Metasurfaces with Embedded Rough Necks for Underwater Low-Frequency Sound Absorption
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Theoretical Model
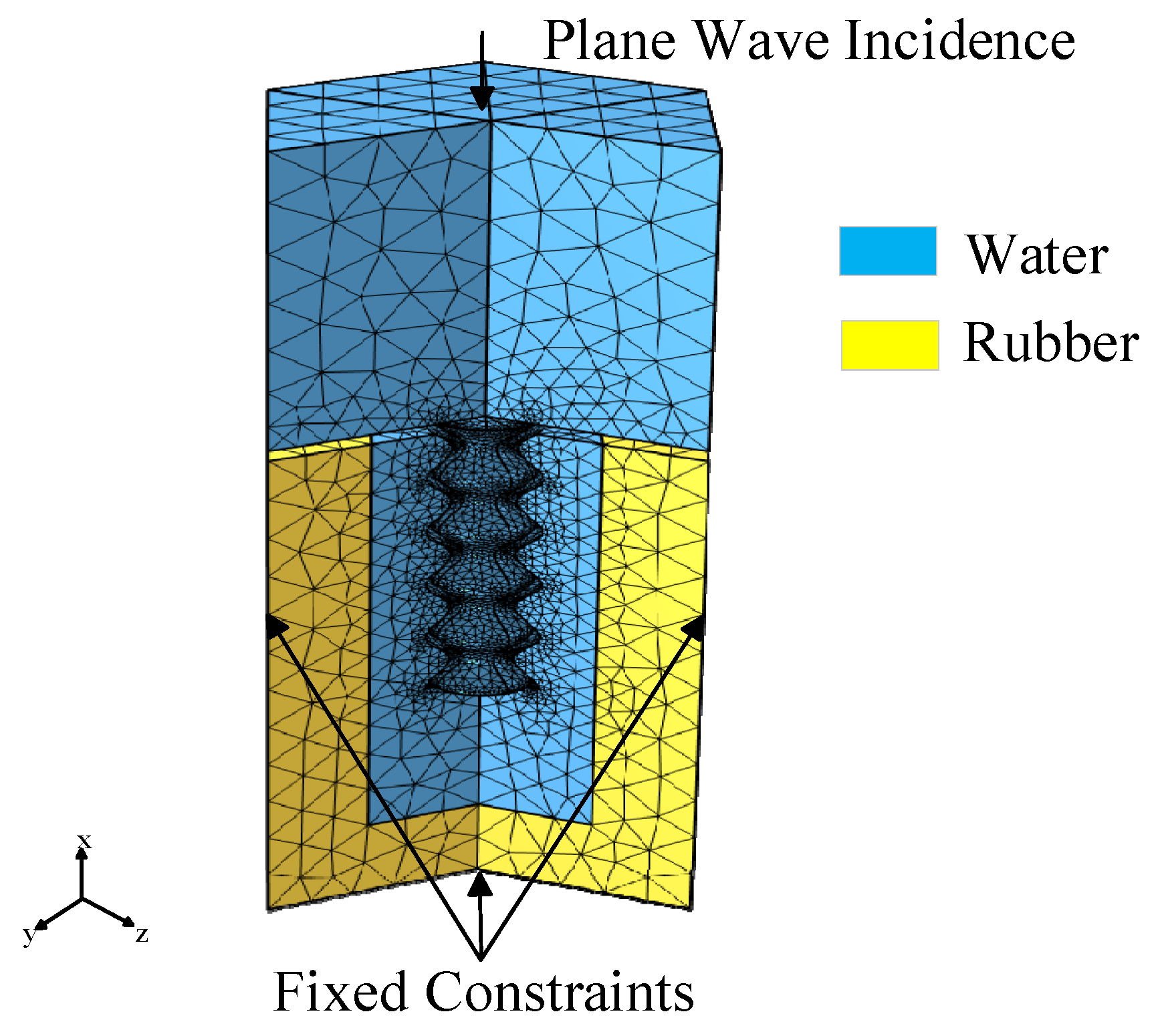
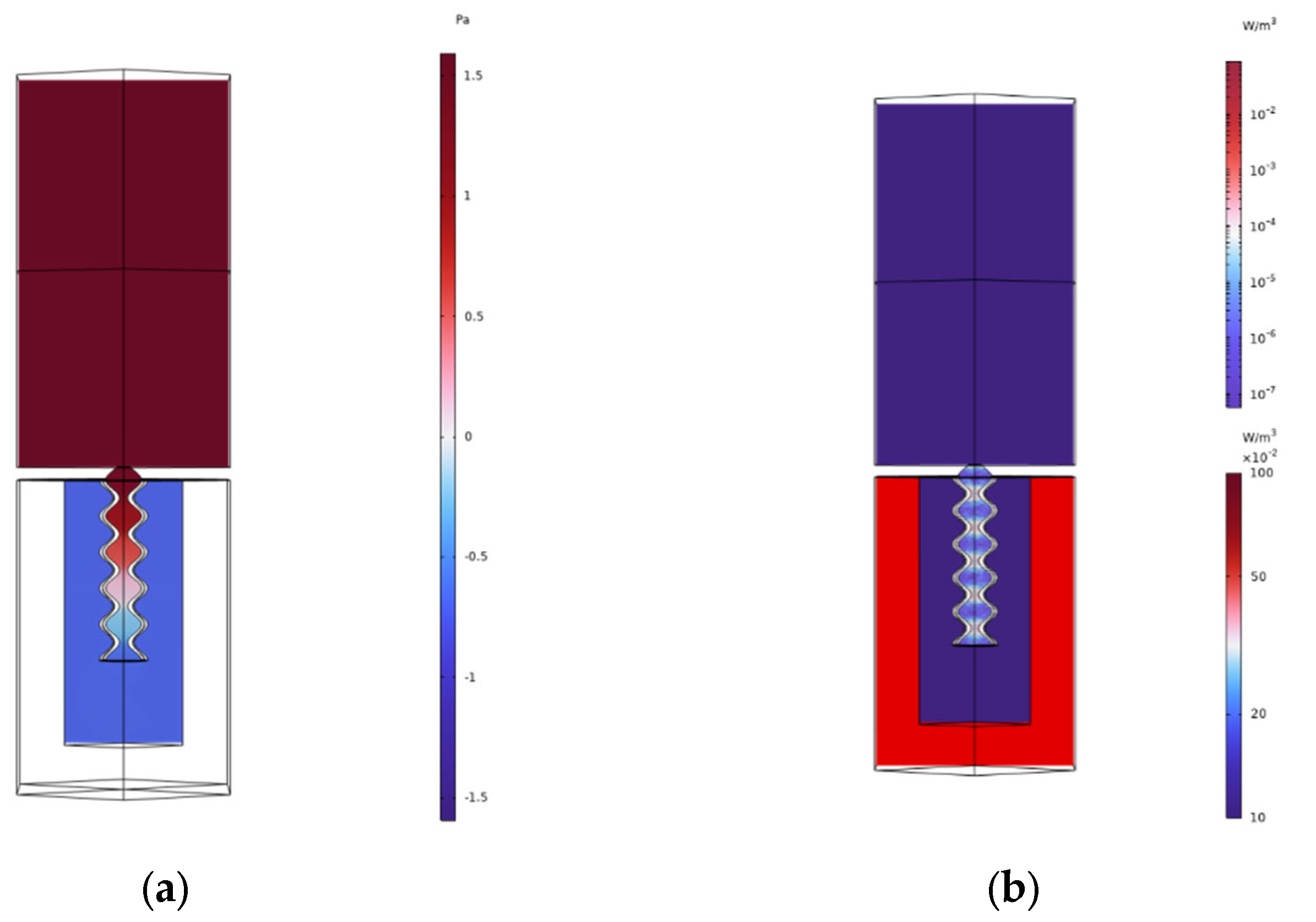
2.2. Finite Element Simulation
3. Results and Discussion
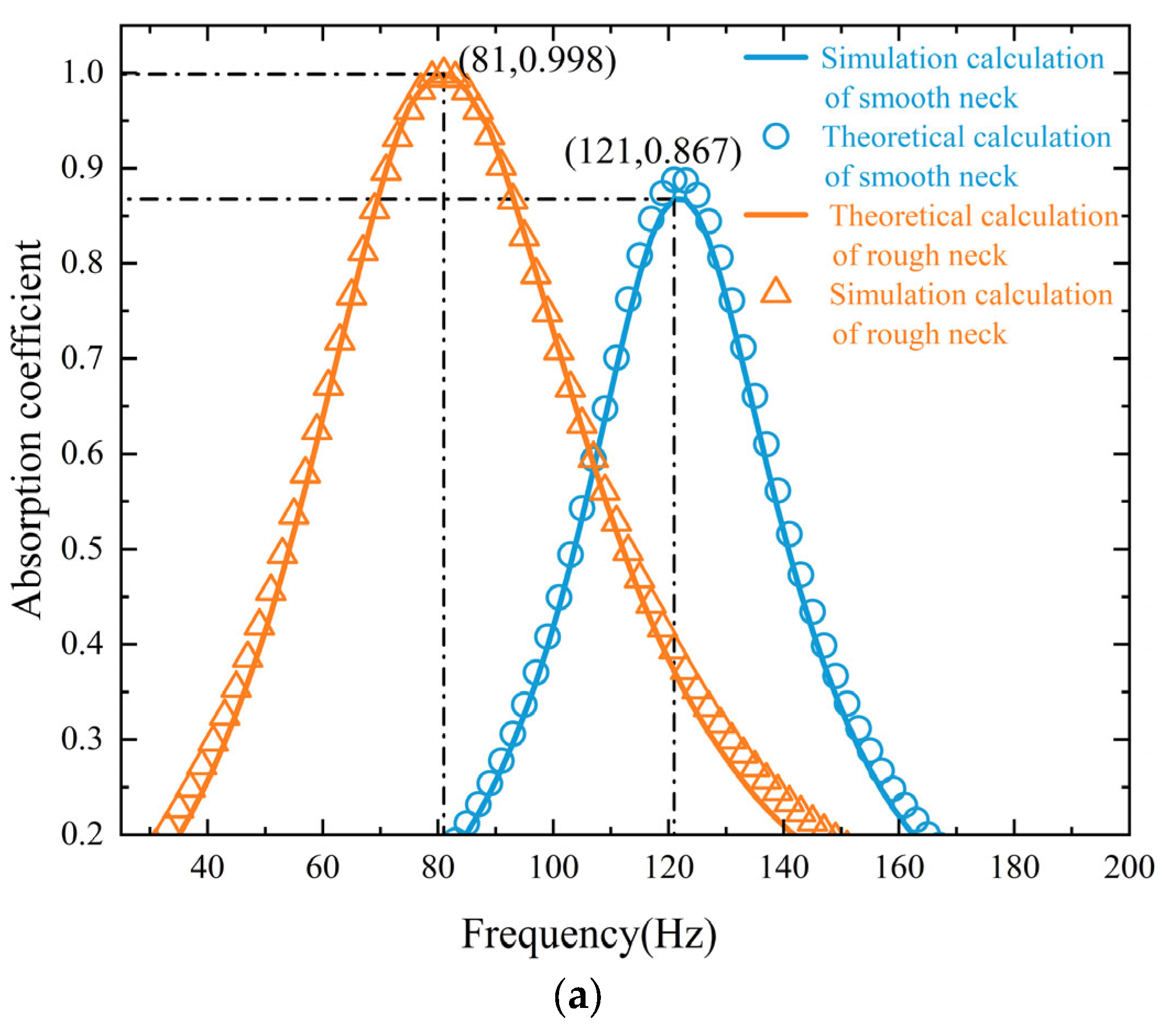
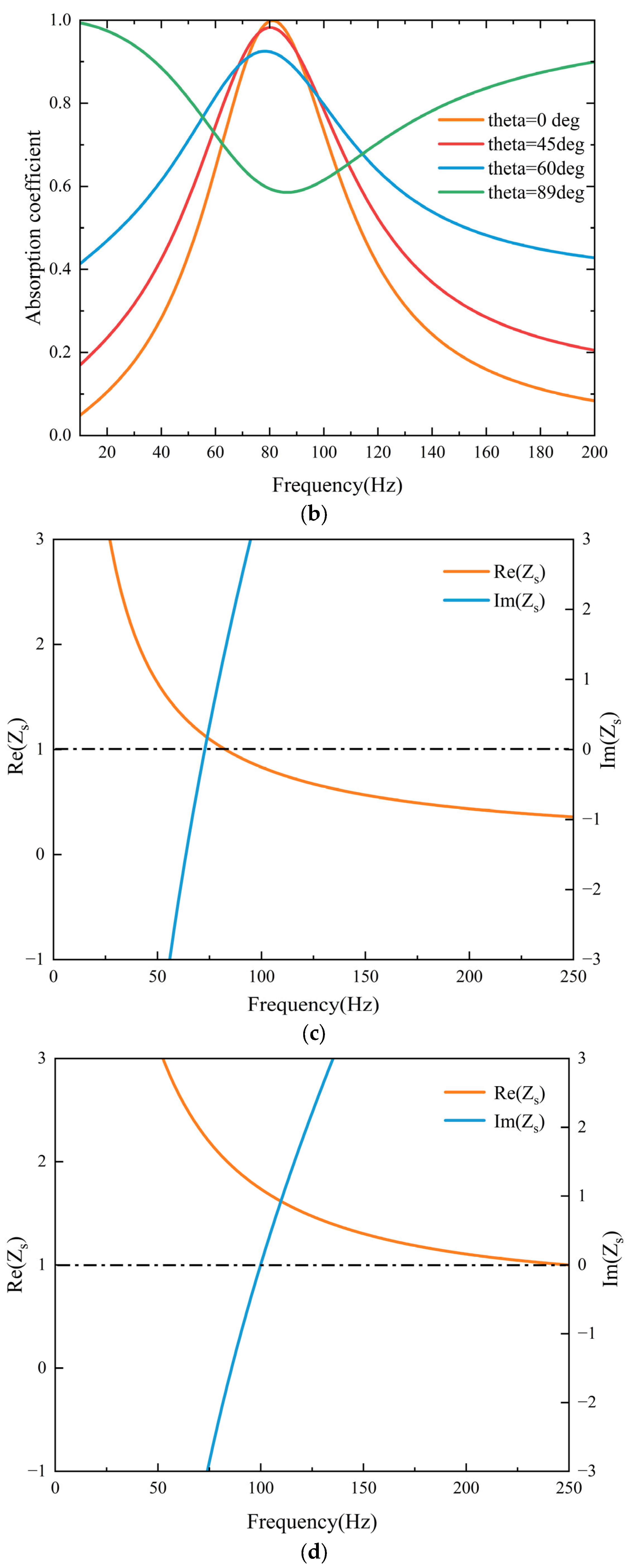
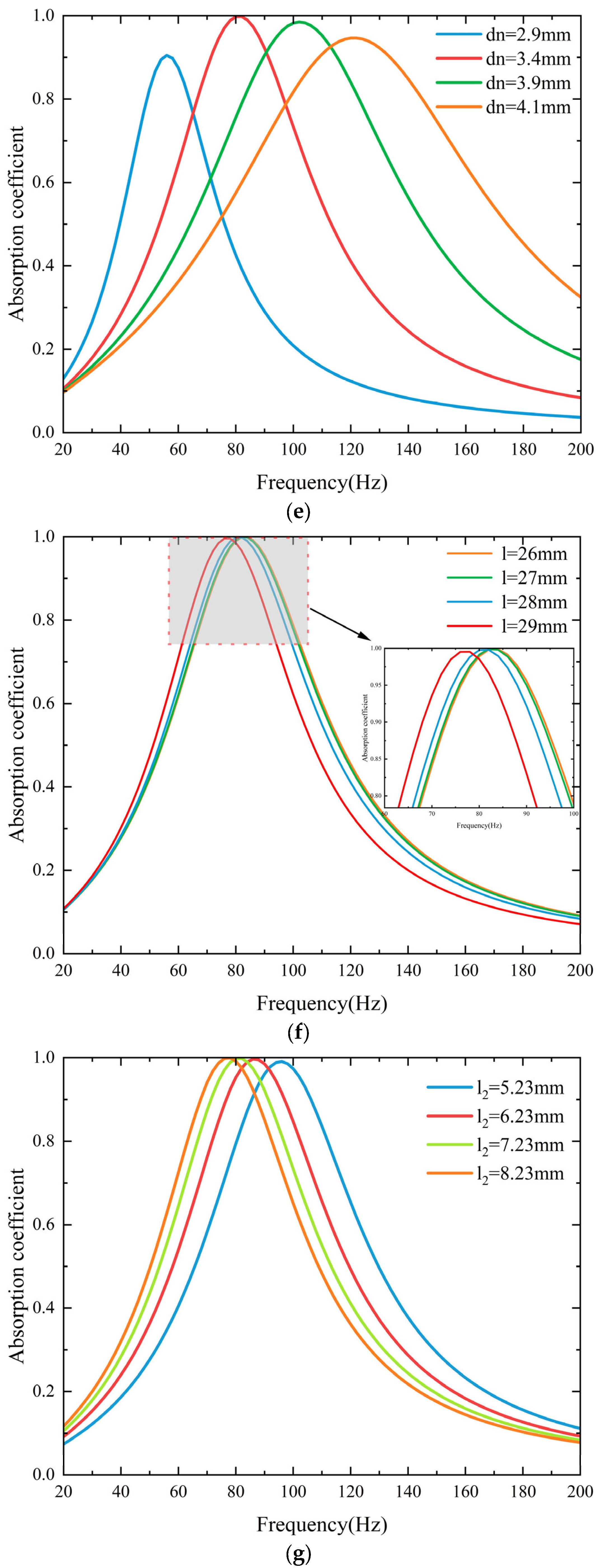
3.1. Acoustic Properties of the Metasurface
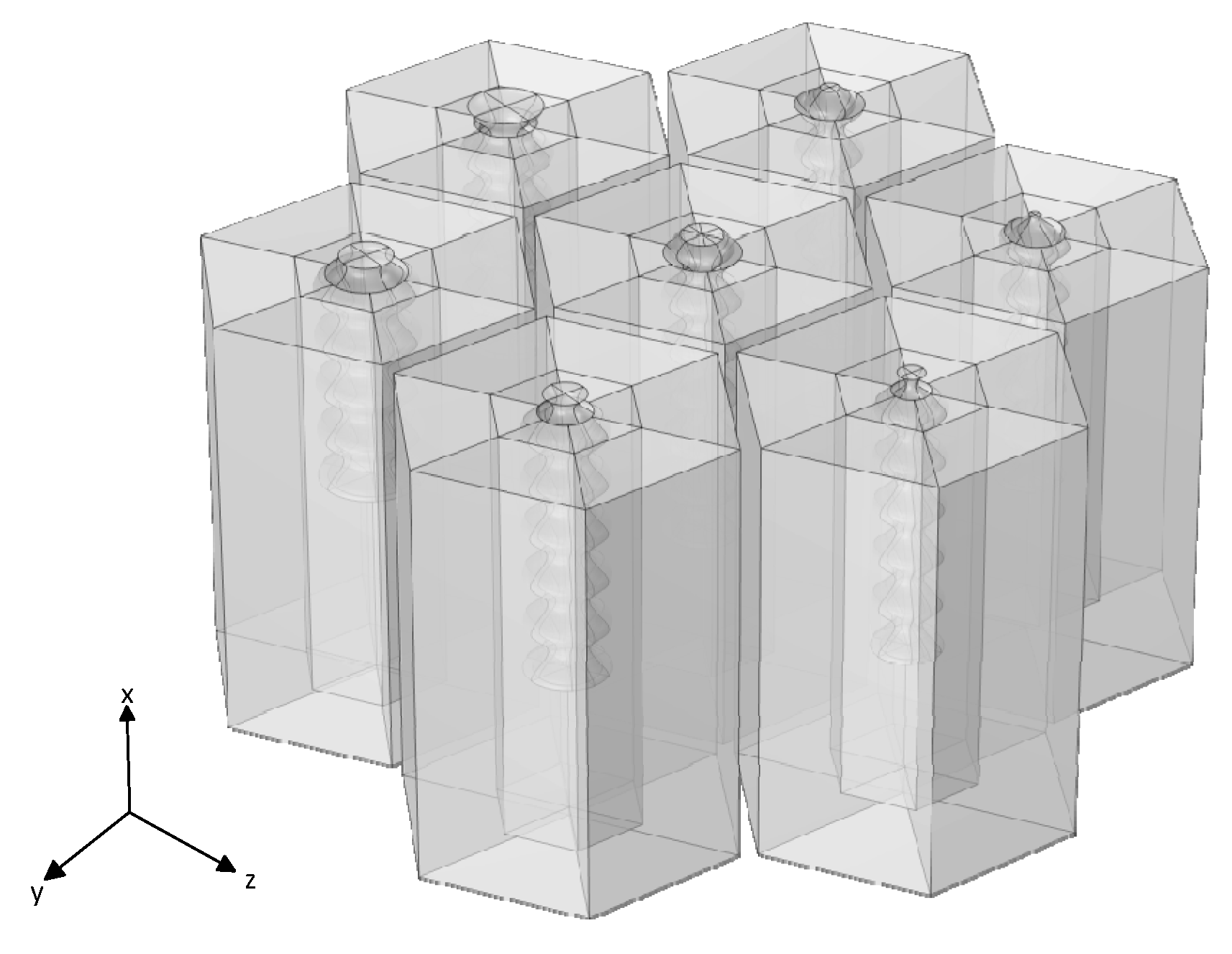
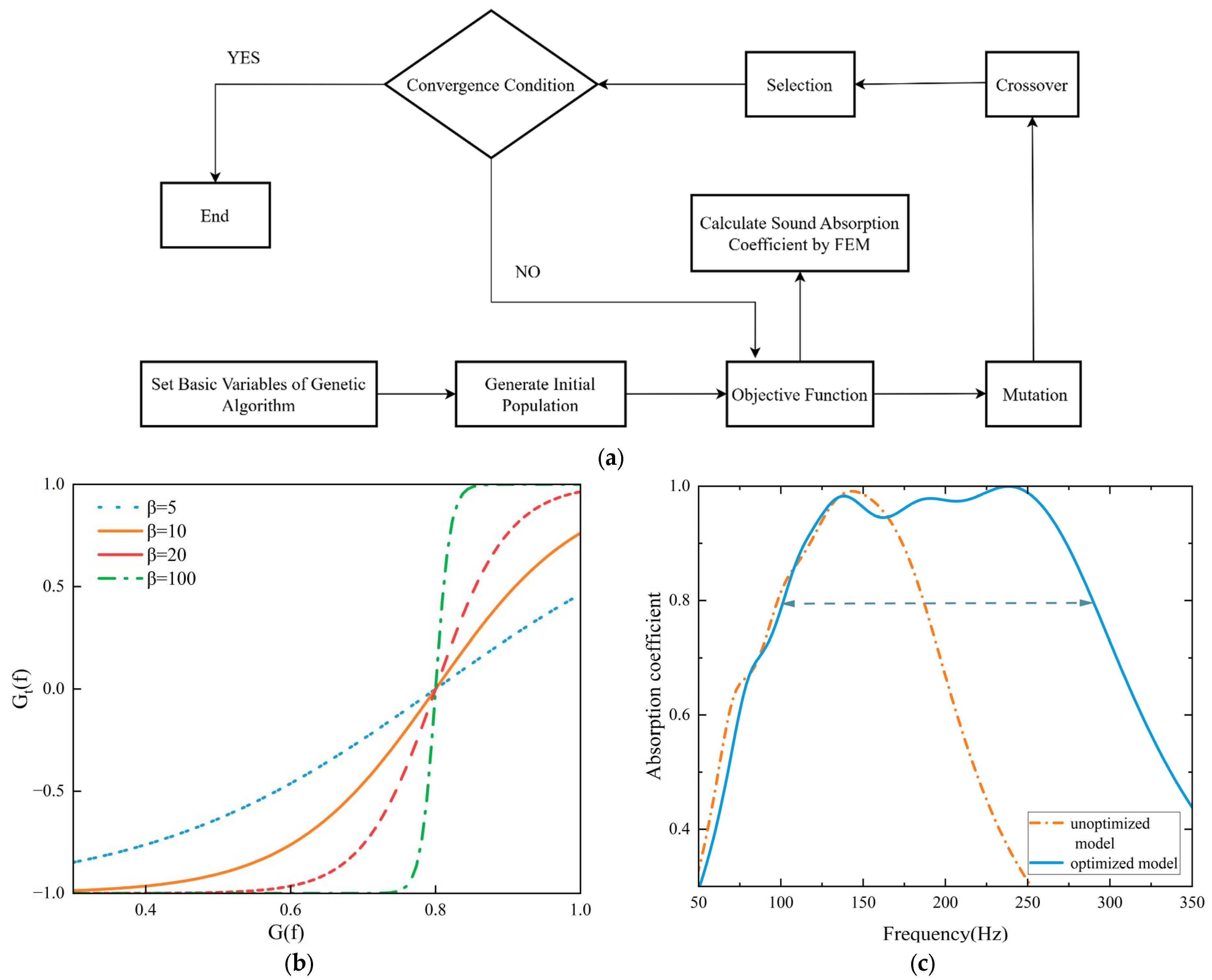
3.2. Multi-Unit Parallel Configuration and Optimization Method
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, Y.; Wang, X.; Miao, X.; Gao, S.; Li, B.; Peng, Z. Optimum design of acoustic stealth shape of underwater vehicle model with conning tower. Front. Phys. 2023, 11, 1105787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Zhong, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Qin, L. Flexible 1-3 piezoelectric composites with soft embedded conductive interconnects for underwater acoustic transducers. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2023, 5, 2686–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wei, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Liu, X. Broadband manipulation of acoustic wavefronts by pentamode metasurface. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 221906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Jia, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z. Design of an underwater acoustic bend by pentamode metafluid. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 143, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhai, S.; Ding, C.; Luo, C.; Zhao, X. Acoustic metamaterial with negative mass density in water. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 094901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, H.; Zhai, S.; Ding, C.; Li, J.; Luo, C.; Zhao, X. Ultrasound acoustic metamaterials with double-negative parameters. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 204902–204908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.; Wen, J.; Yu, D.; Wen, X. Tri-component phononic crystals for underwater anechoic coatings. Phys. Lett. A 2007, 367, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wen, J.; Yang, H.; Lv, L.; Wen, X. Backing effects on the underwater acoustic absorption of a viscoelastic slab with locally resonant scatterers. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 76, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Chen, M.; Yang, W.; Xie, X.; Cai, X.; Jiao, W.; Yang, M. Low-frequency impedance modulation via grid-based Helmholtz resonator cavities. Appl. Acoust. 2025, 239, 110822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, G.; Hang, Z.H.; Hou, B.; Li, J.; Sheng, P. Theoretical requirements for broadband perfect absorption of acoustic waves by ultra-thin elastic meta-films. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Hu, X. Three-dimensional single-port labyrinthine acoustic metamaterial: Perfect absorption with large bandwidth and tunability. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2016, 6, 064025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chang, H.; Zhang, C.; Hu, X. Single-channel labyrinthine metasurfaces as perfect sound absorbers with tunable bandwidth. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 111, 083503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Chen, S.; Fu, C.; Sheng, P. Optimal sound-absorbing structures. Mater. Horiz. 2017, 4, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.H.; Zhu, W.; Wu, P.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Q.; Teng, J.; Shen, Z.; Chong, P.; Liang, Q. Liquid-metal-based metasurface for terahertz absorption material: Frequency-agile and wide-angle. APL Mater. 2017, 5, 066103–066109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Gao, S.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, X. Multiband quasi-perfect low-frequency sound absorber based on double-channel Mie resonator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 033507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Yu, C.; Xu, Z.; Xin, F.; Lu, T.J. Acoustic impedance regulation of Helmholtz resonators for perfect sound absorption via roughened embedded necks. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 117, 151904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Shen, X.; Wang, E.; Yang, F.; Zhang, X.; Yin, Q. Acoustic multi-layer Helmholtz resonance metamaterials with multiple adjustable absorption peaks. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2021, 118, 241904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xin, F. Perfect low-frequency sound absorption of rough neck embedded Helmholtz resonators. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2022, 151, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Rukhlenko, I.D. Graphene-enabled metasurface with independent amplitude and frequency controls in orthogonal polarization channels. Carbon 2023, 206, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaw, Z.; Lai, S.-K.; Gulzari, M. Acoustic resonant metasurfaces with roughened necks for effective low-frequency sound absorption. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2024, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Liu, G.L.; Wang, J.; Huang, L. High-Electron-Mobility MXene-Enhanced Metasurface Biosensors Integrated with Microfluidics for Real-Time Multifunctional Monitoring. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 12007–12020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; He, W.; Xin, F.; Lu, T.J. Sound propagation in porous materials containing rough tubes. Phys. Fluids 2020, 32, 093604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Yang, X.; Xin, F.; Lu, T.J. Modeling of surface roughness effects on Stokes flow in circular pipes. Phys. Fluids 2018, 30, 023604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, X.; Xin, F. Sound absorption of acoustic resonant absorbers with rough oblique perforations. Appl. Acoust. 2024, 217, 109828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pride, S.R.; Morgan, F.D.; Gangi, A.F. Drag forces of porous-medium acoustics. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 47, 4964–4978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maa, D. Theory and design of microperforated panel sound-absorbing constructions. Sci. China Ser. A 1975, 1, 55–71. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, M.; Wu, H.; Ibarias, M.; Sánchez-Dehesa, J. Subwavelength metasurfaces for quasi-omnidirectional broadband sound absorption at low frequencies. Thin-Walled Struct. 2025, 215, 113591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xiong, Z.; Zhuang, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J. An Ultra-Broadband Sound Insulation Based on Helmholtz Resonator Acoustic Metamaterial. Phys. Lett. A 2025, 553, 130721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Lyu, H.; Zhou, J.; Peng, Z.; Qiu, H.; Qi, W.; Gong, S.; Shao, L.; Zhang, W. Vibration enhancement for fiber-optic acoustic sensors via Helmholtz resonator-membrane synergy. J. Sound Vib. 2025, 608, 119063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magomedov, I.; Sebaeva, Z. Comparative study of finite element analysis software packages. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1515, 032073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perić, M.; Stamenković, D.; Milković, V. Comparison of residual stresses in butt-welded plates using software packages Abaqus and Ansys. Sci.-Tech. Rev. 2010, 60, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jia, Y.; Shen, X. An improved adaptive quantum genetic algorithm as classical optimizer for the quantum approximate optimization algorithm on MaxCut problem. Quantum Inf. Process. 2025, 24, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; He, C.; Cui, Z.; Ying, T.; Cai, J.; Tao, M. Topology optimization of multi-material underwater broadband sound absorption metamaterial based on genetic algorithm. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2025, 157, 3482–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Wei, L.; Chen, S.; Sun, X.; Li, P.; Sun, Y.; Xu, J. Prediction of separation performance and optimization of preparation parameters for reverse osmosis membranes using BPNN coupled with genetic algorithm. Desalination 2025, 614, 119149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Yu, C.; Xin, F.; Lu, T.J. Tunable underwater acoustic metamaterials via quasi-Helmholtz resonance: From low-frequency to ultra-broadband. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2021, 118, 071904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
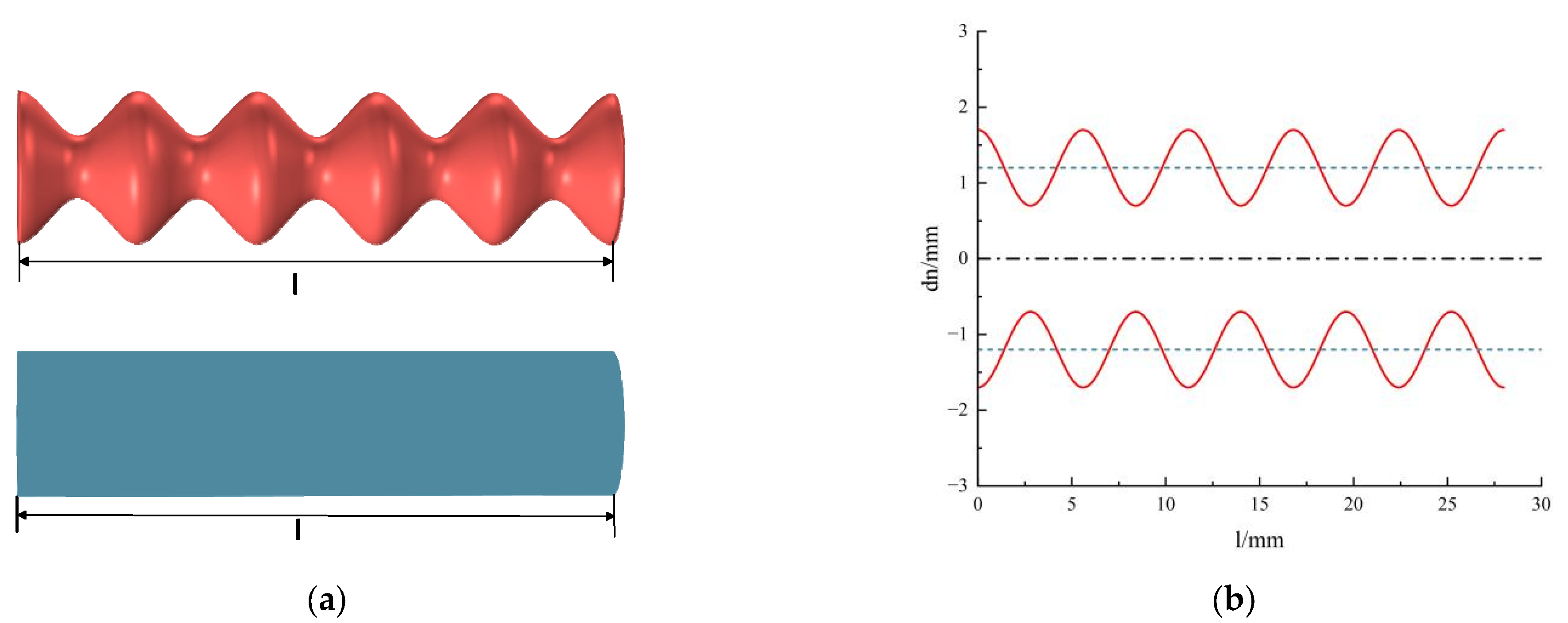
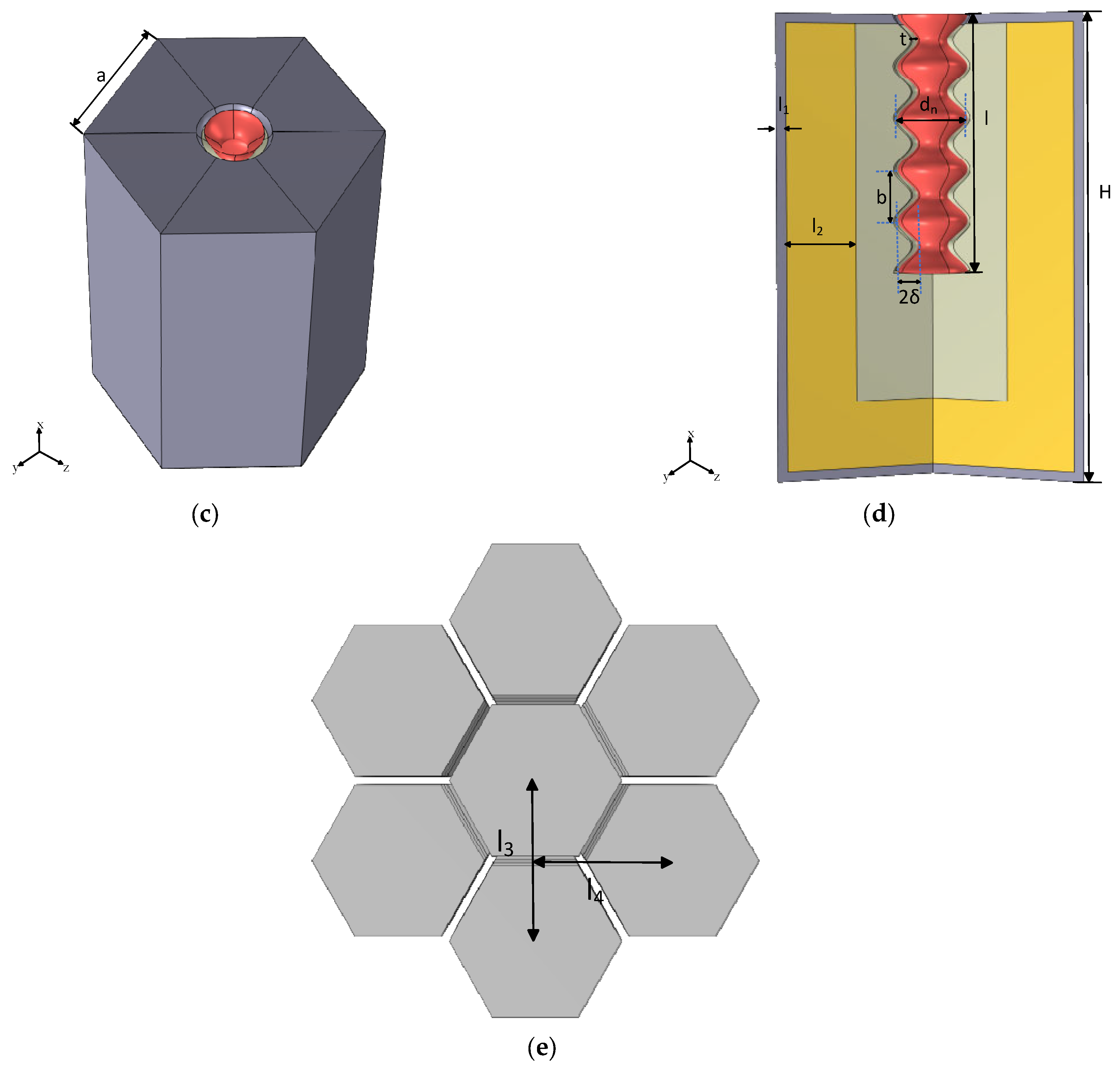

| Parameter | Magnitude | Description |
|---|---|---|
| a | 20 | Side length of resonator |
| H | 50 | Cavity height |
| l | 28 | Length of the rough neck |
| l1 | 1 | Thickness of the panel |
| l2 | 7.23 | Thickness of the rubber lining |
| b | 5.6 | Wavelength of the neck |
| dn | 3.4 | Average diameter of the neck |
| t | 1 | Wall thickness of the neck |
| δ | 1.064 | Amplitude of the embedded rough neck |
| l3 | 34.64 | Center-to-center vertical spacing of the unit cells |
| l4 | 30 | Center-to-center horizontal spacing of the unit cells |
| Feature | COMSOL Multiphysics | ANSYS Mechanical | Abaqus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multiphysics coupling | Strong, supports various coupled physics | Supported, mainly structural and fluid | Supported, mainly structural/materials |
| User interface | Intuitive, graphical | Powerful but steeper learning curve | Powerful but steeper learning curve |
| Module extensibility | Rich modules for different fields | Modular, covers multiple engineering fields | Modular, covers multiple engineering fields |
| Computational efficiency | Lower for large multiphysics models | High for large-scale models | High for large-scale models |
| Diameter | d1 | d2 | d3 | d4 | d5 | d6 | d7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| initial value | 5 | 4 | 6 | 3.4 | 4.8 | 6.2 | 5.5 |
| post-optimization | 5.191 | 3.281 | 8.604 | 4.656 | 10.103 | 6.875 | 5.207 |
| Comparison Dimension | Synergy of Embedded Rough Neck and Rubber Lining | Helmholtz Resonance Enhanced by Roughened Necks [20] | Quasi-Helmholtz Resonance Helmholtz [35] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lowest Absorption Frequency | 81 Hz | 76 Hz | 100 Hz |
| Subwavelength Scale | λ/370 | λ/54 | λ/300 |
| Optimization Method | Genetic algorithm combined with FEM | Not mentioned intelligent algorithms | Not mentioned intelligent algorithms |
| Absorption Bandwidth | 60–260 Hz (α > 0.9) | 76–125 Hz | 306–921 Hz (α > 0.9) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, S.; Bao, Z.; Li, N. Metasurfaces with Embedded Rough Necks for Underwater Low-Frequency Sound Absorption. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9306. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179306
Xu D, Zhu Y, Wang S, Bao Z, Li N. Metasurfaces with Embedded Rough Necks for Underwater Low-Frequency Sound Absorption. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9306. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179306
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Dan, Yazhou Zhu, Sha Wang, Zhenming Bao, and Ningyu Li. 2025. "Metasurfaces with Embedded Rough Necks for Underwater Low-Frequency Sound Absorption" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9306. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179306
APA StyleXu, D., Zhu, Y., Wang, S., Bao, Z., & Li, N. (2025). Metasurfaces with Embedded Rough Necks for Underwater Low-Frequency Sound Absorption. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9306. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179306






