Abstract
This study investigates the surface modification of Ti-6Al-4V alloy through the electrical discharge machining (EDM) process to improve its suitability for orthopedic and dental implant applications. The analysis focused on evaluating the morphological, wettability, roughness, hardness, and biocompatibility properties of the modified surfaces. Samples were subjected to different dielectric fluids and polarities during EDM. Subsequently, optical microscopy, roughness measurements, Vickers microhardness, contact angle tests, and in vitro cytotoxicity assays were performed. The results demonstrated that EDM processing led to the formation of distinct layers on the sample surfaces, with surface roughness increasing under negative polarity by up to ~304% in Ra and 305% in Rz. Additionally, wettability measurements indicated that the modified surfaces presented a lower water contact angle, which suggests enhanced hydrophilicity. Moreover, the modified samples showed a significant increase in Vickers microhardness, with the highest value reaching 1520 HV in the recast layer, indicating improvements in the mechanical properties. According to ISO 10993-5, all treated samples were classified as non-cytotoxic, presenting RGR values above 75%, similar to the untreated Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Therefore, it is concluded that surface modification through the EDM process has the potential to enhance the properties and safety of biomedical implants made with this alloy.
1. Introduction
Among metallic materials, titanium alloys and specifically Ti-6Al-4V are widely employed as implants for the biomedical industry owing to the favorable properties such as biocompatibility, resistance to corrosion in the body fluids [1,2,3,4], a high strength/density ratio [5,6,7], excellent mechanical strength, including tensile and fatigue resistance, as well as a Young’s modulus comparable to or closer to that of the natural human bone [8,9,10].
These titanium-based metals are bioinert and do not form chemical bonds with bone tissue after implantation. Osseointegration results from both physical and chemical interactions between the implant surface and bone tissue. However, in the case of titanium and its alloys, this process is primarily governed by mechanical interlocking, without the occurrence of chemical bonding, which may prolong healing time [11].
Thus, surface modifications have been necessary for materials used in implants, as they contribute significantly to the improvement of osseointegration [12,13]. Apart from surface topography and roughness, surface properties such as chemical composition or surface energy have been reported to influence interfacial reactions of biomedical devices [14,15,16,17,18]. According to the ASME B46.1 standard [19], surface topography refers to the overall morphology of the surface, encompassing all its geometrical features at different scales. Roughness, in turn, refers to the random small-scale irregularities, which can be quantified by parameters such as Ra and Rz. Thus, roughness is a quantitative aspect within the broader context of surface topography [20].
Several techniques have been developed and applied to Ti-6Al-4V to enhance the properties required for biomedical application [21,22,23]. More recent studies have reinforced the role of EDM in biomedical applications, particularly in improving surface roughness, wettability, and biofunctionality [24,25,26,27,28]. Moreover, titanium and its alloys are difficult to machine due to several inherent properties of the material. Titanium is chemically very reactive with almost all cutting tool materials and its low thermal conductivity and elastic modulus range also impair machinability. Therefore, traditional machining techniques are often unable to machine this alloy economically [29].
Electrical discharge machining (EDM) presents a potential solution for the direct fabrication of complex shapes commonly observed in surgical implants [30]. It is a technique traditionally used to remove material from metal workpieces and form cavities by applying electrical discharge [31]. However, beyond its conventional applications, EDM can also be used to deposit materials onto the surface of the machined sample by using dielectric fluids containing conductive powders or chemical elements of interest [32]. This approach can enhance the properties of the workpiece through doping [33,34,35]. Powder-mixed EDM, in particular, has demonstrated promising results in enhancing surface properties through the incorporation of bioactive particles such as hydroxyapatite [36].
Typically, the tool electrode is set to a positive polarity (anodic), while the workpiece is set to a negative polarity (cathodic) [37]. In addition to polarity, the electrode material also significantly influences the surface characteristics resulting from EDM. Copper electrodes can lead to the deposition of metallic residues, such as copper ions, on the machined surface. It has been shown that even low concentrations of these ions can induce cytotoxic effects, depending on the location of the cells and the exposure time [38]. Graphite electrodes, on the other hand, tend to generate surface layers composed of carbon. Although this aspect is not widely discussed in the EDM literature, some studies indicate that carbon-containing surfaces do not impair cell adhesion or proliferation, making graphite a promising alternative for biomedical applications [39,40].
When a potential difference is applied between the electrodes, an electric field is established in the dielectric fluid, causing electrons to migrate toward the anode and positive ions toward the cathode. This movement results in collisions with molecules and particles in the dielectric fluid, generating energy and forming a plasma channel. Electrical discharges occur through this plasma channel, heating the workpiece and causing localized melting and re-solidification of the material [41,42,43]. The dielectric fluid helps absorb and remove the heat generated by the discharges from both the tool electrode and the workpiece [44]. The characteristics of the resulting coating depend on the applied polarity, machine parameters, dielectric fluid, and the tool electrode used [45,46].
Previous studies have investigated the effects of EDM processing on Ti-6Al-4V, analyzing surface morphology, roughness, hardness, and modifications induced by different machining parameters [47,48]. These parameters were explored in terms of their influence on surface characteristics, and different dielectric fluids were evaluated for their role in modifying surface properties. However, none of them assessed the in vitro biocompatibility of EDM-treated Ti-6Al-4V, particularly when using fluorine- and calcium/phosphorus-based dielectric fluids. To date, no studies have conducted a cytotoxicity evaluation of EDM-modified Ti-6Al-4V using these dielectric fluids [49,50].
This study expands upon previous research by introducing an innovative approach that combines two polarity conditions and distinct dielectric fluids, containing fluorine/phosphorus and calcium/phosphorus, to modify the Ti-6Al-4V alloy through the EDM process. Furthermore, it presents, for the first time, an in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of the surfaces obtained with these dielectric fluids applied under both polarity conditions. These findings contribute to a better understanding of how these parameters may influence the surface characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V for biomedical implants applications.
To build on these insights, this work offers a comprehensive and novel analysis of EDM-modified titanium surfaces. The influence of dielectric composition and tool polarity was systematically investigated under controlled conditions. Multiple characterization methods were employed, including optical microscopy, surface roughness measurements, microhardness testing, contact angle analysis, and in vitro cytotoxicity assays. This combination of techniques allowed for a detailed evaluation of morphological, mechanical, physicochemical, and biological properties. The integrative approach not only confirms the surface changes promoted by EDM but also establishes a solid framework for optimizing titanium-based implants for biomedical applications.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
The samples were obtained from a cylindrical bar of Ti-6Al-4V alloy with a predominantly α + β microstructure. The alloy used in this study was Ti-6Al-4V ELI (Extra Low Interstitial), a variant specifically developed for biomedical applications due to its reduced interstitial content and enhanced biocompatibility. This material complies with internationally recognized standards for surgical implants, such as ASTM F136 [51] and ISO 5832-3 [52], ensuring its suitability for use in load-bearing biomedical devices. In α + β titanium alloys, the α phase has a hexagonal close-packed (HCP) crystal structure and contributes to thermal stability, corrosion resistance, and high mechanical strength. The β phase, with a body-centered cubic (BCC) structure, enhances ductility, formability, and toughness. The relative volume fraction of these phases depends on the thermomechanical processing. In Ti-6Al-4V ELI, which is widely applied in biomedical devices, the β phase typically ranges from 5% to 30% by volume, providing a favorable combination of fatigue resistance, strength, and biological compatibility [53].
The samples were fabricated in the desired dimensions using conventional machining by cutting and turning to serve as electrodes in the experiments. Facing and finishing operations were carried out on the frontal face of the electrode for the flattening operation. The dimensions of the workpiece electrode were 9.5 mm in diameter and 12.0 mm in height, and the diameter of the tool electrode was 15.0 mm with 95.0 mm in height. Two samples from each experimental condition were sectioned along their longitudinal axis, perpendicular to the face, and repositioned before being machined using electrical discharge machining (EDM), to analyze the modifications at the lateral section. The chemical composition of the material is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Chemical composition in weight (average%) of the Ti-6Al-4V alloy.
Furthermore, a cylindrical graphite bar was used for the tool electrode, and two different dielectric fluid conditions were employed in the experiment.
The first, termed DF1-F was an aqueous solution containing 0.10 M of hydrofluoric acid () and 0.20 M of phosphoric acid (), with a final pH of 1.5. The second termed as DF2-Ca was an aqueous solution containing 0.05 M of calcium dichloride dihydrate (.) and 0.03 M of sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate (.), acidified with 37% hydrochloric acid () to reach a final pH of approximately 3.5. Both solutions were prepared using reagent-grade chemicals and deionized (DI) water. These fluids were selected for their ability to enrich the surface with elements such as oxygen, phosphorus, and calcium, all of which are known to enhance osseointegration in biomedical applications [50,54]. After EDM processing, they were completely eliminated from the samples through post-processing cleaning and sterilization procedures.
Specifically, for the tests performed with DF1-F, which contains fluorine, a small dielectric reservoir was used to prevent corrosion in the main tank, similar to previous studies [49]. A die sinking type EDM machine (ELETROPLUS EDM-540, from SERVSPARK manufacturer) was used to carry out the experimentation.
Experiments involved two different discharge polarities in separate experiments. One with negative polarity (i.e., the tool electrode (−) and work piece (+)) and another with positive polarity (i.e., the tool electrode (+) and work piece (−)). The use of both negative and positive polarities was based on the understanding that discharge polarity significantly affects the electrical discharge machining (EDM) process. Including both conditions may allow for the evaluation of how polarity influences not only surface morphology but also the incorporation of bioactive elements and biocompatibility [50]. Each process condition was carried out at least three times and referred as indicated in Table 2.

Table 2.
Sample labels and composition of dielectric fluids.
The circulation system responsible for the experimental dielectric fluids was not employed during the tests, as the containers did not allow for proper adaptation of the pump due to their dimensions. Therefore, the dielectric fluids were considered static throughout the experiments. Others corresponding process parameters are given in Table 3.

Table 3.
EDM machine parameters.
2.2. Morphological and Chemical Characterization of Surface
The microstructure of the modified surfaces was observed by optical microscopy, using a Fortel IM-713 microscope (Fortel Industrial e Tecnica Ltda., Sao Paulo, Brazil). The sectioned samples were prepared for analysis following the standard metallographic method [50]. Hot compression mounting was used to hold the specimens. After polishing with silicon carbide sandpaper (up to 1000 mesh) the samples were polished using diamond paste of 9 μm, 3 μm, and 1 μm. Then, the samples were etched using Kroll reagent for 20 s. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images were also taken from samples with SSX-550 Superscan (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) microscope operated at 15 kV and equipped with an energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) unit (Shimadzu). Prior to SEM examination, samples were coated with a thin gold film by sputtering.
2.3. Roughness Measurement
Surface roughness measurements were performed using a TESA Technology Rugosurf 20 roughness gauge under controlled conditions. The instrument complies with ISO 3274, Class 1 [55], ensuring high-precision profilometric measurements in accordance with international metrological standards. Prior to testing, the instrument was calibrated and verified to be within the acceptable tolerance range.
For each Ti-6Al-4V sample, three roughness measurements were taken at different locations on the machined surface to ensure repeatability. Before testing, surface regions were visually inspected to avoid evident cracks, cavities, or discontinuities, ensuring representative areas were selected. The arithmetic mean roughness (Ra) and the mean roughness depth (Rz) were obtained for each sample. The mean values and standard deviations were then calculated to assess surface quality and measurement consistency. All measurements were conducted with a cutoff length of 0.8 mm.
2.4. Vickers Microhardness
The microhardness of the samples was measured on the lateral section in three regions, (1) Recast Layer (RL); (2) Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ), and (3) Base Metal (BM), by means of the Shimadzu HMV-2T microhardness tester. The load defined in the microdurometer was 0.05 kgf and the indentation time was 15 s. The hardness values of the lateral section for each sample region were determined by averaging five measurements (n = 5) for each condition studied.
2.5. Contact Angle Test
The contact angle measurement was carried out in static mode using the sessile drop method, with a deionized water droplet and a Ramé–Hart goniometer. The experiments were conducted at 25 °C and 50% relative humidity. The droplet (~3 μL) was manually formed and dispensed onto the sample surface using a microsyringe. The measurement was performed approximately 5 s after deposition, once the droplet had stabilized. The contact angle was determined using the DROPimage Advanced software package, which calculates it based on a contour fitting algorithm using cubic interpolation and the Axisymmetric Drop Shape Analysis (ADSA) method. Curve fitting was performed using least squares regression, and the final angle was computed from the theoretical profile obtained by numerical integration of the Young–Laplace equation. The reported result corresponds to the mean value of five different measurements of water droplets on the surface for all studied sample conditions. The accuracy of the measurements is approximately ±0.1°, according to the manufacturer.
2.6. In Vitro Test
In vitro testing was conducted to assess the cytotoxicity of the samples when in contact with human cells. This assay was performed with the approval of the Institutional Review Board of Colorado State University. Human adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) at passage four were isolated and generously provided by Dr. Kimberly Cox-York, from the Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition at Colorado State University.
Prior to biological studies, samples were immersed in an ultrasonic bath with pure acetone for 10 min and rinsed gently in deionized water. This process was repeated twice, and an additional cleaning step with deionized water was performed to remove any potential residues of acetone. Then, the samples were placed into the wells of a culture plate, where 70% ethanol was added and maintained for 25 min to promote sterilization. After that the ethanol was aspirated, and the samples were washed with deionized water twice, leaving the plate open to allow for evaporation until drying. A total of three samples were tested for each experimental condition to ensure reproducibility and statistical reliability.
2.6.1. Cell Culture
The volume of 1 mL of frozen cells at −80 °C was diluted in 6 mL of culture medium. The solution was centrifuged at 1000 rpm for 10 min, and the supernatant was aspirated. The pellet was reconstituted in 1 mL of culture media containing DMEM, 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (P/S). This 1 mL solution was added to the cell growth flask along with 12 mL of culture media. The flask was placed in the incubator with 5% at 37 °C. Cells were grown for 7 days, and every 2 days, old media were replaced with fresh media.
After 7 days, the culture medium was aspirated and cells were trypsinized in the flask with 5 mL of Tryple Express, followed by incubation for 5 min with 5% at 37 °C. After that, 7 mL of medium was added to neutralize the Tryple Express and the solution was centrifuged for 10 min. The supernatant was discarded, and the pellet was reconstituted in 1 mL of media.
2.6.2. Cytotoxicity
The lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) assay was used as a quantitative test for the toxicity of the machined samples. The titanium samples pre-sterilized were placed into a 48-well culture plate, and in the sequence, the cells were seeded into the wells at the concentration of 2.0 × 104 cells/chamber. Cells were then allowed to attach for 24 h at 37 °C in a humidity-controlled incubator with 5% . After 24 h, cells in three parallel wells were lysed with Triton at 10% (v/v) from the media to determine the maximum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) released and kept incubated for 45 min.
Afterward, 50 µL of the medium that had reacted with titanium samples was transferred from each well to a new 96-well plate. Equal amounts of lactate dehydrogenase assay substrate, assay dye, and LDH assay cofactor (Invitrogen™ CyQUANT™ LDH Cytotoxicity Assay Kit, Waltham, MA, USA) were then added, and the plate was incubated for an additional 30 min. Subsequently, 50 µL of 1.0M HCl was added to each well to stop the reaction and the absorbance was read at 490 nm and 680 nm (FLUOstar Omega—BMG LABTECH, Ortenberg, Germany).
Cytotoxicity was assessed according to ISO 10993-5 [56], using relative growth rate (RGR) calculated as shown in Equation (1).
where is related to the absorbance measured on the wells that contained the group of samples analyzed. The term refers to the negative control (i.e., only the medium with cells in spontaneous activity), whereas corresponds to the positive control (i.e., wells containing cells lysed with Triton). The means and standard deviations of the RGR results were obtained and statistically analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) at 5% significance level (p < 0.05). This analysis was performed to determine whether there were significant differences in cytotoxicity among the samples. If p < 0.05, significant differences in cytotoxicity were observed. Conversely, if p ≥ 0.05, no significant difference was found, indicating that all samples exhibited similar cytotoxic effects.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological Aspects of the Surface
This study investigates the surface modification of Ti-6Al-4V samples machined using electrical discharge machining (EDM), aiming to evaluate their morphological, chemical, and mechanical characteristics for potential biomedical applications. Specifically, the morphology, chemical composition, and hardness of the recast layer were analyzed, along with the influence of two dielectric fluids and different electrode polarities. In addition, in vitro cytotoxicity analysis was performed to assess the biocompatibility of the modified surfaces.
Considering the critical role of surface roughness (at the micrometric scale) and chemical composition in the performance of biomedical devices, two distinct dielectric fluids were selected for the EDM process. Beyond modifying surface topography, EDM can also enable ionic implantation, depending on the chemical nature of the dielectric fluid used [49,57].
One significant chemical property of the surfaces in such biomedical devices is related to the control of the oxide layer formation [3,58]. Thereby, a fluid-containing fluorine was selected due to its high electronegativity and pronounced corrosive effect, which makes it able to chemically etch the surface of titanium parts. Another selected fluid was composed of calcium and phosphorus ions, known for their role in skeletal composition and involvement in bone repair processes.
Samples subjected to EDM, not only using dielectric fluids DF1-F but also with DF2-Ca, acquired a rough visual and tactile appearance on the surfaces exposed to electrical discharges in both polarities, as shown in the insets in Figure 1.
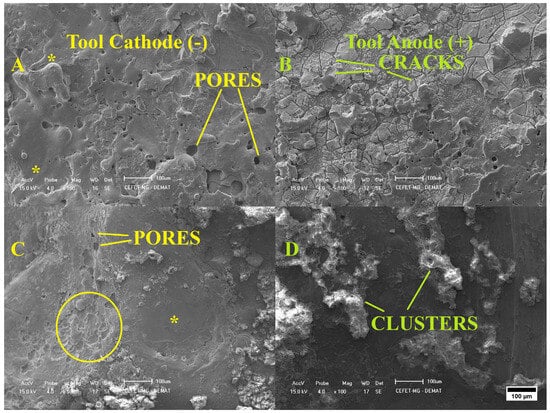
Figure 1.
SEM images of Ti-6Al-4V workpieces after machined at (A) negative and (B) positive polarity using DF1-F, and (C,D) machined with DF2-Ca in the negative and positive polarities, respectively (100× magnification). Inset: Rippled structures (solid circle) and molten and re-solidified material (asterisk) can be observed.
The SEM micrograph in Figure 1A shows the surface topography of samples machined with DF1-F in negative polarity. The surface exhibits a microrelief formed by molten and re-solidified material, along with the presence of small pores. Samples processed with the same fluid but under positive polarity, as shown in Figure 1B, exhibited deep and wide cracks. The surface resembled a scaly structure, with features distributed across the image in a gradient of different sizes. This morphological pattern is commonly associated with materials that develop high residual stress during solidification, which can lead to surface cracking [59]. Additionally, distinct darkened regions were observed, which is consistent with the intense heat generated during discharge. This thermal energy may partially burn the tool, producing carbon compounds that can react with molten titanium and lead to the formation of metallic carbides [60].
Figure 1C,D show the surface morphologies of samples machined in DF2-Ca, a fluid formulated with calcium and phosphorus elements, using negative and positive polarities, respectively. In Figure 1C, the surface exhibits a broad region of molten and re-solidified material, with asymmetrical rippled structures and tiny open pores visible on the left side of the image. In the Figure 1D, the deposited layer consists of prominent islands distributed over the titanium surface, exhibiting a non-uniform morphology. These regions resemble discontinuous clusters of elongated structures, encrusted in a manner similar to splashes of viscous material approximately 50 µm in width. The formation of such morphologies can be explained by the thermal and physicochemical mechanisms involved in the EDM process. In this process, electrical energy is converted into thermal energy due to the plasma channel formed between the two electrodes. The resulting temperature is sufficient to melt the surface of both the workpiece and the tool. At these extreme temperatures, the dielectric medium breaks down, altering the workpiece surface by incorporating dissociated dielectric materials. Additionally, the subsurface experiences a heat-affected zone that does not melt but is exposed to high temperatures [61,62,63,64].
Figure 1A,C show the surfaces machined under negative polarity conditions, while Figure 1B,D correspond to the surfaces obtained under positive polarity. To better understand these results, Figure 2 illustrates the schematic representation of the mechanisms involved in EDM machining with two different dielectric fluids and electrode configurations.
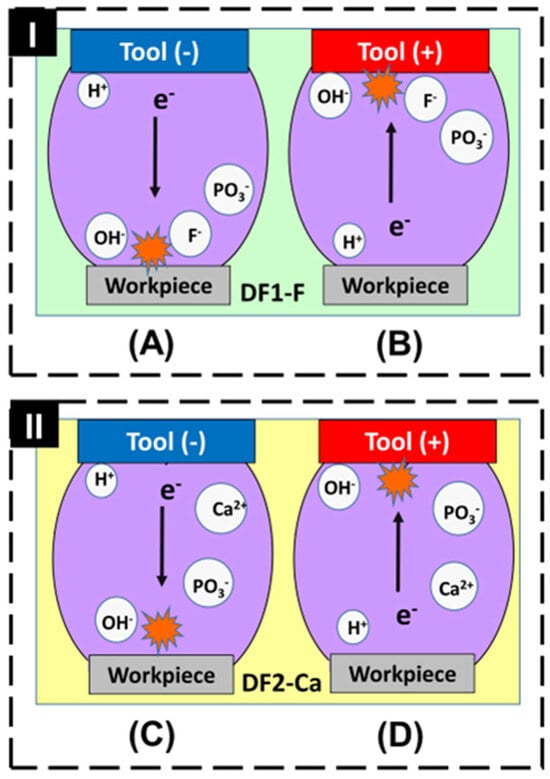
Figure 2.
Scheme of the ions in the inter electrode space with (I) DF1-F and (II) DF2-Ca fluids, in negative (A,C) and positive (B,D) polarities.
In the negative polarity configuration, represented in Figure 2A,C, a greater number of electrons is emitted from the tool electrode and accelerated toward the workpiece, resulting in more intense localized heating. Consequently, a larger volume of workpiece material is melted and evaporated, which leads to a higher material removal rate (MRR) and increased molten pool formation on the surface. These effects contribute to the development of a rougher topography, with more pronounced surface irregularities when compared to positive polarity [65]. Although the surfaces in Figure 1A,C exhibit a visually more uniform appearance in the top-view SEM images, this impression may not accurately reflect the true morphological complexity. The homogeneous distribution of deep pores and re-solidified material can result in a surface that appears smooth but conceals the presence of more pronounced features.
In contrast, the positive polarity configuration, represented in Figure 2B,D, results in lower energy transfer to the workpiece, as fewer electrons are directed toward its surface. This leads to less intense localized heating, producing a smaller molten pool and a lower material removal rate (MRR). Consequently, the thermal effects are milder, which favors the formation of a modified layer with a less rough surface [65]. However, this characteristic is not easily noticeable in the top-view SEM images of Figure 1B,D, which display a visually more irregular surface morphology, with the presence of clusters and cracks. This is because the top-view perspective limits the ability to assess the actual depth of surface features. A cross-sectional view may be more suitable to reveal the reduction in roughness associated with the lower thermal input under positive polarity.
The energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) spectra and the corresponding elemental composition tables for the samples are presented in Figure 3.
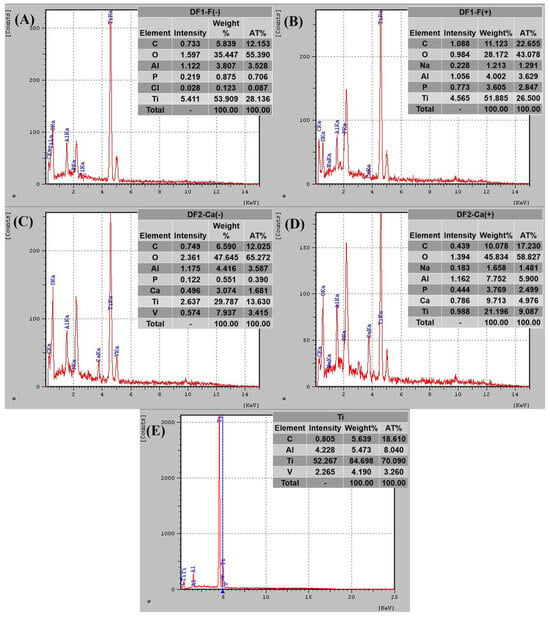
Figure 3.
EDS spectra and elemental composition at top surface for samples machined using tool polarity (A) negative and (B) positive with DF1-F, and (C,D) machined with DF2-Ca in the negative and positive polarities, respectively. The untreated Ti-6Al-4V sample is shown in (E) for reference.
Titanium, oxygen, and aluminum were detected on the machined surfaces of all five samples. Notably, the oxygen peak was more prominent in the sample machined under negative polarity (Figure 3A) compared to the one processed under positive polarity (Figure 3B). Furthermore, the atomic percentage values obtained from the EDS analysis indicate 35.39% oxygen in the DF1-F(−) condition versus 25.62% in the DF1-F(+) condition, suggesting a higher degree of surface oxidation. The presence of titanium oxides was expected, as electrical discharges increase local temperature and oxygen availability, promoting oxide formation [3], which can enhance the biocompatibility of the alloy.
The EDS results in Figure 3C,D confirmed the presence of calcium on the surfaces machined with DF2-Ca. This suggests that chemical species were transferred from the dielectric fluid to the workpiece, which can contribute to increased surface bioactivity and lead to potential improvements in osseointegration. All machined samples also showed higher surface carbon concentrations compared to the untreated alloy (Figure 3E), especially under positive polarity (Figure 3B,D). This behavior may be related to the melting and deposition of material from the graphite electrode [66,67]. High carbon concentrations are commonly associated with the EDM process, particularly due to material transfer from the graphite electrode during electrical discharges. Studies indicate that the carbon structures formed during EDM are biocompatible and do not impair cell adhesion or proliferation. Furthermore, these structures are considered bioinert and well tolerated by biological tissues [39,40].
3.2. Optical Microscopy (MO)
In Figure 4, the cross-sections of the layers modified by machining in DF1-F solution with the tool electrode in negative (Figure 4A) and positive (Figure 4B) polarities are represented by MO. As shown in Figure 4, the modified layer (ML) of samples machined with DF1-F under both polarities was approximately 30 µm thick and exhibited pores and surface irregularities. Under positive polarity, the surface appeared flatter, whereas samples machined under negative polarity displayed more re-entrant features and pronounced irregularities.
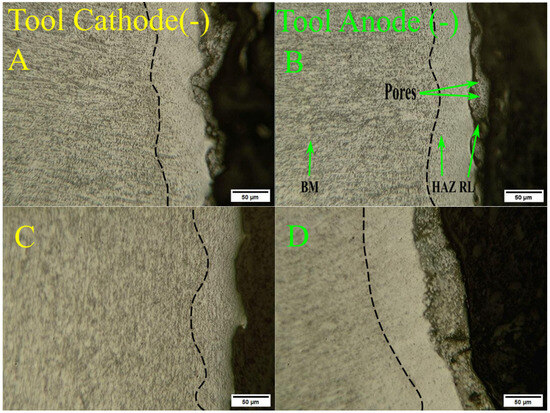
Figure 4.
Cross-sectional optical micrographs of workpieces EDMed at (A) negative and (B) positive polarity using DF1-F, and (C,D) machined with DF2-Ca in the negative and positive polarities, respectively, where the dotted dark line indicates the presence of the HAZ layer.
For samples machined with DF2-Ca under negative polarity, the corresponding microstructure is shown in Figure 4C. In this condition, the recast layer was not evident and appeared to be absent along most of the surface. In contrast, for samples machined with DF2-Ca under positive polarity, the recast layer is visible in Figure 4D, with a measured thickness of approximately 45 µm—greater than that observed in samples treated with DF1-F. Another relevant feature is the significant presence of micro-cracks within the recast layer, which may compromise structural integrity and increase the risk of premature material failure [68].
3.3. Roughness Measurement
The Ra and Rz roughness values obtained through the measurements are presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Roughness and standard deviation of the machined samples with the fluids and polarities used.
The results showed that the DF1-F(−) condition (phosphorus and fluorine under negative polarity) produced the highest roughness values among all samples. The arithmetic mean roughness (Ra) reached 17.37 ± 2.94 µm, while the mean roughness depth (Rz) reached 89.43 ± 12.12 µm. High surface roughness is beneficial for biomedical applications, as it promotes cell adhesion and osseointegration in metallic implants [14,16].
The DF2-Ca(−) condition (calcium under negative polarity) exhibited the second highest values (Ra ≈ 15.44 ± 3.64 µm; Rz ≈ 71.65 ± 16.44 µm), followed by the DF2-Ca(+) condition (calcium under positive polarity), which resulted in intermediate measurements (Ra ≈ 12.09 ± 1.47 µm; Rz ≈ 58.69 ± 9.07 µm). These results suggest that negative polarity enhances surface roughness, likely due to the greater intensity of electrical discharge erosion and the formation of irregular recast layers during the electrical discharge machining (EDM) process [49,50].
In contrast, the DF1-F(+) condition (phosphorus and fluorine under positive polarity) resulted in significantly lower values (Ra ≈ 5.86 ± 1.37 µm; Rz ≈ 36.16 ± 8.72 µm). This reduction may be attributed to more homogeneous material deposition, leading to a smoother finish.
The reference sample (not machined by EDM) exhibited the lowest roughness values (Ra ≈ 4.06 ± 0.48 µm; Rz ≈ 22.10 ± 3.63 µm), confirming that the EDM process significantly modifies the surface topography. Smoother surfaces, such as the reference sample and the DF1-F(+) condition, exhibited lower roughness values, which may limit their ability to promote cell adhesion. Rougher surfaces, on the other hand, tend to increase the contact area and improve cell–surface interactions, favoring attachment and proliferation, factors that are crucial for effective osseointegration [69].
Overall, DF1-F(−) proved to be the most effective condition for increasing surface roughness, reinforcing the role of phosphorus and fluorine under negative polarity in modifying surface topography. These findings highlight the potential of this condition for biomedical applications, particularly those requiring enhanced cell adhesion to improve implant integration and tissue compatibility [70,71,72,73,74].
3.4. Vickers Microhardness
For mechanical analysis, Vickers microhardness experiments were performed on the cross-section of enriched samples to characterize the two typical regions produced by the EDM process, as illustrated in Figure 5.
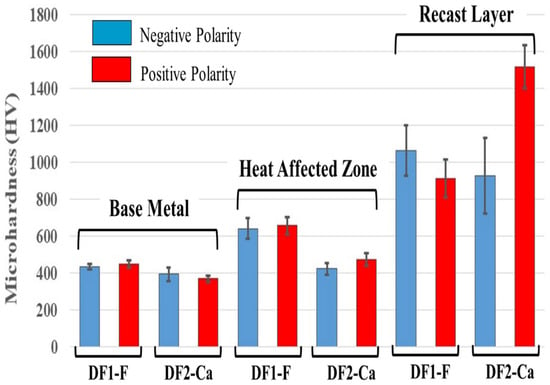
Figure 5.
Data representing means and standard deviations (n = 5) of Vickers microhardness from three regions of each group of machined samples.
The hardness trend of the workpiece surface showed a similar distribution in each zone (base metal, heat-affected zone, and recast layer) from the lower to the upper part of Ti-6Al-4V alloy for each dielectric fluid used, as shown in Figure 5. Two types of behavior for hardness are observed in the thermally affected zone, and a significant hardening in the recast layer compared to the base metal, for both polarities.
The data showed that the heat-affected zone (HAZ) of samples machined by EDM with DF1-F fluid exhibited the highest average hardness, approximately 645 HV, which is about 200 HV higher than that of the base material (BM). For samples processed with DF2-Ca fluid, the hardness was about 450 HV, which was very similar to the BM.
In the recast zone, the values observed ranged from 910 HV to 1060 HV, except for the samples treated with the DF2-Ca in the positive polarity, which displayed 1520 HV in the hardness. The increase in microhardness may be attributed to a combination of factors [75,76]. First, EDS analysis revealed the presence of high oxygen and carbon content on the surface, indicating the formation of titanium oxides (TiO2) and carbides (TiC), which are known to enhance resistance to plastic deformation and fracture [35]. The presence of TiO2 particles dispersed on the surface acts as effective obstacles to dislocation motion. This mechanism, known as oxide dispersion strengthening, requires higher stress for dislocations to bypass or overcome the oxide particles, resulting in increased surface microhardness [77]. Carbides also have extremely high intrinsic hardness and could significantly contribute to the mechanical reinforcement of the recast layer [35]. Moreover, the rapid heating and cooling caused by the electrical discharge machining process may further contribute to hardness enhancement [76]. These improvements in surface microhardness are not only relevant from a mechanical standpoint but may also have practical implications for biomedical applications. In particular, increased hardness can enhance the wear resistance of the implant surface and contribute to its long-term durability. Higher hardness reduces the formation of wear debris and delays corrosion-related degradation, both of which are critical factors for implant longevity [78].
3.5. Contact Angle
The water contact angle of each sample was measured, as shown in Figure 6. The untreated sample exhibited the highest contact angle (30.2° ± 1), indicating low surface wettability. Samples machined with DF1-F presented contact angles of 5.5° ± 1 and 17.8° ± 1 under negative and positive polarities, respectively. In contrast, the surfaces treated with DF2-Ca showed significantly enhanced wettability under both conditions, to the extent that contact angle measurements could not be obtained using a goniometer due to complete droplet spreading. Accordingly, all surfaces can be classified as hydrophilic, with the exception of those treated with DF2-Ca, which demonstrated superhydrophilic behavior.
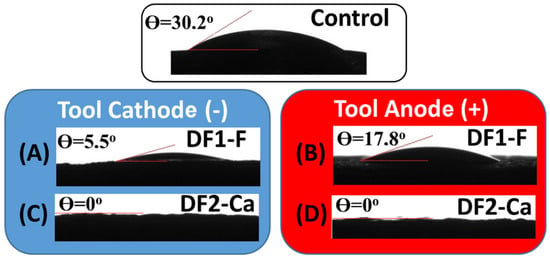
Figure 6.
Water droplets on different surfaces: Ti-6Al-4V control, (A) negative and (B) positive polarity using DF1-F, and (C,D) machined with DF2-Ca in the negative and positive polarities, respectively.
A number of studies have shown that modifying titanium alloy surfaces to obtain oxides as rutile or a mixture of rutile and anatase, is crucial to increased proliferation and differentiation of cells such as osteoblasts. These oxides are chemically stable and have greater hydrophilicity, which promotes cell attachment to the surface. Therefore, it is known that the most desirable contact angle value for hard tissue regeneration ranges from 35 to 80 degrees [79].
Otherwise, hydrophilic surfaces coated with calcium phosphate, such as those machined with DF2-Ca, exhibit a low water contact angle, indicating high wettability. This property may enhance cell coverage, improve osseointegration, and is essential for biomedical applications [80,81]. Although the DF2-Ca samples did not exhibit the highest surface roughness, their superhydrophilic behavior may significantly favor protein adsorption during the early stages of osseointegration. Recent studies have demonstrated that the synergistic effect of combining microroughness with superhydrophilicity leads to enhanced biological response and faster integration of implants with bone tissue [80,81]. Therefore, EDM-treated surfaces like those obtained with DF2-Ca may offer promising biological performance even when roughness is not maximized.
The superhydrophilicity observed in the DF2-Ca samples can be attributed to the combined effect of the porous surface morphology and the incorporation of calcium and phosphate species derived from the dielectric fluid. These elements are known to increase surface energy and enhance water affinity by promoting the formation of polar groups on the material surface [82]. This mechanism leads to the complete spreading of the water droplet, as observed in the wettability test.
Studies indicate that superhydrophilic surfaces favor the adsorption of fibrinogen, a protein that plays an important role in bone healing [83]. In addition, such surfaces can promote osteoblast adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation [84]. These findings suggest that the surface characteristics obtained through the EDM process with DF2-Ca may provide a biologically favorable environment for enhanced cellular response.
3.6. Cytotoxicity
The cell viability and cytotoxicity were assessed by the LDH assay, and the results are presented in histogram Figure 7, as relative growth rate (RGR) calculated according to Equation (1).
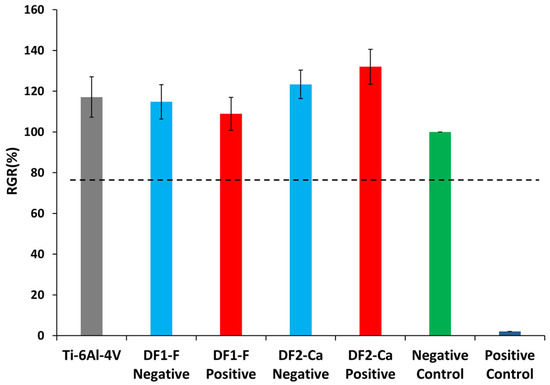
Figure 7.
Relative growth rate obtained in LDH assay for samples machined with DF1-F or DF2-Ca dielectric performed in each polarity.
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) is an enzyme present in the cytoplasm of all cells. It is rapidly released into the media of cell culture when plasma membrane lysis occurs. Thus, LDH detection and quantification method in the culture media is correlated to the amount of formazan product formed during a specific time period and it can be used as a quantitative test for the toxicity of materials and molecules [85].
According to ISO 10993-5 standard, if the percentage of the mean RGR is greater than 75%, the tested group will be considered non-cytotoxic. Therefore, from Figure 7, it can be observed that all tested groups exhibited results above this threshold. Regarding the titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V without the EDM treatment, the results obtained were similar to those found by other studies [86,87]. Statistical analysis showed no significant difference between the groups (p > 0.05). Thus, none of the samples were considered cytotoxic to the cells used in the assay. To build upon these results, additional biological studies, such as cell adhesion, proliferation, gene expression analysis, and in vivo evaluations are recommended to better understand the biological behavior of the modified surfaces [81].
Considering the surface characteristics observed for each experimental condition as a whole, it is possible to identify distinct biomedical applications. The DF1-F(–) condition, which exhibited the highest surface roughness, good wettability, and non-cytotoxic behavior, appears particularly suitable for implants requiring robust initial osseointegration. This includes dental implants and orthopedic screws used in low-density bone regions, where mechanical interlocking and enhanced cellular anchorage are essential [88,89].
On the other hand, the DF2-Ca(+) condition demonstrated exceptionally high surface hardness (up to 1520 HV) and superhydrophilic behavior, while also maintaining cytocompatibility. These characteristics are highly desirable for articulating prostheses and fixation plates, especially in load-bearing applications, such as hip or knee prostheses, where wear resistance and rapid biological interaction are critical [90,91].
4. Conclusions
This study investigated the surface modification of Ti-6Al-4V alloy through electrical discharge machining (EDM) to enhance its suitability for orthopedic and dental implant applications. The influence of dielectric fluid composition and tool polarity was comprehensively analyzed across surface morphology, wettability, roughness, microhardness, and biocompatibility. The results confirmed that EDM effectively tailored the physicochemical and mechanical properties of the alloy, leading to modified surface features. Such modifications may favor biological interactions and support implant integration. Furthermore, the absence of cytotoxic effects observed in the LDH assay suggests initial biocompatibility, although this potential should be further investigated through complementary biological studies. Overall, the findings validate the proposed approach and highlight EDM as a promising technique for optimizing titanium-based biomaterials used in implantable medical devices.
Through optical microscopy (OM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analyses, it was observed that machining with the fluorine-containing dielectric fluid (DF1-F) in negative polarity resulted in surfaces with more reentrances and irregularities, while positive polarity produced flatter surfaces, albeit with deep and wide cracks and an increased concentration of debris. Additionally, the DF2-Ca fluid produced surface features such as open pores, tiny droplets, and encrusted elongated structures, highlighting the influence of polarity and dielectric composition on surface morphology.
Surface roughness measurements showed that samples treated with DF1-F in negative polarity exhibited the highest roughness values, contributing to improved cell adhesion potential for biomedical applications. The roughness values were consistent with the morphological observations, indicating that negative polarity enhances surface irregularities, which are beneficial for osseointegration.
Vickers microhardness testing showed that all recast layers exhibited higher hardness compared to untreated titanium. Samples processed with DF2-Ca in positive polarity displayed the highest microhardness among all tested conditions, demonstrating significant mechanical strength improvements, particularly in the recast and heat-affected zones, which enhances the durability of biomedical implants.
Contact angle measurements revealed that the DF2-Ca dielectric fluid significantly increased surface wettability, achieving superhydrophilic behavior. The DF1-F fluid also displayed a very low contact angle under anodic polarity, indicating improved hydrophilicity, which contributes to tissue integration in medical applications.
Biocompatibility results based on the LDH assay indicated that all surfaces remained non-cytotoxic.
Finally, the most promising EDM conditions identified in this study are as follows:
a. DF1-F with negative polarity: This surface exhibited the highest surface roughness, high hardness from the heat-affected zone (HAZ) to recast layer, good wettability, in addition to non-cytotoxicity, suggesting good biocompatibility.
b. DF2-Ca with positive polarity: In this case, the modified layer was thicker, presenting the highest hardness. Additionally, precipitates of calcium compounds were formed on the surface, leading to a superhydrophilic and non-cytotoxic surface, which may indicate excellent biocompatibility.
These findings highlight the great potential of Ti-6Al-4V alloy processed via EDM for the development of biomaterials intended for bone implants and prostheses.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.A.B.d.S. and H.d.S.C.; methodology, B.A.B.d.S., E.C.S.C., L.Y.C.M., R.M.S. and W.L.; software, E.C.S.C. and W.L.; validation, L.Y.C.M., R.M.S. and K.C.P.; formal analysis, B.A.B.d.S.; investigation, B.A.B.d.S.; resources, K.C.P.; data curation, B.A.B.d.S.; writing—original draft preparation, B.A.B.d.S.; writing—review and editing, R.M.S. and H.d.S.C.; visualization, E.C.S.C., L.Y.C.M. and W.L.; supervision, H.d.S.C.; project administration, R.M.S.; funding acquisition, R.M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES), for financial support; the Federal Center for Technological Education of Minas Gerais (CEFET-MG) and its Department of Materials Engineering (DEMAT) for providing the equipment and technical cooperation for this paper. We would like to acknowledge the contributions of our colleagues Jorge Wanderson Barbosa, Aderci de Freitas Filho, and Lucas Ferreira Barbosa e Oliveira for their assistance with preliminary studies. Finally, the authors would like to thank Kimberly Cox-York from the Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition at Colorado State University for generously providing the human adipose-derived stem cells used in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Fekry, A.M.; El-Sherif, R.M. Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior of Magnesium and Titanium Alloys in Simulated Body Fluid. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 7280–7285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarao, T.P.S.; Singh, H.; Singh, H. Enhancing Biocompatibility and Corrosion Resistance of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy by Surface Modification Route. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2018, 27, 1388–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemot, F.; Porté, M.C.; Labrugère, C.; Baquey, C. Ti4+ to Ti3+ Conversion of TiO2 Uppermost Layer by Low-Temperature Vacuum Annealing: Interest for Titanium Biomedical Applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 255, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.; Misra, R.D.K.; You, C.K.; Rautray, T.R. TiO2 Nanotubes Synthesised on Ti-6Al-4V ELI Exhibits Enhanced Osteogenic Activity: A Potential next-Generation Material to Be Used as Medical Implants. Mater. Technol. 2021, 36, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaszemski, M.J. Biomaterials in Orthopedics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; ISBN 9780824756864. [Google Scholar]
- Moayedee, Y.; Nikzad, L.; Majidian, H. Exploration into the Microstructural, Mechanical, and Biological Characteristics of the Functionally Graded 3Y-TZP/Ti6Al4V System as a Potential Material for Dental Implants. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2024, 151, 106380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- (Sam) Froes, F.H. Titanium for Medical and Dental Applications—An Introduction. In Titanium in Medical and Dental Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahul; Mishra, D.K.; Datta, S.; Masanta, M. Effects of Tool Electrode on EDM Performance of Ti-6Al-4V. Silicon 2018, 10, 2263–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.W. Titanium Alloys for Dental Implants: A Review. Prosthesis 2020, 2, 100–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronoh, K.; Mwema, F.; Dabees, S.; Sobola, D. Advances in Sustainable Grinding of Different Types of the Titanium Biomaterials for Medical Applications: A Review. Biomed. Eng. Adv. 2022, 4, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stich, T.; Alagboso, F.; Křenek, T.; Kovářík, T.; Alt, V.; Docheva, D. Implant-bone-interface: Reviewing the Impact of Titanium Surface Modifications on Osteogenic Processes in Vitro and in Vivo. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2022, 7, e10239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.N.; Ramachandran, M.; Senthil Kumar, S.; Krishnan, V.; Sundaram, R. Osseointegration and More—A Review of Literature. Indian J. Dent. 2012, 3, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabino, R.M.; Mondini, G.; Kipper, M.J.; Martins, A.F.; Popat, K.C. Tanfloc/Heparin Polyelectrolyte Multilayers Improve Osteogenic Differentiation of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells on Titania Nanotube Surfaces. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, M.; Singh, A.K.; Asokamani, R.; Gogia, A.K. Ti Based Biomaterials, the Ultimate Choice for Orthopaedic Implants—A Review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2009, 54, 397–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdun Nafi, M.; Anjir Karim, M.; Lalvani, S.; James, P.F.; Sommers, A.; Jahan, M.P. Investigating Wettability and Corrosion Resistance of the Titanium Alloy Surface Engineered by the WEDM Process. Manuf. Lett. 2023, 35, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morra, M.; Cassinelli, C.; Cascardo, G.; Bollati, D.; Rodriguez y Baena, R. Multifunctional Implant Surfaces: Surface Characterization and Bone Response to Acid-etched Ti Implants Surface-modified by Fibrillar Collagen I. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 94A, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, S.; Piattelli, A.; de Figueiredo, L.C.; Feres, M.; de Melo, L.; Iezzi, G.; Alba, R.C.; Shibli, J.A. Histologic Evaluation of Early Human Bone Response to Different Implant Surfaces. J. Periodontol. 2006, 77, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, E.; Awale, G.; Daneshmandi, L.; Umerah, O.; Lo, K.W.-H. The Roles of Ions on Bone Regeneration. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Society of Mechanical Engineers. ASME B46.1—Surface Texture (Surface Roughness, Waviness, and Lay); American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Von Recum, A.F.; Van Kooten, T.G. The Influence of Micro-Topography on Cellular Response and the Implications for Silicone Implants. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 1996, 7, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elaziem, W.; Darwish, M.A.; Hamada, A.; Daoush, W.M. Titanium-Based Alloys and Composites for Orthopedic Implants Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Mater. Des. 2024, 241, 112850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omarov, S.; Nauryz, N.; Talamona, D.; Perveen, A. Surface Modification Techniques for Metallic Biomedical Alloys: A Concise Review. Metals 2022, 13, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Beri, N.; Kumar, A. Electric Discharge Machining of Titanium and Alloys for Biomedical Implant Applications: A Review. Int. J. Res. Anal. Rev. 2018, 5, 120–128. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, R.; Singh, A.; Debnath, K.; Sabino, R.M.; Popat, K.; Soares, P.; Keshri, A.K.; Borgohain, B. Enhanced Micro-Electric Discharge Machining-Induced Surface Modification on Biomedical Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2022, 144, 071002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Parashar, V. Critical Review on the Impact of EDM Process on Biomedical Materials. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2021, 36, 1701–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, R.; Kamble, D.; Ambhore, N. Performance Evaluation of Electric Discharge Machining of Titanium Alloy—A Review. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2022, 69, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.U.; Anwar, S.; Bhatti, H.A.; Kumar, M.S.; Ali, M.A.; Ammarullah, M.I. Electric Discharge Machining of Ti6Al4V ELI in Biomedical Industry: Parametric Analysis of Surface Functionalization and Tribological Characterization. Materials 2023, 16, 4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekmekci, N.; Efe, Y. The Effect of Nano and Micro Hydroxyapatite Powder Additives on Surface Integrity in Electrical Discharge Machining of Ti6Al4V Alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 445, 128708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasçalık, A.; Çaydaş, U. Electrical Discharge Machining of Titanium Alloy (Ti–6Al–4V). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 9007–9016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, B.; Wei, G.; Li, H. Research Progress of Metal Biomaterials with Potential Applications as Cardiovascular Stents and Their Surface Treatment Methods to Improve Biocompatibility. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, S.K.; Jadoun, R.S. Current Advanced Research Development of Electric Discharge Machining (EDM): A Review. Int. J. Res. Advent Technol. 2014, 2, 273–297. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Amin, M.; Abdul Rani, A.M.; Abdu Aliyu, A.A.; Abdul Razak, M.A.; Hastuty, S.; Bryant, M.G. Powder Mixed-EDM for Potential Biomedical Applications: A Critical Review. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2020, 35, 1789–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.; Varol, T.; Canakci, A.; Kumaran, S.T.; Uthayakumar, M. A Review on the Performance of the Materials by Surface Modification through EDM. Int. J. Lightweight Mater. Manuf. 2021, 4, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossymbayev, A.; Ali, S.; Talamona, D.; Perveen, A. Powder-Mixed Micro Electrical Discharge Machining-Assisted Surface Modification of Ti-35Nb-7Zr-5Ta Alloy in Biomedical Applications. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 6th Eurasia Conference on IoT, Communication and Engineering, Yunlin, Taiwan, 15–17 November 2024; MDPI: Basel, Switzerland, 2025; p. 71. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.K.; Malik, A.; Mali, H.S. Modification of Ti6Al4V Alloy Surfaces Using Hydroxyapatite-Mixed Electric Discharge-Assisted Centerless Turning for Application of Bone-Anchored Limb Prosthesis Fixtures. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2025, 34, 8020–8036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauryz, N.; Omarov, S.; Kenessova, A.; Pham, T.T.; Talamona, D.; Perveen, A. Powder-Mixed Micro-Electro-Discharge Machining-Induced Surface Modification of Titanium Alloy for Antibacterial Properties. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2023, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taqi, S.; Shather, S. Investigation the Effect of Negative Polarity of Surface Roughness and Metal Removal Rate During EDM Process. Eng. Technol. J. 2020, 38, 1852–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortizo, M.C.; de Mele, M.F.L. Cytotoxicity of Copper Ions Released from Metal: Variation with the Exposure Period and Concentration Gradients. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2004, 102, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, S.K.; Cassady, A.I.; Lu, G.Q.; Martin, D.J. The Biocompatibility of Carbon Nanotubes. Carbon 2006, 44, 1034–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokros, J.C. Carbon Biomedical Devices. Carbon 1977, 15, 353–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.S.; Meng, Q.G.; Wang, Z.L. The Application of Research on Powder Mixed EDM in Rough Machining. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2002, 129, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Ji, R.; Cai, B.; Li, H.; Wang, F. A Review of the Current Understanding and Technology of Powder Mixed Electrical Discharge Machining (PMEDM). In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, New York, NY, USA, 5 August 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 2240–2247. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, R. Nitretação Por EDM Do Aço AISI 4140; Universidade Federal de Uberlândia: Uberlândia, Brazil, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.L.; Yan, B.H.; Huang, F.Y. Influence of Kerosene and Distilled Water as Dielectrics on the Electric Discharge Machining Characteristics of Ti–6A1–4V. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1999, 87, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Kong, L.; Lei, W.; He, Y.; Zhang, L.; Han, J.; Li, Q. Study on the Effect of Different Electrode Forms on the Surface Modification of Ti–6Al–4V Alloy by near-Dry Electrical Discharge Machining. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 314, 128801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathan Kumar, P.; Sivakumar, K.; Selvarajan, L. EDM Machining Effectiveness for Ti–6Al–4V Alloy Using Cu–TiB2 Ceramic Composite Electrode: A Parametric Evaluation. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 20118–20132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmiris-Obratański, P.; Papazoglou, E.L.; Leszczyńska-Madej, B.; Zagórski, K.; Markopoulos, A.P. A Comprehensive Study on Processing Ti–6Al–4V ELI with High Power EDM. Materials 2021, 14, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mughal, M.P.; Farooq, M.U.; Mumtaz, J.; Mia, M.; Shareef, M.; Javed, M.; Jamil, M.; Pruncu, C.I. Surface Modification for Osseointegration of Ti6Al4V ELI Using Powder Mixed Sinking EDM. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 113, 104145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.F.B. Ativação da Superfície da Liga Ti-6Al-4V Através de Eletroerosão; Centro Federal de Educação Tecnológica de Minas Gerais: Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, J.B.D. Enriquecimento Superficial Da Liga Ti-6Al-4V Com Cálcio e Fósforo Pelo Processo de Usinagem Por Descargas Elétricas; CEFET-MG: Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- UNS R56401; ASTM International ASTM F136—Standard Specification for Wrought Titanium-6Aluminum-4Vanadium ELI (Extra Low Interstitial) Alloy for Surgical Implant Applications. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- ISO 5832-3:2016; Implants for Surgery—Metallic Materials—Part 3: Wrought Titanium 6-Aluminium 4-Vanadium Alloy. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Pesode, P.; Barve, S. A Review—Metastable β Titanium Alloy for Biomedical Applications. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2023, 70, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.F.B.; Dos Santos, B.A.B.; dos Santos, R.F.; de Souza Costa, H. ATIVAÇÃO DA SUPERFÍCIE DA LIGA TI-6AL-4V ATRAVÉS DO PROCESSO EDM. Rev. Eletrônica Perspect. Ciência Tecnol. 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 3274:1996; Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Surface Texture: Profile Method—Nominal Characteristics of Contact (Stylus) Instruments. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996.
- ISO 10993-5:2009; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices. Part 5: Tests for in Vitro Cytotoxicity. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Mahajan, A.; Sidhu, S.S. Enhancing Biocompatibility of Co-Cr Alloy Implants via Electrical Discharge Process. Mater. Technol. 2018, 33, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-F.; Yang, T.-S.; Wu, Y.-C.; Peng, P.-W. Nanoporous Biocompatible Layer on Ti–6Al–4V Alloys Enhanced Osteoblast-like Cell Response. J. Exp. Clin. Med. 2013, 5, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, P.; Joshi, S.S. Analysis of Micro-Cracks on Machined Surfaces in Dry Electrical Discharge Machining. J. Manuf. Process. 2012, 14, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Paul, S.; Doloi, B. A Gap-Active Electrical Discharge Machining (GA-EDM) to Rectify the Textural Defects of the Processed Surface. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 64, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, V.; Shubham; Kumar, P.; Singh, P.K.; Das, A.K.; Chattopadhyaya, S.; Mandal, A.; Dixit, A.R. Surface Alloying of Miniature Components by Micro-Electrical Discharge Process. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2018, 33, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafi, M.A.; Jahan, M.P. Functional Surface Generation by EDM—A Review. Micromachines 2022, 14, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshaim, A.B.; Muthuramalingam, T.; Moustafa, E.B.; Elsheikh, A. Influences of Tool Electrodes on Machinability of Titanium α-β Alloy with ISO Energy Pulse Generator in EDM Process. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 63, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Ma, J.; Tian, A.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, B.; Tong, X.; Ma, X. Surface Modification Techniques of Titanium and Titanium Alloys for Biomedical Orthopaedics Applications: A Review. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 227, 113339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyril Pilligrin, J.; Asokan, P.; Jerald, J.; Kanagaraj, G.; Mukund Nilakantan, J.; Nielsen, I. Tool Speed and Polarity Effects in Micro-EDM Drilling of 316L Stainless Steel. Prod. Manuf. Res. 2017, 5, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroi, B.K.; Debnath, T.; Jagadish; Patowari, P.K. Machinability Assessment of Titanium Grade 2 Alloy Using Deionized Water in EDM. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 2221–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Ishfaq, K.; Moiduddin, K.; Ali, R.; Al-Shammary, N. Machinability of Titanium Alloy through Electric Discharge Machining. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2019, 34, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, C.; Kansal, H.K.; Pabla, B.; Puri, S.; Aggarwal, A. Electric Discharge Machining—A Potential Choice for Surface Modification of Metallic Implants for Orthopedic Applications: A Review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. B J. Eng. Manuf. 2015, 230, 331–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareidoost, A.; Yousefpour, M.; Ghaseme, B.; Amanzadeh, A. The Relationship of Surface Roughness and Cell Response of Chemical Surface Modification of Titanium. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2012, 23, 1479–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, Z.; Dummer, P.M.H. Properties and Applications of Calcium Hydroxide in Endodontics and Dental Traumatology. Int. Endod. J. 2011, 44, 697–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieser, E.; Tsyganov, I.; Matz, W.; Reuther, H.; Oswald, S.; Pham, T.; Richter, E. Modification of Titanium by Ion Implantation of Calcium and/or Phosphorus. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 111, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holsten, M.; Koshy, P.; Klink, A.; Schwedt, A. Anomalous Influence of Polarity in Sink EDM of Titanium Alloys. CIRP Annals 2018, 67, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.-F.; Wang, C.-Y. Effects of Bioceramic Particles in Dielectric of Powder-Mixed Electrical Discharge Machining on Machining and Surface Characteristics of Titanium Alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 245, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuir-Torres, J.I.; Kotadia, H.R.; Öpöz, T.T. Effect of the Electrical Discharge Machining on Ti6Al4V Corrosion Behaviour in Simulated Body Fluid. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 470, 129830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, N.; Saleem, M.Q.; Farooq, M.U. Performance Evaluation of Surfactant Mixed Dielectric and Process Optimization for Electrical Discharge Machining of Titanium Alloy Ti6Al4V. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2023, 43, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas Filho, A.; Silva, G.C.; Rodrigues, S.C.S.; Santos, A.J. Evaluation of the Effect of Surface Modification of Ti64 and 316L by Addition of Calcium Phosphate through Electrical Discharge Machining Process. Tribol. Int. 2023, 180, 108245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Wu, C.; Mou, G.; Zheng, K. Decomposition Behavior and Strengthening Mechanism of Ti-TiO2 Material in Selective Laser Melting Process. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2025, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unune, D.R.; Brown, G.R.; Reilly, G.C. Thermal Based Surface Modification Techniques for Enhancing the Corrosion and Wear Resistance of Metallic Implants: A Review. Vacuum 2022, 203, 111298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, K.L.; Jones, L. The Impact of Contact Angle on the Biocompatibility of Biomaterials. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2010, 87, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasbi Rad, A.; Solati-Hashjin, M.; Osman, N.A.A.; Faghihi, S. Improved Bio-Physical Performance of Hydroxyapatite Coatings Obtained by Electrophoretic Deposition at Dynamic Voltage. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 12681–12691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittens, R.A.; Scheideler, L.; Rupp, F.; Hyzy, S.L.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J.; Schwartz, Z.; Boyan, B.D. A Review on the Wettability of Dental Implant Surfaces II: Biological and Clinical Aspects. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 2907–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarova, E.G.; Chebodaeva, V.; Sharkeev, Y.P.; Sedelnikova, M. Effect of Surface Topography and Chemical Composition on Wettability of Calcium Phosphate Coatings Formed on Ti-40Nb Alloy. Key Eng. Mater. 2016, 683, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitajima, H.; Hirota, M.; Osawa, K.; Iwai, T.; Saruta, J.; Mitsudo, K.; Ogawa, T. Optimization of Blood and Protein Flow around Superhydrophilic Implant Surfaces by Promoting Contact Hemodynamics. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2022, 67, 568–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, H.; Ma, M.; Wang, Q.; Yan, T.; Zhao, B.; Guo, S.; Tong, S. Advances in the Superhydrophilicity-Modified Titanium Surfaces with Antibacterial and pro-Osteogenesis Properties: A Review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1000401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauhammer, I.; Sacha, M.; Haltner, E. Validation and Stability Analysis of a Modified Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Test Method to Be Employed for an in Vitro Viable Skin Model. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Guo, S.; Lu, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhao, C.; Wu, S.; Lin, J. Cytocompatibility of Cu-Bearing Ti6Al4V Alloys Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting. Mater. Charact. 2018, 143, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xu, D.; Geng, S.; Fan, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, F. Mechanical Properties, Corrosion Behavior and Cytotoxicity of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Metal Deposition. Mater. Charact. 2021, 179, 111302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias Corpa Tardelli, J.; Duarte Firmino, A.C.; Ferreira, I.; Cândido dos Reis, A. Influence of the Roughness of Dental Implants Obtained by Additive Manufacturing on Osteoblastic Adhesion and Proliferation: A Systematic Review. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, C.; Rokaya, D.; Bhattarai, B.P. Contemporary Concepts in Osseointegration of Dental Implants: A Review. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 6170452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, K.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y. Effect of Cryogenic Treatment on Wear Resistance of Ti–6Al–4V Alloy for Biomedical Applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 30, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujita, H.; Nishizaki, H.; Miyake, A.; Takao, S.; Komasa, S. Effect of Plasma Treatment on Titanium Surface on the Tissue Surrounding Implant Material. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).