The Gradual Cyclical Process in Adaptive Gamified Learning: Generative Mechanisms for Motivational Transformation, Cognitive Advancement, and Knowledge Construction Strategy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Design
3. Methodology
3.1. Platform Selection
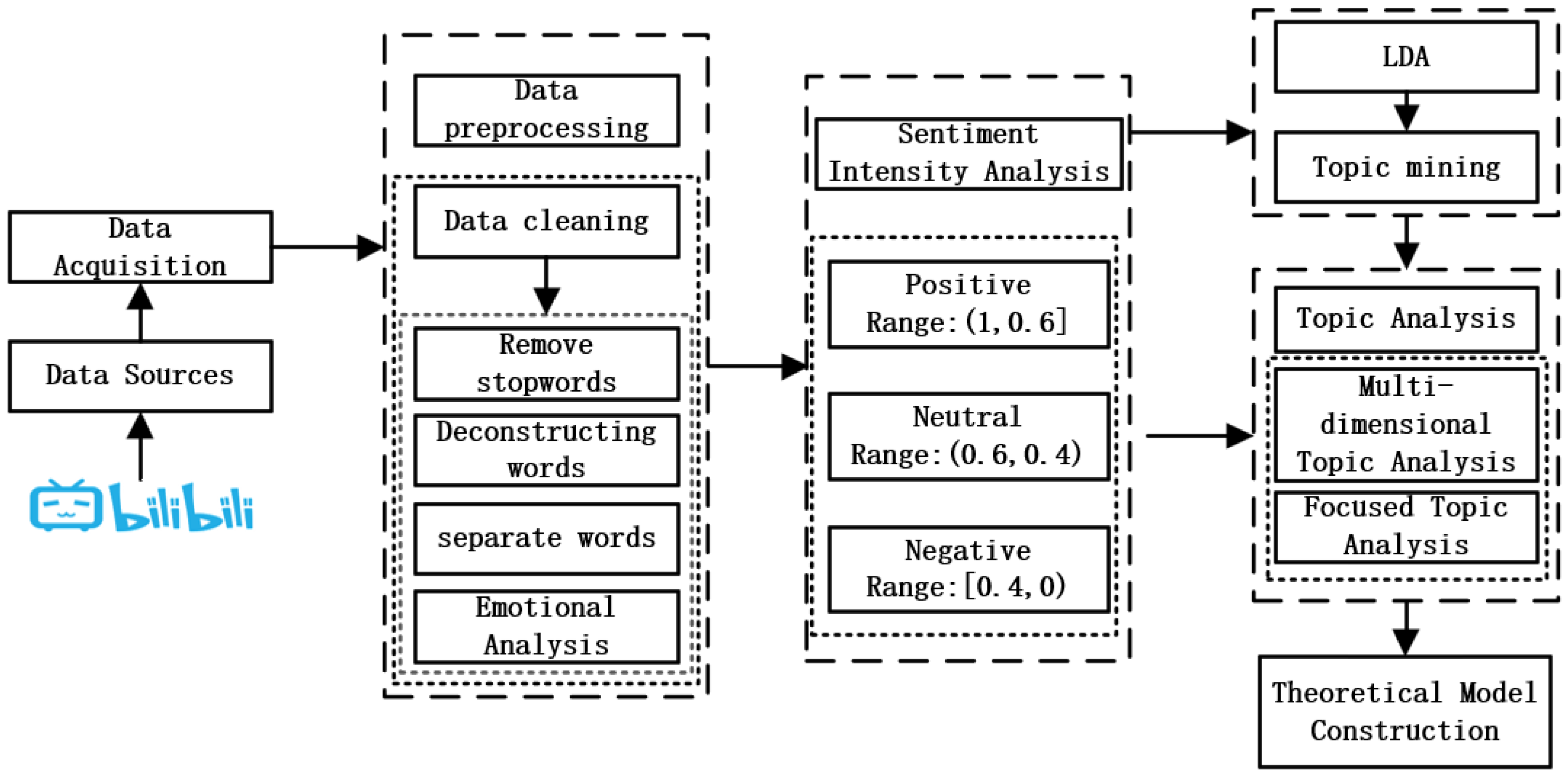
3.2. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
3.3. Deep Data Analysis
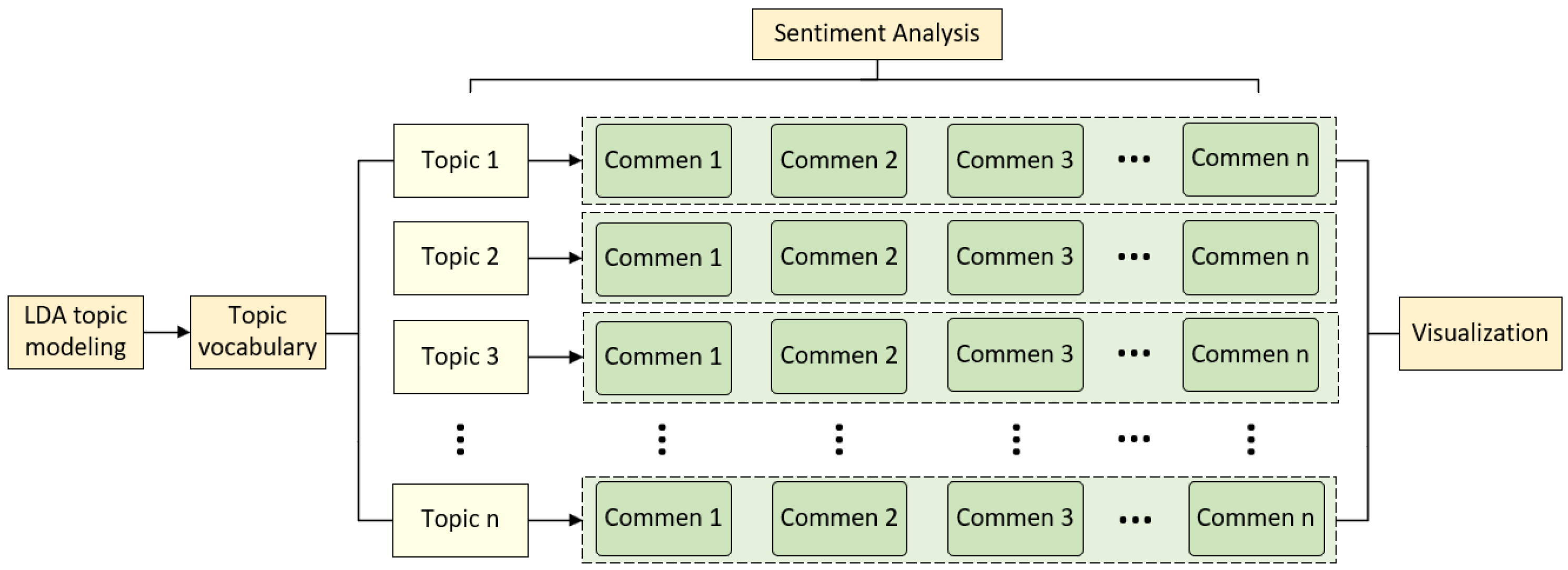
3.3.1. Sentiment Analysis
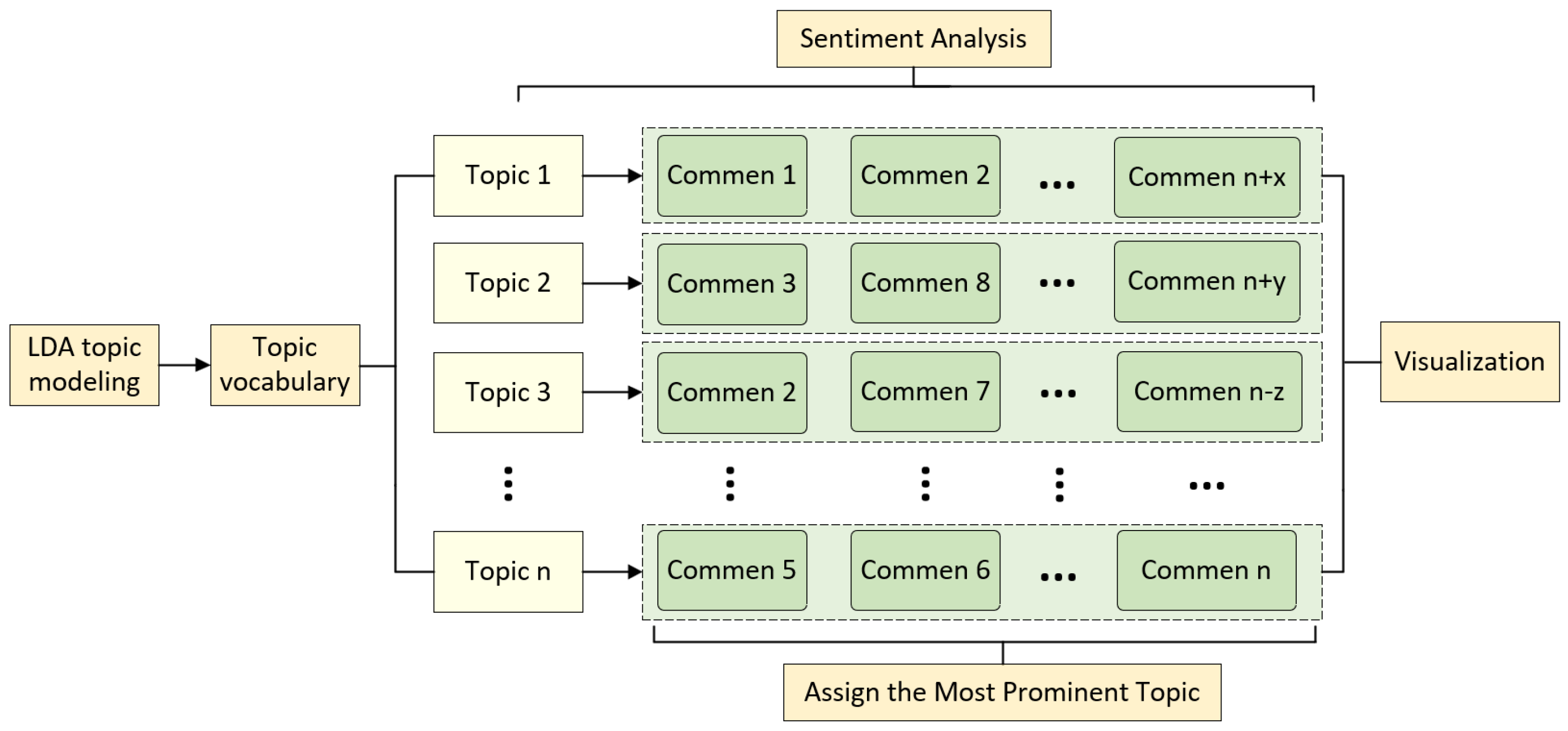
3.3.2. Identify and Analyze Potential Topics
4. Results
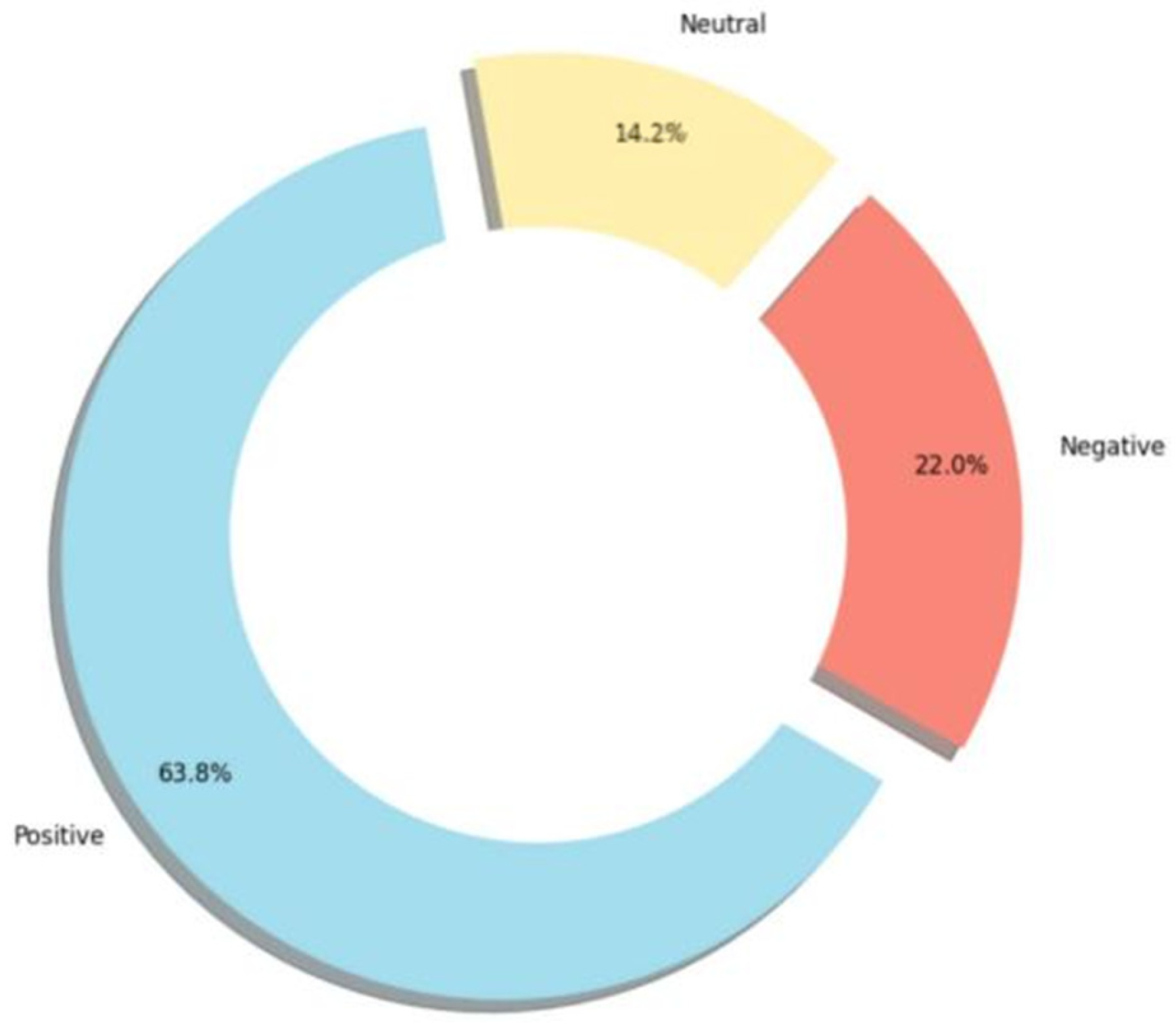
4.1. Emotional Attitude
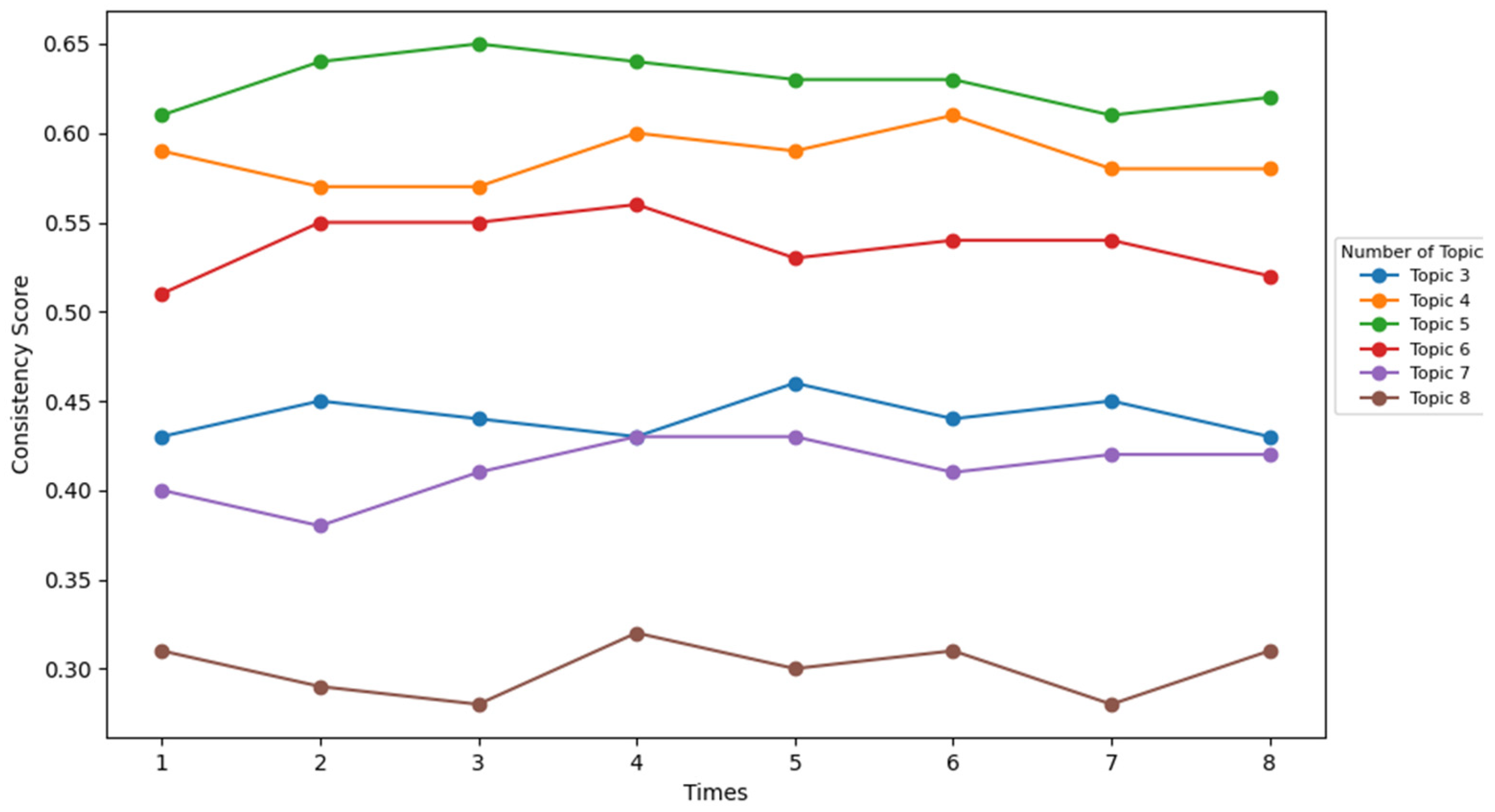
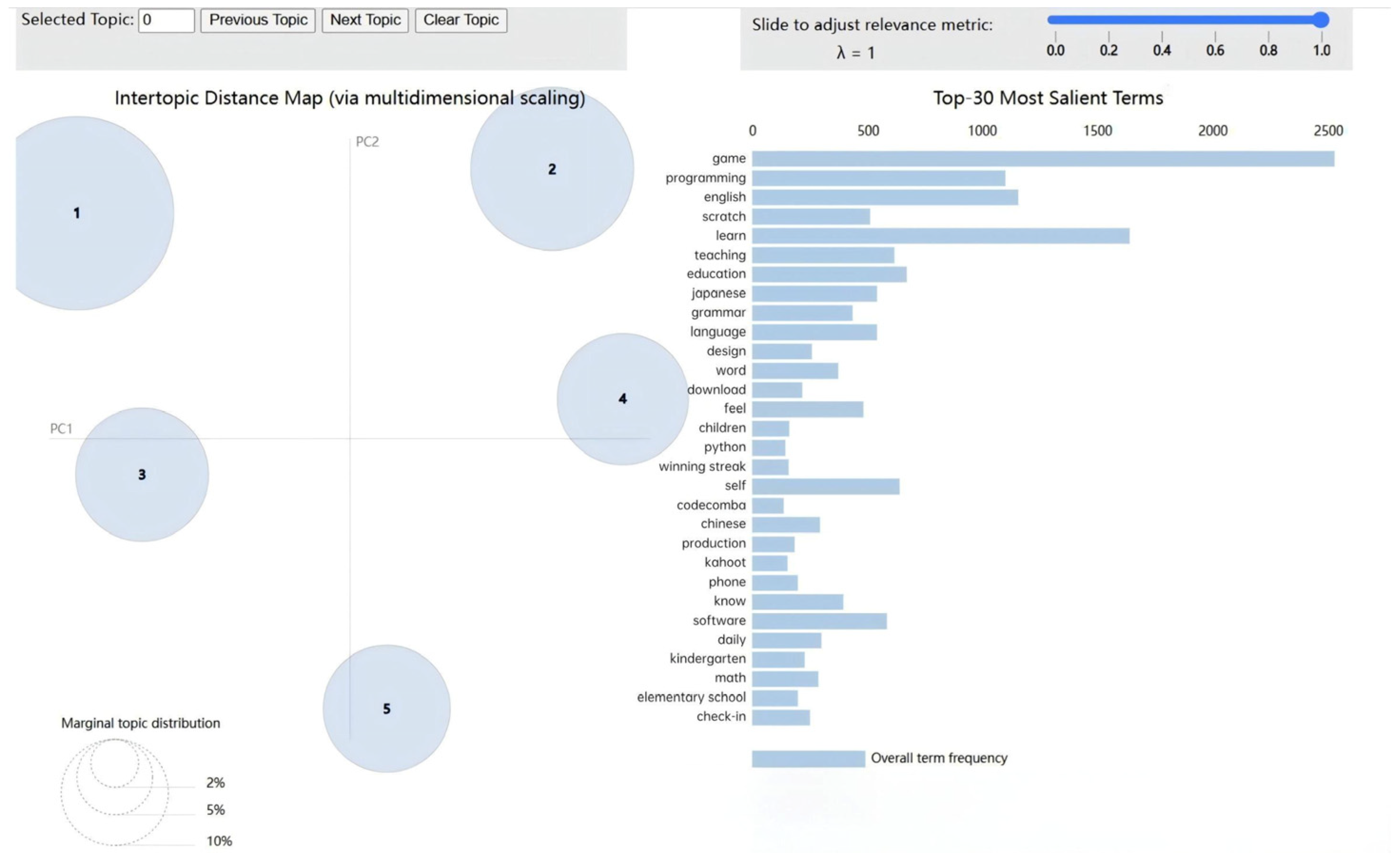
4.2. LDA Topic Modeling
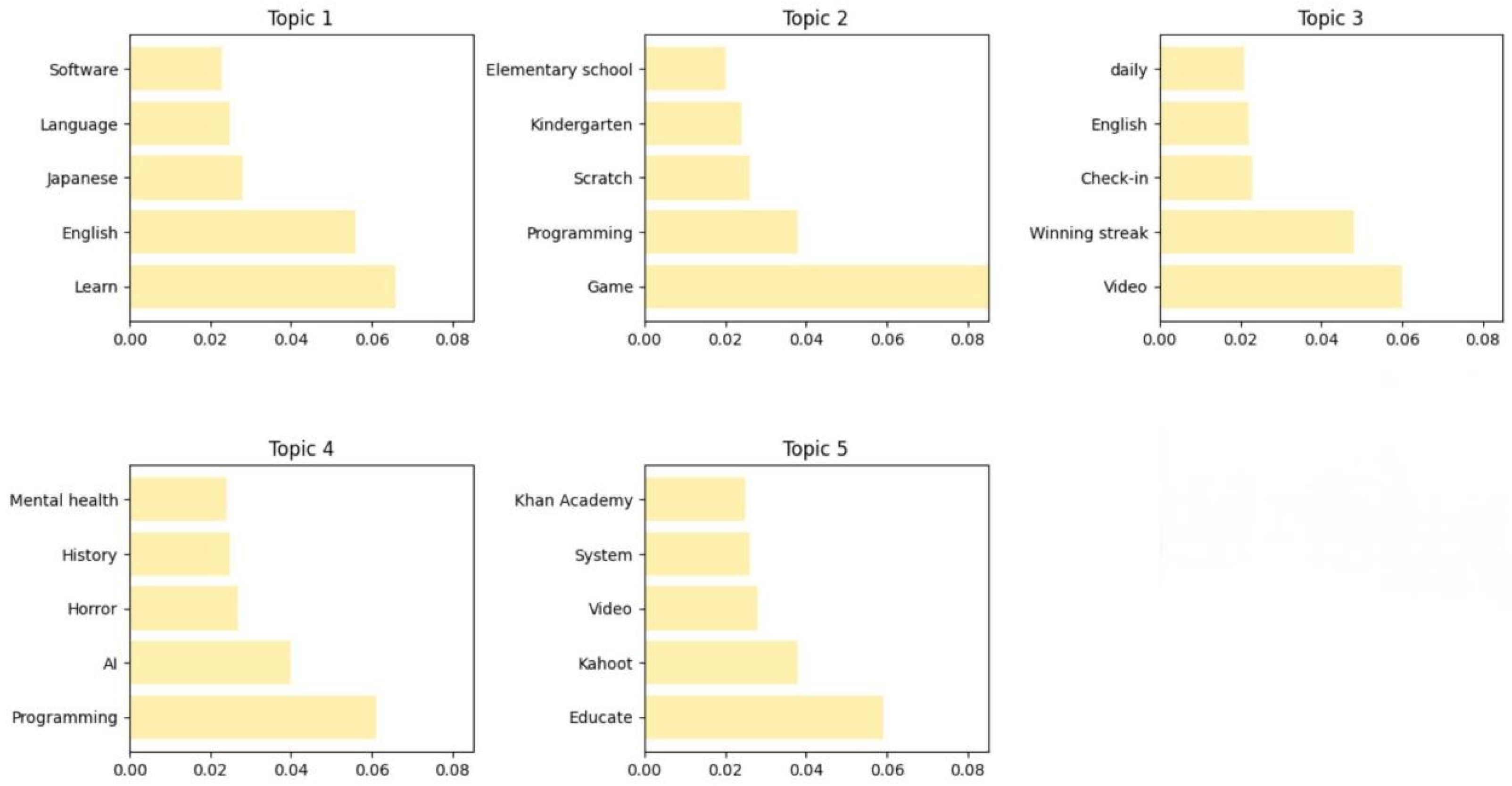
- Topic 1: Multilingual hierarchical construction: task-advanced language acquisition.
- Topic 2: Sorted programming thinking: Cognitive leap in the creative environment of young age.
- Topic 3: Certification-driven chain learning: modular English proficiency and behavioral continuity.
- Topic 4: Cross-domain cognitive fusion: a program learning space for mental resilience and psychological safety.
- Topic 5: Universal educational environment: Innovative exploration of adaptive gamified learning strategies.
4.3. Potential Topic Analysis
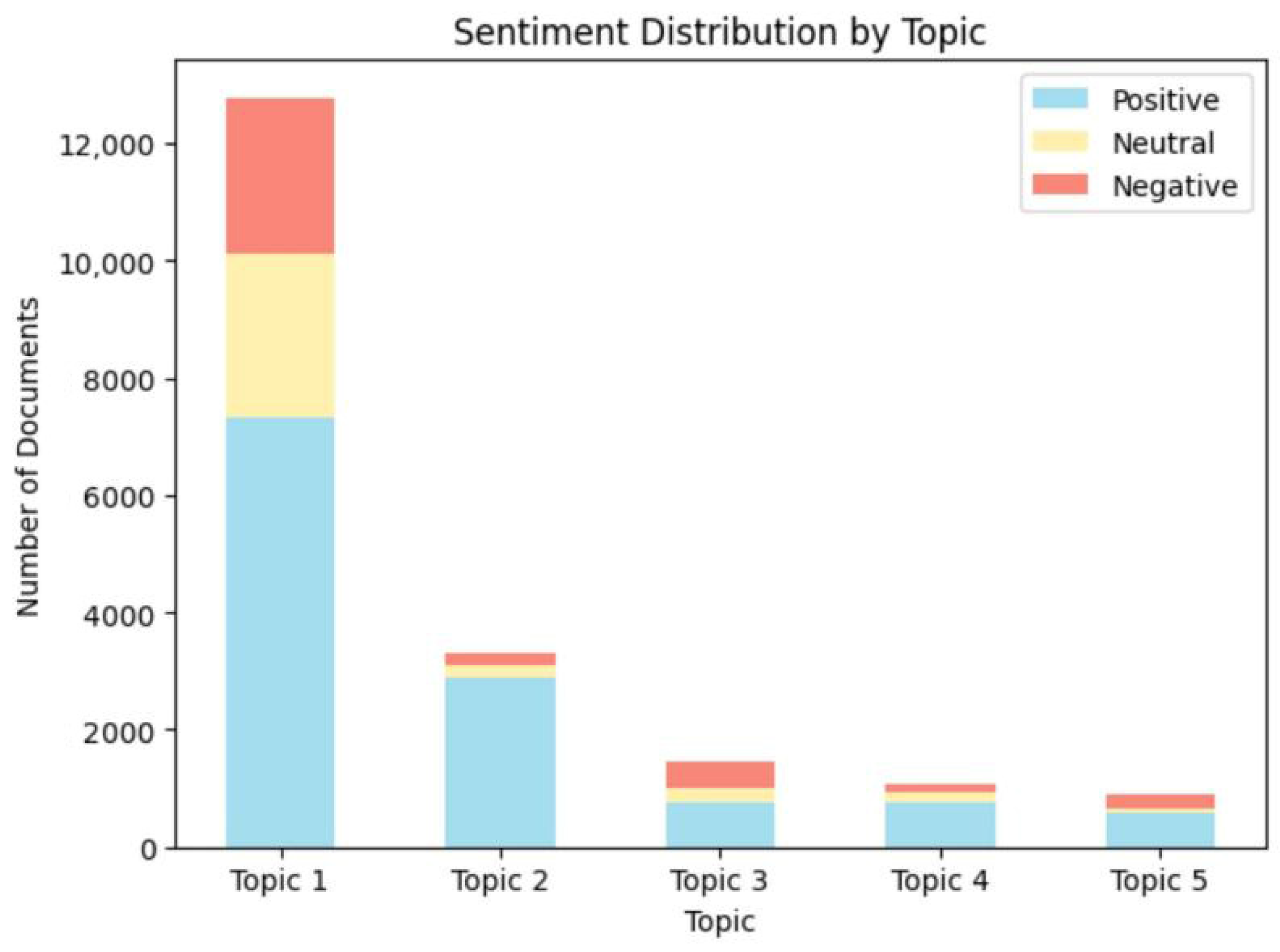
4.3.1. Multidimensional Thematic Sentiment Analysis
4.3.2. Highlight Thematic Sentiment Analysis
5. Discussion and Contribution
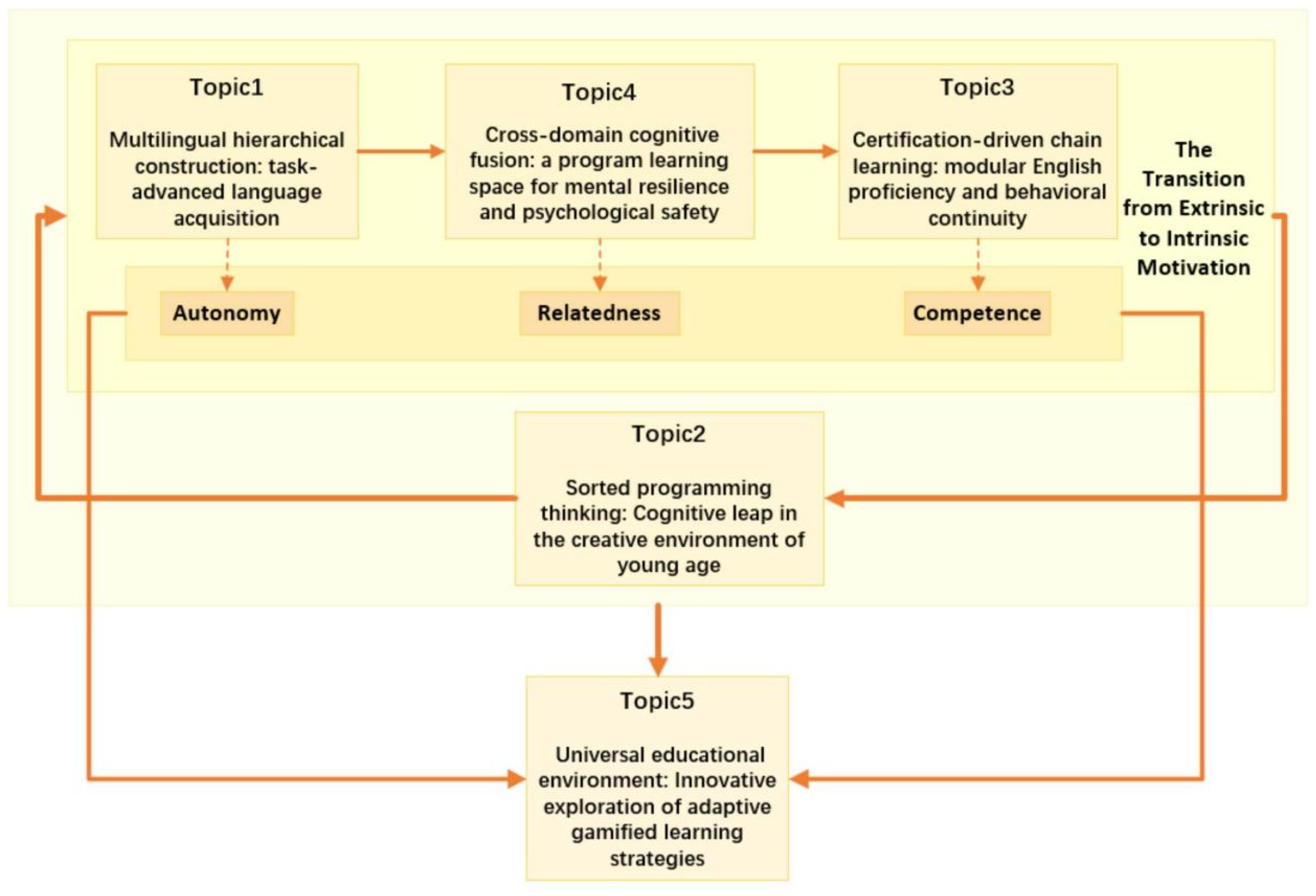
5.1. Topic Discussion
5.1.1. Multidimensional Motivational Fulcrum of Motivation Transformation Driven by Gamification: Autonomy, Relatedness, Competence
5.1.2. The Interactive Cycle Between Motivation Transformation and Cognitive Leap: Advanced Learning from the Perspective of Connectivism
5.1.3. The Mechanism of Strategy Generation and the Integration of Ubiquitous Learning: Innovative Exploration of Adaptive Gamified Learning Strategies
5.2. Research Contributions and Suggestion
5.2.1. Research Contribution
- A.
- Detecting the heterogeneity of adaptive learning emotional motivation and acceptance with the LDA and sentiment analysis fusion model.
- B.
- Fusion of SDT and Connectivism to construct an adaptive gamification theoretical model: the progressive generation mechanism of motivation-cognition-strategy.
- Psychological needs progressive: autonomy → relatedness → competence, which constitutes the fulcrum logic of motivation transformation.
- Cognitive structure expansion: knowledge modularization → cross-domain connection → post-set strategy optimization to drive learners’ cognitive reconstruction.
- Strategy evolution systemization: feedback loop → situational adjustment → personalized path generation to achieve dynamic coupling of motivation-cognition.
5.2.2. Research Suggestion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matthew, U.O.; Kazaure, J.S.; Okafor, N.U. Contemporary development in E-Learning education, cloud computing technology & internet of things. EAI Endorsed Trans. Cloud Syst. 2021, 7, e3. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, L.; Lo, C. Online flipped and gamification classroom: Risks and opportunities for the academic achievement of adult sustainable learning during COVID-19 pandemic. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, M. Improving Student Enjoyment, Time Management, and Performance Using a Secure, Immersive Gamified Learning Platform. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Hew, K.F.; Du, J. Gamification enhances student intrinsic motivation, perceptions of autonomy and relatedness, but minimal impact on competency: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2024, 72, 765–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Yan, H. Causal mechanisms of the psychological needs for online gamified learning and the impact on learning engagement among college students. Interact. Learn Environ. 2025, 33, 2597–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniappan, K.; Noor, N.M. Gamification strategy to support self-directed learning in an online learning environment. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. (IJET) 2022, 17, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firwana, A.; Shouqer, M.A.; Aqel, M. Effectiveness of E-learning environments in developing skills for designing E-tivities based on Gamification for teachers of technology in Gaza. Educ. Knowl. Soc. 2021, 22, e23907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, S.N.M.; Salleh, M.A.M.; Hakim, M.; Hamid, A.; Sui, L.K.M.; Mohd, C. Adaptive learning strategies with gamification to enhance learning engagement. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh Babu, S.; Dhakshina Moorthy, A. Application of artificial intelligence in adaptation of gamification in education: A literature review. Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ. (EKS) 2024, 32, e22683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinjeni, T.P.; Rakhmawati, N.A.; Nadlifatin, R. A systematic literature review on personalized adaptive gamification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Engineering, Network, and Intelligent Multimedia (CENIM), Surabaya, Indonesia, 22–23 November 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 218–223. [Google Scholar]
- Sotirov, M.; Petrova, V.; Nikolova-Sotirova, D. Personalized gamified education: Feedback mechanisms and adaptive learning paths. In Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Innovative Approaches in Smart Technologies (ISAS), İstanbul, Turkiye, 6–7 December 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Alomair, Y.; Hammami, S. A review of methods for adaptive gamified learning environments. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computer Applications & Information Security (ICCAIS), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 19–21 March 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Balci, S.; Secaur, J.M.; Morris, B.J. Comparing the effectiveness of badges and leaderboards on academic performance and motivation of students in fully versus partially gamified online physics classes. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2022, 27, 8669–8704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, S. Leaderboard design principles to enhance learning and motivation in a gamified educational environment: Development study. JMIR Serious Games 2021, 9, e14746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strousopoulos, P.; Troussas, C. Personalized Learning via Gamified Virtual Environments: Exploring Insights and Impact. In Proceedings of the 19th International Workshop on Semantic and Social Media Adaptation & Personalization (SMAP), Athens, Greece, 21–22 November 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Naseer, F.; Khan, M.N.; Tahir, M.; Addas, A.; Aejaz, S.H. Integrating deep learning techniques for personalized learning pathways in higher education. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Ebrahimi, O.V. Gamification: A novel approach to mental health promotion. Curr. Psychiat Rep. 2023, 25, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoharan, A.; Nagulapally, S. Adaptive gamification algorithms for personalized learning experiences in educational platforms. Int. Res. J. Mod. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2024, 6, 2582–5208. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Kim, S. A badge design framework for a gamified learning environment: Cases analysis and literature review for badge design. JMIR Serious Games 2019, 7, e14342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Deng, C.; Hoffman, J.; Hadi Mogavi, R.; Kim, J.J.; Hui, P. Long-Term Gamification: A Survey. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Washington, DC, USA, 29 June–4 July 2024; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 32–43. [Google Scholar]
- Alipour, M.; Tourchi Moghaddam, M.; Vaidhyanathan, K.; Baun Kjærgaard, M. in Toward changing users behavior with emotion-based adaptive systems. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM Conference on User Modeling, Adaptation and Personalization, Limassol, Cyprus, 26–29 June 2023; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H. The influence of test-oriented teaching on Chinese students’ long-term use of English. Int. J. Educ. Humanit. 2023, 6, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.I.; Bailey, S.K.; Mercado, A.D. Does gamification work? Analyzing effects of game features on learning in an adaptive scenario-based trainer. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Copenhagen, Denmark, 19–24 July 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 493–504. [Google Scholar]
- Hallifax, S. Adaptive Gamification of Digital Learning Environments; Université Jean Moulin Lyon 3: Lyon, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Schöbel, S.; Schmidt-Kraepelin, M.; Janson, A.; Sunyaev, A. Adaptive and personalized gamification designs: Call for action and future research. Ais Trans. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2021, 13, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dah, J.; Hussin, N.; Zaini, M.K.; Helda, L.I.; Ametefe, D.S.; Aliu, A.A.; Suqi, W.; Caliskan, A. Gamification equilibrium: The fulcrum for balanced intrinsic motivation and extrinsic rewards in electronic learning systems. Int. J. Serious Games 2023, 10, 83–116. [Google Scholar]
- Kassenkhan, A.M.; Moldagulova, A.N.; Serbin, V.V. Gamification and Artificial Intelligence in Education: A Review of Innovative Approaches to Fostering Critical Thinking. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 98699–98728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zourmpakis, A.; Kalogiannakis, M.; Papadakis, S. Adaptive gamification in science education: An analysis of the impact of implementation and adapted game elements on students’ motivation. Computers 2023, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.M.; Deci, E.L. Self-determination theory. In Encyclopedia of Quality of Life and Well-Being Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 6229–6235. [Google Scholar]
- Botte, B.; Aarts, H.; Bakkes, S.; Veltkamp, R.C. in Motivation through gamification: A Self-Determination Theory perspective for the design of an adaptive reward system, CHI’22. In Proceedings of the 2022 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Louisiana, NO, USA, 29 April 2022; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Neo, M.; Ismat, Z. in Gamifying the student learning process: Enhancing collaborative experiences within a connectivist learning environment. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Education and New Learning Technologies, Palma, Spain, 3–5 July 2023; IATED: Valencia, Spain, 2023; pp. 372–378. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, A. Connectivism learning theory and connectivist approach in teaching and learning: A review of literature. Bhartiyam Int. J. Educ. Res. 2023, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, W.J.; Tasir, Z. Development of a Theoretical Framework of MOOCs with Gamification Elements to Enhance Students’ Higher-Order Thinking Skills: A Critical Review of the Literature. J. Inf. Technol. Educ. Res. 2024, 23, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J. From Embodied Cognition to Playful Interaction: The Construction of an Adaptive Learning Environment. In Proceedings of the 2023 4th International Conference on Education, Knowledge and Information Management (ICEKIM 2023), Nanjing, China, 26–28 May 2023; Atlantis Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 972–980. [Google Scholar]
- Wankhade, M.; Rao, A.C.S.; Kulkarni, C. A survey on sentiment analysis methods, applications, and challenges. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 55, 5731–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.L.; Lee, C.P.; Lim, K.M. A survey of sentiment analysis: Approaches, datasets, and future research. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Ibánez, M.; Casánez-Ventura, A.; Castejón-Mateos, F.; Cuenca-Jiménez, P. A review on sentiment analysis from social media platforms. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 223, 119862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, J.; Heitmann, M.; Siebert, C.; Schamp, C. More than a feeling: Accuracy and application of sentiment analysis. Int. J. Res. Mark. 2023, 40, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, U.; Shah, A. Topic modeling using latent Dirichlet allocation: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2021, 54, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curiskis, S.A.; Drake, B.; Osborn, T.R.; Kennedy, P.J. An evaluation of document clustering and topic modelling in two online social networks: Twitter and Reddit. Inf. Process Manag. 2020, 57, 102034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Batra, I.; Sharma, S.; Malik, A.; Hosen, A.S.; Ra, I. Predicting trends and research patterns of smart cities: A semi-automatic review using latent dirichlet allocation (LDA). IEEE Access 2022, 10, 121080–121095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Rahman, A.; Karim, M.R.; Khan, M.S.I.; Islam, M.J. Normalized approach to find optimal number of topics in Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA). In Proceedings of the International Conference on Trends in Computational and Cognitive Engineering: Proceedings of TCCE 2020, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 17–18 December 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 341–354. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, J.; Qi, Y. Selection of the optimal number of topics for LDA topic model—Taking patent policy analysis as an example. Entropy 2021, 23, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhang, H.; Zuo, T. The Detachment of Function and the Return to Essence: Exploring the Public’s Emotional Attitudes Towards Gamified Education. Educ. Sci. 2025, 15, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yu, L.; Yu, Z. A Content Analysis and Meta-Analysis on the Effects of Classcraft on Gamification Learning Experiences in terms of Learning Achievement and Motivation. Educ. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 9429112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgin, S.; Yüzer, T.V. Analysing adaptive gamification design principles for online courses. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2022, 41, 485–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Sun, Z.; Liu, D.; Yin, H.; Shi, L. Factors associated with academic burnout and its prevalence among university students: A cross-sectional study. BMC Med. Educ. 2023, 23, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luarn, P.; Chen, C.; Chiu, Y. Enhancing intrinsic learning motivation through gamification: A self-determination theory perspective. Int. J. Inf. Learn. Technol. 2023, 40, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A. The Impact of Gamification on Self-Efficacy in Managers. J. Appl. Econ. Sci. 2023, 18, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, A. Theories, strategies and elements of gamified MOOCs: A systematic literature review. Asia Pac. J. Inf. Syst. 2024, 34, 248–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machmud, M.T.; Wattanachai, S.; Samat, C. Constructivist gamification environment model designing framework to improve ill-structured problem solving in learning sciences. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2023, 71, 2413–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, F. The multidimensional influence structure of college students’ online gamified learning engagement: A hybrid design based on QCA-SEM. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaimara, P.; Poulimenou, S.; Deliyannis, I. Digital learning materials: Could transmedia content make the difference in the digital world? In Epistemological Approaches to Digital Learning in Educational Contexts; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2020; pp. 69–87. [Google Scholar]
- Serrano, S.A.; Martinez-Carranza, J.; Sucar, L.E. Knowledge transfer for cross-domain reinforcement learning: A systematic review. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 114552–114572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabilan, M.K.; Annamalai, N.; Chuah, K. Practices, purposes and challenges in integrating gamification using technology: A mixed-methods study on university academics. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 28, 14249–14281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo, R.P.D.; Ktena, A.; Kunicina, N.; Zabasta, A.; Patlins, A.; Mele, D.E. in Advanced practices: Micro learning, practice oriented teaching and gamified learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 61th International Scientific Conference on Power and Electrical Engineering of Riga Technical University (RTUCON), Riga, Latvia, 5–7 November 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Adanyin, A. AI-driven feedback loops in digital technologies: Psychological impacts on user behaviour and well-being. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.09706. [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugasundaram, M.; Tamilarasu, A. The impact of digital technology, social media, and artificial intelligence on cognitive functions: A review. Front. Cogn. 2023, 2, 1203077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, M. Cognitive network science for understanding online social cognitions: A brief review. Top. Cogn. Sci. 2022, 14, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, S. Connectivism. 2022. Available online: https://asianjde.com/ojs/index.php/AsianJDE/article/view/623 (accessed on 27 July 2025).
- Anunpattana, P.; Khalid, M.N.A.; Iida, H.; Inchamnan, W. Capturing potential impact of challenge-based gamification on gamified quizzing in the classroom. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Bañuls, M.; Gómez-Trigueros, I.M.; Rovira-Collado, J.; Rico-Gómez, M.L. Gamification and transmedia in interdisciplinary contexts: A didactic intervention for the primary school classroom. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopoulos, A.; Mystakidis, S. Gamification in education. Encyclopedia 2023, 3, 1223–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Teng, M.F.; Liu, S. Psychosocial profiles of university students’ emotional adjustment, perceived social support, self-efficacy belief, and foreign language anxiety during COVID-19. Educ. Dev. Psychol. 2023, 40, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, D.; McKechnie, J.; Edgerton, E.; Wilson, C. Immersive virtual reality as a pedagogical tool in education: A systematic literature review of quantitative learning outcomes and experimental design. J. Comput. Educ. 2021, 8, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Peña, M.L.; García-Magro, C.; Sánchez-López, J.M. Service design through the emotional mechanics of gamification and value co-creation: A user experience analysis. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2024, 43, 486–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vistorte, A.O.R.; Deroncele-Acosta, A.; Ayala, J.L.M.; Barrasa, A.; López-Granero, C.; Martí-González, M. Integrating artificial intelligence to assess emotions in learning environments: A systematic literature review. Front. Psychol. 2024, 15, 1387089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibisu, A.E. Development of a gamification model for personalized e-learning. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.15301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler-Dominguez, J.L.; Navas-Medrano, S.; Pons, P. in Arcadia: A gamified mixed reality system for emotional regulation and self-compassion. In Proceedings of the 2024 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Honolulu, HI, USA, 11–16 May 2024; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, E.N.M.; Jamali, N.; Suhaimi, A.I.H. Exploring gamification design elements for mental health support. Int. J. Adv. Technol. Eng. Explor. 2021, 8, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chau, P.Y.; Ge, L. Meaningful gamification for psychological empowerment: Exploring user affective experience mirroring in a psychological self-help system. Internet Res. 2021, 31, 11–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, T. Helping Students Learn in a Learner-Centered Environment: A Guide to Facilitating Learning in Higher Education; Taylor & Francis: Oxfordshire, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sailer, M.; Homner, L. The gamification of learning: A meta-analysis. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2020, 32, 77–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincon-Flores, E.G.; Castano, L.; Guerrero Solis, S.L.; Olmos Lopez, O.; Rodríguez Hernández, C.F.; Castillo Lara, L.A.; Aldape Valdés, L.P. Improving the learning-teaching process through adaptive learning strategy. Smart Learn. Environ. 2024, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.H.; Chen, P.Q.; Sin, Z.P.; Jia, Y.; Li, R.C.; Baciu, G.; Cao, J.; Li, Q. From classroom to metaverse: A study on gamified constructivist teaching in higher education. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Web-Based Learning, Sydney, Australia, 26–28 November 2023; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 92–106. [Google Scholar]
- Berasategi, N.; Aróstegui, I.; Jaureguizar, J.; Aizpurua, A.; Guerra, N.; Arribillaga-Iriarte, A. Interdisciplinary learning at university: Assessment of an interdisciplinary experience based on the case study methodology. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, H.M.; Iram, S.; Al-Aqrabi, H.; Alsboui, T.; Hill, R. A comprehensive state-of-the-art survey on data visualization tools: Research developments, challenges and future domain specific visualization framework. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 96581–96601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Xu, S.; Liu, R.; Jiang, Q. Exploring the discrepancy between projected and perceived destination images: A cross-cultural and sustainable analysis using LDA modeling. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagg, L.J.; Merkouris, S.S.; O Dea, G.A.; Francis, L.M.; Greenwood, C.J.; Fuller-Tyszkiewicz, M.; Westrupp, E.M.; Macdonald, J.A.; Youssef, G.J. Examining analytic practices in latent dirichlet allocation within psychological science: Scoping review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2022, 24, e33166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Cui, F.; Zhang, C. Library Similar Literature Screening System Research Based on LDA Topic Model. J. Inf. Knowl. Manag. 2024, 23, 2450077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Narayan, S.; Balaji, P.; Bhowmick, A.; Muthu, R.K. Speech emotion recognition using support vector machine. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.07590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.76 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.74 |
| 2 | 0.77 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.77 |
| 3 | 0.75 | 0.76 | 0.73 | 0.75 |
| 4 | 0.80 | 0.83 | 0.78 | 0.77 |
| 5 | 0.76 | 0.72 | 0.74 | 0.72 |
| Settings | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full model | 0.76 | 0.77 | 0.75 | 0.74 |
| Remove the part of speech | 0.69 | 0.71 | 0.68 | 0.69 |
| Remove the sentiment dictionary match | 0.64 | 0.67 | 0.62 | 0.64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, L.; Zhang, H. The Gradual Cyclical Process in Adaptive Gamified Learning: Generative Mechanisms for Motivational Transformation, Cognitive Advancement, and Knowledge Construction Strategy. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9211. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169211
Ding L, Zhang H. The Gradual Cyclical Process in Adaptive Gamified Learning: Generative Mechanisms for Motivational Transformation, Cognitive Advancement, and Knowledge Construction Strategy. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(16):9211. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169211
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Liwei, and Hongfeng Zhang. 2025. "The Gradual Cyclical Process in Adaptive Gamified Learning: Generative Mechanisms for Motivational Transformation, Cognitive Advancement, and Knowledge Construction Strategy" Applied Sciences 15, no. 16: 9211. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169211
APA StyleDing, L., & Zhang, H. (2025). The Gradual Cyclical Process in Adaptive Gamified Learning: Generative Mechanisms for Motivational Transformation, Cognitive Advancement, and Knowledge Construction Strategy. Applied Sciences, 15(16), 9211. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169211






