A Systematic Review of Research on Urban Streets and Parks Based on Eye-Tracking Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
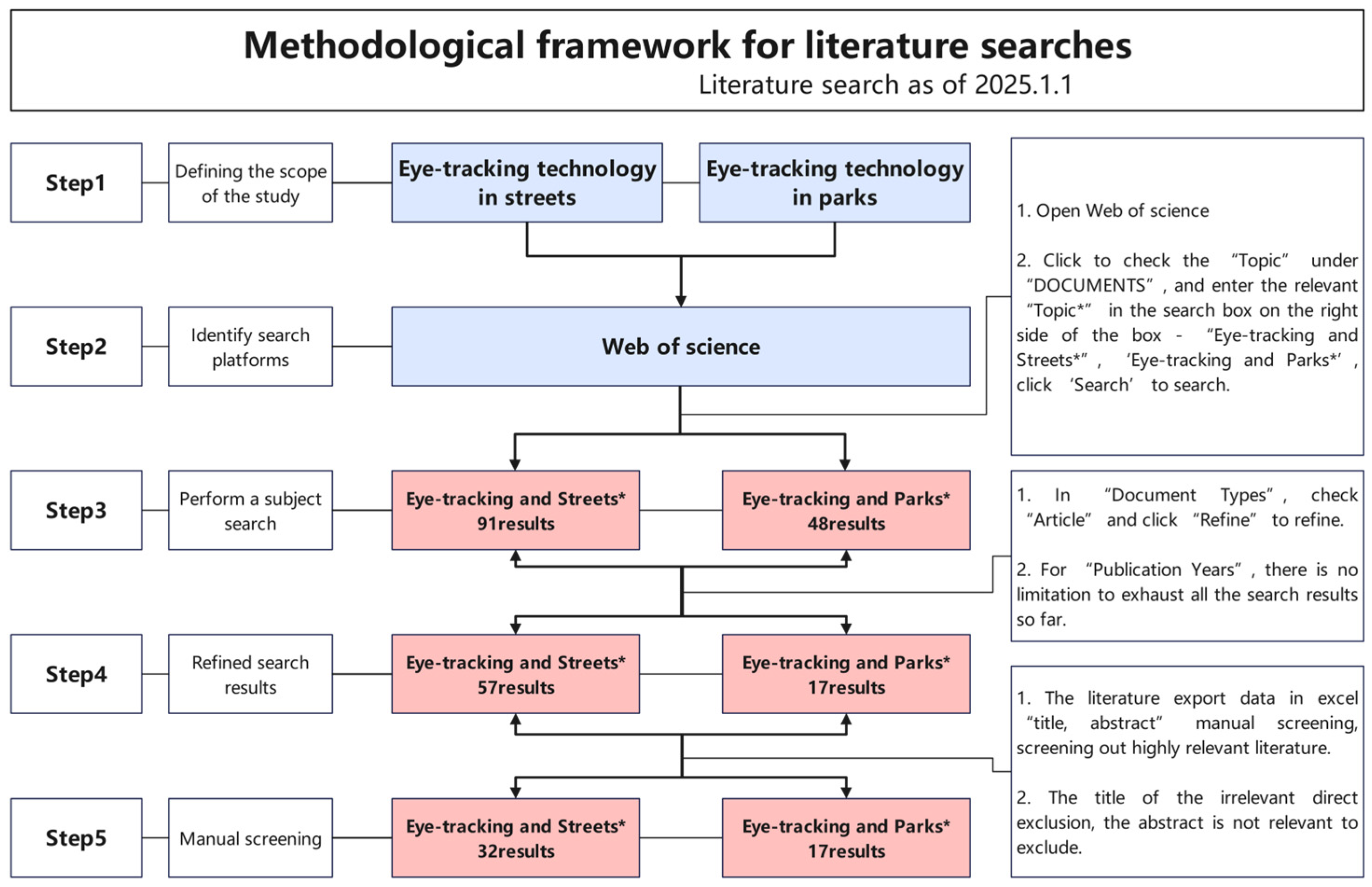
2.1. Literature Search Methodology
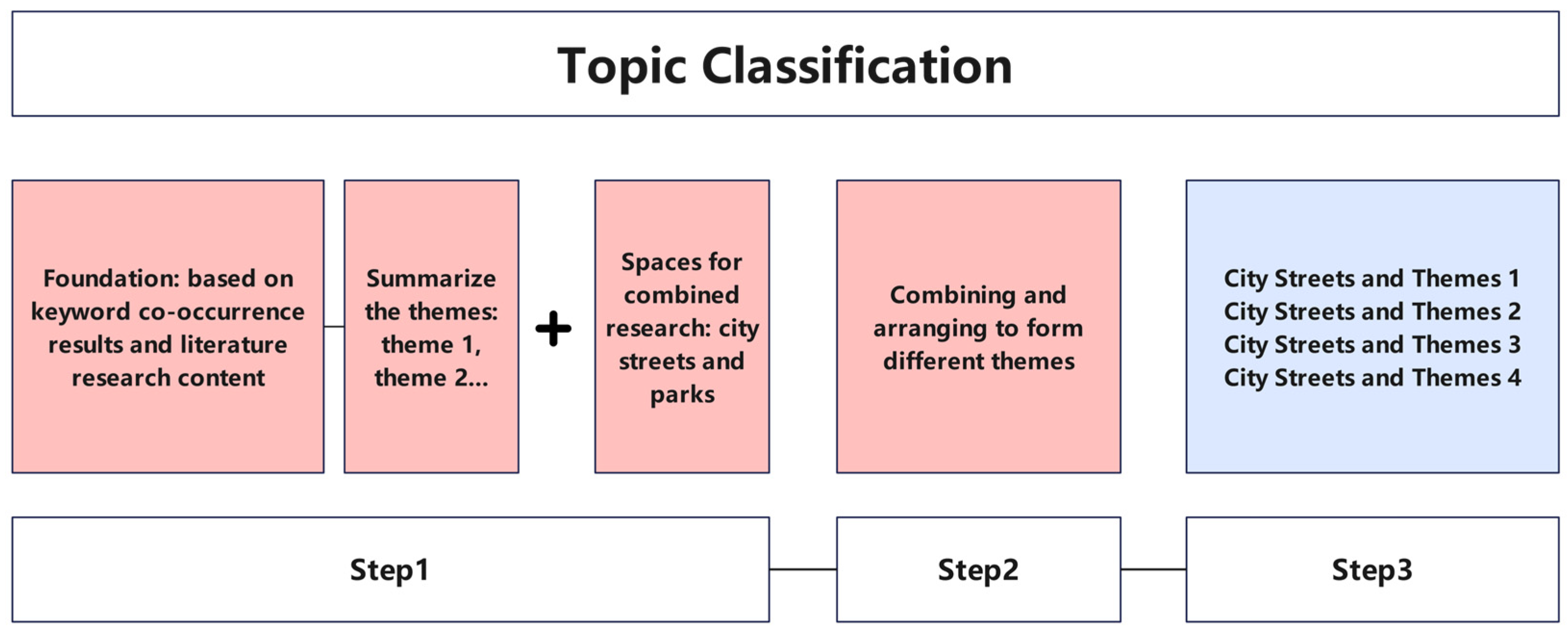
2.2. Literature Analysis Methodology
- Keyword co-occurrence;
- Thematic classification;
3. Results
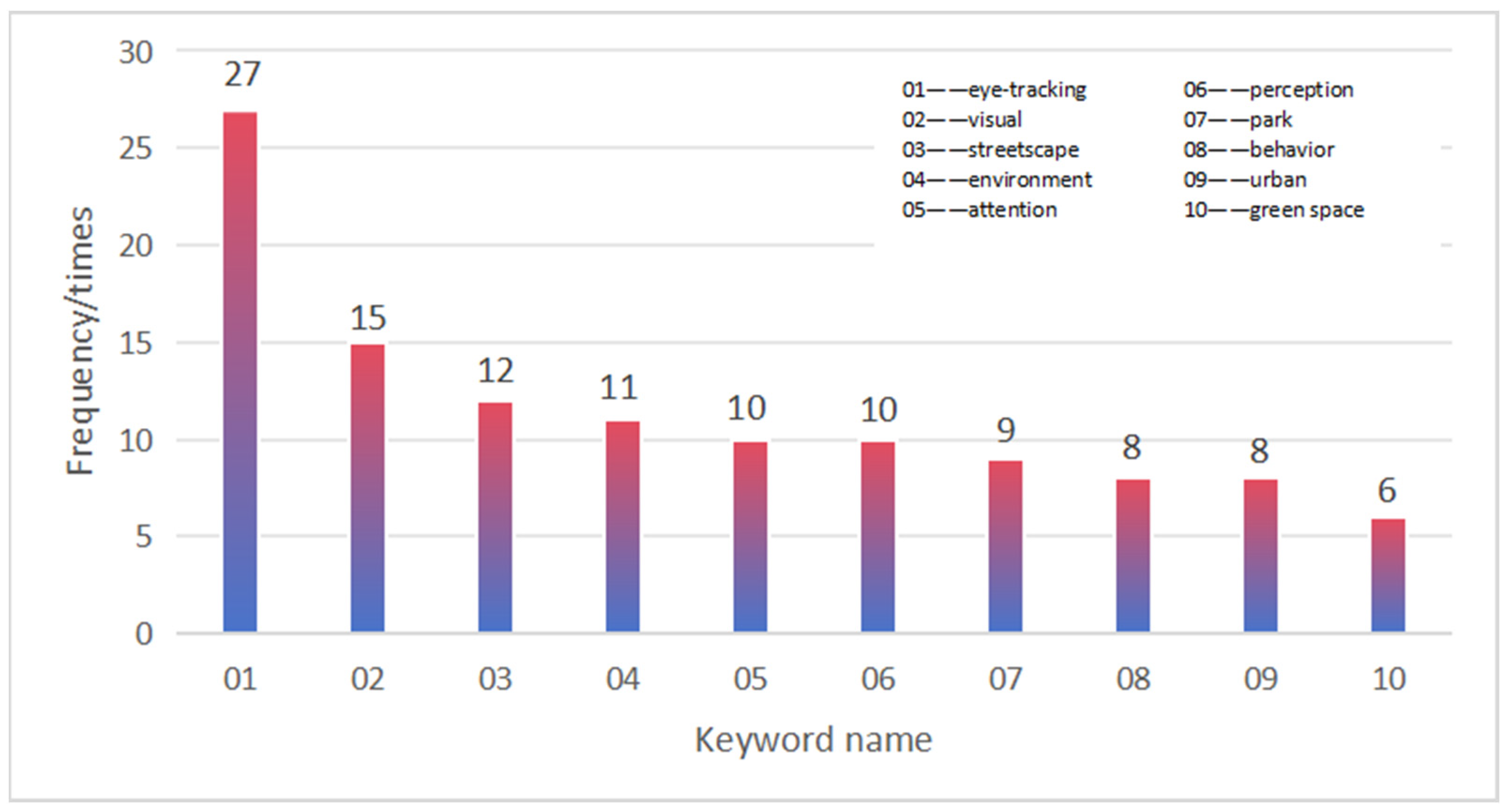
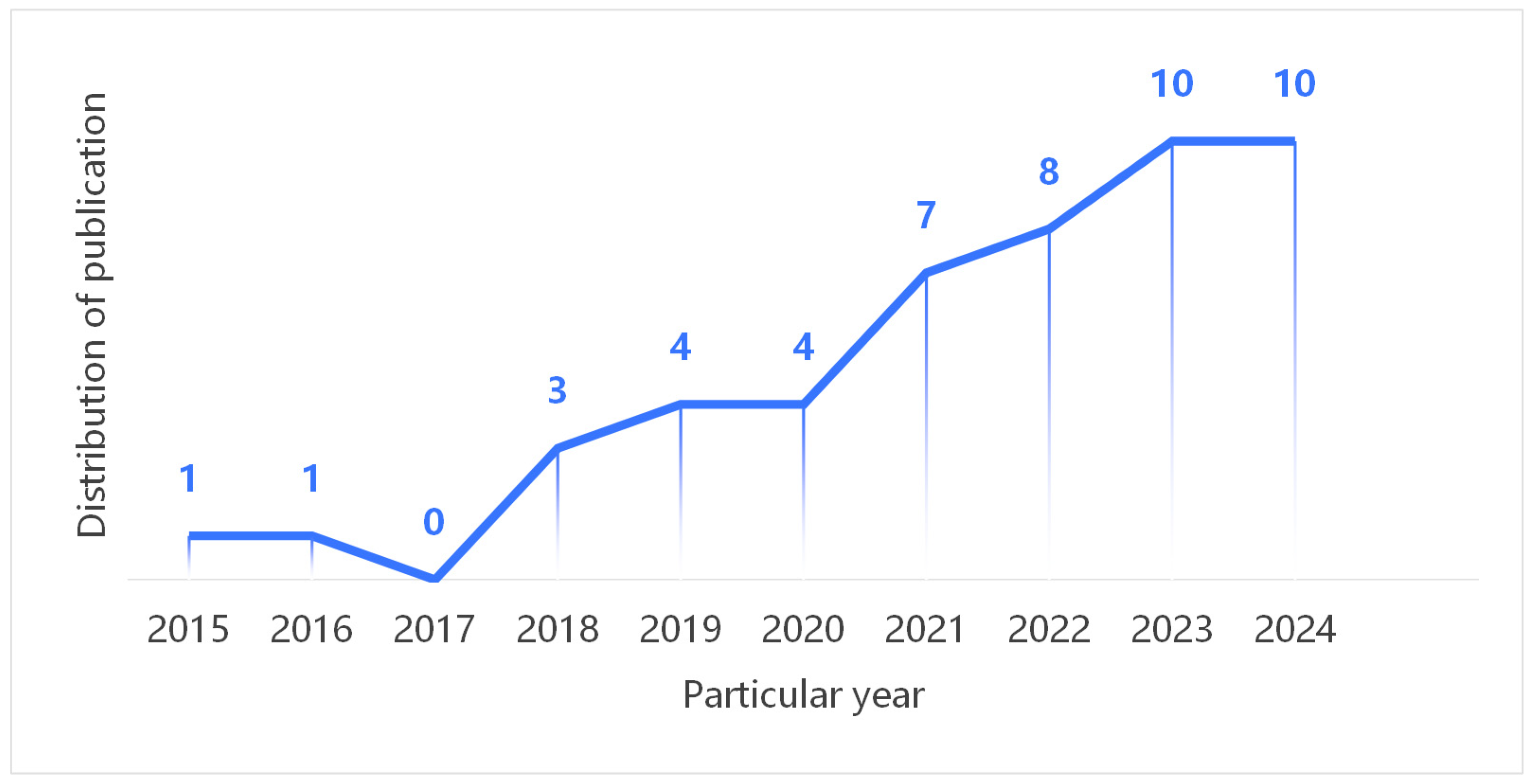
3.1. Keyword Co-Occurrence Results
3.2. Topic Classification Results
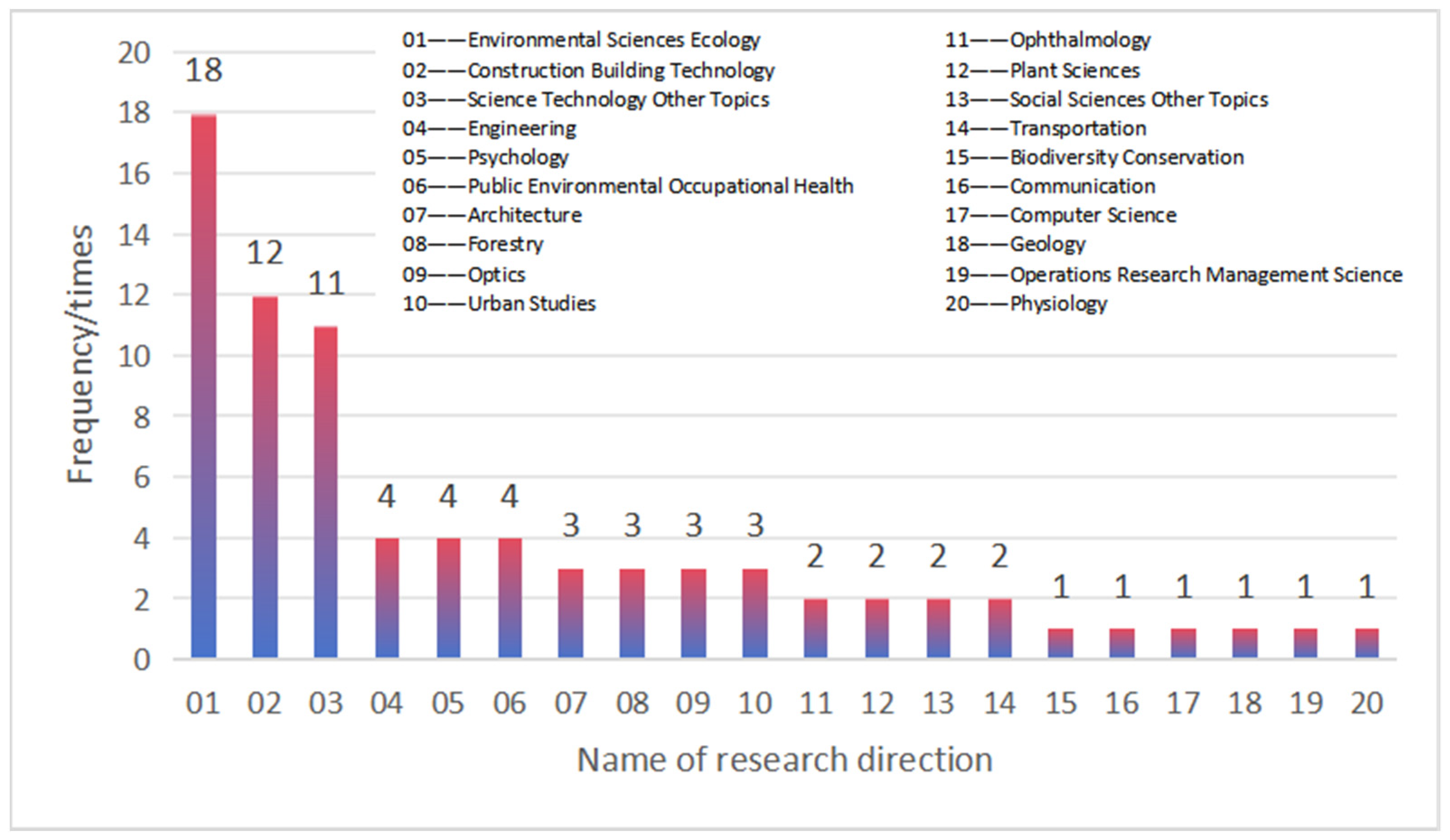
3.3. Citation Analysis Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Eye-Tracking-Based Research on Urban Streets
4.2. Eye-Tracking-Based Research on Urban Parks
4.3. Identified Research Characteristics and Future Research Trends
4.3.1. Increasing Multidisciplinarity
4.3.2. A Focus on Landscape Research
4.3.3. Enhanced Multisensory Interactions
4.3.4. The Shaping of Research Paradigms by Device Technology
4.4. Limiations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nie, W.; Fan, L.; Wei, Y.; Hu, R.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, Z. Quantitative research on street space based on visual perception—Taking the streets within the first ring of Hefei city as an example. Urban Constr. 2021, 18, 176–180. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Kevin, S.; Shao, Y.; Sun, Z. Research on the Balance of the Healing Efficacy and Functional Value of Street Environment—Taking University Road and Guokang Road in Yangpu District of Shanghai as Examples. New Archit. 2021, 4, 55–60. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Al Tuwirqi, A.A. Eye-Tracking Technology in Dentistry: A Review of Literature. Cureus 2024, 16, e55105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cui, L. The Application of Eye-tracking Technology in Multimedia Learning: A Review of Related Studies from 2005 to 2015. Res. Electro.-Educ. 2016, 37, 68–76, 91. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhou, X.; Han, J.; An, J. Eye-tracking: Patterns, Technologies, and Applications. Lab. Res. Explor. 2012, 31, 10–15. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, W.; Qiu, Y.; Xu, W. Research on the Dissemination Model of Architectural Cultural Heritage Based on Natural Interaction—Taking Jinlian Bridge as an Example. Packag. Eng. 2021, 42, 20–25. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L. Misunderstandings and Prospects of Eye-tracking Experiments in Design Research—A Review Based on the Current Research Status in China. Decoration 2017, 8, 122–123. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Sun, M.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y. Research Progress on the Application of Eye-tracking Technology in Landscape Architecture. Landsc. Archit. 2024, 31, 79–86. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Shao, H.; Li, S.; Huang, X.; Yang, W. Integrated Application of Eye Movement Analysis and Beauty Estimation in the Visual Landscape Quality Estimation of Urban Waterfront Park. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2018, 32, 1856010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, Y.; Kawauchi, A.; Motooka, N. Gazing Behavior Exhibited by People with Low Vision While Navigating Streets. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2021, 20, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.A. Eye-Tracking and Visual Preference: Maybe Beauty Is in the Eye of the Beholder? Land 2024, 13, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Byun, G.; Ha, M. Exploring the Association between Environmental Factors and Fear of Crime in Residential Streets: An Eye-Tracking and Questionnaire Study. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2024, 23, 1518–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, J.; Yang, B. Luminance and Saliency Have Impact on Pedestrians’ Fixation Distribution during Natural Walking: Evidence from Mobile Eye-Tracker. Light. Res. Technol. 2021, 53, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Zhang, J.; Zu, R.; Li, Y. Visual Perception Differences and Spatiotemporal Analysis in Commercialized Historic Streets Based on Mobile Eye-tracking: A Case Study in Nanchang Wanshou Palace, China. Buildings 2024, 14, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Wang, P.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y. Investigating Influence of Visual Elements of Arcade Buildings and Streetscapes on Place Identity Using Eye-Tracking and Semantic Differential Methods. Buildings 2023, 13, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xu, Y.; Teng, S.; Wang, B.; Li, M.; Ding, S. Research into the Visual Saliency of Guide Signs in an Underground Commercial Street Based on an Eye-Movement Experiment. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosby, F.; Hermens, F. Does It Look Safe? An Eye-tracking Study into the Visual Aspects of Fear of Crime. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 2019, 72, 599–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mushayt, N.S.; Dal Cin, F.; Barreiros Proença, S. New Lens to Reveal the Street Interface. A Morphological-Visual Perception Methodological Contribution for Decoding the Public/Private Edge of Arterial Streets. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Park, J. The Visual Effect of Signboards on the Vitality of the Streetscapes Using Eye-Tracking. Sustainability 2020, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotios, S.; Yang, B.; Uttley, J. Observing Other Pedestrians: Investigating the Typical Distance and Duration of Fixation. Light. Res. Technol. 2015, 47, 548–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.; Thwaites, K.; Freeth, M. Understanding Visual Engagement with Urban Street Edges along Non-Pedestrianised and Pedestrianised Streets Using Mobile Eye-Tracking. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chana, K.; Mikuni, J.; Schnebel, A.; Leder, H. Reading in the City: Mobile Eye-Tracking and Evaluation of Text in an Everyday Setting. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1205913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Du, M. Designing Attention—Research on Landscape Experience Through Eye-tracking in Nanjing Road Pedestrian Mall (Street) in Shanghai. Landsc. Archit. Front. 2022, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Yu, P.; Wu, H.; Lan, T. Usability Evaluation of Road Map Schematic Representation. Surv. Mapp. Bull. 2021, 224, 81–85. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Ma, J.; Pan, Y. Eye Movement Characteristics of Pedestrians Crossing the Street with and without Signal Control. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2019, 37, 40–47. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.; Homma, R.; Qiu, T.; Zhong, Q. The Mediating Role of Visual Behavior in Perceived Walkability Evaluation. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2024, 03, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietze, P.; Knowles, E.D. Social Class and the Motivational Relevance of Other Human Beings: Evidence From Visual Attention. Psychol. Sci. 2016, 27, 1517–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehove, M.; Mikuni, J.; Podolin, N.; Moser, M.K.; Resch, B.; Doerrzapf, L.; Boehm, P.M.; Prager, K.; Leder, H.; Oberzaucher, E. Exploring the Influence of Urban Art Interventions on Attraction and Wellbeing: An Empirical Field Experiment. Front. Psychol. 2024, 15, 1409086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Cui, Z. Respondent Dynamic Attention to Streetscape Composition in Nanjing, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Liang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y. Research on the Visual Attractiveness and Its Perception Influencing Factors of Commercial Street Space in Cultural Heritage Sites—Taking Kulangsu Longtou Road as an Example. J. Hum. Settl. West China 2022, 37, 114–121. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomoda, M.; Uno, H.; Hashimoto, S.; Yoshiki, S.; Ujihara, T. Analysis on the Impact of Traffic Safety Measures on Children’s Gaze Behavior and Their Safety Awareness at Residential Road Intersections in Japan. Saf. Sci. 2022, 150, 105706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotios, S.; Uttley, J. Illuminance Required to Detect a Pavement Obstacle of Critical Size. Light. Res. Technol. 2018, 50, 390–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Dong, W.; Zhang, W. Research on the Influencing Factors of Perception of the Built Environment in Neighborhoods—Evidence from Behavioral Experiments. Urban Plan. 2022, 46, 99–109. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Amati, M.; McCarthy, C.; Parmehr, E.G.; Sita, J. Combining Eye-Tracking Data with an Analysis of Video Content from Free-Viewing a Video of a Walk in an Urban Park Environment. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 147, e58459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amati, M.; Ghanbari Parmehr, E.; McCarthy, C.; Sita, J. How Eye-Catching Are Natural Features When Walking through a Park? Eye-Tracking Responses to Videos of Walks. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 31, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhuo, Z.; Liu, Q.; Yu, K.; Huang, Q.; Liu, J. The Relationships between Perceived Design Intensity, Preference, Restorativeness and Eye Movements in Designed Urban Green Space. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, Y.; Taghvaei, S.H.; Norouzian-Maleki, S.; Mansouri Sepehr, R. Identifying the Stimulus of Visual Perception Based on Eye-Tracking in Urban Parks: Case Study of Mellat Park in Tehran. J. For. Res. 2021, 26, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Luo, Y.; Furuya, K. Gender Differences and Optimizing Women’s Experiences: An Exploratory Study of Visual Behavior While Viewing Urban Park Landscapes in Tokyo, Japan. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Du, C.; Ge, S.; Tong, T. An Eye-Tracking Study on Visual Perception of Vegetation Permeability in Virtual Reality Forest Exposure. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1089423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Luo, Y.; Furuya, K. Classifying Visually Appealing Elements in Parks Using Social Media Data-Assisted Eye-Tracking: Case Study of Shinsui Parks in Tokyo, Japan. J. Outdoor Recreat. Tour. 2023, 44, 100672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Huang, X. Differences in Visual Attraction between Historical Garden and Urban Park Walking Scenes. Land 2022, 11, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ding, Y.; Lei, M.; Mao, L. Restoration Evaluation of National Forest Park in Greater Khingan Mountains Region, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 11022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yang, W.; Wang, D.; He, Y. Insights into Public Visual Behaviors through Eye-Tracking Tests: A Study Based on National Park System Pilot Area Landscapes. Land 2021, 10, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Cen, Q.; Qiu, H. Effects of Urban Waterfront Park Landscape Elements on Visual Behavior and Public Preference: Evidence from Eye-Tracking Experiments. Urban For. Urban Green. 2023, 82, 127889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W. Differences in Environmental Information Acquisition from Urban Green—A Case Study of Qunli National Wetland Park in Harbin, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Luo, M.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Y. Multi-Sensory Interaction and Spatial Perception in Urban Microgreen Spaces: A Focus on Vision, Auditory, and Olfaction. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Qu, H.; Ma, Y.; Wang, K.; Qu, H. Restorative Benefits of Urban Green Space: Physiological, Psychological Restoration and Eye Movement Analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, E.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, X. A Preliminary Exploration of Using Eye-tracking Analysis for Evaluating the Restorative Environment of Community Parks. South Archit. 2022, 06, 93–99. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Deng, W. Research on Cognitive Differences of Product Image Sketches Based on Eye-tracking Technology. J. Comput.-Aided Des. Comput. Graph. 2019, 31, 287–294. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Pu, Q. Can Eye Movements Represent the Construction of Scientific Knowledge?—Multidimensional Data Analysis from the Perspective of Argumentation. Mod. Educ. Technol. 2025, 35, 62–70. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.C.; Wu, F.W.; Bai, H.; Li, Y.H. The Impact of Visual Stimuli from the Linear Space Layout Forms of the Central Reservation of Urban Expressways on Driving Behavior. China J. Highw. Transp. 2022, 35, 239–251. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollander, J.B.; Sussman, A.; Lowitt, P.; Angus, N.; Situ, M. Analyzing Walkability Through Biometrics: Insights Into Sustainable Transportation Through the Use of Eye-Tracking Emulation Software. J. Phys. Act. Health 2020, 17, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. On Several Important Factors Affecting the Effectiveness of Questionnaire Survey Research Methods in Sports Social Sciences. Zhejiang Sports Sci. 2008, 122, 115–117. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Hao, J.; Wang, H.; Qiao, X. Visualization Analysis of the Evolution of Research on the Educational Application of Virtual Reality Technology. Res. Electro-Educ. 2016, 37, 26–33. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, V.; Kendal, D.; Hahs, A.K.; Threlfall, C.G. Green Space Context and Vegetation Complexity Shape People’s Preferences for Urban Public Parks and Residential Gardens. Landsc. Res. 2018, 43, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, N.; Wang, C.; Wang, M.; Huang, H. A Preliminary Exploration of the Application of Eye-tracking Technology in Campus Tourism Landmark Landscapes—Taking the Peking University Building in Nanjing University as an Example. Acta Agric. Jiangxi 2011, 23, 148–151. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Li, Z.; Xuan, X.; Li, Q.; Shi, L.; Sun, X.; Zhu, K.; Shi, Y. Influence of Hospital Outdoor Rest Space on the Eye Movement Measures and Self-Rating Restoration of Staff. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 855857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, M.; Zhao, B. Interactions between Forest Landscape Elements and Eye Movement Behavior under Audio-Visual Integrated Conditions. J. For. Res. 2020, 25, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wu, M.; Ma, Y.; Qu, H. A Review of the Application of Eye-tracking Technology in the Field of Landscape. J. Hum. Settl. West China 2021, 36, 125–133. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Theme Name | Year | Author | Eye Movement Indicators | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TFD | FF | AFD | PFD | SF | ASA | FSD | APD | Else | |||
| (1) Urban Streets and Visual Preferences | 2024 | Miller. [11] | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| 2024 | Lee et al. [12] | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 2021 | Jiang et al. [13] | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 2024 | Zheng et al. [14] | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 2023 | Fu et al. [15] | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| 2022 | Sun et al. [16] | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| 2019 | Crosby & Hermens. [17] | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| 2021 | Al Mushayt et al. [18] | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| 2021 | Kim & Park. [19] | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 2015 | Fotios et al. [20] | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 2019 | Simpson et al. [21] | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 2023 | Chana et al. [22] | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 2022 | Yiyan et al. [23] | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 2021 | Matsuda et al. [10] | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| 2021 | Gong et al. [24] | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 2019 | Ding et al. [25] | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 2024 | Fang et al. [26] | √ | |||||||||
| 2016 | Dietze & Knowles, n.d. [27] | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 2024 | Dehove et al. [28] | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 2022 | Yue et al. [29] | √ | |||||||||
| 2022 | Li et al. [30] | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 2022 | Tomoda et al. [31] | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| (2) Urban Streets and Healing | 2021 | Al Mushayt et al. [18] | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| 2021 | Kim & Park. [19] | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 2019 | Simpson et al. [21] | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 2018 | Fotios & Uttley. [32] | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 2022 | Wu et al. [33] | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| 2024 | Fang et al. [26] | √ | |||||||||
| (3) Urban Parks and Visual Preferences | 2019 | Amati et al. [34] | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| 2018 | Amati et al. [35] | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 2021 | Wu et al. [36] | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 2021 | Gholami et al. [37] | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 2018 | Sun et al. [9] | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| 2023 | Ma et al. [38] | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| 2023 | Li et al. [39] | √ | |||||||||
| 2023 | Ma et al. [40] | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 2022 | Li & Huang. [41] | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 2024 | Sun et al. [42] | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 2021 | Wang et al. [43] | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| 2023 | Zhou et al. [44] | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| 2020 | Zhu et al. [45] | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| 2024 | Zheng et al. [46] | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| (4) Urban Parks and Healing | 2019 | Amati et al. [34] | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| 2018 | Amati et al. [35] | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 2021 | Wu et al. [36] | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 2018 | Sun et al. [9] | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| 2023 | Li et al. [39] | √ | |||||||||
| 2024 | Sun et al. [42] | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 2022 | Liu et al. [47] | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 2022 | Fu et al. [48] | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 2023 | Zhou et al. [44] | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| 2024 | Zheng et al. [46] | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| Theme Name | Year | Author | Head-Mounted | Desktop | VR/AR Integrated | Remote Contactless | Eye Movement Device Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) Urban Streets and Visual Preferences | 2024 | Miller. [11] | √ | Laboratory Eye-tracking System (Not mentioned) | |||
| 2024 | Lee et al. [12] | √ | Gazepoint GP3 (Gazepoint, Toronto, Canada) | ||||
| 2021 | Jiang et al. [13] | √ | SMI ETG 2w (SMI, Teltow, Germany) | ||||
| 2024 | Zheng et al. [14] | √ | Tobii Glasses 2 (Tobii AB, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2023 | Fu et al. [15] | √ | Tobii Pro Spectrum (Tobii AB, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2022 | Sun et al. [16] | √ | √ | √ | Tobii VR Tobii Pro X3-120 (Tobii AB, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||
| 2019 | Crosby & Hermens. [17] | √ | SR Research Eyelink 1000 (Tobii AB, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2021 | Al Mushayt et al. [18] | √ | Pupil Invisible (Pupil Labs, Berlin, Germany) | ||||
| 2021 | Kim & Park. [19] | √ | Gazepoint GP3 HD (Gazepoint, Vancouver, Canada) | ||||
| 2015 | Fotios et al. [20] | √ | iView X HED (SMI, Berlin, Germany) | ||||
| 2019 | Simpson et al. [21] | √ | SensoMotoric Instruments (SMI) Glasses 2.0 (SMI, Berlin, Germany) | ||||
| 2023 | Chana et al. [22] | √ | Pupil Labs Pupil Core (Pupil Labs GmbH, Berlin, Germany) Tobii Pro Glasses 3 (Tobii AB, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2022 | Yiyan et al. [23] | √ | Ergoneers Dikablis (Ergoneers GmbH, Aschheim, Germany) | ||||
| 2021 | Matsuda et al. [10] | √ | NAC Image Technology EMR-9 (NAC Image Technology Inc, Tokyo, Japan) | ||||
| 2021 | Gong et al. [24] | √ | Gazetech mini (Not mentioned) | ||||
| 2019 | Ding et al. [25] | √ | Tobii Glasses (Tobii AB, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2024 | Dehove et al. [28] | √ | Tobii Pro Glasses 3 (Tobii AB, Stockholm, Sweden) Pupil Invisible Glasses (Pupil Labs, Berlin, Germany) | ||||
| 2022 | Yue et al. [29] | √ | Tobii Pro (Tobii Pro, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2019 | Crosby & Hermens. [17] | √ | SR Research Eyelink 1000 (Tobii AB, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2021 | Al Mushayt et al. [18] | √ | Pupil Invisible (Pupil Labs, Berlin, Germany) | ||||
| 2021 | Kim & Park. [19] | √ | Gazepoint GP3 HD (Gazepoint, Vancouver, Canada) | ||||
| 2015 | Fotios et al. [20] | √ | iView X HED (SMI, Berlin, Germany) | ||||
| 2019 | Simpson et al. [21] | √ | SensoMotoric Instruments (SMI) Glasses 2.0 (SMI, Berlin, Germany) | ||||
| 2023 | Chana et al. [22] | √ | Pupil Labs Pupil Core (Pupil Labs GmbH, Berlin, Germany) Tobii Pro Glasses 3 (Tobii AB, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2022 | Yiyan et al. [23] | √ | Ergoneers Dikablis (Ergoneers GmbH, Aschheim, Germany) | ||||
| 2021 | Matsuda et al. [10] | √ | NAC Image Technology EMR-9 (NAC Image Technology Inc, Tokyo, Japan) | ||||
| 2021 | Gong et al. [24] | √ | Gazetech mini (Not mentioned) | ||||
| 2019 | Ding et al. [25] | √ | Tobii Glasses (Tobii AB, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2024 | Fang et al. [26] | √ | √ | Pico Neo3 Pro Eye-Tracking (VR-HMD) (Not mentioned) | |||
| 2016 | Dietze & Knowles, n.d. [27] | √ | √ | Google Glass (Google Mountain View, California, United States), SR Research EyeLink 1000 (SR Research, Kanata, Ontario, Canada) | |||
| 2024 | Dehove et al. [28] | √ | Tobii Pro Glasses 3 (Tobii Technology, Stockholm, Sweden) Pupil Invisible Glasses (Pupil Labs, Berlin, Germany) | ||||
| 2022 | Yue et al. [29] | √ | Tobii Pro (Tobii Pro, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2022 | Li et al. [30] | √ | Tobii Glasses 2 ( Tobii, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2022 | Tomoda et al. [31] | √ | Ditect QG-Plus (DITEC Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) | ||||
| (2) Urban Streets and Healing | 2021 | Al Mushayt et al. [18] | √ | Pupil Invisible (Pupil Labs, Berlin, Germany) | |||
| 2021 | Kim & Park. [19] | √ | Gazepoint GP3 HD (Gazepoint, Vancouver, Canada) | ||||
| 2019 | Simpson et al. [21] | √ | SensoMotoric Instruments (SMI) Glasses 2.0 (SMI) Glasses 2.0 (SMI, Berlin, Germany) | ||||
| 2018 | Fotios & Uttley. [32] | √ | Head-mounted mobile eye-tracking device (Not mentioned) | ||||
| 2022 | Wu et al. [33] | √ | Tobii Pro Spectrum (Tobii AB, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2024 | Fang et al. [26] | √ | Pico Neo3 Pro Eye-Tracking (VR-HMD) (Not mentioned) | ||||
| (3) Urban Parks and Visual Preferences | 2019 | Amati et al. [34] | √ | Tobii T60 XL (Tobii AB, Stockholm, Sweden) | |||
| 2018 | Amati et al. [35] | √ | Tobii x120 (Tobii AB, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2021 | Wu et al. [36] | √ | Eye-link 1000 plus (SR Research, Kanata, Canada) | ||||
| 2021 | Gholami et al. [37] | √ | SMI Eye-tracking Glasses 2.0 (SMI, Teltow, Germany | ||||
| 2018 | Sun et al. [9] | √ | Tobii X2-30 (Tobii, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2023 | Ma et al. [38] | √ | Tobii Pro Nano | ||||
| 2023 | Li et al. [39] | √ | √ | Ergo VR (Beijing Kingfar Technologies Inc), HTC Vive Pro head-mounted display (HTC Inc.Tai wan, China) | |||
| 2023 | Ma et al. [40] | √ | Tobii Pro Nano (Tobii, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2022 | Li & Huang. [41] | √ | aSee pro (7 Inversum Technology Ltd., Beijing, China) | ||||
| 2024 | Sun et al. [42] | √ | Tobii Pro Glasses 2 (Tobii AB, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2021 | Wang et al. [43] | √ | Tobii Pro X3-120 (Tobii AB, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2023 | Zhou et al. [44] | √ | SMI Eye-tracking Glasses (SMI, Berlin, Germany) | ||||
| 2020 | Zhu et al. [45] | √ | Tobii Pro Glass 2 (Tobii, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2024 | Zheng et al. [46] | √ | Tobii Glasses 2 Pro (Tobii, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| (4) Urban Parks and Healing | 2019 | Amati et al. [34] | √ | Tobii T60 XL (Tobii AB, Stockholm, Sweden) | |||
| 2018 | Amati et al. [35] | √ | Tobii x120 (Tobii AB, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2021 | Wu et al. [36] | √ | Eye-link 1000 plus (SR Research, Kanata, Canada) | ||||
| 2018 | Sun et al. [9] | √ | Tobii X2-30 (Tobii, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2023 | Li et al. [39] | √ | √ | Ergo VR (Beijing Kingfar Technologies Inc), HTC Vive Pro (HTC Inc.Tai wan, China) | |||
| 2024 | Sun et al. [42] | √ | Tobii Pro Glasses 2 (Tobii AB, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2022 | Liu et al. [47] | √ | Tobii Glasses 2 Pro (Tobii, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2022 | Fu et al. [48] | √ | Tobii Pro Glasses 2 (Tobii, Stockholm, Sweden) | ||||
| 2023 | Zhou et al. [44] | √ | SMI Eye-tracking Glasses (SMI, Berlin, Germany) | ||||
| 2024 | Zheng et al. [46] | √ | Tobii Glasses 2 Pro (Tobii, Stockholm, Sweden) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, L.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Bai, C.; Wen, F. A Systematic Review of Research on Urban Streets and Parks Based on Eye-Tracking Technology. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9305. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179305
Yuan L, Yang Z, Wang X, Bai C, Wen F. A Systematic Review of Research on Urban Streets and Parks Based on Eye-Tracking Technology. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9305. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179305
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Lin, Zhaoyi Yang, Xiang Wang, Chuandong Bai, and Fang Wen. 2025. "A Systematic Review of Research on Urban Streets and Parks Based on Eye-Tracking Technology" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9305. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179305
APA StyleYuan, L., Yang, Z., Wang, X., Bai, C., & Wen, F. (2025). A Systematic Review of Research on Urban Streets and Parks Based on Eye-Tracking Technology. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9305. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179305






