Non-Contact Heart Rate Monitoring Method Based on Multi-Source Data Fusion
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Procedures
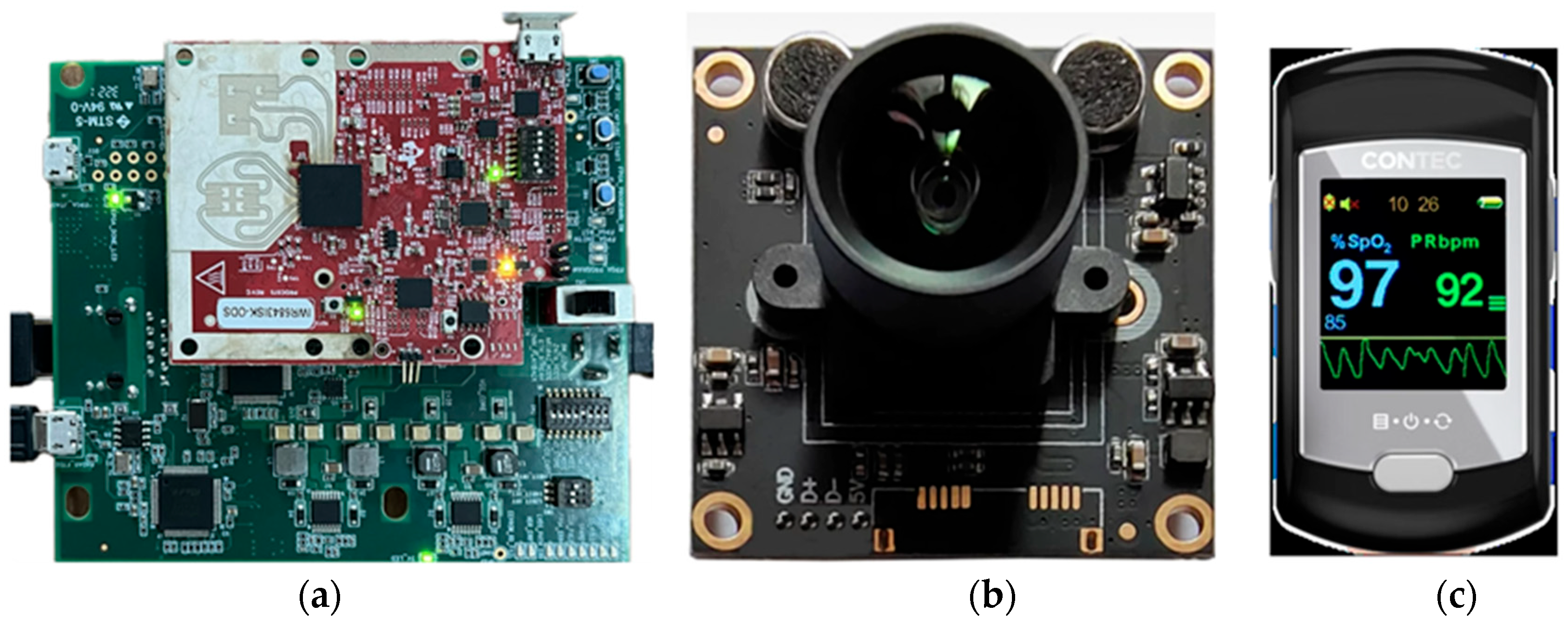
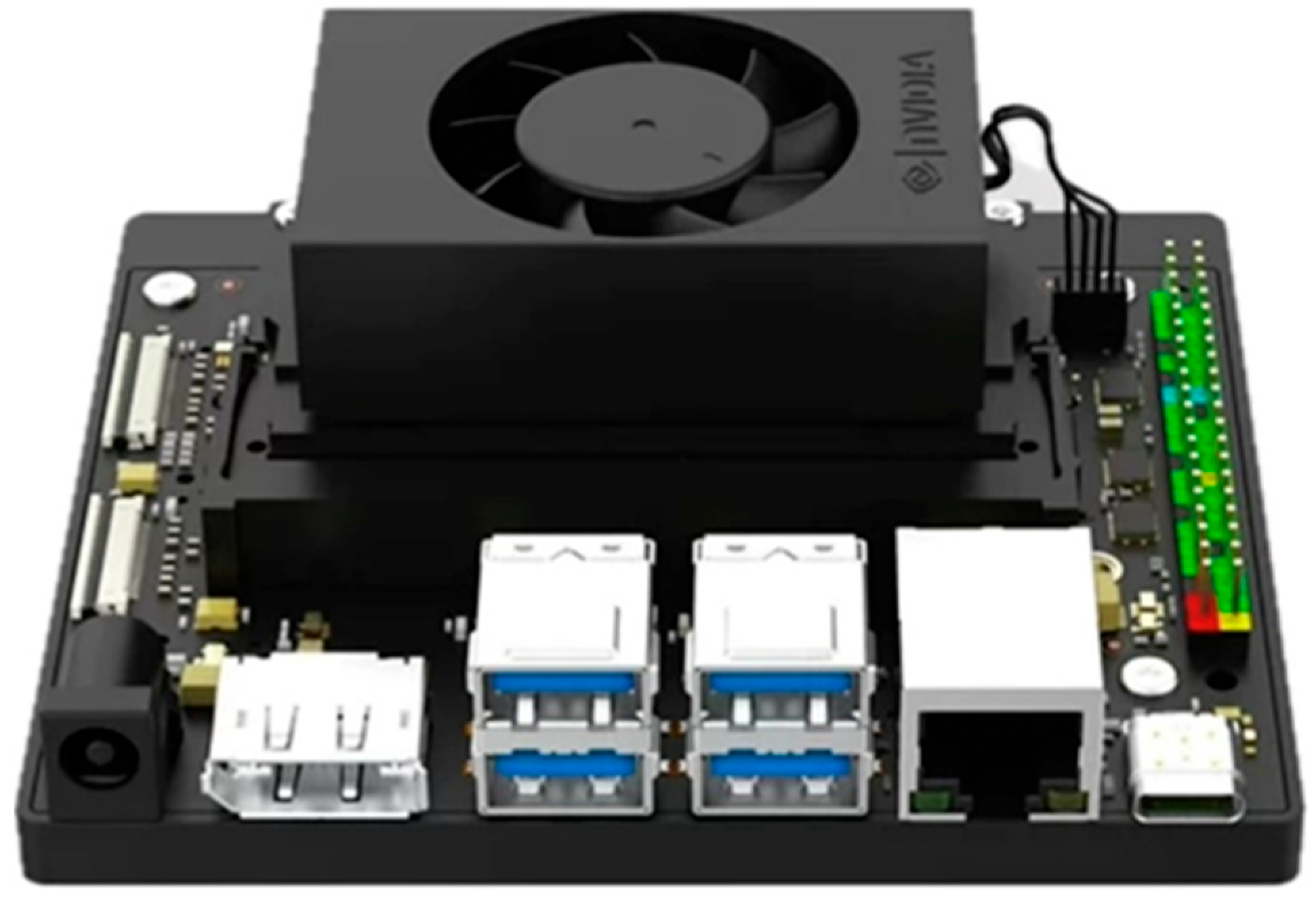
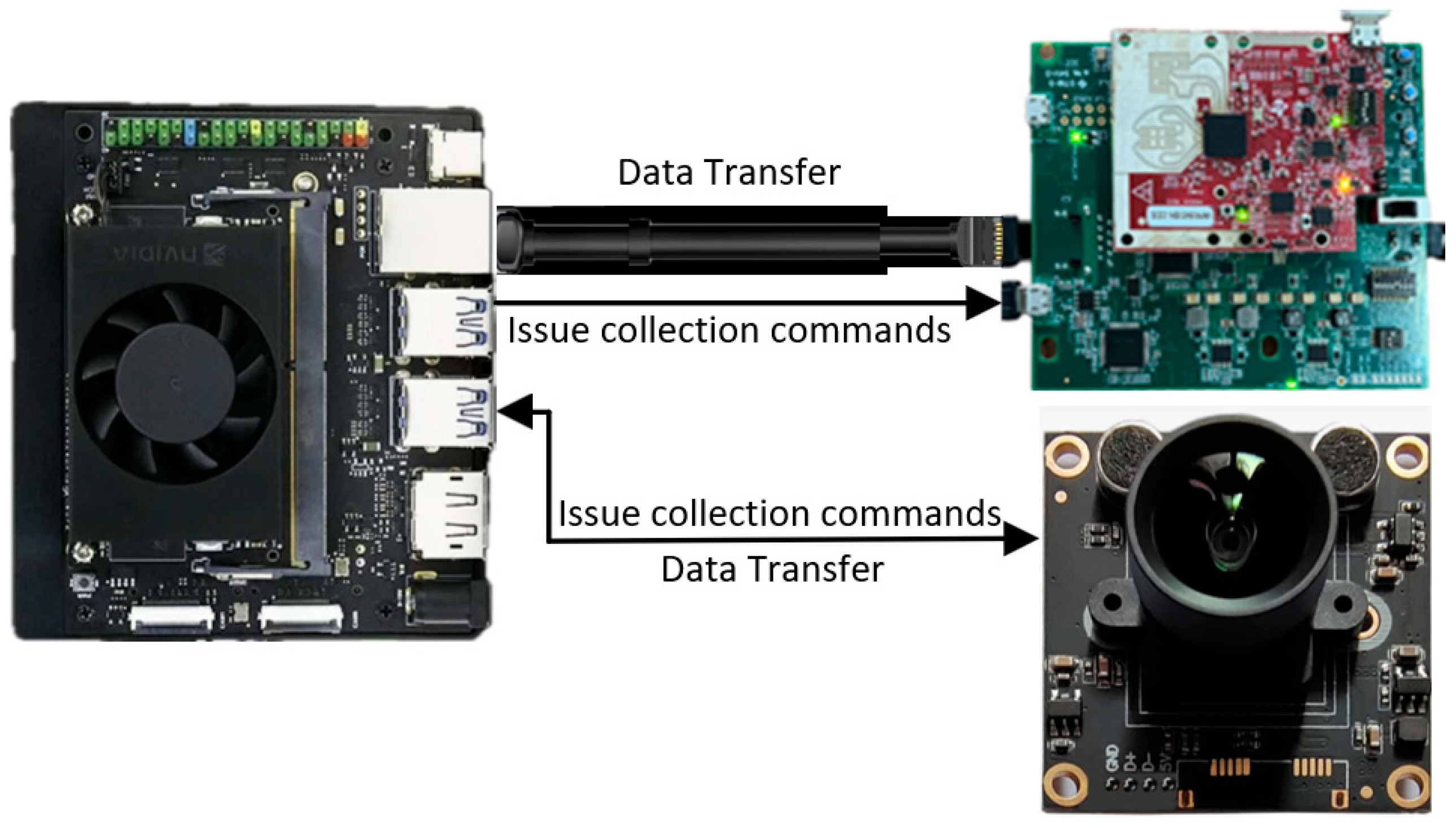
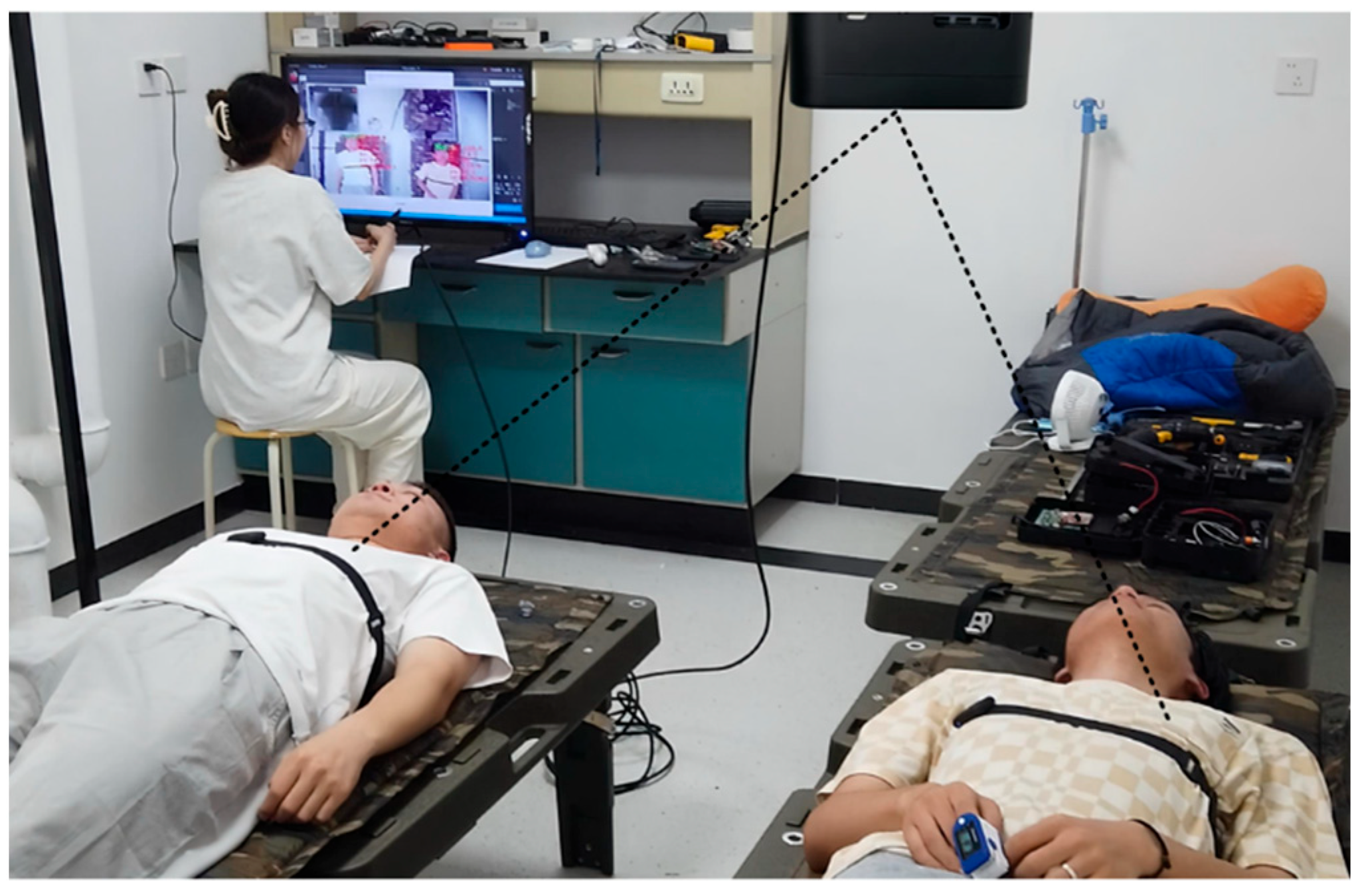
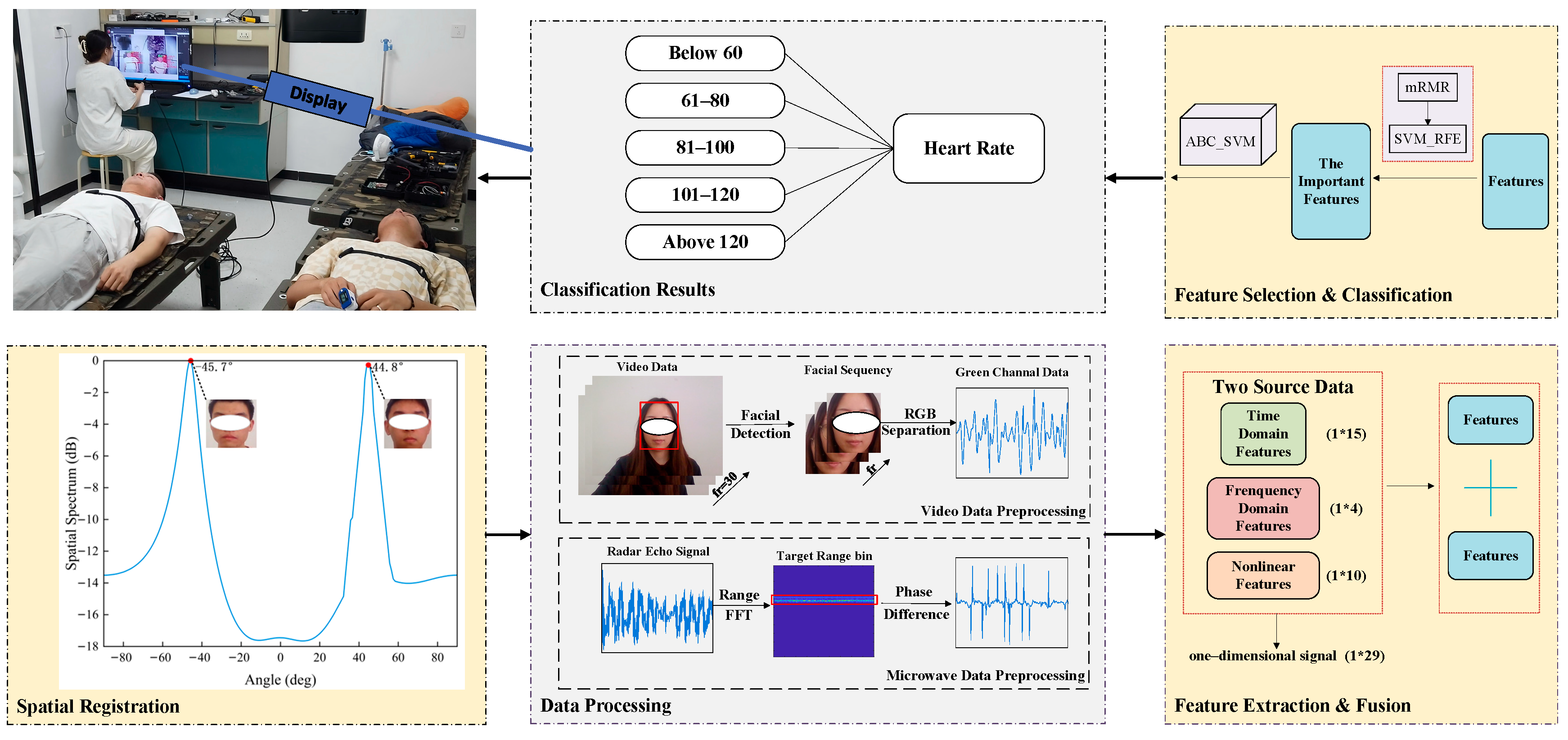
2.1. Data Acquisition
2.1.1. Experimental System Setup
2.1.2. Data Registration
2.2. Proposed Data Fusion Algorithm
2.2.1. Data Preprocessing
2.2.2. Feature Fusion Module
2.2.3. Multi-Source Data Fusion and Classification
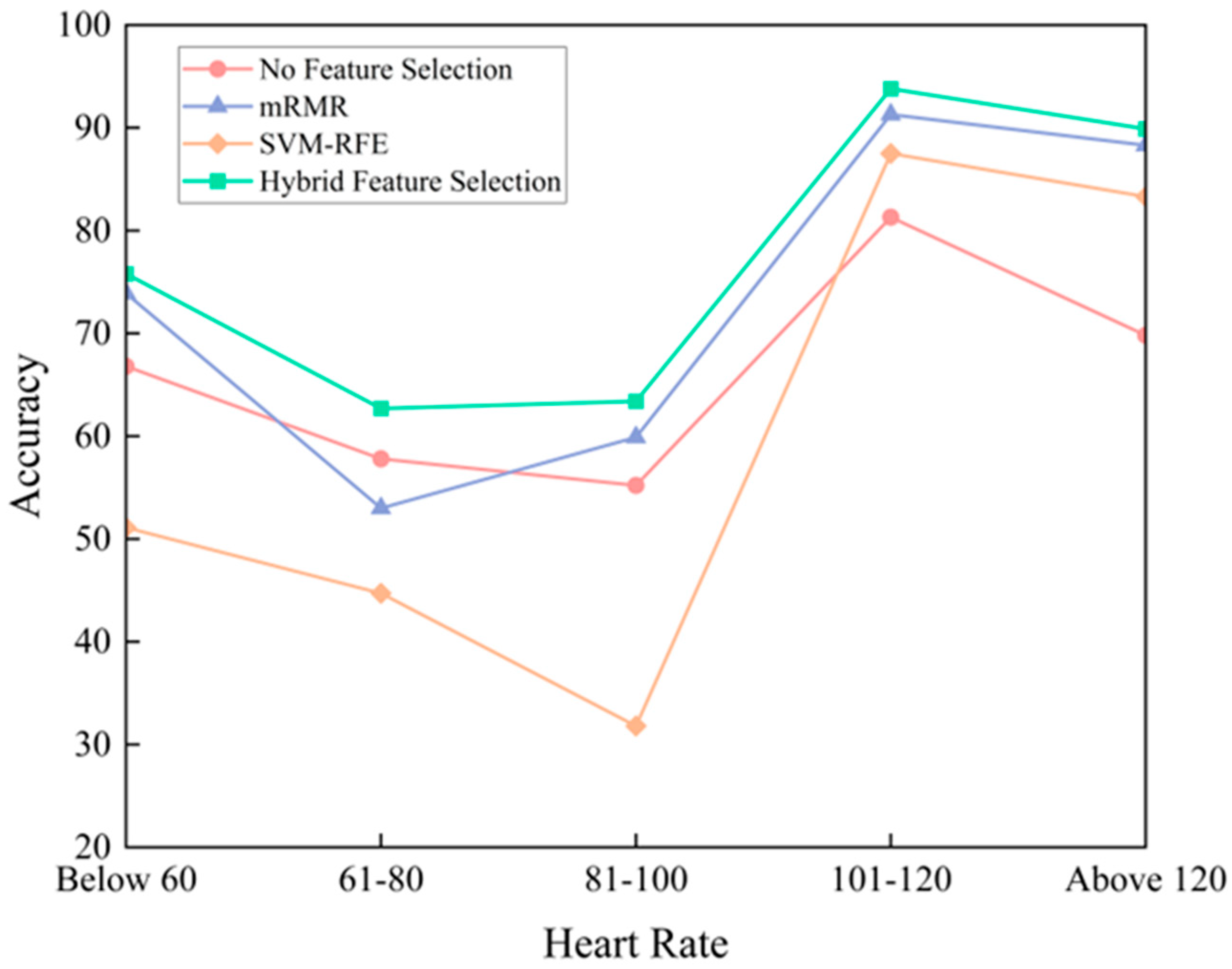
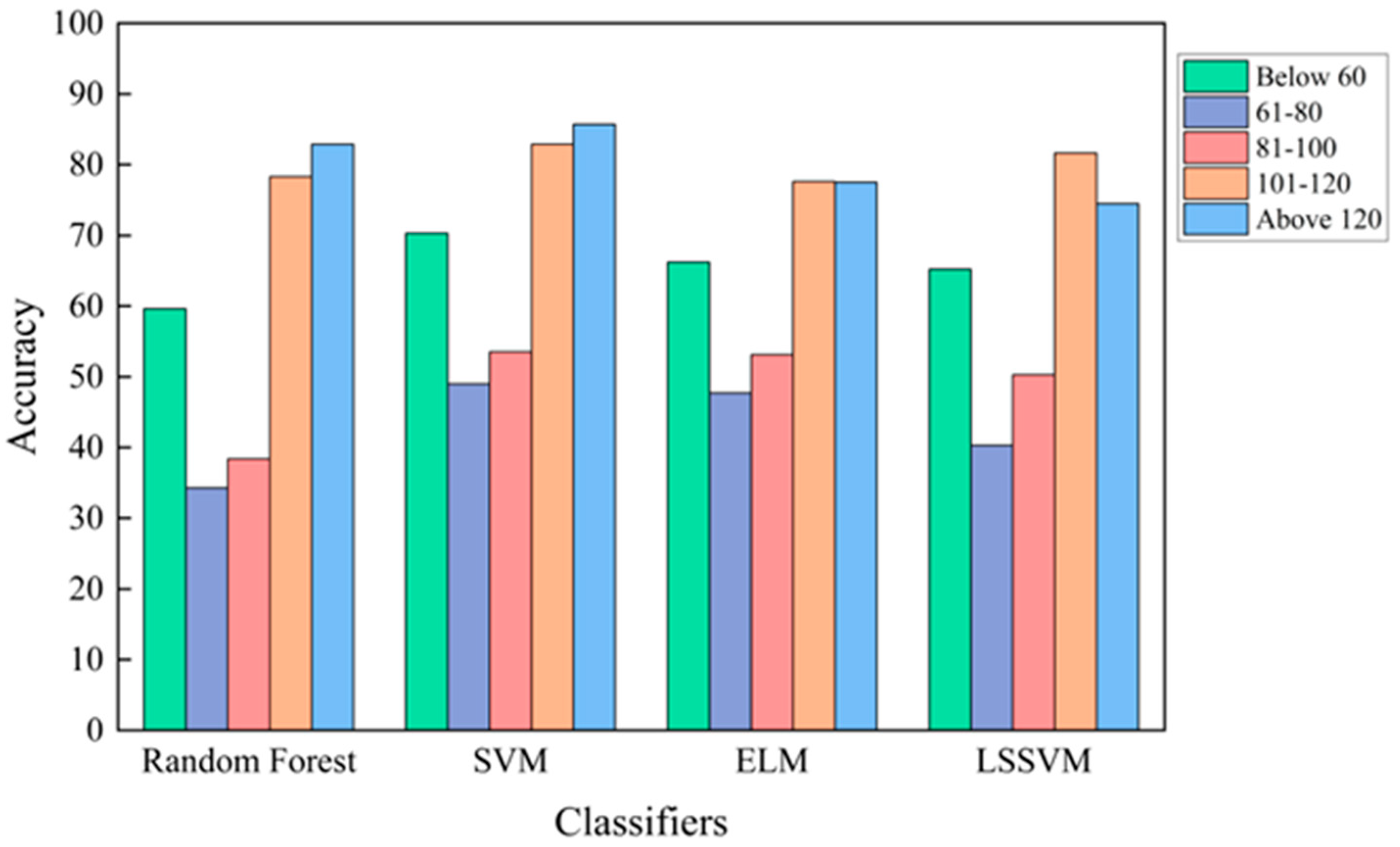
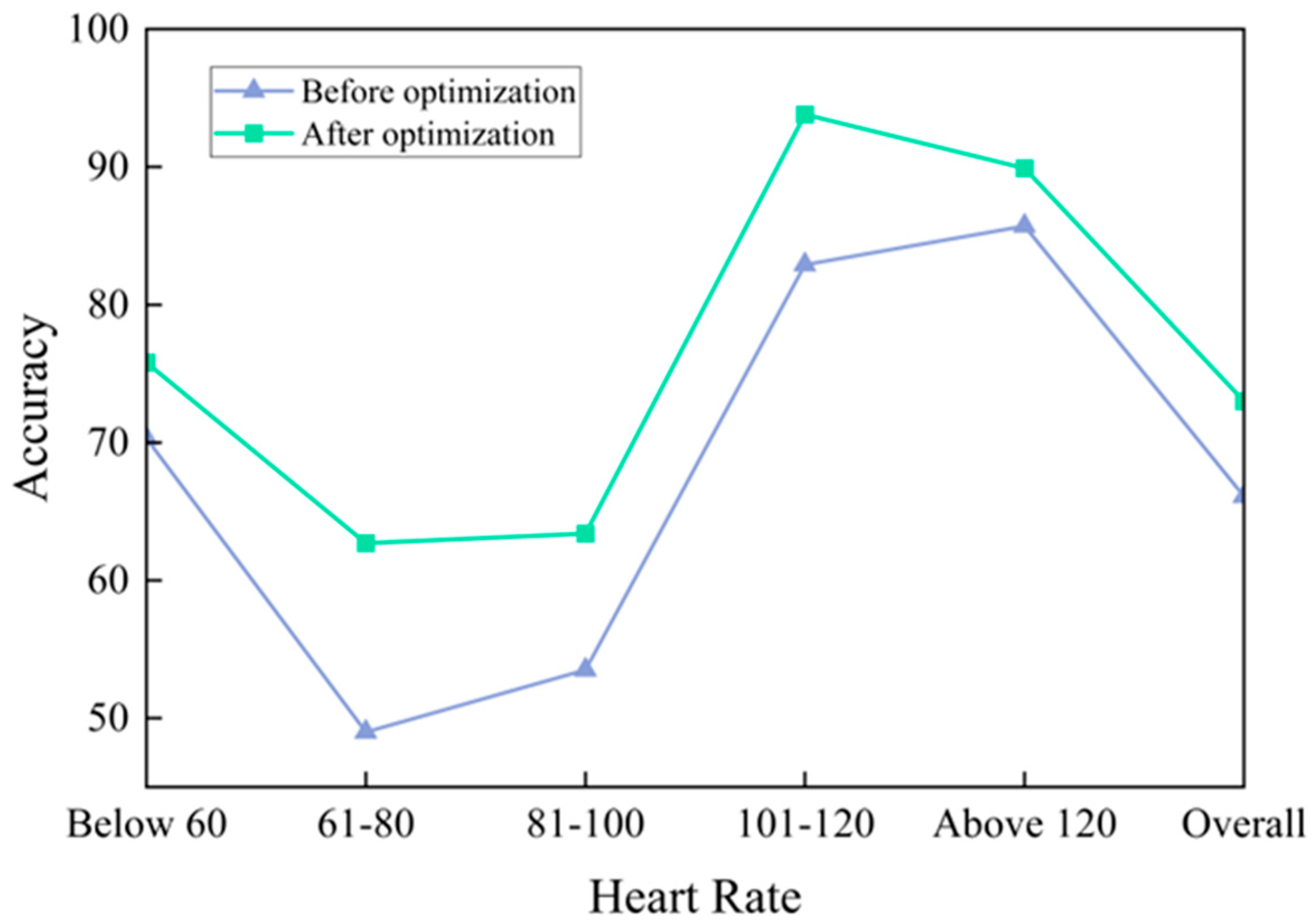
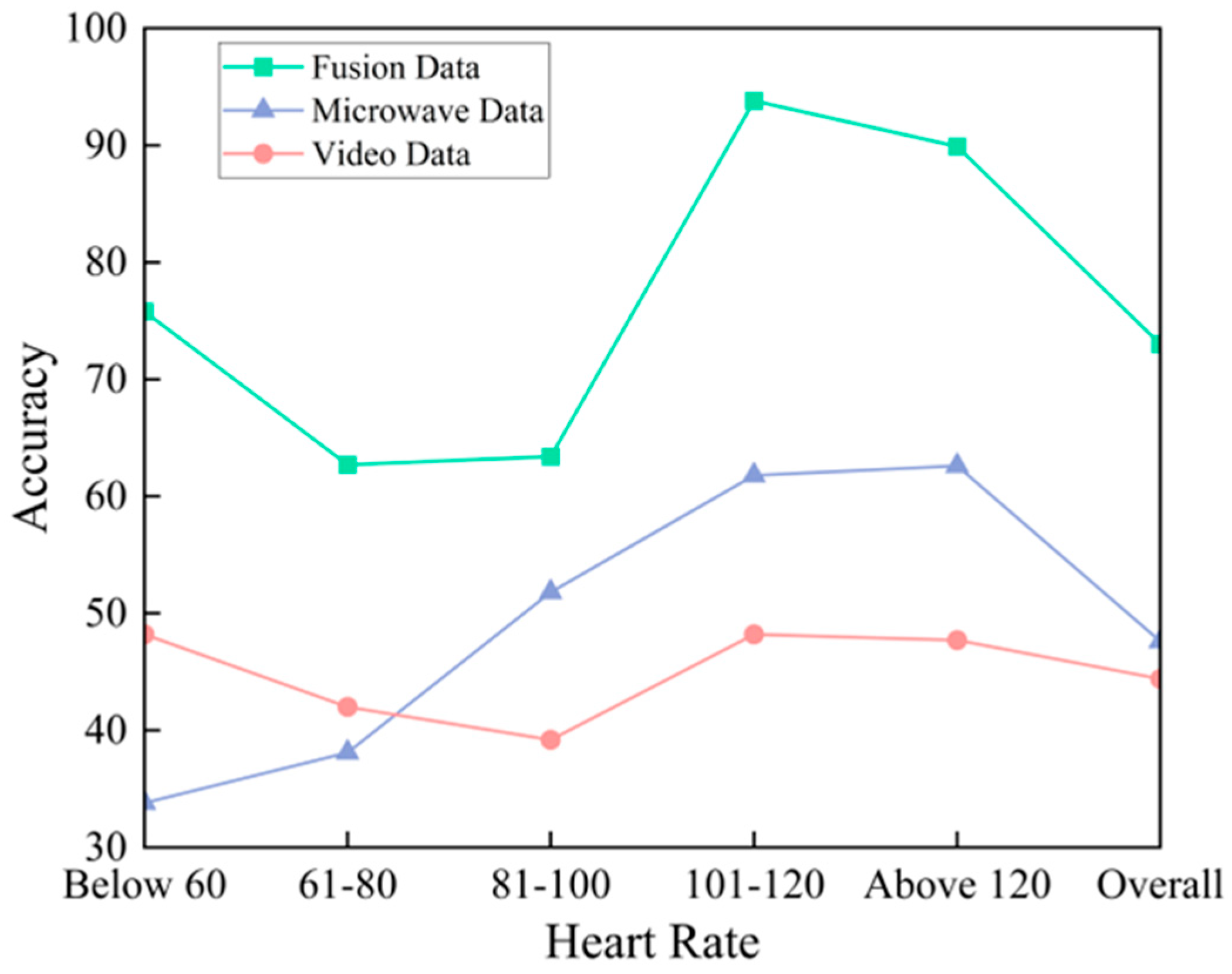
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, S.H.; Yoon, H. Convolutional Neural Networks for the Real-Time Monitoring of Vital Signs Based on Impulse Radio Ultrawide-Band Radar during Sleep. Sensors 2023, 23, 3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seflek, I.; Acar, Y.E.; Yaldiz, E. Small Motion Detection and Non-Contact Vital Signs Monitoring with Continuous Wave Doppler Radars. Elektron. Elektrotechnika 2020, 26, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.-C.; Sung, M.-C.; Wang, F.-K.; Horng, T.-S. Non-contact Vital Sign Detection Using Gain Detection Technique. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Radio-Frequency Integration Technology (RFIT), Hualien, Taiwan, 25–27 August 2021; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.; Kong, L.; Foroughian, F.; Wang, H.; Theilmann, P.; Fathy, A.E. Comparison Study of Noncontact Vital Signs Detection Using a Doppler Stepped-Frequency Continuous-Wave Radar and Camera-Based Imaging Photoplethysmography. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2017, 65, 3519–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. An image enhancement based method for improving rPPG extraction under low-light illumination. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2025, 100 Pt B, 106963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, L. Weighted combination and singular spectrum analysis based remote photoplethysmography pulse extraction in low-light environments. Med. Eng. Phys. 2022, 105, 103822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; Lu, F. Assessment of Deep Learning-Based Heart Rate Estimation Using Remote Photoplethysmography Under Different Illuminations. IEEE Trans. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 2022, 52, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Cheng, X.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, H.; Shi, J. ST-Phys: Unsupervised Spatio-Temporal Contrastive Remote Physiological Measurement. IEEE J. Biomed. Heal. Inform. 2024, 28, 4613–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ho, S.K.; Chin, J.W.; Luo, K.H.; Chan, T.T.; So, R.H.Y.; Wong, K.L. Deep learning-based image enhancement for robust remote photoplethysmography in various illumination scenarios. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 6077–6085. [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp, S.; Borner, U.; Caversaccio, M.; Tschopp, K. Long-term night-to-night variability of sleep-disordered breathing using a radar-based home sleep apnea test: A prospective cohort study. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2024, 20, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majer, F.; Yan, Z.; Broughton, G.; Ruichek, Y.; Krajník, T. Learning to see through haze: Radar-based Human Detection for Adverse Weather Conditions. In Proceedings of the 2019 European Conference on Mobile Robots (ECMR), Prague, Czech Republic, 4–6 September 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Iyer, S.; Zhao, L.; Mohan, M.P.; Jimeno, J.; Siyal, M.Y.; Alphones, A.; Karim, M.F. mm-Wave Radar-Based Vital Signs Monitoring and Arrhythmia Detection Using Machine Learning. Sensors 2022, 22, 3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Dong, S.; Wang, Y.; Gu, C.; Tang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Mao, J. Noncontact Infant Apnea Detection for Hypoxia Prevention With a K-Band Biomedical Radar. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 71, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Tsui, K.-L.; Nussbaum, M.A.; Kim, S.; Lure, F. An Indoor Fall Monitoring System: Robust, Multistatic Radar Sensing and Explainable, Feature-Resonated Deep Neural Network. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2023, 27, 1891–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissacher, D.; Galy, D. Cardiac radar for biometric identification using nearest neighbour of continuous wavelet transform peaks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Identity, Security and Behavior Analysis (ISBA 2015), Hong Kong, China, 23–25 March 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, F.; Song, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Xu, W.; Li, C.; Ren, K. Cardiac Scan: A Non-contact and Continuous Heart-based User Authentication System. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Snowbird, UT, USA, 16–20 October 2017; pp. 315–328. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, P.; Xia, W.; Li, Y. Heart ID: Human Identification Based on Radar Micro-Doppler Signatures of the Heart Using Deep Learning. Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Zhang, H.; Yao, Y.; Liu, C.; Jian, P.; Wang, P.; Du, L.; Chen, X.; Fang, Z.; Wu, Y. Heart signatures: Open-set person identification based on cardiac radar signals. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 72, 103306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dham, V. Programming Chirp Parameters in TI Radar Devices; Texas Instruments: Texas, TX, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, T.K.V.; Oleksak, K.; Kvelashvili, T.; Foroughian, F.; Bauder, C.; Theilmann, P.; Fathy, A.E.; Kilic, O. Enhancement of Remote Vital Sign Monitoring Detection Accuracy Using Multiple-Input Multiple-Output 77 GHz FMCW Radar. IEEE J. Electromagn. RF Microw. Med. Biol. 2022, 6, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Shan, S.; Han, H.; Chen, X. RhythmNet: End-to-End Heart Rate Estimation From Face via Spatial-Temporal Representation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 2409–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tian, J.; Li, D.; Hou, X.; Wang, L. Comparative study on the effect of color spaces and color formats on heart rate measurement using the imaging photoplethysmography (IPPG) method. Technol. Health Care 2022, 30, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinbao, Z.; Tiangang, Z.; Min, W.; Shidong, C. Bearing Fault Diagnosis Based on the Refined Composite Generalized Multi-Scale Bubble Entropy. In Proceedings of the 2021 4th International Conference on Electron Device and Mechanical Engineering (ICEDME), Guangzhou, China, 19–21 March 2021; pp. 172–175. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, R.-V.; Lucero, P.; Vásquez, R.E.; Cerrada, M.; Macancela, J.-C.; Cabrera, D. Feature ranking for multi-fault diagnosis of rotating machinery by using random forest and KNN. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 34, 3463–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Cao, Z.; Chen, Q.; Xiao, W. Extreme Learning Machine for Heartbeat Classification with Hybrid Time-Domain and Wavelet Time-Frequency Features. J. Healthc. Eng. 2021, 2021, 6674695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Geng, B.; Jiao, S. Refined Composite Multi-Scale Reverse Weighted Permutation Entropy and Its Applications in Ship-Radiated Noise. Entropy 2021, 23, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfson, E.J.; Fekete, T.; Loewenstein, Y.; Shriki, O. Multi-scale entropy assessment of magnetoencephalography signals in schizophrenia. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, W.; Tong, J.; Dong, Z.; Pan, H.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, J. Composite Multivariate Multi-Scale Permutation Entropy and Laplacian Score Based Fault Diagnosis of Rolling Bearing. Entropy 2022, 24, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, Z.; Xie, H.; Yu, W. Characterization of Surface EMG Signal Based on Fuzzy Entropy. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2007, 15, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yang, T.; Li, H.; Zhou, Z. Air quality prediction model based on mRMR–RF feature selection and ISSA–LSTM. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshamlan, H.; Badr, G.; Alohali, Y. mRMR-ABC: A Hybrid Gene Selection Algorithm for Cancer Classification Using Microarray Gene Expression Profiling. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 604910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, H.; Valim, C.; Vegas, E.; Oller, J.M.; Reverter, F. SVM-RFE: Selection and visualization of the most relevant features through non-linear kernels. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonneau, M.; Benet, B.; Labrune, Y.; Bailly, J.; Ricard, E.; Canario, L. Predicting sow postures from video images: Comparison of convolutional neural networks and segmentation combined with support vector machines under various training and testing setups. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 212, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Tian, T.; Yao, T.; Zhang, Q. Human Gait Recognition Based on Multiple Feature Combination and Parameter Optimization Algorithms. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 2021, 6693206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


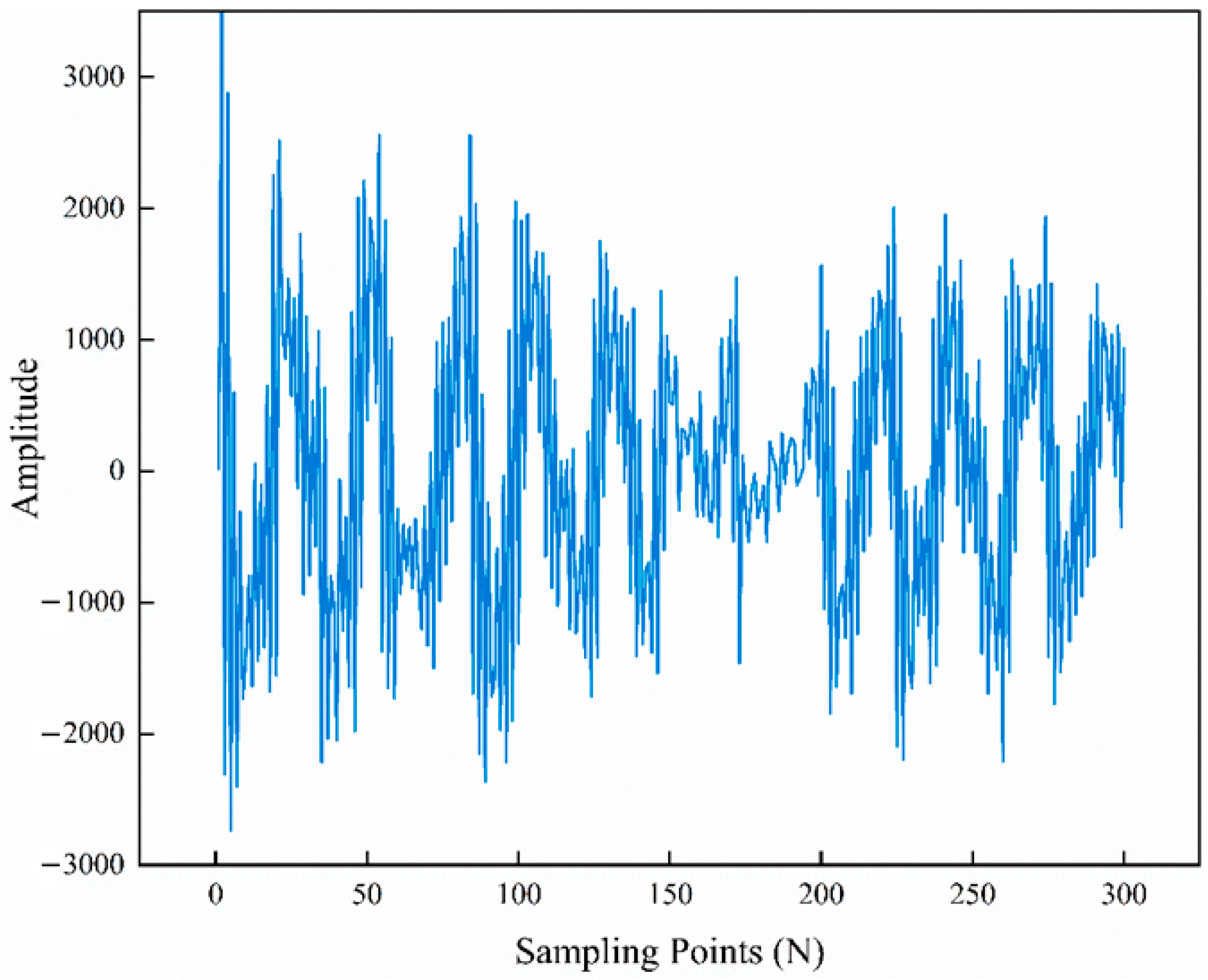

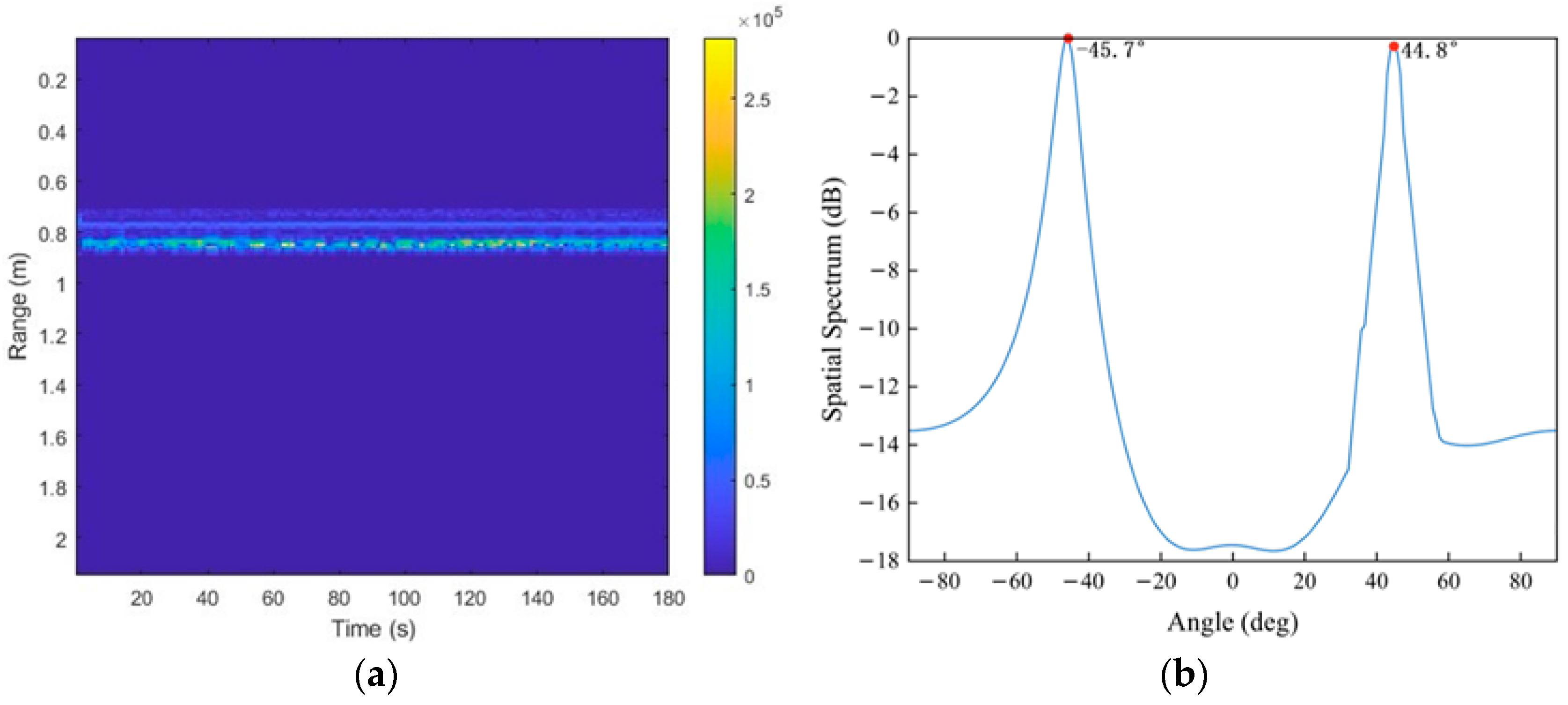

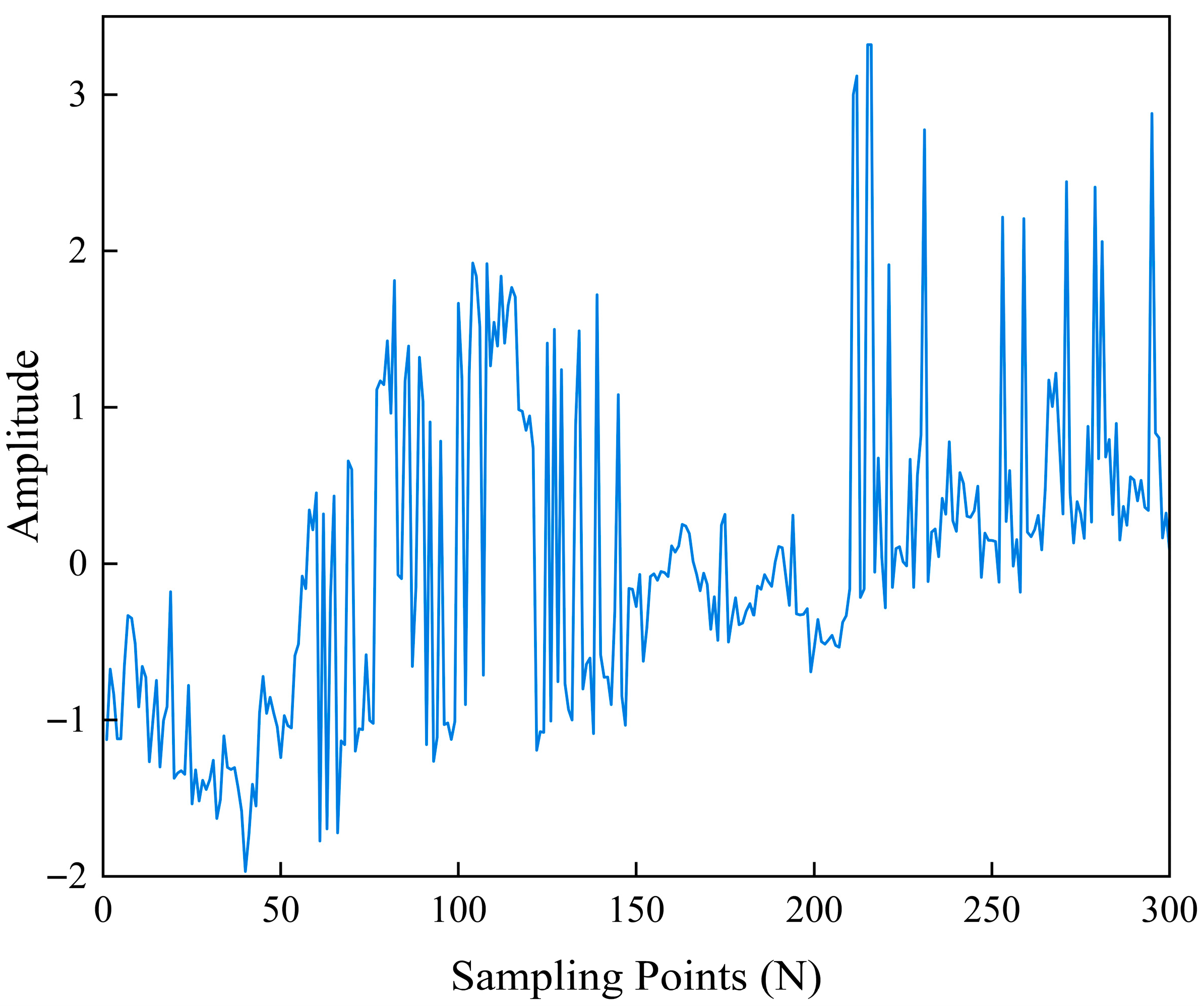
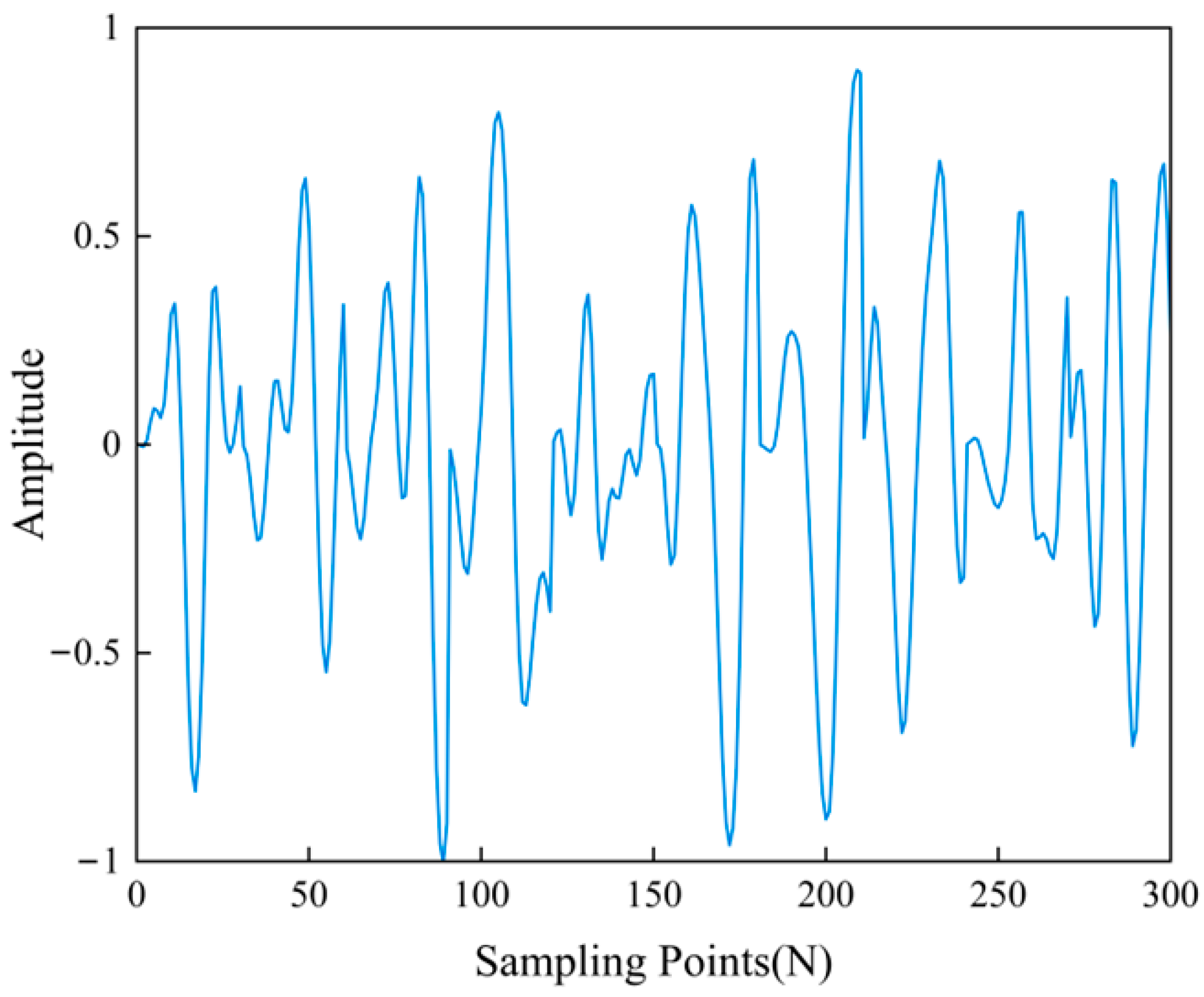
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Start Frequency, | 60 |
| Frequency Slope, | 70 |
| Idle Time | 7 |
| TX Start Time | 1 |
| ADC Start Time | 6 |
| ADC Samples | 200 |
| Ramp End Time | 57 |
| Slow-time Sampling Frequency | 200 |
| Range Resolution | 4.29 |
| Classifiers | Runtime (s) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Random Forest | 4.28 | 61.7 |
| SVM | 2.88 | 66.1 |
| ELM | 2.79 | 63.5 |
| LSSVM | 1.55 | 64.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Teng, Z.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yu, M. Non-Contact Heart Rate Monitoring Method Based on Multi-Source Data Fusion. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9189. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169189
Li Q, Teng Z, Shi Y, Zhang G, Yu M. Non-Contact Heart Rate Monitoring Method Based on Multi-Source Data Fusion. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(16):9189. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169189
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qinwei, Zhongxun Teng, Yuping Shi, Guang Zhang, and Ming Yu. 2025. "Non-Contact Heart Rate Monitoring Method Based on Multi-Source Data Fusion" Applied Sciences 15, no. 16: 9189. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169189
APA StyleLi, Q., Teng, Z., Shi, Y., Zhang, G., & Yu, M. (2025). Non-Contact Heart Rate Monitoring Method Based on Multi-Source Data Fusion. Applied Sciences, 15(16), 9189. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169189






