A Review on Anaerobic Digestate as a Biofertilizer: Characteristics, Production, and Environmental Impacts from a Life Cycle Assessment Perspective
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Digestate as Fertilizer
2.1. Use of Digestate as a Fertilizer
2.2. Challenges of Digestate as Fertilizer
3. LCA as a Tool in Digestate Use
3.1. LCA as a Tool to Measure Environmental Footprint
3.2. LCA Applied to Digestate Production and Uses—A Survey of Recent Studies
4. System and Stages in Digestate Production
4.1. Digestate Production Systems
4.2. Using LCA to Improve Digestate Production Systems
5. Discussion
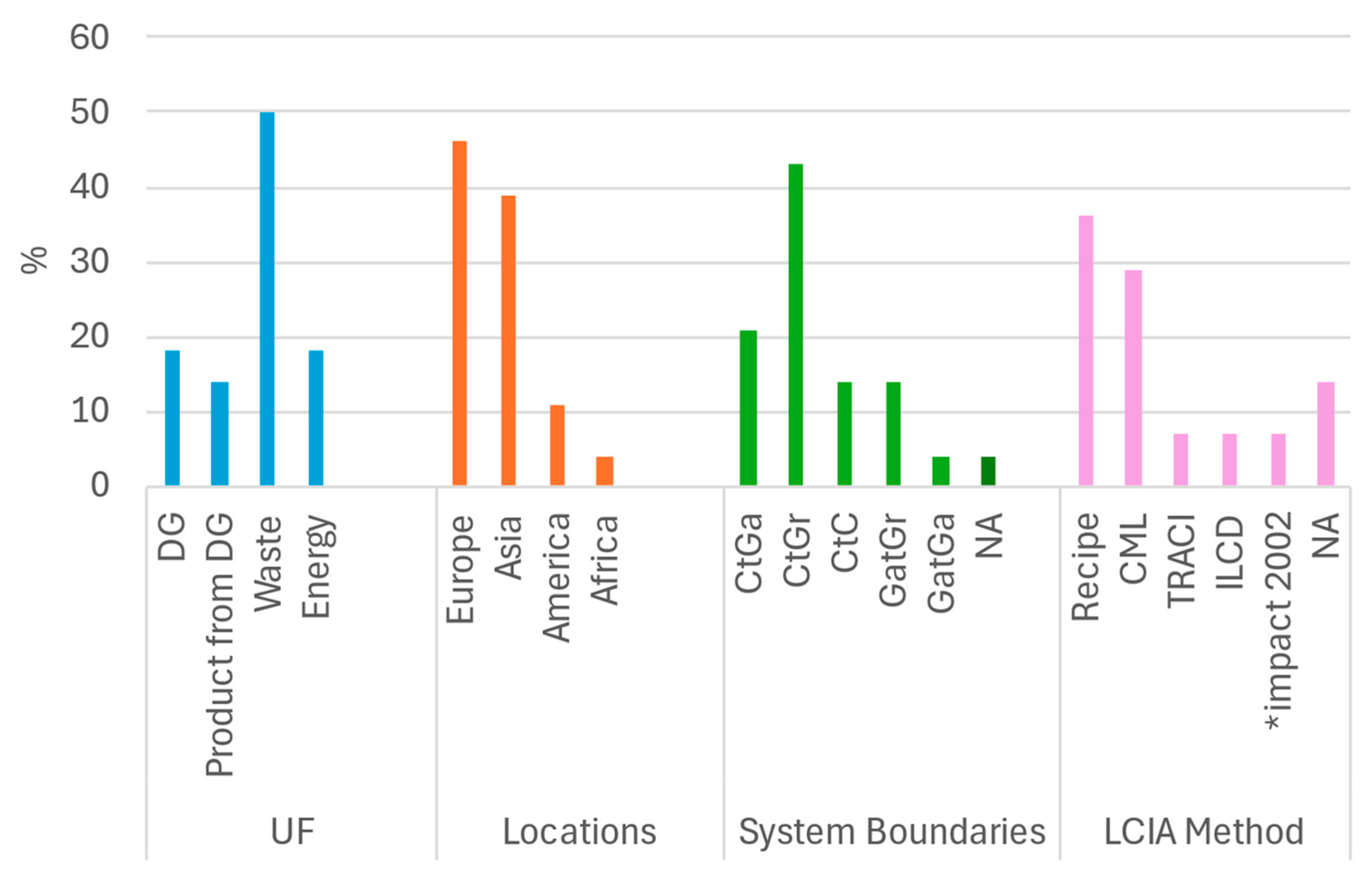
5.1. Choice of Functional Unit and System Boundaries
5.2. Feedstock Choice and Handling Before AD
5.3. Digestate Post-Treatment and Handling After AD
5.4. Impact Allocation and Product Displacement or Substitution
5.5. Policy and Market Barriers to Digestate Utilization
5.5.1. Legal Complexity in the Classification of Digestate
5.5.2. Legal and Commercial Feasibility of Digestate as Fertilizer
5.5.3. Challenges and Uncertainties in the Legal Framework for Digestate
6. Conclusions
- Promote the development and adoption of standardized LCA methodologies to improve comparability and transparency.
- Incentivize digestate post-treatment strategies (e.g., composting, separation) to enhance agronomic quality and environmental safety.
- Establish clear policy frameworks and end-of-waste criteria to enable digestate commercialization.
- Support research on digestate behavior under diverse agronomic and climatic conditions.
- Strengthen regional digestate markets through public procurement, farmer training, and quality certification schemes.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Anaerobic Digestion |
| AM | Animal Manure |
| BG | Biogas |
| CM | Cattle Manure |
| cM | Composted Manure |
| CHN | Calcium Hydrolysis Neutralization |
| CHP | Combined Heat and Power |
| CtC | Cradle to Cradle |
| CtGa | Cradle to Gate |
| CtGr | Cradle to Grave |
| CW | Crop Waste |
| DG | Digestate |
| DM | Dry Matter |
| DS | Distillery Sludge |
| FU | Functional Unit |
| FW | Food Waste |
| GatGa | Gate to Gate |
| GatGr | Gate to Grave |
| GHG | Greenhouse Gases |
| GS | Grass Silage |
| GWP | Global Warming Potential |
| HM | Heavy Metal |
| HTC | Hydrothermal Carbonization |
| IPCC | Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change |
| ISO | International Organization for Standardization |
| IW | Industrial Waste |
| LCA | Life Cycle Assessment |
| LCI | Life Cycle Inventory |
| LCIA | Life Cycle Impact Assessment |
| LF | Liquid Fraction |
| M | Mesophilic |
| MS | Maize Silage |
| MSW | Municipal Solid Waste |
| OM | Organic Matter |
| OMSW | Organic Municipal Solid Waste |
| OW | Organic Waste |
| PEF | Product Environmental Footprint |
| PM | Pig Manure |
| pM | Poultry Manure |
| PS | Pig Slurry |
| Ps | Paper Sludge |
| RS | Residual Straw |
| SF | Solid Fraction |
| SM | Sheep Manure |
| SP | Slaughterhouse Processing Waste |
| T | Thermophilic |
| TOC | Total Organic Carbon |
| TS | Total Solids |
| TW | Tree Waste |
| VS | Volatile Solids |
| WWS | Wastewater Sludge |
References
- Of the European Parliament and of the Council as Regards the Requirements Applicable to EU Fertilising Products Containing Inhibiting Compounds and the Post Processing of Digestate (Text with EEA Relevance). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg_del/2022/1519/oj (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Xu, R.-Z.; Fang, S.; Zhang, L.; Huang, W.; Shao, Q.; Fang, F.; Feng, Q.; Cao, J.; Luo, J. Distribution Patterns of Functional Microbial Community in Anaerobic Digesters under Different Operational Circumstances: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deena, S.R.; Vickram, A.S.; Manikandan, S.; Subbaiya, R.; Karmegam, N.; Ravindran, B.; Chang, S.W.; Awasthi, M.K. Enhanced Biogas Production from Food Waste and Activated Sludge Using Advanced Techniques–A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 355, 127234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelínek, M.; Mazancová, J.; Van Dung, D.; Phung, L.D.; Banout, J.; Roubík, H. Quantification of the Impact of Partial Replacement of Traditional Cooking Fuels by Biogas on Global Warming: Evidence from Vietnam. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 292, 126007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natividad Pérez-Camacho, M.; Curry, R.; Cromie, T. Life Cycle Environmental Impacts of Biogas Production and Utilisation Substituting for Grid Electricity, Natural Gas Grid and Transport Fuels. Waste Manag. 2019, 95, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czekała, W.; Jasiński, T.; Grzelak, M.; Witaszek, K.; Dach, J. Biogas Plant Operation: Digestate as the Valuable Product. Energies 2022, 15, 8275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, F.; Fan, C.; Lee, Y.-Y. From Waste to Value: Addressing the Relevance of Waste Recovery to Agricultural Sector in Line with Circular Economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 415, 137873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, M.; Visvanathan, C. Management Strategies for Anaerobic Digestate of Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste: Current Status and Future Prospects. Waste Manag. Res. 2019, 37, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, S.; Harris, P.W.; Mccabe, B.K. Biogas Recovery by Anaerobic Digestion of Australian Agro-Industry Waste: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 299, 126876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, H.; Xie, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, D. A Critical Review on Sustainable Management and Resource Utilization of Digestate. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 183, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zennaro, B.; Marchand, P.; Latrille, E.; Thoisy, J.C.; Houot, S.; Girardin, C.; Steyer, J.P.; Béline, F.; Charnier, C.; Richard, C.; et al. Agronomic Characterization of Anaerobic Digestates with Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K.; Müller, T. Effects of Anaerobic Digestion on Digestate Nutrient Availability and Crop Growth: A Review. Eng. Life Sci. 2012, 12, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Han, L.; Huang, G. Characterization of Digestate Composting Stability Using Fluorescence EEM Spectroscopy Combining with PARAFAC. Waste Manag. Res. 2019, 37, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhiar, A.; Battimelli, A.; Torrijos, M.; Carrere, H. Comprehensive Characterization of the Liquid Fraction of Digestates from Full-Scale Anaerobic Co-Digestion. Waste Manag. 2017, 59, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gong, H.; He, S.; Shi, C.; Yuan, H.; Zuo, X.; Li, X. Utilizing Hydrolysis and Acidification via Liquid Fraction of Digestate (LFD-HA) for Methane Production Enhancement of Corn Straw: Physicochemical and Microbial Community Characterization. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 326, 129282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambone, F.; Orzi, V.; D’Imporzano, G.; Adani, F. Solid and Liquid Fractionation of Digestate: Mass Balance, Chemical Characterization, and Agronomic and Environmental Value. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Chang, J.-S.; Lee, D.-J. Anaerobic Digestate Valorization beyond Agricultural Application: Current Status and Prospects. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 373, 128742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tampio, E.; Salo, T.; Rintala, J. Agronomic Characteristics of Five Different Urban Waste Digestates. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 169, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdi, L.; Kuikman, P.J.; Orlandini, S.; Mancini, M.; Napoli, M.; Dalla Marta, A. Does the Use of Digestate to Replace Mineral Fertilizers Have Less Emissions of N2O and NH3 ? Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 269, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gielnik, A.; Pechaud, Y.; Huguenot, D.; Cébron, A.; Riom, J.M.; Guibaud, G.; Esposito, G.; van Hullebusch, E.D. Effect of Digestate Application on Microbial Respiration and Bacterial Communities’ Diversity during Bioremediation of Weathered Petroleum Hydrocarbons Contaminated Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slepetiene, A.; Volungevicius, J.; Jurgutis, L.; Liaudanskiene, I.; Amaleviciute-Volunge, K.; Slepetys, J.; Ceseviciene, J. The Potential of Digestate as a Biofertilizer in Eroded Soils of Lithuania. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhi, M.; Guo, J.; Gaballah, M.S.; Li, B.; Zheng, J.; Cui, X.; Sun, H.; Dong, R. Selecting the Optimal Nutrients Recovery Application for a Biogas Slurry Based on Its Characteristics and the Local Environmental Conditions: A Critical Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 814, 152700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamaralalage, D.; Rodgers, S.; Gill, A.; Meredith, W.; Bott, T.; West, H.; Alce, J.; Snape, C.; McKechnie, J. Biowaste to Biochar: A Techno-Economic and Life Cycle Assessment of Biochar Production from Food-Waste Digestate and Its Agricultural Field Application. Biochar 2025, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.F.; Wang, D.H.; Xie, Z.; Zou, H.; Zheng, Y. Producing Insect Protein from Food Waste Digestate via Black Soldier Fly Larvae Cultivation: A Promising Choice for Digestate Disposal. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomone, R.; Saija, G.; Mondello, G.; Giannetto, A.; Fasulo, S.; Savastano, D. Environmental Impact of Food Waste Bioconversion by Insects: Application of Life Cycle Assessment to Process Using Hermetia Illucens. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 890–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, L.-M.; Li, B.; Guo, W.-J.; Ding, X.-L.; Xu, F.-Z. Effect of Fermented Biogas Residue on Growth Performance, Serum Biochemical Parameters, and Meat Quality in Pigs. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 30, 1464–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Grünewald, C.; Ignacio Gayo-Peláez, J.; Ndovela, V.; Wood, E.; Vijay Kapoore, R.; Anne Llewellyn, C. Towards a Circular Economy: A Novel Microalgal Two-Step Growth Approach to Treat Excess Nutrients from Digestate and to Produce Biomass for Animal Feed. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelam, J.S.; Fernandes De Souza, M.; Chaerle, P.; Willems, B.; Michels, E.; Vyverman, W.; Meers, E. Maximizing Nutrient Recycling from Digestate for Production of Protein-Rich Microalgae for Animal Feed Application the Integration of Phototrophic Microalgal Production and Anaerobic Digestion Can Recycle Excess Nutrients across European Surplus Hotspots to Produce Protein-Rich Biomass for Nutritional Applications. Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xiao, K.; Yang, J.; Yu, Z.; Yu, W.; Xu, Q.; Wu, Q.; Liang, S.; Hu, J.; Hou, H.; et al. Phosphorus Recovery from the Liquid Phase of Anaerobic Digestate Using Biochar Derived from IronÀrich Sludge: A Potential Phosphorus Fertilizer. Water Res. 2020, 174, 115629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Xie, S.; Hu, Z.; Wu, G.; Morrison, L.; Croot, P.; Hu, H.; Zhan, X. Nutrient Recovery from Pig Manure Digestate Using Electrodialysis Reversal: Membrane Fouling and Feasibility of Long-Term Operation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 573, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panuccio, M.R.; Papalia, T.; Attinà, E.; Giuffrè, A.; Muscolo, A. Use of Digestate as an Alternative to Mineral Fertilizer: Effects on Growth and Crop Quality. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2019, 65, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.-B.; Yang, L.-B.; Zhang, W.-W.; Zhao, X.-C. Lipids Production and Nutrients Recycling by Microalgae Mixotrophic Culture in Anaerobic Digestate of Sludge Using Wasted Organics as Carbon Source. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Huang, D.; Shao, M.; Xu, Q. Use of Activated Carbon to Reduce Ammonia Emissions and Accelerate Humification in Composting Digestate from Food Waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Huang, D.; Zhang, C.; Shao, M.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J.; Deng, Z.; Xu, Q. Long-Term Characterization and Resource Potential Evaluation of the Digestate from Food Waste Anaerobic Digestion Plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badagliacca, G.; Petrovičovà, B.; Pathan, S.I.; Roccotelli, A.; Romeo, M.; Monti, M.; Gelsomino, A. Use of Solid Anaerobic Digestate and No-Tillage Practice for Restoring the Fertility Status of Two Mediterranean Orchard Soils with Contrasting Properties. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 300, 107010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyeni, M.O.; Stulpinaite, U.; Baksinskaite, A.; Suproniene, S.; Tilvikiene, V. The Effectiveness of Digestate Use for Fertilization in an Agricultural Cropping System. Plants 2021, 10, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slepetiene, A.; Kochiieru, M.; Jurgutis, L.; Mankeviciene, A.; Skersiene, A.; Belova, O. The Effect of Anaerobic Digestate on the Soil Organic Carbon and Humified Carbon Fractions in Different Land-Use Systems in Lithuania. Land 2022, 11, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentinuzzi, F.; Cavani, L.; Porfido, C.; Terzano, R.; Pii, Y.; Cesco, S.; Marzadori, C.; Mimmo, T. The Fertilising Potential of Manure-Based Biogas Fermentation Residues: Pelleted vs. Liquid Digestate. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czekała, W.; Lewicki, A.; Pochwatka, P.; Czekała, A.; Wojcieszak, D.; Waliszewska, H. Digestate Management in Polish Farms as an Element of the Nutrient Cycle. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 242, 118454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecorini, I.; Peruzzi, E.; Albini, E.; Doni, S.; Macci, C.; Masciandaro, G.; Iannelli, R. Evaluation of MSW Compost and Digestate Mixtures for a Circular Economy Application. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.O.; Janetschek, J.; Illmer, P. Using Digestate Compost as a Substrate for Anaerobic Digestion. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2018, 41, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; De Guardia, A.; Dabert, P. Improving Composting as a Post-Treatment of Anaerobic Digestate. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 201, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manasa, M.R.K.; Katukuri, N.R.; Xu, X.; Guo, R. Rehabilitation of Saline Soil with Biogas Digestate, Humic Acid, Calcium Humate and Their Amalgamations. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2020, 51, 1707–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, R.; Lin, R.; Wall, D.M.; Browne, J.D.; Murphy, J.D. A Comparison of Digestate Management Options at a Large Anaerobic Digestion Plant. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigatti, M.; Barbanti, L.; Hassan, M.U.; Ciavatta, C. Fertilizing Potential and CO2 Emissions Following the Utilization of Fresh and Composted Food-Waste Anaerobic Digestates. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandas Tavera, C.; Raab, T.; Holguin Trujillo, L. Valorization of Biogas Digestate as Organic Fertilizer for Closing the Loop on the Economic Viability to Develop Biogas Projects in Colombia. Clean. Circ. Bioecon. 2023, 4, 100035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Guan, D.; Wang, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, J.; Guo, L. A Comprehensive Review on the Preparation of Biochar from Digestate Sources and Its Application in Environmental Pollution Remediation. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 912, 168822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Fang, Y.; Lai, W.; Xu, S.; Lichtfouse, E. Enhancing Thermophilic Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Sewage Sludge and Food Waste with Biogas Residue Biochar. Renew. Energy 2022, 188, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefaniuk, M.; Oleszczuk, P.; Bartmí Nski, P. Chemical and Ecotoxicological Evaluation of Biochar Produced from Residues of Biogas Production. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 318, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abubaker, J.; Risberg, K.; Pell, M. Biogas Residues as Fertilisers-Effects on Wheat Growth and Soil Microbial Activities. Appl. Energy 2012, 99, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häfner, F.; Hartung, J.; Möller, K. Digestate Composition Affecting N Fertiliser Value and C Mineralisation. Waste Biomass Valorization 2022, 13, 3445–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabón-Pereira, C.P.; De Vries, J.W.; Slingerland, M.A.; Zeeman, G.; Van Lier, J.B. Impact of Crop-Manure Ratios on Energy Production and Fertilizing Characteristics of Liquid and Solid Digestate during Codigestion. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 2427–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angouria-Tsorochidou, E.; Thomsen, M. Modelling the Quality of Organic Fertilizers from Anaerobic Digestion–Comparison of Two Collection Systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 304, 127081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzee, T.J.; Edalati, A.; El-Mashad, H.; Wang, D.; Scow, K.; Zhang, R. Digestate Biofertilizers Support Similar or Higher Tomato Yields and Quality Than Mineral Fertilizer in a Subsurface Drip Fertigation System. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2019, 3, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makdi, M.; Tomcsik, A.; Orosz, V. Digestate: A New Nutrient Source-Review. Biogas 2012, 14, 295–312. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, D.R.; Lathwell, D.J. Anaerobically Digested Dairy Manure as Fertilizer for Maize in Acid and Alkaline Soils. Commun Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2004, 35, 1757–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alburquerque, J.A.; De La Fuente, C.; Bernal, M.P. Chemical Properties of Anaerobic Digestates Affecting C and N Dynamics in Amended Soils. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 160, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnane, I.; Taoumi, H.; Lahrech, K.; dîn Fertahi, S.E.; Ghodbane, M. From Waste to Resource: Biogas and Digestate Valorization Strategies for Sustainable Energy and Agriculture. Biomass Bioenergy 2025, 200, 108006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alengebawy, A.; Mohamed, B.A.; Jin, K.; Liu, T.; Ghimire, N.; Samer, M.; Ai, P. A Comparative Life Cycle Assessment of Biofertilizer Production towards Sustainable Utilization of Anaerobic Digestate. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 33, 875–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šatvar Vrbančić, M.; Petek, M.; Lazarević, B.; Jukić, Ž.; Meers, E.; Čoga, L. Solid and Liquid Fraction of Digestate as an Alternative Mineral Nitrogen Source: Two-Year Field Research in Croatia. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačić, Đ.; Lončarić, Z.; Jović, J.; Samac, D.; Popović, B.; Tišma, M. Digestate Management and Processing Practices: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahramian, M.; Krah, C.; Hynds, P.; Priyadarshini, A. An Environmental and Economic Assessment of Household Food Waste Management Scenarios in Ireland. Recycling 2025, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurmessa, B.; Cocco, S.; Ashworth, A.J.; Udawatta, R.P.; Cardelli, V.; Ilari, A.; Serrani, D.; Fornasier, F.; Del Gatto, A.; Pedretti, E.F.; et al. Short Term Effects of Digestate and Composted Digestate on Soil Health and Crop Yield: Implications for Sustainable Biowaste Management in the Bioenergy Sector. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czekała, W.; Nowak, M.; Piechota, G. Sustainable Management and Recycling of Anaerobic Digestate Solid Fraction by Composting: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 375, 128813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthurson, V. Closing the Global Energy and Nutrient Cycles through Application of Biogas Residue to Agricultural Land-Potential Benefits and Drawbacks. Energies 2009, 2, 226–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivard, C.J.; Rodriguez, J.B.; Nagle, N.J.; Self, J.R.; Kay, B.D.; Soltanpour, P.N.; Nieves, R.A. Anaerobic Digestion of Municipal Solid Waste Utility of Process Residues as a Soil Amendment. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1995, 51, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alan, O.; Budak, B.; Sen, F.; Ongun, A.R.; Tepecik, M.; Ata, S. Solid and Liquid Digestate Generated from Biogas Production as a Fertilizer Source in Processing Tomato Yield, Quality and Some Health-Related Compounds. J. Agric. Sci. 2025, 163, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, M.; Demichelis, F.; Deorsola, F.A.; Fino, D.; Saracco, G.; Pugliese, M.; Tommasi, T. Optimizing Biomethane Production and Plants Growth with Biochar-Enhanced Anaerobic Digestion. Results Eng. 2025, 26, 104883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jian, S.; Bi, J.; Li, Y.; Chang, Z.; He, J.; Ye, X. Anaerobic Digestion in Mesophilic and Room Temperature Conditions: Digestion Performance and Soil-Borne Pathogen Survival. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 43, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfa, M.I.; Adie, D.B.; Igboro, S.B.; Oranusi, U.S.; Dahunsi, S.O.; Akali, D.M. Assessment of Biofertilizer Quality and Health Implications of Anaerobic Digestion Effluent of Cow Dung and Chicken Droppings. Renew. Energy 2014, 63, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owamah, H.I.; Dahunsi, S.O.; Oranusi, U.S.; Alfa, M.I. Fertilizer and Sanitary Quality of Digestate Biofertilizer from the Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Human Excreta. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlström, L. A Review of Survival of Pathogenic Bacteria in Organic Waste Used in Biogas Plants. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 87, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamolinara, B.; Pérez-Martínez, A.; Guardado-Yordi, E.; Guillén Fiallos, C.; Diéguez-Santana, K.; Ruiz-Mercado, G.J. Anaerobic Digestate Management, Environmental Impacts, and Techno-Economic Challenges. Waste Manag. 2022, 140, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, L.; Carswell, A.; Misselbrook, T.; Shen, J.; Han, J. Fate and Transfer of Heavy Metals Following Repeated Biogas Slurry Application in a Rice-Wheat Crop Rotation. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkoa, R. Agricultural Benefits and Environmental Risks of Soil Fertilization with Anaerobic Diges-Tates: A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 473–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Ansari, A.J.; Yin, R.; Qi, C.; Song, X. Optimizing Feedstock Organic Composition to Regulate Humification and Heavy Metal Passivation during Solid-State Anaerobic Digestion. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 156071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zou, D.; Wu, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Liu, F.; Xiao, Z. Review on Fate and Bioavailability of Heavy Metals during Anaerobic Digestion and Composting of Animal Manure. Waste Manag. 2022, 150, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshikalange, B.; Bello, Z.A.; Ololade, O.O. Comparative Nutrient Leaching Capability of Cattle Dung Biogas Digestate and Inorganic Fertilizer under Spinach Cropping Condition. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 3237–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, J.; Mickan, B.S.; Rinklebe, J.; Song, H.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Wang, H.; Kirkham, M.B.; Bolan, N.S. Environmental Implications, Potential Value, and Future of Food-Waste Anaerobic Digestate Management: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 318, 115519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.A.; Rengel, Z.; Bolan, N.; Khan, B.A.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Solaiman, Z.M. Adsorption of Ammonium from Anaerobic Food Waste Digestate by Pristine and Modified Eucalyptus Biochar for Nitrogen Fertiliser Use. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2025, 25, 4531–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launay, C.; Houot, S.; Frédéric, S.; Girault, R.; Levavasseur, F.; Marsac, S.; Constantin, J. Incorporating Energy Cover Crops for Biogas Production into Agricultural Systems: Benefits and Environmental Impacts. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 42, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K. Effects of Anaerobic Digestion on Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Turnover, N Emissions, and Soil Biological Activity. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 1021–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyang’au, J.O.; Sørensen, P.; Møller, H.B. Nitrogen Availability in Digestates from Full-Scale Biogas Plants Following Soil Application as Affected by Operation Parameters and Input Feedstocks. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2023, 24, 101675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Biogas Association. Exploring Digestate’s Contribution to Healthy Soils; European Biogas Association: Brussels, Belgium, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlin, J.; Herbes, C.; Nelles, M. Biogas Digestate Marketing: Qualitative Insights into the Supply Side. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 104, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 14040:2006; Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Principles and Framework. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/37456.html (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- ISO 14044:2006; Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Requirements and Guidelines. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- Ziegler-Rodriguez, K.; Josa, I.; Castro, L.; Escalante, H.; Garfí, M. Post-Treatment and Agricultural Reuse of Digestate from Low-Tech Digesters: A Comparative Life Cycle Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 894, 164992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angouria-Tsorochidou, E.; Seghetta, M.; Trémier, A.; Thomsen, M. Life Cycle Assessment of Digestate Post-Treatment and Utilization. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnolo, S.; Tinello, A.; Cavinato, C.; Zabeo, A.; Semenzin, E. Sustainability Assessment of Two Digestate Treatments: A Comparative Life Cycle Assessment. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2019, 18, 2193–2202. [Google Scholar]
- Styles, D.; Adams, P.; Thelin, G.; Vaneeckhaute, C.; Chadwick, D.; Withers, P.J.A. Life Cycle Assessment of Biofertilizer Production and Use Compared with Conventional Liquid Digestate Management. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7468–7476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfelli, F.; Cespi, D.; Ciacci, L.; Passarini, F. Application of Life Cycle Assessment to High Quality-Soil Conditioner Production from Biowaste. Waste Manag. 2023, 172, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Pera, A.; Sellaro, M.; Bencivenni, E. Composting Food Waste or Digestate? Characteristics, Statistical and Life Cycle Assessment Study Based on an Italian Composting Plant. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 350, 131552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, A.; D’Imporzano, G.; Zilio, M.; Pigoli, A.; Rizzi, B.; Meers, E.; Schouman, O.; Schepis, M.; Barone, F.; Giordano, A.; et al. Environmental Performance in the Production and Use of Recovered Fertilizers from Organic Wastes Treated by Anaerobic Digestion vs Synthetic Mineral Fertilizers. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 986–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temizel-Sekeryan, S.; Wu, F.; Hicks, A.L. Life Cycle Assessment of Struvite Precipitation from Anaerobically Digested Dairy Manure: A Wisconsin Perspective. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2021, 17, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Qi, S.; Wang, R.; Li, H.; Song, G.; Li, H.; Yin, Q. Life Cycle Assessment of Food Waste Energy and Resource Conversion Scheme via the Integrated Process of Anaerobic Digestion and Hydrothermal Carbonization. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 52, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, M.; Marini, M.; Angouria-Tsorochidou, E.; Pulselli, F.M.; Thomsen, M. Ex Ante Life Cycle Assessment and Environmental Cost-Benefit Analysis of an Anaerobic Digester in Italy. Clean. Waste Syst. 2022, 3, 100021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Jia, W.; Chen, T.; Ling, Y. Life Cycle Assessment of Food Waste Anaerobic Digestion with Hydrothermal and Ionizing Radiation Pretreatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 338, 130611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Jia, W.; Chen, T.; Ling, Y. Life-Cycle Assessment of Two Food Waste Disposal Processes Based on Anaerobic Digestion in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 293, 126113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Qiu, X.; Feng, H.; Yin, J.; Shen, D. Solid Digestate Disposal Strategies to Reduce the Environmental Impact and Energy Consumption of Food Waste-Based Biogas Systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 325, 124706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhan, X. Improved Environmental Sustainability and Bioenergy Recovery through Pig Manure and Food Waste On-Farm Co-Digestion in Ireland. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 125034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Wang, X.; Lim, E.Y.; Lee, J.T.E.; Ee, A.W.L.; Zhang, J.; Tong, Y.W. Life Cycle Assessment of Food Waste to Energy and Resources: Centralized and Decentralized Anaerobic Digestion with Different Downstream Biogas Utilization. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 150, 111489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhan, X. Environmental Sustainability Assessment of Pig Manure Mono- and Co-Digestion and Dynamic Land Application of the Digestate. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Islas, M.E.; Güereca, L.P.; Sosa-Rodriguez, F.S.; Cobos-Peralta, M.A. Environmental Assessment of Energy Production from Anaerobic Digestion of Pig Manure at Medium-Scale Using Life Cycle Assessment. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rumaihi, A.; McKay, G.; Mackey, H.R.; Al-Ansari, T. Environmental Impact Assessment of Food Waste Management Using Two Composting Techniques. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, N.; Khoshnevisan, B.; Lin, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H. Life Cycle Assessment of Anaerobic Digestion of Pig Manure Coupled with Different Digestate Treatment Technologies. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maria, F.; Sisani, F.; El-Hoz, M.; Mersky, R.L. How Collection Efficiency and Legal Constraints on Digestate Management Can Affect the Effectiveness of Anaerobic Digestion of Bio-Waste: An Analysis of the Italian Context in a Life Cycle Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshnevisan, B.; Tabatabaei, M.; Tsapekos, P.; Rafiee, S.; Aghbashlo, M.; Lindeneg, S.; Angelidaki, I. Environmental Life Cycle Assessment of Different Biorefinery Platforms Valorizing Municipal Solid Waste to Bioenergy, Microbial Protein, Lactic and Succinic Acid. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 117, 109493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Manandhar, A.; Li, G.; Shah, A. Life Cycle Assessment of Integrated Solid State Anaerobic Digestion and Composting for On-Farm Organic Residues Treatment. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Feng, D.; Xia, A.; Nizami, A.S.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, X.; Liao, Q.; Murphy, J.D. A Comparative Life Cycle Assessment of Electro-Anaerobic Digestion to Evaluate Biomethane Generation from Organic Solid Waste. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 196, 114347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou-Ttofa, L.; Foteinis, S.; Seifelnasr Moustafa, A.; Abdelsalam, E.; Samer, M.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Life Cycle Assessment of Household Biogas Production in Egypt: Influence of Digester Volume, Biogas Leakages, and Digestate Valorization as Biofertilizer. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 125468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Oever, A.E.M.; Cardellini, G.; Sels, B.F.; Messagie, M. Life Cycle Environmental Impacts of Compressed Biogas Production through Anaerobic Digestion of Manure and Municipal Organic Waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 306, 127156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timonen, K.; Sinkko, T.; Luostarinen, S.; Tampio, E.; Joensuu, K. LCA of Anaerobic Digestion: Emission Allocation for Energy and Digestate. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 1567–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koido, K.; Takeuchi, H.; Hasegawa, T. Life Cycle Environmental and Economic Analysis of Regional-Scale Food-Waste Biogas Production with Digestate Nutrient Management for Fig Fertilisation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 190, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinee, J.B. Handbook on Life Cycle Assessment Operational Guide to the ISO Standards. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2002, 7, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedkoop, M.; Oele, M. SimaPro Database Manual: Methods Library; PRé Consultants: Amersfoort, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Jolliet, O.; Margni, M.; Charles, R.; Humbert, S.; Payet, J.; Rebitzer, G.; Rosenbaum, R. IMPACT 2002+: A New Life Cycle Impact Assessment Methodology. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2003, 8, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EC-JRC-IES. JRC Annual Report 2011; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Liu, R.; Sun, C. A Review of Methane Production from Agricultural Residues in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Zhang, D.; Tang, Z.; Li, K.; Guo, H.; Niu, X.; Yi, L. Comparative Environmental and Economic Life Cycle Assessment of Dry and Wet Anaerobic Digestion for Treating Food Waste and Biogas Digestate. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 338, 130674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijazi, O.; Munro, S.; Zerhusen, B.; Effenberger, M. Review of Life Cycle Assessment for Biogas Production in Europe. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament; Council of the European Union. Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 November 2008 on Waste and Repealing Certain Directives (Text with EEA Relevance). 2008. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2008/98/oj/eng (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Gobierno de España. 2022. Real Decreto 1051/2022, de 27 de Diciembre, Por el que se Establecen Normas Para la Nutrición Sostenible en Los Suelos Agrarios. Boletín Oficial del Estado, 312, 163364–163440. Madrid, España. Available online: https://www.boe.es/eli/es/rd/2022/12/27/1051 (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- European Parliament. Regulation (EU) 2019/1009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 5 June 2019 Laying down Rules on the Making Available on the Market of EU Fertilising Products and Amending Regulations (EC) No 1069/2009 and (EC) No 1107/2009 and Repealing Regulation (EC) No 2003/2003 (Text with EEA Relevance). 2019. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2019/1009/oj (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Gobierno de España. 2022. Ley 7/2022, de 8 de Abril, de Residuos y Suelos Contaminados Para una Economía Circular. Boletín Oficial del Estado, 85, 1–118. Madrid, España. Available online: https://www.boe.es/eli/es/l/2022/04/08/7 (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Gobierno de España. 2013. Real Decreto 506/2013, de 28 de Junio, Sobre Productos Fertilizantes. Boletín Oficial del Estado, 164, 49488–49560. Madrid, España. Available online: https://www.boe.es/eli/es/rd/2013/06/28/506 (accessed on 29 June 2025).


| Reference | Location | Digestate Production | Digestate Uses | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AD Process | Digestate Fraction | Feedstock Supply | Fertilizer | Soil Conditioning | Animal Feed | Nutrient/Mineral Recovery | Biochar Preparation | Insect Transformation | ||
| [29] | China | LF | WWS | X | X | |||||
| [30] | China | M | SF | PM | X | |||||
| [19] | Italy | M | LF | PM | X | |||||
| [31] | Italy | M | SF, LF | PM, Ps, CM, MS, OW | X | |||||
| [32] | China | LF | WWS | X | ||||||
| [33] | China | SF, LF | FW | X | X | |||||
| [34] | China | SF, LF | FW | X | X | |||||
| [35] | Italy | M | SF | CM, pM, OW, MS | X | |||||
| [36] | Lithuania | CM, PM, pM | X | |||||||
| [37] | Lithuania | SF, LF | CM, PM, pM | X | ||||||
| [38] | Italy | SF, LF | AM | X | ||||||
| [39] | Poland | M | SF, LF | MS, CM, FW | X | |||||
| [40] | Italy | M | SF, LF | WWS | X | X | ||||
| [41] | Austria | T | LF | OMSW | X | |||||
| [42] | France | T | SF, LF | OMSW | X | |||||
| [6] | Poland | SF | WWS, cM, CM, PM, MS, FW | X | X | X | ||||
| [43] | China | MS | X | |||||||
| [44] | Ireland | LF | DS | X | ||||||
| [45] | Italy | T | SF, LF | FW | X | X | ||||
| [46] | Colombia | M | SF, LF | FW | X | |||||
| [25] | Italy | SF | FW | X | ||||||
| [47] | China | M | SF, LF | FW | X | |||||
| [48] | China | T | SF, LF | OW | X | |||||
| [49] | Poland | M, T | SF | OW | X | |||||
| [28] | Belgium | T | LF | FW | X | |||||
| [27] | UK | SF, LF | FW, OW | X | ||||||
| Ref | Goal/Results | Methodology | Feedstock | Post LCA Studies | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location | LCA Software | FU | System Boundaries | End Product | LCIA Method | Plant Biomass | Livestock | Waste | Sensitivity Analysis | Economic Study | |||||||||||||
| CtGa | CtGr | CtC | GatGr | GatGa | RS | GS | CW | TW | CM | PS/M | FW | IW | OW | ||||||||||
| A | [88] | Evaluate and compare treatments of DG for agricultural use. | Colombia | SimaPro 9.3 | 1 m3 treated DG | X | DG, compost | ReCiPe 2016-midpoint (H), IPCC 2021 | X | X | X | ||||||||||||
| B | [89] | Evaluate and compare 3 DG treatment scenarios for use as a biofertilizer. | France | SimaPro 7.3.3 | 1 kg dry matter raw DG | X | Biofertilizer | ReCiPe at midpoint (H) | X | X | |||||||||||||
| C | [59] | Evaluate and compare DG treatment scenarios for its use as a biofertilizer. | China | Open LCA | 1 ton raw DG | X | Biofertilizer, compost | CML 2001 | X | X | X | ||||||||||||
| D | [90] | Evaluate and compare two types of DG treatment for soil application. | Italy | SimaPro 8.3 | 1 ton treated DG | X | Soil improvers | ReCiPe H midpoint, endpoint | X | ||||||||||||||
| E | [91] | Comparison between direct use of DG and use of fertilizers derived from DG. | Sweden | 1 m3 DG | X | Biofertilizer | CLM-baseline | X | |||||||||||||||
| F | [92] | Evaluate impacts of an industrial plant combining AD with vermicomposting. | Italy | SimaPro 9.4 | 1 t packaged soil aconditionator | X | BG, soil conditioner | ReCiPe 2016 | X | X | |||||||||||||
| G | [93] | Evaluate and compare the use direct biocompost and biocompost from DG. | Italy | 1 mg compost used | X | Compost | ReCiPE 2016-midpoint | X | |||||||||||||||
| H | [94] | Evaluate and compare the production and use of recovered and mineral fertilizers. | Italy | SimaPro 9.1.1. | Fertilization of 1 ha of maize | X | Two types of biofertilizers and BG | ReCiPe 2016 midpoint, end point | X | Monte Carlo | |||||||||||||
| I | [95] | Evaluate the environmental impacts of struvite recovery from LF of DG. | USA | SimaPro 8.5.2 | 1 kg LF DG & 1 kg of struvite. | Struvite and BG | TRACI 2.1, BEES (water footprint) | X | X | ||||||||||||||
| J | [96] | Compare coupling AD hydrothermal carbonization vs. AD or composting alone. Best results: AD with hydrothermal carbonisation, followed by untreated AD. | China | SimaPro 9.4.0.1 | 1 ton FW | X | BG, DG and hydrochar | ReCiPe 2016 | X | X | |||||||||||||
| K | [97] | Evaluation of eco-industrial system integrating micro-scale AD and solid-state fermentation to produce RE and bioproducts. | Italy | SimaPro 9.1 | 1 ton wet weight of biowaste treated | X | Electricity heat, biofertilizer and compost | ReCipe 2016 midpoint, end point | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||
| L | [98] | Comparing pretreatment technologies (hydrothermal and ionic radiation) applied to the AD of FW. | China | Open LCA | 1 ton FW | X | Electricity, Fertilizer treated water and biodiesel | X | |||||||||||||||
| M | [99] | Evaluating impacts of liquid AD and solid-liquid mixed AD processes for FW | China | eBalance | 10 ton FW | X | BG and DG | CML 2001 | X | X | |||||||||||||
| N | [100] | Evaluating the impact of 3 solid DG management methods: incineration, composting, and landfill. | China | 1 ton FW | X | BG for electricity and DG | CML 2001 | X | |||||||||||||||
| O | [101] | Compare impacts of co-digesting PM and FW vs. impacts of existing management practices of PM and FW. | Ireland | SimaPro | PM 16 ktpa and FW 10 ktpa | X | BG for CHP and DG | CLM-IA, 2016 | X | X | X | ||||||||||||
| P | [102] | Comparison of incineration and different AD configuration wtih different BG applications. | Singapore | Gabi 8.7 | 1 ton FW | X | BG and DG | ReCipe 2016 | X | X | |||||||||||||
| Q | [103] | Evaluation of 3 PM management methods. | Ireland | SimaPro | PM: 15,070 m3/yr and grass sillage: 1.3 ktpa | X | Heat, electricity, diesel, biofertilizer | CML-IA baseline | X | X | X | ||||||||||||
| R | [104] | Compare electricity generation with composting vs. BG flaring and conventional methods. | Mexico | SimaPro 8.1.1.6 | 1 ton of SM and LM | X | BG, electricity, DG and liquid effluents | CML-IA 2013 | X | X | |||||||||||||
| S | [105] | Evaluate and compare environmental impact associated of two composting techniques. | Qatar | SimaPro 7.1.0 | 1 ton FW | X | BG and compost | CML-baseline 2000 | X | X | |||||||||||||
| T | [106] | Evaluate the impacts AD combined with different types of DG treatment for soil application. | China | 1 ton PM | X | BG, compost, biofertilizer | Impact 2002 + | X | X | ||||||||||||||
| U | [107] | Evaluate relationship between collection efficiency, legal restrictions on DG use, and performance of AD | Italy | SimaPro 9 | 1 mg biowaste | X | BG and fertilizers | Midpoint ILCD 2011+, Impact 2002+ for endpoint for HT | X | ||||||||||||||
| V | [108] | Evaluate use of OFMSW to generate bioenergy and high-value products through biopulp-based biorefineries | Denmanrk | SimaPro 8.5 | 1 ton biopulp | X | BG and DG | Impact 2002+ | X | ||||||||||||||
| W | [109] | Evaluate environmental impacts of waste treatment through AD, composting, and AD plus composting. | China | Green delta | 1 ton dairy manure | X | BG and compost | TRACI 2.1. | X | X | X | ||||||||||||
| X | [110] | Compare impacts of AD and electro-AD of various types of waste. | China | Open LCA | 1 MJ bioCH4 | X | bioCH4, biofertilizers | X | X | X | |||||||||||||
| Y | [111] | Evaluate environmental impact of domestic BG digesters. | Egypt | SimaPro 9.1 | 1 m3 BG | X | BG and DG as residue | ReCipe 2008 at midpoint, endpoint | X | X | |||||||||||||
| Z | [112] | Evaluate and compare 2 scenarios in partial and full substitution options of AD of Manure and MOW. | Europe | 1 MJ LHV compressed bioCH4 | X | BG and DG | EF 3.0 | X | X | X | |||||||||||||
| AA | [113] | Evaluate emissions of complete AD process. | Finland | Semipros | MJ energy and kg N | X | BG and DG | X | |||||||||||||||
| AB | [114] | Evaluate management of a BG plant from environmental, energy, and economic perspectives | Thailand | MilLCA | 1 MJ bioCH4 | X | Impact Assessment Endpoint | X | X | X | |||||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martín-Sanz-Garrido, C.; Revuelta-Aramburu, M.; Santos-Montes, A.M.; Morales-Polo, C. A Review on Anaerobic Digestate as a Biofertilizer: Characteristics, Production, and Environmental Impacts from a Life Cycle Assessment Perspective. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8635. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158635
Martín-Sanz-Garrido C, Revuelta-Aramburu M, Santos-Montes AM, Morales-Polo C. A Review on Anaerobic Digestate as a Biofertilizer: Characteristics, Production, and Environmental Impacts from a Life Cycle Assessment Perspective. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(15):8635. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158635
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartín-Sanz-Garrido, Carmen, Marta Revuelta-Aramburu, Ana María Santos-Montes, and Carlos Morales-Polo. 2025. "A Review on Anaerobic Digestate as a Biofertilizer: Characteristics, Production, and Environmental Impacts from a Life Cycle Assessment Perspective" Applied Sciences 15, no. 15: 8635. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158635
APA StyleMartín-Sanz-Garrido, C., Revuelta-Aramburu, M., Santos-Montes, A. M., & Morales-Polo, C. (2025). A Review on Anaerobic Digestate as a Biofertilizer: Characteristics, Production, and Environmental Impacts from a Life Cycle Assessment Perspective. Applied Sciences, 15(15), 8635. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158635







