Bio-Inspired Visual Network for Detecting Small Moving Targets in Low-Light Dynamic Complex Environments Based on Target Gradient Temporal Features
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Prior Work
2.1. A Network Inspired by Motion Perception Neurons in Insect Vision
2.2. Gradient Features for Object Detection
2.3. Small Object Detection in Infrared Images
3. The Model Framework
3.1. The Motion Perception Module
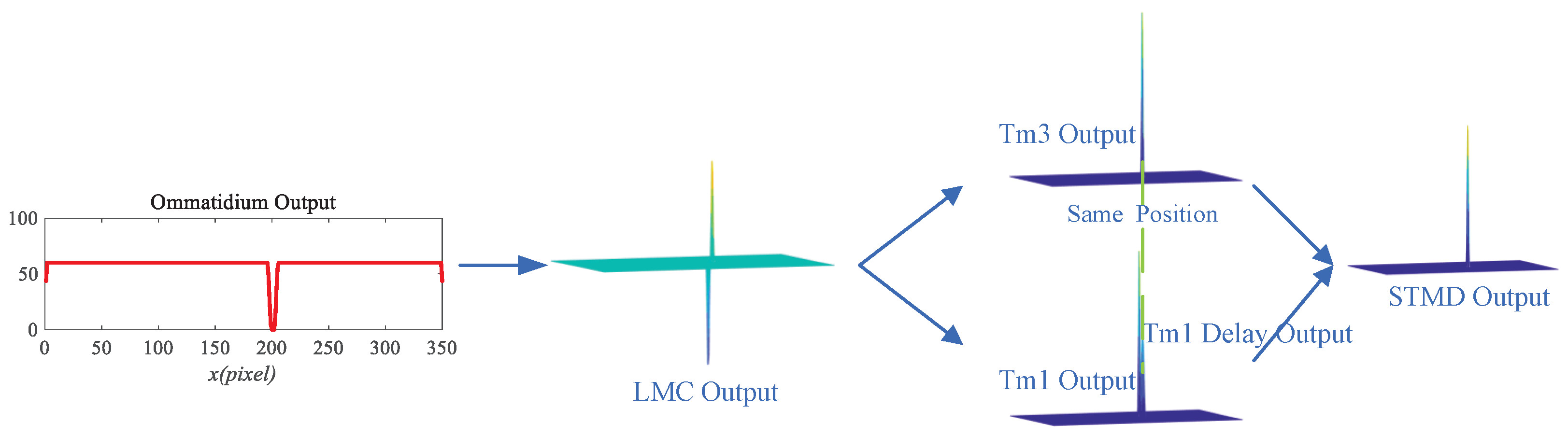
3.1.1. Ommatidia
3.1.2. Large Monopolar Cells
3.1.3. Tm3 and Tm1
3.1.4. STMDs
3.2. The Response Gradient Analysis Module
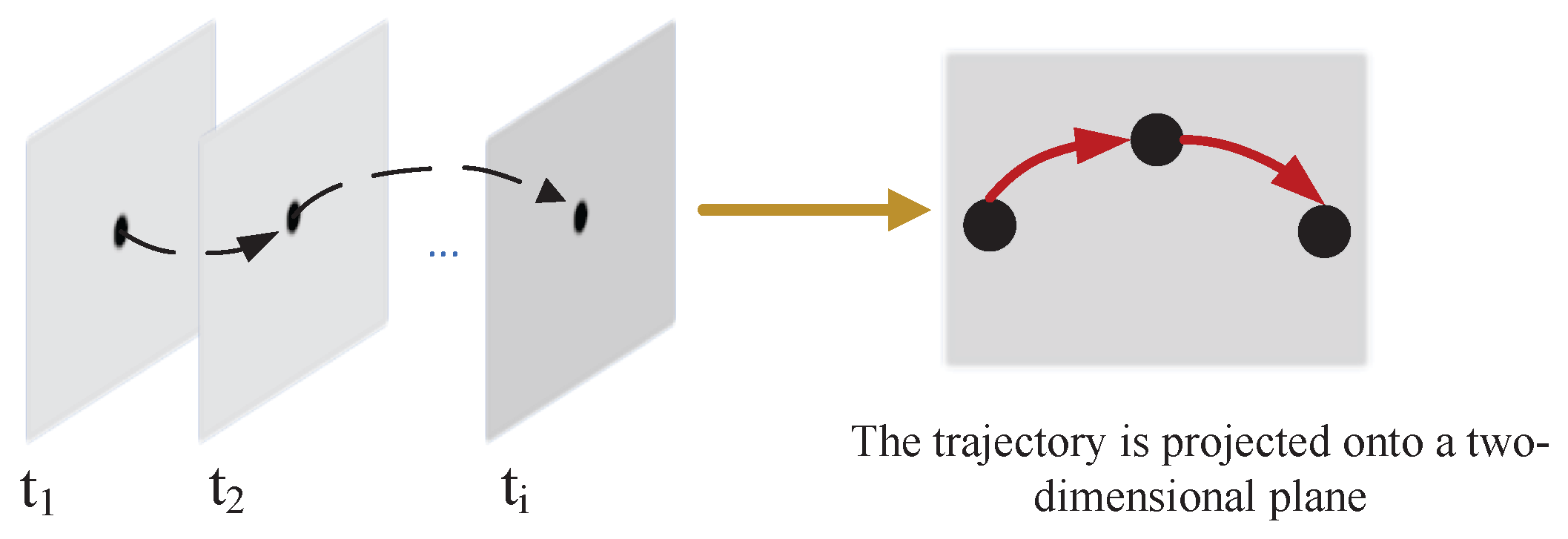
3.2.1. Recording the Motion Trajectory
3.2.2. Extracting Gradient Information and Gradient Trajectories
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
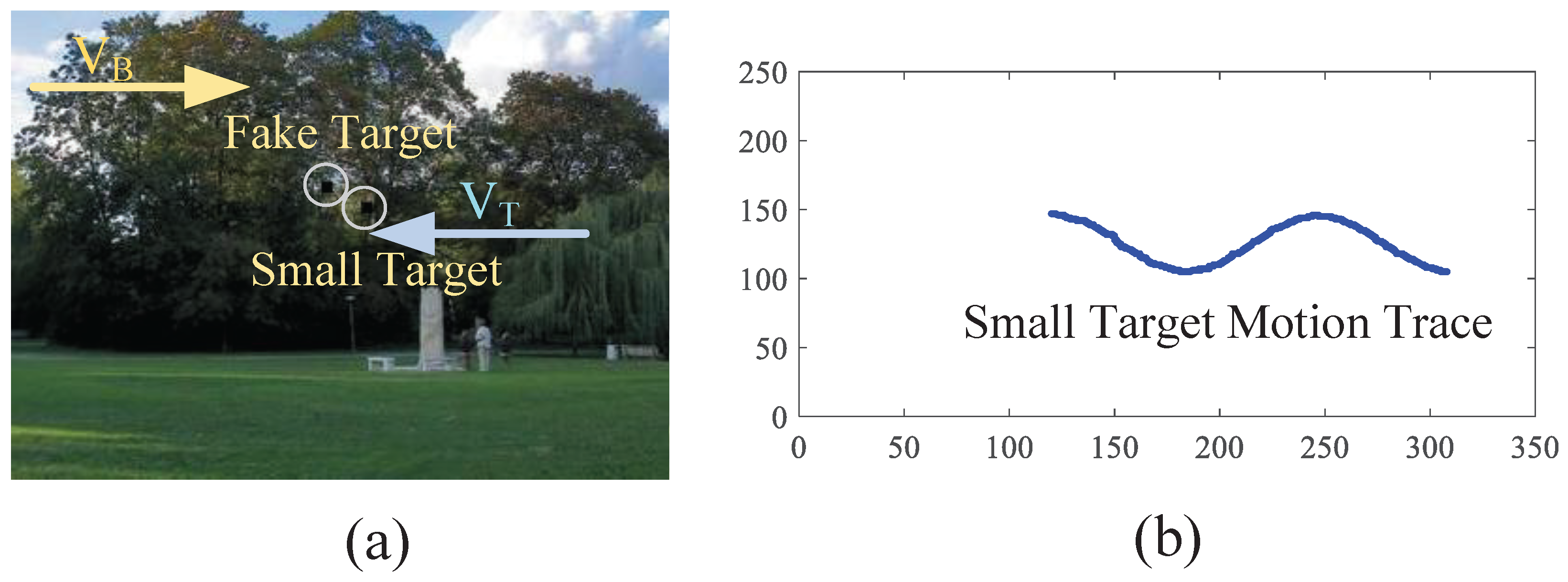
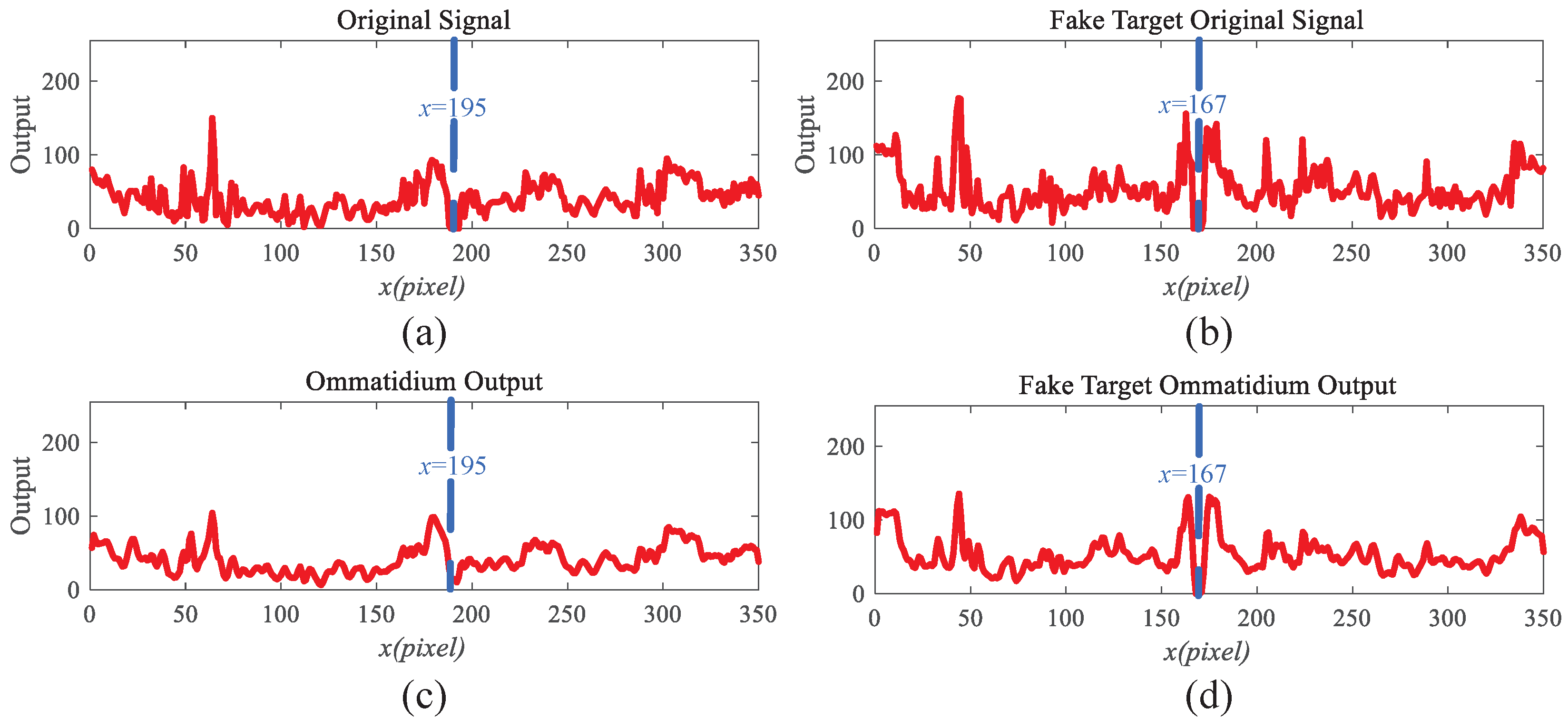
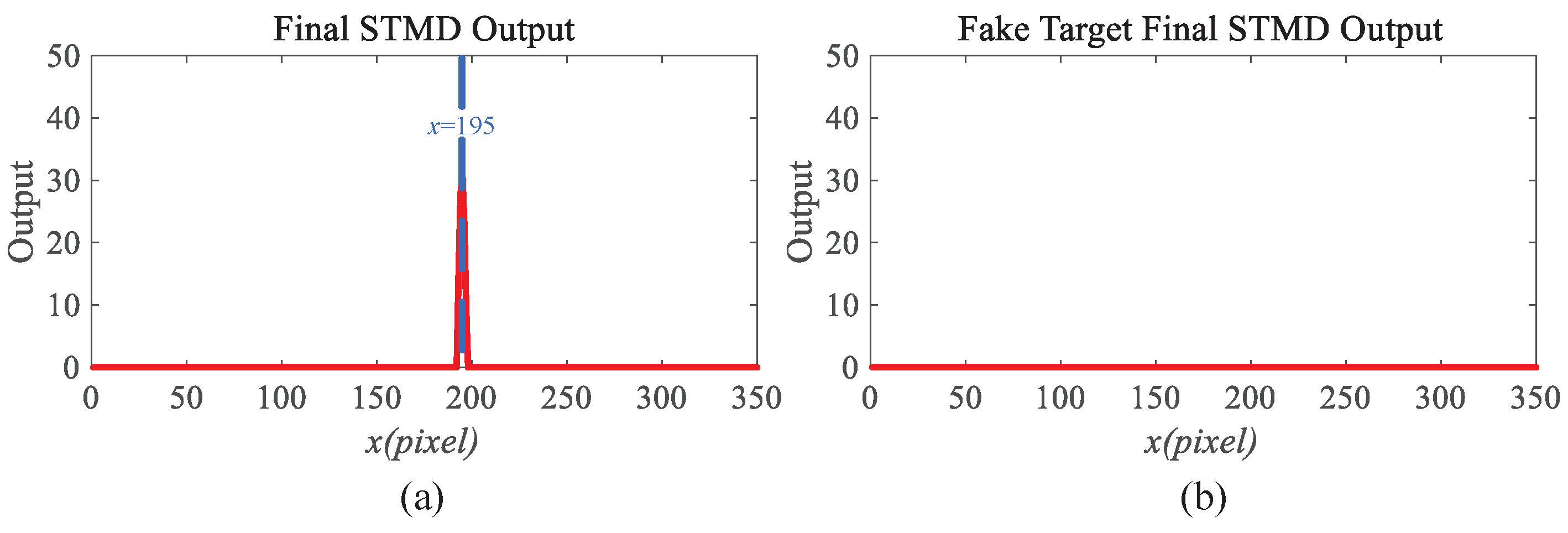
4.1. The Effectiveness of the Motion Perception Module
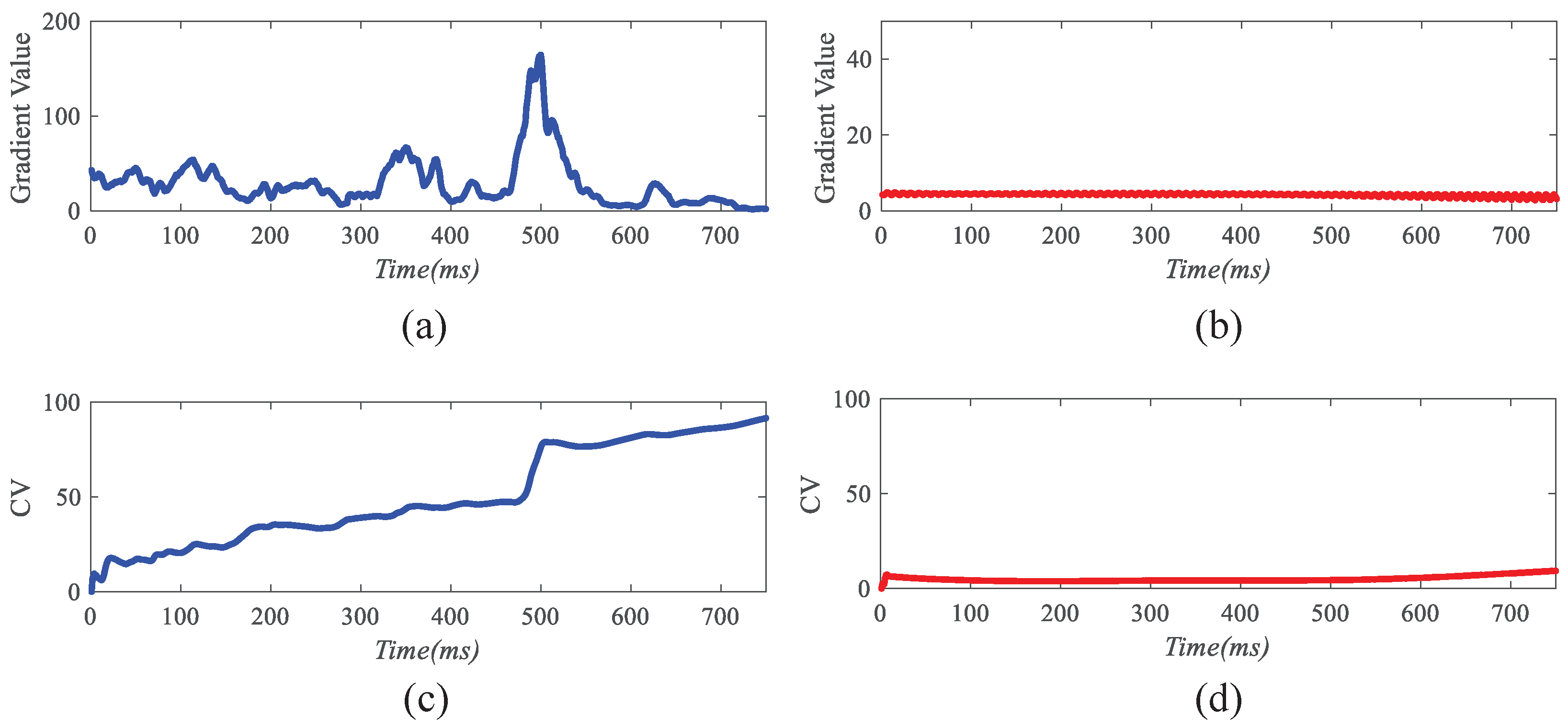
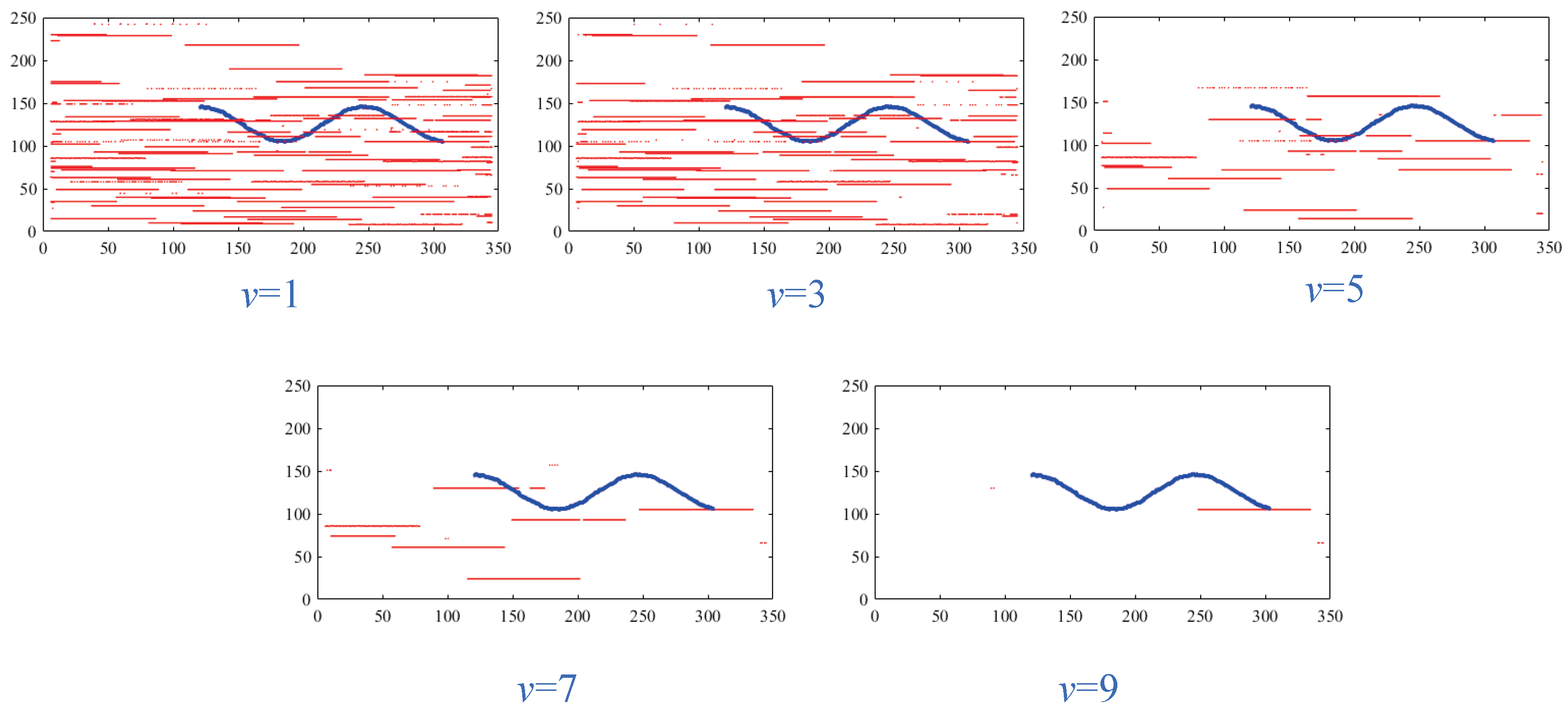
4.2. The Working Mechanisms of the Response Gradient Analysis Module
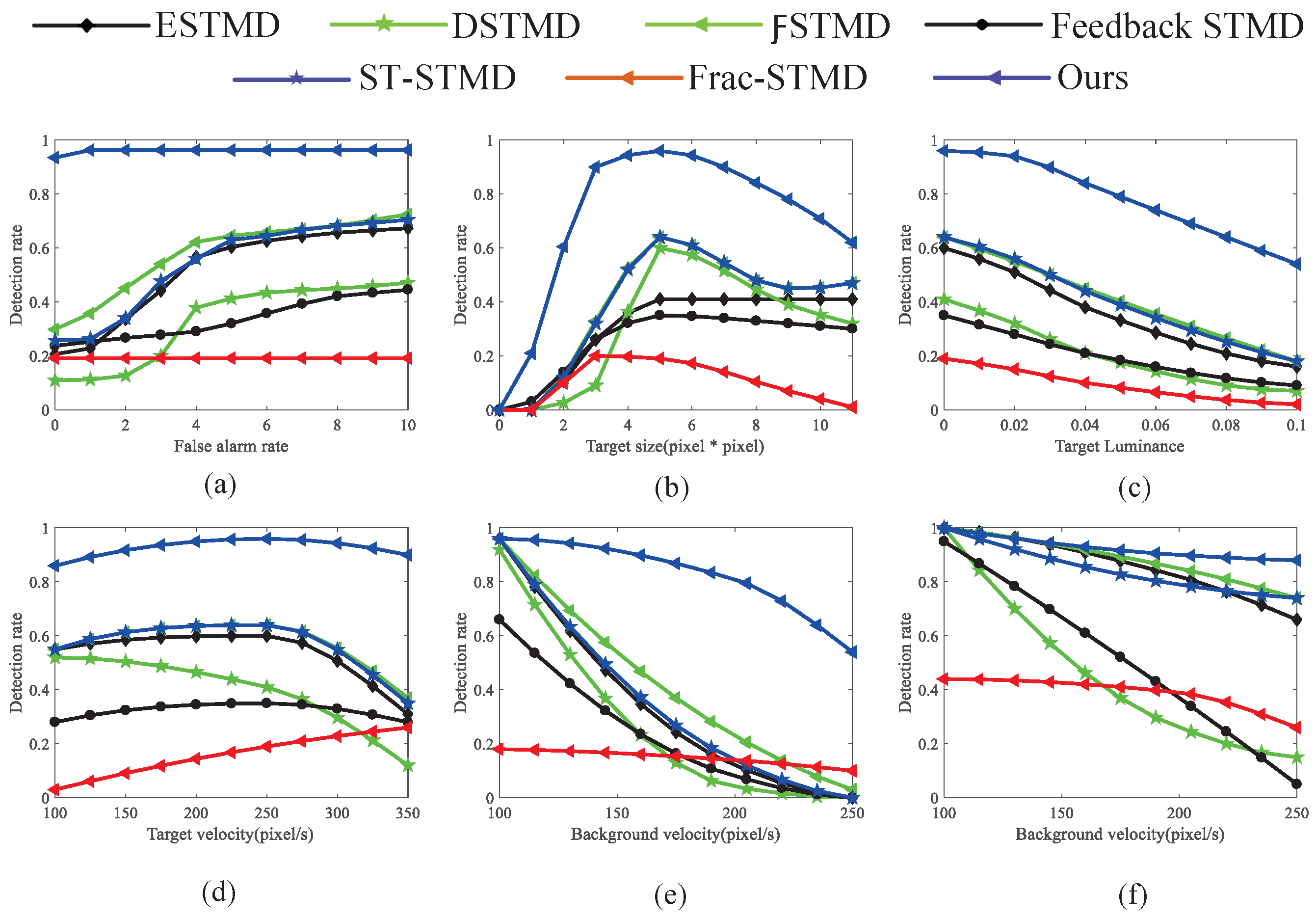
5. The Comparative Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Escobar-Alvarez, H.D.; Ohradzansky, M.; Keshavan, J.; Ranganathan, B.N.; Humbert, J.S. Obstacle avoidance and path planning methods for autonomous navigation of mobile robot. Sensors 2024, 24, 3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaur, B.; Mishra, K.K. Small-object detection based on YOLOv5 in autonomous driving systems. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2023, 168, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teja, Y.D. Static object detection for video surveillance. Multimed Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 21627–21639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalsotra, R.; Arora, S. Background subtraction for moving object detection: Explorations of recent developments and challenges. Vis. Comput. 2022, 38, 4151–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Jiang, K.; Jin, X.; He, J.; Zhang, L.; Lin, C.W. Local-global temporal difference learning for satellite video super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 34, 2789–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Mo, B.; Xu, J.; Li, D.; Zhao, J.; Han, S. Multi-YOLOv8: An infrared moving small object detection model based on YOLOv8 for air vehicle. Neurocomputing 2024, 588, 127685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, M.; Song, W.; Mei, H.; He, Q.; Liotta, A. A systematic review and analysis of deep learning-based underwater object detection. Neurocomputing 2023, 527, 204–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwan, T.; Anirudh, G.; Tembhurne, J.V. Object detection using YOLO: Challenges, architectural successors, datasets and applications. Multimed Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 9243–9275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y. A YOLO-NL object detector for real-time detection. Multimed Tools Appl. 2024, 238, 122256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mischiati, M.; Lin, H.T.; Herold, P.; Imler, E.; Olberg, R.; Leonardo, A. Internal models direct dragonfly interception steering. Nature 2015, 517, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, P.D.; Nordström, K.; O’carroll, D.C. Retinotopic organization of small-field-target-detecting neurons in the insect visual system. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keleş, M.F.; Frye, M.A. Object-detecting neurons in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordström, K.; Barnett, P.D.; O’Carroll, D.C. Insect detection of small targets moving in visual clutter. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederman, S.D.; Shoemaker, P.A.; O’Carroll, D.C. A model for the detection of moving targets in visual clutter inspired by insect physiology. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Peng, J.; Yue, S. A directionally selective small target motion detecting visual neural network in cluttered backgrounds. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 50, 1541–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiederman, S.D.; O’Carroll, D.C. Biologically inspired feature detection using cascaded correlations of off and on channels. J. Artif. Intell. Soft. 2013, 3, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederman, S.D.; O’Carroll, D.C. Biomimetic target detection: Modeling 2 nd order correlation of off and on channels. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence for Multimedia, Signal and Vision Processing (CIMSIVP), Singapore, 16–19 April 2013; pp. 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhao, J.; Hu, C.; Peng, J.; Yue, S. A time-delay feedback neural network for discriminating small, fast-moving targets in complex dynamic environments. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw Learn. Syst. 2021, 34, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhong, Z.; Lei, F.; Peng, J.; Yue, S. Bio-inspired small target motion detection with spatio-temporal feedback in natural scenes. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2024, 33, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.; Wang, H.; Xu, M.; Chen, H.; Li, H.; Peng, J. Mathematical study of neural feedback roles in small target motion detection. Front. Neurorobot. 2022, 16, 984430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Li, H.; Peng, J. A fractional-order visual neural model for small target motion detection. Neurocomputing 2023, 550, 126459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, H.; Hu, C.; Peng, J.; Yue, S. Attention and prediction-guided motion detection for low-contrast small moving targets. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 53, 6340–6352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Fan, B.; Li, H.; Peng, J. Rigid propagation of visual motion in the insect’s neural system. Neural Netw. 2025, 181, 106874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billah, M.A.; Faruque, I.A. Modeling Small-Target Motion Detector Neurons as Switched Systems with Dwell Time Constraints. In Proceedings of the 2022 American Control Conference (ACC), Atlanta, GA, USA, 8–10 June 2022; pp. 3192–3197. [Google Scholar]
- Uzair, M.; Finn, A.; Brinkworth, R.S. Efficient Sampling of Bayer Pattern for Long Range Small Target Detection in Color Images. In Proceedings of the 2023 38th International Conference on Image and Vision Computing New Zealand (IVCNZ), Palmerston North, New Zealand, 29–30 November 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Uzair, M.; Brinkworth, R.S.; Finn, A. Detecting small size and minimal thermal signature targets in infrared imagery using biologically inspired vision. Neuron 2021, 21, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzair, M.; Brinkworth, R.S.A.; Finn, A. A bio-inspired spatiotemporal contrast operator for small and low-heat-signature target detection in infrared imagery. Neuron 2021, 33, 7311–7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöckl, A.L.; O’Carroll, D.C.; Warrant, E.J. Hawkmoth lamina monopolar cells act as dynamic spatial filters to optimize vision at different light levels. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.A.; Demb, J.B. Parallel computations in insect and mammalian visual motion processing. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R1062–R1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztarker, J.; Rind, F.C. A look into the cockpit of the developing locust: Looming detectors and predator avoidance. Dev. Neurobiol. 2014, 74, 1078–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rind, F.C. Recent advances in insect vision in a 3D world: Looming stimuli and escape behaviour. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2024, 63, 101180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffer, L.K.; Xu, C.S.; Januszewski, M.; Lu, Z.; Takemura, S.Y.; Hayworth, K.J.; Huang, G.B.; Shinomiya, K.; Maitlin-Shepard, J.; Berg, S.; et al. A connectome and analysis of the adult Drosophila central brain. eLife 2020, 9, e57443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisak, M.S.; Haag, J.; Ammer, G.; Serbe, E.; Meier, M.; Leonhardt, A.; Schilling, T.; Bahl, A.; Rubin, G.M.; Nern, A.; et al. A directional tuning map of Drosophila elementary motion detectors. Nature 2013, 500, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussaini, M.M.; Evans, B.J.; O’Carroll, D.C.; Wiederman, S.D. Temperature modulates the tuning properties of small target motion detector neurons in the dragonfly visual system. Curr. Biol. 2024, 34, 4332–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, G.; Li, H.; Peng, J. Enhancing LGMD-based model for collision prediction via binocular structure. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1247227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Fu, Q.; Chen, H.; Li, H.; Peng, J. A look into feedback neural computation upon collision selectivity. Neural Netw. 2023, 166, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Z.; Chen, H.; Hua, M.; Fu, Q.; Peng, J. A bio-inspired visual collision detection network integrated with dynamic temporal variance feedback regulated by scalable functional countering jitter streaming. Neural Netw. 2025, 182, 106882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassenstein, B.; Reichardt, W. Systemtheoretische analyse der zeit-, reihenfolgen-und vorzeichenauswertung bei der bewegungsperzeption des rüsselkäfers chlorophanus. Z. FüR Naturforsch. B 1956, 11, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.A.; Bursztyn, L.; Horowitz, M.A.; Schnitzer, M.J.; Clandinin, T.R. Defining the computational structure of the motion detector in Drosophila. Neuron 2011, 70, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrant, E.J. Matched filtering and the ecology of vision in insects. Ecol. Anim. Senses Matched Filters Econ. Sens 2016, 11, 143–167. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zou, Y. Infrared Small Target Detection Based on Adaptive Size Estimation by Multi-directional Gradient Filter. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5007915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ru, J.; Wu, C. Infrared small target detection based on gradient correlation filtering and contrast measurement. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, Y. Infrared small target detection based on gradient-intensity joint saliency measure. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 7687–7699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, Z.; Hou, A.; Qian, X.; Wang, H. Adaptive edge detection of rebar thread head image based on improved Canny operator. IET Image Process. 2024, 18, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, M.; Bhargava, A.; Chaurasia, V.; Shandilya, M.; Siddiqui, E.A.; Bhardwaj, S. Automated lung cancer detection using Prewitt gradient kernel and SVM from CT-Lung images. In Proceedings of the 2023 1st International Conference on Innovations in High Speed Communication and Signal Processing (IHCSP) 2023: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 March 2023; pp. 508–513. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayalakshmi, D.; Nath, M.K. A novel contrast enhancement technique using gradient-based joint histogram equalization. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 40, 3929–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, Z. Infrared small target detection based on partial sum of the tensor nuclear norm. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Qu, S.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Deng, L. An infrared small target detection method based on multiscale local homogeneity measure. Infrared. Phys. Technol. 2018, 90, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, D.; Chen, H. Infrared small target detection based on local intensity and gradient properties. Infrared. Phys. Technol. 2018, 89, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borst, A.; Helmstaedter, M. Common circuit design in fly and mammalian motion vision. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanes, J.R.; Zipursky, S.L. Design principles of insect and vertebrate visual systems. Neuron 2010, 66, 15–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, B.; Príncipe, J. A theory for neural networks with time delays. In Proceedings of the Conference: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 3, Denver, CO, USA, 26–29 November 1990; pp. 162–168. [Google Scholar]
- Joesch, M.; Schnell, B.; Raghu, S.V.; Reiff, D.F.; Borst, A. ON and OFF pathways in Drosophila motion vision. Nature 2010, 468, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straw, A.D. Vision egg: An open-source library for realtime visual stimulus generation. Front. Neuroinform. 2008, 2, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RIST Data Set. 2020. Available online: https://sites.google.com/view/hongxinwang-personalsite/download/ (accessed on 6 April 2020).




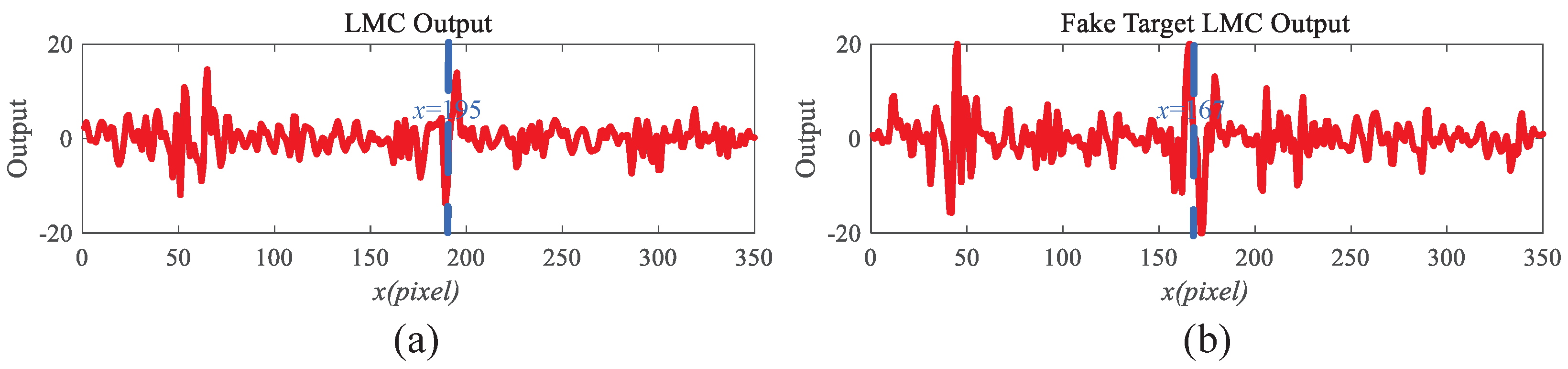
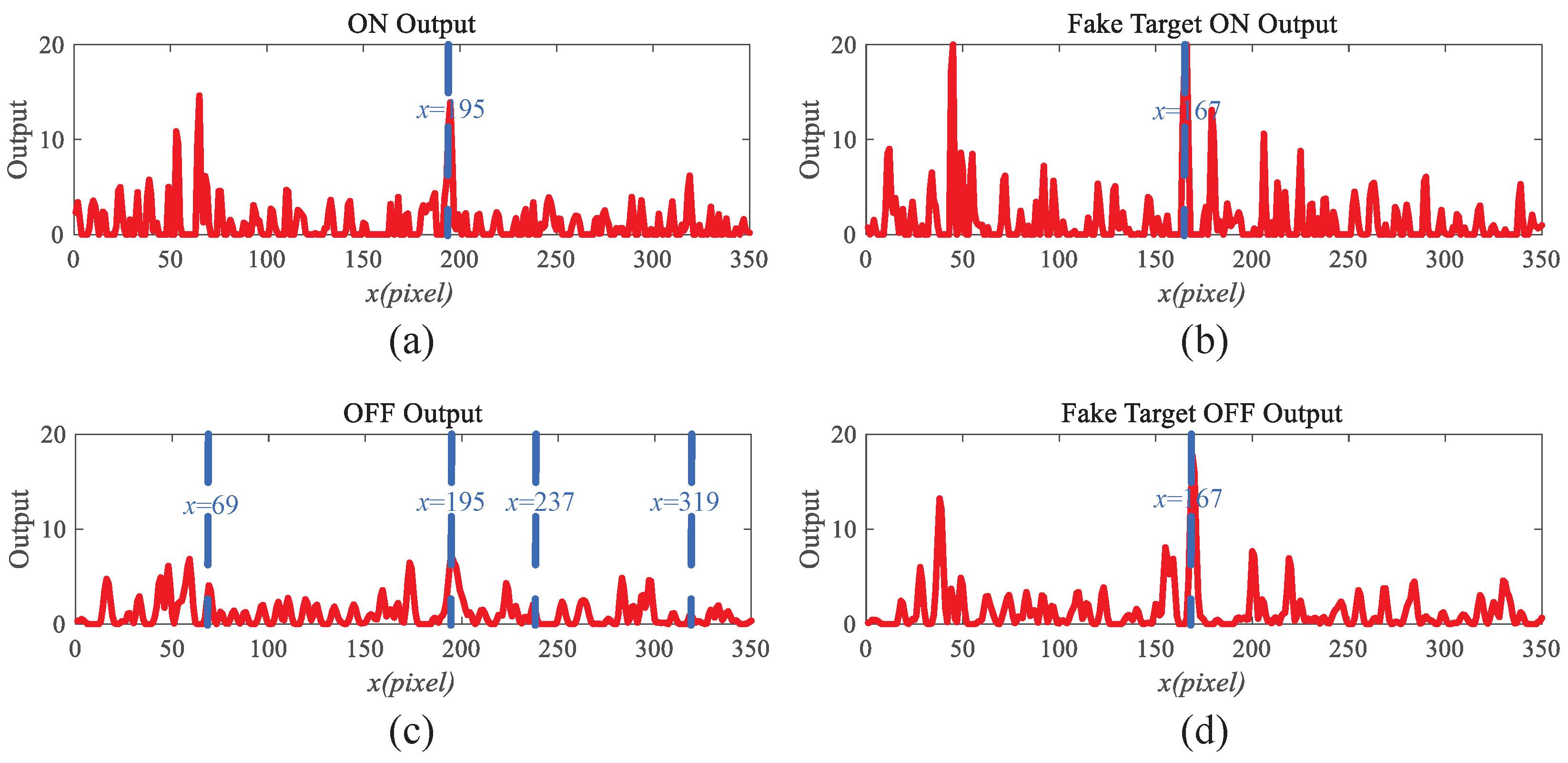
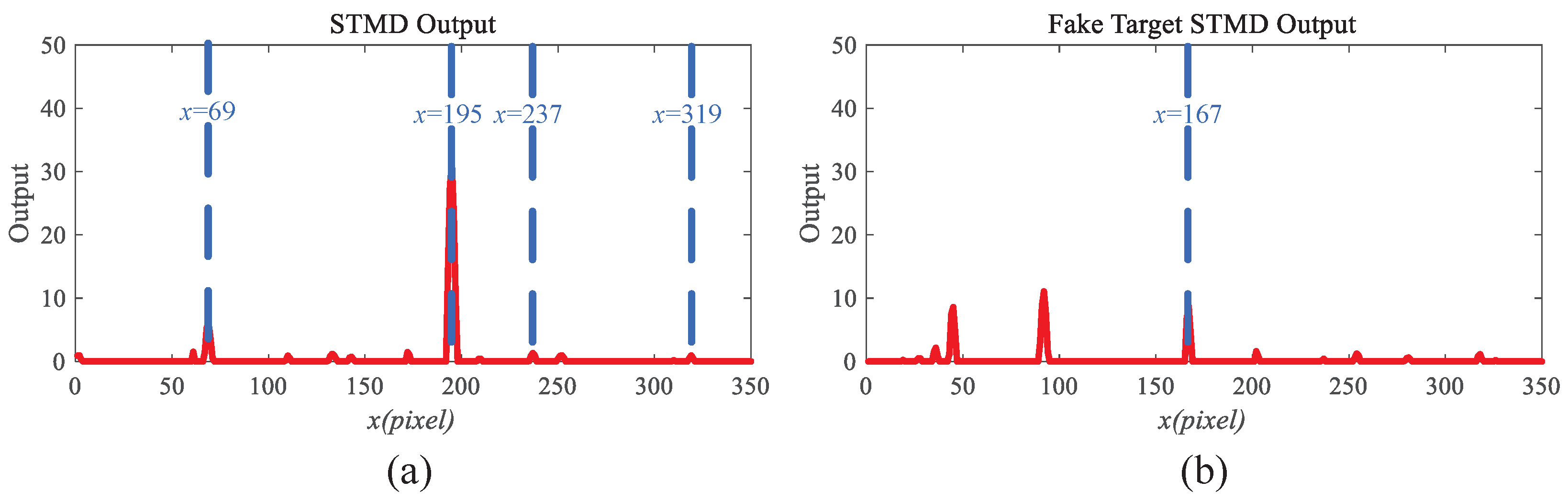
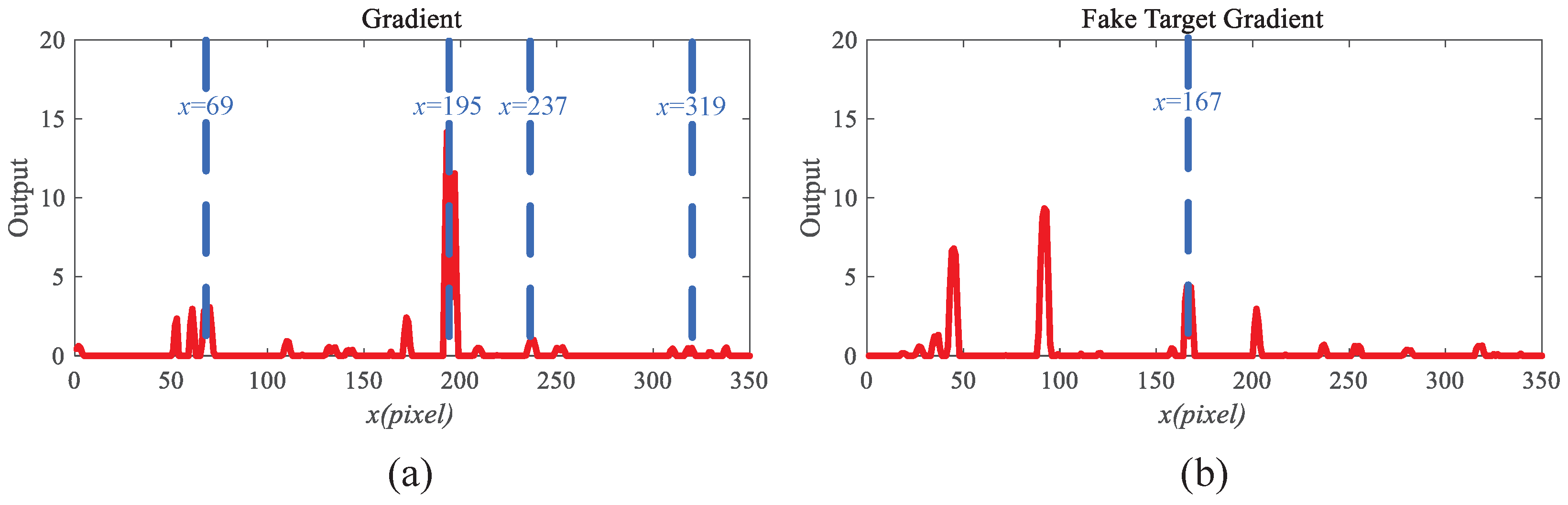




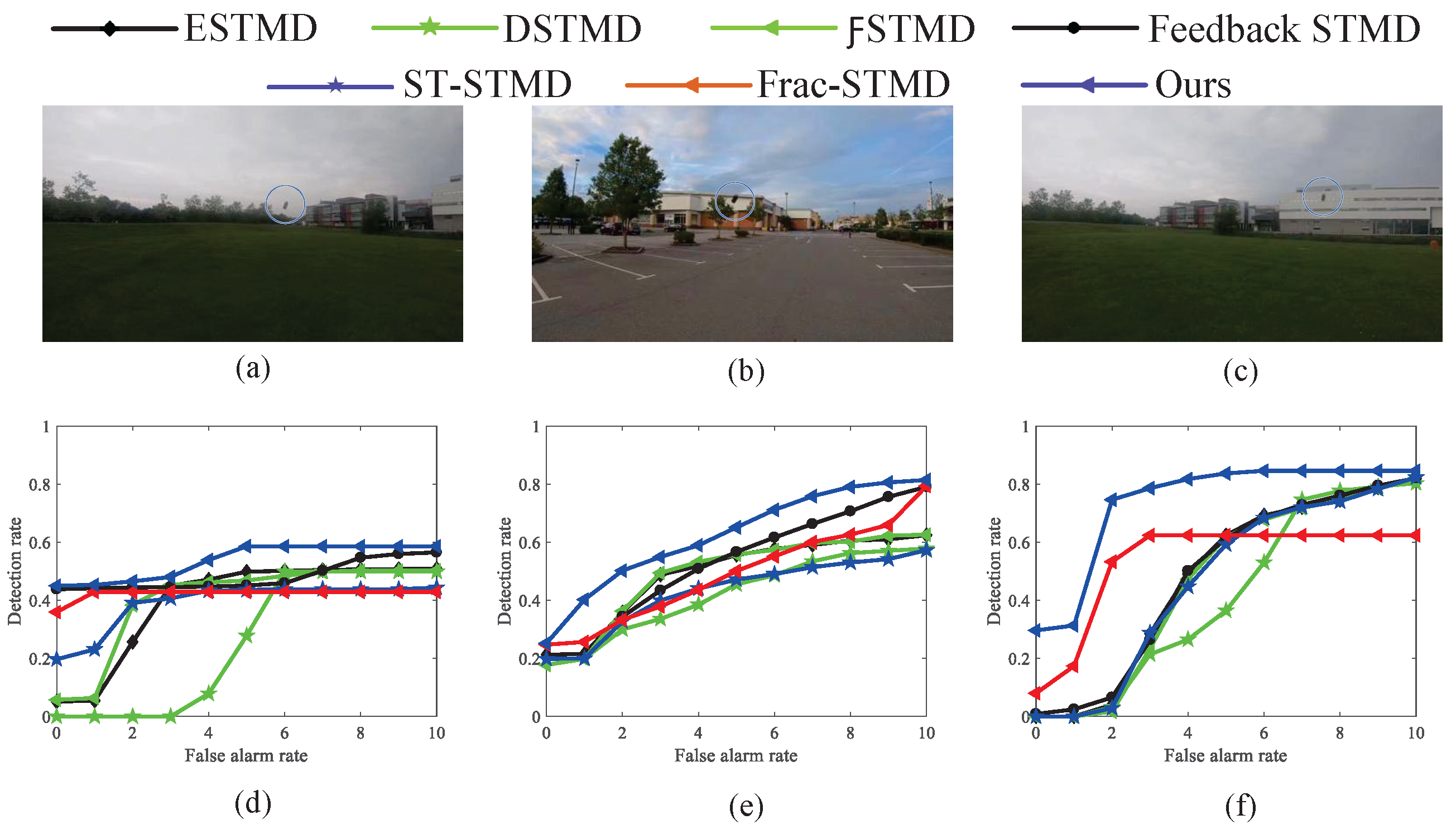
| Video Data | Primary Video | Evaluation One | Evaluation Two | Evaluation Three | Evaluation Four | Evaluation Five |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target scale | ||||||
| Target illumination range | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Target motion speed range (pixels per second) | 250 | 250 | 250 | 250 | 250 | |
| Range of background motion speeds (pixels per second) | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | ||
| Background motion direction | In the right direction | In the right direction | In the right direction | In the right direction | In the right direction | In the left direction |
| Background scene | Figure 7a | Figure 7a | Figure 7a | Figure 7a | Figure 7a | Figure 7a |
| Video | Mean Brightness | GISM | GCF-CM | DSTMD | ESTMD | STMD | Feedback STMD | Frac-STMD | ST-STMD | -STMD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary video | 0.29 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.41 | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.35 | 0.19 | 0.64 | 0.96 |
| Simulated one | 0.24 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.17 | 0.30 | 0.38 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.30 | 0.91 |
| Simulated two | 0.21 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.46 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.37 | 0.32 | 0.49 | 0.71 |
| Simulated three | 0.21 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.52 | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.33 | 0.17 | 0.58 | 0.92 |
| Simulated four | 0.30 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.46 | 0.64 | 0.68 | 0.51 | 0.33 | 0.64 | 0.92 |
| Simulated five | 0.23 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.45 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.51 | 0.25 | 0.59 | 0.73 |
| Simulated six | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.18 | 0.41 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.09 | 0.41 | 0.74 |
| Real one | 0.48 | 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.28 | 0.50 | 0.47 | 0.45 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.59 |
| Real two | 0.44 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.45 | 0.55 | 0.57 | 0.56 | 0.50 | 0.47 | 0.65 |
| Real three | 0.43 | 0.06 | 0.62 | 0.36 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.59 | 0.84 |
| Mean | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.39 | 0.53 | 0.55 | 0.43 | 0.29 | 0.51 | 0.80 |
| Methods | GISM | GCF-CM | DSTMD | ESTMD | STMD | Feedback STMD | Frac-STMD | ST-STMD | -STMD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary video | 0.0048 | 0.0072 | 0.0087 | 0.0070 | 0.0070 | 0.0067 | 0.0071 | 0.0070 | 0.3667 |
| Simulated one | 0.0047 | 0.0062 | 0.0097 | 0.0074 | 0.0074 | 0.0076 | 0.0093 | 0.0074 | 0.1094 |
| Simulated two | 0.0035 | 0.0049 | 0.0101 | 0.0081 | 0.0080 | 0.0061 | 0.0098 | 0.0084 | 0.0857 |
| Simulated three | 0.0035 | 0.0050 | 0.0090 | 0.0078 | 0.0077 | 0.0070 | 0.0093 | 0.0080 | 0.0509 |
| Simulated four | 0.0042 | 0.0056 | 0.0074 | 0.0068 | 0.0068 | 0.0061 | 0.0068 | 0.0068 | 0.0555 |
| Simulated five | 0.0040 | 0.0029 | 0.0078 | 0.0068 | 0.0066 | 0.0061 | 0.0073 | 0.0070 | 0.0316 |
| Simulated six | 0.0038 | 0.0051 | 0.0062 | 0.0058 | 0.0058 | 0.0063 | 0.0063 | 0.0058 | 0.1064 |
| Real one | 0.0044 | 0.0051 | 0.0055 | 0.0045 | 0.0043 | 0.0042 | 0.0046 | 0.0046 | 0.0264 |
| Real two | 0.0039 | 0.0050 | 0.0058 | 0.0042 | 0.0042 | 0.0041 | 0.0046 | 0.0043 | 0.0857 |
| Real three | 0.0031 | 0.0050 | 0.0048 | 0.0037 | 0.0036 | 0.0044 | 0.0042 | 0.0036 | 0.0748 |
| Mean | 0.0040 | 0.0050 | 0.0075 | 0.0062 | 0.0061 | 0.0059 | 0.0069 | 0.0063 | 0.1000 |
| Video | GISM | GCF-CM | DSTMD | ESTMD | STMD | Feedback STMD | Frac-STMD | ST-STMD | -STMD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary video | 0.0096 | 0.0142 | 0.0173 | 0.0139 | 0.0139 | 0.0133 | 0.0141 | 0.0139 | 0.5343 |
| Simulated one | 0.0093 | 0.0123 | 0.0191 | 0.0146 | 0.0146 | 0.0317 | 0.0184 | 0.0147 | 0.1969 |
| Simulated two | 0.0070 | 0.0096 | 0.0200 | 0.0160 | 0.0159 | 0.0121 | 0.0194 | 0.0167 | 0.1565 |
| Simulated three | 0.0070 | 0.0098 | 0.0196 | 0.0154 | 0.0153 | 0.0139 | 0.0185 | 0.0160 | 0.3071 |
| Simulated four | 0.0083 | 0.0110 | 0.0146 | 0.0136 | 0.0135 | 0.0122 | 0.0134 | 0.0135 | 0.1050 |
| Simulated five | 0.0080 | 0.0057 | 0.0154 | 0.0135 | 0.0131 | 0.0122 | 0.0145 | 0.0138 | 0.0611 |
| Simulated six | 0.0076 | 0.0100 | 0.0123 | 0.0115 | 0.0116 | 0.0126 | 0.0125 | 0.0116 | 0.1882 |
| Real one | 0.0087 | 0.0101 | 0.0110 | 0.0090 | 0.0087 | 0.0085 | 0.0091 | 0.0091 | 0.0511 |
| Real two | 0.0078 | 0.0100 | 0.0116 | 0.0084 | 0.0084 | 0.0082 | 0.0091 | 0.0086 | 0.1539 |
| Real three | 0.0063 | 0.0100 | 0.0096 | 0.0073 | 0.0072 | 0.0088 | 0.0083 | 0.0073 | 0.1342 |
| Mean | 0.0080 | 0.0103 | 0.0151 | 0.0123 | 0.0122 | 0.0134 | 0.0137 | 0.0125 | 0.1888 |
| Video | GISM | GCF-CM | DSTMD | ESTMD | STMD | Feedback STMD | Frac-STMD | ST-STMD | -STMD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary video | 145.2 | 627.1 | 91.8 | 23.2 | 27.8 | 35.4 | 21.5 | 234.3 | 108.0 |
| Simulated one | 149.0 | 599.4 | 86.7 | 21.0 | 26.4 | 32.4 | 16.5 | 234.2 | 96.2 |
| Simulated two | 149.2 | 582.8 | 82.1 | 20.3 | 24.3 | 31.0 | 19.7 | 233.8 | 92.3 |
| Simulated three | 137.4 | 610.0 | 96.8 | 20.8 | 24.3 | 35.5 | 19.0 | 234.1 | 94.9 |
| Simulated four | 146.8 | 595.0 | 110.8 | 24.8 | 28.7 | 33.6 | 24.6 | 233.2 | 112.4 |
| Simulated five | 145.2 | 580.7 | 107.8 | 25.8 | 36.2 | 35.6 | 20.7 | 235.0 | 119.8 |
| Simulated six | 175.2 | 602.7 | 90.9 | 25.7 | 29.7 | 39.2 | 21.9 | 245.1 | 115.2 |
| Real one | 118.8 | 490.0 | 53.7 | 15.0 | 15.6 | 24.5 | 16.2 | 212.8 | 41.4 |
| Real two | 183.2 | 730.9 | 98.5 | 24.9 | 31.6 | 47.4 | 25.7 | 278.1 | 71.7 |
| Real three | 107.6 | 437.1 | 48.5 | 13.5 | 14.7 | 18.5 | 15.7 | 200.6 | 36.3 |
| Mean | 145.8 | 585.5 | 86.8 | 21.5 | 25.9 | 33.3 | 20.2 | 234.1 | 88.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ling, J.; Meng, H.; Gong, D. Bio-Inspired Visual Network for Detecting Small Moving Targets in Low-Light Dynamic Complex Environments Based on Target Gradient Temporal Features. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9207. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169207
Ling J, Meng H, Gong D. Bio-Inspired Visual Network for Detecting Small Moving Targets in Low-Light Dynamic Complex Environments Based on Target Gradient Temporal Features. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(16):9207. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169207
Chicago/Turabian StyleLing, Jun, Hecheng Meng, and Deming Gong. 2025. "Bio-Inspired Visual Network for Detecting Small Moving Targets in Low-Light Dynamic Complex Environments Based on Target Gradient Temporal Features" Applied Sciences 15, no. 16: 9207. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169207
APA StyleLing, J., Meng, H., & Gong, D. (2025). Bio-Inspired Visual Network for Detecting Small Moving Targets in Low-Light Dynamic Complex Environments Based on Target Gradient Temporal Features. Applied Sciences, 15(16), 9207. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169207





