Abstract
Arachidonic acid (AA) is a polyunsaturated fatty acid, an essential component of the brain membrane phospholipids. It is released into the bloodstream in response to various pathological conditions. Its potential as a biomarker for oxidative membrane damage determines the importance of its reliable quantification. Therefore, the aim of the current study was to develop a simple and robust LC-MS method that is easy to implement for routine testing of free arachidonic acid (AA) in human serum. The method included a simple two-step sample preparation procedure based on liquid–liquid extraction and protein precipitation, followed by AA analysis by UPLC coupled with PDA and QDa detectors. The ICH M10 guideline was followed for validation studies. The method demonstrated high selectivity and linearity with R2 = 0.9952 for solvent-based and R2 = 0.9979 for matrix-matched calibration. The LODs and LOQs were 0.046 µg/mL and 0.133 µg/mL, respectively. The accuracy and precision were between 6 and 14% RSD. No carry-over and matrix interferences were observed. The method was successfully applied to real serum samples, where AA concentrations ranged from 0.82 to 2.69 µg/mL, consistent with data of other studies. This method provides a reliable, reproducible, and rapid alternative for AA quantification in research and routine practice.
1. Introduction
The brain is highly susceptible to ischemic injury due to its high metabolic activity, energy demands, and reliance on aerobic metabolism. Brain ischemia can lead to irreversible neuronal death within minutes. Therefore, timely diagnosis and treatment are critical in mitigating brain injury [1]. After adipose tissue, the brain is the second-most lipid-rich tissue in the human body. Brain lipids are involved in several key functions, such as maintaining membrane fluidity and permeability, energy storage, and signal transduction [2]. Altered metabolism of brain lipids could be associated with pathogenesis of brain disorders, and thus serve as a diagnostic biomarker [3,4]. Among the different classes of lipid biomarkers for assessing brain function, free fatty acids separated from complex lipids could be a valuable marker for monitoring the progression of neurodegenerative diseases and brain injuries, including cerebral ischemia [5].
Arachidonic acid (AA) is a key component of brain phospholipids, accounting about 20% of brain fatty acid composition [6]. AA is extremely important for brain development, membrane fluidity, selective permeability, and cell–cell signaling throughout life [7]. It has been estimated that the products of AA metabolism are involved in modulating synaptic plasticity and neurotransmission [8].
Various brain pathologic conditions, including stroke, are associated with an uncontrolled release of free AA from brain phospholipids following its extensive oxidative metabolism [9].
The impaired equilibrium between AA release and incorporation in membrane phospholipids is crucial for neuroinflammation and neuronal dysfunction. Overexpression of the enzymes metabolizing AA to its bioactive products, such as COX-2 and 5-LOX, is found to play a significant role in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases and in the progression of cerebral ischemia [7].
There are inconsistent findings about the role of individual free fatty acids (FFAs), including AA, in stroke. Some reports indicate an elevation of circulating FFAs in stroke patients, while others did not find such relations [10]. These discrepancies may be due to differences in study design. It has been shown that the concentration of AA as a separate marker and in correlation with other serum lipids, including classical lipid biomarkers and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 PUFA), can vary depending on age, gender, and stroke subtype [11,12]. It has been demonstrated that a low serum n-3 PUFA/AA ratio may predict neurological deterioration in acute ischemic stroke if measured within 24 h of incidence onset [11].
In addition, serum AA levels may be a valuable marker for interpreting the effectiveness of therapies during recovery after ischemic stroke [13,14].
Despite the potential importance of AA as a biomarker, no commercial chromatography kits have been developed for its determination, and reference ranges have not been established. Therefore, reliable estimation of plasma AA levels could be a valuable prognostic biomarker in stroke patients.
The conventional analytical method for the determination of free fatty acids, including AA, in biological samples is by gas chromatography with flame-ionization (FID) or mass-spectrometry (MS) detector [15,16,17]. In both cases, a preliminary derivatization step of fatty acids to corresponding methyl esters is required. Derivatization is a time-consuming procedure and carries the risk of errors and variations in the result. Direct methods for AA analysis in biological samples, such as liquid chromatography with mass-selective detection, have a number of advantages, the most important of which is that the derivatization step is avoided. Most studies use UPLC coupled with a triple quadrupole MS detector or more sophisticated platforms such as an Orbitrap mass spectrometer [14,18] or high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) with a Triple-TOF mass spectrometer [18]. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to develop a simple and robust LC-MS method with ease of implementation for routine testing of free AA in serum samples from healthy controls and ischemic stroke patients.
2. Materials and Methods
For the purposes of the study, we used UPLC coupled with both photo diode-array (PDA) and a single quadrupole mass-spectrometry detector (QDa), which is robust and reliable for routine analysis, avoiding time-consuming and sample-specific adjustments.
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
An analytical standard of arachidonic acid (cis, cis, cis, cis-5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenoic acid, CAS No 506-32-1, MW 304.47, purity ≥ 97.0%) and octadeuterated arachidonic acid (cis, cis, cis, cis-5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenoic acid-5,6,8,9,11,12,14,15-d8, CAS No 69254-37-1, MW 312.52, ≥98 atom % D, purity ≥ 98%) used as an internal standard (IS) were purchased from Merck Sigma-Aldrich, Co., St. Louis, MO, USA. LC-MS grade acetonitrile, methanol, ethanol, and 2-propanol were purchased from Fisher Scientific, Leics, UK; LC-MS grade formic acid and ammonium formate were obtained from Fisher Chemicals, Brno, the Czech Republic, and ethanol MS grade was obtained from Fisher Scientific, St. Louis, MO, USA. ACS Reagent Grade dichloromethane (Merck Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) was used for sample preparation. Bovine Serum Albumin, CAS No 9048-46-8, was purchased from Sigma Aldrich, Co., St. Louis, MO, USA. For the preparation of pooled human serum, venous blood was drawn from 30 different healthy adult donors in Serum Clot Activator tubes. After centrifugation at 490× g for 15 min, at 20 ± 5 °C the serum was separated. Pooled human serum was prepared by mixing equal aliquots of 2 mL from each donor serum and used to prepare calibration curves and quality control (QC) samples. Aliquots of the pooled serum were stored at −18 °C for validation experiments.
2.2. Preparation of Stock and Working Standard Solutions
The arachidonic acid (AA) stock standard solution was prepared in ethanol at a final concentration of 1 mg/mL. The stock solution of IS was prepared by dissolving 5 mg of the substance in 5 mL of ethanol, with a final concentration of 1 mg/mL. Aliquots of AA and IS stock solutions were kept in glass LC-MS vials at −18 °C for up to two months.
Working AA standard (10 µg/mL) and IS (500 µg/mL) were prepared daily in acetonitrile/isopropanol/water 89:10:1 v/v containing 0.1% formic acid and 5 mM ammonium formate (mobile phase B). Due to the lack of commercially available human serum free of arachidonic acid, we used bovine serum albumin (55 g/L solution in distilled water) as a surrogate matrix for accuracy and precision experiments [19]. The albumin concentration was selected to fall within the reference range for adult individuals (35–55 g/L) [20].
2.3. Preparation of Calibration Standards and Quality Control Samples
Calibration was performed by the method of internal standard. Two different calibration approaches, solvent-based and matrix-matched, were used. Separate stock solutions were used for the preparation of calibration standards and quality controls. For solvent-based calibration, 10 μg/mL AA working standard was diluted with mobile phase B to prepare calibration standards with concentrations 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 4.0, and 5.0 μg/mL. To each calibration standard, 20 μL of IS working solution (500 μg/mL) was added, giving a final IS concentration of 50 μg/mL.
Matrix-matched calibration was performed by spiking both surrogate matrix and authentic matrix (pooled human serum) with working AA standards to achieve the following final AA concentrations: endogenous unspiked, and endogenous spiked with 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, and 5.0 μg/mL AA. Working IS solution was added to each serum calibrator to achieve a concentration of 50 μg/mL. All calibration standards were prepared in triplicate.
Three calibration curves, solvent-based, surrogate matrix- and authentic matrix-matched, were generated. Solvent-based and surrogate matrix-matched calibration curves were constructed with a blank, a zero-blank, and calibration standards in concentrations of 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, and 5.0 μg/mL AA. An authentic matrix-matched calibration curve includes a zero-blank and calibration standards prepared by spiking the matrix with the same concentrations of AA. Parameters such as regression equation, slope, intercept, and linearity, evaluated by calculating the Pearson’s determination coefficient R2, were estimated for each calibration curve.
Due to variations in endogenous AA levels, two types of quality control (QC) samples, QC1 and QC2, were prepared daily and run with each batch. QC1 samples were prepared at three AA concentration levels: unspiked endogenous AA, and endogenous AA spiked with 1.0, and 5.0 μg/mL AA using the same pooled human serum as for the authentic matrix-matched calibration. QC2 samples were prepared daily at concentrations of unspiked endogenous AA and endogenous AA spiked with 2.0 μg/mL AA using pooled serum of all samples analyzed for the day. The choice of this concentration is based on literature data [21,22,23].
2.4. Sample Preparation
Frozen serum samples, QCs, and matrix-matched calibrators were thawed at 4–8 °C, vortexed for 5 min, and 200 μL aliquots of each were transferred into 2 mL polypropylene Eppendorf vials. IS working solution (20 μL, 500 μg/mL) was added to each vial. Removal of the analyte from the matrix was performed by liquid–liquid extraction with protein precipitation (LLE-PP). LLE-PP was done in duplicate using 1500 μL dichloromethane/methanol (2:1 v/v), followed by vigorous vortexing for 3 min, stored at 4 ± 2 °C for 10 min, and centrifuged (13,680× g, 10 ± 2 °C, 10 min). The dichloromethane fraction (bottom layer) was collected and transferred into a clean vial. The analyte remaining in the upper layer was extracted with a new portion of dichloromethane. The combined extracts were evaporated at 35 ± 1 °C under a gentle nitrogen stream to a dry residue. The dry residue was reconstituted in 200 μL mobile phase B, filtered through a 0.2 µm, 4 mm PTFE filter and injected into the chromatographic system.
2.5. UPLC-MS/PDA Instrumentation and Analysis Conditions
Analysis was performed using the Waters ACQUITY H-Class Ultra Performance LC (UPLC) system (Waters, Milford, MA, USA), coupled with both PDA and QDa mass detector.
The PDA detector was set in 2D channel mode at 268 nm with a resolution of 4.8 nm. Additionally, it was operated in 3D mode, scanning from 200–400 nm through the entire method to ensure no interference with the signal of arachidonic acid. The QDa detector operated in ESI negative mode with a capillary voltage of 0.8 kV and a probe temperature of 600 °C. The sampling rate was set at 20 points/s. The following ions for AA were traced: m/z 303.3 Da (CV 15) as quantification ion m/z 304.3 Da (CV 30), and m/z 259.30 Da (CV 35) as confirmation ions. For the internal standard, m/z 311.32 Da (CV 20) was monitored. MS scan (m/z 259–315 Da, CV 15) in negative mode was tracked to determine the purity of the analytical peak.
Chromatographic separation was performed on an AccQ-TAG Ultra C18, 1.7 µm, 2.1 × 100 mm column (Waters, USA), with column temperature of 50 °C. Two mobile phases were used: mobile phase (A) 40/60% v/v acetonitrile/water with 5 mM ammonium formate and 0.1% formic acid; while mobile phase (B) was composed of 89/10/1% v/v acetonitrile/isopropanol/water with 5 mM ammonium formate and 0.1% formic acid. A gradient elution was carried out at a flow rate 0.35 mL/min. Initially, elution started with 10% B and changed to 100% B over 8 min, convex gradient (gradient curve 4). From 8–16 min, 100% B was maintained and, at 16 min, the elution returned to the initial conditions. The total run time was 20 min, with AA eluting at 4.72 min and IS at 4.69 min.
Data analysis and processing were performed using Empower® 3.0 Chromatography Data Software (Waters, USA).
2.6. Method Validation
The UPLC-MS/PDA assay was validated according to the ICH guideline M10 on bioanalytical method validation (USFDA 2022) [19].
The following parameters were validated: accuracy and precision, limit of detection (LOD), lower limit of quantification (LLOQ), selectivity, calibration and linearity, extraction efficiency and matrix effect, and stability of serum samples and extracts.
2.6.1. Accuracy and Precision
Accuracy was defined as the percentage of closeness of the measured concentration to the nominal concentration under the same conditions. As the analyte is also an endogenous molecule, the QCs for accuracy and precision were prepared using a surrogate matrix [19]. QCs were made up by spiking the surrogate matrix with known amounts of AA (0.50 µg/mL, 1.00 µg/mL, and 5.00 µg/mL), followed by processing and analysis anticipated for the study samples. The accuracy was presented as percent recovery and calculated using the following formula [19]:
Precision was defined as the closeness of agreement between a series of measurements obtained from multiple sampling of the same homogeneous sample under prescribed conditions. It was assessed at two levels: intra-day (repeatability) and inter-day precision and expressed as a percent relative standard deviation (%RSD) [19].
Intra- and inter-day precision were determined both using surrogate matrix QCs, and authentic matrix QCs (unspiked, spiked with 0.50 µg/mL, 1 µg/mL, and 5 µg/mL AA), with five replicates each. Inter-day precision was evaluated by analyzing each QC over three consequent days [19].
2.6.2. Limit of Detection (LOD) and Lower Limit of Quantification (LLOQ)
The limit of detection (LOD) was defined as the lowest concentration that gave a signal-to-noise (S/N) ratio of a maximum 3/1. Serial dilutions 2, 5, 10, 20, and 40-fold of a zero blank authentic matrix sample containing endogenous AA were used for LOD determination based on S/N ratio measuring. The same approach was used for evaluation of low limit of quantification (LLOQ), defined as a minimal analyte concentration measured with acceptable accuracy and precision. According to the ICH guideline for instrumental methods, including chromatography, LLOQ is evaluated by S/N ratio 10/1 [19].
2.6.3. Selectivity
Selectivity was evaluated by analyzing serum samples from several donors, including 10 normal, one hemolytic, two lipemic (mild: TAG 2.70 mmol/L; severe: TAG 4.72 mmol/L) and one icteric serum sample (total bilirubin: 120 mmol/L). Peak purity was evaluated by MS scan and PDA scan.
2.6.4. Calibration and Linearity
Solvent-based, surrogate matrix- and authentic matrix-based calibration curves were generated. The calibration curves were constructed by plotting LC-MS peak-area ratios of AA/IS against the corresponding analyte concentration using least-squares linear regression. Each calibration standard was analyzed in triplicate.
2.6.5. Extraction Efficiency and Matrix Effect
Extraction efficiency is defined as the ratio of extracted analyte and the total amount of analyte in a certain sample. Two matrix-matched QC batches with three different analyte concentrations each (unspiked endogenous AA, matrix spiked with 1 µg/mL AA and 5 µg/mL AA), containing the same concentration of IS, were used to assess extraction efficiency. In the first batch, AA standards and IS were added to the matrix prior to the extraction procedure, while in the second batch both AA and IS were added post-extraction. Extraction efficiency (%EE) was calculated as follows [19]:
Matrix effect was evaluated by serial dilutions of the QC serum prior analysis and plotting the ratio AA peak area to IS peak area against the calculated concentrations to test for a linear relationship.
For more reliable results, it is recommended to evaluate the matrix effect by comparing the slope variability of solvent-based, surrogate matrix- and authentic matrix-matched calibration curves [24]. Slopes that vary below 5% were considered to be equivalent [25]. The matrix effect was calculated using the following equation [19]:
Low slope variability would indicate minimal or absent matrix interferences.
2.6.6. Stability
Stability experiments were carried out to evaluate AA loss or gain during different storage periods and temperatures equal to the study sample storage conditions. Stability of the analyte in the matrix was evaluated at endogenous AA concentration.
Short-Term Stability in Matrix (Pooled Serum)
Short-term stability of AA in the matrix stored at 4–8 °C was determined after 24 h and seven days.
Long-Term Stability in Matrix (Pooled Serum)
Long-term stability was assessed in pooled serum samples stored in a refrigerator at −18 ± 2 °C for 24 h, one week, and two months.
Stability of AA in Processed Samples
The stability of AA in processed pooled serum samples was assessed in the autosampler by repeated analyses at 24 h, 48 h, and 14 days at room temperature.
2.6.7. Evaluation of Method Applicability on Real Serum Samples
The applicability of the assay was assessed by analyzing serum samples obtained from 50 healthy adult volunteers. For the purposes of method development, a few serum samples from patients with ischemic stroke were analyzed. Venous blood was collected in a Serum Clot Activator Tubes, equilibrated at 37 ± 1 °C for 30 min, and centrifuged at 490× g for 15 min at room temperature. Serum was separated, aliquoted, and stored at −18 ± 2 °C until analysis. Sample processing and UPLC-MS/PDA analysis were performed as described in previous sections.
2.7. Ethics Statement
The current study was a part of a research project entitled “Molecular mechanisms of CitoDeOx action: New evidence supporting neuroprotective and antioxidant effects” and approved by the local ethics committee, protocol Number 140/01.02.2024.
The study was conducted according to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. All blood samples were collected after obtaining written informed consent from all healthy volunteers and patients enrolled in the study.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. LC-MS Method Development
The development of a robust and reliable method for identification and quantitation of AA in biological samples requires optimization and evaluation of multiple parameters concerning sample preparation procedure, chromatographic separation, identification and quantitation, and method validation parameters.
3.1.1. Sample Preparation
Arachidonic acid is a polyunsaturated fatty acid, a component of the cell membrane phospholipids, especially phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylcholine, and phosphatidylinositol [26,27]. In the bloodstream, it is usually incorporated in plasma lipoproteins. Human plasma contains about 1% free AA [28].
Previous studies [29] have indicated that there is no considerable difference in AA concentrations between serum and plasma. However, plasma can form microfibrinogen clots during freezing and long-term storage, and therefore we preferred blood serum as a biological matrix for AA analysis [30]. With the aim of reducing the risk of gel-separator or anticoagulant interferences, we decided to collect the blood sample and separate the serum in tubes with a clot activator.
Most of the published methods for LC analysis of AA in blood serum include derivatization of the target analyte [31,32] or solid-phase extraction [33,34], both time-consuming procedures. We used a liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) procedure, which, in addition to the purification and isolation of the target analyte, also contributes to the precipitation of serum proteins and the release of AA into the organic layer. Considering that AA is a long-chain lipophilic fatty acid, several organic solvents in different combinations and ratios were tested as extractants: ethanol, methanol, 2-propanol, chloroform, and methanol [35,36,37,38]. An extractant composed of dichloromethane and methanol in a ratio 2/1 was the most effective, both in terms of extracting efficiency of the target analyte from the biological matrix with the least interfering substances and as a protein precipitant. To improve the extraction efficiency of AA, a second LLE step was performed using pure dichloromethane. The optimized LLE procedure for AA was simple and suitable for routine work.
3.1.2. Optimising Chromatographic Separation
For simultaneous separation of AA from other interfering substances in the blood serum, two different C18 chromatographic columns were tested: BEH C18 (1.7 µm, 2.1 × 100 mm) and AccQ-TAG Ultra (1.7 µm, 2.1 × 100 mm), both working at 50 °C. Better resolution and peak shape were achieved using the AccQ-TAG Ultra column. Mobile phases, containing LC-MS water and organic solvents (acetonitrile and isopropanol) in different ratios, were tested. For achieving better ionization of AA and detection as an unfragmented deprotonated molecular ion (M-H)−, as well as to improve peak shape and resolution, mobile phase modifiers 0.1% formic acid and 5 mM ammonium formate were added [35].
Initially, we used isocratic elution starting with a low water ratio in A mobile phase (10 water, 90 acetonitrile, 0.1% formic acid, 5 mM ammonium formate), whereby the target analyte eluted too fast, before the first minute. Therefore, we improved to gradient program and the mobile phase composition, increasing the water ratio in A to 60% and adding isopropanol (IPA) to mobile phase B (89:10:1 IPA:CH3CN: H2O, 0.1% formic acid, 5 mM ammonium formate), which results in improved retention and better separation of AA from the other endogenous compounds in less than 5 min. A flow rate of 0.3 mL/min was used throughout the method development. By running AA standard and d8-AA standard, the retention times (RT) were determined: RT AA 4.72 min, RT d8-AA 4.69 min. By optimizing the chromatographic parameters and conditions, we achieved better retention, resolution, peak shape, and separation, leading to a more reliable chromatographic method for the quantification of AA in serum. This optimized approach serves as a foundation for accurate and reproducible analysis in future studies.
3.1.3. Optimizing MS Detector Parameters
To determine the optimal parameters of the mass spectral detector, ethanolic solutions containing 10 μg/mL of arachidonic acid and 10 μg/mL of d8-AA were directly injected into the mass spectrometer by a deviation valve with a 100 μL loop. Since AA contains a carboxylic group, which is easily deprotonated, the mass detector was set to negative electrospray mode (ESI-) [31]. Negatively formed ions [M-H]− were monitored in a full-scan mode from m/z 100 to m/z 350 Da. Different cone voltages were tested: 15, 20, 25, 30, and 35 V. For arachidonic acid, we obtained better results for m/z 303.3, CV 15 (used as quantifier ion) and m/z 304.3, CV30 and 259.30, CV 35 (used as qualifier ions) and for the IS at m/z 311.32, CV 15. These optimized LC-MS conditions were used for further AA analysis.
Figure 1 and Figure 2 represent LC-MS chromatograms of AA and IS standard solutions, and a real serum sample. Total ion MS spectrum of the real serum sample is shown in Figure 3.
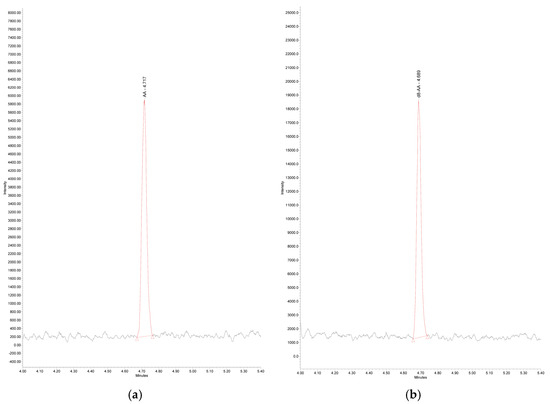
Figure 1.
LC-MS Chromatogram of: (a) arachidonic acid standard solution 1 µg/mL in ethanol: Linear Formula CH3(CH2)4(CH=CHCH2)4CH2CH2CO2H; Molecular formula C20H32O2; RT 4.72 min; Molecular weight 304.47; Monoisotopic mass 304.2 g/mol; Detected mass [M-H]− 303.30 m/z; AA—arachidonic acid; (b) d8-arachidonic acid standard solution 1 µg/mL in ethanol (IS): Linear Formula CH3(CH2)4(CD=CDCH2)4CH2CH2CO2H; Molecular Formula C20H32O2; RT 4.69 min. Molecular weight 312.52; Monoisotopic mass 312.3 g/mol Detected mass [M-H]− 311.32 m/z; d8-AA—d8-arachidonic acid.
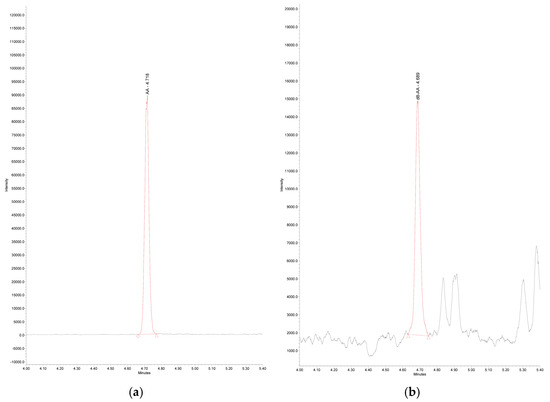
Figure 2.
LC-MS Chromatogram of (a) endogenous arachidonic acid in real serum sample, m/z 303.30, RT: 4.72 min; AA—arachidonic acid; (b) d8-arachidonic acid in real serum sample, m/z 311.32, RT: 4.69 min; d8-AA—d8-arachidonic acid.
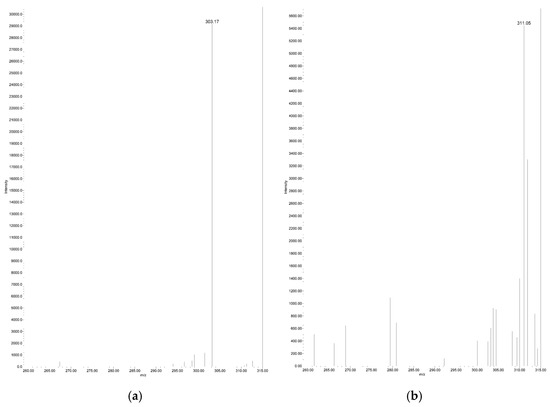
Figure 3.
Total ion MS spectrum of real serum sample (a) endogenous arachidonic acid RT: 4.72 min, m/z 303.17; (b) d8-arachidonic acid RT: 4.69 min, m/z 311.05.
3.2. Method Validation
AA is a metabolite product of the lipolysis of membrane phospholipids and an initial substrate for the production of biologically active eicosanoids. Being a part of human metabolism, it is an endogenous component of blood serum. This makes the development and validation of a reliable method for AA quantification an analytical challenge.
3.2.1. Accuracy and Precision
One important challenge in the evaluation of accuracy and precision is that analyte is an endogenous molecule. According to the ICH guideline (2022), there are several approaches for calibrators and QCs preparation when a biological matrix free of endogenous analyte is not available [19]. One of them is the usage of a surrogate matrix to mimic the authentic one. For the preparation of the calibrators, we used bovine serum albumin in physiologic concentration as a surrogate matrix. We evaluated accuracy and precision by spiking the surrogate matrix with AA at three different concentrations, five replicates each. The accuracy, presented as percent recovery, ranged from 91.95% to 99.19%; % RSD from 5.94 to 14.44 for AA (Table 1).

Table 1.
Accuracy data for AA in spiked serum samples.
Precision was assessed by measuring both intra-day and inter-day variability at three spike levels using the same surrogate matrix-matched samples as for accuracy experiments. The relative standard deviation (%RSD) was below 15% for all tested spike levels, which supported the method’s consistency and robustness in handling biological samples (Table 2).

Table 2.
Precision data for AA in spiked samples.
The current method fulfills the ICH criteria for accuracy and precision [19], which allows us to consider that it is reliable and reproducible. In addition, our results were consistent with the data of others reporting 95% and 105% recovery for AA at spike concentrations 0.1 μg/mL and 0.5 μg/mL, respectively, as well as 4.21% precision at spike concentration 0.5 μg/mL [39].
3.2.2. Limit of Detection (LOD) and Lower Limit of Quantification (LLOQ)
Limit of detection and lower limit of quantitation for AA were determined as described in the experimental part. LOD and LLOQ were 0.046 ± 0.005 µg/mL, and 0.133 ± 0.017 µg/mL, respectively (Figure 4 and Figure 5). Our results are similar to the data of others revealing LOD of AA 0.012 μg/mL and LOQ 0.037 μg/mL in colon tumor tissue, using the more sensitive triple quadrupole ion trap mass spectrometer [27]. Even lower LOD and LOQ for AA in plasma samples, 0.006 µg/mL and 0.018µng/mL, were reported using more sophisticated liquid chromatography–high resolution mass spectrometry [39].
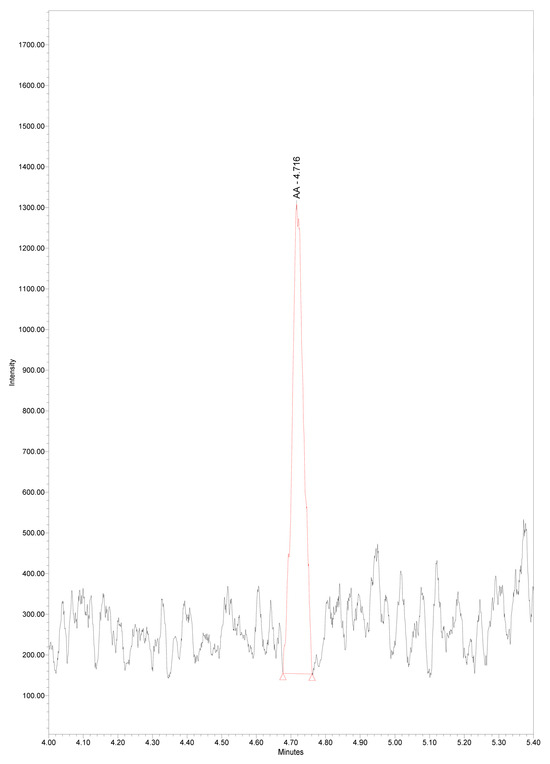
Figure 4.
Chromatogram of serum arachidonic acid at LOD concentration 0.046 µg/mL, m/z 303.3, RT 4.72 min.
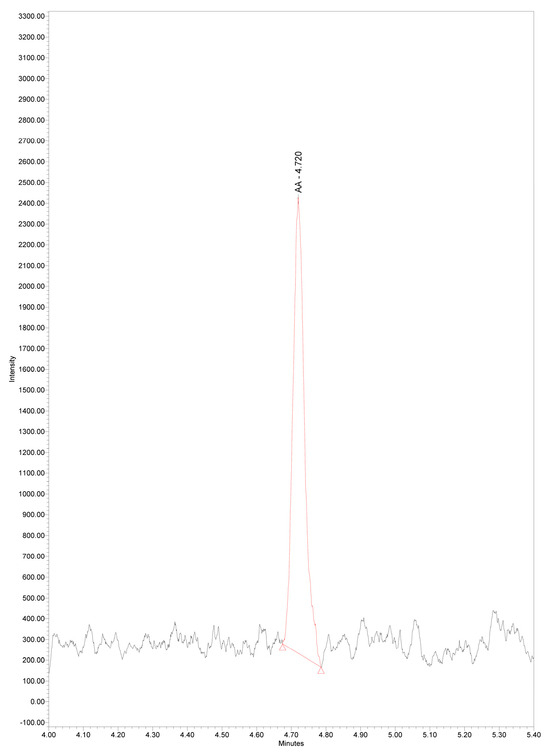
Figure 5.
Chromatogram of serum arachidonic acid at LLOQ concentration 0.133 µg/mL, m/z 303.3, RT 4.72 min.
3.2.3. Selectivity
Selectivity was assessed by using both PDA and MS detectors in 2D and 3D modes, with no interfering peaks detected. Additionally, testing on serum samples from 50 healthy donors (control serum), one hemolyzed, two lipemic (mild and severe lipemia), and one icteric serum revealed no impact on AA identification and quantification. The measured concentrations of AA in normal serum, hemolytic, mild and severe lipemic, and icteric were 2.05, 2.22, 4.32, 5.15, and 1.78 µg/mL, respectively. The deviations from control serum samples did not exceed 15% for samples with hemolysis and high bilirubin. There were no significant variations in the peak areas of AA and the IS, nor ion suppression or enhancement. No interferences were found on the retention time of the analyte and of the IS in the blank samples due to the presence of bilirubin and hemoglobin in the tested serums. The concentration of free AA in the lipemic samples was elevated more than two-fold. Data in the literature examining AA in lipemic, icteric, and serum samples with high hemolysis are incredibly scarce. It could be assumed that elevated serum TAGs are likely a serious interfering factor in the determination of free AA. Therefore, it is advisable to avoid lipemic blood serums for AA analysis.
3.2.4. Calibration Curve and Linearity
Linearity of the method was evaluated by plotting the ratio of AA peak area to IS peak area against the corresponding analyte concentration. Using the simple linear regression model, we determined the regression equations, the slope and the intercept of the calibration plots, and the Pearson’s determination coefficient (R2) for the three calibration curves, solvent-based, surrogate matrix-matched, and authentic matrix-matched in the range of 0.5–5.0 μg/mL free AA. Solvent-based calibration exhibited a regression equation y = 0.766x − 0.152, slope 0.766, y intercept 0.152, R2 0.9952; surrogate matrix-matched calibration showed a regression equation y = 0.587x + 0.097, slope 0.587, y intercept 0.097, R2 0.9984, while authentic matrix-matched calibration revealed a regression equation y = 0.717x + 0.417, slope 0.717, y intercept 0.417, R2 0.9979. Good linearity was established for all calibration curves in the tested concentration range. Gachet et al. [40] reported similar linear range and R2 in plasma samples of 32 healthy male volunteers.
No carryover was observed in a blank following QCs with the highest AA concentration.
3.2.5. Matrix Effect and Extraction Efficiency
Biological samples have a complex matrix, and usually when analyzed by LC/MS co-eluting endogenous substances could interfere with the signal of the target analyte. Matrix effect was evaluated by performing a series of dilutions of the serum sample prior to analysis and plotting the ratio of AA peak area to IS peak area against the calculated concentrations to check for a linear relationship. It was found that the relationship was linear (R2 = 0.9924) in the tested range and exhibited a regression equation y = 1.3279x − 0.3141, slope 1.327, y intercept 0.3141.
Another approach to evaluate a potential matrix effect is by comparing the slopes of solvent-based and authentic matrix-matched calibration curves. We found slope variability of 2.5%, which is below the target value of 5%, and therefore the slopes are considered to be equivalent [25]. When the matrix effect is calculated against a surrogate matrix, the result does not differ significantly from that obtained with a solvent-based matrix, 7.6% vs. 6.4%. We consider that the present method was not interfered with by endogenous substances in the matrix.
The absolute extraction efficiency was 102.7% for d-8 AA (IS) at a concentration of 50 µg/mL; 87.2% for AA at a concentration of 0.67 µg/mL; and 89.64% for AA at a concentration of 2.67 µg/mL.
3.2.6. Stability Experiments
Short-Term Stability in Authentic Matrix
A concentration increase was observed when the samples were stored at 4 °C, even for 24 h (CV 14.6%). A more pronounced increase was indicated on the seventh day, CV 21.4%. A possible explanation of that phenomenon is the release of free arachidonic acid from phospholipids incorporated in plasma lipoproteins by phospholipase A2, which remains active at mild storage conditions.
Long-Term Stability in Authentic Matrix
AA in serum samples remained stable at −18 °C for 24 h (CV 0.9%), for one week (CV 1.7%) and two months (CV 13.0%).
Stability of AA in Processed Samples
The sample extracts stored in the autosampler at room temperature (20 ± 5 °C) were stable within 14 days without significant changes in their concentration (CV 10.0%).
Literature data regarding the stability of AA in human blood serum are extremely scarce. Similar results regarding short-term stability of free fatty acids, including AA in mice plasma, revealed sample stability at room temperature for 6 h. The same authors showed that unprocessed mouse plasma samples were stable for 30 days when stored at −80 °C. Results presented by Yue et al. on processed brain homogenates indicate that processed samples are stable at 4 °C for no more than 14 h [33]. Considering our data, it would be recommended to store serum samples prior to analysis at least at −18 °C for no longer than seven days.
3.2.7. Evaluation Method Applicability to Real Serum Samples
The current method was applied to real serum samples of 50 healthy adult volunteers, with a mean age of 52.2 ± 6.2. For the purpose of quantitative analysis of the samples, a calibration graph was constructed, and the concentrations of the samples were back-calculated from the standard curve. Sample blank and reagent blank were analyzed with each run. The serum concentrations of arachidonic acid in the tested samples ranged between 0.34 and 4.32 μg/mL, with a mean value of 2.05 ± 0.90 μg/mL. This range is consistent with expected values for healthy individuals reported by other studies [40,41], and indicates that the current method can effectively detect and quantify AA in real serum samples. Further, method robustness and reproducibility were assessed by overlaying the chromatograms of 50 serum samples. A clear arachidonic acid peak consistency across the samples was seen with RT variations between 4.75–4.76 min (Figure 6). The variability among samples may be attributed to individual physiological differences, dietary factors, or other biological variables.
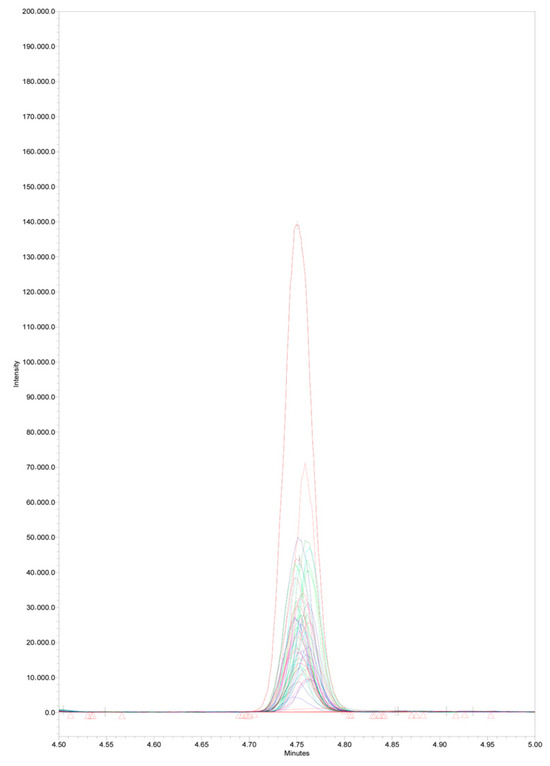
Figure 6.
Overlaid arachidonic acid peaks of 50 serum samples from healthy adult volunteers, m/z 303.3, RT 4.75–4.76 min.
In addition, a few samples of ischemic stroke patients were analyzed with the presented method. The results were in the linear range of the method, showing AA concentration 1.32 ± 0.29 µg/mL.
Currently, there is no established and standardized analytical method for analyzing arachidonic acid in blood serum/plasma. There are also no available commercial calibrators and controls. The methods described in the literature have been developed in-house for the needs of specific studies [33,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50]. Since most of them use GC-MS for quantitative analysis, this requires the derivatization of free AA to more volatile esters [45,48,49]. Sample preparation usually involves the extraction of the analyte from the matrix by liquid–liquid or solid-phase extraction and subsequent derivatization. This is a relatively time-consuming procedure, burdened by potential analyte loss, which can compromise the reproducibility and accuracy of the method, making it difficult to apply in routine clinical testing. In recent years, LC-MS platforms have become increasingly widespread in clinical laboratories due to their potential for automation, high analytical specificity, often superior to immunoassays, and higher throughput than GC-MS. Some of the main requirements for these analytical techniques are easy and fast sample preparation, high analytical reliability, and short analysis time.
We have developed and validated a simple, robust, and selective LC-MS method for the quantification of free arachidonic acid (AA) in human serum. The method requires only a small sample volume and involves a straightforward liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) procedure, eliminating the need for derivatization steps commonly required in GC-MS and even some LC-MS/MS protocols [32,33]. A key advantage of this method is the use of a single-quadrupole (QDa) mass detector, which is more cost-effective and accessible than advanced tandem or high-resolution instruments. Despite its simplicity, the method demonstrates excellent analytical performance, with accuracy and precision comparable to those of more complex triple-quadrupole systems reported by Qian et al. [43] (77.7–109.7%), Gachet et al. [40] (97.7–113.6%), Schött et al. [48] (97.9–101.7%), and Farczádi et al. [50] (94.8–106.8%). Furthermore, the validated lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) is well below the physiological and pathological concentrations of AA reported in the literature [42].
The method was successfully applied to serum samples from healthy individuals, producing AA levels consistent with previously published data [40,41]. Additional analysis of samples from ischemic stroke patients confirmed that their AA concentrations fall within the method’s validated linear range. While further verification is needed before its adoption in routine clinical diagnostics, the validated protocol offers a practical solution in a field where commercial assays are not currently available. Its simplicity and robustness make it a promising tool for expanding clinical studies involving AA as a potential biomarker.
4. Conclusions
The presented method for the analysis of AA in serum samples holds significant implications for both research and clinical settings. The method was developed using a single-quadrupole (QDa) detector, a robust and more common instrument in clinical and hospital laboratories. While highly sensitive platforms like triple-quadrupole or high-resolution mass spectrometers offer lower detection limits, they often require substantial capital investment and specialized technical expertise, limiting their accessibility. Our results demonstrate that despite the simpler instrumentation, the method is “fit-for-purpose,” achieving sufficient sensitivity, accuracy, and precision to reliably quantify arachidonic acid in the clinically relevant range. By combining a straightforward liquid–liquid extraction that avoids time-consuming derivatization with a rapid UPLC analysis, this protocol provides a practical, cost-effective, and readily deployable solution for testing AA as a potential biomarker for ischemic stroke and other neuroinflammatory conditions.
The developed and validated LC-MS method for the quantification of free arachidonic acid (AA) in human serum is simple, robust, and selective.
Author Contributions
D.V.: writing—original draft, visualization, validation, formal analysis, data curation. M.N. (Miglena Nikolova): methodology, formal analysis. M.N. (Milka Nachar): supervision, project administration, funding acquisition, conceptualization, writing—review and editing. B.G.: methodology, validation, conceptualization, writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by European Union-NextGenerationEU, through the National Recovery and Resilience Plan of the Republic of Bulgaria, project No. BG-RRP-2.004-0009-C02 and Medical University of Varna, Science Fund, Project 21015.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by The Research Ethics Committee at the Medical University “Prof. Dr. Paraskev Stoyanov”—Varna (protocol number 140/01.02.2024).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from all subjects involved in the study to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sifat, A.E.; Nozohouri, S.; Archie, S.R.; Chowdhury, E.A.; Abbruscato, T.J. Brain Energy Metabolism in Ischemic Stroke: Effects of Smoking and Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, D.B.; Martín-Jiménez, C.A.; Rojas-Rodríguez, F.; Barreto, G.E.; González, J. Brain Lipidomics as a Rising Field in Neurodegenerative Contexts: Perspectives with Machine Learning Approaches. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2021, 61, 100899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloska, A.; Malinowska, M.; Gabig-Cimińska, M.; Jakóbkiewicz-Banecka, J. Lipids and Lipid Mediators Associated with the Risk and Pathology of Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, G.; Anwar, H.; Rasul, A.; Imran, A.; Qasim, M.; Zafar, S.; Imran, M.; Kamran, S.K.S.; Aziz, N.; Razzaq, A.; et al. Lipids as Biomarkers of Brain Disorders. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 351–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snowden, S.G.; Ebshiana, A.A.; Hye, A.; An, Y.; Pletnikova, O.; O’Brien, R.; Troncoso, J.; Legido-Quigley, C.; Thambisetty, M. Association between Fatty Acid Metabolism in the Brain and Alzheimer Disease Neuropathology and Cognitive Performance: A Nontargeted Metabolomic Study. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rink, C.; Khanna, S. Significance of Brain Tissue Oxygenation and the Arachidonic Acid Cascade in Stroke. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 1889–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Z.; Ma, Q. Arachidonic Acid Metabolism in Health and Disease. MedComm 2023, 4, e363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.H.; Seo, Y.; Jo, Y.S.; Lee, S.; Cho, E.; Cazenave-Gassiot, A.; Shin, Y.-S.; Moon, M.H.; An, H.J.; Wenk, M.R.; et al. Brain Lipidomics: From Functional Landscape to Clinical Significance. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, 9317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Gold, A.; Kaye, S.; Atkinson, J.R.; Tol, M.; Sas, A.; Segal, B.; Tontonoz, P.; Zhu, J.; Gao, J. Arachidonic Acid Mobilization and Peroxidation Promote Microglial Dysfunction in Aβ Pathology. J. Neurosci. 2024, 44, e0202242024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.K.; Cho, Y.; Do, H.J.; Oh, K.; Seo, W.K.; Shin, M.J. Plasma Phospholipid Arachidonic Acid and Lignoceric Acid Are Associated with the Risk of Cardioembolic Stroke. Nutr. Res. 2015, 35, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, S.; Katsumata, T.; Okubo, S.; Kanamaru, T.; Suzuki, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Katsura, K.I.; Katayama, Y. Low Serum N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid/n-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Ratio Predicts Neurological Deterioration in Japanese Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2013, 36, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Yoshioka, K. Features of Serum Fatty Acids in Acute Ischaemic Stroke Patients Aged 50 Years or Older. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2020, 20, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adibhatla, R.M.; Hatcher, J.F. Citicoline Decreases Phospholipase A 2 Stimulation and Hydroxyl Radical Generation in Transient Cerebral Ischemia. J. Neurosci. Res. 2003, 73, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalu, S.; Saber, S.; Ramadan, A.; Elmorsy, E.A.; Hamad, R.S.; Abdel-Reheim, M.A.; Youssef, M.E. Unveiling Citicoline’s Mechanisms and Clinical Relevance in the Treatment of Neuroinflammatory Disorders. FASEB J. 2024, 38, e70030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Guan, C.; Li, K.; Wang, C.; Feng, R.; Sun, C. Free Fatty Acid Metabolic Profile and Biomarkers of Isolated Post-Challenge Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on GC-MS and Multivariate Statistical Analysis. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2010, 878, 2817–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ong, C.N.; Subramaniam, T.; Choi, H.W.; Yuan, J.M.; Koh, W.P.; Pan, A. Metabolic Signatures and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in a Chinese Population: An Untargeted Metabolomics Study Using Both LC-MS and GC-MS. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 2349–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.L.; Meng, L.; Li, L.L.; Ma, L.N.; Mao, X.M. Plasma Free Fatty Acids Metabolic Profile among Uyghurs and Kazaks with or Without Type 2 Diabetes Based on GC-MS. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2017, 126, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmagid, S.A.; Clarke, S.E.; Nielsen, D.E.; Badawi, A.; El-Sohemy, A.; Mutch, D.M.; Ma, D.W.L. Comprehensive Profiling of Plasma Fatty Acid Concentrations in Young Healthy Canadian Adults. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug administration (FDA); U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research; Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research. M10 Bioanalytical Method Validation and Study Sample Analysi Guidance for Industry. 2022; pp. 1–50. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/m10-bioanalytical-method-validation-and-study-sample-analysis (accessed on 4 April 2024).
- Provan, D. (Ed.) Oxford Handbook of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010; ISBN 0199233713. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, L.; He, J.; Liang, Y.; Yuan, D.; Gao, H.; Zhou, H. Simultaneously Quantitative Measurement of Comprehensive Profiles of Esterified and Non-Esterified Fatty Acid in Plasma of Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2007, 150, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clore, J.N.; Harris, P.A.; Li, J.; Azzam, A.; Gill, R.; Zuelzer, W.; Rizzo, W.B.; Blackardl, W.G. Changes in Phosphatidylcholine Fatty Acid Composition Are Associated With Altered Skeletal Muscle Insulin Responsiveness in Normal Man. Metabolism 2000, 49, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clore, J.N.; Allred, J.; White, D.; Li, J.; Stillman, J. The Role of Plasma Fatty Acid Composition in Endogenous Glucose Production in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Metabolism 2002, 51, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yang, S.; Wang, P.G. Matrix Effects and Application of Matrix Effect Factor. Bioanalysis 2017, 9, 1839–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineva, E.M.; Zhang, M.; Rabinowitz, D.J.; Phinney, K.W.; Pfeiffer, C.M. An LC-MS/MS Method for Serum Methylmalonic Acid Suitable for Monitoring Vitamin B12 Status in Population Surveys. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 2955–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallima, H.; El Ridi, R. Arachidonic Acid: Physiological Roles and Potential Health Benefits—A Review. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 11, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leyen, K. Eicosanoids in Cerebrovascular Diseases. In Primer on Cerebrovascular Diseases, 2nd ed.; Caplan, L.R., Biller, J., Leary, M.C., Lo, E.H., Thomas, A.J., Yenari, M., Zhang, J.H., Eds.; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 86–89. ISBN 9780128030585. [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan, C.D.C.; Lust, C.A.C.; Burns, J.L.; Hillyer, L.M.; Martin, S.A.; Wittert, G.A.; Ma, D.W.L. Analysis of Major Fatty Acids from Matched Plasma and Serum Samples Reveals Highly Comparable Absolute and Relative Levels. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2021, 168, 102268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spector, A.A. Plasma Free Fatty Acid and Lipoproteins as Sources of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid for the Brain. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2001, 16, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, G.D.O.; Rumley, A.; Mackie, I.J. Plasma Fibrinogen. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2004, 41, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Püttmann, M.; Krug, H.; Von Ochsenstein, E.; Kattermann, R. Fast HPLC Determination of Serum Free Fatty Acids in the Picomole Range. Clin. Chem. 1993, 39, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Li, R.; Wu, H. Recent Progress in the Analysis of Unsaturated Fatty Acids in Biological Samples by Chemical Derivatization-Based Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Methods. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2023, 1215, 123572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Jansen, S.A.; Strauss, K.I.; Borenstein, M.R.; Barbe, M.F.; Rossi, L.J.; Murphy, E. A Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometric Method for Simultaneous Analysis of Arachidonic Acid and Its Endogenous Eicosanoid Metabolites Prostaglandins, Dihydroxyeicosatrienoic Acids, Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic Acids, and Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acids in Rat Br. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 43, 1122–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xie, B.; Li, L.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, J.; Guan, G.; Qiu, Y. Rapid and Sensitive LC-MS/MS Analysis of Fatty Acids in Clinical Samples. Chromatographia 2014, 77, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Suzuki, H.; Suda, K.; Yamazaki, Y.; Takino, A.; Kim, Y.I.; Goto, T.; Iijima, Y.; Aoki, K.; Shibata, D.; et al. Long-Chain Free Fatty Acid Profiling Analysis by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry in Mouse Treated with Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor α Agonist. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 2288–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munjoma, N.; Isaac, G.; Gethings, L. [APPLICATION NOTE] LipidQuan: HILIC-Based LC-MS/MS High-Throughput Targeted Free Fatty Acid Screen [APPLICATION NOTE]; Waters Corporation: Milford, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Xu, Y. An Extremely Simple Method for Extraction of Lysophospholipids and Phospholipids from Blood Samples. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Yu, M.; Crabb, D.; Xu, Y.; Liangpunsakul, S. Ethanol-Induced Alterations in Fatty Acid-Related Lipids in Serum and Tissues in Mice. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokotou, M.G.; Mantzourani, C.; Batsika, C.S.; Mountanea, O.G.; Eleftheriadou, I.; Kosta, O.; Tentolouris, N.; Kokotos, G. Lipidomics Analysis of Free Fatty Acids in Human Plasma of Healthy and Diabetic Subjects by Liquid Chromatography-High Resolution Mass Spectrometry (LC-HRMS). Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gachet, M.S.; Rhyn, P.; Bosch, O.G.; Quednow, B.B.; Gertsch, J. A Quantitiative LC-MS/MS Method for the Measurement of Arachidonic Acid, Prostanoids, Endocannabinoids, N-Acylethanolamines and Steroids in Human Plasma. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2015, 976–977, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinde, D.D.; Kim, K.B.; Oh, K.S.; Abdalla, N.; Liu, K.H.; Bae, S.K.; Shon, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, D.H.; Shin, J.G. LC-MS/MS for the Simultaneous Analysis of Arachidonic Acid and 32 Related Metabolites in Human Plasma: Basal Plasma Concentrations and Aspirin-Induced Changes of Eicosanoids. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2012, 911, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, H.J.; Lee, J.W.; Bandu, R.; Kang, H.S.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, K.P. A Rapid and Sensitive Profiling of Free Fatty Acids Using Liquid Chromatography Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC/ESI-MS/MS) after Chemical Derivatization. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 32130–32139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Pan, L.; Hu, C. A UPLC-MS/MS Method for Simultaneous Determination of Arachidonic Acid, Stearic Acid, and Related Endocannabinoids in Human Plasma. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterz, K.; Scherer, G.; Ecker, J. A Simple and Robust UPLC-SRM/MS Method to Quantify Urinary Eicosanoids. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 1026–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuszewski, B.K.; Constanzer, M.L.; Chavez-Eng, C.M. Strategies for the Assessment of Matrix Effect in Quantitative Bioanalytical Methods Based on HPLC-MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 3019–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, E.S.; Abdalla, D.S.P. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography of Fatty Acids in Biological Samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 465, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantzourani, C.; Kokotou, M.G. Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) Derivatization-Based Methods for the Determination of Fatty Acids in Biological Samples. Molecules 2022, 25, 5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schött, H.F.; Konings, M.C.J.M.; Schrauwen-Hinderling, V.B.; Mensink, R.P.; Plat, J. A Validated Method for Quantification of Fatty Acids Incorporated in Human Plasma Phospholipids by Gas Chromatography-Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecker, J.; Scherer, M.; Schmitz, G.; Liebisch, G. A Rapid GC–MS Method for Quantification of Positional and Geometric Isomers of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 897, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farczádi, L.; Dobreanu, M.; Huțanu, A.; Imre, S. Development and Validation of an LC-MS/MS Method for the Determination of Plasma and Red Blood Cell Omega Fatty Acids: A Useful Diagnostic Tool. Separations 2024, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).