1. Introduction
The increasing scale and complexity of industrial processes led to a significant rise in the generation of chemically diverse and environmentally hazardous wastewater streams. Industrial effluents, particularly from metal finishing, electroplating, food production, and pharmaceutical sectors, often contain a mixture of heavy metals, complex organic pollutants, surfactants, and non-biodegradable compounds that are not easily removed by conventional treatment technologies [
1,
2,
3]. As the global demand for resource-efficient and ecologically sustainable water management grows, the pressure to modernize wastewater treatment systems with intelligent, adaptive, and robust solutions becomes ever more urgent [
4,
5,
6].
Traditional wastewater treatment systems rely on programmable logic controllers (PLCs) for automation, enabling real-time monitoring and control of processes such as chemical dosing, pH adjustment, aeration, and sedimentation. Integrated with supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems and human–machine interfaces (HMIs), PLCs facilitate precise management of operational parameters, significantly reducing operator error and process delays [
7,
8,
9,
10]. PLCs control not only process parameters, but also the start/stop sequences of devices—pumps, valves, aerators, and chemical dosing pumps. PLCs often manage emergency signals and automatically initiate safety protocols, for example, stopping chemical dosing pumps at critical pH values or overloads, protecting against overflow or leakage. Timers and calendar functions can be integrated into PLC programs, which allow changing control strategies according to seasonal changes (e.g., higher aeration intensity in summer) or time of day (night modes to save energy) [
1,
2,
3]. Some PLCs have the ability to accumulate historical process information on site, allowing analysis of control efficiency, identification of common errors, or optimization of reagent use based on previous data. PLC control programs can be designed to be easily adapted to different wastewater flows—industrial, municipal, or mixed, as well as to respond quickly to sudden fluctuations, for example, due to precipitation or production changes [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5]. However, these systems typically operate under fixed or semi-dynamic logic with pre-programmed threshold values, lacking adaptability to non-linear influent variability and failing to anticipate changes in system dynamics. This makes them reactive rather than predictive, particularly when addressing variable influent quality, fluctuating hydraulic loads, or the need for precise chemical dosing under time constraints [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15]. Mechanical and physical systems alone cannot adequately address dissolved pollutants, and biological treatment efficiency is sensitive to temperature, pH, and toxicant concentrations [
11,
12]. Advanced technologies such as ozonation, membrane separation, and ultraviolet irradiation offer improvements but are capital- and energy-intensive and require precise control to be effective [
16,
17,
18,
19,
20].
To address these limitations, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) emerged as powerful tools for enhancing wastewater treatment performance. Long short-term memory (LSTM) neural networks, a subset of ML, are particularly effective for time series forecasting in dynamic and noisy environments, enabling predictive modeling of critical parameters, such as pH shifts, temperature variation, flow rate, and reagent consumption, using historical and real-time sensor data [
1,
2,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26]. Studies demonstrated AI’s potential to optimize energy usage, reagent dosing, and process performance in applications such as electrocoagulation and photovoltaic-powered systems [
2,
3,
4,
5]. For example, Chavhan et al. [
3] developed an Internet of Things (IoT)-based wastewater monitoring architecture for industrial effluents, enabling remote tracking of pH and conductivity. Su et al. [
4] advocated for AI integration to optimize energy usage in photovoltaic-powered systems, while Adamovic et al. [
2] and Sedaghat et al. [
5] showed process improvements and reduced reagent use through AI-driven electrocoagulation optimization. Edge AI with PLC, some solutions use local (edge computing) devices, minicomputers or industrial controllers, in which the LSTM model is directly implemented. In this case, there is no need for constant data transmission to the cloud or servers, and control is performed locally, reducing latency. LSTM is also used to create “virtual sensors”, models that can predict difficult-to-measure parameters, such as the efficiency of a biological process or the total amount of pollutants, based on available measurements (e.g., pH, DO, and temperature). These indicators are then used to make decisions in the PLC [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5]. However, the practical integration of AI models, particularly LSTM-based architectures, with industrial PLC systems for real-time control remains underexplored. Most research isolates AI components from process control infrastructure, and deployments unifying predictive intelligence with hardware-level automation are rare [
22,
27,
28,
29,
30]. Additionally, few studies address data-driven optimization of reagent dosing and adaptive control of aeration and sedimentation based on predicted system behavior rather than static setpoints [
1,
31,
32,
33]. AI-enhanced systems also offer opportunities for predictive maintenance, such as anomaly detection and degradation trend analysis, which can reduce downtime and extend component lifespan in facilities with high influent variability [
3,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38].
This study complements a gap in the scientific literature concerning the limited integration of artificial intelligence (AI)-based models, particularly LSTM neural networks, with industrial-grade PLCs for real-time management of industrial wastewater treatment processes. While previous research explored AI models or PLC automation independently, there is a lack of studies combining these technologies into a cohesive system capable of adaptively managing variable wastewater characteristics under real industrial conditions [
1,
2,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33]. Furthermore, few studies focus on data-driven optimization of reagent dosing and aeration based on predicted parameters such as pH, temperature, or flow rate, which could reduce operational costs and ensure compliance with environmental standards [
1,
2,
3,
4]. This study introduces a novel integration of a Siemens S7-1214 PLC with a two-layer LSTM neural network developed on the PyTorch 2.2 platform, enabling real-time optimization of industrial wastewater treatment processes. Unlike previous research that often examines AI models or PLC automation in isolation, this work uniquely combines predictive LSTM modeling with industrial-grade PLC control, validated under real-world electroplating and surface treatment conditions. The system ensures compliance with stringent environmental standards, including the EU Water Framework Directive (2000/60/EC) and ISO 14001, through real-time monitoring via the Teltonika TRB255 module. By offering a scalable, data-driven solution that enhances process stability, reduces operational costs, and promotes sustainable resource use, this study provides a pioneering framework for intelligent wastewater treatment, addressing critical gaps in adaptive automation and predictive control. The aim of the research is to develop and evaluate an automated industrial wastewater treatment system integrating a Siemens S7-1214 PLC and a two-layer LSTM neural network to optimize reagent dosing, aeration, and sediment separation based on real-time data, increase treatment efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure compliance with environmental standards.
3. Results and Discussion
The traditional method, tested under real industrial conditions, achieved 68–72% pollutant removal efficiency. During manual control, operators directly monitored pH changes, manually dosed chemical reagents (acids, alkalis, coagulants), and controlled the aeration and sediment separation processes. The effectiveness of this method was limited by human error, inaccurate reagent dosing, and longer response time to changing wastewater parameters such as pH or flow.
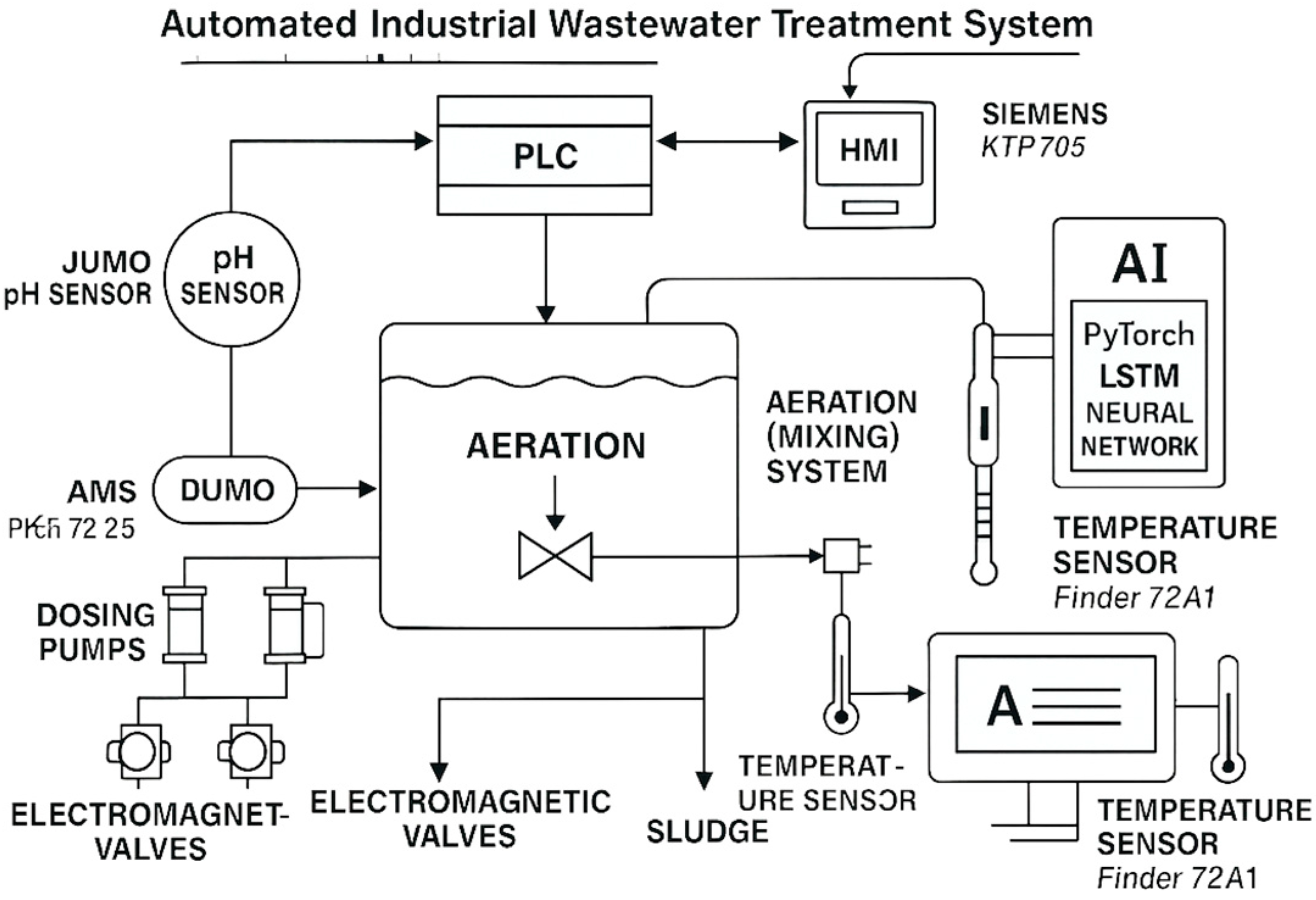
The wastewater treatment system architecture in this study is designed as a modernized, fully automated system for the treatment of industrial wastewater from electroplating, painting, to polishing processes (
Figure 2). The system is based on a Siemens S7-1214 PLC, which coordinates the entire process—from chemical dosing to aeration and sludge separation. The main components of the system are pH sensors, dosing pumps, electromagnetic valves, level sensors, aeration system, SMS communication module, and HMI. The system operates cyclically: the operator starts it, and the PLC automatically controls the acid dosing (to reduce pH), the introduction of calcium chloride and coagulants, alkaline neutralization (to increase pH), the addition of flocculant, and the sedimentation phase [
5]. After the settling phase, the separation of sludge and treated water is performed. The entire operation is monitored in real time, and SMS messages are sent about the progress and malfunctions. Automation reduced process time by 31%, chemical consumption by up to 30%, and operator workload to minimal intervention.
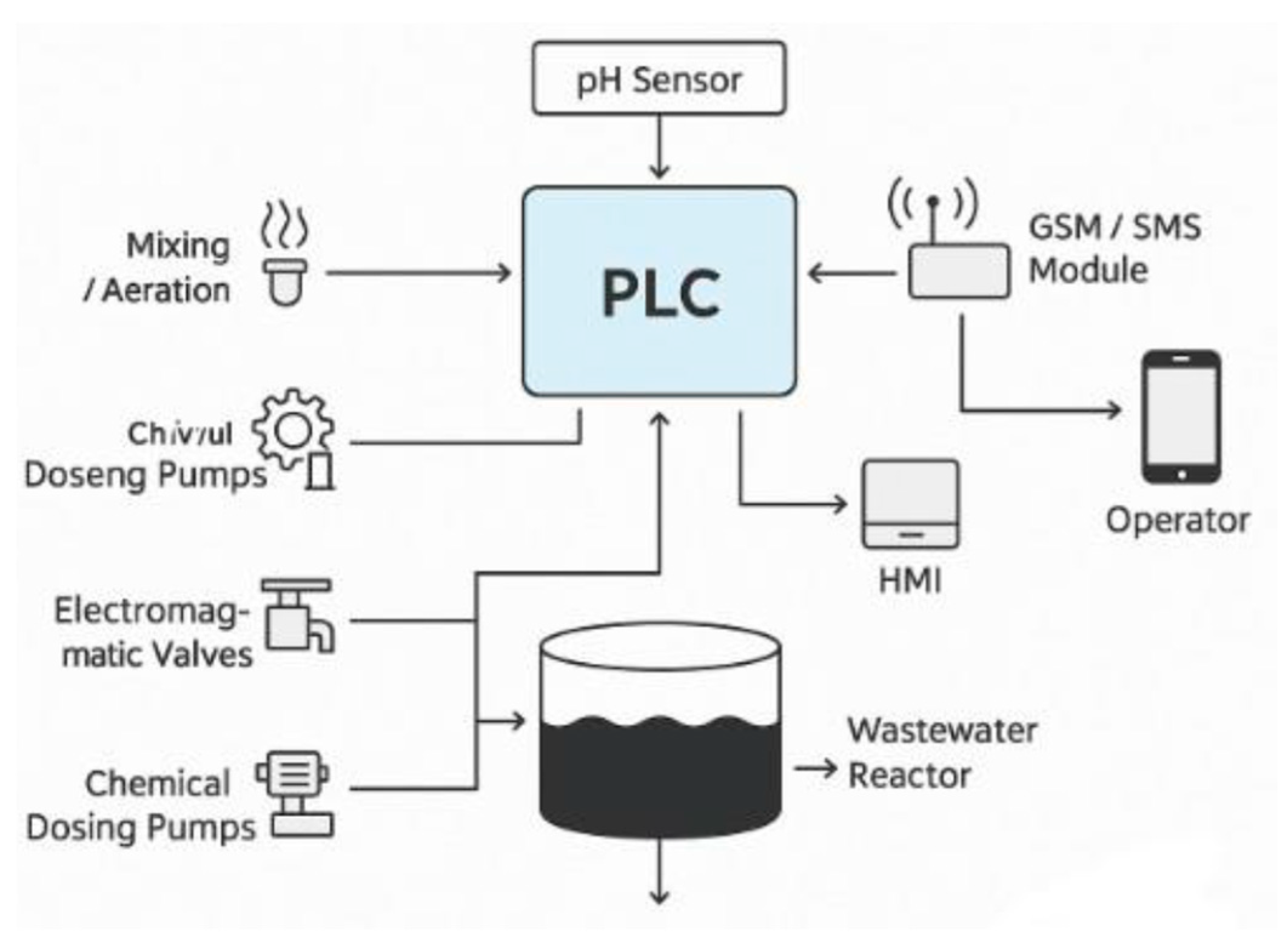
The interface between components in an automated wastewater treatment system is designed to ensure smooth data transfer and precise control of the entire process (
Figure 3). The core of the system is the Siemens S7-1214, PLC, which collects data from pH sensors, level sensors, and other sensors and, based on these data, controls dosing pumps, valves, aeration devices, and other actuators. The entire process is visualized through the HMI—the Siemens KTP400 panel, where the operator can set parameters, monitor the process progress, see errors, and enter phone numbers to which automatic notifications about the process status are sent. Data from the PLC are converted into SMS format via the Teltonika TRB225 industrial gateway, which ensures communication between the automation system and external users. This interface allows real-time monitoring of the process, quick response to malfunctions, reduces the need for human intervention, and increases the overall reliability and efficiency of the system. Benefits include greater accuracy, fewer errors, shorter incident response times, and optimized chemical usage.
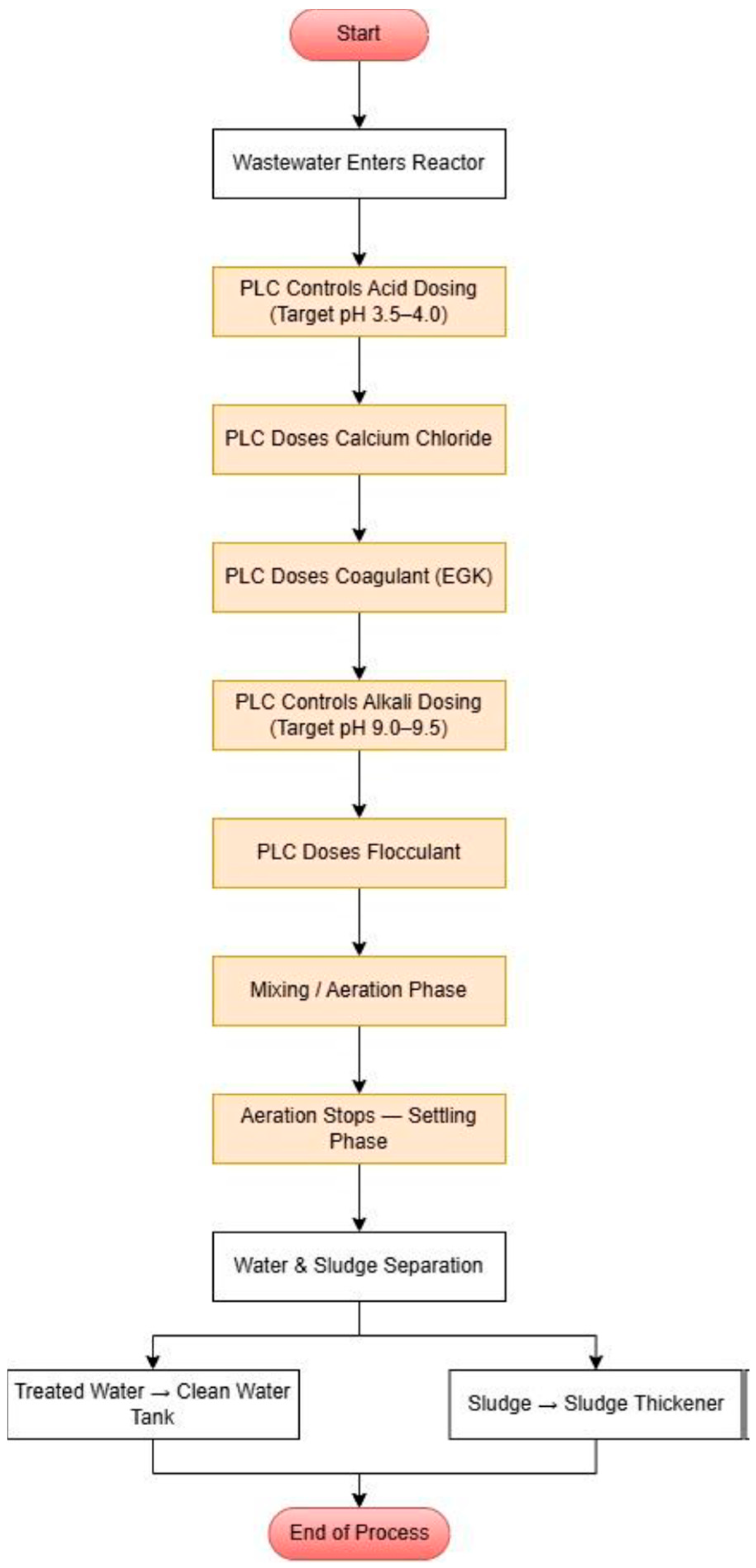
The process workflow of an automated wastewater treatment system is based on a pre-planned, PLC-controlled cycle that ensures consistent and accurate execution of all treatment stages (
Figure 4). It all starts with the operator’s actions—the process is started via the HMI interface, and the PLC checks the status of the sensors and initiates aeration [
6]. Then, based on real-time pH readings, the system automatically doses acid until the pH drops to the range of 3.5–4.0. Later, calcium chloride and coagulants are added at precisely the right time, followed by alkali to raise the pH to 9.0–9.5. Then, the flocculant dosing phase is activated, promoting the separation of solid particles and liquid. This is followed by a 30 min sedimentation phase, during which the aeration is turned off and the wastewater is allowed to settle. Finally, the separated sludge is pumped into a thickening tank, and the treated water is directed to a clean water tank. This operating principle allows for the automatic execution of a complex process without constant human supervision. The main advantages are reduced operator workload, faster process progress (about 31% shorter duration), reduced chemical consumption (20–30%), increased accuracy, and better process control and safety due to integrated sensors, time management, and SMS alerts.
Figure 5 (operator workflow: manual (left), automated process (right)) illustrates the fundamental difference between the operator’s work during the manual and automated wastewater treatment process. During the manual process, the operator must constantly monitor the pH values, take measurements several times per cycle, manually dose chemicals through valves, and actively supervise the entire 90 min process. This requires not only great attention, but also physical effort and constant presence at the equipment. Meanwhile, in the automated process, the operator’s role is limited to starting the process via the HMI interface and adding chemicals when the system sends appropriate messages. All dosing, pH adjustment, mixing, sedimentation, and liquid separation are performed automatically based on PLC. The operating principle is based on sensor data and predefined algorithm steps, which ensures stable and repeatable results. The main advantages of such a solution are significantly reduced physical and psychological load on the operator, reduced risk of human error, freed up working time for other tasks, and increased overall work efficiency and safety.
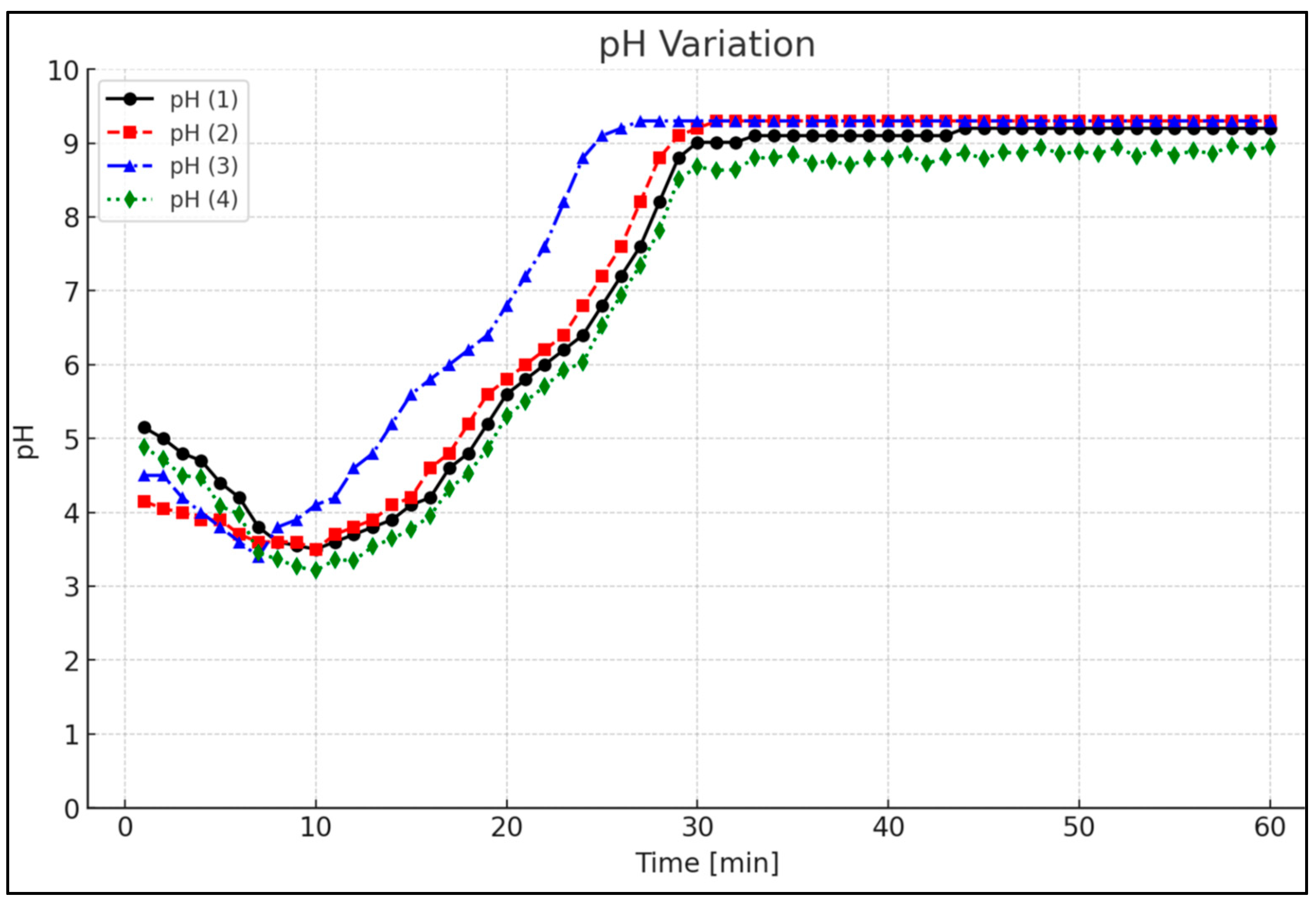
Figure 6 shows the pH variation over time of an automated wastewater treatment process, which clearly distinguishes three main phases. The first, acidification phase (0–10 min) begins when the pH value of about 5 gradually decreases to about 3.3–3.5. In this stage, acid is automatically dosed into the system, the purpose of which is to achieve optimal conditions for coagulation and flocculation, and to precipitate certain heavy metals or contaminants that are most effectively removed at low pH. The second phase, the alkalization phase (15–30 min), is characterized by a sharp pH jump, which indicates the dosing of alkaline chemicals [
8]. The automated control system responds to real-time data recorded by the pH sensor and precisely doses the alkali until the required neutral or alkaline pH level is reached. The third stage, the stabilization phase (30–60 min), begins when the pH reaches about 9–9.5 and this level is maintained for the rest of the time. Small fluctuations (±0.1) are normal and reflect the continuous automatic adaptation of the system to process conditions and fluid dynamics. This consistent pH control proves that the system not only effectively regulates chemical reactions, but also maintains consistent process quality. The main advantages of such control are greater accuracy, faster response times, reduced risk of chemical overdose, and assured quality of contaminant removal. Four different pH values are used, as each corresponds to a different stage of the cleaning process: a pH value of about 5 at the beginning of the process prepares the system for acidification, a pH of 3.3–3.5 in the acidification phase creates conditions for effective coagulation, flocculation, and metal precipitation, a pH of 7–9 during alkalization neutralizes the acid and activates further reactions, and a pH of 9–9.5 in the stabilization phase maintains a constant process and ensures cleaning quality.
Monitoring pH changes in the treatment of wastewater from the electroplating industry ensures effective control of chemical reactions, as pH directly influences the coagulation of heavy metals, the precipitation of phosphates, and the neutralization of organic compounds. Pollutants such as heavy metals or phosphates are only effectively removed within a precise pH range: in an acidic medium (pH 3.5–4.0), metal precipitation occurs, and in an alkaline medium (pH 9.0–9.5), flocculation and decomposition of organic matter occur. Incorrect pH reduces treatment efficiency, causes equipment corrosion, and can violate environmental requirements, such as the EU Water Directive (2000/60/EC) if untreated wastewater is discharged. Automatic real-time pH monitoring using JUMO sensors and Siemens S7-1214 PLC allows for precise dosing of acids or alkalis, ensuring process stability [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10].
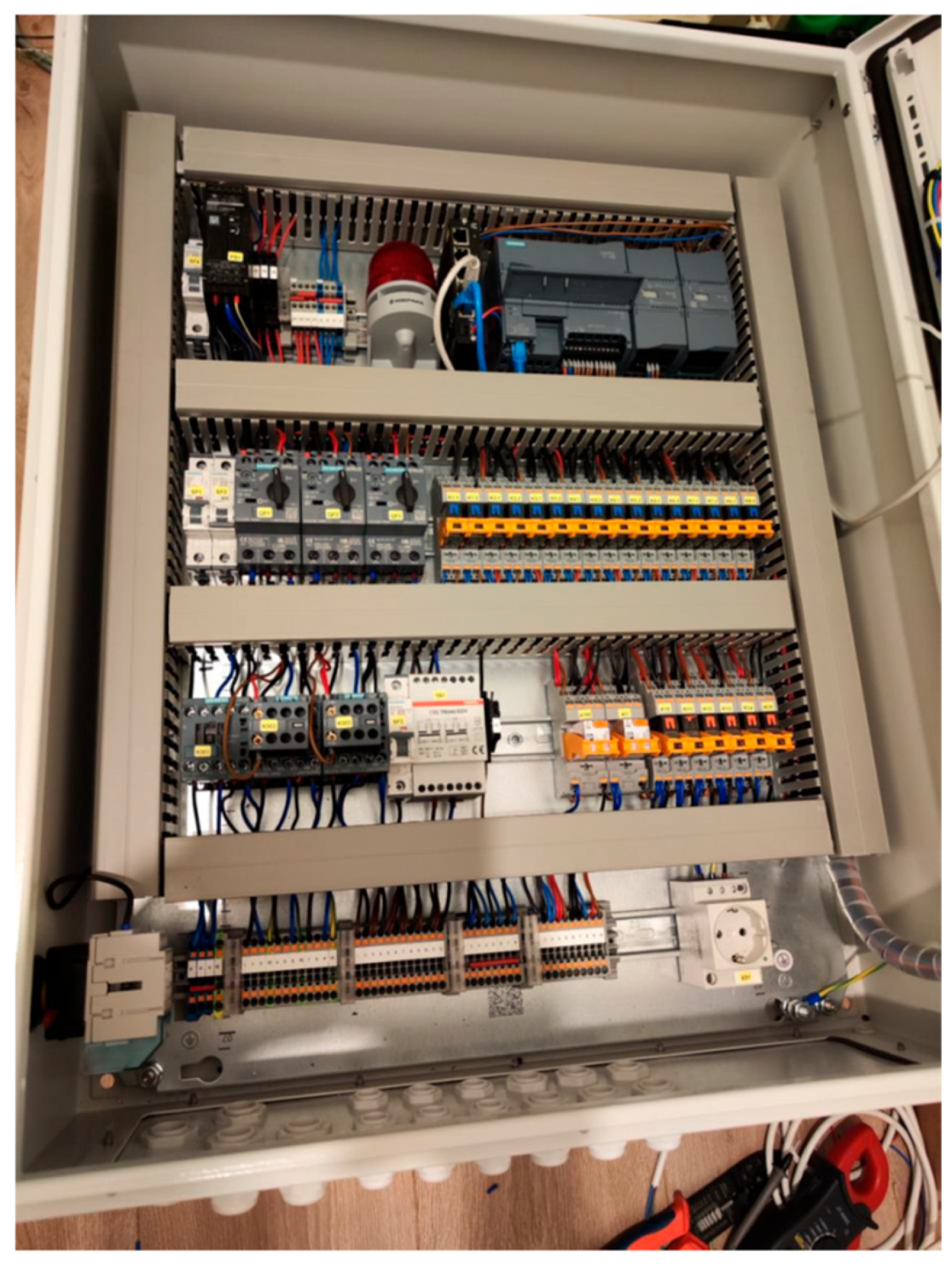
Figure 7 illustrates the control cabinet of the new automated wastewater treatment system, which integrates the main electronic components responsible for controlling the entire process. The main control center of the system is the Siemens S7-1214 programmable logic controller, which collects data from sensors, processes information and controls the executive elements—pumps, valves, dispensers, and aeration equipment. The cabinet also has an HMI interface (Siemens KTP400), which allows the operator to start the system, monitor its status, set parameters, and receive information about errors. The control cabinet acts as a central nervous system, connecting all automation components into a single, effectively coordinated structure. The advantages of such a solution are clear: compact and centralized equipment, simpler management and maintenance, reduced probability of errors, fast service recovery in case of failures, and the ability to integrate smart functions, such as SMS alerts or remote access. This allows us to ensure a stable, reliable, and cost-effective wastewater treatment process [
4,
5,
6].
PyTorch makes it easy to build, train, and adapt advanced neural network architectures that can detect complex patterns in data that are invisible to the human eye, thus ensuring more accurate and reliable predictions. The model was trained on real-time data collected from an automated industrial wastewater treatment system, which operates with various sensors—pH, temperature, level, and other process parameters, integrated with a Siemens PLC controller. These data, which include input parameters, chemical doses, and final cleaning quality, were carefully prepared for training, allowing for the creation of an effective prediction tool that helps optimize the wastewater treatment process before it even starts [
3,
4,
5].
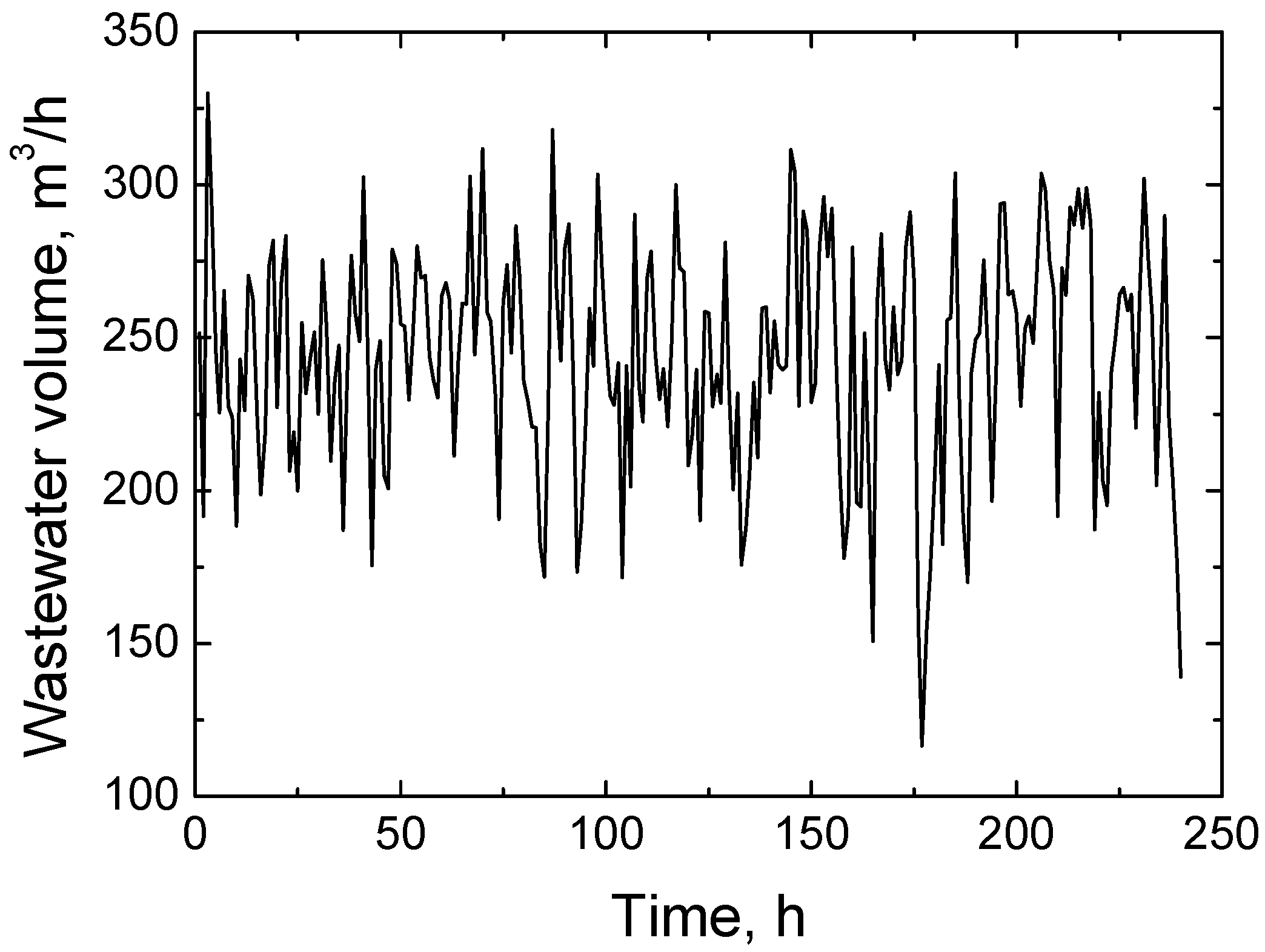
Figure 8 shows the forecast of wastewater volume changes over a 240 h period, which was obtained using an AI model. The forecast curve clearly shows that the wastewater flow rate during this period fluctuated between approximately 130 and 330 cubic meters per hour. Such significant fluctuations reflect real industrial process conditions, where wastewater volume varies depending on production intensity, work shift schedule, or other operational factors. This forecast is created using a PyTorch-based artificial intelligence model that has been trained on historical sensor data. The model is able to process complex time series data and generate accurate flow change forecasts that help to prepare the treatment system for changing loads in advance. This proves that the developed forecasting system is not just theoretical or based on simulation, but reflects a real practical application that allows for data-driven decisions in the real wastewater treatment process.
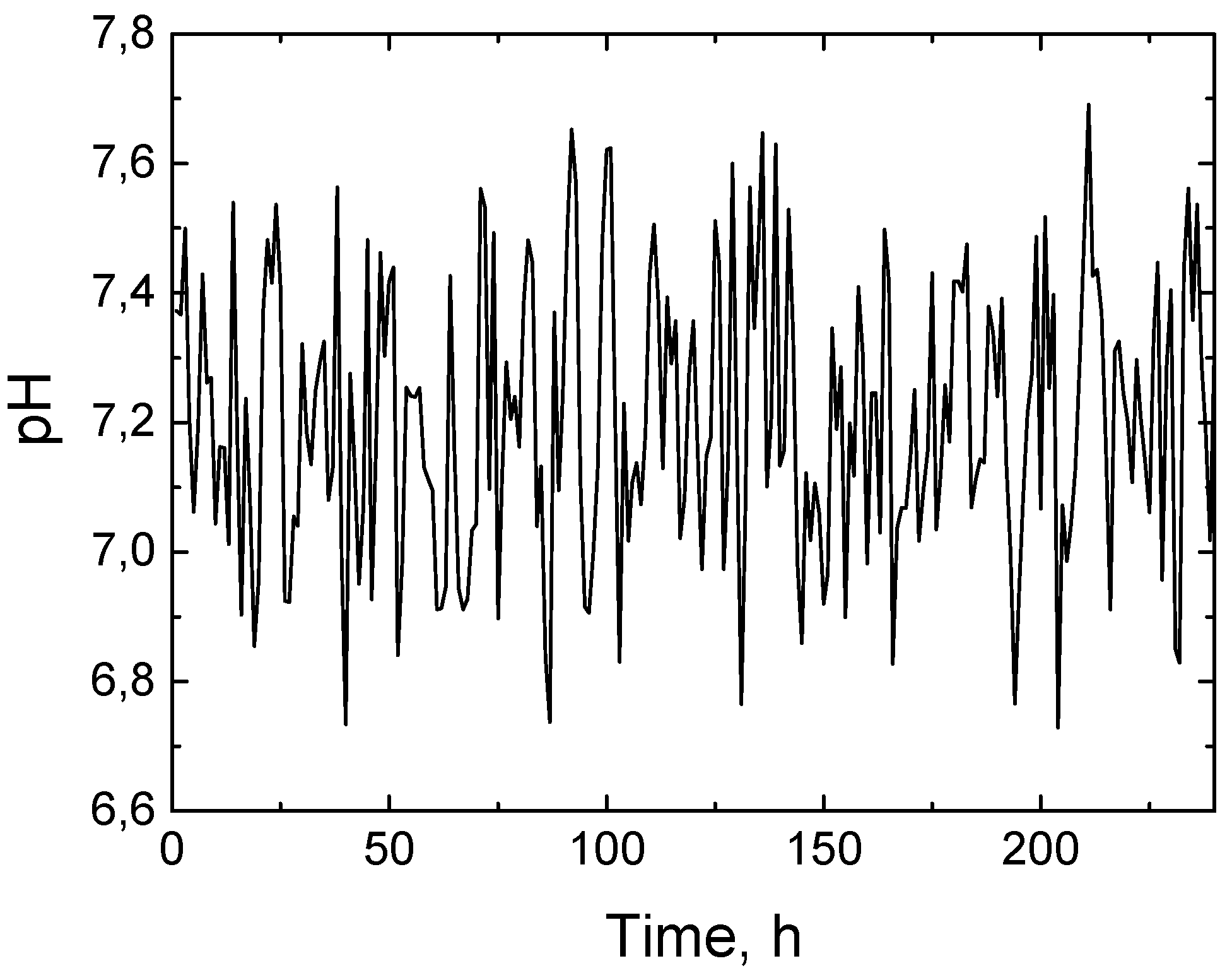
Figure 9 shows the prediction of wastewater pH values over a 240 h period, created using an AI model trained on real historical data. The prediction curve reveals that during this period, pH values ranged from 6.7 to 7.7. This pH range is close to neutral (7.0) and is considered optimal for many wastewater treatment processes, especially for biological and chemical treatment stages. The predicted pH fluctuations are quite narrow, which indicates that the wastewater remains chemically stable and does not change to extremes—this is important both for the protection of equipment (since acidic or alkaline conditions can cause corrosion) and for the activity of microorganisms involved in biological treatment. In addition, this fact confirms that the AI model developed using the PyTorch platform is capable of accurately predicting pH changes based on real-time sensor data. Such prediction ability allows for the planning of appropriate chemical dosages or corrective actions in advance, which increases the efficiency and stability of the treatment process. All this once again shows that integrating AI into wastewater treatment systems is valuable and can significantly contribute to sustainable and automated process management.
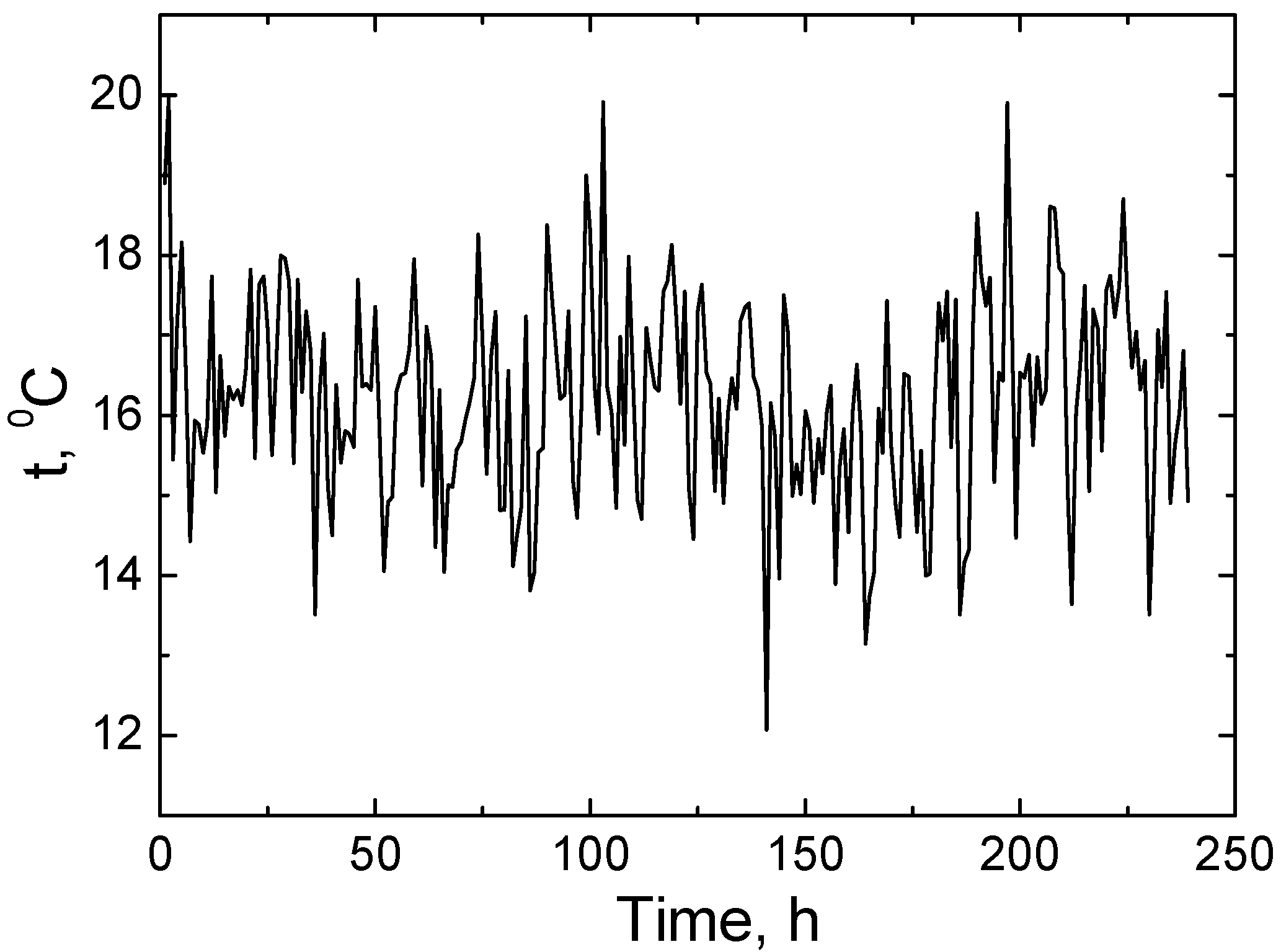
Over a 240 h period, as shown in
Figure 10, the temperature predicted by the AI model varied from 12 °C to 20 °C. This range corresponds to normal climatic conditions and is typical for both domestic and industrial wastewater temperatures. Such fluctuations are favorable for biological treatment processes, since microorganisms that decompose organic matter operate effectively at temperatures of 10–35 °C, and the optimal range is usually 15–25 °C. This forecast indicates a stable and favorable temperature regime for wastewater treatment [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6]. Temperature monitoring is critically important, as it directly determines the reaction rate, microbial activity, as well as the efficiency of coagulation and flocculation, and the solubility and interactions of chemicals. Sudden temperature changes can signal potential treatment process disruptions, equipment failures, or production changes. The forecast is developed using the PyTorch platform and is based on real data, emphasizing its practicality. Such information provision allows control systems and operators to timely adjust processes and optimize reagent doses and aeration time, ensuring smooth, efficient, and economical wastewater treatment [
4,
5,
6,
7].
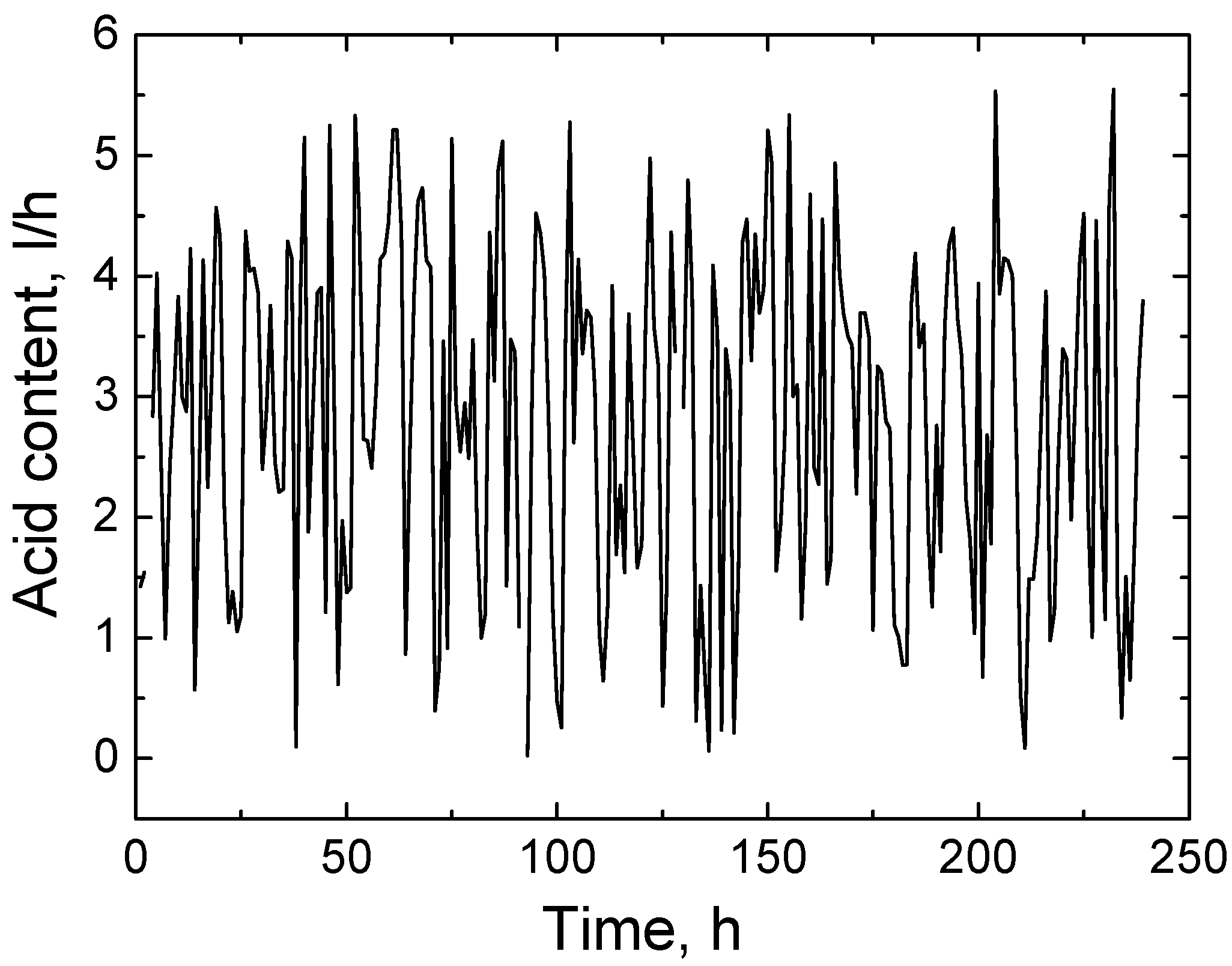
The forecast of the amount of acid used for wastewater neutralization over a 240 h period is presented in
Figure 11. The forecast curve shows that the acid consumption varied from 0.1 to 5.5 L per hour, reflecting the changing demand depending on the composition of the incoming wastewater. These fluctuations are logical, since the amount of acid directly depends on the pH level of the wastewater and the concentration of alkaline compounds in it. When the wastewater contains more alkaline substances, such as alkalis, metal hydroxides, or household chemical residues, a larger amount of acid is required for neutralization to reduce the pH to the desired level. Conversely, if the wastewater is less alkaline or has a near-neutral pH, the acid consumption is minimal. An artificial intelligence model that predicts acid consumption based on pH, temperature, and other input parameters allows for efficient planning of reagent doses, avoiding both overdosing and underdosing. This not only reduces operating costs, but also ensures a stable and safe wastewater treatment process.
The accuracy of the model was evaluated by the root mean square error (RMSE) metric, which reached 0.17 pH units for pH prediction, 0.58 °C for temperature, and 11.2 m3/h for flow rate. These results indicate that the model effectively predicts near-future process states and can be used as an aid in optimizing chemical dosing and control solutions in an automated wastewater treatment system.
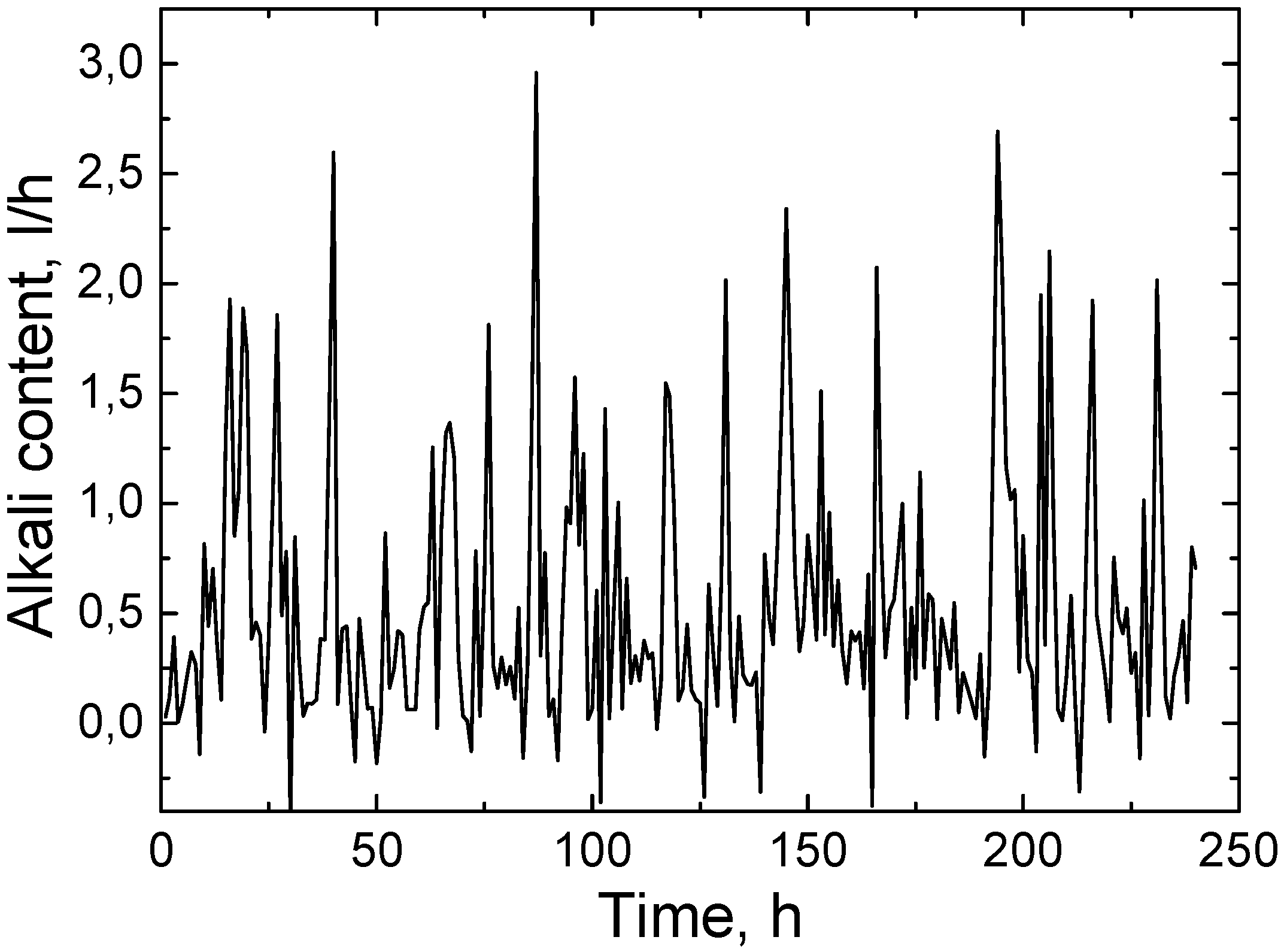
Figure 12 shows the variation in the alkali consumption applied for wastewater neutralization, predicted using an artificial intelligence (AI) model developed with the PyTorch system. This model was trained with real historical data collected from automated wastewater treatment systems; therefore, the forecast provided is practically justified and corresponds to real operating conditions. According to the forecast curve, it can be seen that the alkali consumption varied from 0 to 3 L per hour over a period of 240 h. Such fluctuations are natural and depend on the chemical composition of the incoming wastewater—in particular, its initial pH and the amount of acidic impurities. If more acidic wastewater with a low pH enters the system, alkali dosing becomes necessary in order to raise the pH to the required level (usually not exceeding 9–9.5) and ensure the effective course of coagulation, flocculation, or other chemical reactions. When the wastewater contains fewer acidic pollutants or its pH is close to the required level, the amount of alkali is reduced or not needed at all. The prediction of the DI model allows for a pre-estimation of how much alkali will be needed at different times of the treatment process, which allows for more accurate planning of chemical use, reducing the risk of overdose and optimizing treatment costs. This helps maintain process stability, reduces the need for human intervention, and increases the overall efficiency of the system [
6,
7,
8].
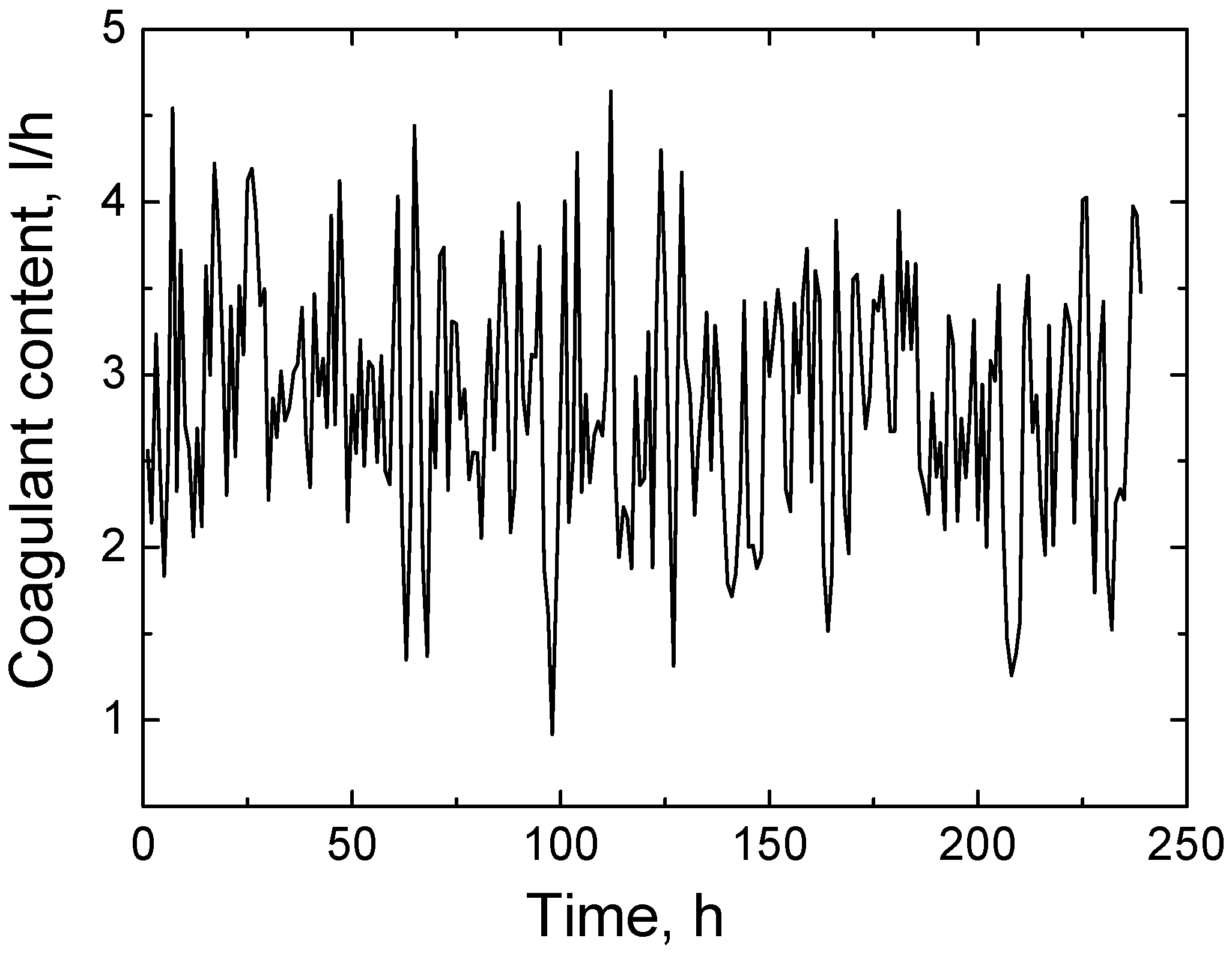
Forecast of coagulant consumption for wastewater neutralization, which was created using an AI model based on the PyTorch machine learning system (
Figure 13). The model was trained on real historical data; therefore, the forecast provided is based on practical observations and reflects real operating conditions. According to the forecast curve, the coagulant consumption over a 240 h period ranged from 1 to 4.5 L per hour. The need for coagulants directly depends on the composition of the wastewater—in particular, on the content of suspended solids (SS), organic pollutants, and phosphates. Coagulants are used to destabilize dissolved or colloidal pollutants, forming a precipitate that can be removed by sedimentation or filtration. If more polluted wastewater containing a lot of fine particles or phosphorus compounds enters the system, more coagulants are needed. Conversely, if the wastewater is cleaner or has already been pre-treated, the coagulant consumption decreases. The AI prediction model allows for accurate estimation of the required amount of coagulants based on the parameters of the incoming wastewater, such as pH, suspended solids, temperature, or flow. This helps to optimize the use of the chemical, avoid overdosing, reduce operating costs, and maintain constant cleaning quality. The integration of AI into such processes provides real practical benefits, as it allows for automated control of complex processes and adaptation to changing conditions without constant human intervention.
The main parameters of the created artificial intelligence model were selected to ensure sufficient forecasting accuracy and stable model operation when working with wastewater treatment data time series. One of the most important parameters is the input window (input_window), which was set to 240 h—this means that the model analyzes 10 days of historical data for each forecast. The hidden layer (hidden_size), in which information is processed, is set to 64 neurons—this value allows the model to learn the relationships between various parameters sufficiently deeply, while maintaining computational efficiency. The number of layers (num_layers), two, means that the model contains two sequentially arranged LSTM layers, which increases the model’s ability to recognize complex data patterns. The dropout value, 0.3, was chosen to reduce the risk of overfitting and improve the overall generalization of the model. The model was trained with 500 epochs, which provided enough iterations to optimize the model weights, and the learning rate (learning_rate) was set to 0.001—this value is balanced between stable convergence and efficient learning speed. The mini-batch size (batch_size) was chosen as 32 to effectively train the model with smaller data portions, improving the overall training process. All these parameters were combined so that the model could accurately predict the dynamics of wastewater parameters, respond to their changes, and be applicable in real environmental management systems.
The results presented in
Table 1 demonstrate that the LSTM-based AI model ensures high prediction accuracy for key parameters of the industrial wastewater treatment process. The low MAE and RMSE values across all variables indicate minimal deviations between predicted and actual values, confirming the model’s reliability. The most precise predictions were achieved for pH (RMSE = 0.17, MAPE = 1.9%), which is particularly important for maintaining chemical stability and treatment efficiency. Wastewater temperature (°C) and wastewater volume (m
3/h) predictions also showed strong performance, with R
2 values of 0.94 and 0.92, respectively, highlighting the model’s capacity to follow dynamic changes over time. Slightly higher MAPE values were observed for reagent forecasts—acid content, alkali content, and coagulant content (ranging from 5.8 to 7.5%)—which is acceptable considering the natural variability in wastewater composition. Nevertheless, all R
2 scores exceeded 0.87, indicating a high level of explanatory power. These results confirm that the AI model is suitable for real-time process optimization, enabling accurate dosing, reducing reagent overuse, and supporting stable, environmentally compliant wastewater treatment operations.
The model is based on the LSTM architecture, which is specifically adapted to analyze time series data. Such a structure allows for effective prediction of changes in wastewater parameters over time, such as pH, temperature, or wastewater volume fluctuations, because it is able to “remember” the values of previous moments and determine their influence on future changes.
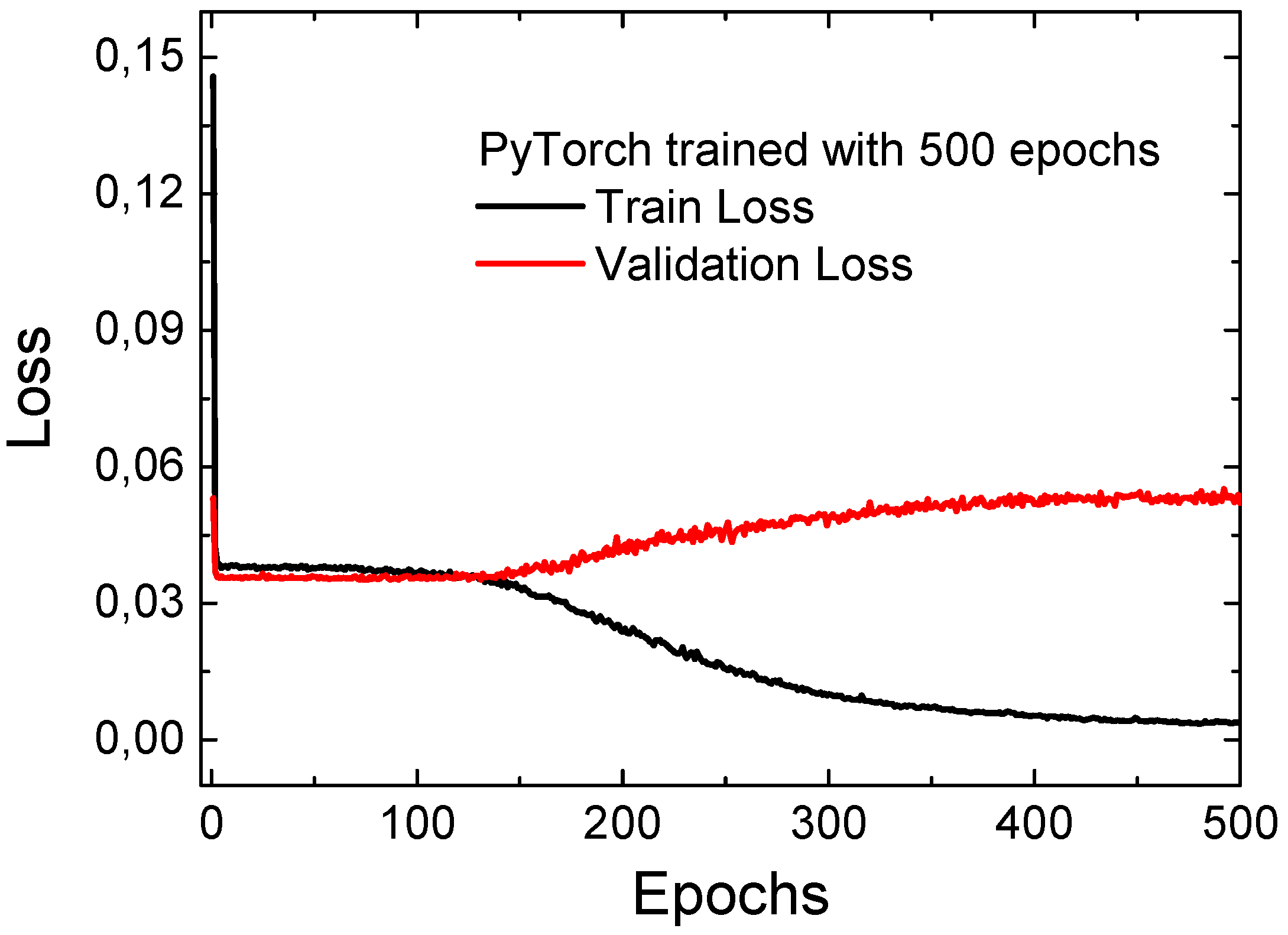
The training and validation phases are clearly separated in the model training process, which allows us to assess the accuracy of the model both during training and with previously unseen data. During each epoch, the loss indicators for both phases are recorded, so it is possible to monitor how the model is learning. This ensures transparency of the training process and helps to adjust the model parameters in a timely manner. The rapid decrease in the training loss at the beginning, when the loss decreases from approximately 0.15 to 0.03 over the first 10 epochs, occurs because the model quickly learns the basic data structures and relationships (
Figure 14). In the initial learning phase, the weights are updated in large steps, so the error decreases significantly. Later, when the model has already been trained for the main trends, the loss decrease slows down and occurs much more slowly—from 0.03 to 0.01 over the remaining 490 epochs. This is because the model tries to make finer adjustments to the weights and optimize the remaining error, which is often related to data noise or more complex details. The learning process can also slow down due to the properties of the optimizer and the model approaching local minima, where the movement towards lower loss becomes slower. Therefore, in the initial stage, fast convergence occurs, and later, fine and slow optimization.
The validation loss decreases rapidly from about 0.05 to 0.04 during the first 10 epochs, as the model quickly learns the basic features of the data and is able to predict new data better. Between epochs 10 and 150, the validation loss remains almost constant, which means that the model reached a certain level of stability—it is no longer learning much better, but it is not becoming worse either, rather, it is simply maintaining its ability to share information with new data. However, from epochs 150 to 500, the validation loss increases slightly from 0.04 to 0.05, which indicates that the model is starting to overfit the training data. However, this behavior is not unusual and is not bad—it is a natural stage of the learning process when the model tries to better adapt its weights and balances sharing and learning details. Such fluctuations in validation loss are common and indicate that the model is learning normally [
3,
4,
5,
6,
7].
In this study, it is important to evaluate different approaches to data prediction and process control. Traditional control methods, such as proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controllers, are widely used in industrial automation, but they are often unable to effectively respond to unexpected process changes or nonlinear relationships between variables. Although they are reliable and fast-response, their effectiveness depends on precise parameter tuning, and in systems with many input variables or complex dynamics, they become limited. Compared to other machine learning algorithms, such as multilevel perceptrons (MLP), random forests (random forest), or support vector machines (SVM), LSTM networks have a significant advantage—the ability to process time series and “memorize” long-term dependencies between data points. Other algorithms, while they may be suitable for classification or regression of static data, lose efficiency when it comes to predicting continuously changing parameters (e.g., pH, flow rate, or temperature) based on long-term historical data. Additionally, some of them require a lot of pre-processing or manual feature engineering, while LSTM networks are able to automatically learn representations from raw time series.
Although the proposed automated wastewater treatment system was developed and tested in the conditions of electrochemical industrial wastewater, its architecture and operating principles are flexible enough to be applied to other types of industrial wastewater—for example, textile, pharmaceutical, food, oil refining, or chemical industries. In many of these areas, wastewater also has a complex, constantly changing composition and requires precise control of pH, temperature, pollutant concentration, and reagent dosing. Since the system is based on a modular PLC architecture (Siemens S7-1214) and integrated sensor, dosing, and control equipment, it can be easily adapted to different technological sequence logics by changing algorithms or adding HMI functions according to the needs of a specific industry. In addition, the artificial intelligence-based forecasting system developed using the LSTM model can be retrained with new data from other industries, adapting it to specific conditions—for example, different pH ranges, organic matter concentrations, or flow dynamics. Such adaptation of the model allows the application of advanced forecasting and optimization tools in various areas where traditional management methods are insufficient. However, for the successful implementation of the system, it is necessary to ensure the appropriate selection of sensors and reagents, as well as high-quality initial data collection for model training. In general, the proposed solution can be considered a universal basis for an advanced, data-driven wastewater management system in various industries.
Forecasting wastewater parameters and the quantities of chemicals used and their variations is of utmost importance in order to ensure an efficient, stable, and economically viable wastewater treatment process. An accurate forecast allows you to anticipate possible fluctuations in wastewater composition—for example, changes in organic matter, nitrogen, or phosphorus concentrations—and adjust the dosage of chemicals accordingly. This helps to avoid both excessive and insufficient use of chemical reagents, reduces operating costs, reduces environmental impact and the risk of not meeting the quality requirements of discharged wastewater. This approach is considered a new, advanced strategy in wastewater treatment system management, as it is based on real-time data analysis, digital tools, and forecasting models, which allow the system to operate not only reactively, but also preventively. Such strategic management becomes especially important with the acceleration of urbanization, growing environmental requirements, and the transition to sustainable and smart infrastructure solutions.