Large Language Models: A Structured Taxonomy and Review of Challenges, Limitations, Solutions, and Future Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
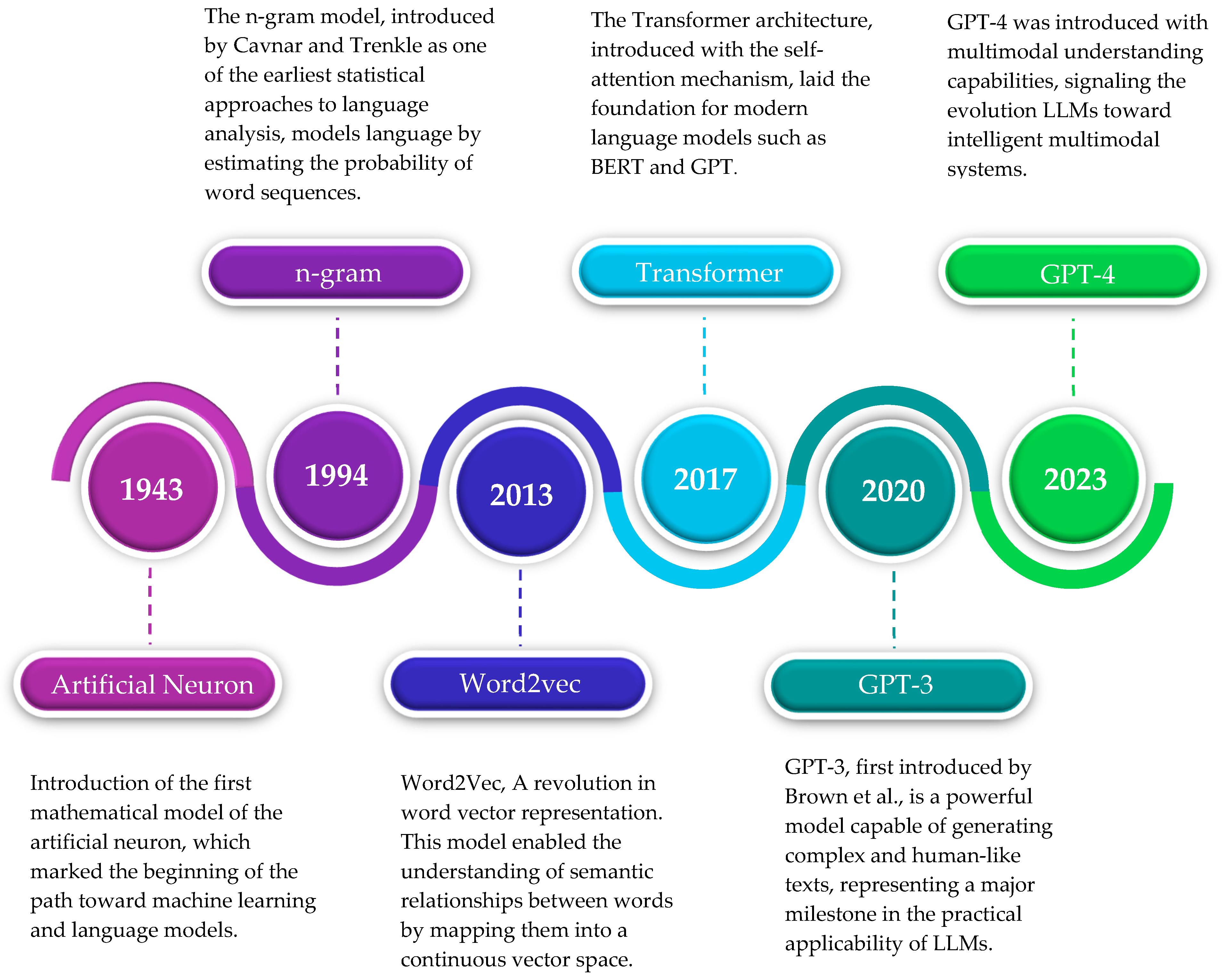
2. Definition of Large Language Models
2.1. Architecture of Large Language Models
- A multi-head self-attention mechanism, which captures intra-sequence dependencies.
- A fully connected feed-forward neural network, applied in a position-wise manner to each token.
- Causal decoder: A structure consisting solely of the decoder part, predicting the next token based on previous ones. The GPT architecture is of this type [2].
- Prefix decoder: In this model, attention is bidirectional, and instead of a strict dependence on the past, the entire sequence is utilized [32].
- Mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture: A sparse and scalable architecture in which only a small portion of the layers (experts) are activated in each step. This structure uses a router to direct tokens to different experts and allows for model enlargement without significantly increasing computational costs [33].
2.2. The Training Process of Large Language Models
- Collecting human pairwise preference labels (“better” vs. “worse”);
- Training a reward model to predict these preferences;
- Optimizing the language model with algorithms such as proximal policy optimization (PPO) to maximize the reward signal.
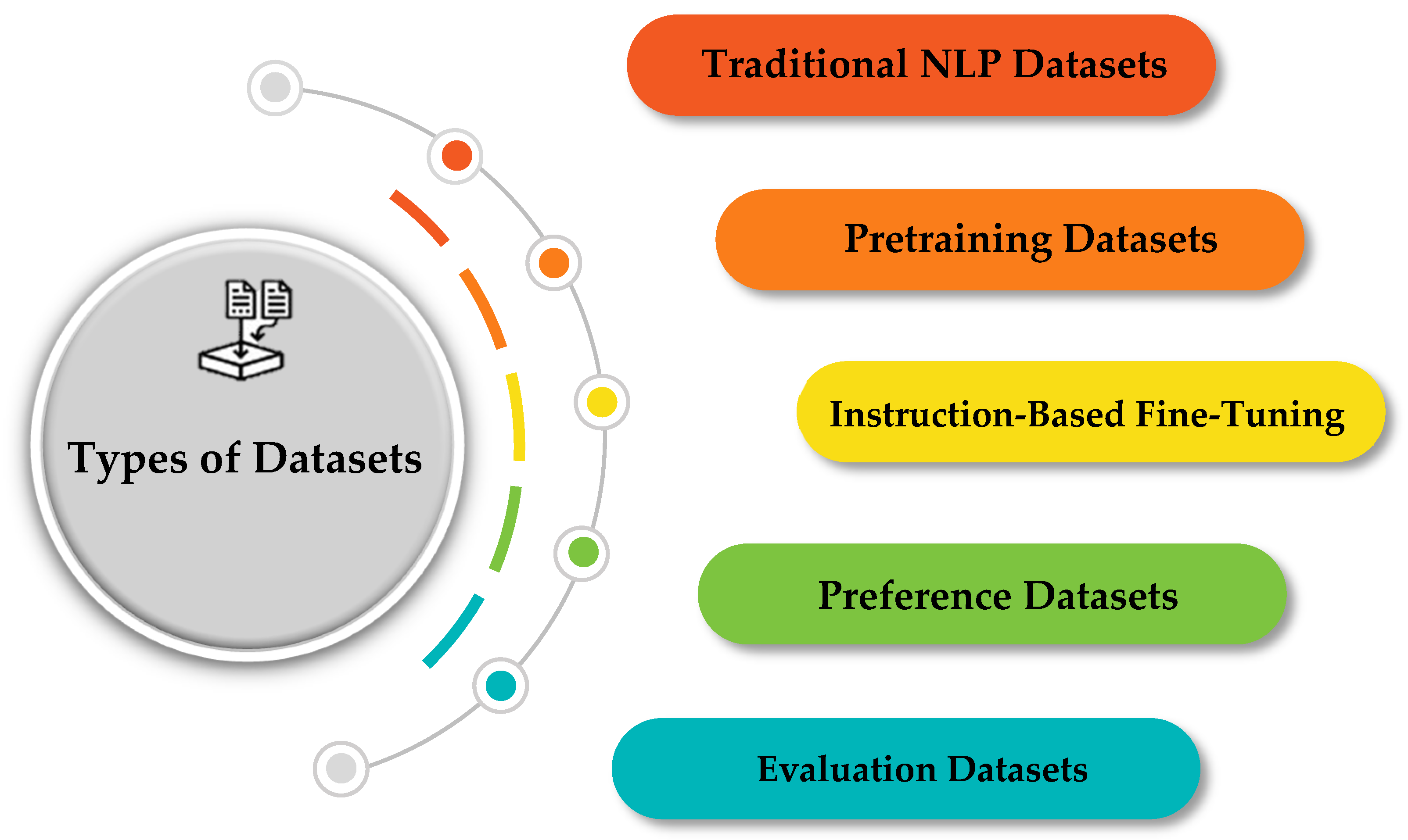
2.3. Large Language Model Datasets
2.3.1. Traditional Natural Language Processing Datasets
2.3.2. Pretraining Datasets
2.3.3. Instruction-Based Fine-Tuning Datasets
- General instruction-based fine-tuning datasets: This category comprises a diverse collection of commands and educational prompts spanning a wide range of domains. These data help models develop a deeper understanding of natural language and human directives, thereby broadening their ability to perform various tasks effectively [50].
- Task-specific instruction classification: In this approach, datasets are organized around particular tasks such as reasoning, text generation, or code understanding. By focusing on domain-specific prompts, this method enables targeted fine-tuning that boosts model performance in specialized areas [51].
- Instruction-based fine-tuning in specialized domains: These datasets are crafted specifically to enhance model performance in fields like medicine, law, or education. They employ the specialized terminology and procedural instructions of each domain so that the model becomes familiar with the unique structure and content requirements of that field [52].
2.3.4. Preference Datasets
2.3.5. Evaluation Datasets
2.4. Features and Capabilities of Large Language Models
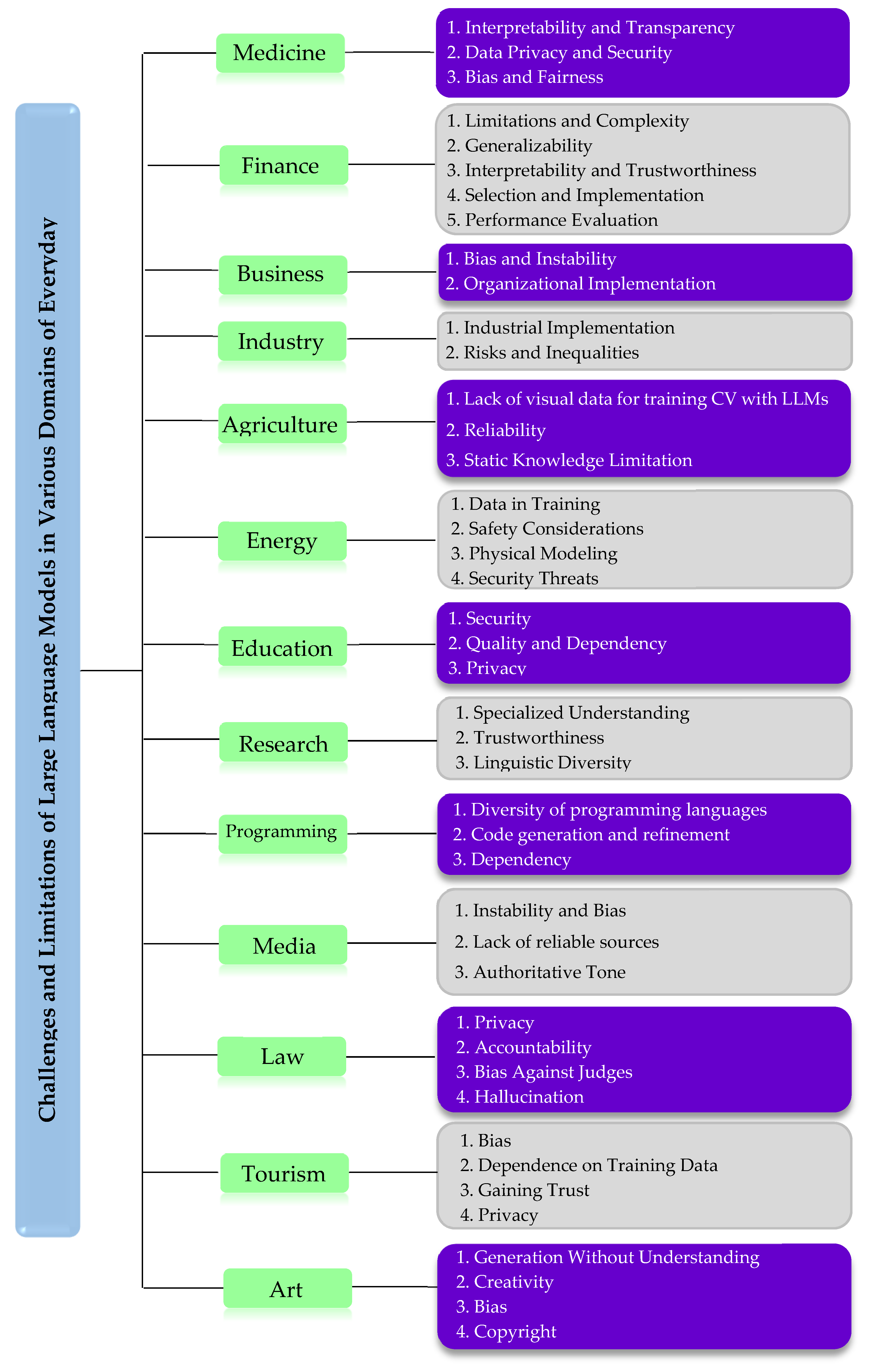
3. The Challenges and Limitations of Large Language Models Across Various Domains of Everyday Life
3.1. Medicine
3.1.1. Interpretability and Transparency
3.1.2. Data Privacy and Security
3.1.3. Bias and Fairness
3.2. Finance
3.2.1. Limitations and Complexity
3.2.2. Generalizability
3.2.3. Interpretability and Trustworthiness
3.2.4. Selection and Implementation
3.2.5. Performance Evaluation
3.3. Business
3.3.1. Bias and Instability
3.3.2. Organizational Implementation
3.4. Industry
3.4.1. Industrial Implementation
3.4.2. Risks and Inequalities
3.5. Agriculture
3.5.1. Lack of Visual Data for Training CV with LLMs
3.5.2. Reliability
3.5.3. Static Knowledge Limitation
3.5.4. Ambiguity in Description
3.6. Energy
3.6.1. Data in Training
3.6.2. Safety Considerations
3.6.3. Physical Modeling
3.6.4. Security Threats
3.7. Education
3.7.1. Security
3.7.2. Quality and Dependency
3.7.3. Privacy
3.8. Research
3.8.1. Specialized Understanding
3.8.2. Trustworthiness
3.8.3. Linguistic Diversity
3.9. Programming
3.9.1. Diversity of Programming Languages
3.9.2. Code Generation and Refinement
3.9.3. Dependency
3.10. Media
3.10.1. Instability and Bias
3.10.2. Lack of Reliable Sources
3.10.3. Authoritative Tone
3.10.4. Unreliable Sources
3.11. Law
3.11.1. Privacy
3.11.2. Accountability
3.11.3. Bias Against Judges
3.11.4. Hallucination
3.12. Tourism
3.12.1. Bias
3.12.2. Dependence on Training Data
3.12.3. Gaining Trust
3.12.4. Privacy
3.13. Art
3.13.1. Generation Without Understanding
3.13.2. Creativity
3.13.3. Bias
3.13.4. Copyright
3.13.5. Lack of Creative Dynamism
4. Technical Challenges and Considerations of LLMs
4.1. Fairness
4.2. Countering Malicious Attacks
4.3. Integration of Heterogeneous Data
4.4. Multimodal Large Language Model Research
4.5. Low-Resource Languages
4.6. Continuous Learning in Language Models
4.7. Ethical Use
4.8. Human Interaction
5. Future Directions
5.1. Technical Dimension
5.2. Ethical Dimension
5.3. Legal Dimension
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bommasani, R.; Hudson, D.A.; Adeli, E.; Altman, R.; Arora, S.; von Arx, S.; Bernstein, M.S.; Bohg, J.; Bosselut, A.; Brunskill, E.; et al. On the opportunities and risks of foundation models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.07258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- OpenAI; Achiam, J.; Adler, S.; Agarwal, S.; Ahmad, L.; Akkaya, I.; Aleman, F.L.; Almeida, D.; Altenschmidt, J.; Altman, S.; et al. Gpt-4 technical report. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.08774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Levy, O.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. Roberta: A robustly optimized bert pretraining approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Touvron, H.; Lavril, T.; Izacard, G.; Martinet, X.; Lachaux, M.-A.; Lacroix, T.; Rozière, B.; Goyal, N.; Hambro, E.; Azhar, F.; et al. Llama: Open and efficient foundation language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.13971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.S. Role of chat gpt in public health. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 51, 868–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driess, D.; Xia, F.; Sajjadi, M.S.M.; Lynch, C.; Chowdhery, A.; Ichter, B.; Wahid, A.; Tompson, J.; Vuong, Q.; Yu, T.; et al. Palm-e: An embodied multimodal language model. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.03378. [Google Scholar]
- Raiaan, M.A.K.; Mukta, S.H.; Fatema, K.; Fahad, N.M.; Sakib, S.; Mim, M.M.J.; Ahmad, J.; Ali, M.E.; Azam, S. A review on large language models: Architectures, applications, taxonomies, open issues and challenges. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 26839–26874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavnar, W.B.; Trenkle, J.M. N-gram-based text categorization. In Proceedings of the SDAIR-94, 3rd Annual Symposium on Document Analysis and Information Retrieval, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 11–13 April 1994; Volume 161175, p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Blunsom, P. Hidden Markov Models. Lect. Notes 2004, 15, 48. [Google Scholar]
- Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1301.3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, J.; Socher, R.; Manning, C.D. Glove: Global vectors for word representation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014; pp. 1532–1543. [Google Scholar]
- Mikolov, T.; Karafiát, M.; Burget, L.; Cernocký, J.; Khudanpur, S. Recurrent neural network based language model. In Proceedings of the Interspeech, Chiba, Japan, 26–30 September 2010; Volume 2, No. 3. pp. 1045–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Si, X.; Hu, C.; Zhang, J. A review of recurrent neural networks: LSTM cells and network architectures. Neural Comput. 2019, 31, 1235–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language models are few-shot learners. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Virtual, 6–12 December 2020; Volume 33, pp. 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Kosmyna, N.; Hauptmann, E.; Yuan, Y.T.; Situ, J.; Liao, X.-H.; Beresnitzky, A.V.; Braunstein, I.; Maes, P. Your brain on chatgpt: Accumulation of cognitive debt when using an ai assistant for essay writing task. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2506.08872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magesh, V.; Surani, F.; Dahl, M.; Suzgun, M.; Manning, C.D.; Ho, D.E. Hallucination-Free? Assessing the Reliability of Leading AI Legal Research Tools. J. Empir. Leg. Stud. 2025, 22, 216–242. [Google Scholar]
- Kasneci, E.; Sessler, K.; Küchemann, S.; Bannert, M.; Dementieva, D.; Fischer, F.; Gasser, U.; Groh, G.; Günnemann, S.; Hüllermeier, E.; et al. ChatGPT for good? On opportunities and challenges of large language models for education. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2023, 103, 102274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidinger, L.; Uesato, J.; Rauh, M.; Griffin, C.; Huang, P.-S.; Mellor, J.; Glaese, A.; Cheng, M.; Balle, B.; Kasirzadeh, A.; et al. Taxonomy of risks posed by language models. In Proceedings of the 2022 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 21–24 June 2022; pp. 214–229. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, F.; Liu, N.; Du, M. Quantifying multilingual performance of large language models across languages. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.11553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zheng, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, H.; Gu, H.; Shen, T.; Qin, C.; Zhu, C.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Q.; et al. A survey on large language models for recommendation. World Wide Web 2024, 27, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.; Gudivada, V. A review of current trends, techniques, and challenges in large language models (llms). Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Su, W.J. A Law of Next-Token Prediction in Large Language Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.13442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, E.M.; Gebru, T.; McMillan-Major, A.; Shmitchell, S. On the dangers of stochastic parrots: Can language models be too big? In Proceedings of the 2021 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency, Virtual, 3–10 March 2021; pp. 610–623. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Du, S.; Li, B.; Luo, Y.; Tang, N. Are Large Language Models Good Statisticians? arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.07815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazrouei, E.; Alobeidli, H.; Alshamsi, A.; Cappelli, A.; Cojocaru, R.; Debbah, M.; Goffinet, É.; Hesslow, D.; Launay, J.; Malartic, Q.; et al. The falcon series of open language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.16867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, H.; Khan, A.U.; Qiu, S.; Saqib, M.; Anwar, S.; Usman, M.; Akhtar, N.; Barnes, N.; Mian, A. A comprehensive overview of large language models. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Hu, W.; Wu, F.; Sengamedu, S. DeTiME: Diffusion-enhanced topic modeling using encoder-decoder based LLM. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.15296. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Xiao, A.; Wu, E.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y. Transformer in transformer. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 15908–15919. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, Y.; Qin, H.; Dong, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Li, Z. Large language model (llm) ai text generation detection based on transformer deep learning algorithm. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.06652. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Mahmood, A. The NLP cookbook: Modern recipes for transformer based deep learning architectures. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 68675–68702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; El Mesbahi, Y.; Kobyzev, I.; Rashid, A.; Mahmud, A.; Anchuri, N.; Hajimolahoseini, H.; Liu, Y.; Rezagholizadeh, M. A short study on compressing decoder-based language models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.08460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shazeer, N.; Mirhoseini, A.; Maziarz, K.; Davis, A.; Le, Q.; Hinton, G.; Dean, J. Outrageously large neural networks: The sparsely-gated mixture-of-experts layer. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1701.06538. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhu, K.; Chen, H.; Yi, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; et al. A survey on evaluation of large language models. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2024, 15, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhery, A.; Narang, S.; Devlin, J.; Bosma, M.; Mishra, G.; Roberts, A.; Barham, P.; Chung, H.W.; Sutton, C.; Gehrmann, S.; et al. Palm: Scaling language modeling with pathways. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2023, 24, 11324–11436. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Qiu, L.; Ross, A.; Akyürek, E.; Chen, B.; Wang, B.; Kim, N.; Andreas, J.; Kim, Y. Reasoning or reciting? Exploring the capabilities and limitations of language models through counterfactual tasks. In Proceedings of the 2024 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Mexico City, Mexico, 16–21 June 2024; Volume 1: Long Papers, pp. 1819–1862. [Google Scholar]
- Christiano, P.F.; Leike, J.; Brown, T.; Martic, M.; Legg, S.; Amodei, D. Deep reinforcement learning from human preferences. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, J.; Liu, C.; Ding, K.; Jin, L. Datasets for large language models: A comprehensive survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.18041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhoest, Q.; del Moral, A.V.; Jernite, Y.; Thakur, A.; von Platen, P.; Patil, S.; Chaumond, J.; Drame, M.; Plu, J.; Tunstall, L.; et al. Datasets: A community library for natural language processing. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.02846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Cui, C.; Khanuja, S.; Liu, P.; Faisal, F.; Ostapenko, A.; Indra Winata, G.; Fikri Aji, A.; Cahyawijaya, S.; Svetkov, Y.; et al. GlobalBench: A benchmark for global progress in natural language processing. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.14716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.; Dikkala, N.; Anand, A.; Devic, P.; Dasgupta, I.; Liu, F.; Fatemi, B.; Awasthi, P.; Gollapudi, S.; Guo, D.; et al. Remi: A dataset for reasoning with multiple images. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 10–15 December 2024; Volume 37, pp. 60088–60109. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Li, J.; Wu, H.; Hovy, E.; Sun, Y. Pre-trained language models and their applications. Engineering 2023, 25, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlini, N.; Tramer, F.; Wallace, E.; Jagielski, M.; Herbert-Voss, A.; Lee, K.; Roberts, A.; Brown, T.; Song, D.; Erlingsson, Ú.; et al. Extracting training data from large language models. In Proceedings of the 30th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 21), Virtual, 11–13 August 2021; pp. 2633–2650. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, X.; Sun, T.; Xu, Y.; Shao, Y.; Dai, N.; Huang, X. Pre-trained models for natural language processing: A survey. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2020, 63, 1872–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, C.; Qu, X.; Ma, Y.; Duan, F.; Bai, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. D-cpt law: Domain-specific continual pre-training scaling law for large language models. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 10–15 December 2024; Volume 37, pp. 90318–90354. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Tinn, R.; Cheng, H.; Lucas, M.; Usuyama, N.; Liu, X.; Naumann, T.; Gao, J.; Poon, H. Domain-specific language model pretraining for biomedical natural language processing. ACM Trans. Comput. Healthc. (HEALTH) 2021, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, M.U.; Al Tashi, Q.; Qureshi, R.; Shah, A.; Muneer, A.; Irfan, M.; Zafar, A.; Shaikh, M.B.; Akhtar, N.; Hassan, S.Z.; et al. Large language models: A comprehensive survey of its applications, challenges, limitations, and future prospects. Authorea Prepr. 2023, 1, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Ippolito, D.; Nystrom, A.; Zhang, C.; Eck, D.; Callison-Burch, C.; Carlini, N. Deduplicating training data makes language models better. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.06499. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Dong, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Hu, R.; Zhang, T.; Wu, F.; et al. Instruction tuning for large language models: A survey. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.10792. [Google Scholar]
- Honovich, O.; Scialom, T.; Levy, O.; Schick, T. Unnatural instructions: Tuning language models with (almost) no human labor. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.09689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.U.; Ficek, A.; Samadi, M.; Huang, J.; Noroozi, V.; Majumdar, S.; Ginsburg, B. OpenCodeInstruct: A Large-scale Instruction Tuning Dataset for Code LLMs. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.04030. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Tian, C.; Yang, X.; Chen, L.; Li, Z.; Petzold, L.R. Alpacare: Instruction-tuned large language models for medical application. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.14558. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, G.; Yuan, L.; Ding, N.; Yao, G.; He, B.; Zhu, W.; Ni, Y.; Xie, G.; Xie, R.; Lin, Y.; et al. Ultrafeedback: Boosting language models with high-quality feedback. In Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 21–27 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, L.; Wu, J.; Jiang, X.; Almeida, D.; Wainwright, C.L.; Mishkin, P.; Zhang, C.; Agarwal, S.; Slama, K.; Ray, A.; et al. Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022; Volume 35, pp. 27730–27744. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, T.A.; Bergen, B.K. Language model behavior: A comprehensive survey. Comput. Linguist. 2024, 50, 293–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Tan, T.F.; Lu, W.; Thirunavukarasu, A.J.; Ting, D.S.W.; Liu, N. Large language models in health care: Development, applications, and challenges. Health Care Sci. 2023, 2, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeniran, A.A.; Onebunne, A.P.; William, P. Explainable AI (XAI) in healthcare: Enhancing trust and transparency in critical decision-making. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2024, 23, 2647–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.C.; Amini, M.H.; Wu, Y. Security and privacy challenges of large language models: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2025, 57, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chang, K.C.C. Towards reasoning in large language models: A survey. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.10403. [Google Scholar]
- Lehman, E.; Jain, S.; Pichotta, K.; Goldberg, Y.; Wallace, B.C. Does BERT pretrained on clinical notes reveal sensitive data? arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.07762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.T.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. “Why should i trust you?” Explaining the predictions of any classifier. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 1135–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Thirunavukarasu, A.J.; Ting, D.S.J.; Elangovan, K.; Gutierrez, L.; Tan, T.F.; Ting, D.S.W. Large language models in medicine. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1930–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeilzadeh, P. Challenges and strategies for wide-scale artificial intelligence (AI) deployment in healthcare practices: A perspective for healthcare organizations. Artif. Intell. Med. 2024, 151, 102861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazi, Z.A.; Peng, W. Large language models in healthcare and medical domain: A review. Informatics 2024, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshjou, R.; Vodrahalli, K.; Novoa, R.A.; Jenkins, M.; Liang, W.; Rotemberg, V.; Ko, J.; Swetter, S.M.; Bailey, E.E.; Gevaert, O.; et al. Disparities in dermatology AI performance on a diverse, curated clinical image set. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabq6147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanzadeh, F.; Josephson, C.B.; Waters, G.; Adedinsewo, D.; Azizi, Z.; White, J.A. Bias recognition and mitigation strategies in artificial intelligence healthcare applications. NPJ Digit. Med. 2025, 8, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, M.; Sorin, V.; Agbareia, R.; Apakama, D.U.; Soroush, A.; Sakhuja, A.; Freeman, R.; Horowitz, C.R.; Richardson, L.D.; Nadkarni, G.N.; et al. Evaluating and addressing demographic disparities in medical large language models: A systematic review. Int. J. Equity Health 2025, 24, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omiye, J.A.; Gui, H.; Rezaei, S.J.; Zou, J.; Daneshjou, R. Large language models in medicine: The potentials and pitfalls: A narrative review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2024, 177, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Y.; Kong, Y.; Dong, X.; Mulvey, J.M.; Poor, H.V.; Wen, Q.; Zohren, S. A survey of large language models for financial applications: Progress, prospects and challenges. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.11903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, N.; Choudhary, S.; Rane, J. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) approaches for transparency and accountability in financial decision-making. SSRN Electron. J. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Guo, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, W.; Liu, J. BizFinBench: A Business-Driven Real-World Financial Benchmark for Evaluating LLMs. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.19457. [Google Scholar]
- Shoeybi, M.; Patwary, M.; Puri, R.; LeGresley, P.; Casper, J.; Catanzaro, B. Megatron-lm: Training multi-billion parameter language models using model parallelism. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.08053. [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan, D.; Shoeybi, M.; Casper, J.; LeGresley, P.; Patwary, M.; Korthikanti, V.A.; Vainbrand, D.; Kashinkunti, P.; Bernauer, J.; Catanzaro, B.; et al. Efficient large-scale language model training on gpu clusters using megatron-lm. In Proceedings of the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis, St. Louis, MO, USA, 14–19 November 2021; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Araci, D. Finbert: Financial sentiment analysis with pre-trained language models. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.10063. [Google Scholar]
- Strubell, E.; Ganesh, A.; McCallum, A. Energy and policy considerations for modern deep learning research. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, No. 09. pp. 13693–13696. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Ding, H.; Chen, H. Large language models in finance: A survey. In Proceedings of the Fourth ACM International Conference on AI in Finance, New York, NY, USA, 27–29 November 2023; pp. 374–382. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, Z.; Guo, H.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, F.; Chen, H.; Xu, W.; Lu, X.; Cui, Q.; Li, L.; et al. Data-centric financial large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.17784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phogat, K.S.; Puranam, S.A.; Dasaratha, S.; Harsha, C.; Ramakrishna, S. Fine-tuning Smaller Language Models for Question Answering over Financial Documents. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.12337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Y.; Peng, X.; Yi, H.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, J.; Xie, Q.; Nie, J.-Y. Fino1: On the transferability of reasoning enhanced llms to finance. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.08127. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Irsoy, O.; Lu, S.; Dabravolski, V.; Dredze, M.; Gehrmann, S.; Kambadur, P.; Rosenberg, D.; Mann, G. BloombergGPT: A large language model for finance. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.17564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Bao, R.; Harimoto, K.; Sun, X. Proxy Tuning for Financial Sentiment Analysis: Overcoming Data Scarcity and Computational Barriers. In Proceedings of the Joint Workshop of the 9th Financial Technology and Natural Language Processing (FinNLP), the 6th Financial Narrative Processing (FNP), and the 1st Workshop on Large Language Models for Finance and Legal (LLMFinLegal), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 19–20 January 2025; pp. 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Gan, W.; Chen, Z.; Wan, S.; Yu, P.S. Multimodal large language models: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (BigData), Sorrento, Italy, 15–18 December 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 2247–2256. [Google Scholar]
- Mirishli, S. Regulating Ai In Financial Services: Legal Frameworks and Compliance Challenges. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.14541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.; Sun, Y.; Kumar, M.; Mutneja, T.; Mukherjee, A.; Yang, H. LLMs Meet Finance: Fine-Tuning Foundation Models for the Open FinLLM Leaderboard. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.13125. [Google Scholar]
- Tavasoli, A.; Sharbaf, M.; Madani, S.M. Responsible Innovation: A Strategic Framework for Financial LLM Integration. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.02165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Nourian, A.; Griest, K. Hidden technical debts for fair machine learning in financial services. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.10510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Arulappan, A.; Naha, R.; Mahanti, A.; Kamruzzaman, J.; Ra, I.H. Large language models and sentiment analysis in financial markets: A review, datasets and case study. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 134041–134061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsamie, M.; Wang, H. Comparative analysis of LLM-based market prediction and human expertise with sentiment analysis and machine learning integration. In Proceedings of the 2024 7th International Conference on Data Science and Information Technology (DSIT), Nanjing, China, 20–22 December 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zaremba, A.; Demir, E. ChatGPT: Unlocking the future of NLP in finance. Mod. Financ. 2023, 1, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidgof, M.; Bachhofner, S.; Mendling, J. Large language models for business process management: Opportunities and challenges. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Business Process Management, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 11–15 September 2023; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 107–123. [Google Scholar]
- Fahland, D.; Fournier, F.; Limonad, L.; Skarbovsky, I.; Swevels, A.J. How well can large language models explain business processes? arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.12846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasseri, M.; Brandtner, P.; Zimmermann, R.; Falatouri, T.; Darbanian, F.; Obinwanne, T. Applications of large language models (LLMs) in business analytics–exemplary use cases in data preparation tasks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Copenhagen, Denmark, 23 July 2023; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 182–198. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, E. Should chatgpt be biased? challenges and risks of bias in large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.03738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Logeswaran, L.; Lee, M.; Lee, H.; Poria, S.; Mihalcea, R. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of large language models for cultural commonsense. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.04655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkon, A.A.; Shaima, M.; Sarker, M.S.U.; Badruddowza; Nabi, N.; Rana, M.N.U.; Ghosh, S.K.; Rahman, M.A.; Esa, H.; Chowdhury, F.R. Advancements and applications of generative artificial intelligence and large language models on business management: A comprehensive review. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. Stud. 2024, 6, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teubner, T.; Flath, C.M.; Weinhardt, C.; Van Der Aalst, W.; Hinz, O. Welcome to the era of chatgpt et al. the prospects of large language models. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2023, 65, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.; Jahangir, Z.; Riaz, M.B.; Saeed, M.J.; Sattar, M.A. Industrial applications of large language models. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 13755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Guo, T.-Z.; Li, D.-P.; He, T.; Li, Z.; Yang, Q.-W.; Wang, H.-H.; Wen, Y.-Y. Systems engineering issues for industry applications of large language model. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 151, 111165. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Piao, L.; Zang, X.; Luo, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Rong, J. Analyzing differences of highway lane-changing behavior using vehicle trajectory data. Phys. A: Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2023, 624, 128980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wei, C.; Xin, Z.; Zhao, J.; Xian, J. Ship detection under low-visibility weather interference via an ensemble generative adversarial network. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, H.; Pan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Shu, P.; Tian, J.; Yang, T.; Xu, S.; et al. Large language models for manufacturing. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.21418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chkirbene, Z.; Hamila, R.; Gouissem, A.; Devrim, U. Large Language Models (LLM) in Industry: A Survey of Applications, Challenges, and Trends. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 21st International Conference on Smart Communities: Improving Quality of Life Using AI, Robotics and IoT (HONET), Doha, Qatar, 3–5 December 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 229–234. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Z.; Lee, N.; Frieske, R.; Yu, T.; Su, D.; Xu, Y.; Ishii, E.; Bang, Y.J.; Madotto, A.; Fung, P. Survey of hallucination in natural language generation. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maatouk, A.; Piovesan, N.; Ayed, F.; De Domenico, A.; Debbah, M. Large language models for telecom: Forthcoming impact on the industry. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2024, 63, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urlana, A.; Kumar, C.V.; Singh, A.K.; Garlapati, B.M.; Chalamala, S.R.; Mishra, R. LLMs with Industrial Lens: Deciphering the Challenges and Prospects—A Survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.14558. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Jiang, H.; Shu, P.; Shi, E.; Hu, H.; Ma, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Large language models for robotics: Opportunities, challenges, and perspectives. J. Autom. Intell. 2025, 4, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayegani, E.; Mamun, M.A.A.; Fu, Y.; Zaree, P.; Dong, Y.; Abu-Ghazaleh, N. Survey of vulnerabilities in large language models revealed by adversarial attacks. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.10844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, J.S.G.; Ng, P.C.; Wang, Z.; McLoughlin, I.; Ng, A.B.; See, S. On-Device LLMs for SMEs: Challenges and Opportunities. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.16070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, N. ChatGPT and similar generative artificial intelligence (AI) for smart industry: Role, challenges and opportunities for industry 4.0, industry 5.0 and society 5.0. Chall. Oppor. Ind. 2023, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Qin, S.; Su, M.; Lin, C.; Li, A.; Gao, J. Harnessing large vision and language models in agriculture: A review. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.19679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, M.; Xiang, L.; Chen, D.; Zhuang, W.; Yin, X.; Li, Z. Large language models and foundation models in smart agriculture: Basics, opportunities, and challenges. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.06668. [Google Scholar]
- Tzachor, A.; Devare, M.; Richards, C.; Pypers, P.; Ghosh, A.; Koo, J.; Johal, S.; King, B. Large language models and agricultural extension services. Nat. Food 2023, 4, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vizniuk, A.; Diachenko, G.; Laktionov, I.; Siwocha, A.; Xiao, M.; Smoląg, J. A comprehensive survey of retrieval-augmented large language models for decision making in agriculture: Unsolved problems and research opportunities. J. Artif. Intell. Soft Comput. Res. 2025, 15, 115–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, R.; Li, X. The application progress and research trends of knowledge graphs and large language models in agriculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 235, 110396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezayi, S.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Dhakal, C.; Ge, B.; Dai, H.; Mai, G.; Liu, N.; Zhen, C.; Liu, T.; et al. Exploring new frontiers in agricultural nlp: Investigating the potential of large language models for food applications. IEEE Trans. Big Data 2024, 11, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, T.A.; Rasool, T.; Veningston, K.; Yaseen, S.M. The role of large language models in agriculture: Harvesting the future with LLM intelligence. Prog. Artif. Intell. 2024, 14, 117–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, H.; Li, Q.; Zhao, C. A review on enhancing agricultural intelligence with large language models. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2025, 15, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, M.; Zhao, Z.; Li, F.; Guo, L. IPM-AgriGPT: A Large Language Model for Pest and Disease Management with a G-EA Framework and Agricultural Contextual Reasoning. Mathematics 2025, 13, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Das, S.; Mondal, A.C. A Study of the Application Domain of a Large Language Models in the Agricultural Sector. Int. J. Innov. Res. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2024, 12, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, S.; Dong, L.; Doudi, F.; Cai, Y.; Tian, C.; Kalathi, D.; Ding, K.; Thatte, A.A.; Li, N.; Xie, L. Exploring the capabilities and limitations of large language models in the electric energy sector. Joule 2024, 8, 1544–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinakis, V. Big data for energy management and energy-efficient buildings. Energies 2020, 13, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, S.; Tavasoli, A.; Astaneh, Z.K.; Pineau, P.O. Large Language Models integration in Smart Grids. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.09059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katamoura, S.; Aksoy, M.S.; AlKhamees, B. Privacy and Security in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Systems for Renewable Energy Big Data. In Proceedings of the 2024 21st Learning and Technology Conference (L&T), Makkah, Saudi Arabia, 15–16 January 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Kaddour, J.; Harris, J.; Mozes, M.; Bradley, H.; Raileanu, R.; McHardy, R. Challenges and applications of large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.10169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rillig, M.C.; Ågerstrand, M.; Bi, M.; Gould, K.A.; Sauerland, U. Risks and benefits of large language models for the environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 3464–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Z. Opportunities and challenges of applying large language models in building energy efficiency and decarbonization studies: An exploratory overview. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.11701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, W.A.; Yang, Z.; Lo, L.J.; Wen, J.; O’Neill, Z. Large language models for building energy applications: Opportunities and challenges. In Building Simulation; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2025; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda, M.; Ruzzetti, E.S.; Santilli, A.; Zanzotto, F.M.; Bratières, S.; Rodolà, E. Preserving privacy in large language models: A survey on current threats and solutions. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.05212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Liang, G.; Zhao, H.; Liu, G.; Sun, X.; Qiu, J.; Xu, Z.; Wen, F.; Dong, Z.Y. Applying large language models to power systems: Potential security threats. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2024, 15, 3333–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buster, G. Large Language Models (LLMs) for Energy Systems Research; No. NREL/PR-6A20-87896; National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2023.
- Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Sun, J. Risks of practicing large language models in smart grid: Threat modeling and validation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.06237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, H.; Gu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J. Large Language Model for Low-Carbon Energy Transition: Roles and Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th Power System and Green Energy Conference (PSGEC), Shanghai, China, 22–24 August 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 810–816. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Z. Opportunities of applying Large Language Models in building energy sector. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 214, 115558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Liang, J.; Tang, J.; Yu, P.S.; Wen, Q. Large language models for education: A survey and outlook. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.18105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, W.; Qi, Z.; Wu, J.; Lin, J.C.W. Large language models in education: Vision and opportunities. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (BigData), Sorrento, Italy, 15–18 December 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 4776–4785. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Gan, W.; Qi, Z.; Wu, J.; Yu, P.S. Large language models for education: A survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.13001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Sha, L.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Martinez-Maldonado, R.; Chen, G.; Li, X.; Jin, Y.; Gašević, D. Practical and ethical challenges of large language models in education: A systematic scoping review. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2024, 55, 90–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Alrazaq, A.; AlSaad, R.; Alhuwail, D.; Ahmed, A.; Healy, P.M.; Latifi, S.; Aziz, S.; Damseh, R.; Alabed Alrazak, S.; Sheikh, J. Large language models in medical education: Opportunities, challenges, and future directions. JMIR Med. Educ. 2023, 9, e48291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milano, S.; McGrane, J.A.; Leonelli, S. Large language models challenge the future of higher education. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2023, 5, 333–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, C.; Fan, C.; Xie, G.; Liu, S.; Yu, L. Utilizing Large Language Models to Boost Innovative Research and Development in Enterprises. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th International Conference on Enterprise Management and Economic Development (ICEMED 2024), Jinan, China, 24–26 May 2024; Atlantis Press: Paris, France, 2024; pp. 392–400. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Han, T.; Ma, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Tian, J.; He, H.; Li, A.; He, M.; Liu, Z.; et al. Summary of chatgpt-related research and perspective towards the future of large language models. Meta-Radiol. 2023, 1, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, J.; Huang, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Lian, Y.; Pan, J.; Ding, L.; Zhou, H.; et al. Large language model inference acceleration: A comprehensive hardware perspective. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.04466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Cui, L.; Cai, D.; Liu, L.; Fu, T.; Huang, X.; Zhao, E.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Siren’s song in the AI ocean: A survey on hallucination in large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.01219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Utkarsh, A.; Ding, W.; Ondracek, I.; Zhao, Z.; Freeman, G.; Vishwamitra, N.; Hu, H. Moderating Illicit Online Image Promotion for Unsafe User Generated Content Games Using Large {Vision-Language} Models. In Proceedings of the 33rd USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 24), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 14–16 August 2024; pp. 5787–5804. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Y.; Viberg, O.; Baker, R.S.; Kizilcec, R.F. Cultural bias and cultural alignment of large language models. PNAS Nexus 2024, 3, pgae346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Jin, B.; Wang, S.; Ji, S.; Wang, W.; Han, J. A comprehensive survey of scientific large language models and their applications in scientific discovery. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.10833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.F.; Alon, U.; Neubig, G.; Hellendoorn, V.J. A systematic evaluation of large language models of code. In Proceedings of the 6th ACM SIGPLAN International Symposium on Machine Programming, San Diego, CA, USA, 13 June 2022; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, J.; Odena, A.; Nye, M.; Bosma, M.; Michalewski, H.; Dohan, D.; Jiang, E.; Cai, C.; Terry, M.; Le, Q.; et al. Program synthesis with large language models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.07732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liventsev, V.; Grishina, A.; Härmä, A.; Moonen, L. Fully autonomous programming with large language models. In Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference, Lisbon, Portugal, 15–19 July 2023; pp. 1146–1155. [Google Scholar]
- Miceli-Barone, A.V.; Barez, F.; Konstas, I.; Cohen, S.B. The larger they are, the harder they fail: Language models do not recognize identifier swaps in python. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.15507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziems, C.; Held, W.; Shaikh, O.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, D. Can large language models transform computational social science? Comput. Linguist. 2024, 50, 237–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinonen, J.; Hellas, A.; Sarsa, S.; Reeves, B.; Denny, P.; Prather, J.; Becker, B.A. Using large language models to enhance programming error messages. In Proceedings of the 54th ACM Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education V. 1, Toronto, ON, Canada, 15–18 March 2023; pp. 563–569. [Google Scholar]
- Raihan, N.; Siddiq, M.L.; Santos, J.C.; Zampieri, M. Large language models in computer science education: A systematic literature review. In Proceedings of the 56th ACM Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education V. 1, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 26 February–1 March 2025; pp. 938–944. [Google Scholar]
- Krüger, T.; Gref, M. Performance of large language models in a computer science degree program. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Kraków, Poland, 30 September–4 October 2023; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 409–424. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, M.; Jam, F.A.; Khan, T.I. Is it harmful or helpful? Examining the causes and consequences of generative AI usage among university students. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2024, 21, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, M.; Cheng, C.T.; Albahlal, B.M.; Muslam, M.M.A.; Raza, M.S. The impact of LLM chatbots on learning outcomes in advanced driver assistance systems education. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, M.R.; Ray, B.; Roychoudhury, A.; Tan, S.H.; Thongtanunam, P. Automatic programming: Large language models and beyond. ACM Trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol. 2024, 34, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törnberg, P.; Valeeva, D.; Uitermark, J.; Bail, C. Simulating social media using large language models to evaluate alternative news feed algorithms. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.05984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törnberg, P. Large language models outperform expert coders and supervised classifiers at annotating political social media messages. Soc. Sci. Comput. Rev. 2024, 08944393241286471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J. The Impact of Large Language Models on Social Media Communication. In Proceedings of the 2024 7th International Conference on Software Engineering and Information Management, Suva, Fiji, 23–25 January 2024; pp. 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Zhang, T.; Kuang, Z.; Xie, Q.; Huang, J.; Ananiadou, S. MentaLLaMA: Interpretable mental health analysis on social media with large language models. In Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2024, Singapore, 13–17 May 2024; pp. 4489–4500. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, H.; Matz, S.C. Large language models can infer psychological dispositions of social media users. PNAS Nexus 2024, 3, pgae231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Wong, K.F. Investigating bias in llm-based bias detection: Disparities between llms and human perception. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.14896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, D.; Mohawesh, R.; Chellaboina, V.I.; Sathvik, A.L.; Venkatesh, P.; Ho, Y.-H.; Henshaw, H.; Alhawawreh, M.; Berdik, D.; Jararweh, Y. Foundation and large language models: Fundamentals, challenges, opportunities, and social impacts. Clust. Comput. 2024, 27, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augenstein, I.; Baldwin, T.; Cha, M.; Chakraborty, T.; Ciampaglia, G.L.; Corney, D.; DiResta, R.; Ferrara, E.; Hale, S.; Halevy, A.; et al. Factuality challenges in the era of large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.05189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Liao, Q.V.; Vorvoreanu, M.; Ballard, S.; Vaughan, J.W. “I’m Not Sure, But…”: Examining the Impact of Large Language Models’ Uncertainty Expression on User Reliance and Trust. In Proceedings of the 2024 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 3–6 June 2024; pp. 822–835. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, J.; Xu, Z.; Huang, T.; Yu, P. Challenges and Innovations in LLM-Powered Fake News Detection: A Synthesis of Approaches and Future Directions. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.00339. [Google Scholar]
- Chelli, M.; Descamps, J.; Lavoué, V.; Trojani, C.; Azar, M.; Deckert, M.; Raynier, J.L.; Clowez, G.; Boileau, P.; Ruetsch-Chelli, C. Hallucination rates and reference accuracy of ChatGPT and Bard for systematic reviews: Comparative analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 26, e53164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farquhar, S.; Kossen, J.; Kuhn, L.; Gal, Y. Detecting hallucinations in large language models using semantic entropy. Nature 2024, 630, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcos, H. Can large language models apply the law? AI Soc. 2024, 40, 3605–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Gan, W.; Wu, J.; Qi, Z.; Yu, P.S. Large language models in law: A survey. AI Open 2024, 5, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surden, H. ChatGPT, AI large language models, and law. Fordham Law Rev. 2023, 92, 1941. [Google Scholar]
- Homoki, P.; Ződi, Z. Large language models and their possible uses in law. Hung. J. Leg. Stud. 2024, 64, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Yang, Z.; Shu, P.; Chen, J.; Sun, H.; Liang, R.; Li, S.; Shi, P.; Ma, L.; et al. Legal evalutions and challenges of large language models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.10137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, M.; Magesh, V.; Suzgun, M.; Ho, D.E. Large legal fictions: Profiling legal hallucinations in large language models. J. Leg. Anal. 2024, 16, 64–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomi, A.; Tussyadiah, I.; Ascenção, M.P. Customized language models for tourism management: Implications and future research. Ann. Tour. Res. 2025, 110, 103863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secchi, L. Knowledge Graphs and Large Language Models for Intelligent Applications in the Tourism Domain. Ph.D. Thesis, Università di Cagliari, Cagliari, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, R.; Yao, X.; Cole, S.; Wang, H. Are Large Language Models Ready for Travel Planning? arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.17333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Yang, M.; Wang, J.; Mao, W.; Xu, J.; Ning, H. Tourllm: Enhancing llms with tourism knowledge. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.12791. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, M.; Chen, Y.; Gui, H.; Yu, S.; Wang, Y.; Jia, J. TraveLLaMA: Facilitating Multi-modal Large Language Models to Understand Urban Scenes and Provide Travel Assistance. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.16505. [Google Scholar]
- Diao, T.; Wu, X.; Yang, L.; Xiao, L.; Dong, Y. A novel forecasting framework combining virtual samples and enhanced Transformer models for tourism demand forecasting. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.19423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumeliotis, K.I.; Tselikas, N.D.; Nasiopoulos, D.K. Leveraging Large Language Models in Tourism: A Comparative Study of the Latest GPT Omni Models and BERT NLP for Customer Review Classification and Sentiment Analysis. Information 2024, 15, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S. The Future of Tourism: Examining the Potential Applications of Large Language Models. Qeios 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhou, X.; Lin, Y.; Feng, S.; Shen, L.; Wu, P. A Survey on Privacy Risks and Protection in Large Language Models. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.01976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ji, X.; Zhao, Z.; Hei, X.; Choo, K.K.R. Ethical considerations and policy implications for large language models: Guiding responsible development and deployment. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.02678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Duan, Y.; Jin, X.; Chang, H.; Tian, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Gao, K.; Zou, H.P.; Jin, Y.; et al. Deconstructing the ethics of large language models from long-standing issues to new-emerging dilemmas. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.05392. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, H.; Chen, X. Exploring Factors Influencing the Integration of AI Drawing Tools in Art and Design Education. ASRI. Arte y Sociedad. Rev. Investig. Artes Humanid. Digit. 2024, 108–128. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty, T.; Laban, P.; Agarwal, D.; Muresan, S.; Wu, C.S. Art or artifice? large language models and the false promise of creativity. In Proceedings of the 2024 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Honolulu, HI, USA, 11–16 May 2024; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhuang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, M.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Z. Exploring the impact of ChatGPT on art creation and collaboration: Benefits, challenges and ethical implications. Telemat. Inform. Rep. 2024, 14, 100138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocmi, T.; Federmann, C. Large language models are state-of-the-art evaluators of translation quality. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.14520. [Google Scholar]
- Giretti, A.; Durmus, D.; Vaccarini, M.; Zambelli, M.; Guidi, A.; di Meana, F.R. Integrating Large Language Models in Art and Design Education; International Association for Development of the Information Society: Lisbon, Portugal, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Franceschelli, G.; Musolesi, M. On the creativity of large language models. AI Soc. 2024, 40, 3785–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisseau, É. Imitation and Large Language Models. Minds Mach. 2024, 34, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chan, J. Large language model in creative work: The role of collaboration modality and user expertise. Manag. Sci. 2024, 70, 9101–9117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y. Open Sharing and Cross-border Integration of Art Laboratory Resources Based on LLM and Virtual Reality. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Interactive Intelligent Systems and Techniques (IIST), Bhubaneswar, India, 4–5 March 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 441–445. [Google Scholar]
- Roush, A.; Zakirov, E.; Shirokov, A.; Lunina, P.; Gane, J.; Duffy, A.; Basil, C.; Whitcomb, A.; Benedetto, J.; DeWolfe, C. LLM as an Art Director (LaDi): Using LLMs to improve Text-to-Media Generators. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.03716. [Google Scholar]
- Hristov, K. Artificial intelligence and the copyright dilemma. Idea 2016, 57, 431. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Guo, C.; Dou, Y.; Dai, X.; Wang, F.Y. Could ChatGPT imagine: Content control for artistic painting generation via large language models. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2023, 109, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.; Hyland-Wood, D. A Primer on Large Language Models and their Limitations. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.04503. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, G.; Chai, Z.; Ling, C.; Wang, S.; Lu, J.; Zhang, N.; Shi, T.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Beyond efficiency: A systematic survey of resource-efficient large language models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.00625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, W.; Luo, Y.; Long, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lin, B.; Cai, D.; He, X. Model compression and efficient inference for large language models: A survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.09748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallegos, I.O.; Rossi, R.A.; Barrow, J.; Tanjim, M.M.; Kim, S.; Dernoncourt, F.; Yu, T.; Zhang, R.; Ahmed, N.K. Bias and fairness in large language models: A survey. Comput. Linguist. 2024, 50, 1097–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhao, J.; Shi, J.; Xie, Z.; Wu, X.; He, L. Fairmonitor: A dual-framework for detecting stereotypes and biases in large language models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.03098. [Google Scholar]
- Kotek, H.; Dockum, R.; Sun, D. Gender bias and stereotypes in large language models. In Proceedings of the ACM Collective Intelligence Conference, Delft, The Netherlands, 6–9 November 2023; pp. 12–24. [Google Scholar]
- Schwinn, L.; Dobre, D.; Günnemann, S.; Gidel, G. Adversarial attacks and defenses in large language models: Old and new threats. In Proceedings of the PMLR, 16 December 2023; pp. 103–117. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, N.; Schwarzschild, A.; Wen, Y.; Somepalli, G.; Kirchenbauer, J.; Chiang, P.-Y.; Goldblum, M.; Saha, A.; Geiping, J.; Goldstein, T. Baseline defenses for adversarial attacks against aligned language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.00614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Chen, K.; Lin, Y.; Li, K.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Huang, X.; Yu, Y. Attack and defense techniques in large language models: A survey and new perspectives. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.00976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Ming, R.; Hu, H.; Sun, J.; Ge, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, X. Disttrain: Addressing model and data heterogeneity with disaggregated training for multimodal large language models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.04275. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimi, B.; Howard, A.; Carlson, D.J.; Al-Hallaq, H. ChatGPT: Can a natural language processing tool be trusted for radiation oncology use? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2023, 116, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Yu, Y.; Dong, J.; Li, C.; Su, D.; Chu, C.; Yu, D. Mm-llms: Recent advances in multimodal large language models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.13601. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Gu, T.; Wu, K.; Jiang, Z.; He, M.; Zhao, B.; Tan, X.; Gan, Z.; et al. Efficient multimodal large language models: A survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.10739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Hong, Y.; Shang, P.; Wang, Q.; Fu, Q.; Liu, K. A Survey of Multimodel Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computer, Artificial Intelligence and Control Engineering, Xi’an, China, 26–28 January 2024; pp. 405–409. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, X.P.; Aljunied, S.M.; Joty, S.; Bing, L. Democratizing LLMs for low-resource languages by leveraging their English dominant abilities with linguistically-diverse prompts. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.11372. [Google Scholar]
- Gurgurov, D.; Hartmann, M.; Ostermann, S. Adapting multilingual llms to low-resource languages with knowledge graphs via adapters. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.01406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.; Singla, K.; Kamath, A.; Kalani, R.; Paul, R.; Vaidya, U.; Chauhan, S.S.; Wartikar, N.; Long, E. Adapting Multilingual LLMs to Low-Resource Languages using Continued Pre-training and Synthetic Corpus. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.14815. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Xu, Z.; Wang, H.; Qin, W.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ebrahimi, S.; Wang, H. Continual learning of large language models: A comprehensive survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Luo, L.; Li, Y.F.; Pan, S.; Vu, T.T.; Haffari, G. Continual learning for large language models: A survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.01364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ding, X.; Huai, T.; Liu, S.; Chen, Q.; Xie, Y.; He, L. Recent advances of foundation language models-based continual learning: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2025, 57, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Ke, Z.; Liu, B. Continual Learning Using Only Large Language Model Prompting. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.15479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza-Yates, R.; Matthews, J. Statement on Principles for Responsible Algorithmic Systems; ACM Technology Policy Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Pasopati, R.U.; Bethari, C.P.; Nurdin, D.S.F.; Camila, M.S.; Hidayat, S.A. Ethical Consequentialism in Values and Principles of UNESCO’s Recommendation on the Ethics of Artificial Intelligence. Proc. Int. Conf. Relig. Sci. Educ. 2024, 3, 567–579. [Google Scholar]
- Anisuzzaman, D.M.; Malins, J.G.; Friedman, P.A.; Attia, Z.I. Fine-Tuning Large Language Models for Specialized Use Cases. Mayo Clin. Proc. Digit. Health 2025, 3, 100184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kermani, A.; Zeraatkar, E.; Irani, H. Energy-efficient transformer inference: Optimization strategies for time series classification. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.16627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlShaikh, R.; Al-Malki, N.; Almasre, M. The implementation of the cognitive theory of multimedia learning in the design and evaluation of an AI educational video assistant utilizing large language models. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassiri, K.; Akhloufi, M.A. Recent advances in large language models for healthcare. BioMedInformatics 2024, 4, 1097–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alayrac, J.-B.; Donahue, J.; Luc, P.; Miech, A.; Barr, I.; Hasson, Y.; Lenc, K.; Mensch, A.; Millican, K.; Reynolds, M.; et al. Flamingo: A visual language model for few-shot learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 23716–23736. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Patel, N.P.; Ehtesham, A.; Kumar, S.; Khoei, T.T. A survey of sustainability in large language models: Applications, economics, and challenges. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE 15th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 6–8 January 2025; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2025; pp. 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Hua, I.; Ding, Y. Unveiling environmental impacts of large language model serving: A functional unit view. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.11256. [Google Scholar]
- Iftikhar, S.; Davy, S. Reducing Carbon Footprint in AI: A Framework for Sustainable Training of Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the Future Technologies Conference, London, UK, 14–15 November 2024; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 325–336. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Song, E. Privacy-Preserving Large Language Models: Mechanisms, Applications, and Future Directions. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.06113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, F. A systematic survey for differential privacy techniques in federated learning. J. Inf. Secur. 2023, 14, 111–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Relevant Domain | Challenges | Challenge Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Medicine |
|
|
| Finance |
|
|
| Business |
|
|
| Industry |
|
|
| Agriculture |
|
|
| Energy |
|
|
| Education |
|
|
| Research |
|
|
| Programming |
|
|
| Media |
|
|
| Law |
|
|
| Art |
|
|
| Technical Focus | Challenges | Challenge Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Fairness and bias mitigation |
|
|
| Adversarial robustness |
|
|
| Heterogeneous data integration |
|
|
| Compute and resource efficiency |
|
|
| Long-term memory and reasoning |
|
|
| Multimodal processing limits |
|
|
| Technical focus |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peykani, P.; Ramezanlou, F.; Tanasescu, C.; Ghanidel, S. Large Language Models: A Structured Taxonomy and Review of Challenges, Limitations, Solutions, and Future Directions. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8103. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148103
Peykani P, Ramezanlou F, Tanasescu C, Ghanidel S. Large Language Models: A Structured Taxonomy and Review of Challenges, Limitations, Solutions, and Future Directions. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(14):8103. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148103
Chicago/Turabian StylePeykani, Pejman, Fatemeh Ramezanlou, Cristina Tanasescu, and Sanly Ghanidel. 2025. "Large Language Models: A Structured Taxonomy and Review of Challenges, Limitations, Solutions, and Future Directions" Applied Sciences 15, no. 14: 8103. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148103
APA StylePeykani, P., Ramezanlou, F., Tanasescu, C., & Ghanidel, S. (2025). Large Language Models: A Structured Taxonomy and Review of Challenges, Limitations, Solutions, and Future Directions. Applied Sciences, 15(14), 8103. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148103







