Automatic 3D Reconstruction: Mesh Extraction Based on Gaussian Splatting from Romanesque–Mudéjar Churches
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. State of the Art

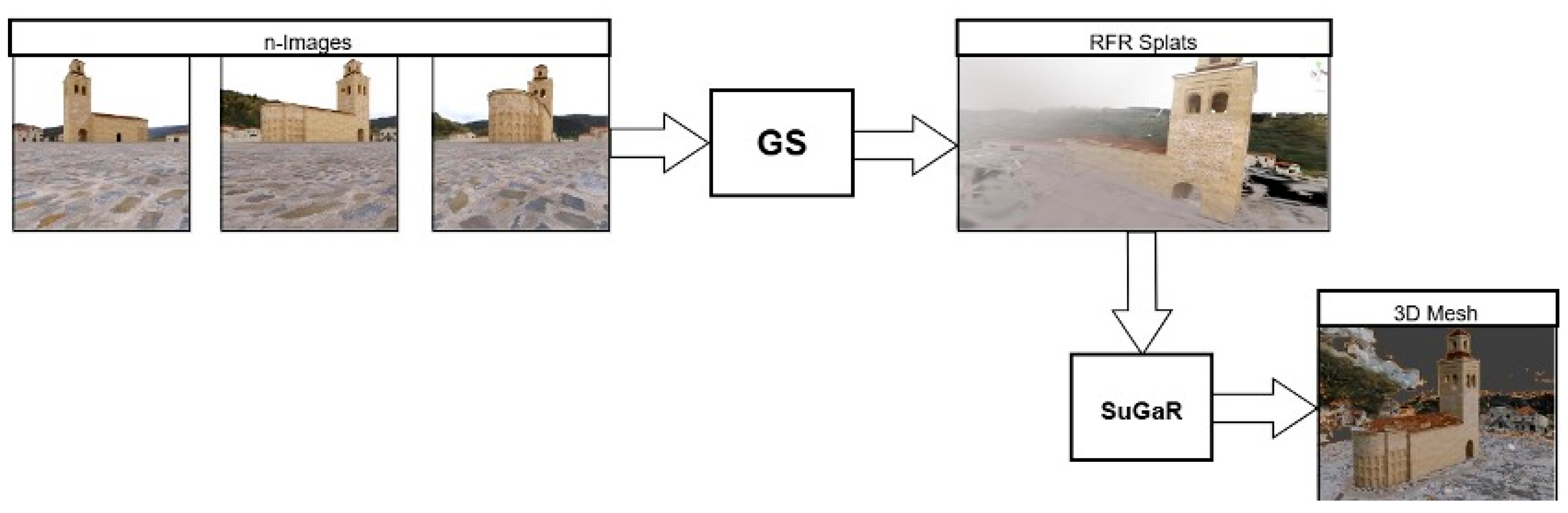
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Dataset Design
3.2. Pre-Processing
3.3. Model Architecture
3.4. Hyperparameter Tuning
3.5. Validation
4. Results and Evaluation
4.1. Objective Evaluation
4.2. Subjective Evaluation
5. Discussion
6. Limitations
7. Conclusions
8. Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AH | Architectural heritage |
| BIM | Building information modeling |
| DL | Deep learning |
| GS | Gaussian splatting |
| HBIM | Heritage BIM |
| LiDAR | Light detection and ranging |
| ML | Machine learning |
| NeRF | Neural radiance fields |
| RFR | Radiance field rendering |
| SfM | Structure from motion |
| SOTA | State-of-the-art |
| SuGaR | Surface-aligned Gaussian splatting for efficient 3D mesh reconstruction |
References
- Jokilehto, J. Definition of Cultural Heritage: References to Documents in History; ICCROM Working Group ‘Heritage and Society’: Rome, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Berndt, E.; Carlos, J. Cultural Heritage in the Mature Era of Computer Graphics. IEEE Comput. Grap. Appl. 2000, 20, 36–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Martos, E.; Carlevaris, L.; Intra Sidola, G.; Pesqueira-Calvo, C.; Nogales, A.; Maitín Álvarez, A.M.; García Tejedor, Á.J. Automatic Virtual Reconstruction of Historic Buildings Through Deep Learning. A Critical Analysis of a Paradigm Shift. In Beyond Digital Representation; Digital Innovations in Architecture, Engineering and Construction; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 415–426. ISBN 978-3-031-36154-8. [Google Scholar]
- Matini, M.R.; Ono, K. Accuracy Verification of Manual 3D CG Reconstruction: Case Study of Destroyed Architectural Heritage, Bam Citadel. In Digital Heritage; Ioannides, M., Fellner, D., Georgopoulos, A., Hadjimitsis, D.G., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 6436, pp. 432–440. ISBN 978-3-642-16872-7. [Google Scholar]
- Kersten, T.P.; Lindstaedt, M. Automatic 3D Object Reconstruction from Multiple Images for Architectural, Cultural Heritage and Archaeological Applications Using Open-Source Software and Web Services. Photogramm. Fernerkund. Geoinf. 2012, 2012, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autran, C.; Guena, F. 3D Reconstruction of a Disappeared Museum. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Virtual Systems & Multimedia (VSMM), Hong Kong, China, 9–12 December 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Autran, C.; Guena, F. 3D Reconstruction for Museums and Scattered Collections Applied Research for the Alexandre Lenoir’s Museum of French Monument. In Proceedings of the 2015 Digital Heritage, Granada, Spain, 28 September–2 October 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Chu, C.H. 3D Building Reconstruction from LiDAR Data. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, San Antonio, TX, USA, 11–14 October 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 3054–3059. [Google Scholar]
- Torresani, A.; Remondino, F. Videogrammetry vs Photogrammetry for Heritage 3D Reconstruction. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-2/W15, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, M.G.; Russo, M.; Giordano, A.; Spallone, R. 3D Reconstruction, Digital Twinning, and Virtual Reality: Architectural Heritage Applications. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces Abstracts and Workshops (VRW), Christchurch, New Zealand, 12–16 March 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 92–96. [Google Scholar]
- Peta, K.; Stemp, W.J.; Stocking, T.; Chen, R.; Love, G.; Gleason, M.A.; Houk, B.A.; Brown, C.A. Multiscale Geometric Characterization and Discrimination of Dermatoglyphs (Fingerprints) on Hardened Clay—A Novel Archaeological Application of the GelSight Max. Materials 2025, 18, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apollonio, F.I.; Gaiani, M.; Sun, Z. 3D Modeling and Data Enrichment in Digital Reconstruction of Architectural Heritage. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2013, XL-5/W2, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campi, M.; Di Luggo, A.; Scandurra, S. 3D Modeling for the Knowledge of Architectural Heritage and Virtual Reconstruction of Its Historical Memory. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, XLII-2/W3, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, M.; Brandonisio, G.; Milani, G.; Luca, A.D. Seismic Response Evaluation of Ten Tuff Masonry Churches with Basilica Plan through Advanced Numerical Simulations. Int. J. Mason. Res. Innov. 2020, 5, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, M. Earthquake Response and Damage Patterns Assessment of Two Historical Masonry Churches with Bell Tower. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 151, 107418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.; McGovern, E.; Pavia, S. Historic Building Information Modelling (HBIM). Struct. Surv. 2009, 27, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogales, A.; Delgado-Martos, E.; Melchor, Á.; García-Tejedor, Á.J. ARQGAN: An Evaluation of Generative Adversarial Network Approaches for Automatic Virtual Inpainting Restoration of Greek Temples. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 180, 115092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekunle, S.A.; Aigbavboa, C.; Ejohwomu, O.A. Scan to BIM: A Systematic Literature Review Network Analysis. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1218, 012057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, R.P.; Borges Monteiro, A.C.; Arthur, R.; Iano, Y. An Overview of Deep Learning in Big Data, Image, and Signal Processing in the Modern Digital Age. In Trends in Deep Learning Methodologies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 63–87. ISBN 978-0-12-822226-3. [Google Scholar]
- Samuel, A.L. Some Studies in Machine Learning Using the Game of Checkers. IBM J. Res. Dev. 1959, 3, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep Learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotella, V.A. From 3D Point Clouds to HBIM: Application of Artificial Intelligence in Cultural Heritage. Autom. Constr. 2023, 152, 104936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerbl, B.; Kopanas, G.; Leimkuehler, T.; Drettakis, G. 3D Gaussian Splatting for Real-Time Radiance Field Rendering. ACM Trans. Graph. 2023, 42, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Chen, A.; Huang, B.; Sattler, T.; Geiger, A. Mip-Splatting: Alias-Free 3D Gaussian Splatting. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 19447–19456. [Google Scholar]
- Guédon, A.; Lepetit, V. SuGaR: Surface-Aligned Gaussian Splatting for Efficient 3D Mesh Reconstruction and High-Quality Mesh Rendering. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mildenhall, B.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Tancik, M.; Barron, J.T.; Ramamoorthi, R.; Ng, R. NeRF: Representing Scenes as Neural Radiance Fields for View Synthesis. Commun. ACM 2020, 65, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yang, J.; Yumer, E.; Guo, Y.; Lee, H. Perspective Transformer Nets: Learning Single-View 3D Object Reconstruction without 3D Supervision. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 29 (NIPS 2016); Lee, D., Sugiyama, M., Sugiyama, U., Guyon, I., Garnett, R., Eds.; Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation Inc. (NeurIPS): San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 1696–1704. [Google Scholar]
- Rezende, D.; Mohamed, S.; Battaglia, P.; Jaderberg, M.; Heess, N. Unsupervised Learning of 3D Structure from Images. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 29 (NIPS 2016); Lee, D., Sugiyama, M., Sugiyama, U., Guyon, I., Garnett, R., Eds.; Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation Inc. (NeurIPS): San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 5003–5011. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, H.; Ushiku, Y.; Harada, T. Neural 3D Mesh Renderer. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pytorch Homepage. Available online: https://pytorch.org/ (accessed on 21 January 2025).
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, C.; Ganin, Y.; Eslami, S.M.A.; Battaglia, P.W. PolyGen: An Autoregressive Generative Model of 3D Meshes. In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 13–18 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Brualla, R.; Radwan, N.; Sajjadi, M.S.M.; Barron, J.T.; Dosovitskiy, A.; Duckworth, D. NeRF in the Wild: Neural Radiance Fields for Unconstrained Photo Collections. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, T.; Evans, A.; Schied, C.; Keller, A. Instant Neural Graphics Primitives with a Multiresolution Hash Encoding. ACM Trans. Graph. 2022, 41, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Müller, T.; Evans, A.; Taylor, R.H.; Unberath, M.; Liu, M.-Y.; Lin, C.-H. Neuralangelo: High-Fidelity Neural Surface Reconstruction. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Poole, B.; Jain, A.; Barron, J.T.; Mildenhall, B. DreamFusion: Text-to-3D Using 2D Diffusion. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.14988. [Google Scholar]
- Rakotosaona, M.-J.; Manhardt, F.; Arroyo, D.M.; Niemeyer, M.; Kundu, A.; Tombari, F. NeRFMeshing: Distilling Neural Radiance Fields into Geometrically-Accurate 3D Meshes. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Davos, Switzerland, 18–21 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Barron, J.T.; Mildenhall, B.; Verbin, D.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Hedman, P. Mip-NeRF 360: Unbounded Anti-Aliased Neural Radiance Fields. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fridovich-Keil, S.; Yu, A.; Tancik, M.; Chen, Q.; Recht, B.; Kanazawa, A. Plenoxels: Radiance Fields without Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 5491–5500. [Google Scholar]
- Snavely, N.; Seitz, S.M.; Szeliski, R. Photo Tourism: Exploring Photo Collections in 3D. ACM Trans. Graph. 2006, 25, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassner, C.; Zollhofer, M. Pulsar: Efficient Sphere-Based Neural Rendering. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1440–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Kazhdan, M.; Bolitho, M.; Hoppe, H. Poisson Surface Reconstruction. In Proceedings of the 4th Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing, Cagliari Sardinia, Italy, 26–28 June 2006; pp. 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Elharrouss, O.; Almaadeed, N.; Al-Maadeed, S.; Akbari, Y. Image Inpainting: A Review. Neural Process. Lett. 2020, 51, 2007–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonberger, J.L.; Frahm, J.-M. Structure-from-Motion Revisited. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 4104–4113. [Google Scholar]
- Schönberger, J.L.; Zheng, E.; Frahm, J.-M.; Pollefeys, M. Pixelwise View Selection for Unstructured Multi-View Stereo. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2016; Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 9907, pp. 501–518. ISBN 978-3-319-46486-2. [Google Scholar]
- Yifan, W.; Serena, F.; Wu, S.; Öztireli, C.; Sorkine-Hornung, O. Differentiable Surface Splatting for Point-Based Geometry Processing. ACM Trans. Graph. 2019, 38, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwicker, M.; Pfister, H.; Van Baar, J.; Gross, M. EWA Volume Splatting. In Proceedings of the Proceedings Visualization, 2001 VIS ’01, San Diego, CA, USA, 21–26 October 2001; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 29–538. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Funkhouser, T.; Hedman, P.; Tagliasacchi, A. MobileNeRF: Exploiting the Polygon Rasterization Pipeline for Efficient Neural Field Rendering on Mobile Architectures. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 16569–16578. [Google Scholar]
- Yariv, L.; Hedman, P.; Reiser, C.; Verbin, D.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Szeliski, R.; Barron, J.T.; Mildenhall, B. BakedSDF: Meshing Neural SDFs for Real-Time View Synthesis. In Proceedings of the Special Interest Group on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 6–10 August 2023; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Interactive Scenes. Available online: https://lumalabs.ai/interactive-scenes (accessed on 25 April 2025).
- Diara, F.; Rinaudo, F. IFC Classification for FOSS HBIM: Open Issues and a Schema Proposal for Cultural Heritage Assets. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Oh, J.; Lee, K.M. Depth-Regularized Optimization for 3D Gaussian Splatting in Few-Shot Images. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–18 June 2023. [Google Scholar]





| Romanesque–Mudejar Dataset | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method/Metric | SSIM ↑ | PSNR ↑ | LPIPS ↓ | Train | FPS | Mem |
| GS Mudéjar 30 K | 0.705 † | 22.61 † | 0.371 † | 0 h 21 min 31 s † | - | 51.8 MB † |
| Mip-splatting Mudéjar/30 K | 0.665 † | 20.66 † | 0.335 † | 0 h 22 min 00 s † | - | 103.9 MB † |
| SuGaR Mudéjar/30 K | 0.482 † | 9.88 † | 0.630 † | 2 h 01 min 15 s † | - | 146.8 MB † |
| Mip-NeRF360 dataset | ||||||
| Plenoxels | 0.626 | 23.08 | 0.463 | 0 h 25 min 49 s | 6.79 | 2.1 GB |
| INGP-Base | 0.671 | 25.30 | 0.371 | 0 h 05 min 37 s | 11.7 | 13 MB |
| INGP-Big | 0.699 | 25.59 | 0.331 | 0 h 07 min 30 s | 9.4 | 348 MB |
| M-NeRF360 | 0.792 | 27.69 | 0.237 | 48 h 10 min 50 s | 0.06 | 8.6 MB |
| GS-Kerbl/7 K | 0.770 | 25.60 | 0.279 | 0 h 06 min 25 s | 160 | 523 MB |
| GS-Kerbl/30 K | 0.815 | 27.21 | 0.214 | 0 h 41 min 33 s | 134 | 734 MB |
| No Mesh Extraction Method (Except SuGaR) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Romanesque–Mudéjar dataset | |||
| Method/metric | SSIM ↑ | PSNR ↑ | LPIPS ↓ |
| SuGaR Romanesque–Mudejar/15 K | 9.88 † | 0.483 † | 0.630 † |
| Mip-NeRF360 dataset | |||
| Plenoxels | 22.02 | 0.542 | 0.465 |
| INGP-Base | 23.47 | 0.571 | 0.416 |
| INGP-Big | 23.57 | 0.602 | 0.375 |
| Mip-NeRF360 | 25.79 | 0.746 | 0.247 |
| 3DGS | 26.40 | 0.805 | 0.173 |
| SuGaR [25]/15 K | 24.40 | 0.699 | 0.301 |
| With the mesh extraction method | |||
| Romanesque–Mudéjar dataset | |||
| Method/metric | SSIM ↑ | PSNR ↑ | LPIPS ↓ |
| SuGaR Romanesque–Mudejar/15 K | 9.88 † | 0.483 † | 0.630 † |
| Mip NeRF360 dataset | |||
| Mobile NeRF | 21.95 | 0.470 | 0.470 |
| NeRFMeshing | 22.23 | - | - |
| BakedSDF | 22.47 | 0.585 | 0.349 |
| SuGaR [25]/2 K | 22.97 | 0.648 | 0.360 |
| SuGaR [25]/7 K | 24.16 | 0.691 | 0.313 |
| SuGaR [25]/15 K | 24.40 | 0.699 | 0.301 |
| Method/Metric | SSIM ↑ | PSNR ↑ | LPIPS ↓ | Train |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GS/30 K | 0.705 | 22.610 | 0.371 | 0 h 21 min 31 s |
| Mip-splatting/30 K | 0.665 | 20.660 | 0.335 | 0 h 22 min 00 s |
| SuGaR/15 K | 0.482 | 9.876 | 0.630 | 2 h 01 min 15 s |
| Average (all methods used) | 0.618 | 17.716 | 0.445 | 2 h 22 min 23 s |
| Element | Description | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Objectives | 3D reconstruction from images | N/A |
| Architecture type | Stochastic gradient descent + k-nearest neighbors | 2 architecture types |
| Model type | GS + SuGaR | 2 models |
| Building dataset | 60 Romanesque–Mudéjar temples | 32,400 synthetic images |
| Input (direct training) | Ruin or complete images | 180 images or one 360° video for the building |
| Output | Reconstructed 3D Mesh | 1 3D-textured mesh model |
| Techniques | Gaussian rasterization + Anti-aliasing + Poisson reconstruction | 3 techniques |
| Training time | Training time without pre-processing | GS = 00H22m; SuGaR = 2H00m |
| Limitations | No BIM classes output | 1,000,000+ pts. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montas-Laracuente, N.; Delgado Martos, E.; Pesqueira-Calvo, C.; Intra Sidola, G.; Maitín, A.; Nogales, A.; García-Tejedor, Á.J. Automatic 3D Reconstruction: Mesh Extraction Based on Gaussian Splatting from Romanesque–Mudéjar Churches. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8379. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158379
Montas-Laracuente N, Delgado Martos E, Pesqueira-Calvo C, Intra Sidola G, Maitín A, Nogales A, García-Tejedor ÁJ. Automatic 3D Reconstruction: Mesh Extraction Based on Gaussian Splatting from Romanesque–Mudéjar Churches. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(15):8379. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158379
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontas-Laracuente, Nelson, Emilio Delgado Martos, Carlos Pesqueira-Calvo, Giovanni Intra Sidola, Ana Maitín, Alberto Nogales, and Álvaro José García-Tejedor. 2025. "Automatic 3D Reconstruction: Mesh Extraction Based on Gaussian Splatting from Romanesque–Mudéjar Churches" Applied Sciences 15, no. 15: 8379. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158379
APA StyleMontas-Laracuente, N., Delgado Martos, E., Pesqueira-Calvo, C., Intra Sidola, G., Maitín, A., Nogales, A., & García-Tejedor, Á. J. (2025). Automatic 3D Reconstruction: Mesh Extraction Based on Gaussian Splatting from Romanesque–Mudéjar Churches. Applied Sciences, 15(15), 8379. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158379







