Abstract
The review enumerates the predominant applications of large language models (LLMs) in natural language processing (NLP) tasks, with a particular emphasis on the years 2023 to 2025. A particular emphasis is placed on applications pertaining to information retrieval, named entity recognition, text or document classification, text summarization, machine translation, question-and-answer generation, fake news or hate speech detection, and sentiment analysis of text. Furthermore, metrics such as ROUGE, BERT, METEOR, BART, and BLEU scores are presented to evaluate the capabilities of a given language model. The following example illustrates the calculation of scores for the aforementioned metrics, utilizing sentences generated by ChatGPT 3.5, which is free and publicly available.
1. Introduction
The field of generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) is experiencing unprecedented growth and transformation. This rapid development is closely intertwined with the human domain, bringing about profound and often irreversible changes across multiple aspects of society. From communication and education to creative industries and scientific research, GenAI is redefining the boundaries of what machines can achieve. It is increasingly evident that the future will be shaped by a range of innovations, enhancements, and opportunities for individuals and organizations that harness the potential of artificial intelligence (AI).
The remarkable capabilities of GenAI—such as generating human-like text, images, code, and even decision-making insights—have drawn significant attention from academia, industry, and policymakers alike. This growing interest stems not only from the technological sophistication of AI systems but also from their broad applicability and societal impact. However, it is equally critical to acknowledge the accompanying challenges. As with many emerging technologies, the rise of GenAI presents complex ethical, technical, and regulatory concerns. Issues related to data privacy, misinformation, algorithmic bias, and the potential displacement of human labor are already prompting intense debate.
Moreover, skepticism remains prevalent within segments of the scientific community. Some researchers question the reliability, transparency, and long-term implications of delegating cognitive tasks to machines. Others advocate for more cautious and responsible development, emphasizing the need for robust oversight and inclusive dialogue. In this context, the continued evolution of GenAI represents not only a technological milestone but also a societal crossroads—one that calls for a balanced and informed approach to innovation.
1.1. The State of the Art
Reference [1] analyzes the impact of GenAI on individuals, organizations, and society. GenAI is grounded in LLMs and related generative technologies. The author posits that while LLMs are driving a paradigm shift in language processing and work automation, they simultaneously pose risks such as the spread of misinformation, the reinforcement of biases, and the erosion of users’ cognitive abilities. He concludes by emphasizing that the development of these technologies is inevitable; however, their ethical and equitable use requires informed political and societal decisions. Manduva [2] observes that, despite the growing adoption of LLMs in corporate contexts, implementation remains in its early stages, with many organizations still in the pilot phase. The use of these models is primarily aimed at a few objectives, f.e., to enhance decision-making processes or to support the development of new products. The author argues that software based on LLMs should be developed in a standardized manner, thereby increasing the potential to achieve measurable business outcomes. The influence of artificial intelligence based on LLMs on daily life is expanding. The article by Okaiyeto [3] elaborates on the potential of generative artificial intelligence and large language models in education, highlighting their ability to enable personalized instruction, automate tasks, and foster creativity. It is essential to acknowledge the associated ethical challenges, the possibility of inaccuracies, and the need for appropriate regulations and educational programs for users. A similar viewpoint is presented by Lim at el. [4]. The article argues that despite the facilitation offered by large-scale models, a critical stance regarding the credibility of the generated content remains crucial. The author of [5] provides a comprehensive analysis of large language models in the context of higher education, emphasizing the role of natural language processing in personalizing learning, automating administrative processes, and supporting data analysis. The integration of AI with innovative educational frameworks and the cultivation of digital competencies are deemed imperative. Additionally, proper legal regulations must be enacted to fully harness AI’s potential in the educational sector. Reference [6] analyzes the influence of large language models, such as GPT, on programming education and student learning outcomes. It demonstrates that LLMs can facilitate the learning process by assisting with coding, clarifying complex concepts, and providing immediate feedback. At the same time, it stresses that effective use of these tools requires adequate oversight to prevent overreliance on AI without critical thinking and to promote the development of independent programming skills. The article hypothesizes that incorporating LLMs into pedagogical practice may improve student performance; however, maintaining a balance between technological support and autonomous problem-solving remains essential.
AI technology is used in medicine. Reference [7] provides a thorough review of the applications of generative artificial intelligence, including large language models and multimodal systems. It offers an in-depth analysis of the use of generative AI across various medical domains, addressing a wide range of stakeholders such as clinicians, patients, clinical trial coordinators, researchers, and students. The reviewed document highlights several benefits, including improved clinical documentation, diagnostic support, automation of research protocols, and the facilitation of medical education. However, it also emphasizes key challenges, such as concerns regarding privacy and data security, the interpretability of AI models, the mitigation of errors (e.g., hallucinations), and the need for robust evaluation of the real-world impact of these technologies. This summary aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the subject. The authors advocate for continued research and development focused on user interfaces, regulatory frameworks, and ethical standards to ensure a balanced integration of innovation, safety, and equity in healthcare AI applications. In [8], researchers present a discussion of the potential of LLMs, such as GPT-4 and BERT, to transform the field of healthcare through their capacity to support diagnostic processes, therapeutic interventions, medical education, and research endeavors in both textual and multimodal forms, including images, audio, and video. LLMs facilitate the automation of clinical documentation, the analysis of patient data, the creation of educational materials, and the streamlining of medical administration. These capabilities contribute to reducing the workload for healthcare professionals and enhancing system efficiency. Concurrently, the authors identify significant challenges, including reliability issues (such as model hallucination), content bias, privacy issues, interpretive difficulties, and the necessity for a regulatory and ethical framework for integrating LLMs into healthcare. The article “An Evaluation Framework for Clinical Use of Large Language Models in Patient Interaction Tasks” [9] introduces a novel evaluation framework—CRAFT-MD (Conversational Reasoning Assessment Framework for Testing in Medicine)—designed to assess LLMs in clinical contexts. The aim of the study is to evaluate the preparedness of LLMs for real-world medical applications involving patient interactions. Unlike traditional approaches based on structured medical examinations, the CRAFT-MD framework emphasizes the importance of natural dialogue. It employs simulated AI agents to interact with the LLMs in a controlled environment. The evaluated models include GPT-4, GPT-3.5, Mistral-v1-7b, Mistral-v2-7b and LLaMA-2-7b. The introduction of CRAFT-MD marks a significant step forward in the evaluation of clinical LLMs, with its central goal being to ensure that these models can provide effective, safe, and ethically responsible support in medical practice. The growing popularity of language models across various medical specialties still necessitates numerous improvements. The study conducted by Shahid and colleagues [10] focuses on comparing the performance of LLMs with that of cardiologists in responding to cardiology-related clinical queries, utilizing questions from the American College of Cardiology Self-Assessment Program (ACCSAP) question bank. A total of 70 clinical questions were selected for the study, categorized by diagnostic phase (pre- or post-diagnosis) and user profile (patient or physician). Three experienced cardiologists, blinded to the identity of the models, evaluated each response based on scientific accuracy, completeness, clarity, and consistency. The experiments and results presented underscore the importance of adapting language models to specific domains of medicine and highlight the necessity of human oversight for the safe integration of LLMs into clinical practice. This study provides empirical evidence for the responsible use of LLMs in healthcare and serves as a benchmark for future research and regulatory efforts concerning artificial intelligence in medicine.
Artificial intelligence based on large language models is also being utilized in the field of radiology. Nevertheless, there is a pressing need to standardize education and raise awareness regarding the capabilities of AI-driven tools. The authors of [11] emphasize that despite the growing importance of these technologies, the preparedness of specialists to effectively use them remains insufficient. It is therefore essential to implement appropriate training programs aimed at disseminating knowledge about the practical application of the available tools. This is particularly important due to the growing evaluative and diagnostic capabilities demonstrated by LLMs. Research [12] has shown comparisons between the diagnosis of chest radiology cases performed by LLMs and by clinical radiologists, highlighting the relevance and potential utility of these models. While LLMs are not capable of analyzing images directly, they can provide significant support in processing key aspects of patient history, test results, and radiologists’ written reports. LLMs may assist in retrieving relevant information, generating reports, and composing differential diagnosis lists. Models like GPT-4 and Claude-3-Opus can effectively transform complex IR reports into patient-centered, simplified narratives while maintaining clarity and reliability [13]. Even top-performing models exhibit occasional clinically critical errors, underscoring the importance of human oversight, quality control, and domain adaptation before real-world clinical usage. Success in this task requires a multi-dimensional evaluation combining both qualitative clinician feedback and quantitative readability assessment to capture both accuracy and accessibility.
The application of LLMs may prove valuable in the context of emergency surgery [14]. In conditions where there is high stress and limited time—typical in emergency departments—artificial intelligence can assist physicians by analyzing clinical information, preparing medical documentation, or performing any tasks related to text processing or generation. The authors emphasize that despite the significant facilitation provided by AI-based technologies, clinical oversight remains essential. Language models cannot replace the experience of a surgeon. Once again, researchers highlight the necessity of developing legal and ethical frameworks that enable the integration of AI into clinical surgery. The authors of article [15] argue that clinical artificial intelligence—including machine learning and large language models—is reaching a pivotal moment, poised to reshape surgical care pathways from preoperative screening to postoperative follow-up. They explore AI applications across surgical domains: from early diagnosis and risk stratification, through intraoperative robotics and computer vision, to postoperative monitoring and administrative assistance. While AI and LLMs hold clear promise for enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and workflow optimization in surgical practice, the article stresses that realizing these benefits requires rigorous validation, human oversight, patient privacy protection, and robust governance frameworks.
The development of LLMs has enabled the creation of systems capable of processing data to make decisions and perform certain actions during surgical procedures. The authors of [16] presented a model that integrates natural language understanding with image analysis, allowing the robot to operate effectively and contextually in surgical environments. The presented study demonstrates that such systems can significantly enhance the autonomy of surgical robots by enabling them to independently recognize the need for blood suction and perform the task accordingly, thereby reducing the burden on surgeons and increasing the precision of the intervention. Generative AI has also found applications in genetics, where it supports the analysis of large genomic datasets, including data from genomics, transcriptomics, and proteomics [17]. Artificial intelligence also contributes to the advancement of personalized medicine by aiding in disease detection and drug development. In the aforementioned article, as in all previously discussed works, the authors highlight the challenges related to data privacy and protection. Once again, the necessity for legal regulations concerning the ethical use of AI-based tools is emphasized. The information presented in reference [18] expounds on the evolution of the methodology used to evaluate the risk of developing lung cancer. The significance of this research area is reinforced when evaluated in the context of the ongoing Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. The progress of this research area has led to the ability to predict such events more accurately in other fields, such as marketing [19], risk analysis [20], and natural language processing. The utilization of artificial intelligence has enabled the evaluation of voluminous datasets that were formerly challenging to process. These datasets necessitated substantial investments of human labor, temporal resources, and financial capital for analysis. It is also noteworthy that once trained, models can be re-trained, thereby enabling a more precise determination of relationships between data or the prediction of subsequent events.
The primary objective of GenAI is to generate novel entities, such as objects, content, or data, drawing upon existing information. This requires the utilization of substantial datasets, from which it can develop its knowledge. The models exhibit significant heterogeneity, with each model’s foundation being distinct sets of data, contingent upon its specific objective. Consequently, an increasing number of collections are being made available online. Statistical evidence underscores the exponential growth of interest in GenAI. The most critical aspect of using AI is to meticulously delineate the objective of the research study and to specify the anticipated outcomes, the criteria for selecting data, and the potential constraints. The fulfillment of these aspects will provide a solid foundation for the proper preparation of the model that will be subjected to machine learning. The definition of the topic provides direction, enabling subsequent stages of the work to be carried out with a greater degree of efficacy. The selection of a database is of paramount importance [21]. It is imperative to acknowledge that the evaluation of the collected materials’ usefulness is contingent upon the specific purpose of the evaluation. It is important that the data be both diverse and comprehensive in order to effectively capture the underlying patterns or relationships that exist between events. In the digital realm, researchers have made available a variety of benchmark databases [22].
1.2. Novelty of This Paper
This paper presents a collection of information regarding GenAI. LLMs have received special attention as they are used for specific NLP tasks. The number of issues utilizing language models has been limited to 10, which can be categorized as follows:
- Information retrieval;
- Named entity recognition;
- Text classification;
- Machine translation;
- Text summarization;
- Question and answering generation;
- Fake news detection;
- Hate speech detection;
- Text generation;
- Sentiment analysis.
This work is a set of knowledge based on publications from 2023 to 2025. As a result, readers can become familiar with innovations, the development process, and changes that occurred during the dissemination of artificial intelligence based on large language models. The issues are described in terms of the specific tasks performed using LLMs, as well as their usefulness in various aspects of everyday life. Another feature of the work is the presentation of metrics that allow researchers to evaluate generated content quality. The work includes detailed descriptions, formulas, and explanations of the usability of these metrics:
- ROGUE (Recall-Oriented Understudy for Gisting Evaluation).
- METEOR (Metric for Evaluation of Translation with Explicit ORdering).
- BLEU (Bilingual Evaluation Understudy).
- BERTScore.
- BARTScore (Bidirectional and Auto-Regressive Transformers).
We believe that this work will be a valuable resource for readers with varying levels of experience with large language models. This article offers general and detailed information on the key aspects of working with large language models. The subsequent sections of the article contain the following:
- A thorough examination of contemporary scholarly publications pertaining to LLMs is presented, offering both a comprehensive review and a detailed analysis of the extant literature.
- An examination of the benefits and risks associated with the implementation of artificial intelligence.
- A description of text generation.
- A classification and description of ten NLP tasks, with the use of LLMs.
- A detailed exposition of five widely accepted metrics for the evaluation of the quality of content that has been generated.
- A discussion on the potential for the development of artificial intelligence that uses large language models.
2. Materials and Methods
The use of AI to generate content has become a subject of considerable controversy. There is an emerging discourse surrounding the authenticity of the content in question, with questions being raised about its authorship and the possibility of it being a fabrication of a language model. According to researchers, contemporary AI methodologies have enabled the development of text-generating systems capable of producing written compositions that bear a notable similarity to those crafted by human authors. The discernment of human-crafted expressions is becoming increasingly challenging. The authors of the study report that there is still a discrepancy in the quality of writing, with a noticeable gap remaining between detailed descriptions of facts and the overall lower quality of texts created by computers [23]. In the mentioned publication, the authors investigated the writing style, as well as the similarities and differences between AI-generated and human-generated scientific content. During the analyses, a number of factors were given full consideration, including consistency, content issues, and linguistic redundancy. A similar perspective is expressed in other sources [24]. Despite the extensive capabilities of GenAI, scientists have asserted that the detection of texts generated by artificial intelligence remains a viable task. Text generation has several main tasks that can be split into smaller batches. We use the division to obtain the results, which will include a summary of the text; discuss all the steps; and present the models that are readily used to reach the goals for the listed tasks of natural language processing.
2.1. Large Language Models
Large Language Models [25,26,27] are characterized by a vast number of parameters and impressive learning abilities, enabling them to understand and generate human-like language. The high quality of their output often makes it difficult to distinguish from human-authored content. LLMs predict word sequences based on input data, often relying on Transformer architectures [28], which have revolutionized NLP through their efficiency in handling sequential data and identifying contextual relationships.
While early models, such as the N-gram [29], laid foundational principles for probabilistic language modeling, modern LLMs excel at processing unstructured data without predefined formats. However, challenges remain, particularly in handling rare expressions and adapting to the evolving nature of natural language. Recent advancements by OpenAI and others have produced models like ChatGPT, PaLM [30], and Bard (Gemini) [31], which are capable of performing at human, professional, and academic levels [32]. These models are widely used across sectors, including education and marketing [33], where they have shown to improve efficiency and outcomes.
Nonetheless, LLMs are subject to criticism. Common concerns include their lack of semantic understanding, potential to reproduce training data, limited symbolic reasoning, and susceptibility to factual errors or “hallucinations” [34,35]. Some argue that LLMs cannot truly replicate human language learning, which is grounded in interaction and smaller datasets. Others highlight the models’ inability to represent formal linguistic systems, though emerging research suggests some transformers can capture hierarchical syntactic structures [36,37,38].
Despite these limitations, LLMs have proven valuable in applications such as sentiment analysis, medical image interpretation, and adapting to novel instructions through reinforcement learning [39]. The debate surrounding their capabilities underscores the need for continued evaluation and responsible development.
2.2. The Tasks of Natural Language Processing Using the GenAI with Large Language Models
2.2.1. Information Retrieval
Information extraction aims [40] to capture the content precisely described in a user-written query. This data comes from large repositories. The Information Retrieval (IR) system evaluates the relevancy of the data and creates a ranking of the data expected to yield the most relevant results. A well-known model for linking queries to information is the Boolean model. This model uses Boolean operators to ensure that only content linked to a query by satisfying the appropriate conditions is considered [41]. Another solution for combining queries and results is the so-called “bag-of-words” method. In this method, a vector space model is created that represents queries as vectors and stores documents in the space. Using an inverted index has made this method more precise. Relevance assessment is performed by comparing the lexical similarity between the query and the available documents [42]. In recent years, there has been an increase in the popularity of the neural infrared paradigm [43,44,45]. This solution is based on a representation of neural networks that can capture the semantic and lexical relationships between queries and documents. This significantly improves search performance. There are various models based on corresponding learning systems: HyDE [46,47] and LameR [48] use zero-shot prompting methods, Query2doc [49,50] uses a few-shot method, and CoT [51], flanT5 [52], and GRM [53] are based on a chain-of-thought method.
2.2.2. Named Entity Recognition
Another NLP task is named entity recognition (NER), which is the identification and classification of elements in unstructured content [54,55]. This technology plays a crucial role in machine translation [56], creating answers to questions or IR. Many articles discuss NER systems that translate text into different languages, primarily English, but there are also systems for Chinese [57,58], Japanese [59,60], or German [61,62]. The original NER solutions were based on algorithms that examined lexical, orthographic, and grammatical correctness [63]. Subsequent algorithms were based on machine learning [64], neural networks [65], and transformers [40]. Examples of applications using NER include
- Information extraction;
- Information retrieval;
- Text or document summarization;
- Social media monitoring;
- Named entity recognition;
- Question answering;
- Machine translation.
2.2.3. Text and Document Classification
Classifying text and documents [66,67,68] is an area that has long occupied researchers. In order to classify text or documents, it is necessary to go through the following four stages [69,70]:
- Text preparation, including size reduction;
- Feature extraction;
- Choice of classifier;
- Classification.
The first step is to organize the text, which was previously characterized as unstructured. Text data should have a numerical representation. Therefore, it is necessary to project the text data into a feature space. Without this step, it is impossible to extract relevant features. Appropriately preparing the collected information in the first stage of work, it is essential for the correct performance of classification algorithms and obtaining the expected results in further text processing [71]. First, unnecessary characters and words must be removed. In this case, they are considered unnecessary if they do not significantly impact the meaning of the information. After introducing appropriate structures to the text, it is represented in the form of a bag of words or as n-grams. After this stage, the amount of data is limited and formal feature extraction methods can be applied. Popular approaches include techniques based on frequency of occurrence, such as inverse document frequency (TF-IDF) [72,73,74], Term frequency (TF) [75,76], Word2Vec [77], Hmm2Vec [78], and Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) [79], as well as global vectors to represent each word (GloVe) [80]. The next step is the selection of a classifier. Its choice determines the performance of the requested text classification. Methods used for this task include The Naïve Bayes classifier (NBC), logistic regression [81,82], K-Nearest Neighbor, Support Vector Machine (SVM) [83], decision trees, Deep Neural Network (DNN) [84], convolutional neural network [85], and Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) [86]. One of the most popular methods is the use of LLMs, such as BERT, DeBERTa, the Robustly Optimized BERT Approach (RoBERTa), and the cross-lingual language model XLM-RoBERTa. LLMs have proven the possibility of in-context learning (ICL) [87,88,89,90]. The models produced results comparable to those of supervised learning; in some cases, they were even better. However, the results depended on the task set for the model.
2.2.4. Machine Translation
Machine translation has made significant progress in recent years. A basic requirement for high-quality machine translation is maintaining consistency. Pre-approved rules and terminology must be followed. It is still particularly complicated to adjust the translation in real time. According to the research in [91], the quality of the translation using multiple context learning may surpass the quality of existing learning methods based on the encoder–decoder solution. This type of research is especially important for less popular languages than English, Chinese, or German. Technologies to improve the quality of machine translation include the use of GPT language models. This makes it possible to conduct a Stylized Machine Translation [92], which allows us to generate translations in a specific genre and form, i.e., formal or informal, rhyming, or prose, etc. [93]. Stylized Machine Translation (SMT) [94] is a difficult to accomplish task, but using a zero-shot learning language model there is the possibility to translate a text into a specific language or make translations and then adjust the translation style. The next available solution is Interactive Machine Translation (IMT) [95], which allows the user to participate in the translation. This is performed through a combination of MT systems using large language models and interactive interfaces that make it possible for users to send their feedback or comments on the translated text. These developments are possible in real time. It should be remembered that this method requires a considerable amount of improvement in areas such as easiness or intuitiveness for the user to make adjustments and check the correctness of the proposed changes [96]. Another method used in machine learning is Transfer-based Machine Translation. This has been proposed for many years. However, the proposed methods and results are still a matter of contention for researchers. In some cases, researchers have proven that the use of semantically similar examples has no significant effect on improving the quality of translation [97,98,99,100]. On the other hand, there are publications proving the effectiveness of introducing fuzzy matching, which has an important impact on the evaluation of translation quality [91]. In addition to the lack of a clear assessment of this aspect of machine translation [101], there are concerns about the privacy and security of this solution [101,102,103].
2.2.5. Text Summarization
The development of machine learning has enabled the creation of brief summaries. The selection of information included in the summary is determined by the selected standards [104]. Creating summaries helps reduce information overload, an increasingly common problem [105]. Researchers have mainly focused on creating new abbreviations in the generation of summaries. Text summaries are particularly useful for conversations between two or more people. However, this is a difficult task due to the lack of restrictions on subject matter or the use of linguistic nuances, diminutives, or mental abbreviations by the interlocutors. The demand for this type of solution increased significantly during lockdowns and the widespread adoption of remote work and learning. Short summaries were invaluable for those who had just joined the discussion. They helped people understand the topics being discussed and capture the conversation’s key content. This technology achieves the desired results for solutions such as daily conversations [106], medical consultations [107], or customer service [108]. Language models are used to generate summaries, that are both pre-trained, for example BART [109,110] and Pegasus [111], or non-pretrained—PGN [112], Fast-Abs [113], and HRED [114]. In this case, language models such as LLaMa [115] or ChatGPT [116,117] can be really useful. As can be seen, activities based on large language models are still quite limited. It is an inspiration and a challenge to create new solutions to improve results summarization [118].
2.2.6. Question-and-Answer Generation
Question answering (QA) is a popular natural language processing (NLP) task. This is undoubtedly connected to the release of ChatGPT, which has swept the world. Models such as ChatGPT [119,120], LLaMA [121], and PaLM [122] allow answers to questions asked by users to be generated. This is a technology of critical importance in the field of human–computer interaction. Testing the performance, efficiency, and accuracy of these systems is important for these solutions. It must be admitted that large language models perform well in terms of task quality control [123,124]. This potential could and should be developed [125]. There has been an increase in the popularity of publications that provide an assessment of the difficulty of a question [126]. The point is that the difficulty ranking can only be based on the content of the question. Advances in technology and natural language processing are forcing researchers to focus on Question Difficulty Estimation from Text (QDET) [127]. Nowadays, there are a lot of publications focused on question generation [128,129]. The listed publications omitted studies that did not focus on QDET. The literature review is incomplete in this regard and is a field for further research.
2.2.7. Fake News Detection
It is evident that tools such as ChatGPT have the capacity to generate information that is devoid of factual foundation. The subsequent argument is that LLMs have the capacity to generate disinformation in a manner analogous to that of humans. In their seminal work, the esteemed authors of [130] pose a thought-provoking question: can the information generated by artificial intelligence (AI) can be more detrimental to society than the content created by human authorship? A subsequent division was established for the purpose of identifying and addressing emerging disinformation. The main objective is to determine the authenticity of specific content. This process is referred to as “verifying” or “denying” content as “authentic” or “inauthentic.” The generation of disinformation by the language model may be more difficult to detect and may cause more damage than that generated by a human. A further disadvantage associated with large language models is the possibility that they will be intentionally used to generate false content. The authors of paper [130] propose three types of methods based on life scenarios: hallucination generation (HG), arbitrary misinformation generation (AMG), and controllable misinformation generation (CMG). As indicated previously, hallucination is defined as the phenomenon of creating content that lacks a factual foundation. In the context of AMG, the adversary’s primary objective is to circumvent the security mechanisms of an LLM to generate fraudulent content. CMG is defined as the manipulation of information, including the authorship of text and the production of deceptive content. The objective of this initiative is to deliberately introduce content that is factually inaccurate. The mentioned attacks can be combined with a jailbreak attack [131,132,133,134].
2.2.8. Hate Speech Detection
The advent of technology and the evolution of communication networks have precipitated the widespread use of the Internet and the propagation of personal opinions by individuals worldwide. The perceived anonymity of Internet users has been identified as a contributing factor to the rise in hate speech incidents that have few consequences. The identification of hate speech on the Internet is a critical component in addressing this issue, as it plays a pivotal role in the limitation of such activities. A review of the available literature on hate speech reveals the need for a comprehensive analysis of the manifestations, dynamics, and consequences of this solution. The majority of research dissertations presented techniques focused on filtering harmful content using artificial intelligence (AI). Various publications demonstrate the potential for automated identification of hate speech [135,136,137,138]. However, this issue requires careful analysis and the development of innovative solutions. Recent years have shown a marked increase in hate crimes within the United States [139]. Despite the difficulty in establishing a definitive correlation between the criminal act and published content, there are documented cases that underscore the importance of hate speech in the context of judicial proceedings [140,141]. The development of methodologies to mitigate and ultimately eradicate this phenomenon is necessary. Various methodologies are used to identify hate speech, with machine learning being a prominent approach. This encompasses the use of pre-trained language models and deep learning with word-embedding methods, among other techniques [142]. The detection of offensive content has been facilitated by the implementation of models such as BERT, RoBERTa, and ALBERT (a lite version of BERT) [143]. It has been demonstrated that techniques grounded in convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are capable of achieving satisfactory performance, Refs. [144,145], as well as the LSTM (long short-term memory) used in Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNa) [146].
A review of existing studies reveals a predominant focus on general hate speech. There is a notable lack of academic research specifically addressing hate speech based on national, ethnic, racial, or religious differences. Various platforms have been developed to target specific areas, such as age, disability, and even the use of profane language. A summary of the key findings is available in [137]. The authors expounded upon the definition of hate speech as established by various institutions, including the Code of Conduct between the European Union Commission and companies, international minority associations, academic institutions, and prominent social media platforms such as Facebook, X (Twitter), and YouTube. In addition to the categorization, examples of the expressions that, despite the presence of words considered offensive, would not be considered as hate speech, as well as the opposite situation, can also be found. The findings indicate a persistent necessity for solutions that are tailored to the detection of hate speech within specific domains.
2.2.9. Text Generation
Another task for NLP is automatic text generation. The evaluation of the quality of automatically generated text presents a substantial challenge for researchers. The prevalence of large language models can be attributed to their capacity to generate content and assess the quality of text analysis. To date, a variety of metrics have been used to evaluate the quality of generated content. However, large language models, such as ChatGPT, demonstrate a performance that exceeds the majority of available metrics, including the Explicit Score. The presented paper provides additional data on the performance of each indicator for the text under analysis [147]. The primary objective of the authors was to evaluate the effectiveness of existing methodologies and to compare the results with either the implicit score (text-davinci-001, text-davinci-003) or the explicit score (ChatGPT). The explicit score method is a quantitative approach that quantifies the evaluation of superficial aspects of the text. In such cases, exact character matching or phrase similarity without reliance on underlying representations or embeddings may assume a significant role. On the other hand, the implicit score method focuses on the presence or absence of semantic similarity between the analyzed words or sentences. In this case the exact phrase matching is ignored.
The metrics of explicit score are based on predefined rules. They are a set of quantitative metrics that quantify the quality of a given entity. The quality is defined by specific criteria or by the entity’s overall performance. Examples of explicit scoring formulas include the BLEU, ROUGE, and METEOR scores, which are described below. The example of implicit score involves the formulation of the problem as a binary question. The answers “Yes” or “No” represent the confidence level of the response. This calculation is based on the maximum occurrence of “Yes” and “No” tokens [147]. Other examples of implicit scoring formulas include BARTScore and BERTScore. A variety of language models are used in the creation of content. Popular pre-trained language models include BERT and ChatGPT from OpenAI [148] or Gemini from Google. It is noteworthy that pre-trained models consistently achieve high accuracies on numerous natural language processing (NLP) tasks. Large language models have demonstrated an ability to generate fluent utterances without requiring training in this domain. One of the challenges that must be addressed is establishing individual constraints, which should be defined by the user [149].
Another popular method is the generative adversarial network (GAN) model, which was first introduced by Ian Goodfellow [150]. This solution consists of a generator and a discriminator. The initial component facilitates the generation of novel content, while the subsequent component assesses the generator’s precision. The discriminator is capable of differentiating between authentic data and data that has been generated by the model [151]. The objective of this case is to generate outcomes that obfuscate the distinction between input and generated content. In the aforementioned work [152], the authors emphasize that the humans find it challenging to recognize fake images and videos created by neural networks. A number of platforms have already implemented requirements for indicating the percentage of human participation in the generation of particular content. Generative adversarial network (GAN) models have demonstrated a high degree of efficacy in generating images of a high quality, while concurrently offering a substantial degree of control over the generation process [153,154]. However, their performance is suboptimal in video generation tasks, such as videos referred to as “talking heads”. As stated by the authors, Diffusion Models demonstrate superior performance in this particular aspect [155]. It is noteworthy that the aforementioned models demonstrate efficacy in both graphics and text generation. It is also worth acknowledging that architectures based on deep learning enable the representation of input data in a distributed form, thereby establishing the foundational framework for deep generative models [156,157]. This approach has been particularly effective in a variety of tasks related to NLP [158,159]. The representation of data in a non-dispersed manner has been demonstrated to compromise the efficacy of this method. Firstly, it is important say that an augmentation in structure signifies an escalation in the dimensionality of the data, which in turn exerts an influence on the quality of semantic information. Consequently, as the dimensionality of the data increases, the model’s ability to map input data becomes more challenging. In recent developments, a considerable number of models have been formulated to obtain distributed representations for input data. Among the most widely utilized models are
- Word2Vec [160];
- Node2Vec [161];
- Gene2Vec [162].
A selection of notable deep learning algorithms used for text generation includes
- RNNs [163];
- Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) [164];
- BiDirectional RNNs (BRNNs) [165];
- CNNs [166];
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) [167].
2.2.10. Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis [168] is one of the techniques available in natural language processing. Its main task is to determine the emotional tone accompanying a given sentence. Sentiment analysis is sometimes described as opinion analysis or opinion mining [169]. One of the most important tasks of sentiment analysis is determining the tone of a statement. Content is usually divided into three categories: positive, negative, or neutral [170]. This procedure is known as polarization [171]. Researchers are constantly improving available solutions to achieve more accurate results. Classification is performed at different levels: document, sentence, phrase, or feature [169,172]. Detecting the emotions (emotion detection) that dominate an opinion is possible when the tone of speech is captured [173]. The so-called aspect-based approach is also used to recognize the emotions accompanying particular events or products [174,175,176]. Studies on sentiment analysis are predominantly based on machine learning methodologies [177]. These include classic techniques such as support vector machines (SVMs) [178] and naive Bayes [179]. Classical approaches can be improved using deep learning or neural networks [180,181,182]. These approaches produce more accurate results for image classification and speech recognition tasks. For this reason, they have also been used to refine sentiment analysis techniques [183,184]. It is worth remembering that rule-based techniques are lexicon based. These techniques include pre-defined rules and sentiment evaluation, which is usually categorized as positive, negative, or neutral [185].
2.3. Metrics Used to Assess Text Quality
2.3.1. ROUGE Score
ROUGE (Recall-Oriented Understudy for Gisting Evaluation) [186,187] is a set of metrics used to assess the quality of results performance by automatic text generation. Primarily, it is used to evaluate natural language tasks involving the summarization, generation, or machine translation of text. The calculation utilizes recall, precision, and F1-score for the original sentence (O) and the generated text (G). Precision (P) is determined by the comparison of true positives (TP) and the total number of predictions made by the model (TPM). The latter is defined as the sum of TP and false positives (FP).
The recall (R) is defined as the number of positive predictions made. Therefore, it can be designated as a measure of true positives, as it quantifies the number of correctly predicted outcomes by the model. This relationship can be represented by a formula, where recall is defined as the quotient of TP phrases with the difference of TP and TN.
The F1 score (F1) is defined as the harmonic average of P and R, thereby enabling the assessment of the efficacy of the model’s results. It is imperative to acknowledge that the F1 measure will attain a value of zero if any of the indicators—precision or recall—attain a value of zero. The following formula can be used to represent this relationship:
Types of ROUGE Score:
- ROUGE-L;
- ROUGE-W;
- ROUGE-N;
- ROUGE-S.
ROUGE-L (ROUGE Longest Common Subsequence) [188]. The basis for determining similarities between reference and generated texts is the Longest Common Subsequence (LCS). A positive correlation is observed between the length of the common sequence in the analyzed texts and the degree of similarity among them.
ROUGE-W (ROUGE Weighted Longest Common Subsequence) [189] is metric to measure the overlap of the LCS of two texts. The proposed methodology places greater emphasis on sequential matches. The results of this study are particularly useful when comparing text similarities, where sequential matches of words are more important than scattered matches.
ROUGE-N (ROUGE-N-gram) [189] is a metric that is distinct from the others under consideration. It is a metric of another type, in which similarities are determined at the level of the number of n-grams of words in the reference and generated sentences. Furthermore, similarities can be distinguished at the level of individual words—unigrams (ROUGE-1), bigrams (ROUGE-2), etc.
ROUGE-S (ROUGE-Skipgram) [187] is a technique measuring the overlap of skip-bigrams between a candidate translation and a set of reference translations. The term “translation quality” is employed to denote the degree to which a translation adheres to the source text’s linguistic nuances and structural integrity. To illustrate the functionality, if a sentence contains six skip-bigrams, it can be compared to the set of reference translations. This approach is more intuitive than BLEU-2 and ROUGE-L, as it does not require consecutive matches, though it remains sensitive to the order of words.
ROUGE is a widely applied metric for evaluating the quality of summarization, machine translation, text generation, and paraphrasing. It is essential to acknowledge that, despite its simplicity in implementation, text evaluation must be grounded in a comprehensive reference text. ROUGE’s evaluation is exclusively based on the presence of word or sentence repetitions. The system is incapable of recognizing semantic dependencies in statements or their syntax. When employed in the context of text evaluation, this metric is often accompanied by supplementary assessments, including those conducted by human evaluators.
2.3.2. METEOR
The METEOR score [190] is a metric used to evaluate the quality of NLP tasks, such as machine translation. It compares pairs of words—one from the hypothesis (H) and the other from the reference (R). A key advantage of METEOR is its ability to consider not only exact word matches but also synonyms, paraphrases, and stemmed forms. The metric is composed of modules responsible for aligning words and assigning scores across various categories. When multiple matches of the same cardinality are found, additional modules are activated to refine the matching process. By default, METEOR begins with exact matching, followed by Porter stemming, and then synonym evaluation. The final METEOR score ranges from 0 to 1, where 0 indicates no match and 1 indicates a perfect match [191]. METEOR facilitates the evaluation of translations not only in English but also in European languages such as Spanish, German, and French. This approach has been shown to yield optimal results, particularly in the evaluation of English language proficiency [192]. METEOR leverages language-specific stemmers, along with human evaluation data from sources such as NIST and WMT, to support assessments across multiple languages. Extensions are continuously being developed to expand support for additional languages. In 2010, METEOR-NEXT was introduced to improve alignment with the Human-targeted Translation Edit Rate (HTER) [193]. In 2015, synonym matching capabilities were enhanced through integration with DBnary, enabling support for an additional 20 languages [194]. By 2019, further improvements were made with the introduction of syntactic paraphrase matching, made possible through the use of skip-grams [195]. The following formulas are used to facilitate the generation of matches [190]:
The equation to calculate Penalty is
where
- Chunks is the number of consecutive sequences of matched words that appear in the same order in generated translation (hypothesis) and human translation (reference);
- MatchedWords is total number of matched words, which are average over references and hypothesis;
- and are tuned parameters (tuning procedure formula below, commonly is set 0.5 and ).
- is equal to matcher weight;
- defines word weight value;
- and are tuned parameters (tuning procedure formula below, default value is set 0.9);
- is the number of content words matched in the references;
- is the count of function words matched in the references.
Each value can be described as follows:
- is equal to matcher weight;
- defines word weight value;
- and are tuned parameters (tuning procedure formula below);
- is the number of content words matched in the hypothesis;
- is the count of function words matched in the hypothesis.
The tuning procedure is Kendall’s correlation ()
where cp is count of concordant pairs, dp is number of discordant pairs, and tp is equal to sum of cp and dp.
2.3.3. BLEU
The Bilingual Evaluation Understudy (BLEU) is a linguistic evaluation tool that assesses the quality of generated text in relation to the provided data. This is achieved by identifying matches of phrases or sentences represented as n-grams, as outlined in [196]. BLEU employs a modified n-gram precision metric in lieu of the WER′s distance metric, a more stringent approach. This has been modified to eliminate duplicates. The evaluation of the generated text is conducted on a scale ranging from 0 to 1, with 1 denoting an exact match between the generated text and the original text. The BLEU score is determined through the calculation of precision, defined as the ratio of duplicate n-grams present within the compared texts to the total number of n-grams contained within the generated content. To outguess the inflation of scores for brief content, a brevity penalty (BP) has been implemented. The BLEU score is calculated using the following formula [197]:
The formula uses a set of values. Here is how they can be described:
- N is the highest n-gram order is typically identified as 4.
- is the weight for each n-gram precision.
- is the modified precision for n-grams and is a basic BLEU metric. It checks how many continuous sequences of words occur, with the length defined as n, and it avoids inflating repetition results thanks to the pruning rule.
- The BP is calculated based on the length of the hypothetical translation corpus (ch) and the reference corpus (rc). If ch > rc, then BP is equal to 1. In case of a ch that is greater than or equal to rc, then BP has the value .
The evaluation of the effectiveness of large language models is a subject that can be approached in a variety of ways. This is of particular importance in the present moment due to the large number of language models that are currently available. The most prevalent open-source large language model is GPT-3.5. Recently, the field has witnessed the emergence of a notable competitor in the form of the Chinese deepseek model. In the case of the latter, however, concerns have emerged regarding the reliability and safety of this model. The discussion addressed the security of responses to controversial topics, as well as the number of model refusals to answer risky queries, which were classified into various categories, including propagating violence and pornography or occupational discrimination. In the case of DeepSeek-V3 and DeepSeek-R1, the number of refusals to answer was equal to 0. DeepSeek-V3 refused to answer in the field of health discrimination for 0.05 of the questions asked, and for the category defined by the authors as promoting terrorism, the result was 0.18. Refer to the work of Zhang [198] for a detailed discussion of safety issues. The data presented unequivocally underscores the imperative for enhanced security measures in the formulation of responses by AI systems.
2.3.4. BERTScore
In a similar manner, the ROUGE Score is used to evaluate the quality of text in tasks associated with natural language processing [199]. These criteria encompass the evaluation of the quality of text summarization, machine translation, or text generation in a broader sense. This metric has also been demonstrated to be effective in verifying the assessment of semantic similarity when comparing content. The BERTScore has demonstrated its versatility by finding application in a variety of disciplines. A multitude of variations of this evaluation exist, having been trained on an array of thematic corpora [200]. Indicators for finance-related topics are included among the pre-trained models that are available within BERTScore FinBERT [201], medicine BioBERT [202,203], PubMedBERT [204], ClinicalBERT, or LegalBERT [205]; the latter is used for the evaluation of content related to legal issues. In addition to the variety of trained language models, it is possible to fine-tune the values that affect the quality of the created assessments. This objective can be accomplished through a variety of methods, including the meticulous alignment of training data or the supplementation of training data with synonyms or analogous expressions pertinent to the subject matter. The BERT score is determined by precision, recall, and F1 measures. The F1 score is calculated using the Formula (5), which is applicable to the ROUGE Score. The precision and recall metrics are employed to identify the maximum cosine similarity between the embedding of tokens from the reference and the generated text. Consequently, a matrix is formulated that contains values appropriate for each embedding. This enables the calculation of the cosine distance between individual words. It is imperative to acknowledge the functionality of BERTScores, which facilitate the allocation of weights to relevant tokens. Consequently, significant words that appear less frequently in the text can be identified. Precision for BERT score is calculated according to the following formula [206]:
In this formula, #X is the set containing the generated contents, denoted as , #Y is the set of reference expressions, denoted as , and CS is cosine similarity between generated and referenced expressions.
2.3.5. BARTScore
The BARTScore model is a text evaluation model based on transforms. As posited by the authors of BARTscore [207], the evaluation of generated text, summaries, machine translations, and named entity recognition (NER) is a common practice in the field [208]. The application of this technology is also evident in tasks that involve the generation of image captions, as evidenced in [209]. BART Score uses prompt-base learning [210]. This approach enables automated evaluation in multiple directions, as illustrated below:
- Unsupervised matching is a method that enables the measurement of semantic equivalence between a reference and a hypothesis.
- Regression is a statistical technique that enables the prediction of human judgments based on a parameterized regression layer.
- The process of ranking involves the systematic allocation of higher ratings to hypotheses that demonstrate a higher degree of validity and relevance generation.
The evaluation process involves bidirectional encoding of the original text and auto-regressive decoding of the generated text. The model is capable of leveraging semantic dependencies between the analyzed sentences. The evaluation is constructed using three indicators that correspond to those employed in conventional metrics. The metrics employed include precision recall, faithfulness (which measures the degree to which the generated text corresponds to the input data), and F-score, calculated based on the harmonic mean of precision and completeness. The F-score is used to assess the semantic similarity among the analyzed texts. The implementation of this metric is characterized by its versatility, as it can be applied to a wide range of examples and languages. It is also notable for its ability to adapt to human judgments, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation process. Furthermore, it is capable of recognizing semantic and information dependencies, which enhances its overall functionality. It is imperative to acknowledge that the model under consideration is pre-trained on BART, a model equivalent to duplicating the training errors of the aforementioned model. This approach is computationally intensive, particularly when dealing with large datasets. The most general formula for BARTScore is
where
- is model seq2seq parameter;
- is target sequence of n tokens;
- is target sequence of l tokens;
- is probability of y conditioned on x.
2.3.6. Comparison of the Described Metrics
The metrics presented in this study provide a foundation for evaluating similarity in generated content. It is important to note that ROUGE, METEOR, and BLEU scores range from 0 to 1, where higher values indicate greater similarity to the reference text. BERTScore also typically falls within this range, offering the capability to assess semantic relationships by leveraging contextual embeddings derived from the BERT model. Due to its semantic awareness, BERTScore is often considered more robust than traditional n-gram-based metrics.
The BARTScore range may vary depending on the specific implementation; however, higher values generally reflect greater coherence and semantic alignment with the reference. This score is typically computed based on the log-likelihood of the generated sequence relative to the reference, using a BART language model.
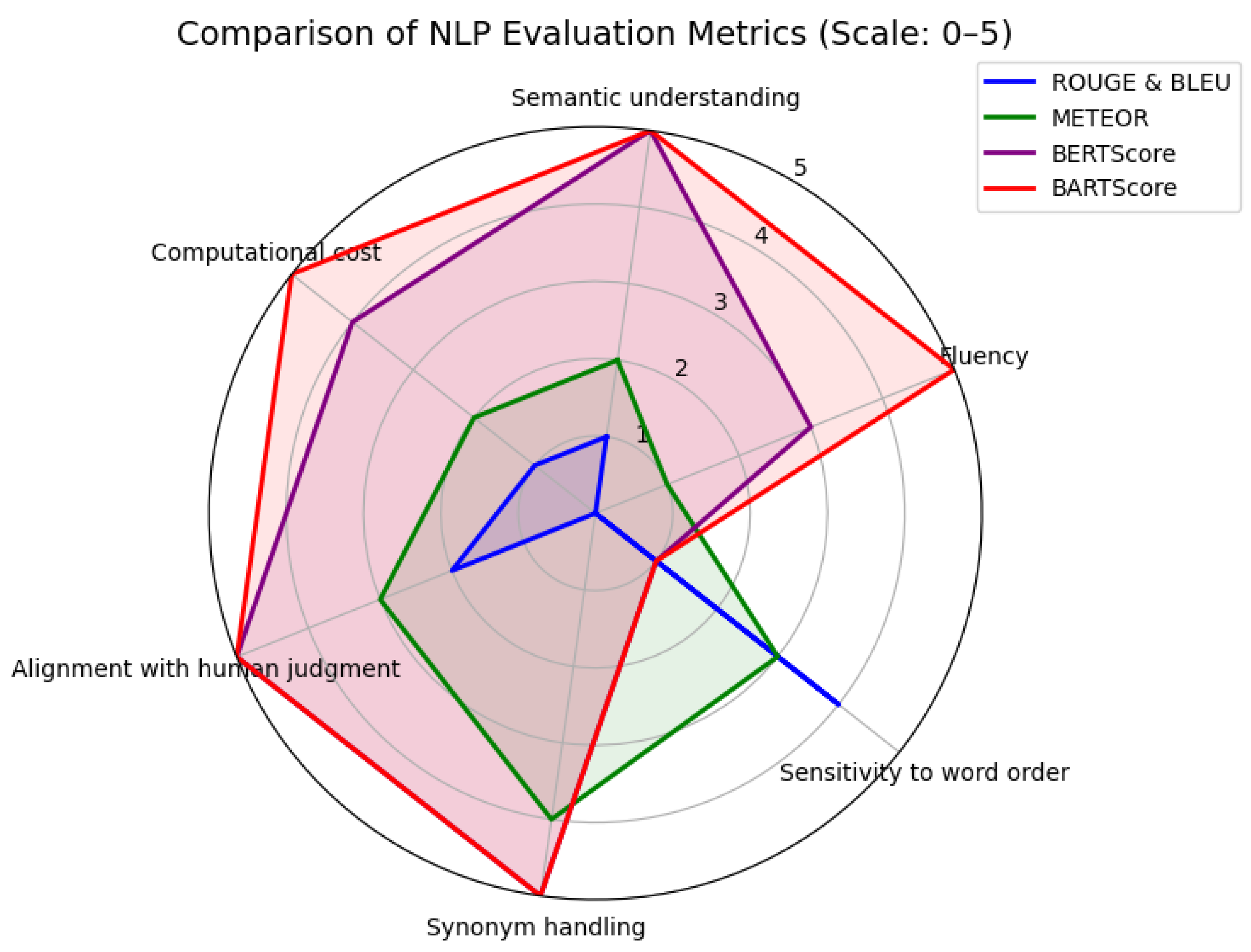
Compared to ROUGE, METEOR, and BLEU, both BERTScore and BARTScore are more computationally intensive, as they rely on large pre-trained language models. BLEU, ROUGE, and METEOR support evaluation against multiple reference sentences, which is particularly advantageous when several equally valid formulations of the same idea exist. The choice of metric should be aligned with the nature of the task. For evaluating surface-level similarity and n-gram overlap, BLEU, ROUGE, and METEOR are effective tools. In contrast, BERTScore and BARTScore offer superior performance in assessing semantic similarity and fluency due to their reliance on deep contextual representations from pre-trained models. The Figure 1 contains a radar chart with a comparison of NLP evaluation metrics across six key dimensions. It illustrates how each NLP metric—ROUGE, METEOR, BLEU, BERTScore, and BARTScore—performs across the key evaluation dimensions
Figure 1.
This figure presents the radar chart with a comparison of described metrics in 6 evaluation dimensions.
- Semantic understanding;
- Fluency;
- Sensitivity to word order;
- Synonym handling;
- Alignment with human judgment;
- Computational cost.
ROUGE, BLEU, and METEOR remain useful for quick, lexical-level assessments, especially when multiple references are available or computational efficiency is needed. Although BERTScore and BARTScore are more computationally demanding, they are strongly recommended for the evaluation of LLMs.
Table 1 provides a comparative overview of five widely used evaluation metrics in NLP, particularly in the context of LLMs. ROUGE, BLEU, and METEOR are efficient and well-established metrics that offer quick, lexical-level assessments, but they fall short in capturing deeper semantic meaning and often penalize valid paraphrases. In contrast, BERTScore and BARTScore, though computationally more demanding, demonstrate a stronger alignment with human judgment by accounting for contextual meaning, fluency, and coherence. Each metric excels in specific tasks: BLEU remains a standard in machine translation, METEOR performs well in paraphrasing and short-form generation, while BARTScore is particularly effective in evaluating open-ended text generation. Overall, model-based metrics such as BERTScore and BARTScore are better suited for assessing the nuanced and diverse outputs generated by LLMs, where traditional n-gram-based metrics may underestimate quality.

Table 1.
The table provides a comparative overview of the ROUGE, BLEU, METEOR, BERTScore, and BARTScore evaluation metrics, examining their advantages, drawbacks, and specific limitations when applied to the evaluation of LLMs.
2.3.7. Example Evaluation of Generated Text
The examples shown in Table 2 illustrate how generated sentences, despite lexical variation, can preserve the core meaning of the original reference. These variants serve as a practical basis for assessing how different evaluation metrics respond to lexical changes, paraphrasing, and semantic similarity. Traditional metrics such as ROUGE and BLEU tend to penalize such outputs due to reduced n-gram overlap, even when the semantic content remains accurate. In contrast, BERTScore and BARTScore demonstrate greater effectiveness in capturing meaning and fluency, reinforcing their suitability for evaluating the output quality of large language models.

Table 2.
Examples of original and generated sentences.
The Table 3 presents the results of the evaluation of the quality of the original sentences and three sets of generated sentences, denoted as , , and , using several established metrics for assessing textual similarity and quality. The ROUGE-L metric quantifies the degree of overlap at the level of the longest common subsequence and is widely employed in the evaluation of summaries and machine translations. In the presented results, the highest ROUGE-L score is attained by (0.70), indicating a closer resemblance to the original text compared to (0.68) and (0.66). The METEOR metric, which accounts for precision, recall, and the capacity to align synonyms and paraphrases, exhibits a consistent trend with ROUGE-L, as achieves the highest score of 0.65, whereas and register slightly lower values of 0.60 and 0.58, respectively. BLEU, an n-gram-based precision metric extensively used in natural language generation evaluation, yields comparatively lower scores; nonetheless, again attains the highest value of 0.45, followed by and with 0.42 and 0.40, respectively. BERTScore leverages contextual embeddings from pretrained language models to evaluate semantic similarity, emphasizing meaning over exact lexical matches. All three generated sets receive high BERTScore values or approximately between 0.91 and 0.92, suggesting strong semantic consistency with the source sentences. BARTScore, grounded in the BART generative model, assesses the quality of the text through a probabilistic generative framework; the negative scores observed, ranging from −1.5 to −2.5 across all variants, suggest moderate complexity or divergence within the generated texts. The absence of substantial variation in BARTScore between the original and generated sentences implies a comparable level of generative quality. In conclusion, while the ROUGE-L, METEOR, and BLEU metrics indicate a gradual decrease in the quality of generated sentences from to , the BERTScore results demonstrate preservation of high semantic fidelity across all variants. Concurrently, the BARTScore results imply a similar overall quality among all examined texts from the standpoint of the underlying generative model.

Table 3.
Example results of evaluation original and generated sentences.
3. Discussion
The field of generative artificial intelligence within the broader domain of NLP has emerged as one of the most dynamic and rapidly evolving areas of contemporary computational research. The period between 2023 and 2025 has clearly demonstrated the immense potential of advanced AI technologies, particularly those grounded in large language models. At the same time, these developments have brought to light a wide range of technical, ethical, and interpretability challenges that still require further optimization and refinement. There is little doubt, however, that artificial intelligence has the capacity to provide substantial support across numerous areas of human activity. Technologies based on generative language models enable significant improvements in domains such as education, content creation, healthcare, legal analysis, and customer service. These models are capable of generating coherent and contextually relevant texts and drawing upon vast repositories of knowledge—often extending far beyond the cognitive limits of individual human users.
Beyond the generation of outputs such as summaries, answers to user queries, machine translations, or paraphrased expressions, an equally important issue is the evaluation of the quality of these outputs. Assessing the effectiveness of NLP models requires the use of reliable evaluation metrics that allow researchers to compare generated texts with reference outputs and to estimate their linguistic and semantic fidelity. This paper presents an overview of the most widely used metrics for evaluating the quality of texts generated by language models, including ROUGE, BLEU, METEOR, BERTScore, and BARTScore. Due to the divergent theoretical assumptions and computational mechanisms underlying these metrics, relying on a single measure can produce incomplete or misleading assessments. As a result, multi-metric evaluation strategies are increasingly recommended in contemporary NLP research. For example, the combination of ROUGE (which measures structural similarity) and BERTScore (which evaluates semantic correspondence) enables a more comprehensive analysis of both the syntactic fidelity and semantic richness of the generated text.
We believe that addressing the topic of generative artificial intelligence in the context of NLP with LLMs, along with consolidating essential information on common NLP tasks and evaluation metrics, provides a valuable contribution to the field. This article is intended to serve as a compact yet comprehensive reference guide, useful both for those beginning their work with language models and for researchers seeking a concise overview of current evaluation approaches. We hope that this compilation will foster a deeper understanding of the capabilities and limitations of modern NLP systems and support ongoing efforts toward their improvement and responsible application.
4. Challenges and Future Directions
Equally significant to the advancement of LLMs is the ongoing development of natural language processing technologies, including information retrieval, text classification, fake news detection, and hate speech identification. These systems play a crucial role in facilitating human–machine interaction and in ensuring the reliability of digital information. However, the effectiveness and fairness of such technologies are inherently dependent on the quality and representativeness of the training data. In practice, datasets used to train these models frequently include not only valuable content but also ideologically, culturally, or socially biased information. As a result, in our opinion, there is a risk that models inadvertently learn and replicate such biases. Language models trained on such datasets do not merely absorb factual patterns—they also internalize latent biases and flawed assumptions. These elements can then manifest in the models’ outputs, potentially leading to misleading, discriminatory, or ethically problematic results. According to us, this underscores the pressing need for research focused on enhancing the transparency and interpretability of LLMs, as well as on developing robust methodologies for detecting misinformation and verifying factual consistency in generated texts.
As previously noted, the implementation of comprehensive and harmonized legal frameworks is imperative. We think such regulation should standardize the procedures for the ethical use of artificial intelligence technologies and establish safeguards against misuse. A growing body of research emphasizes the urgency of defining ethical guidelines and accountability mechanisms to ensure the safe and responsible deployment of AI-based tools across sectors such as media, education, healthcare, and governance. It is also critical to reaffirm that, despite their increasing sophistication, LLM-based tools are not yet capable of fully replacing human judgment. These systems should be understood as augmentative rather than substitutive—they can support human reasoning and productivity but cannot replicate human intuition, contextual awareness, or ethical discernment. Human oversight remains essential in evaluating the credibility, intent, and implications of generated content.
In the domain of machine translation, another challenge emerges. The quality of translations generated by LLMs often correlates strongly with the availability of training data for the target language. High-resource languages, such as English, Chinese, or German, typically yield more accurate translations than low-resource languages like Finnish or Czech. This disparity highlights the need for continued model optimization and the expansion of multilingual training corpora to ensure equitable performance across diverse linguistic contexts. Moreover, the ability to reliably detect AI-generated texts represents an increasingly vital area of research. As generative models become more advanced, distinguishing between human-written and machine-generated content becomes more difficult—but this remains an achievable and necessary goal. Future efforts must prioritize the development of AI systems capable of identifying synthetic content and recognizing misinformation or deceptive narratives embedded within texts. Analogous to the field of cybersecurity, where human error often constitutes the weakest link, the human factor remains a significant vulnerability in the information ecosystem shaped by AI. This emphasizes the critical importance of public education and awareness-raising initiatives. Users must be equipped with the skills to critically evaluate digital content and resist passive consumption of AI-generated materials. A balanced approach is required—one that promotes technological innovation while simultaneously enhancing human capacity for critical interpretation and ethical oversight.
Consequently, our future work will focus on proposing systematic methods for evaluating language models using standardized metrics and benchmark datasets, as well as developing protocols for identifying disinformation and harmful language. Recognizing the need to curtail the spread of false information and hate speech is not only a technical imperative but also a societal responsibility.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: T.H.; methodology: J.G. and T.H.; software: J.G.; validation: J.G.; investigation, J.G.; data curation: J.G.; writing—original draft preparation J.G.; writing—review and editing: J.G. and T.H.; visualization: J.G.; funding acquisition, J.G. and T.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sætra, H.S. Generative AI: Here to stay, but for good? Technol. Soc. 2023, 75, 102372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manduva, V.C. Current State and Future Directions for AI Research in the Corporate World. Metascience 2024, 2, 70–83. [Google Scholar]
- Okaiyeto, S.A.; Bai, J.; Xiao, H. Generative AI in education: To embrace it or not? Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2023, 16, 285–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.M.; Gunasekara, A.; Pallant, J.L.; Pallant, J.I.; Pechenkina, E. Generative AI and the future of education: Ragnarök or reformation? A paradoxical perspective from management educators. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 2023, 21, 100790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Cai, M.; Lee, H.J.; Evans, R.; Zhu, C.; Ming, C. AI in Medical Education: Global situation, effects and challenges. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2024, 29, 4611–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jošt, G.; Taneski, V.; Karakatič, S. The impact of large language models on programming education and student learning outcomes. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, D.; Agrawal, M.; Movva, R.; Chen, I.Y.; Ghassemi, M.; Jacobs, M.; Pierson, E. Generative AI in medicine. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.10337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Meng, X.; Yan, X.; Ji, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; et al. Revolutionizing health care: The transformative impact of large language models in medicine. J. Med. Internet Res. 2025, 27, e59069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johri, S.; Jeong, J.; Tran, B.A.; Schlessinger, D.I.; Wongvibulsin, S.; Barnes, L.A.; Zhou, H.Y.; Cai, Z.R.; Van Allen, E.M.; Kim, D.; et al. An evaluation framework for clinical use of large language models in patient interaction tasks. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, A.; Shetty, N.S.; Patel, N.; Gaonkar, M.; Arora, G.; Arora, P. Evaluating Cardiology Certification Using the ACCSAP Question Bank: Large Language Models vs Physicians. In Mayo Clinic Proceedings; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; Volume 100, pp. 160–163. [Google Scholar]
- Salastekar, N.V.; Maxfield, C.; Hanna, T.N.; Krupinski, E.A.; Heitkamp, D.; Grimm, L.J. Artificial intelligence/machine learning education in radiology: Multi-institutional survey of radiology residents in the United States. Acad. Radiol. 2023, 30, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunes, Y.C.; Cesur, T. The diagnostic performance of large language models and general radiologists in thoracic radiology cases: A comparative study. J. Thorac. Imaging 2025, 40, e0805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, E.; Uller, W.; Vogt, K.; Doppler, M.C.; Busch, F.; Bayerl, N.; Ellmann, S.; Kader, A.; Elkilany, A.; Makowski, M.R.; et al. Large language models for simplified interventional radiology reports: A comparative analysis. Acad. Radiol. 2025, 32, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Li, Z.; Guo, Q.; Sun, Z.; Wu, H.; Li, C. Emergency surgery in the era of artificial intelligence: ChatGPT could be the doctor’s right-hand man. Int. J. Surg. 2023, 109, 1816–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guni, A.; Varma, P.; Zhang, J.; Fehervari, M.; Ashrafian, H. Artificial intelligence in surgery: The future is now. Eur. Surg. Res. 2024, 65, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zargarzadeh, S.; Mirzaei, M.; Ou, Y.; Tavakoli, M. From Decision to Action in Surgical Autonomy: Multi-Modal Large Language Models for Robot-Assisted Blood Suction. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2025, 10, 2598–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilhekar, R.S.; Rawekar, A. Artificial intelligence in genetics. Cureus 2024, 16, e52035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.; Jayaswal, N.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, P.K.; Behl, T.; Khalid, A.; Mohan, S.; Najmi, A.; Zoghebi, K.; Alhazmi, H.A. Unveiling the potential of proteomic and genetic signatures for precision therapeutics in lung cancer management. Cell. Signal. 2024, 113, 110932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routray, B.B. The Spectre of Generative AI Over Advertising, Marketing, and Branding. Authorea 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, B.; Kim, J.; Park, S.; Ahn, C.R.; Oh, T. Harnessing Generative Pre-Trained Transformers for Construction Accident Prediction with Saliency Visualization. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, H.; Sun, W.; Min, X.; Liu, X.; Zhai, G.; Lin, W. AGIQA-3K: An Open Database for AI-Generated Image Quality Assessment. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.04717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandi, A.; Adapa, P.V.S.R.; Kuchi, Y.E.V.P.K. The power of generative ai: A review of requirements, models, input–output formats, evaluation metrics, and challenges. Future Internet 2023, 15, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Yi, F. Is this abstract generated by ai? A research for the gap between ai-generated scientific text and human-written scientific text. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.10416. [Google Scholar]
- Sardinha, T.B. AI-generated vs human-authored texts: A multidimensional comparison. Appl. Corpus Linguist. 2024, 4, 100083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Tay, Y.; Bommasani, R.; Raffel, C.; Zoph, B.; Borgeaud, S.; Yogatama, D.; Bosma, M.; Zhou, D.; Metzler, D.; et al. Emergent abilities of large language models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.07682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasneci, E.; Seßler, K.; Küchemann, S.; Bannert, M.; Dementieva, D.; Fischer, F.; Gasser, U.; Groh, G.; Günnemann, S.; Hüllermeier, E.; et al. ChatGPT for good? On opportunities and challenges of large language models for education. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2023, 103, 102274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheddar, H. Transformers and large language models for efficient intrusion detection systems: A comprehensive survey. Inf. Fusion 2025, 124, 103347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, P.F.; Della Pietra, V.J.; Desouza, P.V.; Lai, J.C.; Mercer, R.L. Class-based n-gram Models of Natural Language. Comput. Linguist. 1992, 18, 467–480. [Google Scholar]
- Mavrych, V.; Ganguly, P.; Bolgova, O. Using large language models (ChatGPT, Copilot, PaLM, Bard, and Gemini) in gross anatomy course: Comparative analysis. Clin. Anat. 2025, 38, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urman, A.; Makhortykh, M. The silence of the LLMs: Cross-lingual analysis of guardrail-related political bias and false information prevalence in ChatGPT, Google Bard (Gemini), and Bing Chat. Telemat. Inform. 2025, 96, 102211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.K. What is the impact of ChatGPT on education? A rapid review of the literature. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.V. Revolutionizing Marketing Efficiency with ChatGpt; Technical Report; GSFC University: Vadodara, India, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, H.; Liu, T.; Zhang, A.; Hua, W.; Jia, W. Cognitive mirage: A review of hallucinations in large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.06794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farquhar, S.; Kossen, J.; Kuhn, L.; Gal, Y. Detecting hallucinations in large language models using semantic entropy. Nature 2024, 630, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, E.G.; Gauthier, J.; Hu, J.; Qian, P.; Levy, R. Learning syntactic structures from string input. In Algebraic Structures in Natural Language; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 113–138. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Bai, J.; Yu, J.; Tong, Y. Syntax-BERT: Improving pre-trained transformers with syntax trees. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.04350. [Google Scholar]
- Baroni, M. On the proper role of linguistically-oriented deep net analysis in linguistic theorizing. In Algebraic Structures in Natural Language; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta, I.; Kaeser-Chen, C.; Marino, K.; Ahuja, A.; Babayan, S.; Hill, F.; Fergus, R. Collaborating with language models for embodied reasoning. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yuan, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Deng, C.; Dou, Z.; Wen, J.R. Large language models for information retrieval: A survey. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.07107. [Google Scholar]
- Salton, G. Modern Information Retrieval; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Salton, G.; Wong, A.; Yang, C.S. A vector space model for automatic indexing. Commun. ACM 1975, 18, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, B.; Craswell, N. Neural models for information retrieval. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.01509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.X.; Liu, J.; Ren, R.; Wen, J.R. Dense text retrieval based on pretrained language models: A survey. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.14876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Chen, Z.; Liang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, M.; Qin, B. Infrared-LLaVA: Enhancing Understanding of Infrared Images in Multi-Modal Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2024, Miami, FL, USA, 12–16 November 2024; pp. 8573–8591. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Ma, X.; Lin, J.; Callan, J. Precise zero-shot dense retrieval without relevance labels. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.10496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, K.; Raman, K.; Samanta, A.; Liao, L.; Bertelli, L.; Bendersky, M. QUILL: Query intent with large language models using retrieval augmentation and multi-stage distillation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.15718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Long, G.; Geng, X.; Tao, C.; Zhou, T.; Jiang, D. Large Language Models are Strong Zero-Shot Retriever. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.14233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, N.; Wei, F. Query2doc: Query Expansion with Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.07678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagerman, R.; Zhuang, H.; Qin, Z.; Wang, X.; Bendersky, M. Query Expansion by Prompting Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.03653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, A.; Li, M.; Zhao, H.; Karypis, G.; Smola, A. Multimodal chain-of-thought reasoning in language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.00923. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Toro, P.A.; Dineley, J.; Iniesta, R.; Zhang, Y.; Matcham, F.; Siddi, S.; Lamers, F.; Haro, J.M.; Penninx, B.W.; Folarin, A.A.; et al. Exploring Biases Related to the Use of Large Language Models in a Multilingual Depression Corpus. JMIR Ment Health 2025, 12, e57986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, I.; Sekulic, I.; Chatterjee, S.; Dalton, J.; Crestani, F. GRM: Generative Relevance Modeling Using Relevance-Aware Sample Estimation for Document Retrieval. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.09938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keraghel, I.; Morbieu, S.; Nadif, M. A survey on recent advances in named entity recognition. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.10825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, T.; Tsai, C.Y.; Lu, Y.; Yao, L. Evolution and emerging trends of named entity recognition: Bibliometric analysis from 2000 to 2023. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Katyayan, P.; Joshi, N. Improving the Quality of Neural Machine Translation Through Proper Translation of Name Entities. In Proceedings of the 2023 6th International Conference on Information Systems and Computer Networks (ISCON), Mathura, India, 3–4 March 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X.; Feng, T. A Research Toward Chinese Named Entity Recognition Based on Transfer Learning. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2023, 16, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lai, P.; Fang, R.; Fu, Y.; Ye, F.; Wang, Y. FE-CFNER: Feature Enhancement-based approach for Chinese Few-shot Named Entity Recognition. Comput. Speech Lang. 2025, 90, 101730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, K. Application-Oriented Machine Translation: Design and Evaluation. Ph.D. Thesis, Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, S.F.; Mutlu, F.B.; Balaban, I.; Kozat, S.S. TMD-NER: Turkish multi-domain named entity recognition for informal texts. Signal Image Video Process. 2024, 18, 2255–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gallardo, C.E.; Tran, H.T.H.; Hamdi, A.; Doucet, A. Leveraging open large language models for historical named entity recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Theory and Practice of Digital Libraries, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 24–27 September 2024; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 379–395. [Google Scholar]
- Frei, J.; Kramer, F. German Medical Named Entity Recognition Model and Data Set Creation Using Machine Translation and Word Alignment: Algorithm Development and Validation. JMIR Form. Res. 2023, 7, e39077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, L.F. Extracting company names from text. In Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE Conference on Artificial Intelligence Application, Miami Beach, FL, USA, 24–28 February 1991; IEEE Computer Society: Los Alamitos, CA, USA, 1991; pp. 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Nadeau, D.; Sekine, S. A survey of named entity recognition and classification. Lingvisticae Investig. 2007, 30, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collobert, R. Deep learning for efficient discriminative parsing. In JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings, Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 11–13 April 2011; JMLR: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 224–232. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Hu, T.; Xiao, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ning, H.; Zhu, R.; Li, Z.; Ye, X. GPT, large language models (LLMs) and generative artificial intelligence (GAI) models in geospatial science: A systematic review. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2024, 17, 2353122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, Q.; Tiwari, P.; Qin, J. Pushing the limit of LLM capacity for text classification. In Proceedings of the Companion Proceedings of the ACM on Web Conference 2025, Sydney, Australia, 28 April–2 May 2025; pp. 1524–1528. [Google Scholar]
- Fields, J.; Chovanec, K.; Madiraju, P. A survey of text classification with transformers: How wide? How large? How long? How accurate? How expensive? How safe? IEEE Access 2024, 12, 6518–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivinayagam, A.; El-Bayeh, C.Z.; Damaševičius, R. Twenty Years of Machine-Learning-Based Text Classification: A Systematic Review. Algorithms 2023, 16, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowsari, K.; Jafari Meimandi, K.; Heidarysafa, M.; Mendu, S.; Barnes, L.; Brown, D. Text classification algorithms: A survey. Information 2019, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparetto, A.; Marcuzzo, M.; Zangari, A.; Albarelli, A. A survey on text classification algorithms: From text to predictions. Information 2022, 13, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Alphonse, P. A comparative study on tf-idf feature weighting method and its analysis using unstructured dataset. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.04037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Yang, X.; Luo, W.; Zhou, L.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X. Rumorllm: A rumor large language model-based fake-news-detection data-augmentation approach. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benlahbib, A.; Boumhidi, A.; Fahfouh, A.; Alami, H. Comparative Analysis of Traditional and Modern NLP Techniques on the CoLA Dataset: From POS Tagging to Large Language Models. IEEE Open J. Comput. Soc. 2025, 6, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juraev, G.; Bozorov, O. Using TF-IDF in text classification. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2023; Volume 2789. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. A Large Language Model-based Approach for Personalized Search Results Re-ranking in Professional Domains. Int. J. Lang. Stud. 2025, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakshit, P.; Sarkar, A. A supervised deep learning-based sentiment analysis by the implementation of Word2Vec and GloVe Embedding techniques. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2025, 84, 979–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, A.S.; Pandya, V.; Di Troia, F.; Stamp, M. Malware classification with word2vec, hmm2vec, bert, and elmo. J. Comput. Virol. Hacking Tech. 2023, 19, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Pennington, J.; Socher, R.; Manning, C.D. Glove: Global vectors for word representation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014; pp. 1532–1543. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, S.; Wen, J. Logistic Regression Matching Pursuit algorithm for text classification. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 277, 110761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazaydeh, L.; Abuhelaleh, M.; Al Tawil, A.; Elleithy, K. Clinical Text Classification with Word Representation Features and Machine Learning Algorithms. Int. J. Online Biomed. Eng. 2023, 19, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlak, B.; Uysal, A.K. A novel filter feature selection method for text classification: Extensive Feature Selector. J. Inf. Sci. 2023, 49, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, D.; Lima, R.H.; Pozo, A. Creating deep neural networks for text classification tasks using grammar genetic programming. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 135, 110009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umer, M.; Imtiaz, Z.; Ahmad, M.; Nappi, M.; Medaglia, C.; Choi, G.S.; Mehmood, A. Impact of convolutional neural network and FastText embedding on text classification. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 5569–5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Jin, J.; Gerontitis, D.; Qiu, L.; Zhu, J. Improved recurrent neural networks for text classification and dynamic Sylvester equation solving. Neural Process. Lett. 2023, 55, 8755–8784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Wu, J.; Jiang, X.; Almeida, D.; Wainwright, C.; Mishkin, P.; Zhang, C.; Agarwal, S.; Slama, K.; Ray, A.; et al. Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 27730–27744. [Google Scholar]
- Thoppilan, R.; De Freitas, D.; Hall, J.; Shazeer, N.; Kulshreshtha, A.; Cheng, H.T.; Jin, A.; Bos, T.; Baker, L.; Du, Y.; et al. Lamda: Language models for dialog applications. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.08239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doveh, S.; Perek, S.; Mirza, M.J.; Lin, W.; Alfassy, A.; Arbelle, A.; Ullman, S.; Karlinsky, L. Towards Multimodal In-context Learning for Vision and Language Models. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Dublin, Ireland, 17–18 September 2025; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025; pp. 250–267. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.; Yu, X.; Wen, H.; Sun, J.; Yue, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Z. Exploring the robustness of in-context learning with noisy labels. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2025—2025 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Hyderabad, India, 6–11 April 2025; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Moslem, Y.; Haque, R.; Kelleher, J.D.; Way, A. Adaptive machine translation with large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.13294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshevska, M.; Gievska, S. A review of text style transfer using deep learning. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2021, 3, 669684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makridakis, S.; Petropoulos, F.; Kang, Y. Large language models: Their success and impact. Forecasting 2023, 5, 536–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Li, F. Improving Machine Translation Formality with Large Language Models. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2025, 82, 2061–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Qiu, B.; Ding, L.; Xie, L.; Tao, D. Error analysis prompting enables human-like translation evaluation in large language models: A case study on chatgpt. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.13809. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, J.; Ye, F.; Wong, D.F.; Yu, D.; Shi, S.; Tu, Z.; Wang, L. Salute the classic: Revisiting challenges of machine translation in the age of large language models. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2025, 13, 73–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar, D.; Freitag, M.; Cherry, C.; Luo, J.; Ratnakar, V.; Foster, G. Prompting PaLM for Translation: Assessing Strategies and Performance. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Liu, H.; Dong, Q.; Xu, J.; Huang, S.; Kong, L.; Chen, J.; Li, L. Multilingual Machine Translation with Large Language Models: Empirical Results and Analysis. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żelasko, P.; Chen, Z.; Wang, M.; Galvez, D.; Hrinchuk, O.; Ding, S.; Hu, K.; Balam, J.; Lavrukhin, V.; Ginsburg, B. Emmett: Efficient multimodal machine translation training. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2025—2025 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Hyderabad, India, 6–11 April 2025; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Miah, M.S.U.; Kabir, M.M.; Sarwar, T.B.; Safran, M.; Alfarhood, S.; Mridha, M. A multimodal approach to cross-lingual sentiment analysis with ensemble of transformer and LLM. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Dai, W.; Ghosh, E.; Roy, S.; Schwartz, D.; Laine, K. Does Prompt-Tuning Language Model Ensure Privacy? arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.03472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Li, K.; Xu, M.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, Z.; Cheng, X. On protecting the data privacy of large language models (llms): A survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.05156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.C.; Amini, M.H.; Wu, Y. Security and privacy challenges of large language models: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2025, 57, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Liu, Y.; Ren, S.; Zhu, K.Q. Taxonomy of Abstractive Dialogue Summarization: Scenarios, Approaches, and Future Directions. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 56, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, A.; Morris, A. The problem of information overload in business organisations: A review of the literature. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2000, 20, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y. DialogSum: A real-life scenario dialogue summarization dataset. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.06762. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, A.; Katariya, N.; Amatriain, X.; Kannan, A. Dr. summarize: Global summarization of medical dialogue by exploiting local structures. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.08666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhao, L.; Kang, Y.; Lin, J.; Peng, M.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, X.; Liu, X. Topic-oriented spoken dialogue summarization for customer service with saliency-aware topic modeling. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 14665–14673. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, M.; Liu, Y.; Goyal, N.; Ghazvininejad, M.; Mohamed, A.; Levy, O.; Stoyanov, V.; Zettlemoyer, L. Bart: Denoising sequence-to-sequence pre-training for natural language generation, translation, and comprehension. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.13461. [Google Scholar]
- Golec, J.; Hachaj, T.; Sokal, G. TIPS: A Framework for Text Summarising with Illustrative Pictures. Entropy 2021, 23, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Saleh, M.; Liu, P. Pegasus: Pre-training with extracted gap-sentences for abstractive summarization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 13–18 July 2020; PMLR: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 11328–11339. [Google Scholar]
- See, A.; Liu, P.J.; Manning, C.D. Get to the point: Summarization with pointer-generator networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Bansal, M. Fast abstractive summarization with reinforce-selected sentence rewriting. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.11080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serban, I.; Sordoni, A.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.; Pineau, J. Building end-to-end dialogue systems using generative hierarchical neural network models. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 12–17 February 2016; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Touvron, H.; Lavril, T.; Izacard, G.; Martinet, X.; Lachaux, M.A.; Lacroix, T.; Rozière, B.; Goyal, N.; Hambro, E.; Azhar, F.; et al. Llama: Open and efficient foundation language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.13971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenAI, T. Chatgpt: Optimizing Language Models for Dialogue; OpenAI: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bang, Y.; Cahyawijaya, S.; Lee, N.; Dai, W.; Su, D.; Wilie, B.; Lovenia, H.; Ji, Z.; Yu, T.; Chung, W.; et al. A Multitask, Multilingual, Multimodal Evaluation of ChatGPT on Reasoning, Hallucination, and Interactivity. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Fu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, S.; Tian, Z.; Ding, L. Recursively summarizing enables long-term dialogue memory in large language models. Neurocomputing 2025, 639, 130193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenAI, R. Gpt-4 technical report. View Artic. 2023, 2, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Aydin, O.; Karaarslan, E. OpenAI ChatGPT interprets radiological images: GPT-4 as a medical doctor for a fast check-up. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.06269. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, M. A survey of large language model agents for question answering. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.19213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhery, A.; Narang, S.; Devlin, J.; Bosma, M.; Mishra, G.; Roberts, A.; Barham, P.; Chung, H.W.; Sutton, C.; Gehrmann, S.; et al. Palm: Scaling language modeling with pathways. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2023, 24, 11324–11436. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, P.; Tsai, S.; He, Y.; Jia, X.; Zhen, D.; Yu, N.; Wang, Q.; Ahuja, J.K.; Wei, C.I. Large language models in food science: Innovations, applications, and future. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 148, 104488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fecher, B.; Hebing, M.; Laufer, M.; Pohle, J.; Sofsky, F. Friend or foe? Exploring the implications of large language models on the science system. AI Soc. 2025, 40, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhu, K.; Chen, H.; Yi, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; et al. A survey on evaluation of large language models. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2024, 15, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, L.; Cremonesi, P.; Caines, A.; Buttery, P.; Cappelli, A.; Giussani, A.; Turrin, R. A survey on recent approaches to question difficulty estimation from text. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlKhuzaey, S.; Grasso, F.; Payne, T.R.; Tamma, V. Text-based question difficulty prediction: A systematic review of automatic approaches. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2024, 34, 862–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ch, D.R.; Saha, S.K. Automatic multiple choice question generation from text: A survey. IEEE Trans. Learn. Technol. 2018, 13, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdi, G.; Leo, J.; Parsia, B.; Sattler, U.; Al-Emari, S. A systematic review of automatic question generation for educational purposes. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2020, 30, 121–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Shu, K. Can llm-generated misinformation be detected? arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.13788. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, A.; Haghtalab, N.; Steinhardt, J. Jailbroken: How does llm safety training fail? arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.02483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, A.; Wang, Z.; Kolter, J.Z.; Fredrikson, M. Universal and transferable adversarial attacks on aligned language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.15043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joachim, M.; Castelló, I.; Parry, G. Moving Beyond “Facts Are Facts”: Managing Emotions and Legitimacy After a Fake News Attack. Bus. Soc. 2024, 00076503241281632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.B.; Gaurav, A.; Arya, V.; Waheeb Attar, R.; Bansal, S.; Alhomoud, A.; Chui, K.T. Sustainable supply chain security through BEART-based fake news detection on supplier practices. Enterp. Inf. Syst. 2025, 2462972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahi, H.; Kılıç, Y.; Saǧlam, R.B. Automated detection of hate speech towards woman on Twitter. In Proceedings of the 2018 3rd International Conference on Computer Science and Engineering (UBMK), Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 20–23 September 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 533–536. [Google Scholar]
- Fortuna, P.; Nunes, S. A survey on automatic detection of hate speech in text. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2018, 51, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, M.S.; Oussalah, M. A systematic review of Hate Speech automatic detection using Natural Language Processing. Neurocomputing 2023, 546, 126232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, E. Automated hate speech detection in a low-resource environment. J. Digit. Humanit. Assoc. South. Afr. 2024, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikkisetti, D.; Mustafa, R.U.; Melillo, W.; Corizzo, R.; Boukouvalas, Z.; Gill, J.; Japkowicz, N. Using LLMs to discover emerging coded antisemitic hate-speech emergence in extremist social media. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.10841. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, E.L. Hate Crime Recorded by Law Enforcement, 2010–2019; US Department of Justice, Office of Justice Programs, Bureau of Justice Assistance: Washington, DC, USA, 2021.
- Stroud, S. Hate by Numbers: Exploring Hate Crime Reporting Across Crime Type and Among Special Interest Groups Using the NCVS; University of Missouri-Kansas City: Kansas City, MO, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, D.; Sain, M.K. Comparative Analysis and Assesment on Different Hate Speech Detection Learning Techniques. J. Algebr. Stat. 2023, 14, 29–48. [Google Scholar]
- Wiedemann, G.; Yimam, S.M.; Biemann, C. UHH-LT at SemEval-2020 task 12: Fine-tuning of pre-trained transformer networks for offensive language detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.11493. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, H.; Alhothali, A.; Moria, K. Detection of hate speech using bert and hate speech word embedding with deep model. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 37, 2166719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miran, A.Z.; Yahia, H.S. Hate Speech Detection in Social Media (Twitter) Using Neural Network. J. Mob. Multimed. 2023, 19, 765–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, A.; Kolanchery, A.J.; Kanjookaran, A.A.; Jose, B.T.; Dhanya, P. Hate speech detection in Twitter using different models. In Proceedings of the ITM Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Ulis, France, 2023; Volume 56, p. 04007. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, R.; Jiang, H.; Shi, S.; Xu, R. Exploring the use of large language models for reference-free text quality evaluation: A preliminary empirical study. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.00723. [Google Scholar]
- Min, B.; Ross, H.; Sulem, E.; Veyseh, A.P.B.; Nguyen, T.H.; Sainz, O.; Agirre, E.; Heintz, I.; Roth, D. Recent advances in natural language processing via large pre-trained language models: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 56, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Jiang, Y.E.; Wilcox, E.; Cotterell, R.; Sachan, M. Controlled text generation with natural language instructions. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; PMLR: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 42602–42613. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial networks. Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Sharma, H.K. A GAN-based model of deepfake detection in social media. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 218, 2153–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.; Osindero, S. Conditional Generative Adversarial Nets. arXiv 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patashnik, O.; Wu, Z.; Shechtman, E.; Cohen-Or, D.; Lischinski, D. Styleclip: Text-driven manipulation of stylegan imagery. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 2085–2094. [Google Scholar]
- Karras, T.; Laine, S.; Aittala, M.; Hellsten, J.; Lehtinen, J.; Aila, T. Analyzing and improving the image quality of stylegan. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 8110–8119. [Google Scholar]
- Stypułkowski, M.; Vougioukas, K.; He, S.; Zięba, M.; Petridis, S.; Pantic, M. Diffused heads: Diffusion models beat gans on talking-face generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024; pp. 5091–5100. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, T.; Qureshi, S. The survey: Text generation models in deep learning. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 2515–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zuo, W. Personalized image generation with deep generative models: A decade survey. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.13081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Wang, S.; Li, K.; Li, X.; Sun, F. When Feature Encoder Meets Diffusion Model for Sequential Recommendations. Inf. Sci. 2025, 702, 121903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Tian, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Shen, K.; Tong, Y.; Wang, M. Mmada: Multimodal large diffusion language models. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.15809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1301.3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, A.; Leskovec, J. node2vec: Scalable feature learning for networks. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 855–864. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Jia, P.; Dai, Y.; Tao, C.; Zhao, Z.; Zhi, D. Gene2vec: Distributed representation of genes based on co-expression. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherstinsky, A. Fundamentals of recurrent neural network (RNN) and long short-term memory (LSTM) network. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2020, 404, 132306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, M.; Raiko, T.; Honkala, M.; Kärkkäinen, L.; Vetek, A.; Karhunen, J.T. Bidirectional recurrent neural networks as generative models. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; Volume 28. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, S.; Xu, L.; Liu, K.; Zhao, J. Recurrent convolutional neural networks for text classification. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Austin, TX, USA, 25–30 January 2015; Volume 29. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2014), Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; Volume 27. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, D.M.E.D.M. A survey on sentiment analysis challenges. J. King Saud Univ.-Eng. Sci. 2018, 30, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wankhade, M.; Rao, A.C.S.; Kulkarni, C. A survey on sentiment analysis methods, applications, and challenges. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 55, 5731–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Lee, L. Opinion mining and sentiment analysis. In Foundations and Trends® in Information Retrieval; Now Publishers Inc.: Hanover, MA, USA, 2008; Volume 2, pp. 1–135. [Google Scholar]
- Schouten, K.; Frasincar, F. Survey on aspect-level sentiment analysis. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2015, 28, 813–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, M.; Shaila, S.; Vadivel, A. Polarity classification on twitter data for classifying sarcasm using clause pattern for sentiment analysis. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 32789–32825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, L.P.; Alias, S. Beyond sentiment analysis: A review of recent trends in text based sentiment analysis and emotion detection. J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inform. 2023, 27, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, H.H.; Prasad, P.W.; Maag, A.; Alsadoon, A. Deep learning for aspect-based sentiment analysis: A comparative review. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 118, 272–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, A.; Rao, Y.; Wu, L.; Sun, L. Issues and challenges of aspect-based sentiment analysis: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2020, 13, 845–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truşcǎ, M.M.; Frasincar, F. Survey on aspect detection for aspect-based sentiment analysis. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 3797–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, B.; Mittal, N.; Agarwal, B.; Mittal, N. Machine learning approach for sentiment analysis. In Prominent Feature Extraction for Sentiment Analysis; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 21–45. [Google Scholar]
- Tanveer, M.; Rajani, T.; Rastogi, R.; Shao, Y.H.; Ganaie, M. Comprehensive review on twin support vector machines. Ann. Oper. Res. 2024, 339, 1223–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha, J.; Kumaran, U. A hybrid optimization algorithm using BiLSTM structure for sentiment analysis. Meas. Sens. 2023, 25, 100619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutinda, J.; Mwangi, W.; Okeyo, G. Sentiment analysis of text reviews using lexicon-enhanced bert embedding (LeBERT) model with convolutional neural network. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarandi, A.K.; Mirzaei, S. A survey of aspect-based sentiment analysis classification with a focus on graph neural network methods. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 56619–56695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, A.; Jovanovic, L.; Bacanin, N.; Antonijevic, M.; Savanovic, N.; Zivkovic, M.; Milovanovic, M.; Gajic, V. Exploring metaheuristic optimized machine learning for software defect detection on natural language and classical datasets. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, N.C.; Moreno-García, M.N.; De la Prieta, F. Sentiment analysis based on deep learning: A comparative study. Electronics 2020, 9, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.L.; Lee, C.P.; Lim, K.M. Roberta-Gru: A hybrid deep learning model for enhanced sentiment analysis. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miazga, J.; Hachaj, T. Evaluation of most popular sentiment lexicons coverage on various datasets. In Proceedings of the 2019 2nd International Conference on Sensors, Signal and Image Processing, Prague, Czech Republic, 8–10 October 2019; pp. 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Goutte, C.; Gaussier, E. A probabilistic interpretation of precision, recall and F-score, with implication for evaluation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Retrieval, Compostela, Spain, 21–23 March 2005; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 345–359. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.Y. Rouge: A package for automatic evaluation of summaries. In Proceedings of the Text Summarization Branches Out, Barcelona, Spain, 25–26 July 2004; pp. 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Salam, S.; Rafea, A. Performance study on extractive text summarization using BERT models. Information 2022, 13, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, L.; Ramalingam, K.J.; Beyer, M.; Zimmermann, A. WRF: Weighted Rouge-F1 Metric for Entity Recognition. In Proceedings of the 4th Workshop on Evaluation and Comparison of NLP Systems, Bali, Indonesia, 1 November 2023; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Denkowski, M.; Lavie, A. Meteor 1.3: Automatic metric for reliable optimization and evaluation of machine translation systems. In Proceedings of the Sixth Workshop on Statistical Machine Translation, Edinburgh, UK, 30–31 July 2011; pp. 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, S.; Lavie, A. METEOR: An automatic metric for MT evaluation with improved correlation with human judgments. In Proceedings of the ACL Workshop on Intrinsic and Extrinsic Evaluation Measures for Machine Translation and/or Summarization, Arbor, MI, USA, 29 June 2005; pp. 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Lavie, A.; Denkowski, M.J. The METEOR metric for automatic evaluation of machine translation. Mach. Transl. 2009, 23, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denkowski, M.J.; Lavie, A. Extending the METEOR Machine Translation Evaluation Metric to the Phrase Level. In Proceedings of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Elloumi, Z.; Blanchon, H.; Serasset, G.; Besacier, L. METEOR for multiple target languages using DBnary. In Proceedings of the MT Summit 2015, Miami, FL, USA, 30 October–3 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Hu, J. Meteor++ 2.0: Adopt syntactic level paraphrase knowledge into machine translation evaluation. In Proceedings of the Fourth Conference on Machine Translation (Volume 2: Shared Task Papers, Day 1), Florence, Italy, 1–2 August 2019; pp. 501–506. [Google Scholar]
- Papineni, K.; Roukos, S.; Ward, T.; Zhu, W.J. Bleu: A Method for Automatic Evaluation of Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 7–12 July 2002; pp. 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callison-Burch, C.; Osborne, M.; Koehn, P. Re-evaluating the role of BLEU in machine translation research. In Proceedings of the 11th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Trento, Italy, 3–7 April 2006; pp. 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Lei, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, N.; Long, Z.; Yang, P.; Zhao, J.; Hua, M.; Ma, C.; Wang, K.; et al. Safety evaluation of deepseek models in chinese contexts. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.11137. [Google Scholar]
- McDermott, M.B.; Yap, B.; Szolovits, P.; Zitnik, M. Structure-inducing pre-training. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2023, 5, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchin, A.; Masharsky, S.; Zitnik, M. Comparison of BERT implementations for natural language processing of narrative medical documents. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2023, 36, 101139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.H.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y. FinBERT: A large language model for extracting information from financial text. Contemp. Account. Res. 2023, 40, 806–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf, S.; Anoop, V. An analysis on large language models in healthcare: A case study of BioBERT. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.07282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollapally, N.M.; Geller, J. Clinical BioBERT Hyperparameter Optimization using Genetic Algorithm. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.03822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapathy, N.; Chary, P.S.; Pithani, T.V.R.K.; Kavati, P. A Multimodal Approach For Endoscopic VCE Image Classification Using BiomedCLIP-PubMedBERT. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.19944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darji, H.; Mitrović, J.; Granitzer, M. German BERT model for legal named entity recognition. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.05388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Kishore, V.; Wu, F.; Weinberger, K.Q.; Artzi, Y. Bertscore: Evaluating text generation with bert. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.09675. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, W.; Neubig, G.; Liu, P. Bartscore: Evaluating generated text as text generation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 27263–27277. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y. Template-based named entity recognition using BART. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.01760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.; Das, R.; Das, K. Deep Learning Based Bengali Image Caption Generation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Systems and Management Science, Msida, Malta, 6–9 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 49–59. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, T.; Razeghi, Y.; Logan IV, R.L.; Wallace, E.; Singh, S. Autoprompt: Eliciting knowledge from language models with automatically generated prompts. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.15980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).