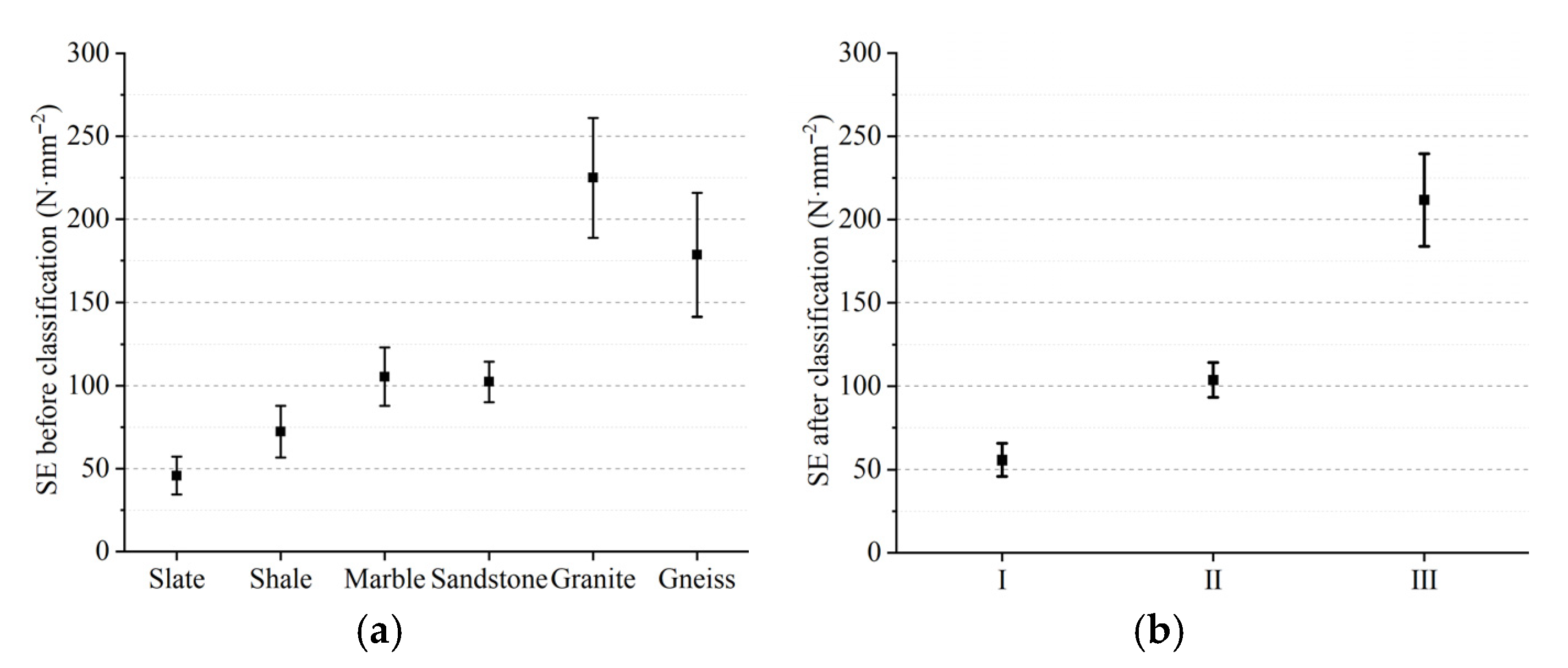
3.1. Rock Classification
3.2. Mechanical Index Results
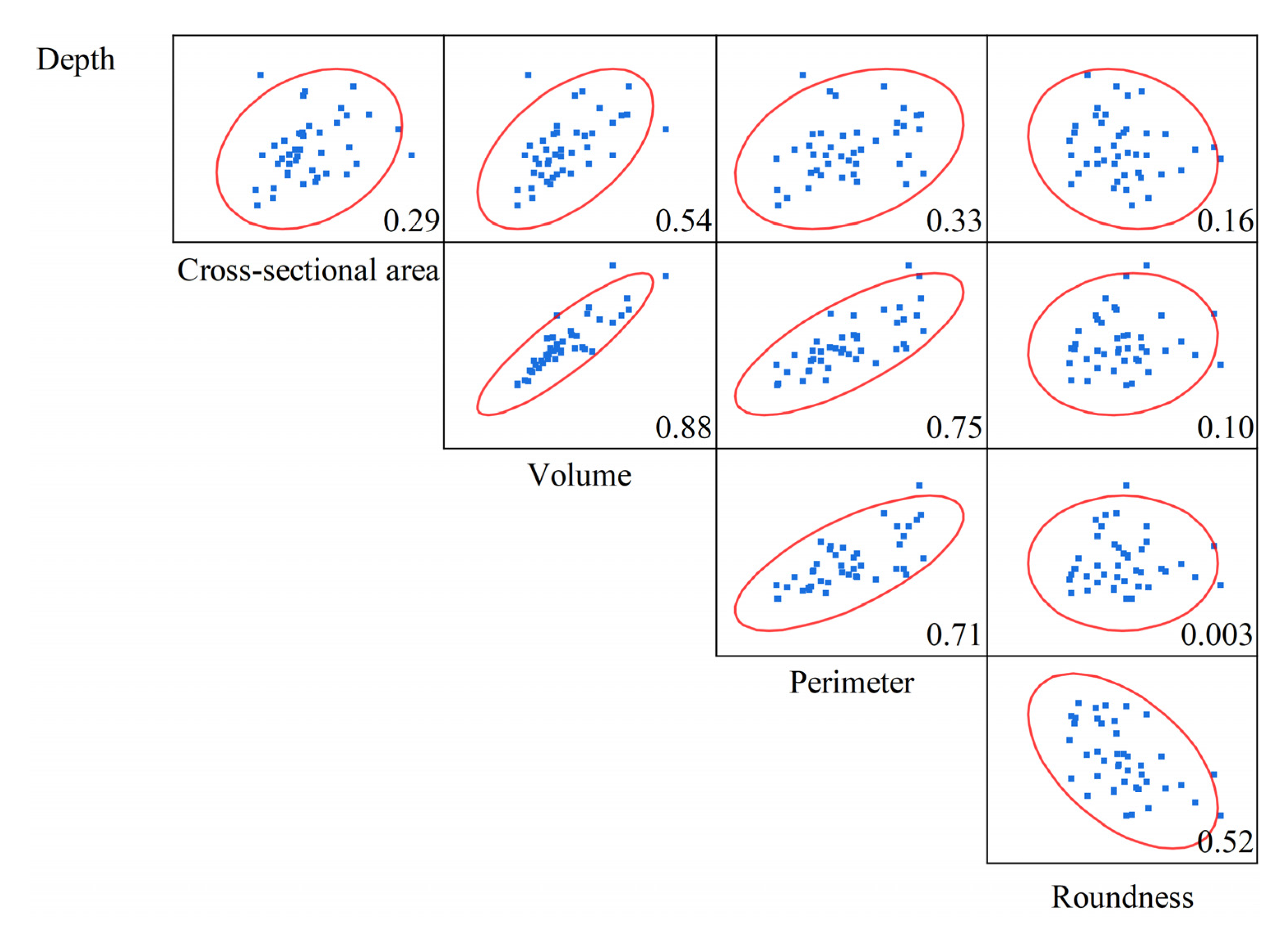
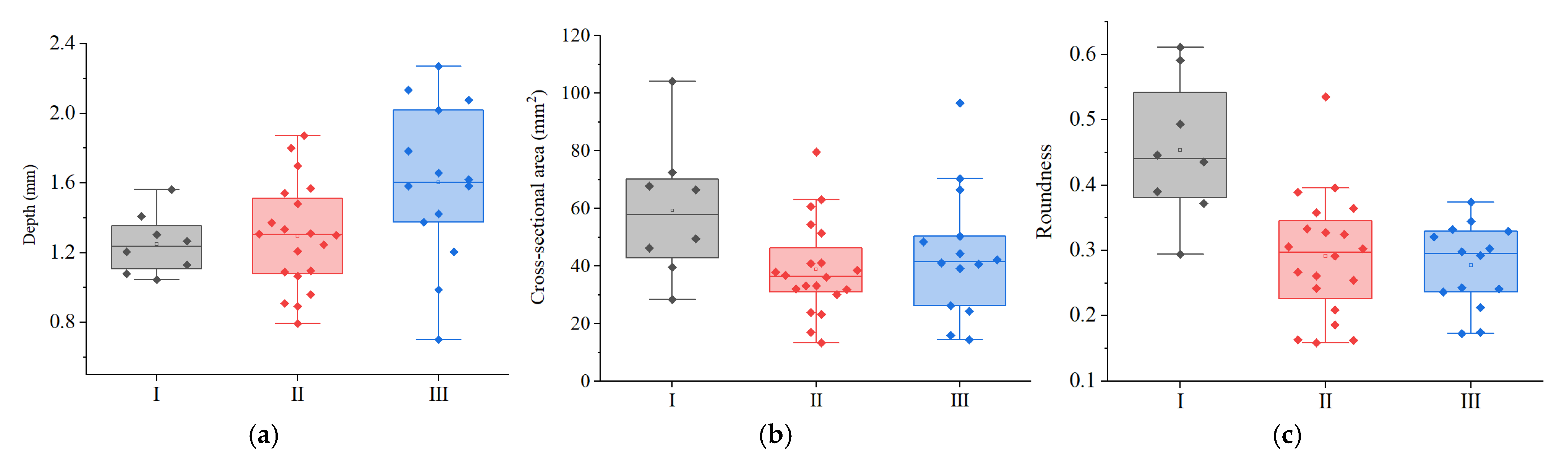
3.3. Selection and Characterization of Morphological Parameters
3.3.1. Correlation Analysis of Morphological Parameters
3.3.2. Crater Morphological Analysis
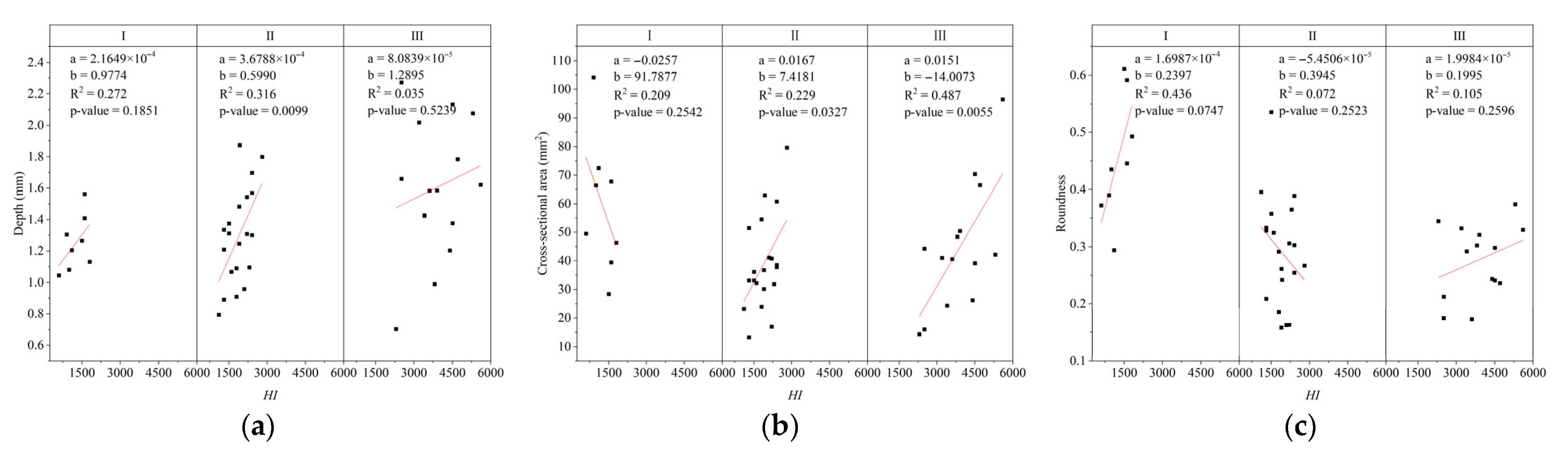
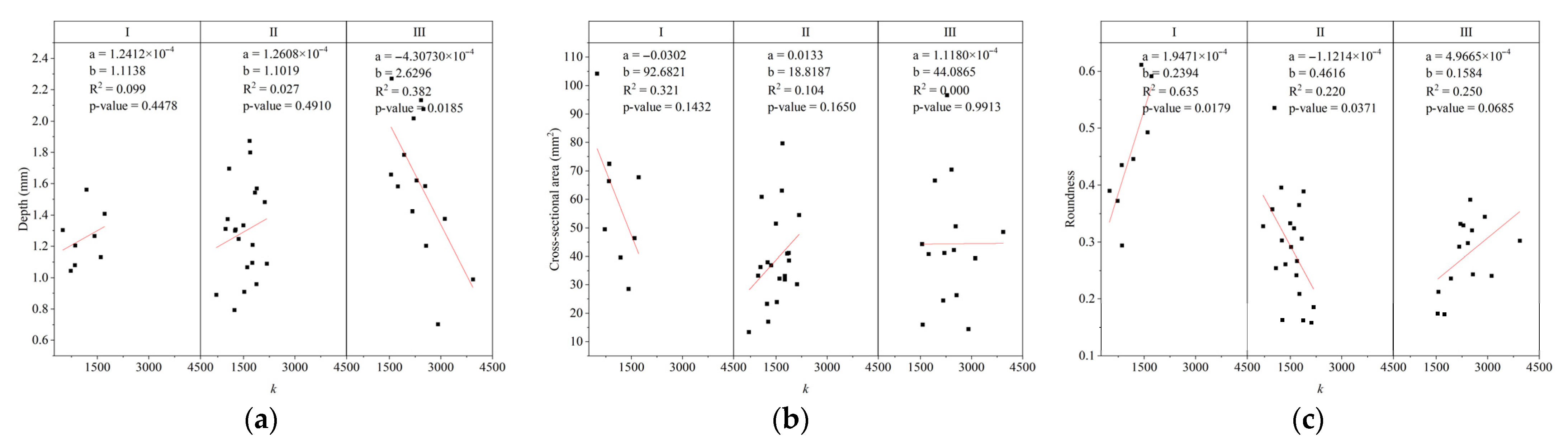
3.4. Relationship Between Mechanical Indicators and Crater Morphology
4. Conclusions
- Quantitative studies indicate that fracture depth, cross-sectional area, and contour roundness are three independent morphological indicators that can serve as characteristic parameters for fracture crater morphology. Qualitative and quantitative analyses after classification reveal significant differences among rock types in terms of indentation state at the crater bottom, fracture surface morphology, contour roundness, and fracture depth. These differences are related to mineral distribution and localized micro-deformation: mineral distribution affects crack paths, thereby shaping distinct contour features and surface morphology, while localized micro-deformation may cause variations in crater bottom indentations. Qualitative and quantitative results are consistent.
- Linear fitting between fracture morphology and mechanical indicators shows that multiple post-classification morphological prediction models are statistically significant. However, the same morphological indicator exhibits inconsistent patterns across categories, attributable to inherent rock properties (e.g., structure, grain homogeneity), which may influence mechanical behavior. Further research on fracture crater formation mechanisms is needed.
- Classifying the six rocks into three types based on SE is meaningful. Post-classification, significant differences in mechanical and morphological parameters were observed, uncovering previously obscured correlations. However, due to limited data, linear fitting yielded low correlation values (0.220–0.635), and the Class I lacked significant predictive models. Future studies should expand sample sizes and experimental repetitions to refine these findings.
- Furthermore, the rock samples used in this study were sourced from different geological regions, and thus, variations in their structural homogeneity cannot be ruled out. This heterogeneity may also contribute to the relatively low correlations observed in the results. Additionally, the indentation tests in this work were conducted using a 60° indenter angle. Future studies could investigate the influence of different indenter angles to further validate the applicability of the conclusions drawn herein.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HI | Hardness index |
| Indentation stiffness index | |
| SE | Specific energy |
References
- Li, A.L. Rock Indentation Characteristics Induced by Spherical Button Subjected to Dynamic and Quasi-Static Loads. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2023, 56, 5253–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Kou, S.Q.; Lindqvist, P.A.; Tang, C.A. Numerical Simulation of the Rock Fragmentation Process Induced by Indenters. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2002, 39, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, P.A.; Lai, H.H.; Alm, O. Indentation Fracture Development in Rock Continuously Observed with a Scanning Electron Microscope. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1984, 21, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadati, M.; Weddfelt, K.; Larsson, P.L. A Spherical Indentation Study on the Mechanical Response of Selected Rocks in the Range from Very Hard to Soft with Particular Interest to Drilling Application. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2020, 53, 5809–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishnaevsky, L.L. Physical Mechanisms of Hard Rock Fragmentation under Mechanical Loading: A Review. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1995, 32, 763–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Yang, X.M.; Xie, W.Q.; Liu, Q.S.; Tang, S.H. Comparison and Selection of Index for Macro-Indentation Test of Brittle Rock. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2023, 56, 6375–6394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.Q. Some Basic Problems in Rock Breakage by Blasting and by Indentation. Ph.D. Thesis, Luleå University of Technology, Luleå, Sweden, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Zhou, X. A Review of Rock Macro-Indentation: Theories, Experiments, Simulations, and Applications. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2024, 16, 2351–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, X. Bonded-Cluster Simulation of Tool-Rock Interaction Using Advanced Discrete Element Method. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2019, 72, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Shi, H.; Yuan, G.; Xia, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, T. Experimental Study of the Energy Transfer Efficiency and Rock Fragmentation Characteristics in Percussive Drilling. Geothermics 2022, 105, 102497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldannawy, H.A.; Rouabhi, A.; Gerbaud, L. Percussive Drilling: Experimental and Numerical Investigations. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2022, 55, 1555–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariati, H.; Saadati, M.; Weddfelt, K.; Larsson, P.; Hild, F. A Damage Model for Granite Subjected to Quasi-static Contact Loading. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2022, 46, 374–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.S.; Shi, H.Z.; Dai, X.W.; Song, H.Y.; Li, G.S.; Shen, Z.H. Fragmentation Characteristics of Rocks under Indentation by a Single Polycrystalline Diamond Compact Cutter. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2021, 143, 100903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, K.; Hu, W.R.; Li, J.C.; Dehkhoda, S.; Zhang, Q.B. Quantification of Dynamic Damage and Breakage in Granite under Confined Indentation. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 144, 104763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Huang, Z.; Zou, W.; Wu, X.; Shi, H. Failure Characteristics of Rocks Subjected to PDC Cutter Indentation. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 207, 108992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.Q.; Yang, W.H.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.F.; Gao, M. Experimental Investigation on Hard Rock Fragmentation of Inserted Tooth Cutter Using a Newly Designed Indentation Testing Apparatus. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Peng, J.M.; Zhang, P.Y.; Huang, C.Y. Hard Rock Fragmentation in Percussion Drilling Considering Confining Pressure: Insights from an Experimental Study. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 148, 104961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, C. Rock Indentation: Experiments and Analyses; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-0-429-01995-1. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Mao, K.; Liu, J.; Zhang, K.X. Analysis of Fracture Surface Morphology and Study of Seepage Diffusion Characteristics. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2023, 28, 428–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MŁynarczuk, M. Description and Classification of Rock Surfaces by Means of Laser Profilometry and Mathematical Morphology. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2010, 47, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.P.; Wang, J.A.; Kwaśniewski, M.A. Multifractal Characterization of Rock Fracture Surfaces. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 1999, 36, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.Z.; Hao, H.C.; Xue, S.N.; Lu, T.; Cui, P.F.; Gao, Y.A.; Xie, J.; Yang, B.G.; Xie, H.P. Discing Behavior and Mechanism of Cores Extracted from Songke-2 Well at Depths below 4,500 m. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2022, 149, 104976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldannawy, H.A.; Gerbaud, L.; Rouabhi, A. On the Influence of Tool Shape on Percussive Drilling in Hard Rocks. In Proceedings of the 55th U.S. Rock Mechanics/Geomechanics Symposium, Virtual, 18–25 June 2021; p. ARMA-2021-1145. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Z.S.; Jiang, J.B.; Shi, H.; Li, B. Experimental Studies on Rock Failure Mechanisms under Impact Load by Single Polycrystalline Diamond Compact Cutter. Pet. Sci. 2023, 20, 3100–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yu, J.; Ren, C.; Elbaz, K.; Zhu, D.; Cai, Y. Fatigue Behaviour Characteristics and Life Prediction of Rock under Low-Cycle Loading. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2025, 35, 737–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Jin, J.; Li, Y. Macro-Micro Failures of Shear Creep and Creep Damage Model of Deep Hard Rocks Induced by Initial Disturbances. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2025, 324, 111269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fu, X.F.; Liu, G.R.; Li, S.B.; Li, W.; Qu, S. Models for Evaluating Craters Morphology, Relation of Indentation Hardness and Uniaxial Compressive Strength via a Flat-End Indenter. Open Geosci. 2018, 10, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Qian, S.; Zhang, G.; Maochu, Z. An Experimental Investigation of the Influence of Loading Rate on Rock Tensile Strength and Split Fracture Surface Morphology. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2021, 54, 1969–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Zhao, K.; He, Z.; Yu, X.; Yan, Y.; Li, Q.; Shao, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y. Fractal Characteristics of Rocks and Mesoscopic Fractures at Different Loading Rates. Geomech. Energy Environ. 2023, 33, 100431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Sheng, Q.; Cui, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, G. Effect of loading rate on tensile strength of rock materials and morphology of fracture joint surface. Rock Soil Mech. 2020, 41, 1169–1178+1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, W.; Xue, Y.; Li, Z.; Kong, F.; Kong, R.; Wang, G. Approach to Characterize Rock Fracture Surface: Insight from Roughness and Fractal Dimension. Eng. Geol. 2023, 325, 107302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souissi, S.; Hamdi, E.; Sellami, H. Microstructure Effect on Hard Rock Damage and Fracture During Indentation Process. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2015, 33, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajibose, O.K.; Wiercigroch, M.; Akisanya, A.R. Experimental Studies of the Resultant Contact Forces in Drillbit–Rock Interaction. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2015, 91, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.C.; Kou, S.Q.; Lindqvist, P.A. Application of the DDM and Fracture Mechanics Model on the Simulation of Rock Breakage by Mechanical Tools. Eng. Geol. 1998, 49, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, W. The Rock Fragmentation Mechanism and Plastic Energy Dissipation Analysis of Rock Indentation. Geomech. Eng. 2018, 16, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
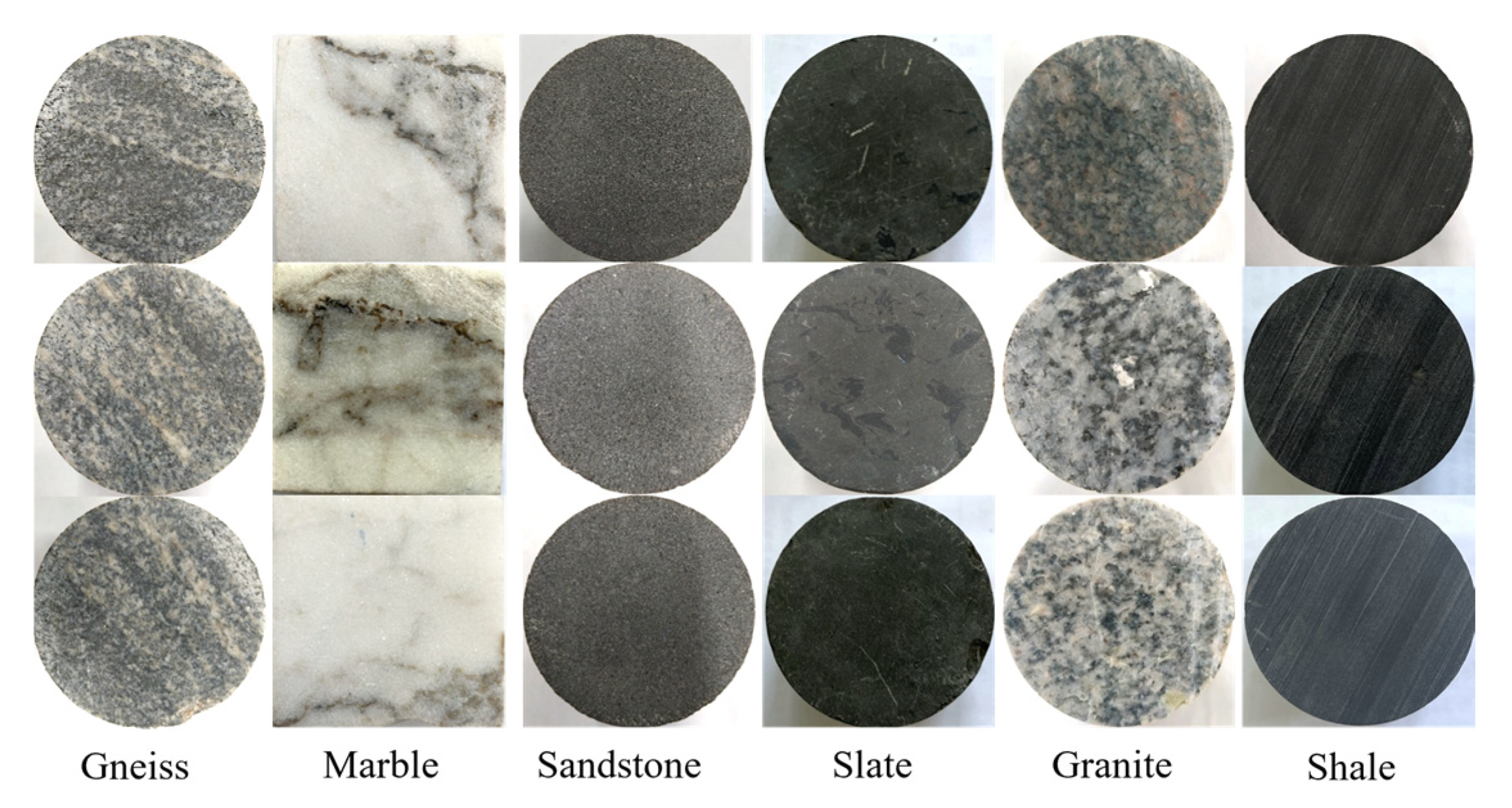




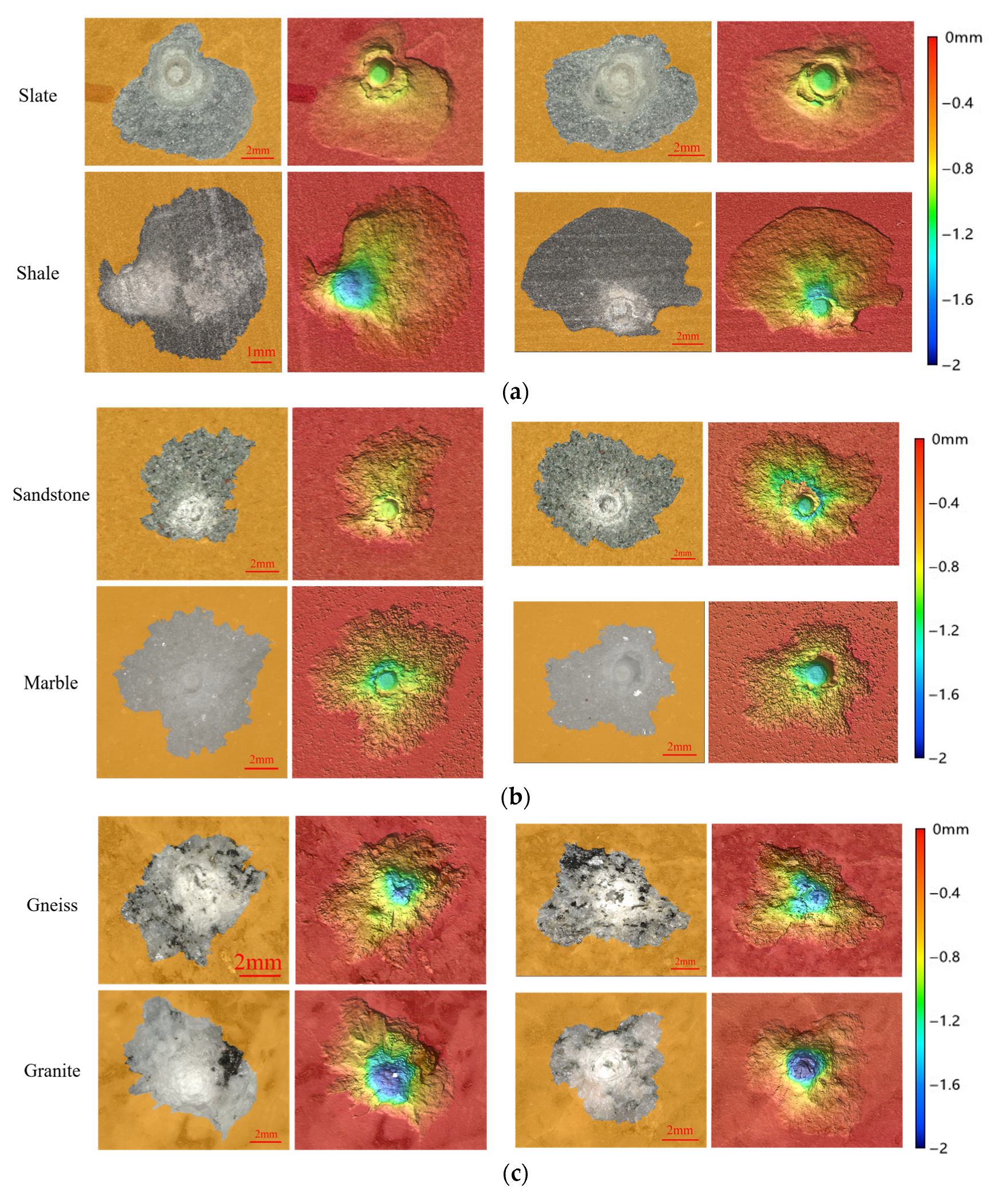
| Rock Type | Shale | Slate | Marble | Sandstone | Gneiss | Granite |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test number | 3 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 4 | 10 |
| Classification | Indicator | Overall Anova Prob > F | Homogeneity of Variance Test | Powers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | SE | 2.4392 × 10−4 | 0.0074 | 0.9914 |
| Depth | 0.0883 | 0.1403 | 0.6250 | |
| Volume | 0.7039 | 0.5728 | 0.1934 | |
| Yes | - | 9.3880 × 10−6 | 0.0058 | 0.9990 |
| Class | N Analysis | Mean/N·mm−2 | Standard Deviation | t-Critical Value | Lower Limit | Upper Limit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 8 | 55.68283 | 27.8282 | 2.365 | 32.41 | 78.95 |
| II | 20 | 103.81461 | 46.52104 | 2.093 | 82.04 | 125.58 |
| III | 14 | 211.73696 | 103.87048 | 2.160 | 151.78 | 271.70 |
| Class | SE Range/N·mm−2 | Rock Types |
|---|---|---|
| I | ≤80 | Slate, shale |
| II | 80~140 | Sandstone, marble |
| III | ≥140 | Gneiss, granite |
| Class | Mechanical Indicator | Morphological Parameter | Slope | Intercept | R2 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | HI | Cross-sectional area | 0.00251 | 38.5396 | 0.023 | 0.3367 |
| Depth | 1.4657 × 10−4 | 1.0320 | 0.252 | * 6.9953 × 10−4 | ||
| Roundness | −2.3902 × 10−5 | 0.3757 | 0.076 | ** 0.0773 | ||
| k | Cross-sectional area | −0.0027 | 49.3311 | 0.008 | 0.5670 | |
| Depth | 6.6056 × 10−5 | 1.27404 | 0.016 | 0.4314 | ||
| Roundness | −3.7781 × 10−5 | 0.3829 | 0.058 | 0.1259 | ||
| I | HI | Cross-sectional area | −0.0257 | 91.7877 | 0.209 | 0.2542 |
| Depth | 2.1649 × 10−4 | 0.9774 | 0.272 | 0.1851 | ||
| Roundness | 1.6987 × 10−4 | 0.2397 | 0.436 | 0.0747 | ||
| k | Cross-sectional area | −0.0302 | 92.6821 | 0.321 | 0.1432 | |
| Depth | 1.2412 × 10−4 | 1.1138 | 0.099 | 0.4478 | ||
| Roundness | 1.9471 × 10−4 | 0.2394 | 0.635 | * 0.0179 | ||
| II | HI | Cross-sectional area | 0.0167 | 7.4181 | 0.229 | * 0.0327 |
| Depth | 3.6788 × 10−4 | 0.5990 | 0.316 | * 0.0099 | ||
| Roundness | −5.4506 × 10−5 | 0.3945 | 0.072 | 0.2523 | ||
| k | Cross-sectional area | 0.0133 | 18.8187 | 0.104 | 0.1650 | |
| Depth | 1.2608 × 10−4 | 1.1019 | 0.027 | 0.4910 | ||
| Roundness | −1.1214 × 10−4 | 0.4616 | 0.220 | * 0.0371 | ||
| III | HI | Cross-sectional area | 0.0151 | −14.0073 | 0.487 | * 0.0055 |
| Depth | 8.0839 × 10−5 | 1.2895 | 0.035 | 0.5239 | ||
| Roundness | 1.9984 × 10−5 | 0.1995 | 0.105 | 0.2596 | ||
| k | Cross-sectional area | 1.1180 × 10−4 | 44.0865 | 0.000 | 0.9913 | |
| Depth | −4.30730 × 10−4 | 2.6296 | 0.382 | * 0.0185 | ||
| Roundness | 4.9665 × 10−4 | 0.1584 | 0.250 | ** 0.0685 |
| Class | Morphological Parameters | Predict Model |
|---|---|---|
| I | Depth | - |
| Cross-sectional area | - | |
| Roundness | Y = 1.9471 × 10−4 × k + 0.2394 (R2 = 0.635) | |
| II | Depth | Y = 3.6789 × 10−4 × HI + 0.5990 (R2 = 0.316) |
| Cross-sectional area | Y = 0.0167 × HI + 7.4181 (R2 = 0.229) | |
| Roundness | Y = −1.1214 × 10−4 × k + 0.4616 (R2 = 0.220) | |
| III | Depth | Y = −4.3073 × 10−4 × k + 2.6296 (R2 = 0.382) |
| Cross-sectional area | Y = 0.0151 × HI − 14.0073 (R2 = 0.487) | |
| Roundness | * Y = 4.9666 × 10−5 × k + 0.1584 (R2 = 0.250) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Z.; Gao, H.; Yang, Y.; Tan, S.; Fang, X.; Hu, Y.; Duan, L. The Study on the Relation Between Rock Indentation Crater Morphology and Rock Mechanical Index Based on Indentation Experiments. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9410. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179410
Wu Z, Gao H, Yang Y, Tan S, Fang X, Hu Y, Duan L. The Study on the Relation Between Rock Indentation Crater Morphology and Rock Mechanical Index Based on Indentation Experiments. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9410. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179410
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Zhenkun, Hui Gao, Ying Yang, Songcheng Tan, Xiaohong Fang, Yule Hu, and Longchen Duan. 2025. "The Study on the Relation Between Rock Indentation Crater Morphology and Rock Mechanical Index Based on Indentation Experiments" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9410. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179410
APA StyleWu, Z., Gao, H., Yang, Y., Tan, S., Fang, X., Hu, Y., & Duan, L. (2025). The Study on the Relation Between Rock Indentation Crater Morphology and Rock Mechanical Index Based on Indentation Experiments. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9410. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179410





