Abstract
(1) Background: Over the years, technology and space missions have advanced, although the development of potential functional food and food supplements must be improved for maintaining astronauts’ health and helping them overcome space-specific challenges during long missions. (2) Scope and approach: Using a review approach, this study aimed to investigate the potential of functional food to counteract radiation and microgravity spaceflight-related health problems. (3) Results: Microgravity and space radiation affect the body’s biochemical processes and increase levels of reactive oxygen species, which may lead to health problems, including musculoskeletal deconditioning, cardiovascular degeneration, disruptions in gastrointestinal health, ocular problems, alterations to the immune system, and hormonal imbalances, among others. In addition to medical care, functional food plays a key role as a countermeasure against space-induced physiological issues. Previous research showed that functional food rich in flavonoids, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, minerals, antioxidant compounds, proteins, probiotics, or prebiotics strengthens the immune system and reduces risks associated with long spaceflights, such as bone density loss, muscle atrophy, oxidative stress, and other health alterations. (4) Conclusions: Despite the fundamental role of functional food in spaceflights, the main challenges remain in preserving and packaging these foods to ensure their safety on long space missions. Future innovations include 3D food printing, space algae cultivation, and novel preservation technologies.
1. Introduction
Over the years, humans have developed new tools that have created the world we know today. However, in a period of less than 150 years, the technological revolution has been so great that it has changed the way we see the world, the way we communicate, and the way we behave [1]. For example, inventions such as the light bulb or the telephone were precursors to the electrical grid that supplies the entire world, or the improvement in telecommunications, allowing us to talk to other people thousands of kilometers away, perform operations on a patient with a robot, or even leave planet Earth in a spaceship (Figure 1).
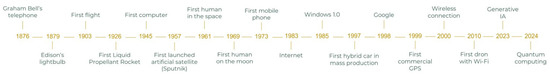
Figure 1.
Chronology of the advances in technology.
In the latter case, the possibility and viability of reaching Mars, or civilian space travel, or even colonizing other planets, is being considered [2]; this would open the door to the possibility that anyone can undertake space travel.
Although it would be a unique opportunity to observe planet Earth from outside and see it from another perspective, the reality is quite different. The changes that the human body undergoes psychologically and physiologically are many and of various types; for this reason, astronauts are professionals who prepare for years to ensure that the tasks entrusted to them are carried out correctly and without putting their lives at risk.
First, candidates are presented, and a selection process is carried out based on their academic qualifications. Once this has been carried out, they are called for an initial interview, a medical evaluation, and basic psychological tests.
Once the results have been obtained, they are used to carry out another selection process, and the selected candidates are called again for an in-depth medical evaluation, another personal interview, and psychological and psychiatric tests to determine their performance under stress, communication, teamwork, and response to fatigue due to lack of sleep.
Practical cases are also put forward to assess their capacity for reaction, speed in decision-making, and the candidate’s personality in moments of tension. This entire process, which has been briefly summarized, lasts for months to finally obtain a selection of suitable candidates [3]. However, after all this selection process, there is still the training to become an astronaut. This process is divided into several types of training: basic training, advanced training, mission-specific training, onboard training, and maintaining competence. All this training ranges from technical knowledge (robotics, system operation, etc.) to new skills or improving acquired skills (diving, aircraft flight, etc.); they are even trained in extreme survival conditions in case the landing is not in the right place and there is a deviation on re-entry to Earth. Therefore, they would be prepared to survive until the necessary help arrived [3].
The five risks associated with space missions that have been classified by NASA to be taken into account for mission planning are the following (Figure 2) [4,5]:
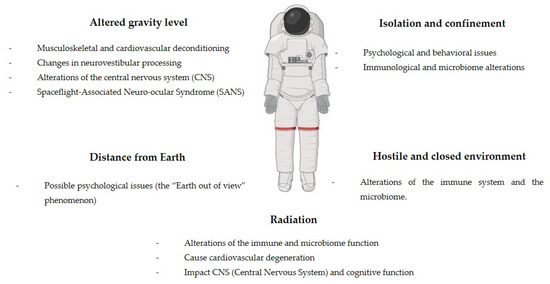
Figure 2.
Main risks and effects in spaceflights.
- -
- Altered gravity level;
- -
- Isolation and confinement;
- -
- Distance from Earth;
- -
- Hostile and closed environment;
- -
- Radiation.
One of the most important aspects of taking care of the crew’s health is food. The characteristics that are taken into account regarding food during space travel are safety, stability, palatability, nutritiousness, not producing a large amount of waste, variety, and reliability in extreme environments [6].
2. Scientific Literature Review
In identifying interesting scientific publications that address problems associated with spaceflight and astronauts, as well as potential solutions through functional foods, this review was based on the 2020 update of the PRISMA approach [7]. The literature was searched in different databases: (i) Scopus, (ii) FSTA, and (iii) ScienceDirect; the keywords used were the following: “spaceflights”, “astronauts”, “functional foods”, “radiation”, “bioactive compounds”, and “microgravity”. In the search for articles, there was overlap, mainly between Scopus and ScienceDirect, although for the identification figures, this overlap was resolved without duplicating the selected articles. Most of the articles that were selected (71%, from 2018 to 2025) were included in the Journal Citation Reports (JCRs). The selection process is shown in Figure 3. The review is structured in different sections: (i) Health Problems Associated with Spaceflights, (ii) The Essential Role of Functional Food in Spaceflights, (iii) Challenges and Future Perspectives, and (iv) Conclusions.
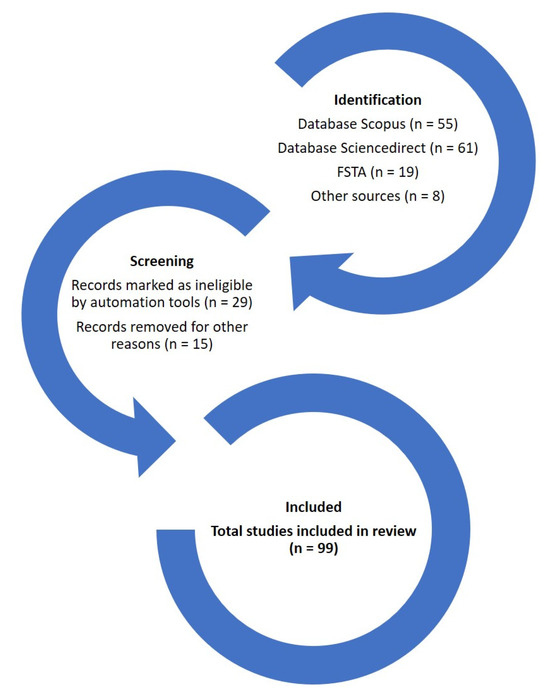
Figure 3.
Diagram of the selection of scientific publications.
3. Health Problems Associated with Spaceflights
Microgravity affects the body’s biochemical processes by altering the physiological conditions under which organisms have evolved on Earth. The absence of gravitational mechanical stress, changes in fluid distribution, disruptions in cellular signaling, sensory modifications, and other environmental factors in microgravity contribute to these biochemical alterations. Furthermore, space radiation exposure can increase levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), inducing neuroinflammation in the brain [8,9].
Therefore, the main biochemical changes that may occur include the following:
- -
- Musculoskeletal deconditioning, as a loss of bone and muscle mass;
- -
- Cardiovascular degeneration;
- -
- Disruptions to gastrointestinal health;
- -
- Ocular problems;
- -
- Alterations to the immune system;
- -
- Hormonal imbalances;
- -
- Effects of oxidative stress, increasing ROS.
3.1. Loss of Bone and Muscle Mass
Microgravity-induced bone loss can be more severe than osteopenia on Earth, and prolonged exposure to weightlessness may increase the risk of osteoporosis and bone fractures. Bone loss begins rapidly and can be detected within the first few months of exposure to microgravity, whereas bone density recovery and remineralization in Earth gravity are slower processes and, in some cases, are not fully restored.
Despite individual variability in bone mass, not all regions of the skeleton are equally affected by weightlessness. According to NASA, astronauts can lose 1% to 1.5% of bone density per month in the proximal femur, the hip, and the spine, and the loss of bone mass in the whole body and legs, which are rich in cortical bone, is 0.3–0.4% per month. This rapid bone loss can put space members at risk of bone fractures and early-onset osteoporosis due to spaceflight, since recovery after return to Earth may take at least three to four years [10].
Bone demineralization during spaceflight also increases urinary calcium excretion and elevates the risk of kidney stone formation. Under physiological conditions, blood calcium and phosphate kinetics are regulated by the parathyroid gland through the secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH), which influences bone remodeling, renal homeostasis, and intestinal Ca2+ absorption through stimulation of active vitamin D production. As a consequence of microgravity-induced bone demineralization, released calcium reaches high levels in the blood, which suppresses PTH secretion. This inhibition reduces vitamin D production in the intestine, decreases renal Ca2+ reabsorption, and causes hypercalciuria, increasing the risk of kidney stones. Then, microgravity may disrupt the hormonal balance, which regulates bone metabolism [11,12].
Regarding muscle mass, without gravitational loading, skeletal muscle enters a state of disuse. Previous research indicates that muscle loss does not occur at a constant rate throughout a mission, with the most significant reductions observed in antigravity muscles, including the lower back, abdominals, thighs, and lower legs. Notable muscle atrophy has been recorded in knee extensors, ranging from −5% to −15%, knee flexors, ranging from −5% to −14%, plantar flexors, ranging from −6% to −15%, and intrinsic lower back muscles (around −10%), even during short missions [13].
A decline of around −46% in muscle protein synthesis appears to be the main factor driving muscle atrophy. These physiological changes lead to decreased strength, slower contraction speed, and reduced power output, limiting the transfer of energy to the tendons and bones necessary for joint movement [14].
Microgravity-induced osteopenia and muscle loss represent a significant health risk for astronauts (Figure 4). Therefore, dietary supplementation such as functional food could be a feasible countermeasure to employ to prevent and reduce bone and muscle mass loss during long-duration space missions.
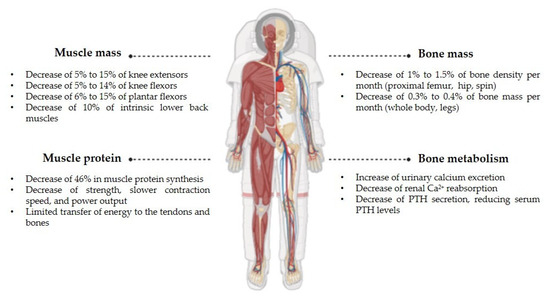
Figure 4.
Main alterations in the bones and muscles of astronauts during spaceflights.
3.2. Cardiovascular Problems
Cardiovascular problems are a significant concern for astronauts due to the unique conditions of space travel. These effects can pose risks during re-entry and recovery, making it essential to monitor cardiovascular health and develop countermeasures to protect astronauts during long-duration missions.
One of the most common disorders that astronauts face during space flights, caused by weightlessness, is cardiovascular deconditioning. This problem leads to orthostatic intolerance, with an estimated 80% of astronauts experiencing orthostatic intolerance upon returning to Earth [15], higher resting heart rate, hypovolemia (reduction in circulating blood volume), or even a decrease in cardiac baroreflex sensitivity (heart rate readjustment system) [16].
In a very well-schematized summary table prepared by Baselet, Miranda, Rehnberg, Van Rompay, Baatout, and Tabury [15], the differences in the different parameters of the cardiovascular system between short- and long-duration space flights are evident (Table 1).

Table 1.
Changes induced in astronauts’ cardiovascular system.
The baroreflex system is essential in the human body because it maintains the balance between all the body’s systems in order to survive and function properly (this is known as homeostasis). When, for example, a person is upright in gravity conditions on Earth, blood pressure is low and cardiac output is low; however, when this parameter of gravity is altered, it produces vasoconstriction and elevated cardiac output and a change in blood volume, all of which are conditions that are not ideal for the human body [16]. Several studies have also described loss of muscle mass in the heart (myocardial atrophy); in one of them, the loss of mass reached 12% in the left ventricle, and in another, approximately 0.74 g per week also in the left ventricle [17,18,19]. Apart from these cardiac problems, arrhythmias are a problem that has been described in several studies on such renowned special missions as Apollo, SkyLab, or Mir, where, in some of them, the majority of the crew showed some problem with arrhythmia. However, this problem is not only problematic now but can also pose a risk for long journeys such as those planned for Mars. Although at present, it is not known specifically what can cause these arrhythmias, it is hoped that these symptoms will be alleviated in the future [19,20,21,22].
3.3. Disruptions to Gastrointestinal Health
The space environment presents relevant challenges to human physiology, such as disruptions in gastrointestinal health. Efficient nutrient absorption is essential for maintaining overall health, especially in extreme environments such as space. The intestinal barrier plays a crucial role in regulating nutrient uptake while preventing harmful substances from entering the bloodstream. However, increased intestinal permeability, often referred to as “leaky gut”, can compromise this balance, leading to systemic inflammation and impaired nutrient absorption [23].
The gut microbiota, particularly the bacterial communities residing in the colon, significantly influence intestinal permeability and digestive efficiency. Beneficial microbes contribute to the breakdown of complex carbohydrates, fiber fermentation, and the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which help maintain gut barrier integrity and support metabolic functions. A well-balanced microbiota enhances the absorption of essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and amino acids while preventing the proliferation of harmful bacteria that can disrupt intestinal homeostasis. Therefore, a diverse and rich microbiome is generally associated with gut health, with Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes as the dominant phyla, which contribute to immune regulation and cytokine synthesis, and influence metabolism, nutrition, and appetite control through SCFA production [24]. Nevertheless, disruptions in microbiota composition, due to stress, diet, or environmental factors like microgravity, can lead to increased intestinal permeability, reducing the body’s ability to absorb nutrients efficiently. For instance, a decline in key bacterial species involved in fiber degradation and anti-inflammatory processes can weaken the gut barrier, leading to systemic effects such as inflammation, glucose dysregulation, and immune dysfunction (Figure 5).
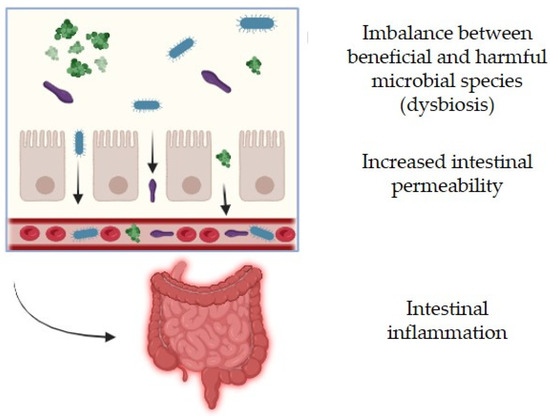
Figure 5.
Alterations to intestinal health. Created by BioRender.com.
Previous research on microbiome changes in spaceflight conditions has been conducted on animals and humans. Dong et al. [25] studied the fecal microbiome and short-chain fatty acids of crew members with periodic intake of prepackaged food in a ground-based space station simulator for 50 days. This study showed significant changes in some bacterial genera, like the increase in Ruminococcus compared to control individuals. Additionally, this increase was related to the higher abundance of SCFA, especially the levels of butyric acid, since Ruminococcus is a butyrate-producing population, which has anti-inflammatory properties. This increase might be an adaptation that facilitates reduced inflammation. Changes in microbiome composition have also been observed in ground-based spaceflight analog missions. With the MARS500 study, the longest controlled human confinement study to date, important changes in the relative abundance of astronaut microbiome species were revealed during a long-term confinement of 520 days, monitoring the gut microbiome of six male crew members in a simulated Mars habitat. During this period, they performed tasks similar to those of a real mission, and fecal samples were collected at different times [26].
The results revealed significant alterations in microbiome composition over time, including a decrease in species involved in resistant starch degradation, anti-inflammatory processes, and insulin sensitivity (Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, Rumino-coccus bromii, Blautia luti, Anaerostipes hadrus, Roseburia faecis, and Lactobacillus rogosae), aligning with crew-reported symptoms associated with intestinal inflammation and insulin resistance.
Ilyin [27] also showed alterations in the composition of the gut microbiome in post-flight astronauts, having a deficiency in Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus and an increased isolation of conventional pathogens (E. coli, Enterobacterium, and Clostridium). This generated dysbiosis because of the imbalance between beneficial and harmful microbial species, suggesting a potential link between microbiome shifts and physiological or metabolic disturbances in the host. In the context of astronaut health, such dysbiosis could compromise intestinal integrity, leading to increased permeability, inflammation, and impaired nutrient absorption. Given the critical role of gut microbiota in immune function and metabolic regulation, these imbalances may contribute to gastrointestinal discomfort, weakened immunity, and heightened susceptibility to illness during space missions. Understanding and mitigating these microbiome alterations is essential for maintaining astronaut health and optimizing performance in space.
Furthermore, previous studies showed similar trends in the gut microbiome compared to ground controls, analyzing fecal samples from mice on spaceflight-induced changes over 37 days. These changes included an altered community structure, specifically, an increased Firmicutes-to-Bacteroides ratio and a reduction in Lactobacillus [28]. Other research also demonstrated that a simulated weightlessness environment has a significant impact on gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism in rats, which may trigger changes in inflammatory cytokines and lead to intestinal tissue inflammation [29].
Therefore, in space missions, where optimal nutrient utilization is critical for astronauts’ health, maintaining a stable gut microbiota and preventing excessive intestinal permeability is vital. Strategies such as dietary interventions, prebiotics, probiotics, and fiber-rich foods can help sustain a resilient gut microbiome, ensuring effective nutrient absorption and overall physiological stability. Understanding the intricate relationship between nutrient absorption, intestinal permeability, and microbiota is essential for both space exploration and addressing gastrointestinal health challenges on Earth.
3.4. Ocular Problems
Space travel presents unique challenges for astronauts, and one of the most intriguing is the impact on their eye health. The microgravity environment, along with other factors such as radiation and confined living conditions, can lead to various ocular issues. As space exploration continues to advance, understanding and addressing these eye-related challenges is crucial for ensuring the safety and well-being of astronauts on missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
There are various eye problems associated with space flights, one of which is also common in the civilian population, namely cataracts. Several studies have confirmed that astronauts are more likely to suffer from cataracts, mainly due to the effects of radiation [30,31].
Another of the most worrying eye problems for astronauts or for the correct efficiency of the mission is Spaceflight Associated Neuro-Ocular Syndrome (SANS). It has been detected in astronauts on missions of more than 6 months and produces edema in the optic disc, a flattening of the eyeball, and other types of problems, meaning it produces visual and morphological changes in the eye itself [32,33,34]. Despite the many studies carried out on SANS, there is still no single consensus on its formation, but a plausible cause has been established, which is the displacement of the cephalic fluid towards the brain, as well as the orbits, due to the conditions in microgravity [32].
Another syndrome associated with eye problems is Dry Eye Syndrome (DES). Data shows that up to 30% of the crew on the ISS (International Space Station) suffer from this syndrome. Microgravity affects the distribution of fluids on the surface of the eye, which leads to an impairment in tear drainage [35].
Another eye problem associated with astronauts is the decrease in Dynamic Visual Acuity (DVA). This ability is based on visualizing moving objects; a decrease in this ability can cause dizziness or even endanger the mission or the astronaut if it happens when they are performing a critical task [34].
3.5. Alterations to the Immune System
The immune system’s response to the changes that occur during spaceflight has also been studied to protect crew members. The effects described in the studies include decreased immune cell activity, reduced production of signaling cells, and impaired phagocytic function; these differences in normal function have been associated with microgravity [36]. However, radiation is not the only factor that can affect the immune system. Radiation can also weaken the immune system, causing direct damage to immune cells and, thus, suppressing immune function [8]. In addition, confinement in a spacecraft can be another factor that alters the immune system, due to the reduced exposure to other types of micro-organisms, which can cause alterations in immune cells and their proper function [37].
A study by Mehta et al. [38] showed the first confirmed case of herpes zoster in a laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). Normally, T cells are responsible for dealing with this type of herpesvirus; however, with the aforementioned weakening of the immune system, the weakening of these cells’ functions allows for the reactivation of this already latent herpesvirus in the individual. Possible causes in astronauts include stress, microgravity, circadian rhythm disturbance, or even isolation.
3.6. Hormonal Imbalances
In humans, spaceflights cause disruptions in the body’s normal hormone levels due to the unique conditions of space, such as microgravity, radiation, and altered sleep cycles. These imbalances can affect various physiological processes, including metabolism, immune function, bone density, stress response, and cardiovascular regulation, among others.
Previous studies found significant changes in the endocrine system’s response to stress and metabolic challenges during spaceflights, demonstrating the physiological adaptations humans undergo in microgravity. This research found higher levels in plasma of growth hormone, prolactin, and catecholamines, compared to preflight responses. Additionally, plasma glucose and insulin levels were elevated both during spaceflight and in the post-flight period [39]. Thus, the secretion of growth hormone, which plays a crucial role in metabolism, muscle maintenance, and bone growth, could be affected due to microgravity and other space-related stressors. The increased levels may be a compensatory response to muscle and bone loss, having also an impact on Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1), since the growth hormone regulates IGF-1 production, which is essential for tissue growth and repair. In space, IGF-1 levels may decrease, contributing to reduced muscle and bone regeneration [8].
In addition, microgravity exposure triggers a stress response, leading to altered cortisol levels. Elevated cortisol due to spaceflight-related stress can have widespread physiological effects, including disruptions in glucose regulation and energy balance, suppressed immune response, increased vulnerability to infections, and accelerated bone loss due to impaired calcium metabolism. Additionally, microgravity-induced stress affects the levels of epinephrine and norepinephrine, which can have an impact on cardiovascular function and potential long-term effects on the body’s ability to adapt to microgravity environments [40,41].
Regarding the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis and the hypothalamic–pituitary–ovarian axis, which regulate reproductive hormone function in men and women, respectively, some alterations occurred. Previous studies showed a reduction in circulating testosterone during spaceflight, which may even have an impact on the secretion of growth hormone in male astronauts. In women astronauts, spaceflight-related stress, circadian rhythm disruptions, and altered hormonal signaling may lead to irregular or suppressed menstrual cycles, and potential alterations in estrogen and progesterone secretion may occur, which could impact bone health, metabolism, and immune function [42,43,44,45]. In fact, one of the most worrying changes detected in macaques undergoing radiation in the 1980s was endometriosis. This condition was observed from 7 days to 17 years after irradiation, making it a vitally important factor for women to monitor [46].
Mathyk et al. [47] also confirmed that insulin and estrogen signaling were altered during and after spaceflight in rodents and humans. Pathway analysis demonstrated spaceflight-induced changes in insulin resistance, estrogen signaling, stress response, and viral infection.
The effects of spaceflight on reproductive hormone regulation in both men and women remain an important area of research, especially for long-duration missions where prolonged hormonal disruptions may impact astronaut health and fertility. Further studies are needed to fully understand how spaceflight alters reproductive function and whether these changes have long-term consequences.
3.7. Effects of Oxidative Stress
Spaceflight exposes astronauts to unique environmental conditions, such as microgravity, space radiation, metabolic changes, intense physical activity, and psychological stress, which contribute to oxidative stress, a condition where the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) exceeds the body’s ability to neutralize them with antioxidants, leading to cellular damage and long-term health risks.
Microgravity alters mitochondrial function, leading to excessive ROS production [48]. Additionally, the reduced activity of antioxidant enzymes makes it more difficult for cells to neutralize oxidative damage, further increasing stress on cellular systems. Microgravity might induce changes in fluid distribution within the body, affecting oxygen delivery, blood flow, and waste removal, leading to increased ROS production and contributing to oxidative stress [8]. Recent research confirmed that extended exposure to microgravity has been linked to increased lipid peroxidation and its byproducts in both human and rodent brains post-flight, signaling heightened oxidative stress levels. Similarly, ground-based microgravity simulations demonstrated significant alterations in oxidative stress markers (reactive nitrogen species, malondialdehyde, and total antioxidant capacity) in various regions of the rat brain [49].
Exposure to charged particle radiation, such as galactic cosmic rays and solar particle events, is known to intensify oxidative stress, leading to central nervous system dysfunction and cognitive impairment. Then, high-energy radiation increases DNA damage, lipid peroxidation, and protein oxidation. These ionizing radiations interact with water molecules in the body, generating highly reactive ROS radicals, which can lead to long-term cellular mutations, an increased risk of cancer, and other degenerative diseases [50].
Altered metabolism and intense exercise can also play a role. In microgravity, calcium imbalances affect mitochondrial activity, contributing to oxidative stress. Furthermore, astronauts must engage in high-intensity exercise to counteract muscle and bone loss, which leads to increased oxygen consumption and greater ROS generation [48].
These combined factors make oxidative stress a significant concern for astronauts, particularly during long-duration missions, where prolonged exposure to these stressors can have serious health implications (Table 2).

Table 2.
Main effects of oxidative stress during spaceflights.
4. The Essential Role of Functional Food in Spaceflights
In addition to medical care, nutrients are essential for maintaining astronauts’ health and helping them overcome space-specific challenges during long missions. While macronutrient recommendations for spaceflight are similar to those on Earth, previous research has shown that certain nutrients play a key role as countermeasures against space-induced physiological issues [9] (Figure 6).
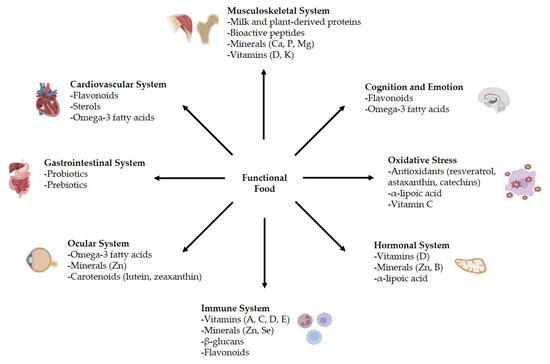
Figure 6.
Main roles of functional food in spaceflight-related diseases.
Functional food contains bioactive compounds that offer both nutritional and pharmaceutical benefits; these could help to maintain overall health in astronauts during long-duration space missions, strengthen the immune system, and reduce risks associated with microgravity, such as bone density loss, muscle atrophy, oxidative stress, and other health alterations [51].
Recent research is focused on optimizing astronaut health, with supplemental food in tablet form being an additional practical solution due to its stability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of administration [52]. These tablets contain essential nutrients such as vitamins (C, E, B-complex, A, and K), minerals (calcium, zinc, magnesium, and iron), proteins, carbohydrates, and other bioactive compounds, being designed to prevent diseases, accelerate recovery, and enhance physiological functions, critical aspects for astronauts facing extreme conditions in space.
Therefore, functional food offers a promising approach to counteracting negative health impacts and maintaining the optimal health of astronauts.
Protein-based functional food, such as whey protein and plant-derived proteins, supports muscle maintenance, while essential amino acids stimulate muscle protein synthesis [53,54]. Calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, vitamin D, and vitamin K play a crucial role in bone health, reducing the risk of osteoporosis in space [55,56]. Additionally, some bioactive peptides, like collagen-derived peptides, have shown promise in supporting bone regeneration and mineralization [57]. In addition to nutrition, astronauts can reduce the risk of bone loss through an effective exercise program and minimal amounts of medication [8].
Functional food rich in antioxidant compounds (polyphenols and flavonoids), plant sterols, or omega-3 fatty acids has been shown to promote cardiovascular health by reducing inflammation, improving circulation, and maintaining healthy cholesterol levels [58].
For gastrointestinal health, probiotics (like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species) can help restore gut balance, while prebiotics (fiber-rich oligosaccharides) serve as fuel for beneficial bacteria. Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome is crucial for nutrient absorption, metabolic regulation, and immune system integrity. Previous research showed the positive impacts of prebiotics on the gut microbiome in mice under altered gravity [51,59]. Buckley et al. [60] reported that fermented soy-based foods, enriched with probiotic lactic acid bacteria (Streptococcus thermophilus ST5, Bifidobacterium longum R0175, and Lactobacillus helveticus R0052) and soy isoflavones, offer a promising dietary solution, showing in vitro anti-inflammatory properties, and improving vitamin B1 and B6 levels and enhanced isoflavone biotransformation, increasing the availability of bioactive aglucone forms.
Moreover, it is essential to confirm whether microgravity affects the resilience and functionality of probiotics. Recent studies evaluated Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 4356 under simulated microgravity conditions, comparing its growth, stress tolerance, and gene expression to standard conditions. The results showed no significant differences, suggesting that L. acidophilus retains its probiotic properties in space, making it a viable option for astronaut health support [61].
Apart from this micro-organism, Table 3 (prepared by Sonali et al. [62]) clearly and concisely shows the tolerance of these micro-organisms in microgravity and radiation conditions.

Table 3.
Suitability of probiotics under radiation/microgravity conditions.
Many astronauts experience ocular problems, so micronutrients, like carotenoids (lutein, zeaxanthin), minerals (zinc), and omega-3 fatty acids, may support retinal health and reduce oxidative damage [63,64,65]. Additionally, other antioxidants such as resveratrol, tocopherols, and anthocyanins contained in functional food also help to protect against radiation-induced visual impairments [66].
Regarding the immune system, vitamins A, C, D, and E, along with zinc and selenium, play critical roles in immune defense, enhancing white blood cell function and reducing inflammation [67]. Additionally, beta-glucans and plant-derived flavonoids have shown potential in modulating immune responses and reducing the impact of radiation-induced immune suppression [68].
Spaceflight also disrupts hormonal homeostasis. Zinc, vitamin D, and boron support a positive effect in hormonal changes and promising therapy against cancer [69,70,71]. Berberine, alpha-lipoic acid, and cinnamon extract enhance glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity [72,73,74].
Antioxidants such as resveratrol, curcumin, astaxanthin, and green tea catechins help neutralize high levels of oxidative stress as free radicals and protect cellular integrity [75,76,77,78]. Mitochondria-targeted compounds like alpha-lipoic acid and N-acetylcysteine may further enhance cellular defense mechanisms [79,80]. Recent studies revealed that vitamin C-rich vegetables could help mitigate oxidative stress due to radiation [81].
Cognitive performance and emotional stability are essential for astronauts, as prolonged isolation, disrupted circadian rhythms, and high-stress situations can impair decision-making and reaction time. Omega-3 fatty acids, flavonoids, and polyphenols have demonstrated neuroprotective effects, supporting brain function and reducing the risk of cognitive decline [82,83,84]. Additionally, compounds like melatonin and adaptogens can help regulate sleep patterns and mitigate stress-related effects, crucial for maintaining psychological resilience in space.
Nevertheless, one of the greatest challenges in space missions is food storage and nutrient preservation. Traditional space food, often freeze-dried or vacuum-sealed, has limitations in nutrient retention over time. Supplementation tablets, also called nutraceutical tablets, provide a compact and efficient alternative, delivering concentrated doses of essential nutrients in a stable form that resists degradation [52].
Additionally, tablets reduce storage volume and weight—critical factors in spacecraft design. By integrating key macronutrients (proteins, carbohydrates, and fats) and bioactive compounds into small, easy-to-consume formats, astronauts can meet their dietary requirements without excessive food bulk. Furthermore, since microgravity can alter digestion and metabolism, carefully engineered products ensure optimal bioavailability and absorption, enhancing their effectiveness in space conditions [52].
Space food needs to be lightweight, compact, and easy to store. Several techniques to preserve and package space food have been developed, such as freeze-drying, dehydration, and irradiation, to make it safe and long-lasting. Over time, space food has evolved, and astronauts now have a wider range of options [8].
5. Future Perspectives, Challenges, and Limitations
Developing food systems that can provide adequate nutrition for extended periods while maintaining freshness, taste, and nutritional value is a major focus. Scientists are exploring ways to formulate personalized nutrition tailored to an astronaut’s individual needs [85]. Future innovations may involve the incorporation of new food processing techniques or 3D-printed functional food, which could allow astronauts to customize their nutrient intake in real-time based on their health status. Ensuring food safety in space is essential to prevent contamination and adverse health effects.
Another promising field is algae-based functional food, such as spirulina, due to its high nutritional content [86]. Research is also underway into their cultivation in space, such as spirulina and microgreens, which could serve as fresh sources of bioactive compounds and antioxidants during long-duration missions, thus reducing dependence on prepackaged supplies.
The continued development of these functional food supplements represents a key step in preparing for deep-space missions and future colonization efforts.
5.1. Algae
Generally, the most common form of food on a spacecraft is packaged products, although a partial alternative to this type of food would be algae. These living organisms could be used for long-duration space travel and could be cultivated onboard the spacecraft [87]. The beneficial properties associated with algae are diverse; a study by Chellamanimegalai et al. [88] analyzed the composition of eight different algae. The results showed that they could provide proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates, as a basic contribution to the human body. Apart from this basic composition, the contribution of minerals was analyzed, and the results showed that the content in both macrominerals and microminerals, even minerals and magnesium (515–1138 mg/100 g), had a range that is double or triple (according to algae) what is necessary per day in both men and women. These magnesium values are important due to the previous mention of this mineral in the musculoskeletal system.
It is important to note that Dictyota Flabellata reached a zinc concentration of 4.5 mg/100 g, which is a third of what is necessary per day in adults. In Section 4, the relationship and direct benefit of zinc were established for the eye system, the hormonal system, and the immune system.
One of the most important compounds in algae is beta-glucan; this compound has been shown to have antioxidant capacity and anti-inflammatory activities, fundamental properties to avoid oxidative stress and reinforce the immune system of astronauts [89].
At the level of other benefits, content in Omega-3, which is fundamental for the cardiovascular system, the ocular system, or even for cognition and emotion [90], has also been described in five different algae of the Baltic Sea, as shown in Figure 6.
Moreover, the benefit of algae is that everything is edible; therefore, no waste would be generated. However, for growth, it would be necessary to generate energy onboard the spacecraft to illuminate the photobioreactor and enable photosynthesis [91]. Solving these problems with algae would be a major step toward changing the way food is fed during spaceflight.
5.2. Pressure-Assisted Thermal Sterilization (PATS)
Pressure-assisted thermal sterilization (PATS) is a technique based on high-pressure processing (HPP), except that the sample undergoes reduced sterilization. This technique maintains properties such as texture, color, flavor, etc., in better condition than other thermal processes. NASA applied this technique to fruits and found that both the color and the internal cellular structure remained better than with other techniques, although it has also been observed that some pigments, such as chlorophyll, suffer degradation. However, this technique has not yet been implemented and needs to be developed on a large scale to corroborate its viability for shelf life [92,93]. The improvement of this technique would make it possible to keep food intact (in terms of properties) to send to space for nutrition, providing astronauts with a more complete range of compounds.
5.3. Microwave-Assisted Thermal Sterilization (MATS)
MATS technology pursues the same objective as PATS technology, that is, to preserve food properties to the maximum. The application of technology is carried out over a short time, at high temperature, and at a frequency lower than that of a domestic microwave. NASA already used it to evaluate its viability, and the results in color and texture were promising, although the container seal was not adequate, and the function of the container as an oxygen barrier did not occur. This leads to the loss of pigments such as chlorophyll, vitamins, and oxidation of fats. The FDA is strict in its requests when evaluating a new system; therefore, the requirements of this organization with respect to MATS technology were not met, including microbiological validation [94,95].
5.4. 3D Food Printing
One of the most promising alternatives is 3D printing, a highly versatile technology that allows for everything from creating surgical instruments to improving astronaut nutrition. Regarding the latter, the creation of this type of food has unique characteristics, so it is important to understand the standard 3D printing process [96].
The most widely used option is extrusion; however, not all materials used in the development of these foods are equal. Some materials are printable in their native form, such as starches, but there are also so-called non-printable materials, which cannot be printed directly and require preprocessing. This preprocessing sometimes involves adding hydrocolloids or other types of products to the material to improve the quality of these foods and make them printable [97]. However, the process continues with post-processing based on different conventional techniques (drying, cooking, etc.), which is a fundamental part of the process for the final quality of the food [98].
The implementation of this technology in spaceflight poses several challenges that must be overcome, such as the cost of the machinery, the changes that can occur in materials influenced by microgravity, legislation, and even safety, among others [97]. If all these obstacles are overcome, it would be possible to create food in situ (on the spacecraft), which could reduce the necessary food storage and supply chain, thereby benefiting from time and energy savings—critical elements in this type of mission. It could also be more sensorially acceptable [99].
5.5. Challenges and Limitations
The challenges facing the future in this area are numerous, although potential options for improvement are already emerging. This review identified several limitations worth highlighting, as they are intrinsically related to the challenges. First, the lack of concrete data, which organizations such as NASA, ESA, or Roscosmos may have but which are not made available to the scientific community. These cases include, for example, concrete data on the compositional changes in food subjected to different environments or the bioavailability/bioaccessibility of astronauts, among other cases.
Another limitation of this study is the alternatives presented in Section 5. These proposals require a greater number of studies to thoroughly understand their net benefits and to develop them appropriately for the proper applicability of all these promising techniques.
Moreover, at the overall level of studies, the number of individuals who can be subjected to these environments is small, as they are limited exclusively to astronauts. All these challenges will be overcome in the future, just like many others that have already been overcome and are a thing of the past.
6. Conclusions
The data presented in this review demonstrate that the role of functional food in preventing or repairing these damages at different levels of the human body is fundamental. By simultaneously addressing multiple physiological challenges, functional food constitutes a crucial tool for maintaining astronaut health and performance during space missions. The variety of nutrients and compounds provided demonstrates that a balanced diet may aid in preparing astronauts to prevent or minimize health problems during long-term space missions. Therefore, the integration of customized and space-optimized functional food formulations in any format will play a vital role in ensuring the long-term success of human space exploration, including missions to Mars.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.C.-V. and D.C.-B.; writing—original draft preparation, J.C.-V. and D.C.-B.; writing—review and editing, J.C.-V. and D.C.-B.; supervision, D.C.-B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Prado, C.G. How Technology Is Changing Human Behavior: Issues and Benefits, 1st ed.; Praeger: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.M. The Evolution of Life: Big Bang to Space Colonies; Precocity Press: Dallas, TX, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sgobba, T.; Landon, L.B.; Marciacq, J.-B.; Groen, E.; Tikhonov, N.; Torchia, F. Chapter 16—Selection and training. In Space Safety and Human Performance; Sgobba, T., Kanki, B., Clervoy, J.-F., Sandal, G.M., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Waltham, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 721–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelhamer, M.; Fogarty, J. Chapter 3—Crew health—Psychological, biological, and medical issues and the need for a systems approach. In Interstellar Travel; Johnson, L., Roy, K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 81–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandial, R.; Hoshide, R.; Waters, J.D.; Limoli, C.L. Space-brain: The negative effects of space exposure on the central nervous system. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2018, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, P.; Hughes, J.; Gamage, T.V.; Knoerzer, K.; Ferlazzo, M.L.; Banati, R.B. Long term food stability for extended space missions: A review. Life Sci. Space Res. 2022, 32, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakkumadugula, A.; Pankaj, L.; Alqahtani, A.S.; Ullah, R.; Ercisli, S.; Murugan, R. Space nutrition and the biochemical changes caused in Astronauts Health due to space flight: A review. Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 100875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M. Food systems for long-term spaceflight: Understanding the role of non-nutrient polyphenols in astronauts’ health. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.K. Osteoclasts and Microgravity. Life 2020, 10, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genah, S.; Monici, M.; Morbidelli, L. The Effect of Space Travel on Bone Metabolism: Considerations on Today’s Major Challenges and Advances in Pharmacology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, J.; Takeda, T.; Sato, Y. Interventions to prevent bone loss in astronauts during space flight. Keio J. Med. 2005, 54, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narici, M.V.; de Boer, M.D. Disuse of the musculo-skeletal system in space and on earth. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 403–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackney, K.J.; English, K.L. Protein and Essential Amino Acids to Protect Musculoskeletal Health during Spaceflight: Evidence of a Paradox? Life 2014, 4, 295–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselet, B.; Miranda, S.; Rehnberg, E.; Van Rompay, C.; Baatout, S.; Tabury, K. Chapter 30—Cardiovascular diseases in spaceflight. In Precision Medicine for Long and Safe Permanence of Humans in Space; Krittanawong, C., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariom, S.K.; Nelson, E.J.R. Cardiovascular adaptations in microgravity conditions. Life Sci. Space Res. 2024, 42, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett-Bakelman, F.E.; Darshi, M.; Green, S.J.; Gur, R.C.; Lin, L.; Macias, B.R.; McKenna, M.J.; Meydan, C.; Mishra, T.; Nasrini, J.; et al. The NASA Twins Study: A multidimensional analysis of a year-long human spaceflight. Science 2019, 364, eaau8650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacNamara, J.P.; Dias, K.A.; Sarma, S.; Lee, S.M.C.; Martin, D.; Romeijn, M.; Zaha, V.G.; Levine, B.D. Cardiac Effects of Repeated Weightlessness During Extreme Duration Swimming Compared with Spaceflight. Circulation 2021, 143, 1533–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernice, N.A.; Meydan, C.; Afshinnekoo, E.; Mason, C.E. Long-term spaceflight and the cardiovascular system. Precis. Clin. Med. 2020, 3, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anzai, T.; Frey, M.A.; Nogami, A. Cardiac arrhythmias during long-duration spaceflights. J. Arrhythmia 2014, 30, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, Z.S.; Brunstetter, T.J.; Tarver, W.J.; Whitmire, A.M.; Zwart, S.R.; Smith, S.M.; Huff, J.L. Red risks for a journey to the red planet: The highest priority human health risks for a mission to Mars. NPJ Microgravity 2020, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, R.; Qaisar, R.; Al-Dahash, K.; Altelly, A.H.; Elmoselhi, A.B.; Khan, N.A. Cardiovascular changes under the microgravity environment and the gut microbiome. Life Sci. Space Res. 2024, 40, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.S.; Wang, J.; Yannie, P.J.; Ghosh, S. Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction, LPS Translocation, and Disease Development. J. Endocr. Soc. 2020, 4, bvz039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesei, D.; Jewczynko, A.; Lynch, A.M.; Urbaniak, C. Understanding the Complexities and Changes of the Astronaut Microbiome for Successful Long-Duration Space Missions. Life 2022, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.-S.; Lan, H.-Y.; Yu, Y.-B.; Li, H.-F.; Lin, J.-M. Altered fecal microbiomes and short chain fatty acids of crew members with periodic intake of prepackaged food in a ground-based space station simulator for 50 days. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 36, 101480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brereton, N.J.B.; Pitre, F.E.; Gonzalez, E. Reanalysis of the Mars500 experiment reveals common gut microbiome alterations in astronauts induced by long-duration confinement. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 2223–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, V.K. Microbiological status of cosmonauts during orbital spaceflights on Salyut and Mir orbital stations. Acta Astronaut. 2005, 56, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Green, S.J.; Chlipala, G.E.; Turek, F.W.; Vitaterna, M.H. Reproducible changes in the gut microbiome suggest a shift in microbial and host metabolism during spaceflight. Microbiome 2019, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, S.; Zhong, C.; Liu, L.; Wang, G.; Huang, X.; Yang, X.; Yang, H.; Li, L. The influence of simulated weightlessness on the composition and function of gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism products. Life Sci. Space Res. 2024, 41, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chylack, L.T., Jr.; Peterson, L.E.; Feiveson, A.H.; Wear, M.L.; Manuel, F.K.; Tung, W.H.; Hardy, D.S.; Marak, L.J.; Cucinotta, F.A. NASA study of cataract in astronauts (NASCA). Report 1: Cross-sectional study of the relationship of exposure to space radiation and risk of lens opacity. Radiat. Res. 2009, 172, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastegar, Z.; Eckart, P.; Mertz, M. Radiation-induced cataract in astronauts and cosmonauts. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2002, 240, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.G.; Mader, T.H.; Gibson, C.R.; Tarver, W.; Rabiei, P.; Riascos, R.F.; Galdamez, L.A.; Brunstetter, T. Spaceflight associated neuro-ocular syndrome (SANS) and the neuro-ophthalmologic effects of microgravity: A review and an update. NPJ Microgravity 2020, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, J.; Tarver, W.; Brunstetter, T.; Mader, T.H.; Gibson, C.R.; Mason, S.S.; Lee, A. Spaceflight associated neuro-ocular syndrome: Proposed pathogenesis, terrestrial analogues, and emerging countermeasures. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 107, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waisberg, E.; Ong, J.; Paladugu, P.; Kamran, S.A.; Zaman, N.; Lee, A.G.; Tavakkoli, A. Dynamic visual acuity as a biometric for astronaut performance and safety. Life Sci. Space Res. 2023, 37, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, A.; Ong, J.; Waisberg, E.; Lee, A.G. Neurostimulation as a technology countermeasure for dry eye syndrome in astronauts. Life Sci. Space Res. 2024, 42, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayzafoon, M.; Meyers, V.E.; McDonald, J.M. Microgravity: The immune response and bone. Immunol. Rev. 2005, 208, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogoli, A. Space flight and the immune system. Vaccine 1993, 11, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.K.; Suresh, R.; Brandt, K.; Diak, D.M.; Smith, S.M.; Zwart, S.R.; Douglas, G.; Nelman-Gonzalez, M.; Clemett, S.; Brunstetter, T.; et al. Immune system dysregulation preceding a case of laboratory-confirmed zoster/dermatitis on board the International Space Station. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Glob. 2024, 3, 100244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macho, L.; Koška, J.; Kšinantová, L.; Pacak, K.; Hoff, T.; Noskov, V.B.; Grigoriev, A.I.; Vigaš, M.; Kvetňanský, R. The response of endocrine system to stress loads during space flight in human subject. Adv. Space Res. 2003, 31, 1605–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St-Martin, P.; Le Roux, E.; Bergouignan, A. Chapter 8—Metabolic adaptations to microgravity. In Precision Medicine for Long and Safe Permanence of Humans in Space; Krittanawong, C., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2025; pp. 91–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronca, A.E.; Baker, E.S.; Bavendam, T.G.; Beck, K.D.; Miller, V.M.; Tash, J.S.; Jenkins, M. Effects of sex and gender on adaptations to space: Reproductive health. J. Women’s Health 2014, 23, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimunová, M.; Paludo, A.C.; Bernaciková, M.; Bienertova-Vasku, J. The effect of space travel on human reproductive health: A systematic review. NPJ Microgravity 2024, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strollo, F. Adaptation of the human endocrine system to microgravity in the context of integrative physiology and ageing. Pflüg. Arch. 2000, 441, R85–R90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strollo, F.; Vassilieva, G.; Ruscica, M.; Masini, M.; Santucci, D.; Borgia, L.; Magni, P.; Celotti, F.; Nikiporuc, I. Changes in stress hormones and metabolism during a 105-day simulated Mars mission. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2014, 85, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strollo, F.; Vernikos, J. Aging-like metabolic and adrenal changes in microgravity: State of the art in preparation for Mars. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 126, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almukhtar, L.; Halicigil, C.; Patel, S.; Kohut, A.; Mathyk, B. Chapter 21—Spaceflight implications for precision medicine in the field of obstetrics and gynecology and its subspecialties. In Precision Medicine for Long and Safe Permanence of Humans in Space; Krittanawong, C., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2025; pp. 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathyk, B.A.; Tabetah, M.; Karim, R.; Zaksas, V.; Kim, J.; Anu, R.I.; Muratani, M.; Tasoula, A.; Singh, R.S.; Chen, Y.-K.; et al. Spaceflight induces changes in gene expression profiles linked to insulin and estrogen. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.P.; Tran, P.H.; Kim, K.-S.; Yang, S.-G. The effects of real and simulated microgravity on cellular mitochondrial function. NPJ Microgravity 2021, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.W.; Pecaut, M.J.; Stanbouly, S.; Nelson, G. Oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and the blood-brain barrier biomarkers on the brain response to spaceflight. Life Sci. Space Res. 2024, 43, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, K.B.; Mi, K.L.; Nelson, G.A.; Norman, R.B.; Patel, Z.S.; Huff, J.L. Ionizing radiation, cerebrovascular disease, and consequent dementia: A review and proposed framework relevant to space radiation exposure. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1008640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taroncher, M.; Vila-Donat, P.; Tolosa, J.; Ruiz, M.J.; Rodríguez-Carrasco, Y. Biological activity and toxicity of plant nutraceuticals: An overview. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, M.F.; Riaz, S.; Verma, D.K.; Waseem, M.; Goksen, G.; Ali, A.; Zeng, X.-A. Nutraceutical tablets: Manufacturing processes, quality assurance, and effects on human health. Food Res. Int. 2024, 197, 115197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennings, B.; Boirie, Y.; Senden, J.M.G.; Gijsen, A.P.; Kuipers, H.; van Loon, L.J.C. Whey protein stimulates postprandial muscle protein accretion more effectively than do casein and casein hydrolysate in older men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijk, F.J.; Hofman, Z.; Luiking, Y.C.; Furber, M.J.W.; Roberts, J.D.; van Helvoort, A.; van Dijk, M. Muscle Protein Synthesis with a Hybrid Dairy and Plant-Based Protein Blend (P4) Is Equal to Whey Protein in a Murine Ageing Model after Fasting. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coxam, V.; Davicco, M.-J.; Wauquier, F.; Wittrant, Y. Vitamine K et physiologie osseuse. Cah. Nutr. Diét. 2009, 44, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Behmadi, H.; Azarpazhooh, E.; Ramaswamy, H.S. Chapter 12—Functional foods for bone and joint health: Building a solid foundation. In Unleashing the Power of Functional Foods and Novel Bioactives; Sarkar, T., Smaoui, S., Petkoska, A.T., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2025; pp. 233–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, E. Osteogenic peptides in bone regeneration. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 3391–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, R.S.; Nirmal, N.P. Chapter 3—Functional foods for cardiovascular health: Nurturing a strong heart. In Unleashing the Power of Functional Foods and Novel Bioactives; Sarkar, T., Smaoui, S., Petkoska, A.T., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2025; pp. 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, D.; Blasco, S.; Hopkins, S.; Kelley, T.; Thompson, R.; Wilson, C.; Pecaut, M.; Fleshner, M. Impacts of prebiotic diet and altered gravity on mouse immune response, gut microbiome, and home cage behavior. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 114, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, N.D.; Champagne, C.P.; Masotti, A.I.; Wagar, L.E.; Tompkins, T.A.; Green-Johnson, J.M. Harnessing functional food strategies for the health challenges of space travel—Fermented soy for astronaut nutrition. Acta Astronaut. 2011, 68, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Wallace, S.; Stahl, S.; Voorhies, A.; Lorenzi, H.; Douglas, G.L. Response of Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 4356 to low-shear modeled microgravity. Acta Astronaut. 2017, 139, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonali, L.; Drisya Raj, M.P.; Pavithra, R.; Kanimozhi, N.V.; Suneetha, C.; Roopa Shri, B.; Sukumar, M. Functional foods for astronauts: Enhancing health and performance in microgravity and extreme environments. Space Habitat. 2025, 1, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grahn, B.H.; Paterson, P.G.; Gottschall-Pass, K.T.; Zhang, Z. Zinc and the Eye. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2001, 20, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, P.S.; Li, B.; Vachali, P.P.; Gorusupudi, A.; Shyam, R.; Henriksen, B.S.; Nolan, J.M. Lutein, zeaxanthin, and meso-zeaxanthin: The basic and clinical science underlying carotenoid-based nutritional interventions against ocular disease. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2016, 50, 34–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britten-Jones, A.C.; Craig, J.P.; Downie, L.E. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and corneal nerve health: Current evidence and future directions. Ocul. Surf. 2023, 27, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goz, B.; Ersoy, B.; Gulsunoglu-Konuskan, Z. Chapter 18—Functional foods for ocular health and vision. In Unleashing the Power of Functional Foods and Novel Bioactives; Sarkar, T., Smaoui, S., Petkoska, A.T., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2025; pp. 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojadoost, B.; Yitbarek, A.; Alizadeh, M.; Kulkarni, R.R.; Astill, J.; Boodhoo, N.; Sharif, S. Centennial Review: Effects of vitamins A, D, E, and C on the chicken immune system. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 100930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaclav, V.; Petr, S.; Luca, V. Chapter 8—Beta Glucan as Therapeutic Food. In Therapeutic Foods; Holban, A.M., Grumezescu, A.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, B.K.; Das, A. Chapter 9—Anticancer drugs from hormones and vitamins. In Natural Products as Anticancer Agents; Krishna Banik, B., Das, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 369–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taslim, N.A.; Rampengan, D.D.C.H.; Ramadhan, R.N.; Rahmawati, B.A.; Yumnanisha, D.A.; Wiyarta, E.; Mayulu, N.; Kim, B.; Surya, E.; Nurkolis, F. The Effect of Zinc Supplementation on Endocrine Parameters and Hormonal Profiles in Women Diagnosed with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2024, 8, 103758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, J.; Li, R.; Lin, J.; Gui, L.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Z.; Xia, W.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, S.; et al. Novel promising boron agents for boron neutron capture therapy: Current status and outlook on the future. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 511, 215795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pang, D.; Xing, D.; Wang, W.; Li, Q.; Liao, S.; Li, E.; Zou, Y. Cinnamon free phenolic extract regulates glucose absorption in intestinal cells by inhibiting glucose transporters. Food Biosci. 2023, 52, 102405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, M.; Paolini, E.; Meroni, M.; Jericó, D.; Córdoba, K.M.; Battistin, M.; Gatti, S.; Di Pierro, E.; Fontanellas, A.; Dongiovanni, P. The Alpha-Lipoic Acid Improves Glucose Metabolism and Hyperinsulinemia in Acute Intermittent Porphyria: A Nutritional Concept for the Management of Rare Disorders. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 17, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palai, S. Chapter 21—Berberine. In Nutraceuticals and Health Care; Kour, J., Nayik, G.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başak, F.; Kuşat, T.; Ersan, Y.; Kahraman, T. Titanium dioxide-induced fibrotic liver model and the therapeutic effect of resveratrol by modulation of α-SMA and 8-oHdG expressions, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Tissue Cell 2025, 93, 102748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, P. Chapter 13—Tea catechins as potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agents: Possibilities of drug development to promote healthy aging. In Plant Bioactives as Natural Panacea Against Age-Induced Diseases; Pandey, K.B., Suttajit, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Seidi, F.; Cai, Y.; Sun, Z.; Bian, H.; Dai, H.; Xu, T. Construction of curcumin-conjugated pH-responsive lignin-based nanoparticles for alleviating oxidative stress: Stability, antioxidant activity and biocompatibility. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 302, 140036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, A.; Sly, P.D.; Khachatryan, L.; Begum, N.; Yeo, A.J.; Robinson, P.D.; Cormier, S.A.; Fantino, E. Astaxanthin protects against environmentally persistent free radical-induced oxidative stress in well-differentiated respiratory epithelium. Redox Biol. 2025, 81, 103542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, E.J.; Agathokleous, E.; Dhawan, G.; Kapoor, R.; Calabrese, V. Protective effects of alpha lipoic acid (ALA) are mediated by hormetic mechanisms. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 177, 113805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.P.M.; Carlos, L.; Gayotto, C.; Tatai, C.; Della Nina, B.I.; Oliveira, M.G.; Shishido, S.M.; Lima, E.S.; Abdalla, D.S.; Laurindo, F.R.; et al. Protective effect of S-nitroso-acetilcysteine (SNAC) in experimental liver steatosis induced by choline deficient diet. Gastroenterology 2003, 124, A757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, A.; Yarbaksh, H.; Zarandi, B.F.B.B.; Yarbakhsh, R.; Ghadimi-Moghaddam, F.; Mortazavi, S.M.J.; Haghani, M.; Firoozi, D.; Sihver, L. Cultivation of Vitamin C-Rich Vegetables for Space-Radiation Mitigation. Radiation 2024, 4, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandradhara, D.; Amalraj, A.; Gopi, S. Chapter 12—Efficacy of dietary polyphenols for neuroprotective effects and cognitive improvements. In Nutraceuticals in Brain Health and Beyond; Ghosh, D., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhao, T.; Ma, W. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids attenuate cognitive impairment via the gut-brain axis in diabetes-associated cognitive dysfunction rats. Brain Behav. Immun. 2025, 127, 147–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.Y.H.; Sun, M.Y.Y.; Sommerville, N.; Ngan, M.P.; Ponomarev, E.D.; Lin, G.; Rudd, J.A. Soy flavonoids prevent cognitive deficits induced by intra-gastrointestinal administration of beta-amyloid. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 141, 111396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brawley, H.N.; Smith, S.M.; Zwart, S.R. Chapter 3—Spaceflight precision nutrition. In Precision Medicine for Long and Safe Permanence of Humans in Space; Krittanawong, C., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2025; pp. 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Bai, N.; Sun, Y.; Li, K.; Ruan, H.; Yan, B.; Hu, J.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, H.; et al. Spirulina platensis components mitigate bone density loss induced by simulated microgravity: A mechanistic insight. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockhart, J.A. The care and feeding of spacemen. Eng. Sci. 1959, 22, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Chellamanimegalai, P.; Deshmukhe, G.; Balange, A.K.; Layana, P. Unveiling the nutritional and antioxidant properties of brown algae resources (Dictyota J.V. Lamouroux) from the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea, Indian coast. Heliyon 2025, 11, e40693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Bhoyar, M.S.; Mohanty, C.S.; Chauhan, P.S.; Toppo, K.; Ratha, S.K. Untapping the potential of algae for β-glucan production: A review of biological properties, strategies for enhanced production and future perspectives. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 348, 122895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhila, Õ.; Paalme, T.; Tanilas, K.; Sarand, I. Omega-3 fatty acid and B12 vitamin content in Baltic algae. Algal Res. 2022, 67, 102860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayak, V. Chapter 20—Algae as sustainable food in space missions. In Biomass, Biofuels, Biochemicals; Varjani, S., Pandey, A., Bhaskar, T., Mohan, S.V., Tsang, D.C.W., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 517–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perchonok, M.H.; Douglas, G.L. The Spaceflight Food System: A Case Study in Long Duration Preservation. In Encyclopedia of Food Chemistry; Melton, L., Shahidi, F., Varelis, P., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Sun, D.-W.; Hogan, E.; Kelly, A.L. Chapter 1—High-Pressure Processing of Foods: An Overview. In Emerging Technologies for Food Processing, 2nd ed.; Sun, D.-W., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V.; Medina-Meza, I.; Candoğan, K.; Bermúdez-Aguirre, D. Advanced retorting, microwave assisted thermal sterilization (MATS), and pressure assisted thermal sterilization (PATS) to process meat products. Meat Sci. 2014, 98, 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, G.L.; Cooper, M.R.; Bermudez-Aguirre, D.; Sirmons, T. Risk of Performance Decrement and Crew Illness Due to an Inadequate Food System; NTRS-NASA Technical Reports Server: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, J.Y. 3D Printing Applications for Space Missions. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 2016, 87, 580–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhoshkumar, P.; Negi, A.; Moses, J.A. 3D printing for space food applications: Advancements, challenges, and prospects. Life Sci. Space Res. 2024, 40, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theagarajan, R.; Nimbkar, S.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Effect of post-processing treatments on the quality of three-dimensional printed rice starch constructs. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 44, e13772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caulier, S.; Doets, E.; Noort, M. An exploratory consumer study of 3D printed food perception in a real-life military setting. Food Qual. Prefer. 2020, 86, 104001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).