Multi-Feature Fusion Diffusion Post-Processing for Low-Light Image Denoising
Abstract
1. Introduction
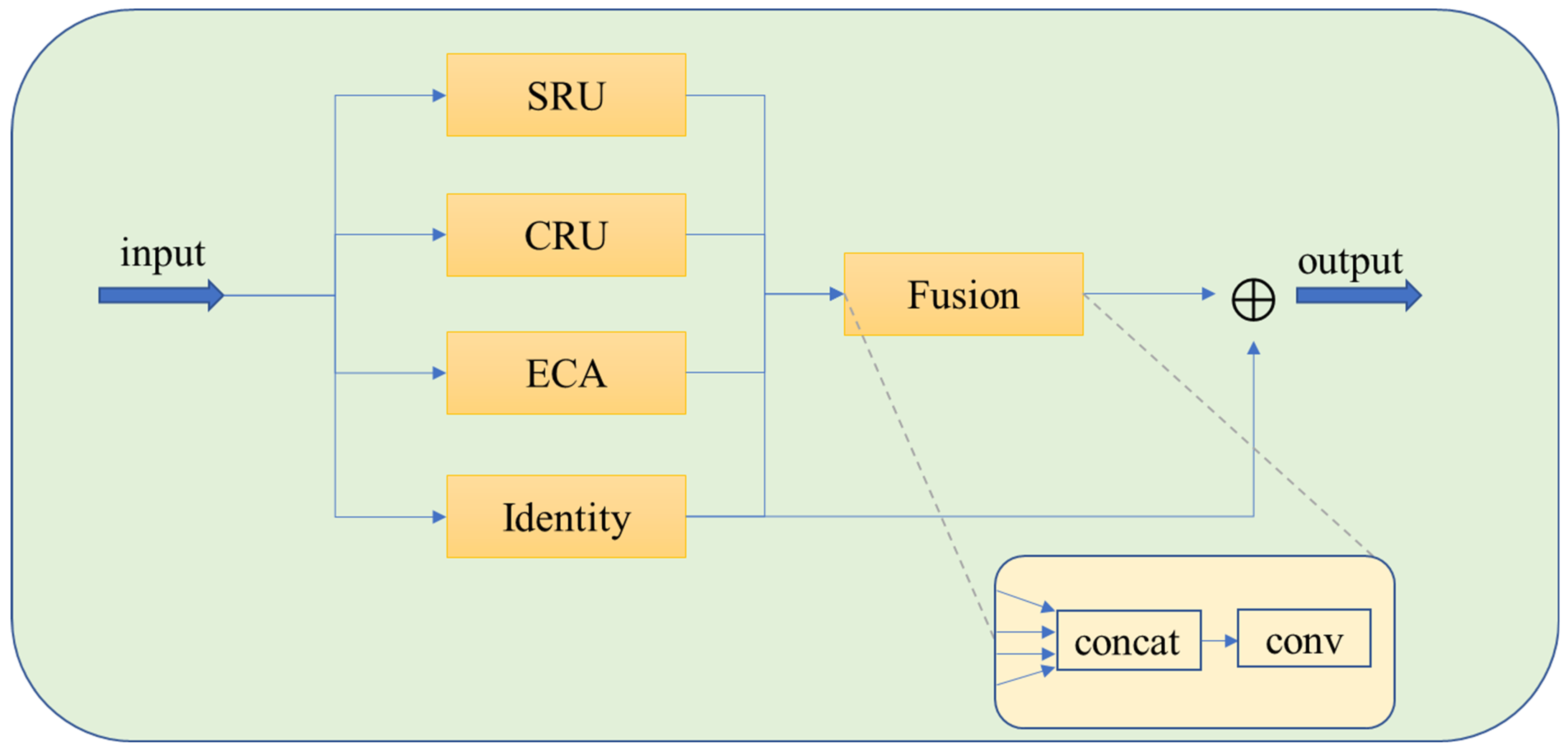
- Hierarchical Feature Extraction Mechanism: We design a Spatial Gated Recombination Unit (SRU) that employs dynamic thresholds to isolate noise regions from crucial details (e.g., edges and textures). Local contrast is enhanced through cross-scale feature recombination. Additionally, we construct a Channel Refinement Unit (CRU), leveraging group convolution and adaptive fusion strategies to mitigate issues of color distortion and uneven local luminance. An Efficient Channel Attention (ECA) module is further integrated to model global channel dependencies in a lightweight manner, effectively suppressing noise-dominated feature responses.
- Multimodal Feature Fusion Architecture: Four parallel branches (SRU, CRU, ECA, and Identity) are proposed to extract complementary features: spatial details, refined channel relationships, global semantic information, and original feature representations. Efficient information aggregation is achieved via convolutional compression and residual connections. This design effectively overcomes the multi-scale feature degradation problem characteristic of conventional U-Net architectures.
- Solving local brightness imbalance: Traditional convolutional layers treat RGB channels equally, which cannot correct the noise or over-enhancement of specific channels. Color correction in different illumination areas lacks synergy. CRU achieves refined color correction and brightness equalization through channel grouping optimization and adaptive feature fusion.
2. Related Work
2.1. Low-Light Image Enhancement
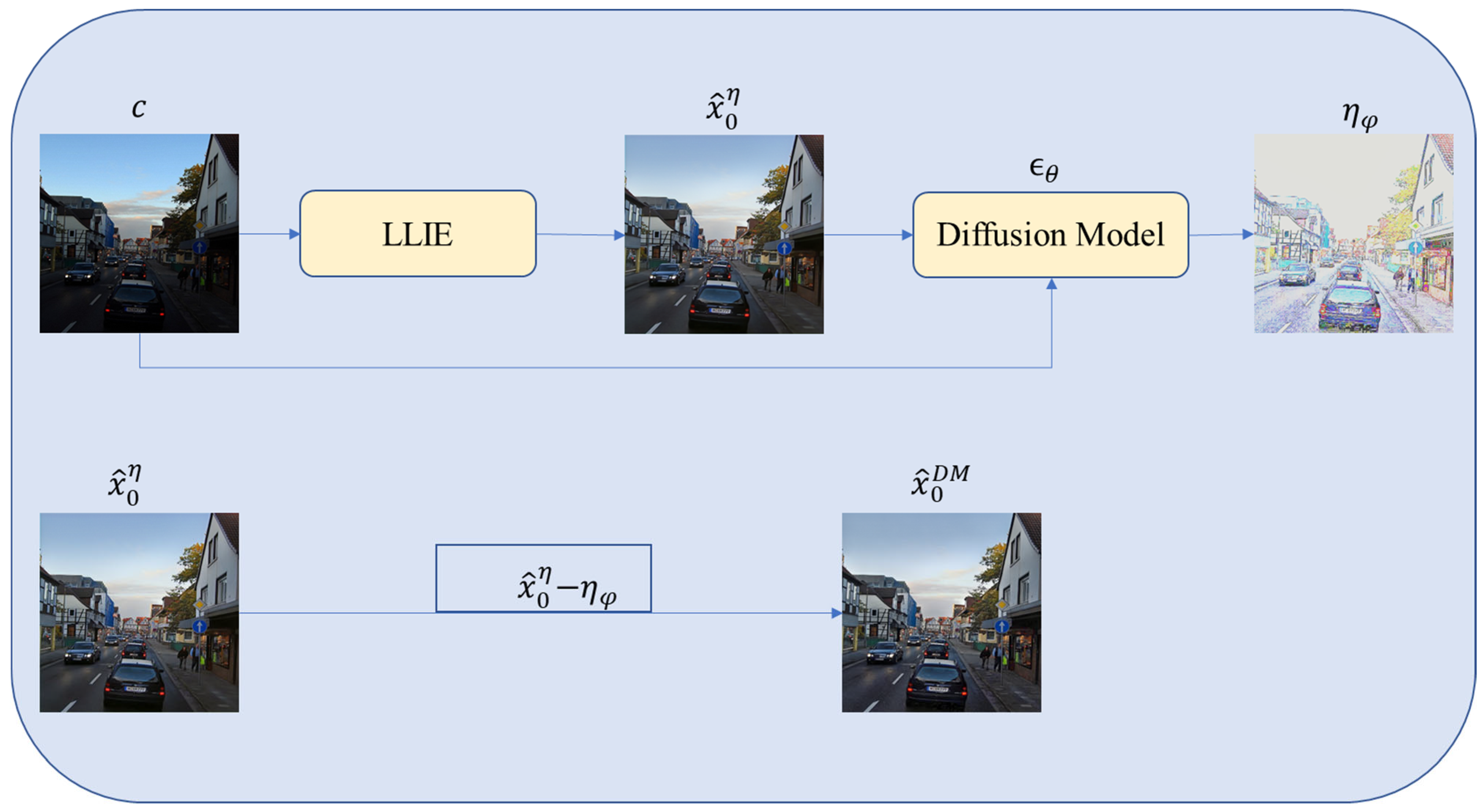
2.2. Post-Processing Denoising
3. Method
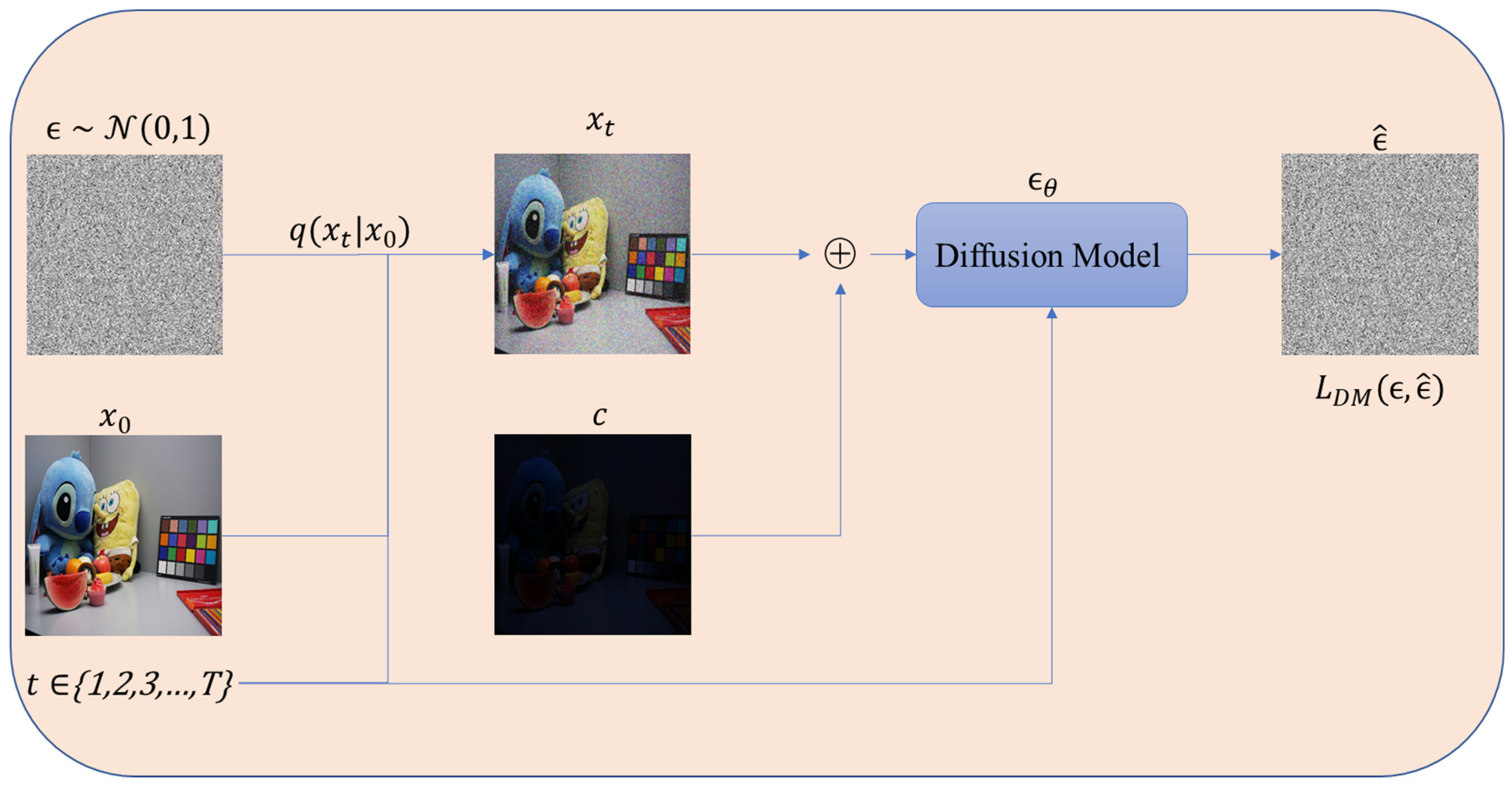
3.1. Diffusion Model (DM)
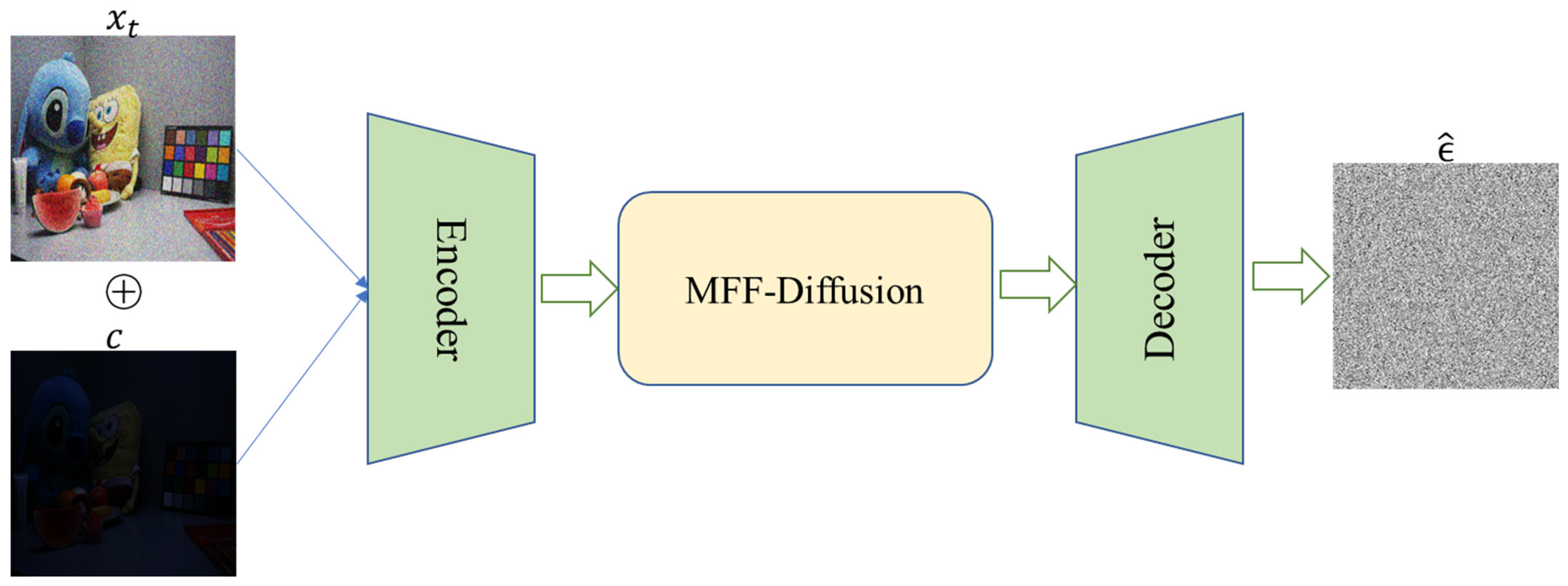
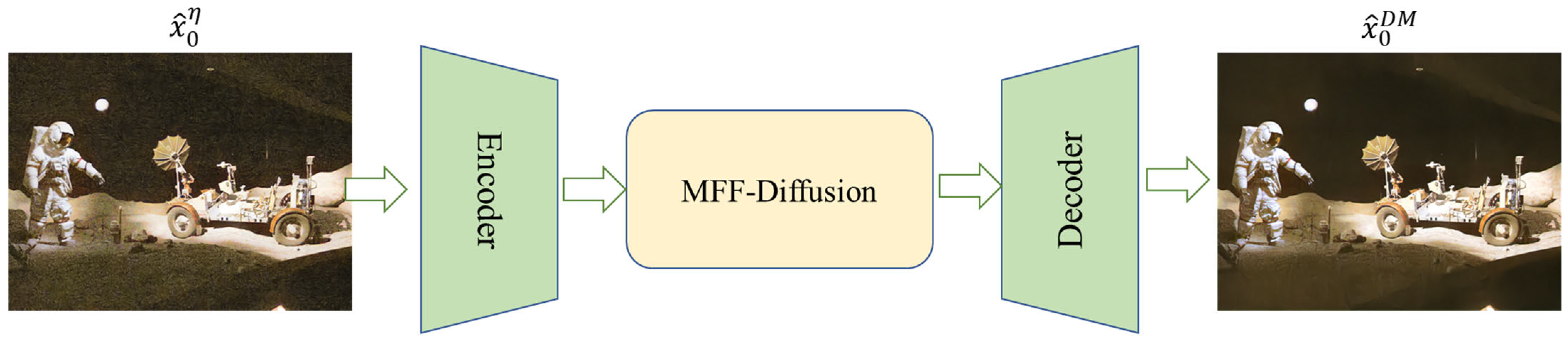
3.2. MFF-Diffusion
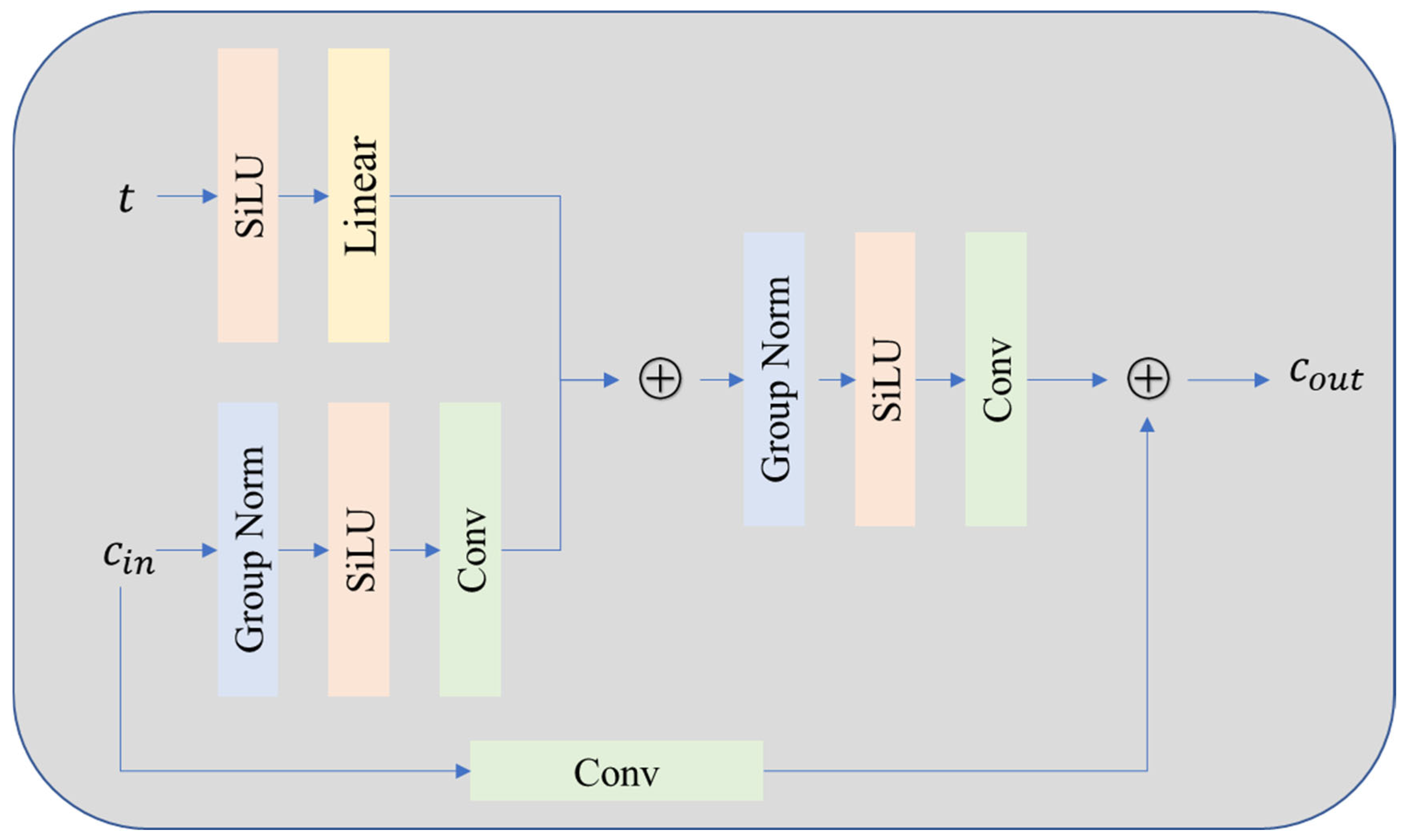
3.2.1. Residual Block
3.2.2. Feature Fusion Module
- Features above the threshold are kept directly (hard thresholding).
- Features below the threshold are suppressed by soft weighting. The output achieves cross-group information interaction via a channel reorganization operation to enhance the robustness of local features.
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset Selection
4.2. Experimental Details
4.3. Benchmark for MFF-Diffusion
4.4. Comparison with Alternative Denoisers
4.5. Ablation Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Ling, H. LIME: Low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process 2017, 26, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xu, D.; Yang, W.; Fan, M.; Huang, H. Benchmarking low-light image enhancement and beyond. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 1153–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lore, K.G.; Akintayo, A.; Sarkar, S. LLNet: A deep autoencoder approach to natural low-light image enhancement. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 61, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Gupta, G. Semantic-guided zero-shot learning for low-light image/video enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022; pp. 581–590. [Google Scholar]
- Thepade, S.D.; Pardhi, P.M. Contrast enhancement with brightness preservation of low light images using a blending of CLAHE and BPDHE histogram equalization methods. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 2022, 14, 3047–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, Z.; Han, P.; Li, Q.; Yuan, Z. Low-Illumination Road Image Enhancement by Fusing Retinex Theory and Histogram Equalization. Electronics 2023, 12, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, W.; Feng, X.; Li, M. Deep parametric Retinex decomposition model for low-light image enhancement. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2024, 241, 103948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, R.; Wang, W.; Gao, W. A low-light image enhancement method for both denoising and contrast enlarging. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 27–30 September 2015; pp. 3730–3734. [Google Scholar]
- Dabov, K.; Foi, A.; Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K. Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform-domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process 2007, 16, 2080–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chu, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J. Simple baselines for image restoration. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2022, Proceedings of the 17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 17–33. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Pfister, H.; Wei, D. Learning to generate realistic noisy images via pixel-level noise-aware adversarial training. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 3259–3270. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiao, J.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Shi, H.; Huang, T. When awgn-based denoiser meets real noises. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 13074–13081. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.; Jain, A.; Abbeel, P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 6840–6851. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Gong, X.; Liu, D.; Cheng, Y.; Fang, C.; Shen, X.; Yang, J.; Zhou, P.; Wang, Z. Enlightengan: Deep light enhancement without paired supervision. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2340–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagiotou, S.; Bosman, A.S. Denoising diffusion post-processing for low-light image enhancement. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 156, 110799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Tang, L.; Ma, J. Diff-retinex: Rethinking low-light image enhancement with a generative diffusion model. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 12302–12311. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.; Zhu, Z.; Hou, J.; Liu, H.; Zeng, H.; Yuan, H. Global structure-aware diffusion process for low-light image enhancement. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 36, 79734–79747. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, Z.; Aamir, M.; Gulzar, K.; Bhutto, J.A.; Ishfaq, M.; Dayo, Z.A.; Mohammadani, K.H. A Non-Reference Low-Light Image Enhancement Approach Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Deep Learning for Multimedia Processing Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 146–159. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Yan, L.; Peng, Y.; Zheng, K.; Gao, R.; Ling, H. Low-light image enhancement base on brightness attention mechanism generative adversarial networks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 10341–10365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Luo, A.; Fan, H.; Han, S.; Liu, S. Low-light image enhancement with wavelet-based diffusion models. ACM Trans. Graph. 2023, 42, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ye, Z. Brightness preserving histogram equalization with maximum entropy: A variational perspective. Consum. Electron. IEEE Trans. 2005, 51, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Shih, J.L.; Lien, C.C.; Han, C.C. Adaptive Multiscale Retinex for Image Contrast Enhancement. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Signal-image Technology & Internetbased Systems, Kyoto, Japan, 2–5 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zhu, J.; Bi, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y. A low-light image enhancement method with brightness balance and detail preservation. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, E.H. The Retinex Theory of Color Vision. Sci. Am. 1978, 237, 108–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Land, E.H.; Mccann, J.J. Lightness and Retinex theory. Josa 1971, 61, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Wang, W.; Huang, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, J. Sparse Gradient Regularized Deep Retinex Network for Robust Low-Light Image Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2072–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, M.T.; Guo, G.; Shi, D.; Khan, H.; Cheng, X. An Empirical Study on Retinex Methods for Low-Light Image Enhancement. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wen, C.; Liu, W.; He, W. A depth iterative illumination estimation network for low-light image enhancement based on retinex theory. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F.; Lu, F.; Wu, J.; Lim, C. MBLLEN: Low-Light Image/Video Enhancement Using CNNs; BMVC: Newcastle, UK, 2018; Volume 220, p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Guo, J.; Porikli, F.; Pang, Y. LightenNet: A Convolutional Neural Network for Weakly Illuminated Image Enhancement. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2018, 104, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation Using Cycle Consistent Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Hong, Y.; Chen, L.; You, S. LE-GAN: Unsupervised Low-Light Image Enhancement Network Using Attention Module and Identity Invariant Loss. Knowl. Based Syst. 2022, 240, 108010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, T.G.; Mahboub, M.A.A. Improving Breast Cancer Diagnosis with AI Mammogram Image Analysis. Medinformatics 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichol, A.Q.; Dhariwal, P. Improved denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning Research, Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, Baltimore, MD, USA, 17–23 July 2022; Volume 139, pp. 8162–8171. [Google Scholar]
- Murugesan, S.; Naganathan, A. Edge Computing-Based Cardiac Monitoring and Detection System in the Internet of Medical Things. Medinformatics 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheivya, I.; Kumar, G.S. VSegNet–A Variant SegNet for Improving Segmentation Accuracy in Medical Images with Class Imbalance and Limited Data. Medinformatics 2025, 2, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
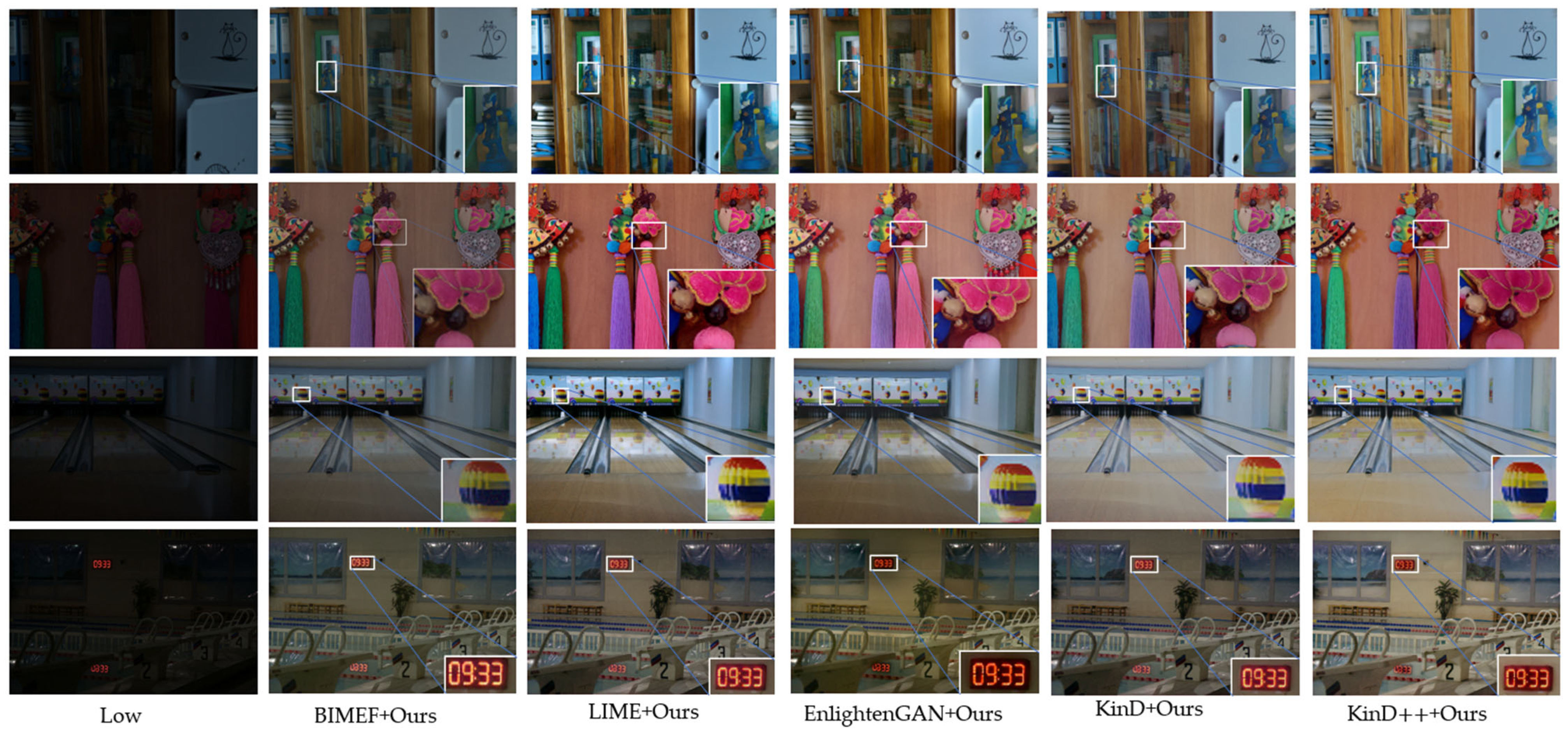


| Methods | PSNR↑ | SSIM↑ | MAE↓ | LPIPS↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIMEF | 13.875 | 0.595 | 0.206 | 0.306 |
| BIMEF + NAFNet | 13.356 | 0.652 | 0.203 | 0.344 |
| BIMEF + MIRNet* | 13.946 | 0.669 | 0.204 | 0.313 |
| BIMEF + LPDM | 13.873 | 0.674 | 0.207 | 0.217 |
| BIMEF + Ours | 13.894 | 0.696 | 0.208 | 0.201 |
| LIME | 17.181 | 0.484 | 0.124 | 0.372 |
| LIME + NAFNet | 18.216 | 0.746 | 0.118 | 0.253 |
| LIME + MIRNet | 18.125 | 0.772 | 0.113 | 0.248 |
| LIME + LPDM | 17.692 | 0.652 | 0.121 | 0.239 |
| LIME + Ours | 17.977 | 0.735 | 0.118 | 0.176 |
| EnlightenGAN | 17.483 | 0.652 | 0.135 | 0.322 |
| EnlightenGAN + NAFNet | 17.622 | 0.739 | 0.143 | 0.251 |
| EnlightenGAN + MIRNet | 17.863 | 0.764 | 0.134 | 0.231 |
| EnlightenGAN + LPDM | 18.524 | 0.745 | 0.118 | 0.193 |
| EnlightenGAN + Ours | 18.607 | 0.769 | 0.117 | 0.177 |
| KinD | 17.648 | 0.771 | 0.123 | 0.175 |
| KinD + NAFNet | 17.566 | 0.763 | 0.124 | 0.249 |
| KinD + MIRNet | 17.605 | 0.770 | 0.126 | 0.248 |
| KinD + LPDM | 17.733 | 0.795 | 0.123 | 0.144 |
| KinD + Ours | 17.745 | 0.796 | 0.123 | 0.140 |
| KinD++ | 17.752 | 0.758 | 0.113 | 0.198 |
| KinD++ + NAFNet | 17.759 | 0.755 | 0.126 | 0.251 |
| KinD++ + MIRNet | 17.820 | 0.777 | 0.116 | 0.236 |
| KinD++ + LPDM | 17.955 | 0.790 | 0.115 | 0.171 |
| KinD++ + Ours | 18.039 | 0.799 | 0.111 | 0.177 |
| LLFlow | 21.133 | 0.852 | 0.084 | 0.119 |
| LLFlow + NAFNet | 20.662 | 0.810 | 0.089 | 0.221 |
| LLFlow + MIRNet | 20.867 | 0.814 | 0.089 | 0.196 |
| LLFlow + LPDM | 21.421 | 0.844 | 0.084 | 0.115 |
| LLFlow + Ours | 21.385 | 0.845 | 0.083 | 0.114 |
| LLFormer | 23.346 | 0.819 | 0.067 | 0.168 |
| LLFormer + NAFNet | 22.799 | 0.807 | 0.069 | 0.234 |
| LLFormer + MIRNet | 22.956 | 0.818 | 0.068 | 0.234 |
| LLFormer + LPDM | 23.734 | 0.866 | 0.065 | 0.113 |
| LLFormer + Ours | 23.750 | 0.872 | 0.065 | 0.109 |
| RetinexNet | 16.774 | 0.425 | 0.126 | 0.474 |
| RetinexNet + NAFNet | 17.521 | 0.719 | 0.124 | 0.309 |
| RetinexNet + MIRNet | 17.826 | 0.722 | 0.117 | 0.329 |
| RetinexNet + LPDM | 18.051 | 0.693 | 0.113 | 0.240 |
| RetinexNet + Ours | 18.191 | 0.761 | 0.111 | 0.211 |
| URetinexNet | 19.842 | 0.824 | 0.099 | 0.128 |
| URetinexNet + NAFNet | 19.482 | 0.774 | 0.100 | 0.222 |
| URetinexNet + MIRNet | 19.667 | 0.803 | 0.105 | 0.197 |
| URetinexNet + LPDM | 20.115 | 0.817 | 0.097 | 0.129 |
| URetinexNet + Ours | 20.119 | 0.822 | 0.096 | 0.123 |
| ZeroDCE++ | 15.357 | 0.573 | 0.176 | 0.335 |
| ZeroDCE++ + NAFNet | 15.628 | 0.704 | 0.172 | 0.288 |
| ZeroDCE++ + MIRNet | 15.630 | 0.707 | 0.172 | 0.297 |
| ZeroDCE++ + LPDM | 15.486 | 0.682 | 0.177 | 0.219 |
| ZeroDCE++ + Ours | 15.532 | 0.712 | 0.177 | 0.204 |
| Methods | DICM | MEF | NPE | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NIQE↓ | BRISQUE↓ | SPAQ↑ | NIQE↓ | BRISQUE↓ | SPAQ↑ | NIQE↓ | BRISQUE↓ | SPAQ↑ | |
| BIMEF | 3.827 | 23.588 | 64.375 | 3.330 | 15.262 | 67.352 | 3.330 | 15.262 | 67.352 |
| BIMEF + Ours | 3.015 | 9.323 | 68.372 | 3.981 | 22.591 | 66.471 | 3.981 | 22.591 | 66.471 |
| LIME | 3.812 | 23.356 | 63.301 | 3.558 | 16.337 | 70.911 | 3.558 | 16.337 | 70.911 |
| LIME + Ours | 2.726 | 9.011 | 69.782 | 3.768 | 19.356 | 70.632 | 3.768 | 19.356 | 70.632 |
| EnlightenGAN | 3.561 | 18.808 | 63.124 | 3.221 | 14.332 | 68.701 | 3.221 | 14.332 | 68.701 |
| EnlightenGAN + Ours | 2.925 | 10.038 | 70.479 | 3.894 | 22.712 | 69.556 | 3.894 | 22.712 | 69.556 |
| KinD++ | 3.786 | 26.314 | 68.086 | 3.737 | 28.635 | 70.250 | 3.737 | 28.635 | 70.250 |
| KinD++ + Ours | 3.063 | 17.728 | 71.441 | 4.126 | 29.774 | 68.937 | 4.126 | 29.774 | 68.937 |
| LLFormer | 3.850 | 14.610 | 63.080 | 3.682 | 17.043 | 63.139 | 3.682 | 17.043 | 63.139 |
| LLFormer + Ours | 3.491 | 11.363 | 66.839 | 4.242 | 20.813 | 69.072 | 4.242 | 20.813 | 69.072 |
| RetinexNet | 4.451 | 29.339 | 68.805 | 4.416 | 20.068 | 74.386 | 4.416 | 20.068 | 74.386 |
| RetinexNet + Ours | 3.076 | 9.344 | 73.354 | 3.757 | 14.877 | 73.510 | 3.757 | 14.877 | 73.510 |
| Methods | PSNR↑ | SSIM↑ | MAE↓ | LPIPS↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIMEF + Ours | 13.893 | 0.689 | 0.208 | 0.201 |
| BIMEF + Remove_SRU | 13.871 | 0.688 | 0.208 | 0.207 |
| BIMEF + Remove_GRU | 13.934 | 0.698 | 0.208 | 0.181 |
| BIMEF + Remove_Both | 13.868 | 0.689 | 0.208 | 0.208 |
| LIME + Ours | 17.971 | 0.739 | 0.118 | 0.171 |
| LIME + Remove_SRU | 17.841 | 0.684 | 0.119 | 0.222 |
| LIME + Remove_GRU | 17.765 | 0.684 | 0.120 | 0.208 |
| LIME + Remove_Both | 17.848 | 0.695 | 0.119 | 0.217 |
| EnlightenGAN + Ours | 18.613 | 0.767 | 0.117 | 0.171 |
| EnlightenGAN + Remove_SRU | 16.771 | 0.734 | 0.159 | 0.189 |
| EnlightenGAN + Remove_GRU | 16.794 | 0.736 | 0.159 | 0.176 |
| EnlightenGAN + Remove_Both | 16.728 | 0.736 | 0.159 | 0.192 |
| KinD + Ours | 17.745 | 0.796 | 0.123 | 0.143 |
| KinD + Remove_SRU | 17.697 | 0.794 | 0.123 | 0.143 |
| KinD + Remove_GRU | 17.787 | 0.797 | 0.123 | 0.141 |
| KinD + Remove_Both | 17.714 | 0.792 | 0.123 | 0.148 |
| KinD++ + Ours | 18.042 | 0.801 | 0.110 | 0.153 |
| KinD++ + Remove_SRU | 17.982 | 0.796 | 0.111 | 0.154 |
| KinD++ + Remove_GRU | 18.028 | 0.797 | 0.110 | 0.160 |
| KinD++ + Remove_Both | 18.025 | 0.799 | 0.111 | 0.155 |
| LLFlow + Ours | 21.185 | 0.845 | 0.083 | 0.112 |
| LLFlow + Remove_SRU | 21.175 | 0.844 | 0.084 | 0.108 |
| LLFlow + Remove_GRU | 21.316 | 0.847 | 0.083 | 0.108 |
| LLFlow + Remove_Both | 21.063 | 0.837 | 0.085 | 0.120 |
| LLFormer + NAFNet | 23.742 | 0.857 | 0.065 | 0.107 |
| LLFormer + MIRNet | 23.714 | 0.850 | 0.066 | 0.111 |
| LLFormer + LPDM | 23.836 | 0.858 | 0.065 | 0.109 |
| LLFormer + Ours | 23.550 | 0.848 | 0.067 | 0.116 |
| RetinexNet + Ours | 18.172 | 0.761 | 0.111 | 0.209 |
| RetinexNet + Remove_SRU | 17.841 | 0.634 | 0.115 | 0.294 |
| RetinexNet + Remove_GRU | 17.838 | 0.635 | 0.115 | 0.281 |
| RetinexNet + Remove_Both | 17.856 | 0.641 | 0.115 | 0.288 |
| URetinexNet + Ours | 20.115 | 0.819 | 0.096 | 0.124 |
| URetinexNet + Remove_SRU | 19.926 | 0.826 | 0.098 | 0.123 |
| URetinexNet + Remove_GRU | 20.015 | 0.830 | 0.097 | 0.121 |
| URetinexNet + Remove_Both | 19.879 | 0.821 | 0.098 | 0.133 |
| ZeroDCE++ + Ours | 15.539 | 0.714 | 0.177 | 0.199 |
| ZeroDCE++ + Remove_SRU | 15.499 | 0.707 | 0.177 | 0.206 |
| ZeroDCE++ + Remove_GRU | 15.519 | 0.713 | 0.177 | 0.186 |
| ZeroDCE++ + Remove_Both | 15.500 | 0.711 | 0.177 | 0.210 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, J.; Huang, J.; Guan, L.; Chen, W. Multi-Feature Fusion Diffusion Post-Processing for Low-Light Image Denoising. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8850. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168850
Shi J, Huang J, Guan L, Chen W. Multi-Feature Fusion Diffusion Post-Processing for Low-Light Image Denoising. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(16):8850. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168850
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Jihui, Jijiang Huang, Lei Guan, and Weining Chen. 2025. "Multi-Feature Fusion Diffusion Post-Processing for Low-Light Image Denoising" Applied Sciences 15, no. 16: 8850. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168850
APA StyleShi, J., Huang, J., Guan, L., & Chen, W. (2025). Multi-Feature Fusion Diffusion Post-Processing for Low-Light Image Denoising. Applied Sciences, 15(16), 8850. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168850





