Hybrid Electrocoagulation with Al Electrodes Assisted by Magnet and Zeolite: How Effective Is It for Compost Wastewater Treatment?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Setup and Procedure
2.3. Analytical Methods and Process Evaluation
- (a)
- Monitoring of Physico-Chemical Parameters
- (b)
- Hybrid Process Efficiency
- (c)
- Quantifying and Electrode Loss, Faradaic Efficiency, and Energy Input
- (d)
- Surface Morphology Analysis of Electrodes
- (e)
- Sedimentation Behavior of Treated Suspensions
3. Results
3.1. Assessment of Process Efficiency: Linking Physico-Chemical Indicators with Process Performance
3.1.1. Comparative Temperature and pH Profiles
3.1.2. Comparative COD Decrease
3.1.3. Comparative Turbidity Removal
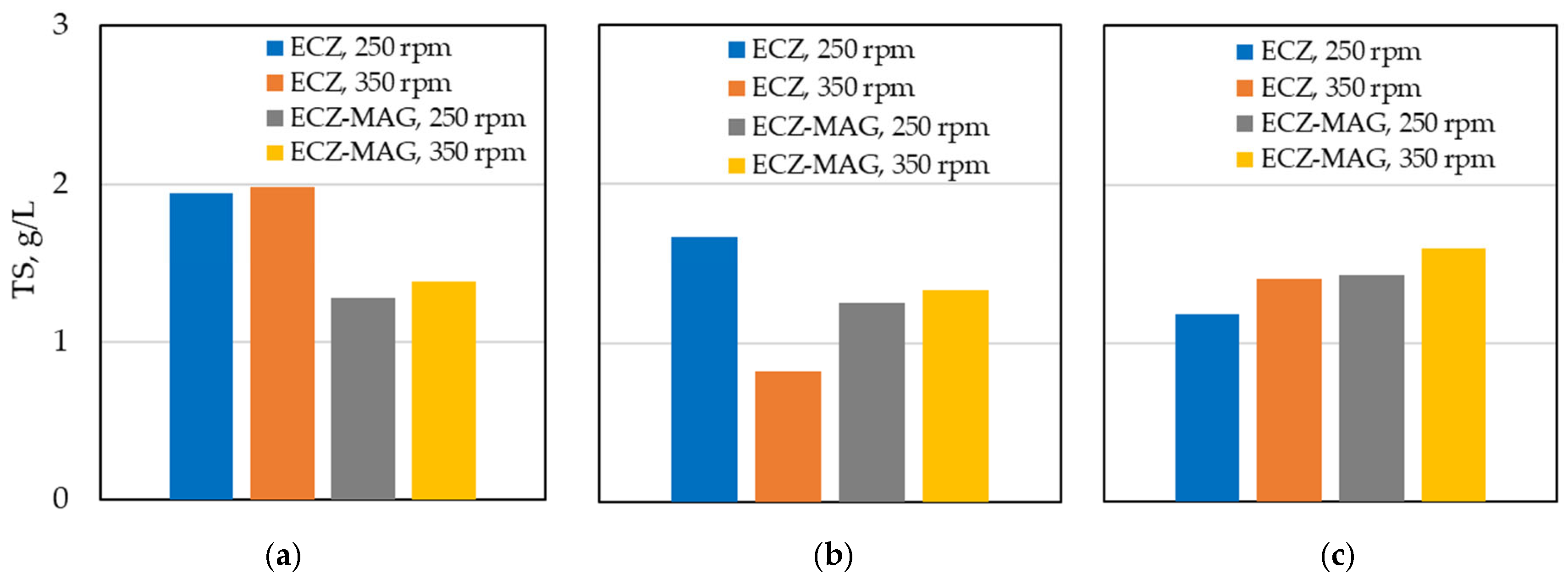
3.1.4. Comparative Total Solids Values
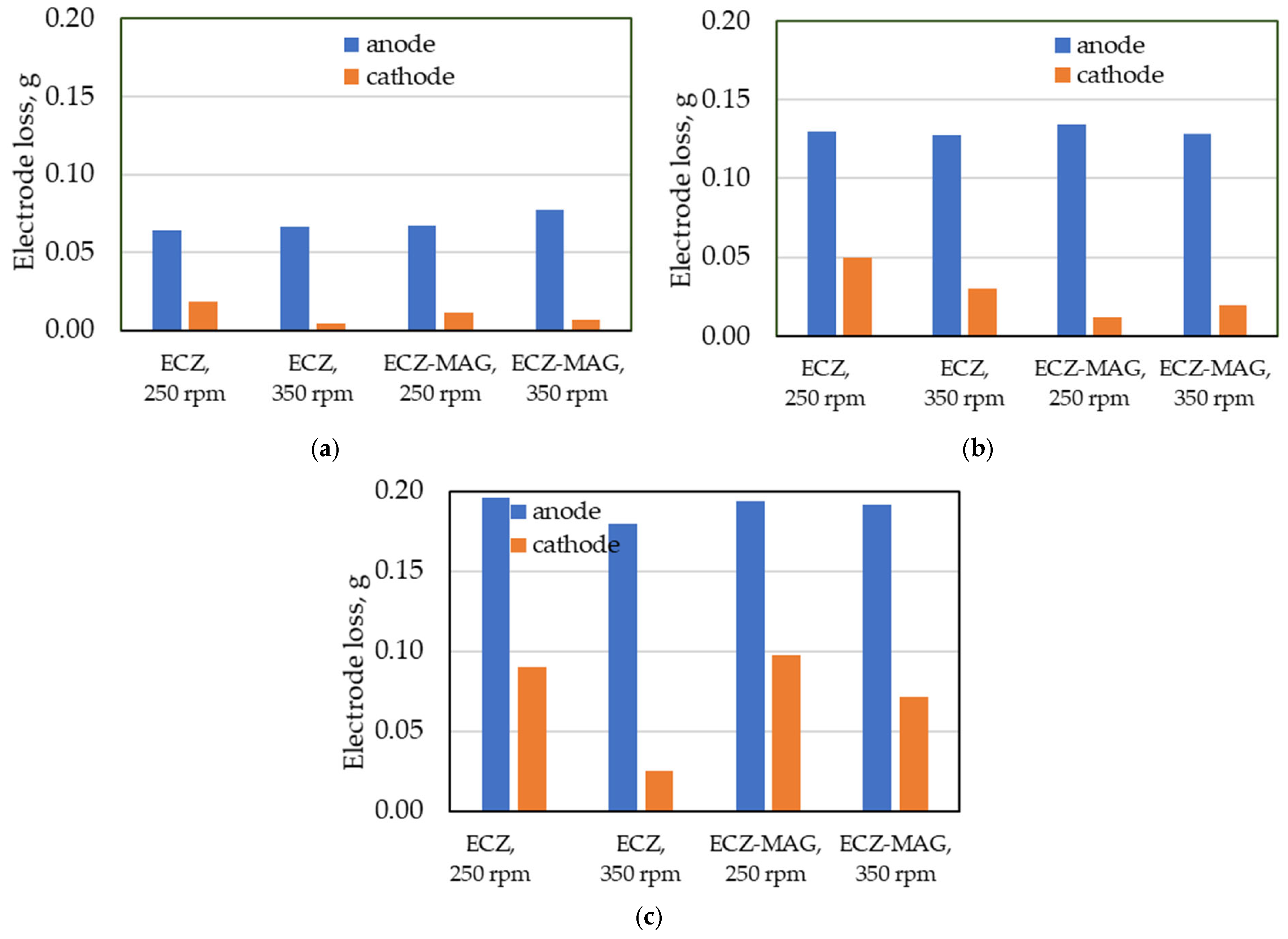
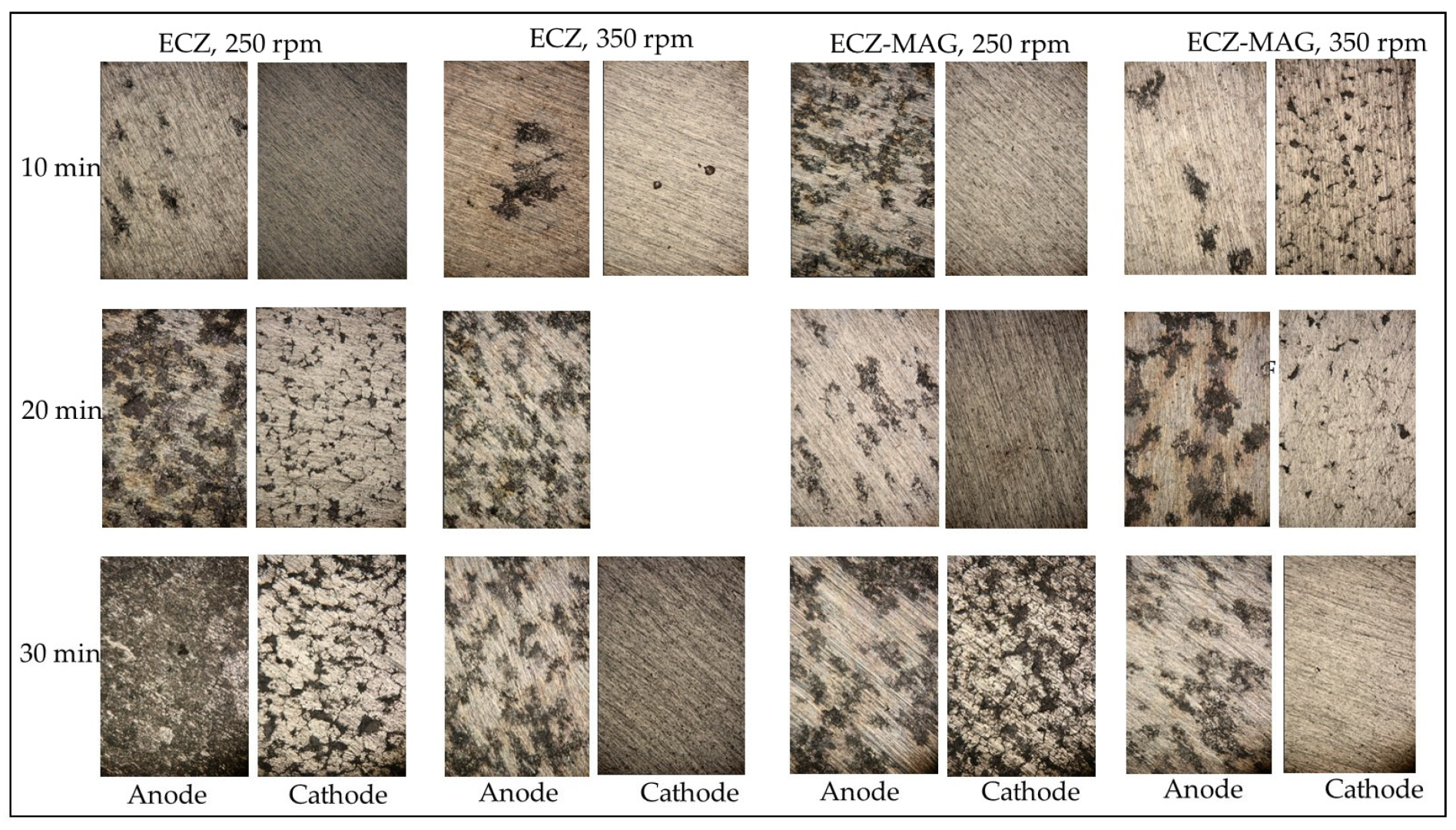
3.2. Mechanistic Insights into Electrode Dissolution and Mass Loss
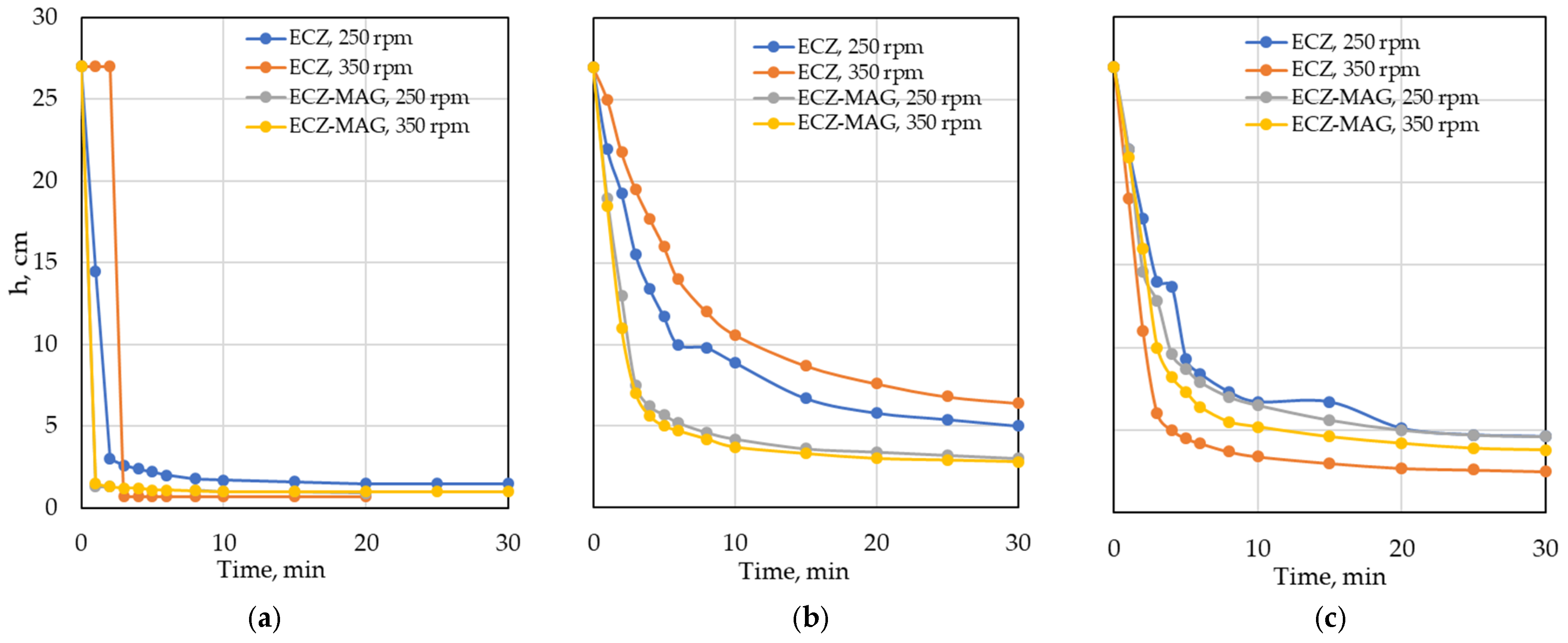
3.3. Solid–Liquid Separation Dynamics
3.4. Quantifying Energy Input and Electrode Loss
3.5. Taguchi-Based Process Optimization: Unraveling Interactions Between Physico-Chemical Process Efficiency, Electrode Dissolution, and Settling Behavior
3.5.1. COD Reduction
3.5.2. Settling Velocity
3.5.3. Electrode Loss
3.5.4. Turbidity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, N.; Poonia, T.; Siwal, S.S.; Srivastav, A.L.; Sharma, H.K.; Mittal, S.K. Challenges of Water Contamination in Urban Areas (Chapter 9); Srivastav, A.L., Madhav, S., Bhardwaj, A.K., Valsami, J., Eds.; Current Directions in Water Scarcity Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 6, pp. 173–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairone, S.; Hasan, S.W.; Choo, K.-H.; Lekkas, D.F.; Fortunato, L.; Zorpas, A.A.; Korshin, G.; Zarra, T.; Belgiorno, V.; Naddeo, V. Revolutionizing wastewater treatment toward circular economy and carbon neutrality goals: Pioneering sustainable and efficient solutions for automation and advanced process control with smart and cutting-edge technologies. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 63, 105486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshad, J.; Rehman, R.U. Innovative approaches to sustainable wastewater treatment: A comprehensive exploration of conventional an emerging technologies. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2025, 4, 189–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinpally, S.; Kolla, A.; Kainthola, J.; Kodali, R.; Vemuri, J. A state-of-the-art review of the electrocoagulation technology for wastewater treatment. Water. Cycle 2023, 4, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zailani, L.W.M.; Zin, N.S.M. Application of Electrocoagulation In Various Wastewater And Leachate Treatment-A Review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 140, 012052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, M.H.M.; Kamaruddin, M.A.; Norashiddin, F.A.; Niza, N.M.; Shadi, A.M.H.; Sabri, M.N.I.M.; Zawawi, M.H. Landfill leachate treatment technology via electrocoagulation: A review of operating parameters, intensification, and modelling. Desalin. Water Treat. 2022, 260, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phu, T.K.C.; Nguyen, P.L.; Phung, T.V.B. Recent progress in highly effective electrocoagulation-coupled systems for advanced wastewater treatment. iScience 2025, 28, 111965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebba, M.; Asaithambi, P.; Alemayehu, E. Investigation on operating parameters and cost using an electrocoagulation process for wastewater treatment. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, S.A.M.; Gaber, G.A.; Hussein, W.A.; Ahmed, A.S.I. Electrocoagulation process with Fe/Al electrodes to eliminate pollutants from real and synthetic wastewater. Results Mater. 2024, 23, 100606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Cotterill, S. Examining Current and Future Applications of Electrocoagulation in Wastewater Treatment. Water 2023, 15, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegladza, I.D.; Xu, Q.; Xu, K.; Lv, G.; Lu, J. Electrocoagulation processes: A general review about role of electro-generated flocs in pollutant removal. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 146, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorayyaei, S.; Raji, F.; Rahbar-Kelishami, A.; Ashrafizadeh, S.N. Combination of electrocoagulation and adsorption processes to remove methyl orange from aqueous solution. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 102018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratiwi, N.I.; Mukimin, A.; Zen, N.; Septarina, I. Integration of electrocoagulation, adsorption and wetland technology for jewelry industry wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 279, 119690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twizerimana, P.; Wu, Y. Overview of integrated electrocoagulation-adsorption strategies for the removal of heavy metal pollutants from wastewater. Discov. Chem. Eng. 2024, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svilović, S.; Vukojević Medvidović, N.; Vrsalović, L.; Kulić, A. Combining natural zeolite and electrocoagulation with different electrode materials–electrode surface analysis and Taguchi optimization. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2022, 12, 100330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukojević Medvidović, N.; Vrsalović, L.; Svilović, S.; Bobanović, A. Electrocoagulation vs. Integrate Electrocoagulation-Natural Zeolite for Treatment of Biowaste Compost Leachate—Whether the Optimum Is Truly Optimal. Minerals 2022, 12, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukojević Medvidović, N.; Vrsalović, L.; Svilović, S.; Magaš, K.; Jozić, D.; Čović, A. Electrocoagulation Combined with Synthetic Zeolite—Does the Size of Zeolite Particles Matter? Minerals 2023, 13, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasri, N.; Nightingale, M.; Cleland, K.J.; Roberts, E.P.L. The impact of a magnetic field on electrode fouling during electrocoagulation. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinas, G.; Lozon, C.; Kuhn, A. Unconventional applications of the magnetohydrodynamic effect in electrochemical systems. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2023, 38, 101220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibiya, N.P.; Amo-Duodu, G.; Tetteh, E.K.; Rathilal, S. Magnetic Field Effect on Coagulation Treatment of Wastewater Using Magnetite Rice Starch and Aluminium Sulfate. Polymers 2023, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayoumi, S.; Moharram, N.A.; Fayed, M.; El-Maghlany, W.M. Assessing the efficacy of magnetic water treatment: A concise review and experimental investigation. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 318, 100369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni’am, M.F.; Othman, F. Experimental Design of Electrocoagulation and Magnetic Technology for Enhancing Suspended Solids Removal from Synthetic Wastewater. Int. J. Sci. Eng. 2014, 7, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jiang, L.; Yao, X.; Hou, X.; Li, C.; Zou, Z.; Shen, F.; Li, C. Effect of permanent magnetic field on scale inhibition property of circulating water. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 1981–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafidi, M.Y.E.; Hafidi, M.E. Existing scale deposits removal by magnetic water treatment: Theoretical study and experiment. Int. J. Water Wastewater Treat. 2017, 3, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantawy, M.A.; Alomari, A.A.; Alghamdi, H.M.A.; Alzahrani, R.; Alsehami, S. Reducing formation of CaCO3 scales of groundwater by magnetic treatment reducing formation of CaCO3 scales of groundwater by magnetic treatment. Int. J Eng. Res. Technol. 2015, 4, 824–828. Available online: www.ijert.org (accessed on 15 June 2025).
- Elaoud, A.; Salah, N.B.; Moueddeb, E.K.; Amor, B.H.; Salah, B.; Elmoueddeb, K. Effect of magnetic treatment on surface tension and water evaporation. Int. J. Adv. Ind. Eng. 2017, 5, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheikh, O.; Elaoud, A.; Ben, A.H.; Hozayn, M. Effect of permanent magnetic field on the properties of static water and germination of cucumber seeds. Int. J. Multidiscip Curr. Res. 2018, 6, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, R.; Umber, M.; Satwat, H.A.; Komel, K.; Naseer, A.M. Magnetized irrigation water treatment for resolving salinity stress. FUUAST J. Biol. 2020, 10, 153–157. [Google Scholar]
- Medvidović, N.; Vrsalović, L.; Svilović, S.; Gudić, S.; Bućma, S. Magnetically Assisted Electrocoagulation Combined with Zeolite: Opportunities and Challenges in Compost Wastewater Treatment. In New Technologies, Development and Application VII.NT 2024; Lecture Notes in Networks and, Systems; Karabegovic, I., Kovačević, A., Mandzuka, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukojević Medvidović, N.; Vrsalović, L.; Svilović, S.; Gudić, S.; Čule, I. Sono- and Zeolite-Assisted Electrocoagulation for Compost Wastewater Treatment: Does Ultrasound Power Make a Difference? Minerals 2024, 14, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, A.D.; Clesceri, L.S.; Rice, E.W.; Greenberg, A.E.; Franson, M.A.H. (Eds.) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association (APHA): Cincinnati, OH, USA; Water Environment Federation (WEF): Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kordala, N.; Wyszkowski, M. Zeolite Properties, Methods of Synthesis, and Selected Applications. Molecules 2024, 29, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni’am, M.; Othman, F.; Sohaili, J.; Fauzia, Z. Combined Magnetic Field and Electrocoagulation Process for Suspended Solid Removal from Wastewater. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Natural Resources Engineering & Technology, Putrajaya, Malaysia, 24–25 July 2006; pp. 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozyonar, F.; Karagozoglu, B. Operating cost analysis and treatment of domestic wastewater by electrocoagulation using aluminium electrodes. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2011, 20, 173–179. Available online: https://www.pjoes.com/pdf-88543-22402?filename=Operating%20Cost%20Analysis.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2025).
- Eskibalci, M.F.; Ozkan, M.F. Comparison of conventional coagulation and electrocoagulation methods for dewatering of coal preparation plant. Miner. Eng. 2018, 122, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graça, N.S.; Rodrigues, A.E. The Combined Implementation of Electrocoagulation and Adsorption Processes for the Treatment of Wastewaters. Clean Technol. 2022, 4, 1020–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
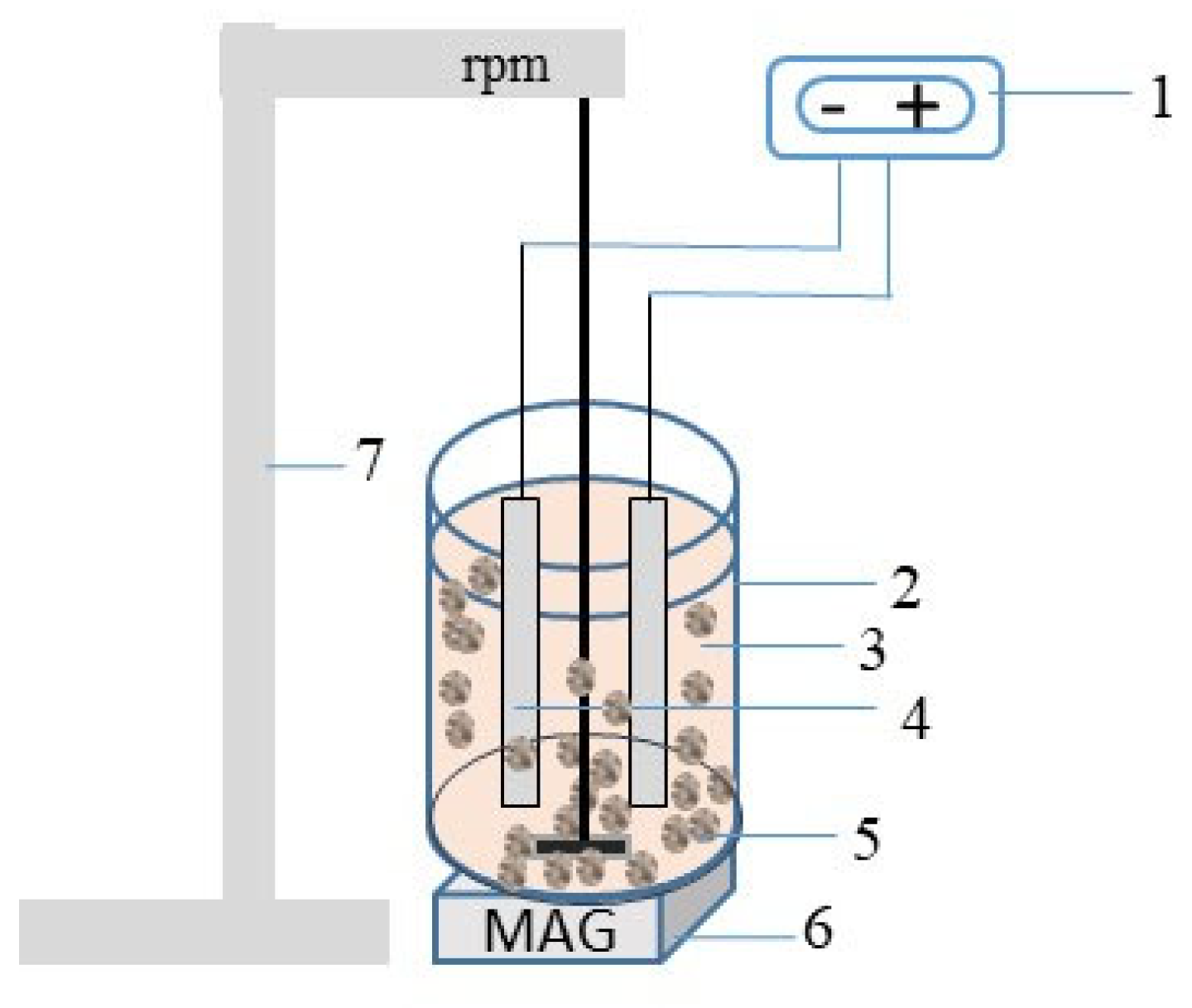
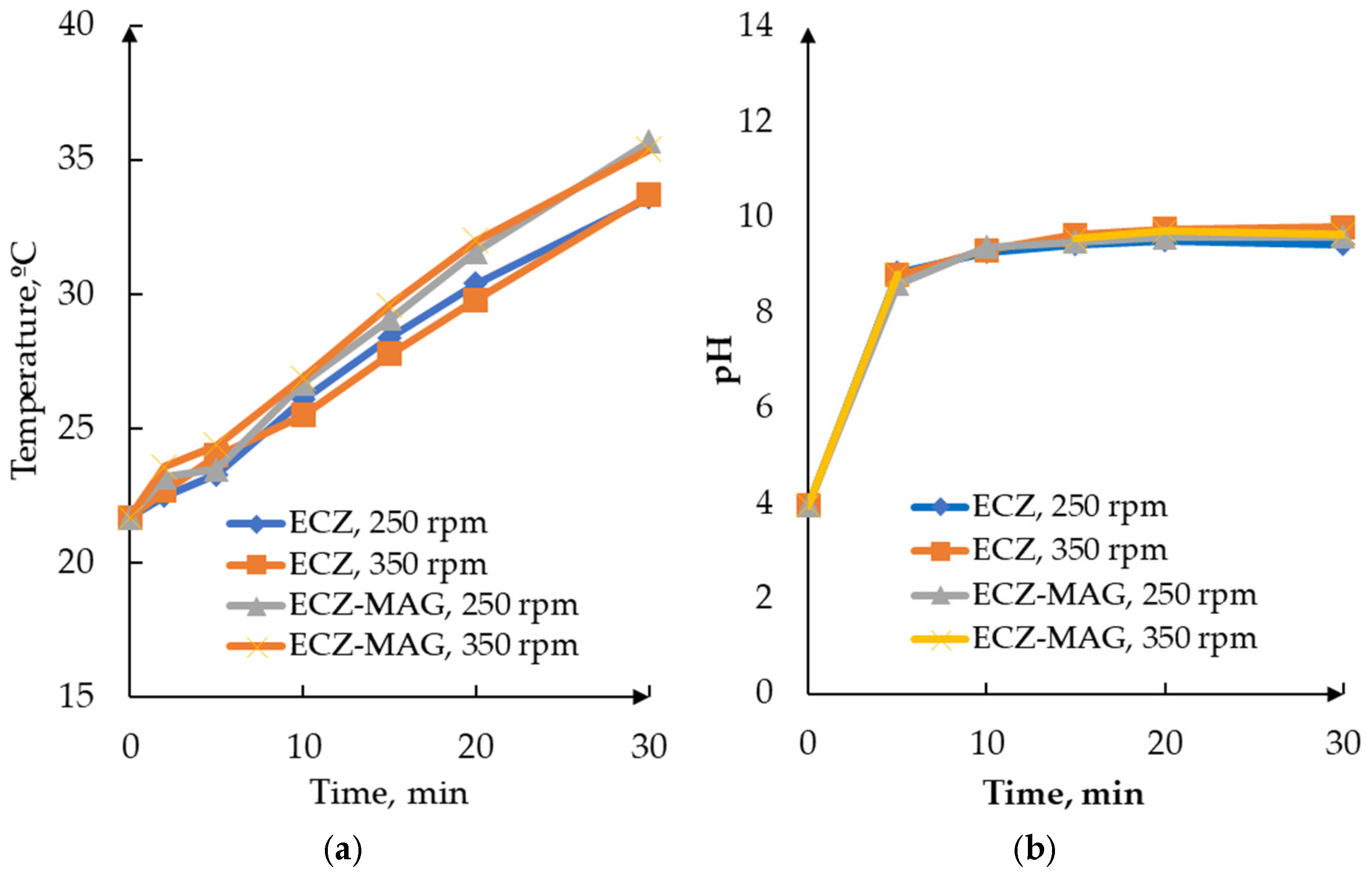
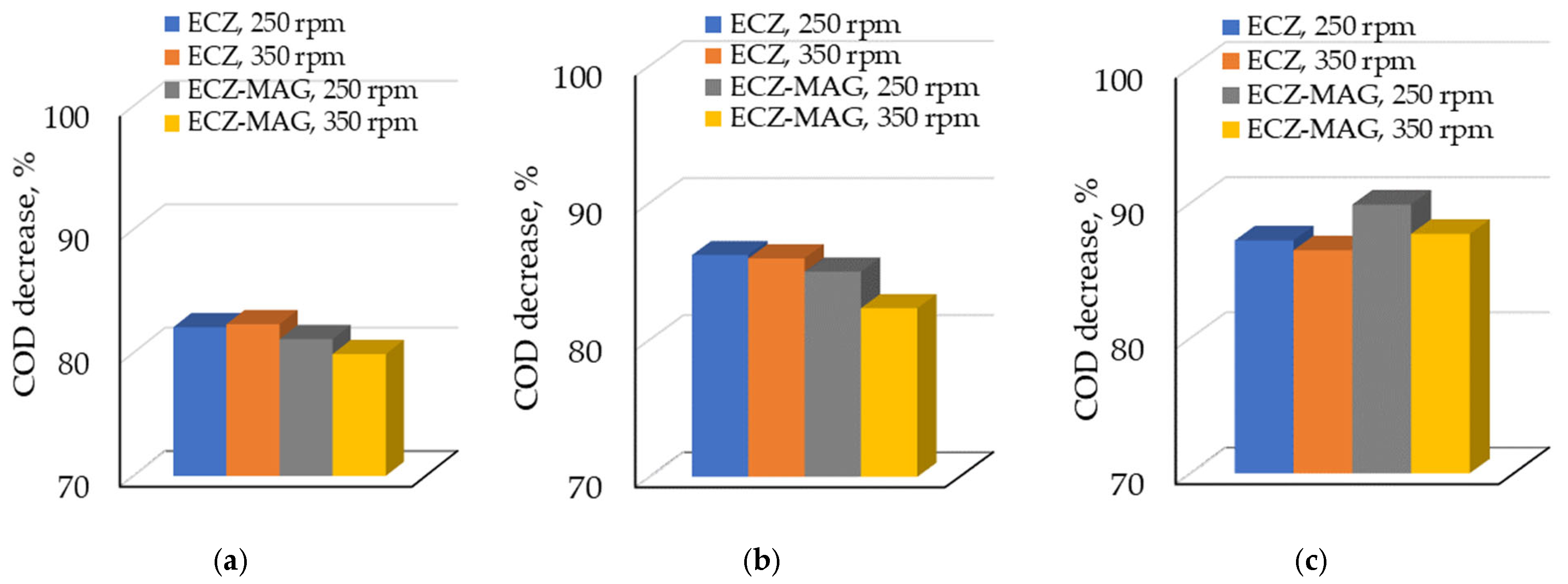
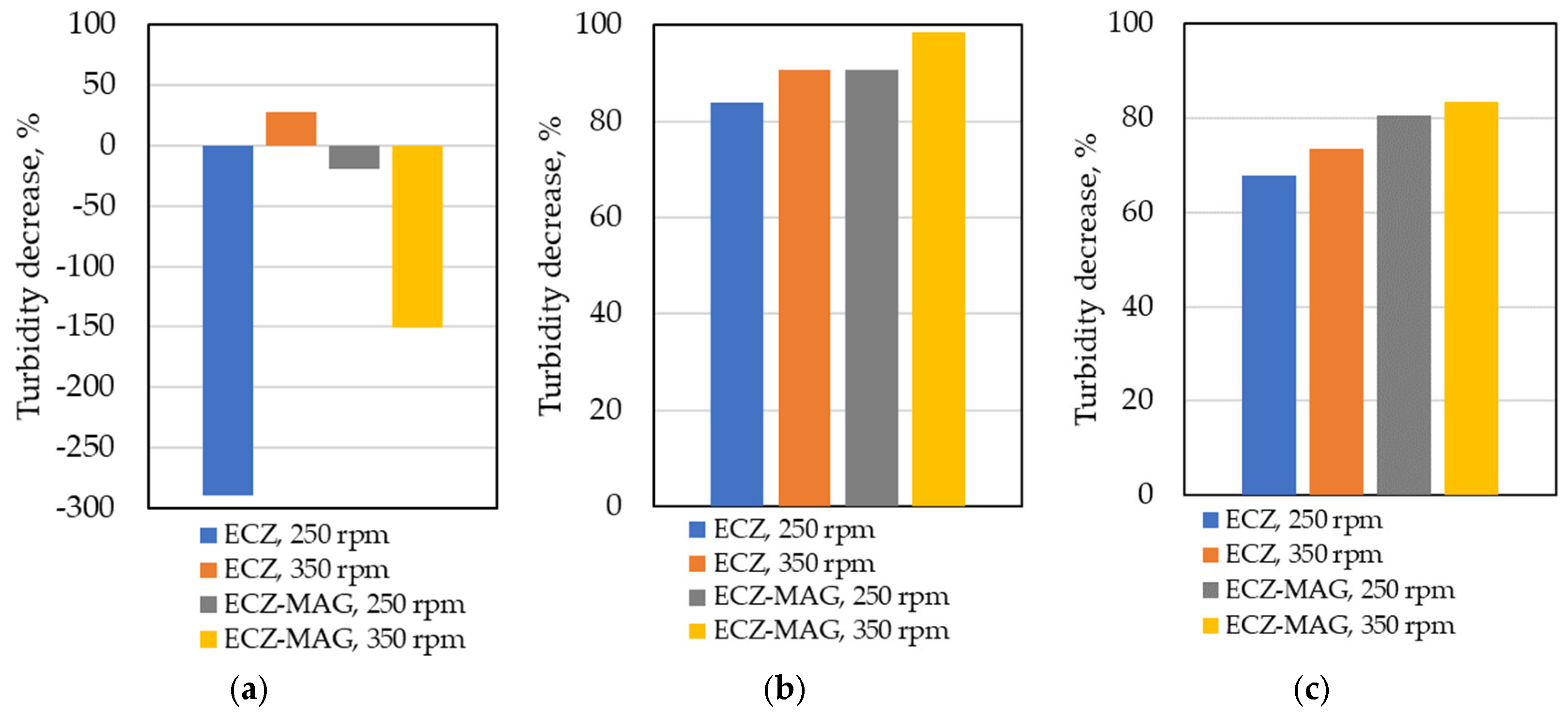
| Exp. Mark | Magnet | Mixing Speed, rpm | Contact Time, min |
|---|---|---|---|
| ECZ, 10 min, 250 rpm | no | 250 | 10 |
| ECZ, 20 min, 250 rpm | no | 250 | 20 |
| ECZ, 30 min, 250 rpm | no | 250 | 30 |
| ECZ, 10 min, 350 rpm | no | 350 | 10 |
| ECZ, 20 min, 350 rpm | no | 350 | 20 |
| ECZ, 30 min, 350 rpm | yes | 350 | 30 |
| ECZ-MAG, 10 min, 250 rpm | yes | 250 | 10 |
| ECZ-MAG, 20 min, 250 rpm | yes | 250 | 20 |
| ECZ-MAG, 30 min, 250 rpm | yes | 250 | 30 |
| ECZ-MAG, 10 min, 350 rpm | yes | 350 | 10 |
| ECZ-MAG, 20 min, 350 rpm | yes | 350 | 20 |
| ECZ-MAG, 30 min, 350 rpm | yes | 350 | 30 |
| Experiment Mark | U, V | Cenergy, kwh/m3 | Ctheor anode, kg/m3 | Cactual anode, kg/m3 | FE, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECZ, 10 min, 250 rpm | 20.81 | 6.03 | 0.24 | 0.13 | 54.23 |
| ECZ, 20 min, 250 rpm | 21.93 | 12.72 | 0.47 | 0.26 | 55.25 |
| ECZ, 30 min, 250 rpm | 21.63 | 18.77 | 0.71 | 0.39 | 55.62 |
| ECZ, 10 min, 350 rpm | 28.08 | 8.14 | 0.24 | 0.13 | 56.69 |
| ECZ, 20 min, 350 rpm | 23.99 | 13.91 | 0.47 | 0.26 | 55.25 |
| ECZ, 30 min, 350 rpm | 21.60 | 18.75 | 0.71 | 0.36 | 50.89 |
| ECZ-MAG, 10 min, 250 rpm | 23.33 | 6.76 | 0.24 | 0.13 | 57.03 |
| ECZ-MAG, 20 min, 250 rpm | 23.91 | 13.86 | 0.47 | 0.27 | 57.03 |
| ECZ-MAG, 30 min, 250 rpm | 25.41 | 22.06 | 0.71 | 0.39 | 54.88 |
| ECZ-MAG, 10 min, 350 rpm | 20.62 | 5.98 | 0.24 | 0.15 | 65.62 |
| ECZ-MAG, 20 min, 350 rpm | 22.52 | 13.06 | 0.47 | 0.26 | 54.40 |
| ECZ-MAG, 30 min, 350 rpm | 24.31 | 21.10 | 0.71 | 0.38 | 53.83 |
| Exp. Mark | Factor | COD Reduction, % | vt, cm/min | Turbidity, NTU | Electrodes Loss, g | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | |||||
| T1 | not present | 250 rpm | 10 min | 82.06 | 2.250 | 979.67 | 0.0820 |
| T2 | not present | 250 rpm | 20 min | 86.18 | 2.667 | 40.80 | 0.1800 |
| T3 | not present | 350 rpm | 10 min | 82.31 | 2.833 | 183.00 | 0.0713 |
| T4 | not present | 350 rpm | 20 min | 85.94 | 2.833 | 23.85 | 0.1581 |
| T5 | present | 250 rpm | 10 min | 81.09 | 0.560 | 300.50 | 0.0785 |
| T6 | present | 250 rpm | 20 min | 84.97 | 0.458 | 23.30 | 0.1465 |
| T7 | present | 350 rpm | 10 min | 79.88 | 1.956 | 630.50 | 0.0843 |
| T8 | present | 350 rpm | 20 min | 82.31 | 1.956 | 3.55 | 0.1478 |
| Exp. mark | S/NLB COD Reduction | S/NLB Settling Velocity | S/NSB Turbidity | S/NSB Electrodes Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 38.283 | 7.044 | −59.822 | 21.723 |
| T2 | 38.708 | 8.521 | −32.213 | 14.895 |
| T3 | 38.309 | 9.045 | −45.249 | 22.938 |
| T4 | 38.684 | 9.045 | −27.549 | 16.021 |
| T5 | 38.179 | −5.026 | −49.557 | 22.103 |
| T6 | 38.585 | −6.783 | −27.347 | 16.683 |
| T7 | 38.049 | 5.827 | −55.994 | 21.483 |
| T8 | 38.309 | 5.827 | −11.005 | 16.607 |
| Response | COD Reduction—Means | COD Reduction—S/N Ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor | A | B | C | A | B | C |
| Level 1 | 84.12 | 83.58 | 81.34 | 38.50 | 38.44 | 38.20 |
| Level 2 | 82.06 | 82.61 | 84.85 | 38.28 | 38.34 | 38.57 |
| Delta | 2.06 | 0.97 | 3.52 | 0.22 | 0.10 | 0.37 |
| Rank | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| Response | Settling velocity—means | Settling velocity—S/N ratio | ||||
| Factor | A | B | C | A | B | C |
| Level 1 | 2.646 | 1.484 | 1.900 | 8.413 | 0.936 | 4.220 |
| Level 2 | 1.232 | 2.394 | 1.978 | −0.041 | 7.436 | 4.152 |
| Delta | 1.413 | 0.911 | 0.79 | 8.454 | 6.500 | 0.068 |
| Rank | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Response | Electrode Loss—Means | Electrode Loss—S/N Ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor | A | B | C | A | B | C |
| Level 1 | 0.123 | 0.122 | 0.079 | 18.89 | 18.85 | 22.06 |
| Level 2 | 0.114 | 0.115 | 0.158 | 19.22 | 19.26 | 16.05 |
| Delta | 0.009 | 0.007 | 0.079 | 0.32 | 0.41 | 6.01 |
| Rank | 2 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| Response | Turbidity—means | Turbidity—S/N ratio | ||||
| Factor | A | B | C | A | B | C |
| Level 1 | 306.83 | 336.07 | 523.42 | −41.21 | −42.23 | −52.66 |
| Level 2 | 239.46 | 210.22 | 22.88 | −35.98 | −34.95 | −24.53 |
| Delta | 67.37 | 125.84 | 500.54 | 5.98 | 7.29 | 28.13 |
| Rank | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| Response | COD Reduction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor | A | B | C | Error |
| DF | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| SS | 8.487 | 1.862 | 24.710 | 2.727 |
| MS | 8.487 | 1.862 | 24.710 | 0.682 |
| pC, % | 22.46 | 4.93 | 65.39 | 7.22 |
| p-value | 0.024 | 0.174 | 0.004 | - |
| Significance | significant | not significant | highly significant | - |
| Response | Settling velocity | |||
| Factor | A | B | C | Error |
| DF | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| SS | 3.995 | 1.659 | 0.012 | 0.655 |
| MS | 3.995 | 1.659 | 0.012 | 0.164 |
| pC, % | 63.20 | 26.25 | 0.20 | 10.36 |
| p-value | 0.008 | 0.033 | 0.797 | - |
| Significance | highly significant | significant | not significant | - |
| Response | Electrode loss | |||
| Factor | A | B | C | Error |
| DF | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| SS | 0.00015 | 0.00008 | 0.01251 | 0.00059 |
| MS | 0.00015 | 0.00008 | 0.01251 | 0.000147 |
| pC, % | 1.10 | 0.61 | 93.87 | 4.42 |
| p-value | 0.374 | 0.499 | 0.001 | - |
| Significance | not significant | not significant | highly significant | - |
| Response | Turbidity | |||
| Factor | A | B | C | Error |
| DF | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| SS | 9077 | 31,673 | 501,086 | 345,156 |
| MS | 9077 | 31,673 | 501,086 | 86,289 |
| pC, % | 1.02 | 3.57 | 56.49 | 38.91 |
| p-value | 0.762 | 0.577 | 0.074 | - |
| Significance | not significant | not significant | marginally significant | - |
| Response | COD Reduction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor | A | B | C | Error |
| DF | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| SS | 0.0927 | 0.0205 | 0.2689 | 0.0291 |
| MS | 0.0927 | 0.0205 | 0.2689 | 0.0073 |
| pC, % | 22.55 | 4.98 | 65.39 | 7.08 |
| p-value | 0.023 | 0.169 | 0.004 | - |
| Significance | significant | not significant | highly significant | - |
| Response | Settling velocity | |||
| Factor | A | B | C | Error |
| DF | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| SS | 142.958 | 84.496 | 0.009 | 57.458 |
| MS | 142.958 | 84.496 | 0.009 | 14.365 |
| pC, % | 50.17 | 29.66 | 0.00 | 20.17 |
| p-value | 0.034 | 0.072 | 0.981 | - |
| Significance | significant | marginally significant | not significant | - |
| Response | Electrode loss | |||
| Factor | A | B | C | Error |
| DF | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| SS | 0.211 | 0.338 | 72.25 | 2.716 |
| MS | 0.211 | 0.338 | 72.25 | 0.679 |
| pC, % | 0.28 | 0.45 | 95.68 | 3.60 |
| p-value | 0.607 | 0.519 | 0.000 | - |
| Significance | not significant | not significant | highly significant | - |
| Response | Turbidity | |||
| Factor | A | B | C | Error |
| DF | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| SS | 54.76 | 106.16 | 1582.22 | 225.19 |
| MS | 54.76 | 106.16 | 1582.22 | 56.26 |
| pC, % | 2.78 | 5.39 | 80.39 | 11.43 |
| p-value | 0.380 | 0.242 | 0.006 | - |
| Significance | not significant | not significant | highly significant | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vukojević Medvidović, N.; Vrsalović, L.; Svilović, S.; Gudić, S.; Peran, L. Hybrid Electrocoagulation with Al Electrodes Assisted by Magnet and Zeolite: How Effective Is It for Compost Wastewater Treatment? Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8194. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158194
Vukojević Medvidović N, Vrsalović L, Svilović S, Gudić S, Peran L. Hybrid Electrocoagulation with Al Electrodes Assisted by Magnet and Zeolite: How Effective Is It for Compost Wastewater Treatment? Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(15):8194. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158194
Chicago/Turabian StyleVukojević Medvidović, Nediljka, Ladislav Vrsalović, Sandra Svilović, Senka Gudić, and Lucija Peran. 2025. "Hybrid Electrocoagulation with Al Electrodes Assisted by Magnet and Zeolite: How Effective Is It for Compost Wastewater Treatment?" Applied Sciences 15, no. 15: 8194. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158194
APA StyleVukojević Medvidović, N., Vrsalović, L., Svilović, S., Gudić, S., & Peran, L. (2025). Hybrid Electrocoagulation with Al Electrodes Assisted by Magnet and Zeolite: How Effective Is It for Compost Wastewater Treatment? Applied Sciences, 15(15), 8194. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158194








