Synthetic Approaches to 1,3,4-Oxadiazole-Containing Boronic Derivatives
Abstract
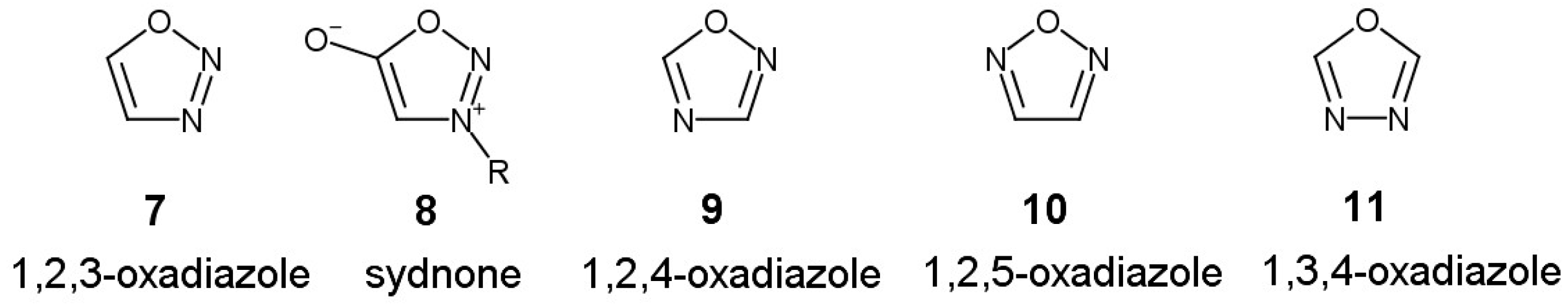
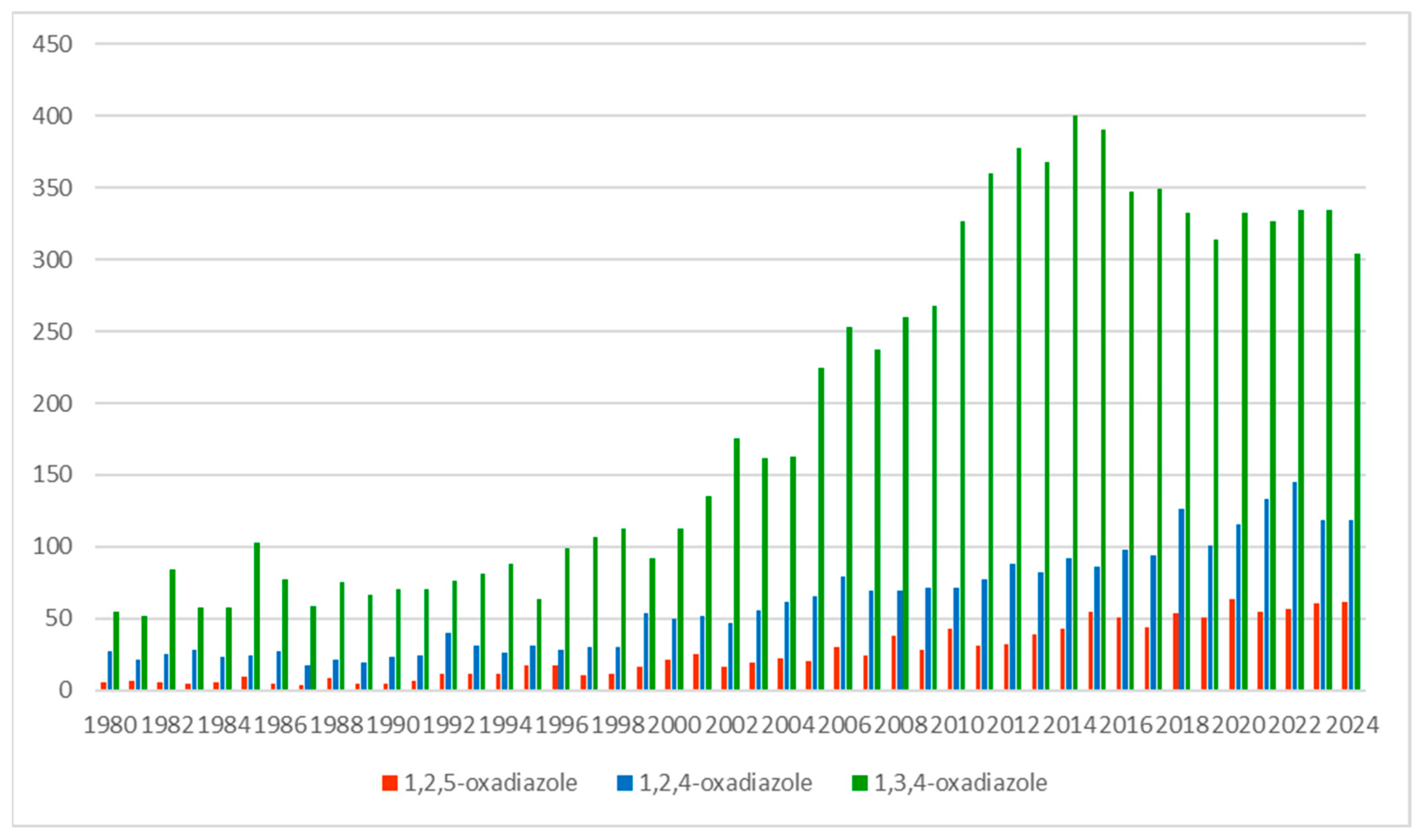
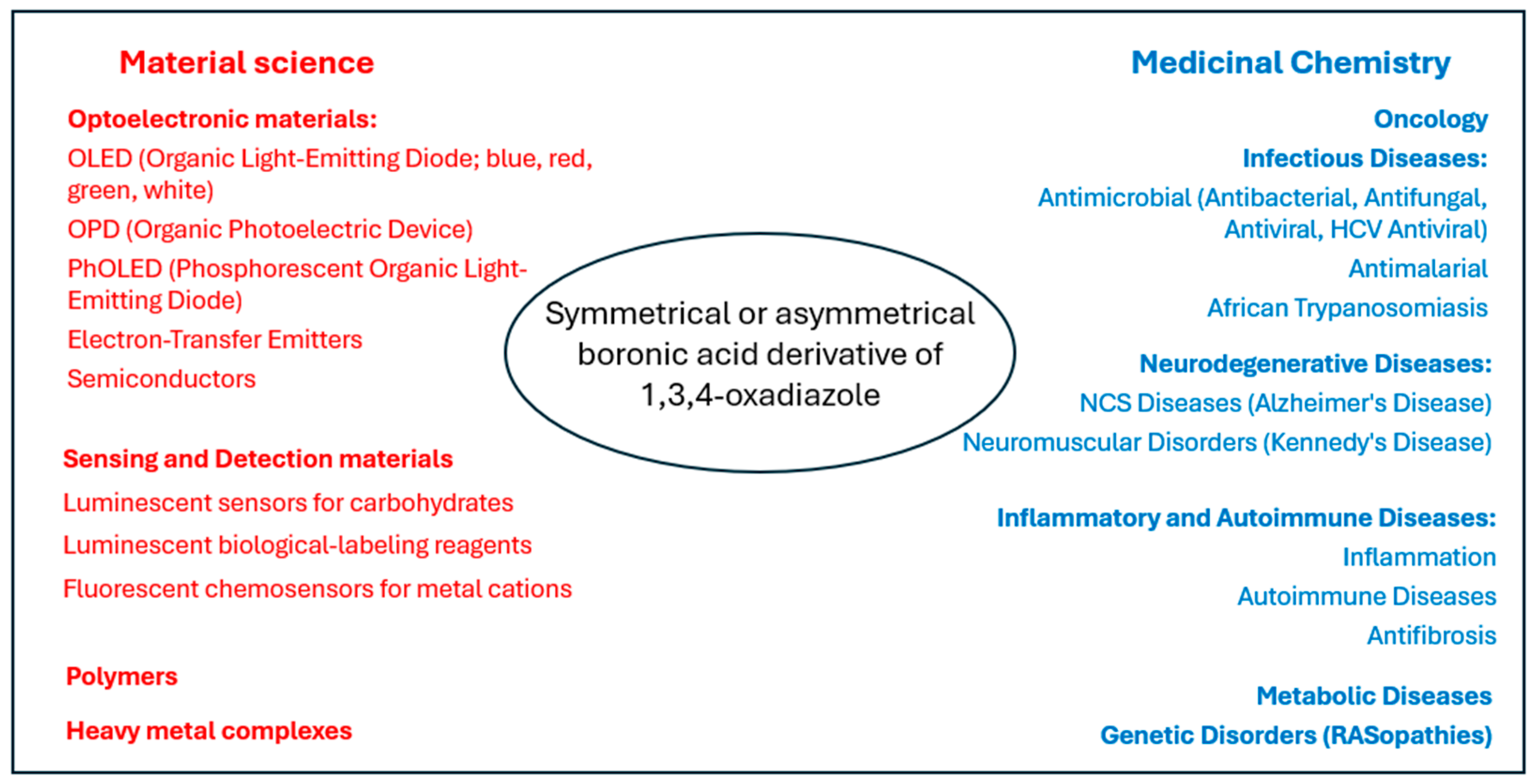
1. Introduction
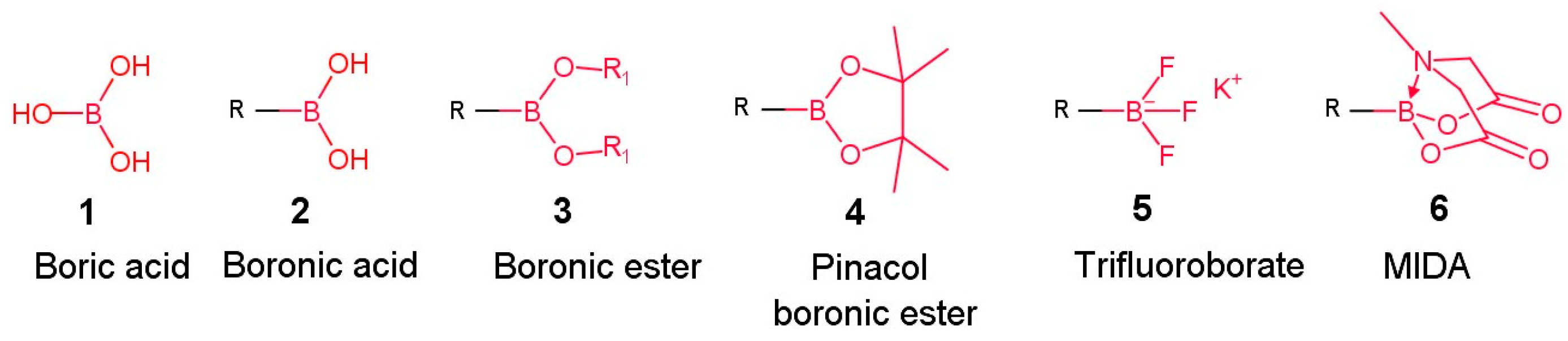
2. General Approaches for the Synthesis of Organoboron Derivatives
- (a)
- Halogen–metal–boron exchange in aromatic compounds (method A),
- (b)
- Miyaura borylation of aryl and vinyl halides using bis(pinacolato)diboron (method B),
- (c)
- formation of the 1,3,4-oxadiazole ring from acyclic reagents already containing a boronic ester moiety (method C).
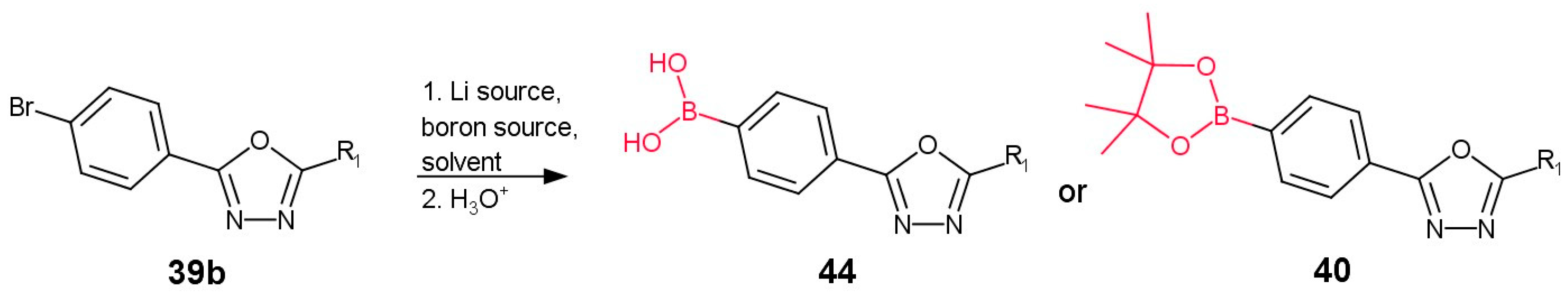
2.1. Method A: Lithium/Magnesium–Boron Exchange
2.2. Method B: Miyaura Borylation
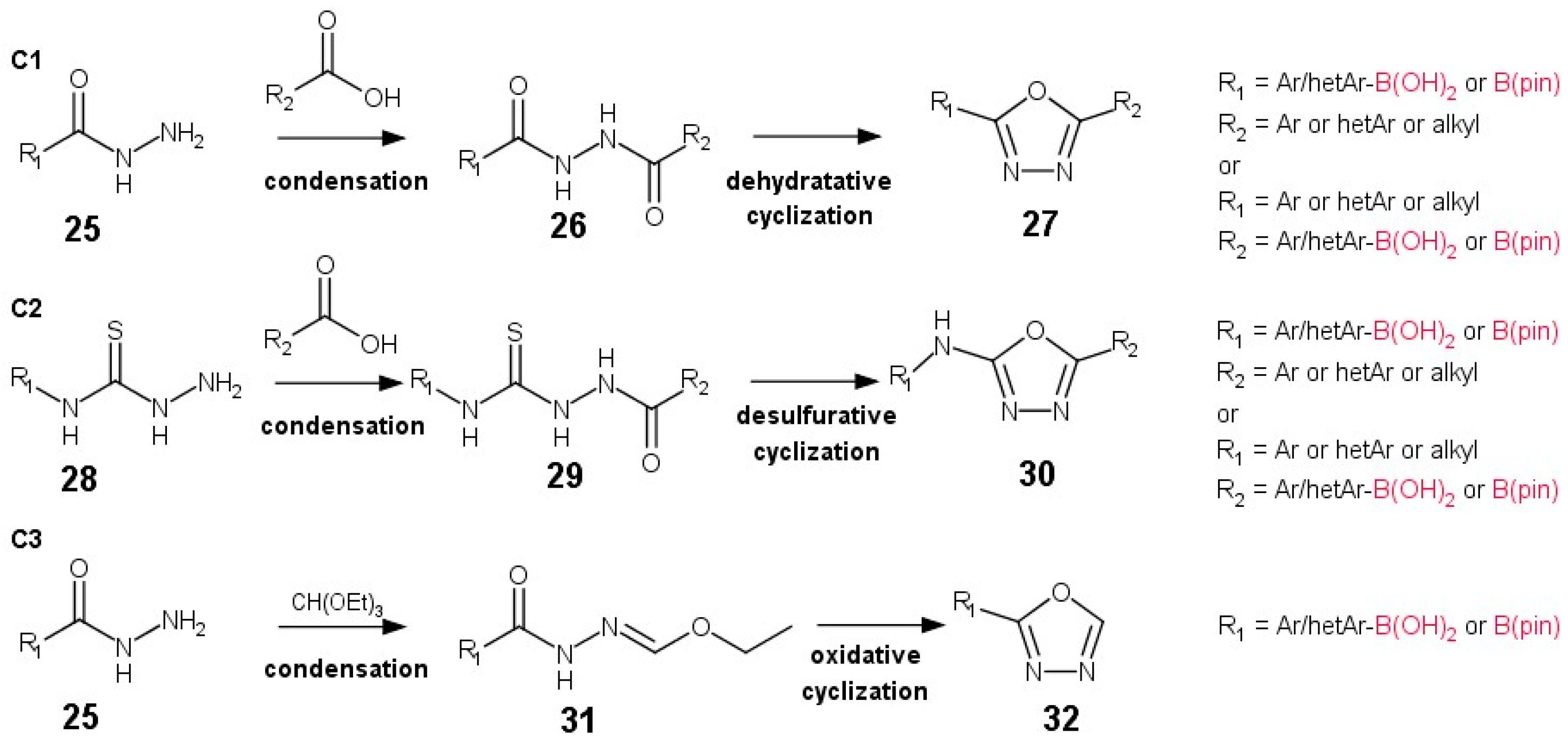
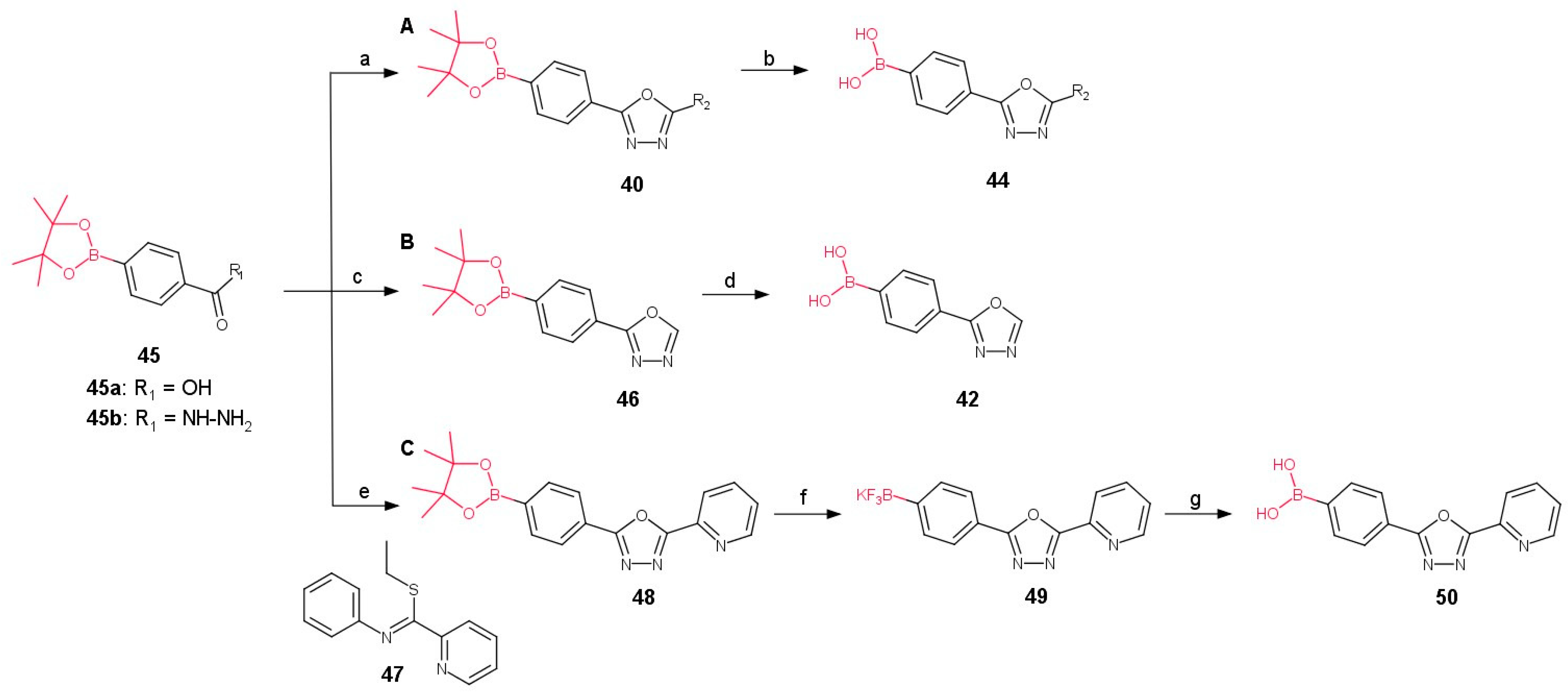
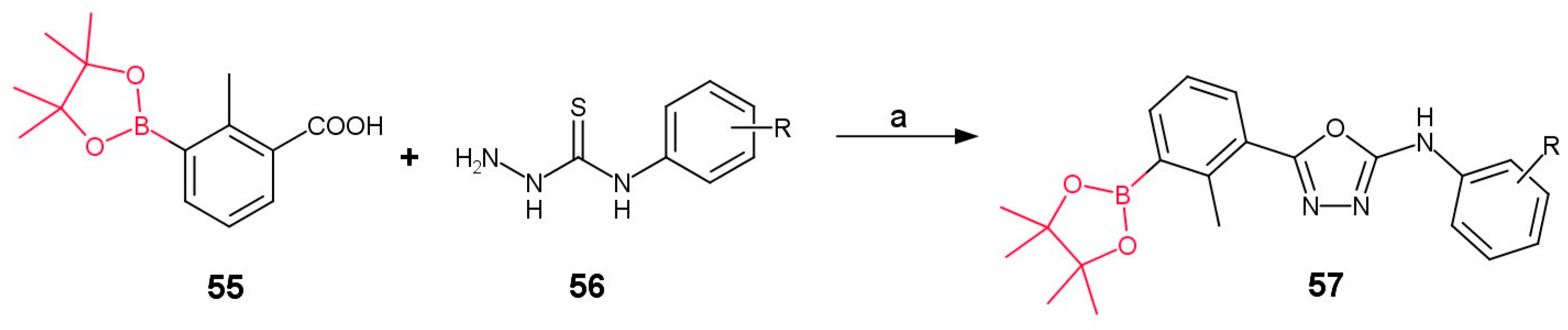
2.3. Method C: 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Ring Formation
3. Synthesis of Boronic Derivatives from Reagents Containing 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Moiety
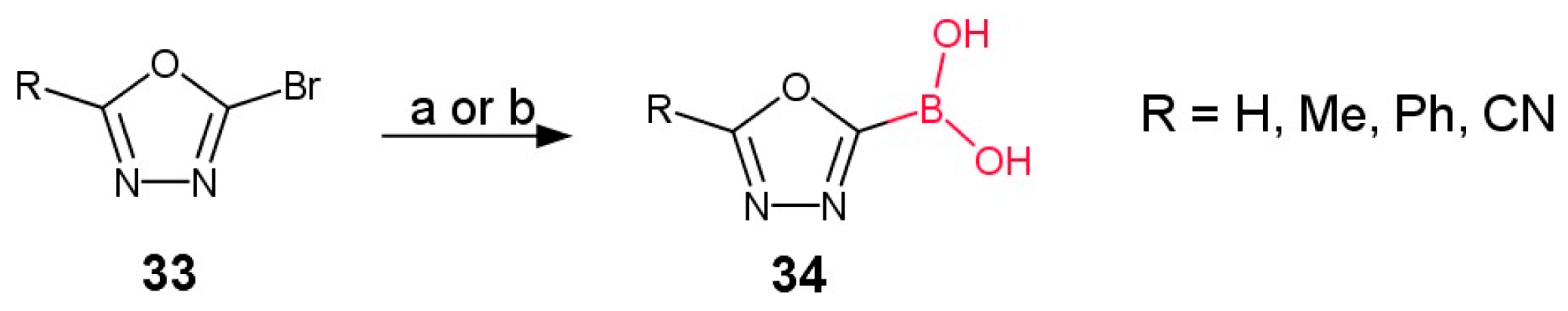
3.1. Direct Connection of Boron with 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Ring
3.2. Indirect Connection of Boron with 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Ring via Phenylene Linker
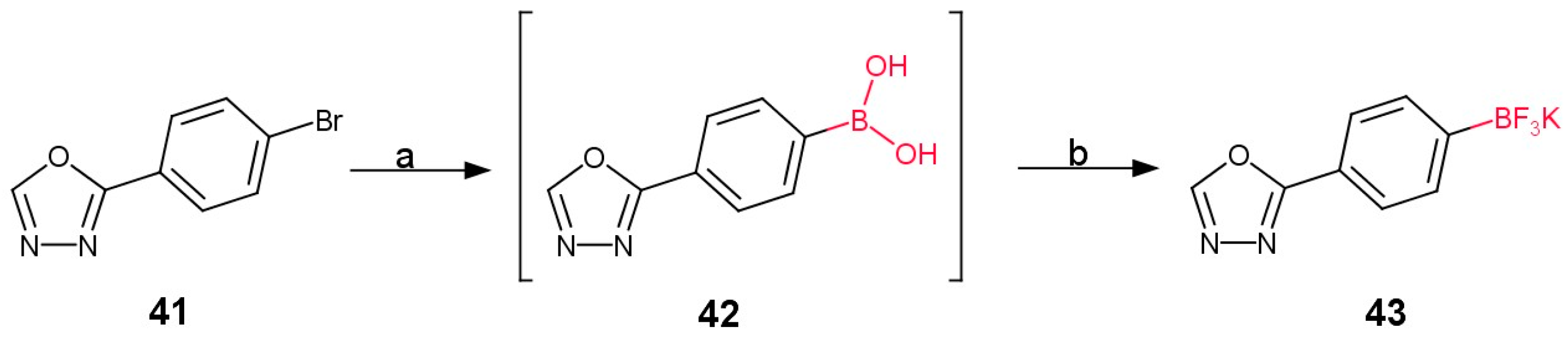
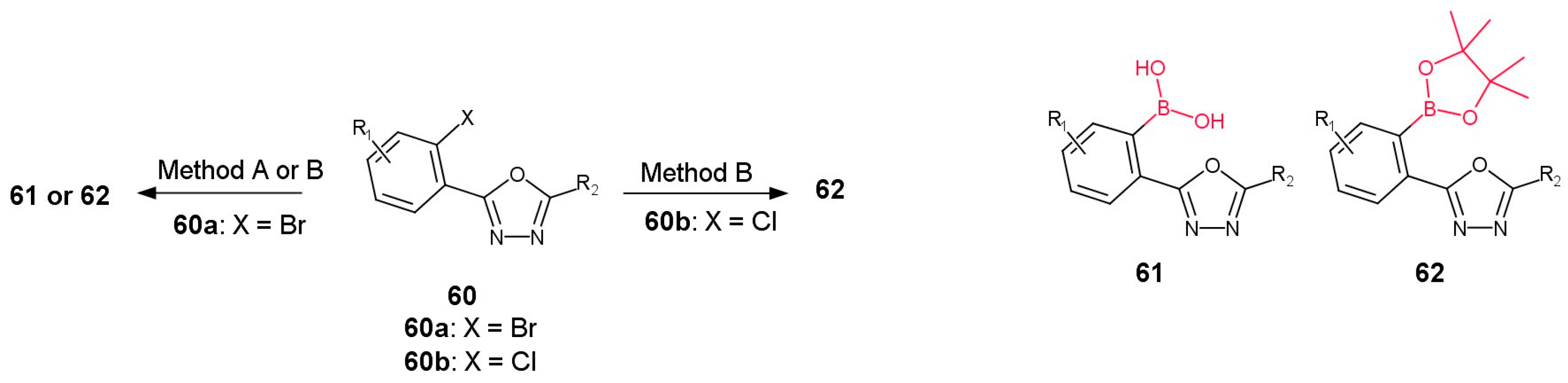
3.2.1. Derivatives of Para-Substituted (1,3,4-Oxadiazol-2-yl)phenyl)boronic Acid
3.2.2. Derivatives of Meta-Substituted (1,3,4-Oxadiazol-2-yl)phenylboronic Acid
3.2.3. Derivatives of Ortho-Substituted (1,3,4-Oxadiazol-2-yl)phenylboronic Acid
3.3. Indirect Connection of Boron with 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Ring via Heterocyclic Linker
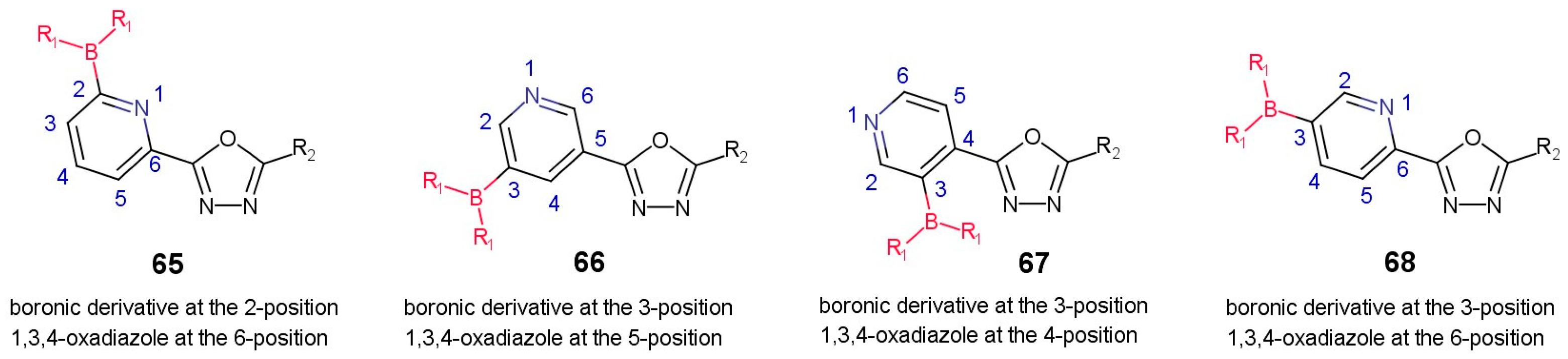
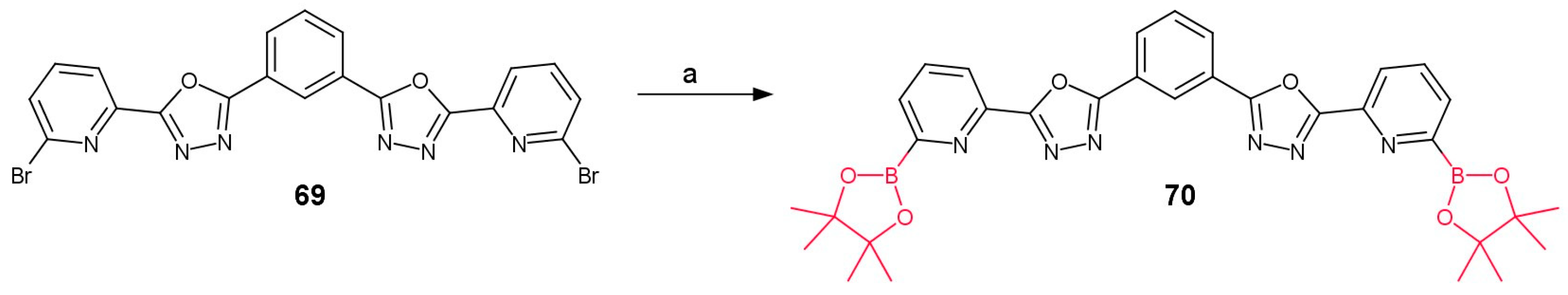
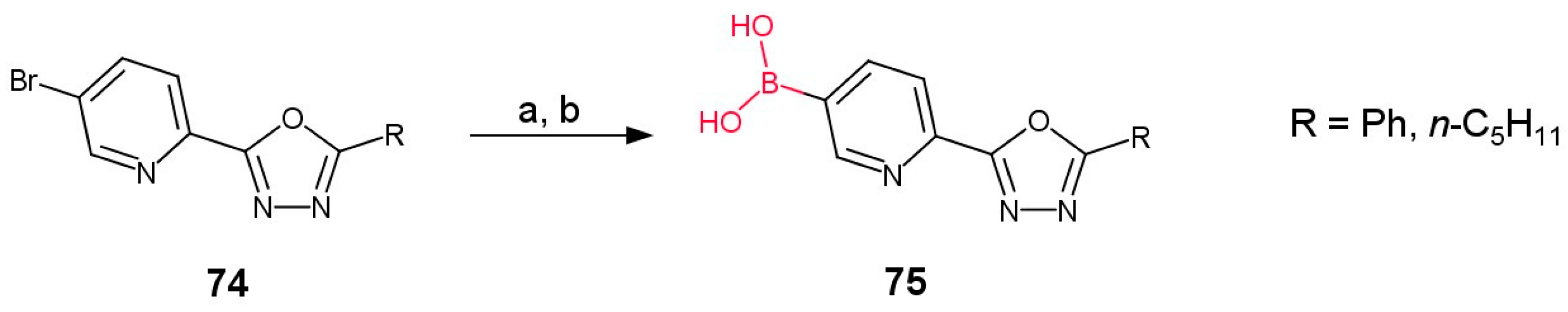
3.3.1. Boronic Acid Derivatives of (1,3,4-Oxadiazol-2-yl)pyridines
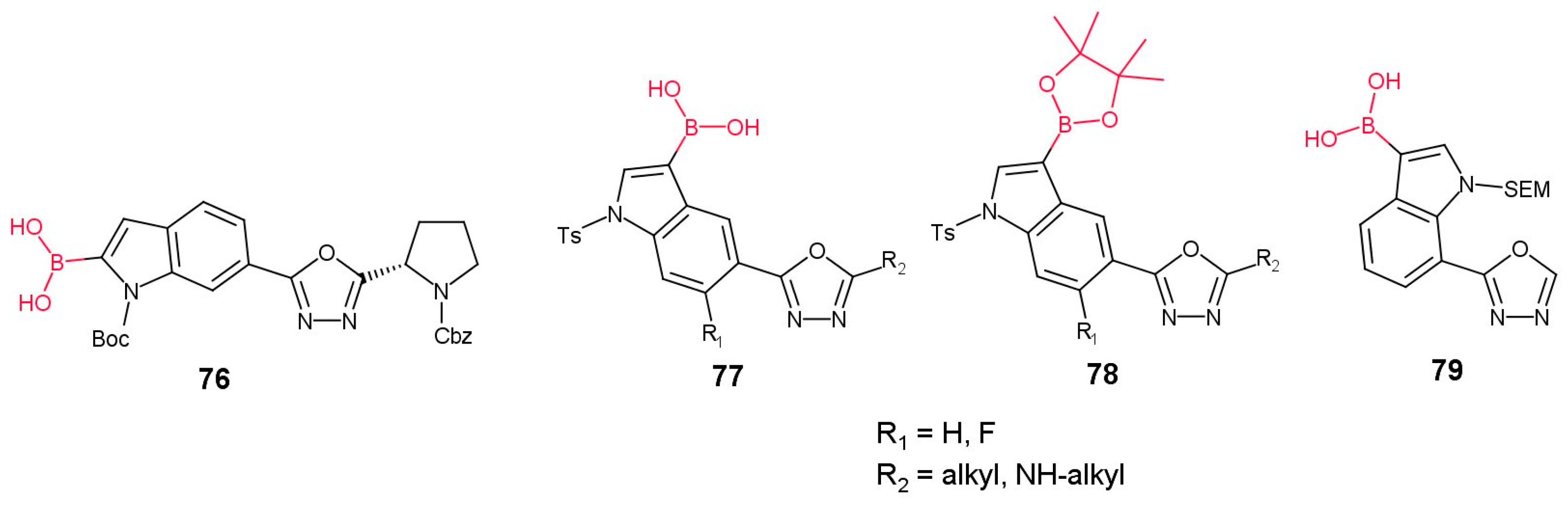
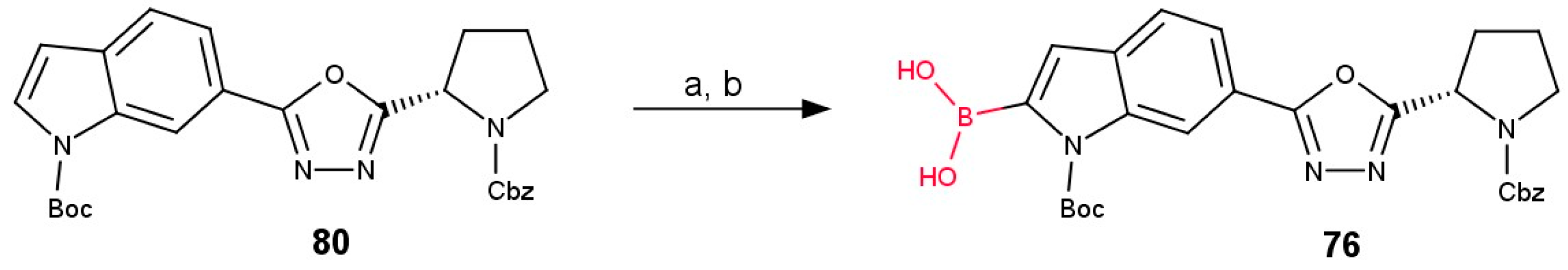
3.3.2. Boronic Acid Derivatives of 1,3,4-Oxadiazol-2-yl-indoles
3.3.3. Boronic Acid Derivatives of 1,3,4-Oxadiazol-2-yl-thiophenes, 1,3,4-Oxadiazol-2-yl-furan and 1,3,4-Oxadiazol-2-yl-ethenyl Derivatives
3.3.4. Other Boronic Acid Derivatives of 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Substituted with Dibenzothiophene, Dibenzofuran, Naphthalene, and Biphenyl
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hosmane, N.S. (Ed.) Boron Science: New Technologies and Applications, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, G.L. Boron: Compounds, Production and Application, UK ed.; NOVA Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, H.; Michalland, J.; Huang, Q.; Zard, S.Z. A Versatile Route to Acyl (MIDA)boronates. Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 29, e202302235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, D.G. Structure, Properties, and Preparation of Boronic Acid Derivatives: Overview of Their Reactions and Applications. In Boronic Acids: Preparation and Applications in Organic Synthesis, Medicine and Materials, 2nd ed.; Hall, D., Ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiller, N.J.; do Amaral e Silva, N.A.; Tavares, T.A.; Faria, R.X.; Eberlin, M.N.; de Luna Martins, D. Arylboronic Acids and their Myriad of Applications Beyond Organic Synthesis. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 2020, 4841–4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, K.Z.; Szczepankiewicz, W. 1,3,4-Oxadiazoles. In Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry IV, 1st ed.; Black, D., Cossy, J., Stevens, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2022; Volume 5, pp. 252–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joule, J.A.; Mills, K. Heterocycles Containing More Than Two Heteroatoms. In Heterocyclic Chemistry, 5th ed.; Joule, J., Mills, K., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell, John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 569–574. [Google Scholar]
- Piccionello, A.P.; Pibiri, A.; Pace, A.; Buscemi, S.; Vivona, N. 1, 2, 4-Oxadiazoles. In Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry IV, 1st ed.; Black, D., Cossy, J., Stevens, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2022; Volume 5, pp. 147–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostrom, J.; Hogner, A.; Llinas, A.; Wellner, E.; Plowright, A.T. Oxadiazoles in Medicinal Chemistry. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 1817–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennox, A.J.J.; Lloyd-Jones, G.C. Selection of boron reagents for Suzuki–Miyaura coupling. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 412–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyet, M.; Chabaud, L.; Pucheault, M. Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Borinic Acid Derivatives. Molecules 2023, 28, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.P.; Saraiva, L.; Pinto, M.; Sousa, M.E. Boronic Acids and Their Derivatives in Medicinal Chemistry: Synthesis and Biological Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiyama, T.; Murata, M.; Miyaura, N. Palladium(0)-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reaction of Alkoxydiboron with Haloarenes: A Direct Procedure for Arylboronic Esters. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 7508–7510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiyama, T.; Ishida, K.; Miyaura, N. Synthesis of pinacol arylboronates via cross-coupling reaction of bis(pinacolato)diboron with chloroarenes catalyzed by palladium(0)–tricyclohexylphosphine complexes. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 9813–9816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnke, M.L.; Castro, A.C.; Evans, C.A.; Grenier, L.; Grogan, M.J.; Liu, T.; Snyder, D.A.; Tibbitts, T.T. Preparation of Oxadiazolylphenylboronic Acid Derivatives and Analogs for Use as Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase Inhibitors. WO 2009126691 A1, 15 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Vollmueller, F.; Haber, S.; Meudt, A.; Noerenberg, A.; Scherer, S. Preparation of p-Oxadiazolylphenylboronic Acids. DE 19857765 A1, 21 June 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, B.S.; Kim, J.A.; Chang, J.H.; Nam, T.G. Preparation of 6-Heteroarylamino-2,4,5-Trimethylpyridin-3-ol Derivatives for Prevention or Treatment of Inflam Matory Bowel Diseases and Autoimmune Diseases. WO 2019194556 A1, 10 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Cai, H. Aromatic Compound and Organic Electroluminescent Device Thereof. CN 108976177 A, 11 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.T.; Ahn, H.C.; Ham, H.W.; Kim, D.J.; Han, J.U. Preparation of Organic Light Emitting Compound Substituted with Deuterium. KR 2014091496 A, 21 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Holownia, A.; Tien, C.-H.; Diaz, D.B.; Larson, R.T.; Yudin, A.K. Carboxyboronate: A Versatile C1 Building Block. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 15148–15153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, J.S.; Heo, J.O.; Heo, D.U.; Kim, S.S.; Chun, M.S.; Cho, H.M. Preparation of Aromatic Heterocyclic Compound for Organic Light-Emitting Device. KR2021004849 A, 13 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Steeneck, C.; Kinzel, O.; Gege, C.; Kleymann, G.; Hoffmann, T. Preparation of Pyrrolocarboxamides as Modulators of Orphan Nuclear Receptor R AR-Related Orphan Receptor-Gamma (RORγ, NR1F3) Activity and for the Treatment of Chronic Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases. WO 2013079223 A1, 6 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hasvold, L.A.; Hexamer, L.; Li, G.; Lin, N.-H.; Sham, H.; Sowin, T.J.; Sullivan, G.M.; Wang, L.; Xia, P. Preparation of Dibenzo [b,e][1,4]Diazepin-11-Ones as Kinase Inhibitors for Treatment of Cancer. US 20070254867 A1, 11 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wołek, B.; Werłos, M.; Komander, M.; Kudelko, A. Efficient Synthesis of Novel 1,3,4-Oxadiazoles Bearing a 4-N,N-Dimethylaminoquinazoline Scaffold via Palladium-Catalyzed Suzuki Cross-Coupling Reactions. Molecules 2020, 25, 5150–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.; Landis, C.A.; Dhar, B.M.; Jung, B.J.; Sun, J.; Sarjeant, A.; Lee, J.-H.; Katz, H.E. Synthesis, Structural Characterization, and Unusual Field-Effect Behavior of Organic Transistor Semiconductor Oligomers: Inferiority of Oxadiazole Compared with Other Electron-Withdrawing Subunits. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1692–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Z.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xie, G.; Liu, Y. Near-infrared emission of dinuclear iridium complexes with hole/electron transporting bridging and their monomer in solutionprocessed organic light-emitting diodes. Dyes Pigm. 2018, 149, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzzio, M.; Lucas, B. Preparation of Substituted Thiadiazoles as Small Molecule Splicing Modulator Compounds for Modulating Splicing of mRNA. WO 2020163323 A1, 13 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Luzzio, M.; Lucas, B. Preparation of Substituted Pyridazines as small Molecule Splicing Modulator Compounds for Modulating Splicing of mRNA. WO 2020163647 A1, 13 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, H.-S.; Yoo, M.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Lim, J.-I.; Son, M.-H.; Kim, M.-K.; Shin, C.-Y.; Kim, J.-K.; Park, S.-K.; Chae, Y.-N.; et al. Novel Phenylpropionic Acid Derivatives as Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Gamma Receptor Modulators, Method of Preparing the Same, and Pharmaceutical Composition Comprising the Same. WO 2008108602 A1, 12 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, A.K.; Nagle, A.S.; Paraselli, P.; Leong, S.Y.; Roland, J.T.; Mishra, P.K.; Yeung, B.K.S.; Zou, B. Preparation of Imidazopyrazines for Treating Parasitic Diseases. WO 2014078813 A1, 22 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Grenz, D.C.; Rose, D.; Wossner, J.S.; Wilbuer, J.; Adler, F.; Hermann, M.; Chan, C.-Y.; Adachi, C.; Esser, B. Spiroconjugated Tetraaminospirenes as Donors in Color-Tunable Charge-Transfer Emitters with Donor-Acceptor Structure. Chem. Eur. J. 2022, 28, 202104150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, T.; Luo, H.-B.; Fan, H.H.; Wong, M.S. Star-shaped triazine-cored ladder-type ter(p-phenylene)s for high-performance multiphoton absorption and amplified spontaneous blue emission. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 1768–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslin, M.J.; Fraley, M.E.; Loughran, H.M.; Mulhearn, J.J.; Roecker, A.J.; Schirripa, K.M.; Stachel, S.J. Preparation of Modified Isoindolinones as Glucosylceramide Synthase Inhibitors. WO 2022115301 A1, 6 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.G.; Choi, Y.H.; Lee, B.S.; Moon, S.Y.; Hwang, S.P.; Park, H.G.; Cho, H.M.; Lee, D.W. Preparation of Organic Electronic Device Materials. KR2014094408 A, 30 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Linton, K.E.; Fisher, A.L.; Pearson, C.; Fox, M.A.; Palsson, L.-O.; Bryce, M.R.; Petty, M.C. Colour tuning of blue electrolumi-nescence using bipolar carbazole–oxadiazole molecules in single-active-layer organic light emitting devices (OLEDs). J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 11816–11825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoull, W.; Boyd, S.; Brown, M.R.; Coen, M.; Collingwood, O.; Davies, N.L.; Doherty, A.; Fairley, G.; Goldberg, K.; Hardaker, E.; et al. Optimization of an Imidazo [1,2-a] pyridine Series to Afford Highly Selective Type I1/2 Dual Mer/Axl Kinase Inhibitors with In Vivo Efficacy. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 13524–13539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, K.; Xing, K.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Deng, X.; Zhu, M.; Zhu, W. Conjugated and nonconjugated bipolar-transporting dinuclear europium(III) complexes involving triphenylamine and oxadiazole units: Synthesis, photophysical and electroluminescent properties. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 4679–4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiyoshi, H.; Aoyama, T.; Wada, T.; Sonoda, T.; Mataka, S. Synthesis and properties of disk-shaped bipolar symmetric cyclic triindole derivative. Heterocycles 2009, 77, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Lei, P.; Sohail, A.; Ablajan, K. I2-Mediated Synthesis of 1,3,4-Oxa/thiadiazoles from Aroylhydrazide and Acetonitrile/Thioacetamide. J. Org. Chem. 2024, 89, 15490–15496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallinger, A.; Crumpler, S.; Pichowicz, M.; Waalboer, D.; Stubbs, M.; Adeniji-Popoola, O.; Wood, B.; Smith, E.; Thai, C.; Henley, A.T.; et al. Discovery of Potent, Orally Bioavailable, Small-Molecule Inhibitors of WNT Signaling from a Cell-Based Pathway Screen. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 1717–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckman, B.O.; Nicholas, J.B.; Emayan, K.; Seiwert, S.D.; Yuan, S. N-Heteroaryl Carbamates as Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor Antagonists and their Preparation. WO 2014113485 A1, 24 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, S.; Wang, R.; Li, T.; Sun, Q.; Yang, W. Preparation of Compounds with Fluorene as Core and its Application in Organic Electroluminescent Devices. WO 2023070700 A1, 4 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, H.-G.; Kang, U.-S.; Park, J.-S.; Kim, N.-S.; In, K.-Y.; Kang, E.-S.; Chae, M.-Y. Novel Compound for Organic Photoelectric Device and Organic Photoelectric Device Including the Same. WO 2009051454 A2, 23 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Zhao, L.; He, L.; Tang, Y.; Di, Q.; Zhang, H.; Bian, K.; Liu, D. Preparation of Oxadiazole Based Heterocyclic Compound and its Application in OLED. CN 116023374 A, 28 April 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bachand, C.; Belema, M.; Deon, D.H.; Good, A.C.; Goodrich, J.; Hamann, L.G.; James, C.A.; Langley, D.R.; Lavoie, R.; Lopez, O.D.; et al. Preparation of Biphenyls and Biheteroaryls End-Capped with Amino Acid or Peptide Derivatives as Hepatitis C Virus Inhibitors. WO 2008144380 A1, 11 November 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, D.L.; Kaufman, M.D.; Patt, W.C.; Petillo, P.A. Preparation of Heterocyclic Ureas as Kinase Inhibitors Useful for the Treatment of Prolife Rative and Inflammatory Diseases. WO 2008034008 A2, 20 March 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Molander, G.A.; Trice, S.L.J.; Kennedy, S.M.; Dreher, S.D.; Tudge, M.T. Scope of the Palladium-Catalyzed Aryl Borylation Utilizing Bis-Boronic Acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 11667–11673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Li, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zuo, J.; You, X. Oxadiazolyl-Containing Green Ir(III) Complex, its Preparation Process and Application. CN 102659773 A, 12 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Li, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zuo, J.; You, X. Preparation Method of Red-Emitting Iridium(III) Complexes with Oxadiazole Group. CN 102875542 A, 16 January 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.-L.; Li, H.-Y.; Wang, C.-C.; Zhang, S.; Li, T.-Y.; Jing, Y.-M.; Zheng, Y.-X.; Huang, W.; Zuo, J.-L.; You, X.-Z. Synthesis, structure, photophysical and electrochemical properties of series of new fac-triscyclometallated iridium complexes with carbazole or oxadiazole moieties. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2012, 391, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, C.; Ma, Y.; Wang, C.; Shen, Y. Synthesis, Structure and Photophysical Properties of Silole-Oxadiazole Copolymers. Chin. J. Chem. 2013, 31, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Tan, H.; Zhu, W. Study on influence of end group on photoelectric performance of polyfluorene derivatives containing D-A structure and red phosphorescent group. Nat. Sci. J. Xiangtan Univ. 2012, 34, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Butlin, M.A.; Butlin, R.J.; Hogan, P.J.; Meudt, A. Chemical Process in Preparation of Oxadiazolylphenylboronic Acid Used in Preparation of Pyrazinyl Oxadiazolyl Pyridine Sulfonamide Endothelin Receptor. WO 2005080403 A2, 1 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hashemzadeh, T.; Haghighatbin, M.A.; Agugiaro, J.; Wilson, D.J.D.; Hogan, C.F.; Barnard, P.J. Luminescent iridium(iii)–boronic acid complexes for carbohydrate sensing. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 11361–11374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erra Sola, M.; Carrascal Riera, M.; Taltavull Moll, J.; Caturla Javaloyes, J.F.; Bernal Anchuela, F.J.; Pages Santacana, L.M.; Mir Cepeda, M.; Casals Coll, G.; Hernandez Olasagarre, M.B. Pyrrolotriazinone Derivatives as PI3K Inhibitors and their Prepar Ation. WO 2014060432 A1, 24 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, T.; Zhu, P.; Xie, L.; Zhang, J. Preparation of Heterocyclic Substituted Biphenyl Compounds and its Application in Preparation of Medicament for Treatment of Diseases Mediated by PD-1/PD-L1. CN 116730940 A, 12 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Cui, R.; Yin, J.; Zheng, M.; Chen, N.; Lv, Y. Preparation of Imidazopyridazine Derivatives and Application as PIM Kinase Inhibitor. CN 114409656 A, 29 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, Q.; Gu, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhong, C.; Ma, D.; Qina, J.; Yang, C. Efficient deep-blue emitters comprised of an anthracene core and terminal bifunctional groups for nondoped electroluminescence. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 6409–6415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro Palomino Laria, J.C.; Terricabras Belart, E.; Erra Sola, M.; Navarro Romero, E.; Fonquerna Pou, S.; Cardus Figueras, A.; Lozoya Toribio, M.E. Azabiphenylaminobenzoic Acid Derivatives as Dhodh Inhibitors. WO 2009021696 A1, 19 February 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.-L.; Burnett, D.A.; Stamford, A.; Cumming, J.N.; Asberom, T.; Bennett, C.; Sasiskumar, T.K.; Scott, J.D. Preparation of Spiroiminothiazine Derivatives for Use as BACE Inhibitors. WO 2013028670 A1, 28 February 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, E.J.; Cumming, J.N.; Stamford, A.W.; Yu, Y.; Scott, J.D.; Iserloh, U.; Wang, L.; Caldwell, J.P. Preparation of Tricyclic Substituted Thiadiazine Dioxide Compounds as BACE Inhibitors, Compositions, and their Therapeutic Use. WO 2014062553 A1, 24 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bentsen, J.G.; Goplen, N.P.; Li, Y.; Roberts, R.R. Electron Transport Agents for Organic Electronic Devices. US 20040214036 A1, 28 October 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, T.-H.; Chen, Y. Solution-processable bipolar host materials composed of fluorenyl, carbazolyl and 1,3,4-oxadiazolyl derivatives: Synthesis and application in phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 5091–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-C.; Lin, S.-W.; Hong, W.-Y.; Fang, G.-C.; Zheng, S.-X. Electron Transmission Material and Organic Light-Emitting Element. TWI 501959 B, 10 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Miwatashi, S.; Kaieda, A.; Takahashi, M.; Inui, H.; Okamoto, R. Preparation of Fused Heterocyclic Compounds as p38 M AP Kinase Inhibitors and Inhibitors of TNF-α Production. WO 2011021678 A1, 24 February 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Kakegawa, K.; Sugiyama, H.; Miyazaki, T.; Arikawa, Y.; Okawa, T.; Yonemori, J.; Kubo, O.; Toita, A.; et al. Heterocyclic Compound Having Histone Deacetylase Inhibiting Activity, and Pharmaceutical Composition. WO 2020158762 A1, 6 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, H.; Han, J. Supramolecular brush polymers prepared from 1,3,4-oxadiazole and cyanobutoxy functionalised pillar[5]arene for detecting Cu2+. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2021, 19, 1287–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, J.I.; Hopper, D.W.; Torres, N.; Dutia, M.D.; Berger, D.M.; Wang, X.; Di Grandi, M.J.; Zhang, C.; Dunnick, A.L. Preparation of bridged, bicyclic heterocyclic or spiro bicyclic heterocyclic derivatives of pyrazolo [1,5-a] Pyrimidines as Raf Kinase Inhibitors. WO 2009108838 A1, 3 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.-L.; Burnett, D.A.; Stamford, A.W.; Cumming, J.N.; Bennett, C.E.; Gilbert, E.J.; Peng, X.; Scott, J.D.; Yu, Y. Preparation of 5-substituted iminothiazines and their mono- and dioxides as BACE inhibitors. WO 2012139425 A1, 18 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.N.; Shin, Y.S.; Park, D.; Yoon, K.J.; Lim, S.K.; Kim, D.; Ki, D.H.; Kim, E.J.; Nam, J.; Han, W.; et al. Preparation of Heterocyclic Carboxamides as SOS1 Inhibitor. WO 2023022497 A1, 23 February 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Cordi, A.; Desos, P.; Lestage, P.; Danober, L. Preparation of Phenoxy Dihydrobenzoxathiazepine Derivatives and their Use as Positive Allosteric Modulators of A MPA Receptors. CA 2752131 A1, 16 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Angell, R.M.; Bamborough, P.; Cockerill, G.S.; Walker, A.L. Preparation of 2′-Methyl-5′-(1,3,4-Oxadiazol-2-yl)-1, 1′-Biphenyl-4-Carboxamides as p38 Kinase Inhibitors. WO 2003032986 A1, 24 April 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Qi, Z.; Ye, K.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, T. Discovery of Novel PD-L1 Inhibitors That Induce the Dimerization, Internalization, and Degradation of PD-L1 Based on the Fragment Coupling Strategy. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 16807–16827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, L.; Wu, H.; Huang, S.; Dong, P.; Li, X.; Hu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; et al. Preparation of Spiro Compound Derivatives as Raf Inhibitor and Used for Treatment of Cancer. CN 113264945 A, 17 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Piettre, S.R.; André, C.; Chanal, M.-C.; Ducep, J.-B.; Lesur, B.; Piriou, F.; Raboisson, P.; Rondeau, J.-M.; Schelcher, C.; Zimmermann, P.; et al. Monoaryl- and Bisaryldihydroxytropolones as Potent Inhibitors of Inositol Monophosphatase. J. Med. Chem. 1997, 40, 4208–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Zheng, C.; Li, S. Cumarin Derivative, its Preparation Process and Application in white Light Organic Electroluminescent Device. CN 102101852 A, 22 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Eastwood, P.R.; Gonzalez Rodriguez, J.; Vidal Juan, B.; Aguilar Izquierdo, N. Preparation of New Substituted Spiro[Cycloalkyl-1, 3′-indol]-2′(1′H)-one Derivatives and their Use as p38 Mitogen–Activated Kinase Inhibitors. WO 2009124692 A1, 15 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Eastwood, P.; González, J.; Gómez, E.; Caturla, F.; Aguilar, N.; Mir, M.; Aiguadé, J.; Matassa, V.; Balagué, C.; Orellana, A.; et al. Indolin-2-one p38α inhibitors III: Bioisosteric amide replacement. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 6253–6257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiguade Bosch, J.; Carranco Moruno, I. Preparation and Compositions of 7-Phenyl-[1,2,4]Triazolo [4,3-a] Pyridin-3(2H)-One Derivatives as p38 MAP Kinase Inhibitors. WO 2011057757 A1, 19 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- De, S.; Kumar, S.K.A.; Shah, S.K.; Kazi, S.; Sarkar, N.; Banerjee, S.; Dey, S. Pyridine: The scaffolds with significant clinical diversity. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 15385–15406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, D.; Sreekanth, P.S.R.; Behera, P.K.; Pradhan, M.K.; Patnaik, A.; Salunkhe, S.; Cep, R. Advances in synthesis, medicinal properties and biomedical applications of pyridine derivatives: A comprehensive review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. Rep. 2024, 12, 100210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, A.-Y.; Liu, C.-L.; Sun, X.-F.; Xie, Y.; Wang, M.-A. Discovery of pyridine-based agrochemicals by using Intermediate Derivatization Methods. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakharychev, V.V.; Martsynkevich, A.M. Development of novel pyridine-based agrochemicals: A review. Adv. Agrochem. 2025, 4, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, X.A.F.; de Gombert, A.; McKnight, J.; Pantaine, L.R.R.; Willis, M.C. The 2-Pyridyl Problem: Challenging Nucleophiles in Cross-Coupling Arylations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 11068–11091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Milo, L.J., Jr.; Lai, J.H. Recent progress in the synthesis of pyridinylboronic acids and esters. ARKIVOC 2013, 2013, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.G.; Bae, S.H. Preparation of Urea Compound for Organic Electric Device, Organic Electric Device Using Same, and Electronic Device Thereof. KR 2289502 B1, 13 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.G.; Seo, M.H. Preparation of Organic Compound for Organic Electric Device. KR 2021095268 A, 2 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.A.; Lloyd, J.; Finlay, H.; Jiang, J.; Neels, J.; Dhondi, N.K.; Gunaga, P.; Banerjee, A.; Adisechan, A. Preparation of 5-Phenylquinazoline Derivatives as Potassium Ion Channel Inhibitors. WO 2011028741 A1, 10 March 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc, C.; Pulz, R.A.; Stiefl, N.J. Preparation of pyrrolopyrimidines and Pyrrolopyridines for Treating ALK-5 and ALK-4 Receptor-Mediated Diseases. WO 2009087225 A2, 16 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bist, S.; Dangel, B.; Sherer, B. Preparation of Heterocyclic Urea Derivatives as Antibacterials. WO 2009106885 A1, 3 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gordeev, M.F.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q. Indoline Derivatives as Monoamine Oxidase A Inhibitors and their Preparation, Pharmaceutical Compositions and Use in the Treatment of Bacterial Infections. US 20100069441 A1, 18 March 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, A.; Singh, R.K. Medicinal chemistry of indole derivatives: Current to future therapeutic prospectives. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 89, 103021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, S.F.; Song, L.; Guo, H.Y.; Deng, H.; Huang, X.; Shen, Q.K.; Quan, Z.S.; Yin, X.M. Research status of indole-modified natural products. RSC Med. Chem. 2023, 14, 2535–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erden, K.; Dengiz, C. 3-Alkynylindoles as Building Blocks for the Synthesis of Electronically Tunable Indole-Based Push–Pull Chromophores. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 4385–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coburn, C.A.; Ludmerer, S.W.; Liu, K.; Wu, H.; Soll, R.; Zhong, B.; Zhu, J. Preparation of Amino Acid and Dipeptide Derivatives as Inhibitors of Hepatitis C Virus Replication. US 20190127365 A1, 2 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Coburn, C.A.; McCauley, J.A.; Ludmerer, S.W.; Liu, K.; Vacca, J.P.; Wu, H.; Hu, B.; Soll, R.; Sun, F.; Wang, X.; et al. Preparation of L-Prolinamide Derivatives as Inhibitors of Protein NS5A of Hepatitis C Virus. WO 2010111483 A1, 30 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wurz, R.P.; Pettus, L.H.; Jackson, C.; Wu, B.; Wang, H.-L.; Herberich, B.; Cee, V.; Lanman, B.A.; Reed, A.B.; Chavez, F.; et al. The discovery and optimization of aminooxadiazoles as potent Pim kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.-L.; Cee, V.C.; Herberich, B.J.; Jackson, C.L.M.; Lanman, B.A.; Nixey, T.; Pettus, L.H.; Reed, A.B.; Wu, B.; Wurz, R.; et al. Indoles and Related Compounds as PIM Kinase Inhibitors and Their Preparation and Use for the Treatment of P IM Kinase-Related Diseases. WO 2012129338 A1, 27 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bakary-Barry, T.; Gallop, M.A.; Barsanti, P.A. Preparation of Indole Compounds as Androgen Receptor Modulators. WO 2022020342 A1, 27 January 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Archna, S.P.; Chawla, P.A. Thiophene-based derivatives as anticancer agents: An overview on decade’s work. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 101, 104026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nivrutti, G.P. Furan: A Promising Scaffold for Biological Activity. Int. J. Adv. Biol. Biomed. Res. 2024, 12, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogacz, D.; Lewkowski, J.; Malinowski, Z.; Matusiak, A.; Morawska, M.; Rychter, P. Effect of New Thiophene-Derived Aminophosphonic Derivatives on Growth of Terrestrial Plants. Part 2. Their Ecotoxicological Impact and Phytotoxicity Test Toward Herbicidal Application in Agriculture. Molecules 2018, 23, 3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbarella, G.; Zangoli, M.; Di Maria, F. Chapter Three—Synthesis and Applications of Thiophene Derivatives as Organic Materials. Adv. Heterocycl. Chem. 2017, 123, 105–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Huang, H. Furan semiconductors and their application in organic field-effect transistors. Mater. Today Nano 2023, 21, 100284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Huo, L. Recent Advances of Furan and Its Derivatives Based Semiconductor Materials for Organic Photovoltaics. Small Methods 2021, 5, 2100493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




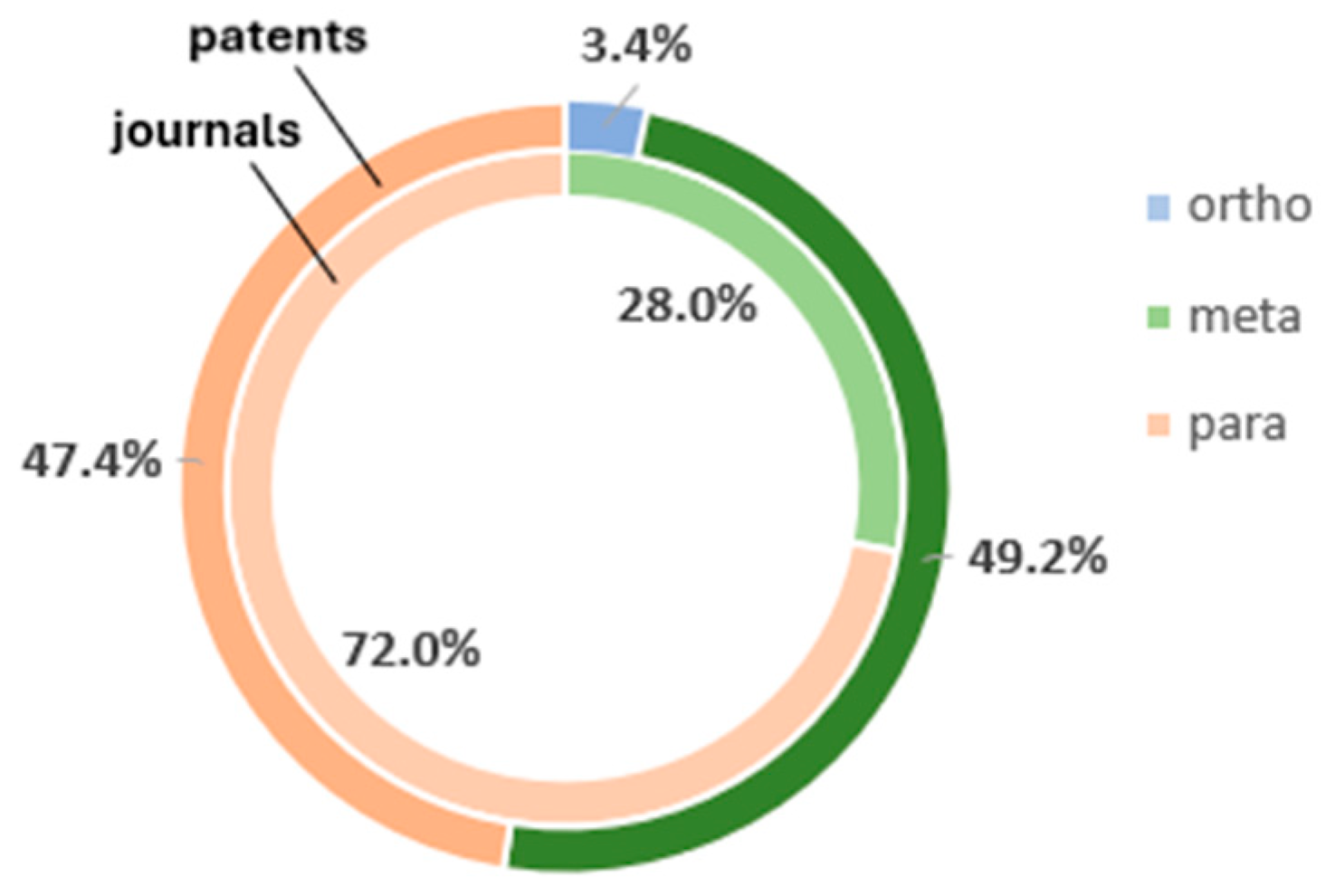











| Publication Type | 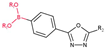 para |  meta | 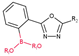 ortho |
|---|---|---|---|
| Journals | 18 | 7 | 0 |
| Patents | 28 | 29 | 2 |
| Entry | Catalyst | Ligand 1 | Solvent | Temp./Time | Yield | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X = Cl (39a) | ||||||
| 1 | Pd(AcO)2 | A | THF | 110 °C/20 h | 79% | [17] |
| 2 | Pd(AcO)2 | B | 1,4-dioxane | 100 °C/20 h | 84–88% | [21] |
| 3 | Pd(dppf)Cl2 | - | 1,4-dioxane | 80 °C/on | na | [22] |
| 4 | Pd2(dba)3 | C | 1,4-dioxane | 85 °C/on | na | [23] |
| X = Br (39b) | ||||||
| 5 | Pd(dppf)Cl2 | - | 1,4-dioxane | 100 °C/na or on or 2 h | 80–92% | [24,25,26,27,28] |
| 6 | Pd(dppf)Cl2 | - | 1,4-dioxane | 90 °C/2 h | 70–85% | [29] |
| 7 | Pd(dppf)Cl2 | - | 1,4-dioxane | 80 °C/na or 12 h–4 d | 21–78% | [28,29,30,31,32,33] |
| 8 | Pd(dppf)Cl2 | - | DMF | 90 °C/na | 78% | [34] |
| 9 | Pd(dppf)Cl2 | - | DMF | 80 °C/15–16 h | 51–83% | [35,36] |
| 10 | Pd(dppf)Cl2 | - | DMSO | 80 °C/4–24 h | 45–61% | [37,38] |
| 11 | Pd(dppf)Cl2 | - | DMSO | 80 °C/on | 83% | [39] |
| 12 | Pd(dppf)Cl2 | - | DME | 80 °C/on | 81% | [40] |
| 13 | Pd(dppf)Cl2·DCM | - | 1,4-dioxane | 80 °C/2 h | 77–88% | [41] |
| 14 | Pd(dppf)Cl2·DCM | - | 1,4-dioxane | 90 °C/12 h | na | [42] |
| 15 | Pd(dppf)Cl2·DCM | - | DMF | 80 °C/12 h | 53% | [43] |
| 16 | CuI, Pd(dppf)Cl2 | - | DMF | 90 °C/12 h | 82% | [44] |
| X = I (39c) | ||||||
| 17 | Pd(PPh3)4 | - | 1,4-dioxane | 100 °C/12 h | 22% 2 | [45] |
| X = OTf (39d) | ||||||
| 18 | Pd(dppf)Cl2 | - | DMF | 95 °C/on | 86% | [46] |
| Entry | Lithium Source | Boron Source 1 | Solvent | Temp. | Yield | Product | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | n-BuLi | A | Et2O | na | na | 44 | [48,49] |
| 2 | n-BuLi | A | THF | −40 °C to −78 °C | 81% | 44 | [18] |
| 3 | n-BuLi | A | THF | −50 °C | 42% | 44 | [50] |
| 4 | n-BuLi | A | THF | −78 °C | 74% | 44 | [51] |
| 5 | n-BuLi | A | Toluene/THF | −78 °C | 62% | 44 | [39] |
| 6 | n-BuLi | B | Toluene/THF | −78 °C | na | 44 | [15] |
| 7 | n-BuLi | C | THF | Na | 61% 2 | 40 | [52] |
| 8a | 1. MeLi 2. n-BuLi | B | THF | −65 °C | 82% | 44 | [53] |
| 8b | 1. Li, 4-chlorotoluene 2. n-HexLi | B | THF | −35 °C to −65 °C | 89% | 44 | |
| 8c | 1. Li, 2-chlorotoluene, biphenyl 2. n-HexLi | A | THF | −30 °C to −65 °C | 60% | 44 | |
| 8d | 1. Li, 2-chlorotoluene 2. n-HexLi | A | THF | −30 °C to −65 °C | 76% | 44 | |
| 8e | 1. Li, chlorobenzene, biphenyl 2. n-HexLi | A | THF | −30 °C to −65 °C | 84% | 44 |
| Entry | Catalyst | Ligand 1 | Solvent | Temp./Time | Yield | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X = Br (53a) | ||||||
| 1 | Pd(dppf)Cl2 | - | 1,4-dioxane | 120 °C/20 min or on | 44–90% | [55] |
| 2 | Pd(dppf)Cl2 | - | 1,4-dioxane | 100 °C/6 h | 53–80% | [56] |
| 3 | Pd(dppf)Cl2 | - | 1,4-dioxane | 90 °C/on | 99% | [57] |
| 4 | Pd(dppf)Cl2 | - | 1,4-dioxane | 85 °C/on | 88–90% | [58] |
| 5 | Pd(dppf)Cl2·DCM | - | DMSO | 130 °C/45 min | 62% | [59] |
| 6 | Pd(dppf)Cl2·DCM | - | DMSO | 80 °C/16 h | na | [60,61] |
| 7 | Pd(dppf)Cl2·DCM | - | DMSO | 80 °C/18 h | na | [62] |
| 8 | Pd(dppf)Cl2·DCM | - | DMF | 90 °C/15 h | 76% | [63] |
| 9 | Pd(dppf)Cl2·DCM | - | DMF | 80 °C/12 h | 71% | [40] |
| 10 | Pd(dppf)Cl2 | - | THF | 85 °C/12 h | 80% | [64] |
| 11 | Pd(dppf)Cl2 | - | dimethoxyethane | 101 °C/14 h or 120 °C/45 min | na | [65,66] |
| 12 | Pd(PPh3)2Cl2 | - | 1,4-dioxane | n/a | 35% 2 | [67] |
| 13 | Pd(PPh3)2Cl2 | - | DMSO | 80 °C/4.5 h | 22% | [68] |
| 14 | Pd(AcO)2 | A | THF | 101 °C/2 h | n/a | [61] |
| 15 | Pd(AcO)2 | A | THF | 75 °C/2 h | 78% | [69] |
| 16 | Pd(AcO)2 | A | THF | 75 °C/3 h | 84% | [70] |
| X = I (53b) | ||||||
| 17 | Pd(AcO)2 | - | DMF | 85 °C/3 h | na | [71] |
| 18 | Pd(dppf)Cl2 | - | DMF | 80 °C/4 h | na | [72] |
| X = Cl (53c) | ||||||
| 19 | Pd(AcO)2 | B | 1,4-dioxane | 101 °C | 79–85% | [21] |
| Entry | Product | Catalyst | Solvent | Base | Temp./Time | Yield | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 71a, R1 = NH2 | Pd(dppf)Cl2·DCM | 1,4-dioxane 1 | AcOK | 120 °C/45 min | na | [88] |
| 2 | 71b, R1 = H | Pd(dppf)Cl2 | ACN 1 | AcOK | 160 °C/15 min | na | [89] |
| 3 | 71b, R1 = H | Pd(dppf)Cl2 | DMSO | AcOK | 80 °C/24h | 15% | [69] |
| 4 | 72 | Pd(PPh3)2Cl2 | 1,4-dioxane | AcOK | 70 °C/12.5h | 76% | [90] |
| 5 | 73 | Pd(dppf)Cl2·DCM | DMSO | AcOK, Et3N | 80 °C/2h | 35% | [91] |
| Method A | Method B | Method C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advantages |
|
|
|
| Limitations |
|
|
|
| Average yield | 22–88% | 40–99% | 43–77% |
| Applicability | Bromides, Iodides | Chlorides, Bromides, Iodides, Triflates | Carboxylic acids, Hydrazides, Thiosemicarbazides |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wołek, B.; Kudelko, A. Synthetic Approaches to 1,3,4-Oxadiazole-Containing Boronic Derivatives. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8054. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148054
Wołek B, Kudelko A. Synthetic Approaches to 1,3,4-Oxadiazole-Containing Boronic Derivatives. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(14):8054. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148054
Chicago/Turabian StyleWołek, Barbara, and Agnieszka Kudelko. 2025. "Synthetic Approaches to 1,3,4-Oxadiazole-Containing Boronic Derivatives" Applied Sciences 15, no. 14: 8054. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148054
APA StyleWołek, B., & Kudelko, A. (2025). Synthetic Approaches to 1,3,4-Oxadiazole-Containing Boronic Derivatives. Applied Sciences, 15(14), 8054. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148054







