The Impact of Damon Self-Ligating Orthodontic Therapy on Soft Tissue and Incisor Inclination: Extraction vs. Non-Extraction Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of the Study and Ethical Approval
2.2. Patient Population
2.3. Treatment Duration and Growth Considerations
2.4. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.5. Data Collection and Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Intra-Group Comparisons (T0–T1)
3.1.1. Group Ex
3.1.2. Group NonEx
3.2. Inter-Group Comparison (T0–T1 Changes)
3.3. Comparison of Two-Premolar Extraction in the Upper Arch and Four-Premolar Extraction (2 Each in the Upper and Lower Arch) in Group Ex
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sayahpour, B.; Lau, D.; Eslami, S.; Buehling, S.; Kopp, S.; Jamilian, A.; Chhatwani, S. Posttreatment stability following therapy using passive self-ligating brackets: Extraction vs. nonextraction. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2023, 86, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschneck, C.; Proff, P.; Reicheneder, C.; Lippold, C. Short-term effects of systematic premolar extraction on lip profile, vertical dimension and cephalometric parameters in borderline patients for extraction therapy—A retrospective cohort study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2016, 20, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, S.J. The Esthetic Impact of Extraction and Nonextraction Treatments on Caucasian Patients. Angle Orthod. 2000, 70, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tepedino, M.; Esposito, R.; Potrubacz, M.I.; Xhanari, D.; Ciavarella, D. Evaluation of the relationship between incisor torque and profile aesthetics in patients having orthodontic extractions compared to non-extractions. Clin. Oral Investig. 2023, 27, 5233–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhling, S.; Schmied, S.; Eslami, S.; Brandt, S.; Plein, N.; Kopp, S.; Sayahpour, B. Changes in the arch width and buccal corridor after fixed orthodontic treatment with Damon self-ligating system: Premolar extraction vs. non-extraction. Dent. Press. J. Orthod. 2024, 29, e2423159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdinc, A.E.; Nanda, R.S.; Dandajena, T.C. Profile changes of patients treated with and without premolar extractions. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2007, 132, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zierhut, E.C.; Joondeph, D.R.; Artun, J.; Little, R.M. Long-Term Profile Changes Associated with Successfully Treated Extraction and Nonextraction Class II Division 1 Malocclusions. Angle Orthod. 2000, 70, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocadereli, I. Changes in soft tissue profile after orthodontic treatment with and without extractions. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2002, 122, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnie, D.; Harradine, N. The Extraction Non-Extraction Decision. In Excellence in Orthodontics Course Manual Chapter 6; Excellence in Orthodontics: Solihull, UK, 2016; pp. 79–92. [Google Scholar]
- Iiksal, E.; Hazar, S.; Akyalin, S. Smile esthetics: Perception and comparison of treated and untreated smiles. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2006, 129, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janson, G.; Mendes, L.M.; Junqueira, C.H.Z.; Garib, D.G. Soft-tissue changes in Class II malocclusion patients treated with extractions: A systematic review. Eur. J. Orthod. 2016, 38, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, H. BiAS. f \ u r Windows Handbuch Version 11.12. 2020. Available online: https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/topic/windows-10-update-history-53c270dc-954f-41f7-7ced-488578904dfe (accessed on 20 July 2025).
- Bishara, S.E.; Cummins, D.M.; Jakobsen, J.R.; Zaher, A.R. Dentofacial and soft tissue changes in Class II, Division 1 cases treated with and without extractions. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1995, 107, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, C.; Cohen, P.; West, S.; Aiken, L. Applied Multiple Regression/Correlation Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal, R. Meta-Analytic Procedures for Social Research; Sage: Beverly Hills, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, J. Straightforward Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences; Thomson Brooks/Cole Publishing Co.: Monterey, CA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Bishara, S.E.; Jakobsen, J.R.; Hession, T.J.; Treder, J.E. Soft tissue profile changes from 5 to 45 years of age. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1998, 114, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertini, P.; Barbara, L.; Albertini, E.; Willeit, P.; Lombardo, L. Soft-tissue profile changes in adult patients treated with premolar extractions. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2024, 166, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wholley, C.J.; Woods, M.G. The effects of commonly prescribed premolar extraction sequences on the curvature of the upper and lower lips. Angle Orthod. 2003, 73, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basciftci, F.A.; Usumez, S. Effects of extraction and nonextraction treatment on class I and class II subjects. Angle Orthod. 2003, 73, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekstam, A.; Sonesson, M.; Hellén-Halme, K. Effects of Premolar Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment in Adolescents: A Retrospective Cephalometric Study. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2024, 82, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, K.G.; Sivamurthy, G.; Bearn, D.R. Extraction vs. Nonextraction Orthodontic Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Angle Orthod. 2024, 94, 83–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, T.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, C.; Kook, Y.A.; Larson, B.E.; Lee, N.K. Changes in Maximum Lip-Closing Force after Extraction and Nonextraction Orthodontic Treatments. Korean J. Orthod. 2020, 50, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantonis, D.; Vasileiou, D.; Papageorgiou, S.N.; Eliades, T. Soft Tissue Changes Following Extraction vs. Nonextraction Orthodontic Fixed Appliance Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2018, 126, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Gao, L.; Zhang, C. Three-Dimensional Changes in Lip Vermilion Morphology After Extraction and Non-Extraction Orthodontic Treatment: A CBCT-Based Study. J. Dent. 2019, 85, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
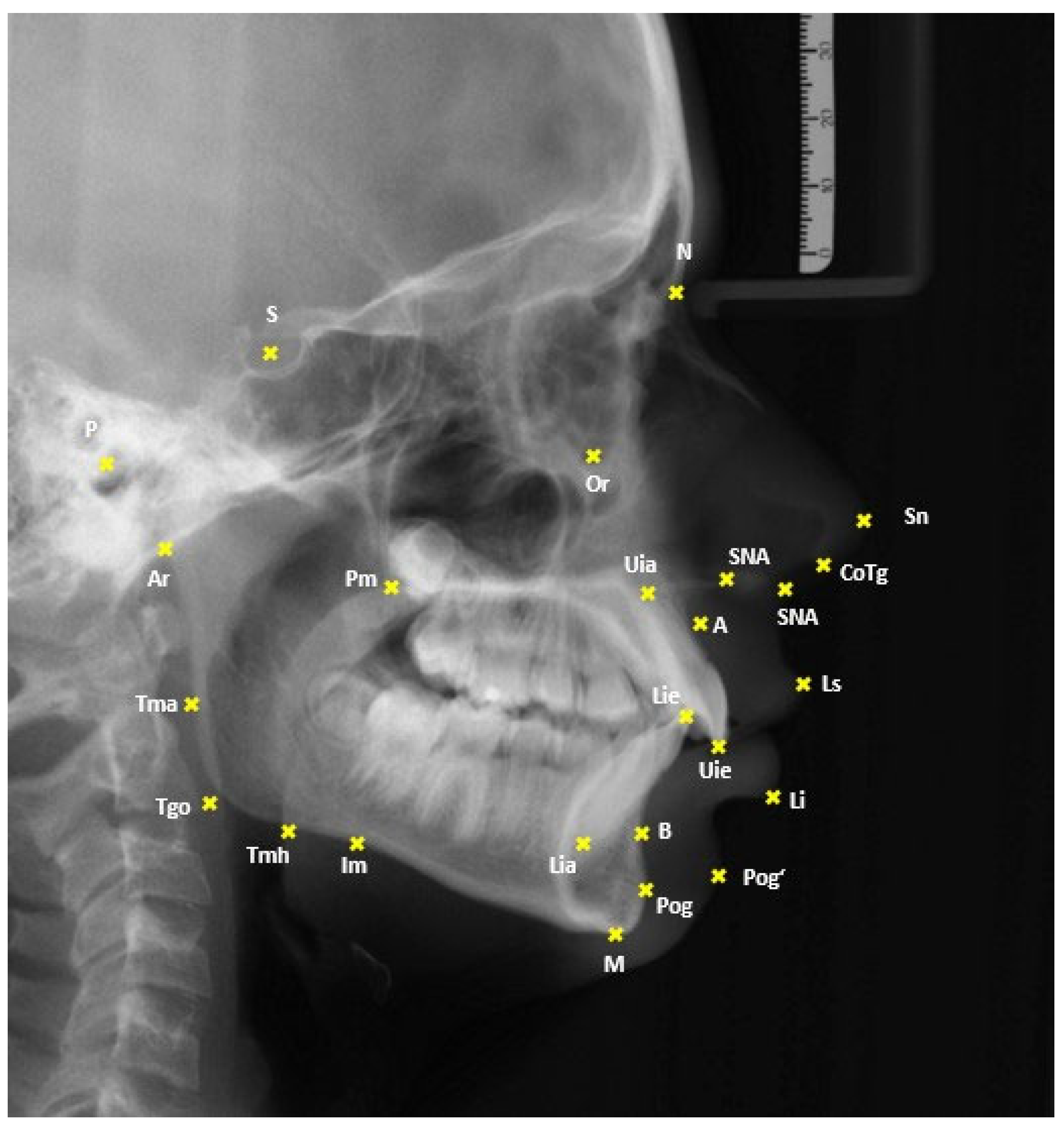
| Landmark/Measurement | Abbreviation | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Sella | S | Center of the pituitary fossa |
| Nasion | N | Most anterior point along the nasofrontal suture |
| Anterior Nasal Spine | ANS | Tip of the anterior nasal spine |
| Pterygomaxillary Fissure | Pm | Intersection of the posterior margin of the maxillary body with the contour of both soft and hard palates |
| Point A | A | Deepest point of the concavity on the frontal contour of the alveolar process of the maxilla |
| Upper Incisal Edge | Uie | Incisal tip of the most anterior upper central incisor |
| Upper Incisal Apex | Uia | Root apex of the most anterior upper central incisor |
| Lower Incisal Edge | Lie | Incisal tip of the most anterior lower central incisor |
| Lower Incisal Apex | Lia | Root apex of the most anterior lower central incisor |
| Point B | B | Deepest point of the concavity on the frontal contour of the alveolar process of the mandible |
| Menton | M | Lowest point of the mandibular symphysis |
| Masseteric Notch | Im | Point of the deepest cranial concavity of the horizontal mandibular ramus |
| Articulare | Ar | Intersection of the posterior contour of the mandibular condyle with the clivus of the cranial base |
| Tagent Menton Horizontal | Tmh | Tangential point from Menton to the horizontal ramus at the mandibular angle |
| Tagent Menton Ascendance | Tma | Tangential point from Articulare to the ascending ramus at the region of the mandibular angle |
| Gonion Tangential Point | Tgo | Intersection of the lines Me-Tmh and Ar-Tma |
| Porion | P | Most superior point of the external auditory meatus |
| Orbitale | Or | Most inferior point of the bony orbit |
| Upper Lip | Ls | Point of greatest anterior projection of the upper lip |
| Lower Lip | Li | Point of greatest anterior projection of the lower lip |
| Nasal Tip | Ns | Most anterior point of the nasal tip |
| Soft Tissue Pogonion | Pog’ | Most anterior point of the soft tissue chin |
| Subnasale | Sn | Point where the upper lip meets the nasal columella |
| Columella Tangent Point | CoTg | Tangential point from Subnasale to the nasal columella |
| SNA Angle | SNA | This angle is made by the reference lines S-N and N-A; it provides information about the positional relationship of the maxilla to the cranial base. |
| SNB Angle | SNB | This angle is formed by the reference lines S-N and N-B. It allows assessment of the sagittal position of the mandible. |
| ANB Angle | ANB | This angle is formed by the reference lines Nasion-Point A and Nasion-Point B. It provides insight into the sagittal relationship between the mandible and maxilla. |
| Interincisal Angle | UiLi | This angle is built by the axes of the upper incisors (Uie-Uia) and the lower incisors (Lie-Lia). It is measured dorsally and shows the relationship between the axes of the anterior teeth. It is also a good indicator of bimaxillary dental protrusion. A smaller angle indicates more protruded anterior teeth. |
| Upper Incisor Angle | UiSNAPm | This angle is constructed between the axis of the upper incisors and the maxillary plane (Spa-Pm). It provides information about the inclination of the first upper incisors in relation to the basal plane of the maxilla. |
| Lower Incisor Angle | LiMeTmh | This angle is between the axis of the lower incisors and the mandibular plane (Me-Tmh). It shows the inclination of the first mandibular incisors relative to the mandibular plane. |
| Upper Incisor to Nasion Line Angle | UiNS | This angle is formed by the axis of the upper incisors and the NS line. It provides information about the inclination of the first upper incisors relative to the N-S line. |
| Mandibular Incisor to Frankfurt Horizontal Angle | LiFH | This angle is formed by the axis of the lower incisors and the Frankfurt Horizontal (P-Or). It shows the inclination of the first lower incisors relative to the Frankfurt Horizontal plane. |
| Distance Ls-Esthetic Plane | Ls-E | This distance is measured from the upper lip to the Ricketts Esthetic Plane (Ns-Pog‘) at a 90-degree angle. It assesses the harmonious appearance of the lip profile relative to the soft tissue components of the nose and chin. |
| Distance Li-Esthetic Plane | Li-E | This distance is measured from the lower lip to the Esthetic Plane according to Ricketts, vertical to the Esthetic Plane. It also provides insight into the harmonious appearance of the lip profile relative to the soft tissue components of the nose and chin. |
| Distance Ls-SR Line | Ls-SR | This distance is measured from the upper lip to the SR Line (a perpendicular to the Nasion–Sella line, minus seven degrees at the Sella). It helps in evaluating the lip position relative to a bony reference plane. |
| Distance Li-SR Line | Li-SR | This distance is measured from the lower lip to the SR Line (a perpendicular to the Nasion–Sella line, minus seven degrees at the Sella). It helps in evaluating the lip position relative to a bony reference plane. |
| Nasolabial Angle | LsSnCoTg | This angle is formed by the upper lip tangent (Ls-Sn) and the columella tangent (Sn-CoTg).42 It gives information about the upper part of facial convexity, specifically the prominence of the upper lip in profile. |
| Anterior Face Height | AFH | This distance is measured from the Nasion to the Menton. It describes the anterior facial height. |
| Posterior Face Height | PFH | This distance is measured from the Sella to the Gonion Tangent Point. It describes the posterior facial height. |
| Facial Height Ratio | S-Tgo/N-Me | This is calculated using the formula Ratio = (Distance S-Tgo * 100)/Distance N-Me. The ratio indicates the proportion of posterior to anterior facial height. |
| Groups | Ex | NonEx | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time Point | T0 | T1 | T0 | T1 | ||||
| Measurements | Average/Median * | SD/1. -3. Quartile ** | Average/Median * | SD/1. -3. Quartile ** | Average/Median * | SD/1. -3. Quartile ** | Average/Median * | SD/1. -3. Quartile ** |
| SNA (°) | 79.49 | 3.87 | 79.41 | 4.12 | 80.74 | 3.66 | 80.54 | 3.84 |
| SNB (°) | 75.56 | 3.87 | 75.68 | 3.98 | 76.4 | 3.67 | 76.86 | 3.83 |
| ANB (°) | 3.92 | 2.34 | 3.73 | 2.2 | 4.37 | 1.98 | 3.66 | 2 |
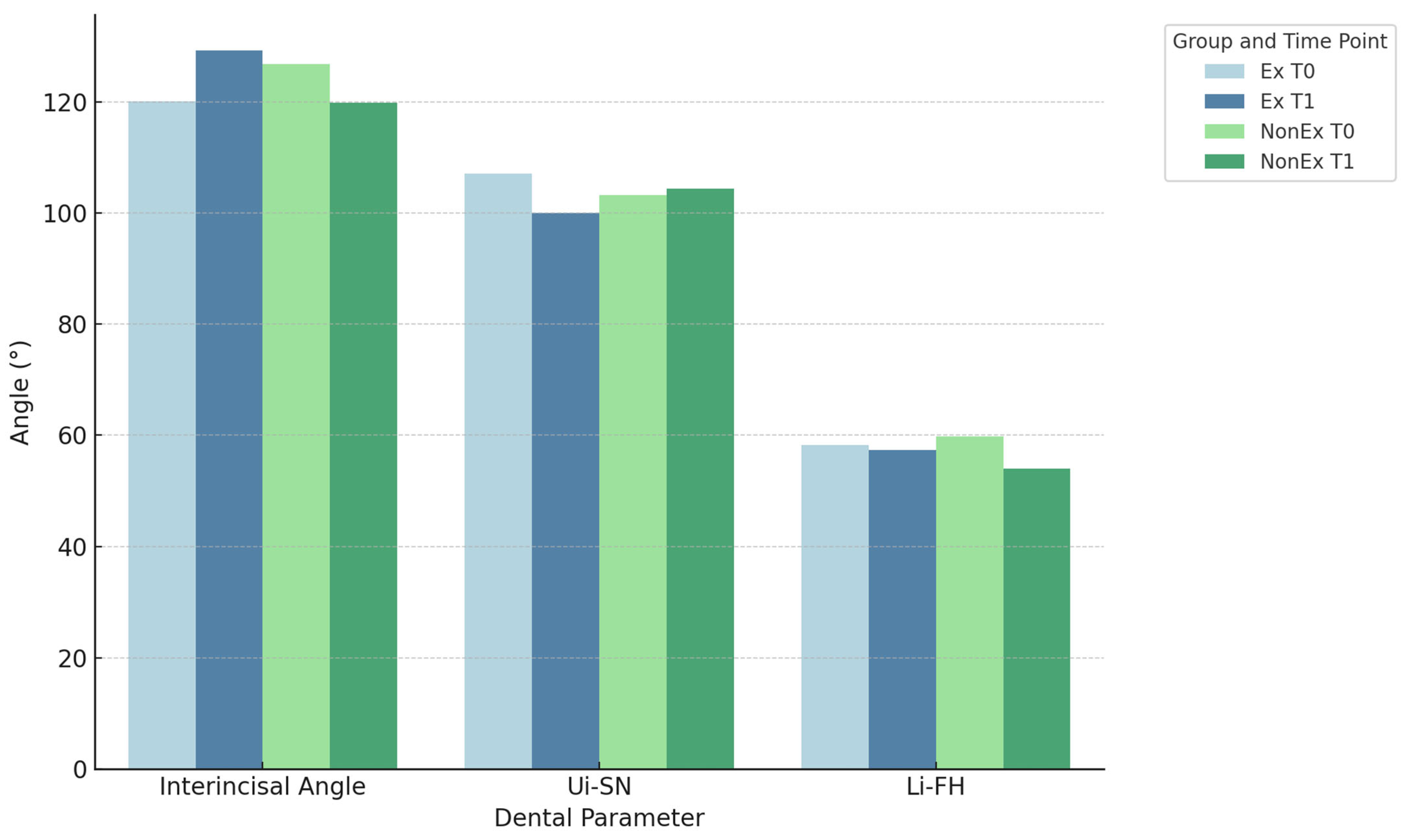
| Interincisal angle (°) | 120.07 | 12.08 | 129.23 * | 122.31–133.48 ** | 126.84 | 9.03 | 119.85 * | 114.73–123.85 ** |
| Nasiolabial angle (°) | 99.21 | 12.52 | 101.25 * | 99.08/104.98 | 99.97 | 8.7 | 101.4 * | 92.98–106.6 ** |
| Ui-SN (°) | 107.1 | 9.07 | 99.98 | 6.35 | 103.18 | 7.1 | 104.36 | 7.57 |
| Li-FH (°) | 58.25 | 6.77 | 57.4 * | 54.23–62.98 ** | 59.77 | 7.37 | 54.05 * | 51.03–59.9 ** |
| Ui—SNA-Pm (°) | 65.95 * | 58.1–70.25 ** | 71.78 | 5.91 | 68.95 * | 64.58–71.4 ** | 67.11 | 7.02 |
| Li-Me-Tmh (°) | 82.6 | 6.59 | 84.19 | 8.23 | 83 | 6.6 | 79.53 | 8.29 |
| Ls-E (mm) | −1.18 | 3.2 | −3.13 | 2.8 | −1.25 | 2.09 | −2.84 | 2.35 |
| Li-E (mm) | 1.18 | 3.74 | −0.09 | 3.56 | 0.53 | 2.54 | 0.15 | 2.72 |
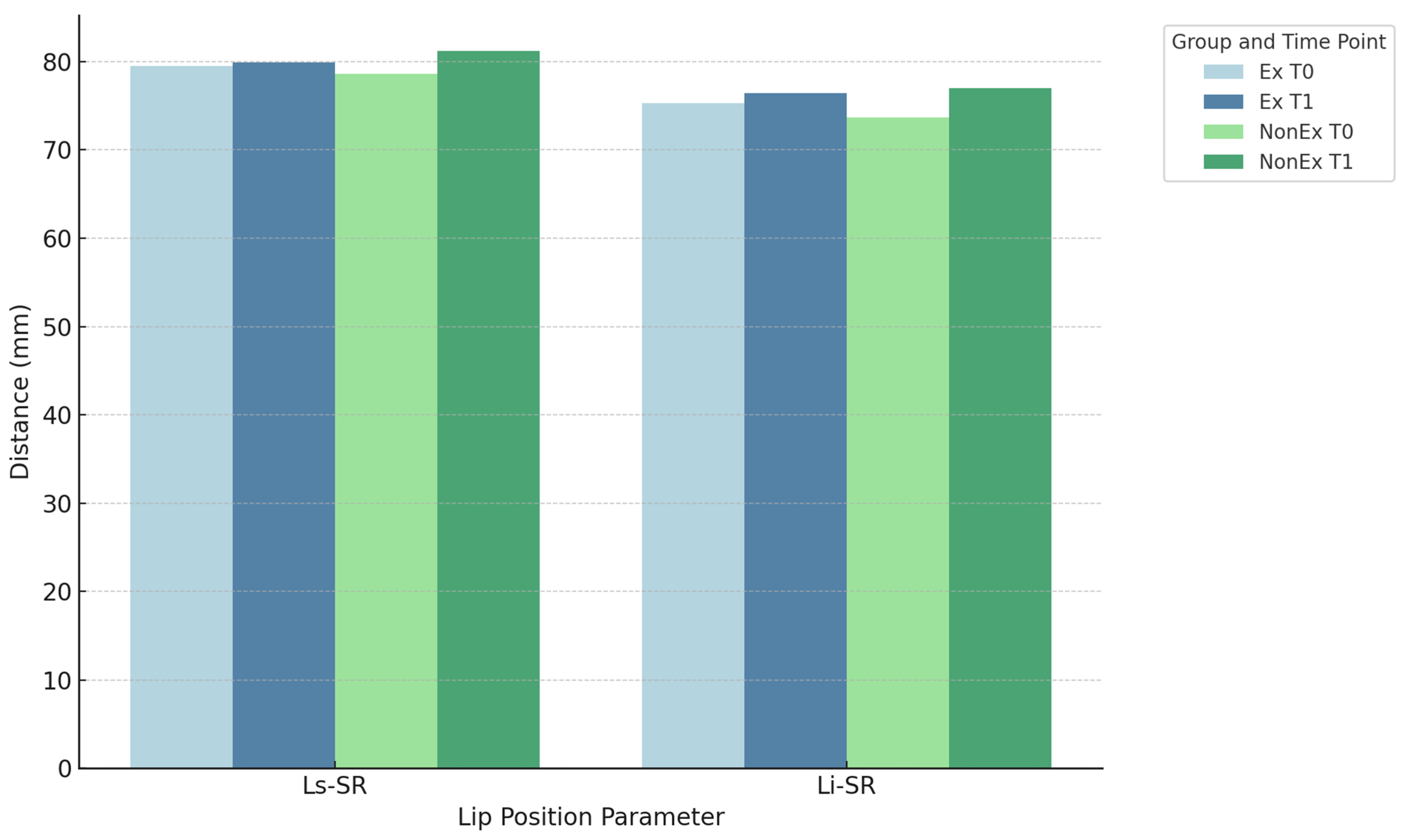
| Ls-SR (mm) | 79.53 | 5.75 | 79.9 | 5.89 | 78.61 | 5.26 | 81.2 | 5.68 |
| Li-SR (mm) | 75.29 | 6.88 | 76.4 | 6.78 | 73.68 | 5.37 | 77.02 | 6.92 |
| AFH (mm) | 107.1 * | 105–109.7 ** | 110.58 * | 108.69–114.54 ** | 106.8 * | 103.3–111.85 ** | 114.85 * | 109.23–122.43 ** |
| PFH (mm) | 67.37 | 5.29 | 70.95 | 5.87 | 70.83 | 6.11 | 77.04 | 6.5 |
| S-Tgo/N-Me | 63.36 | 5.23 | 64.38 | 5.48 | 65.64 | 4.97 | 66.27 | 5.26 |
| Group Ex | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurements | Average/Median * | SD/1. -3. Quartile ** | p-Value | Effect Size Cohen/Rosenthal | Rating |
| SNA (°) | 0.15 | 1.4 | 0.55 | 0.1 | 1 |
| SNB (°) | −0.17 | 1.28 | 0.44 | 0.14 | 1 |
| ANB (°) | 0.39 | 1.24 | 0.08 | 0.32 | 1 |
| Interincisal angle (°) | −9.14 | 12.1 | <0.01 | 0.76 | 2 |
| Nasiolabial angle (°) | −2.66 | 10.28 | 0.15 | 0.26 | 1 |
| Ui-SN (°) | 7.01 | 7.98 | <0.01 | 0.88 | 3 |
| Li-FH (°) | −1.06 | 7.76 | 0.43 | 0.14 | 1 |
| Ui—SNA-Pm (°) | −7.38 | 7.6 | <0.01 | 0.97 | 3 |
| Li-Me-Tmh (°) | −1.68 | 7.79 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 1 |
| Ls-E (mm) | −2.19 | 1.07 | <0.01 | 2.05 | 3 |
| Li-E (mm) | −1.25 | 1.94 | <0.01 | 0.65 | 2 |
| Ls-SR (mm) | −0.15 * | −7.3–3.7 ** | 0.77 | 0.05 | 0 |
| Li-SR (mm) | −1.54 | 3.64 | 0.06 | 0.42 | 1 |
| AFH (mm) | −3.65 * | −13.5–−0.1 ** | <0.01 | 0.62 | 3 |
| PFH (mm) | −3.93 | 3.14 | <0.01 | 1.3 | 3 |
| S-Tgo/N-Me | −0.97 | 1.47 | <0.01 | 0.66 | 2 |
| Group NonEx | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurements | Average/Median * | SD/1. -3. Quartile ** | p-Value | Effect Size Cohen/Rosenthal | Rating |
| SNA (°) | −0.1 * | −2.4–2.9 ** | 0.73 | 0.04 | 0 |
| SNB (°) | −0.45 | 1.43 | 0.06 | 0.32 | 1 |
| ANB (°) | 0.65 | 1.31 | <0.01 | 0.5 | 2 |
| Interincisal angle (°) | 5.05 | 8.23 | <0.01 | 0.61 | 2 |
| Nasiolabial angle (°) | 0.22 | 6.78 | 0.85 | 0.03 | 1 |
| Ui-SN (°) | −0.88 | 6.28 | 0.4 | 0.14 | 1 |
| Li-FH (°) | 3.57 | 5.34 | <0.01 | 0.67 | 2 |
| Ui—SNA-Pm (°) | 1.3 | 5.97 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 1 |
| Li-Me-Tmh (°) | 3.46 | 5.39 | <0.01 | 0.64 | 2 |
| Ls-E (mm) | −2 * | −4.8–4.7 ** | <0.01 | 0.5 | 3 |
| Li-E (mm) | −0.42 | 1.45 | 0.09 | 0.29 | 1 |
| Ls-SR (mm) | −2.6 | 2.7 | <0.01 | 0.95 | 3 |
| Li-SR (mm) | −3.4 | 3.25 | <0.01 | 1.05 | 3 |
| AFH (mm) | −8.51 | 6.01 | <0.01 | 1.41 | 3 |
| PFH (mm) | −6.24 | 3.93 | <0.01 | 1.59 | 3 |
| S-Tgo/N-Me | −0.69 | 1.33 | <0.01 | 0.52 | 2 |
| Measurements | p-Value | Effect Size Cohen/Rosenthal | Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| SNA (°) | 0.77 | 0.04 | 1 |
| SNB (°) | 0.39 | 0.2 | 1 |
| ANB (°) | 0.39 | 0.21 | 1 |
| Interincisal angle (°) | <0.01 | 1.38 | 3 |
| Nasiolabial angle (°) | 0.18 | 0.33 | 1 |
| Ui-SN (°) | <0.01 | 1.11 | 3 |
| Li-FH (°) | 0.01 | 0.7 | 2 |
| Ui—SNA-Pm (°) | <0.01 | 1.28 | 3 |
| Li-Me-Tmh (°) | <0.01 | 0.77 | 2 |
| Ls-E (mm) | 0.28 | 0.14 | 1 |
| Li-E (mm) | 0.06 | 0.51 | 2 |
| Ls-SR (mm) | <0.01 | 0.39 | 2 |
| Li-SR (mm) | 0.05 | 0.55 | 2 |
| AFH (mm) | 0.02 | 0.29 | 1 |
| PFH (mm) | 0.02 | 0.63 | 2 |
| S-Tgo/N-Me | 0.4 | 0.2 | 1 |
| Measurements | p-Value | Effect Size Cohen/Rosenthal | Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| SNA (°) | 0.47 | 0.25 | 1 |
| SNB (°) | 0.17 | 0.49 | 1 |
| ANB (°) | 0.02 | 0.83 | 3 |
| Interincisal angle (°) | 0.02 | 0.86 | 3 |
| Nasiolabial angle (°) | 0.43 | 0.28 | 1 |
| Ui-SN (°) | 0.96 | 0.02 | 0 |
| Li-FH (°) | <0.01 | 0.47 | 2 |
| Ui—SNA-Pm (°) | 0.67 | 0.15 | 0 |
| Li-Me-Tmh (°) | <0.01 | 1.2 | 3 |
| Ls-E (mm) | 0.02 | 0.49 | 2 |
| Li-E (mm) | 0.03 | 0.94 | 3 |
| Ls-SR (mm) | 0.12 | 0.34 | 2 |
| Li-SR (mm) | 0.34 | 0.41 | 1 |
| AFH (mm) | 0.09 | 0.37 | 2 |
| PFH (mm) | 0.01 | 1.18 | 3 |
| S-Tgo/N-Me | <0.01 | 0.45 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bühling, S.; Schmied, S.; Eslami, S.; Brandt, S.; Plein, N.; Kopp, S.; Sayahpour, B. The Impact of Damon Self-Ligating Orthodontic Therapy on Soft Tissue and Incisor Inclination: Extraction vs. Non-Extraction Treatment. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9265. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179265
Bühling S, Schmied S, Eslami S, Brandt S, Plein N, Kopp S, Sayahpour B. The Impact of Damon Self-Ligating Orthodontic Therapy on Soft Tissue and Incisor Inclination: Extraction vs. Non-Extraction Treatment. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9265. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179265
Chicago/Turabian StyleBühling, Sarah, Sabrina Schmied, Sara Eslami, Silvia Brandt, Nicolas Plein, Stefan Kopp, and Babak Sayahpour. 2025. "The Impact of Damon Self-Ligating Orthodontic Therapy on Soft Tissue and Incisor Inclination: Extraction vs. Non-Extraction Treatment" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9265. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179265
APA StyleBühling, S., Schmied, S., Eslami, S., Brandt, S., Plein, N., Kopp, S., & Sayahpour, B. (2025). The Impact of Damon Self-Ligating Orthodontic Therapy on Soft Tissue and Incisor Inclination: Extraction vs. Non-Extraction Treatment. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9265. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179265






