A Comparative Study of Indoor Accuracies Between SLAM and Static Scanners
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
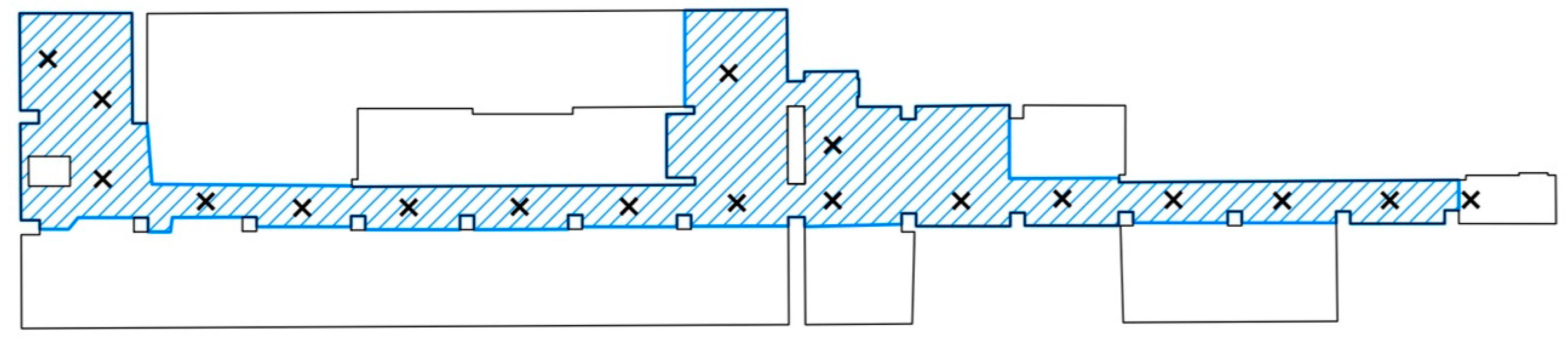
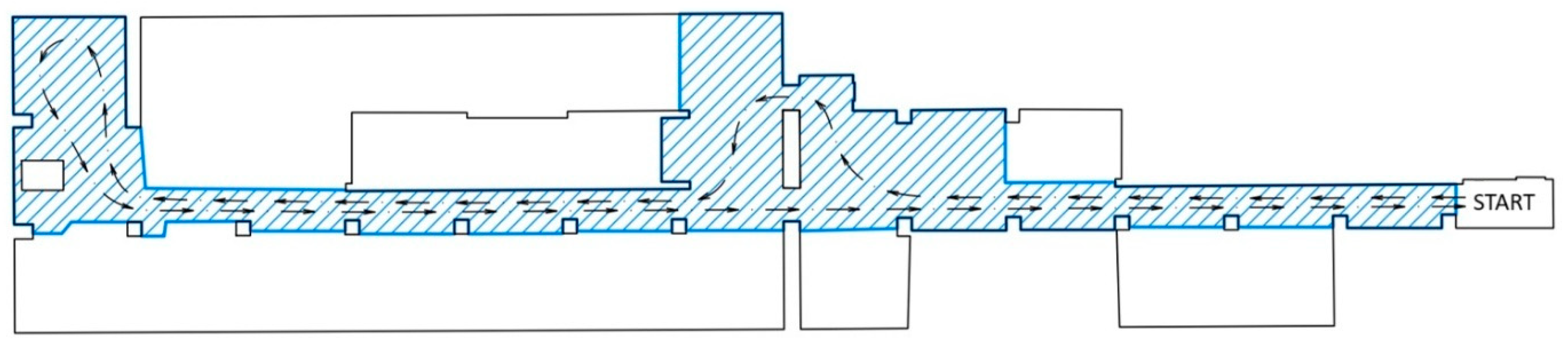
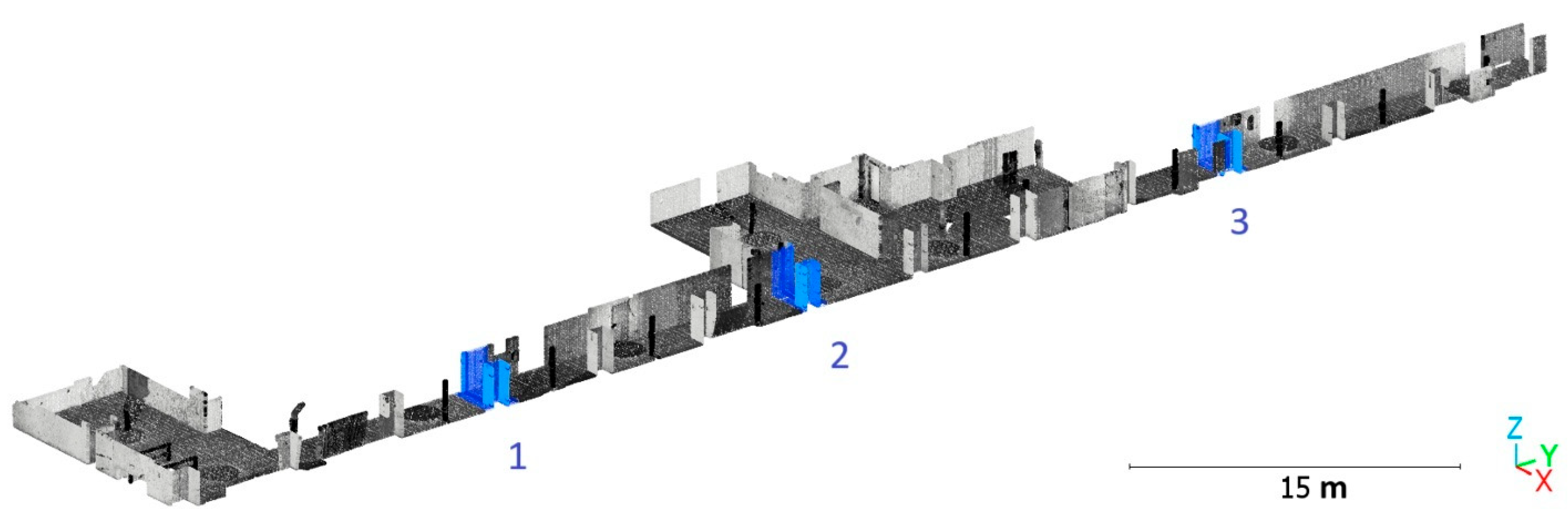
2.1. Testing Space
2.2. Used Instruments
2.3. Reference Cloud Acquisition
2.4. Measurements with the Tested Scanners
2.5. Principles of the Evaluation of the Individual Clouds
2.6. Processing and Evaluation of the Acquired Data
2.6.1. Initial Processing
2.6.2. Transformation of the Clouds to Spherical Targets
2.6.3. The Overall Accuracy of Individual Clouds After the Initial Transformation
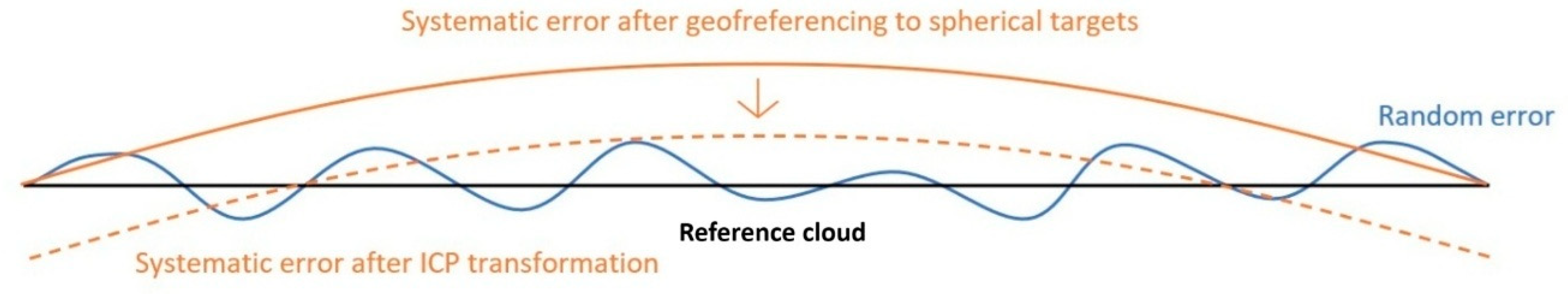
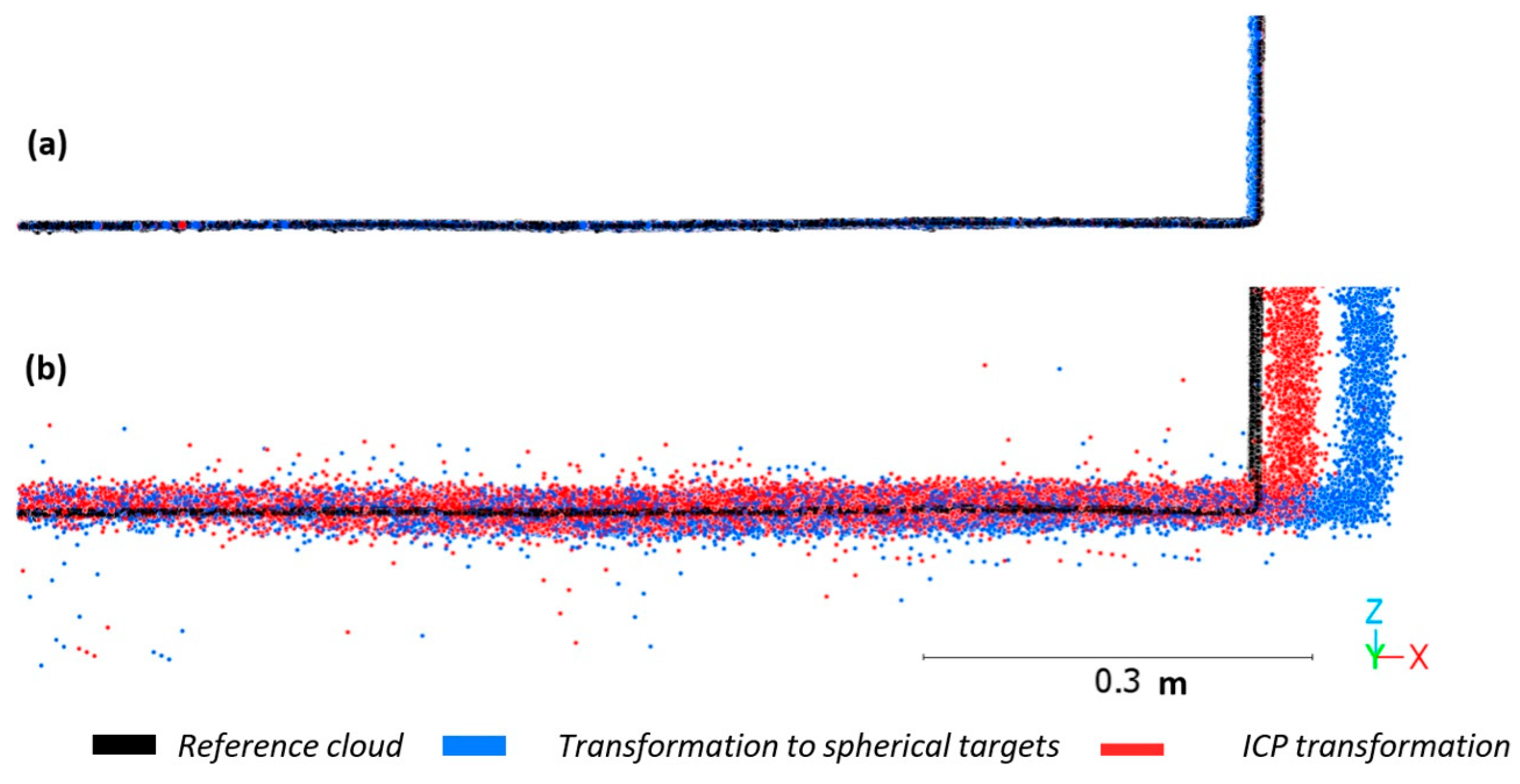
2.6.4. ICP Transformation and Evaluation of the Transformed Clouds
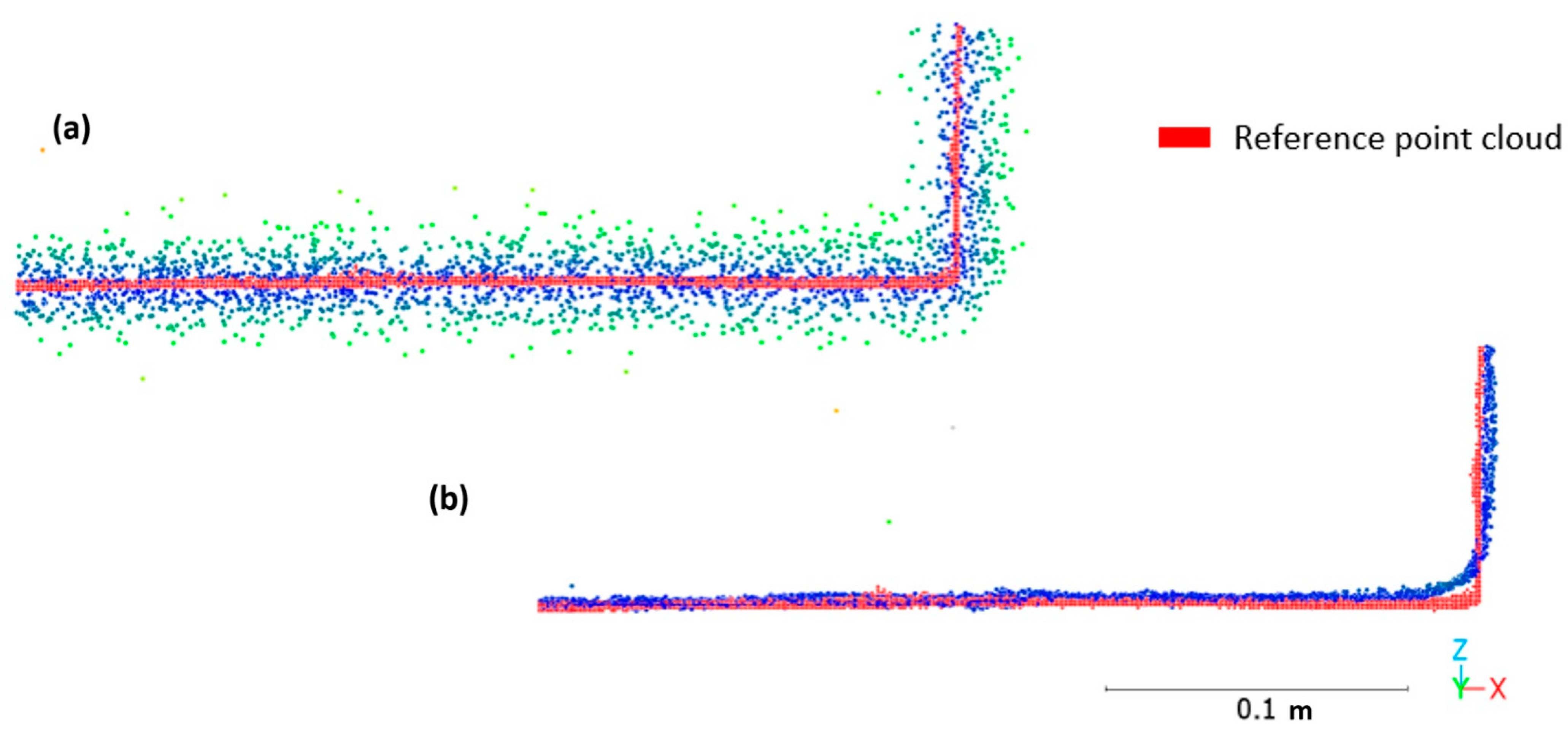
2.6.5. Local ICP Transformation for Evaluation of Profiles
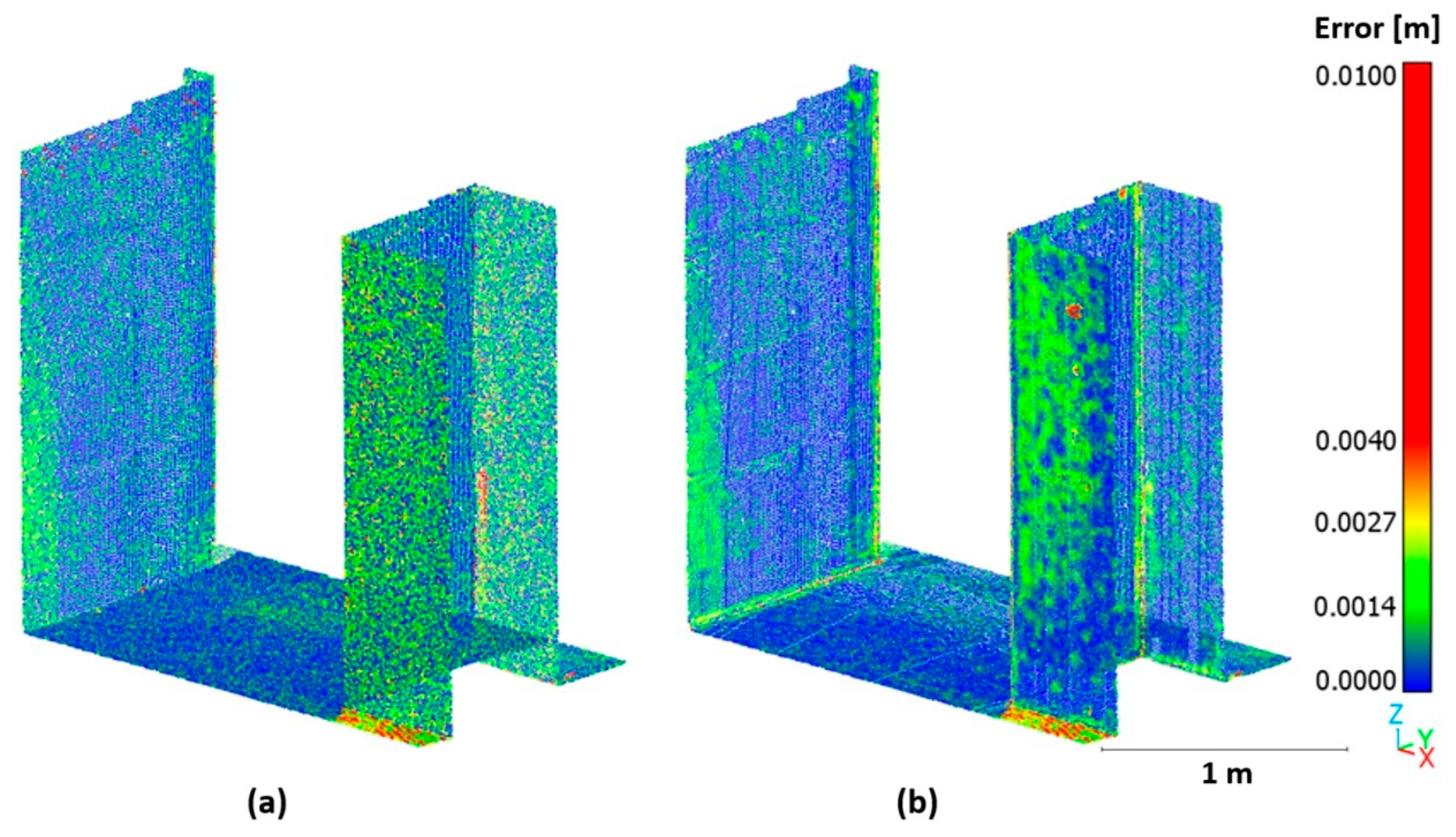
2.6.6. Noise Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Initial Transformation to Spherical Targets
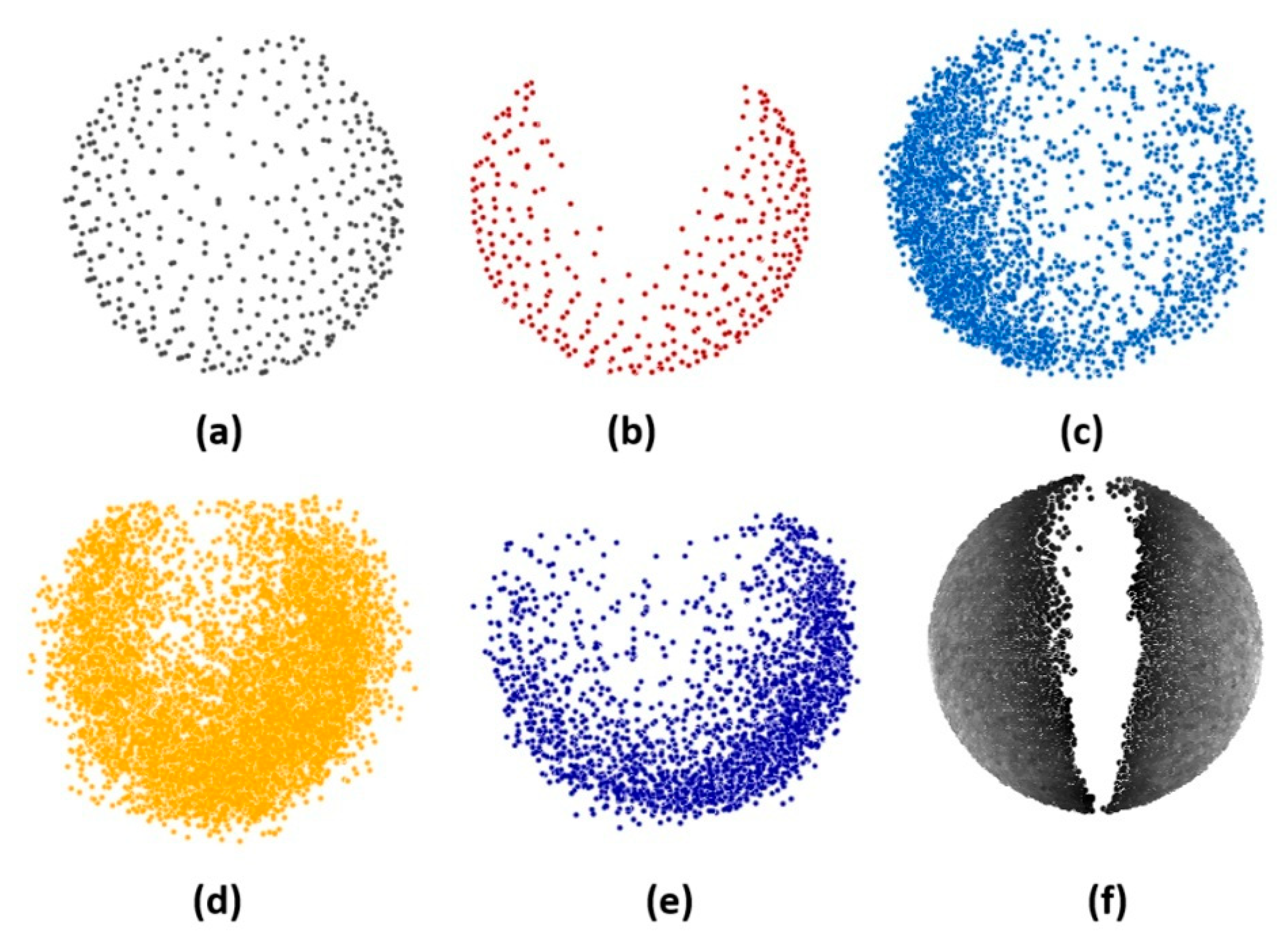
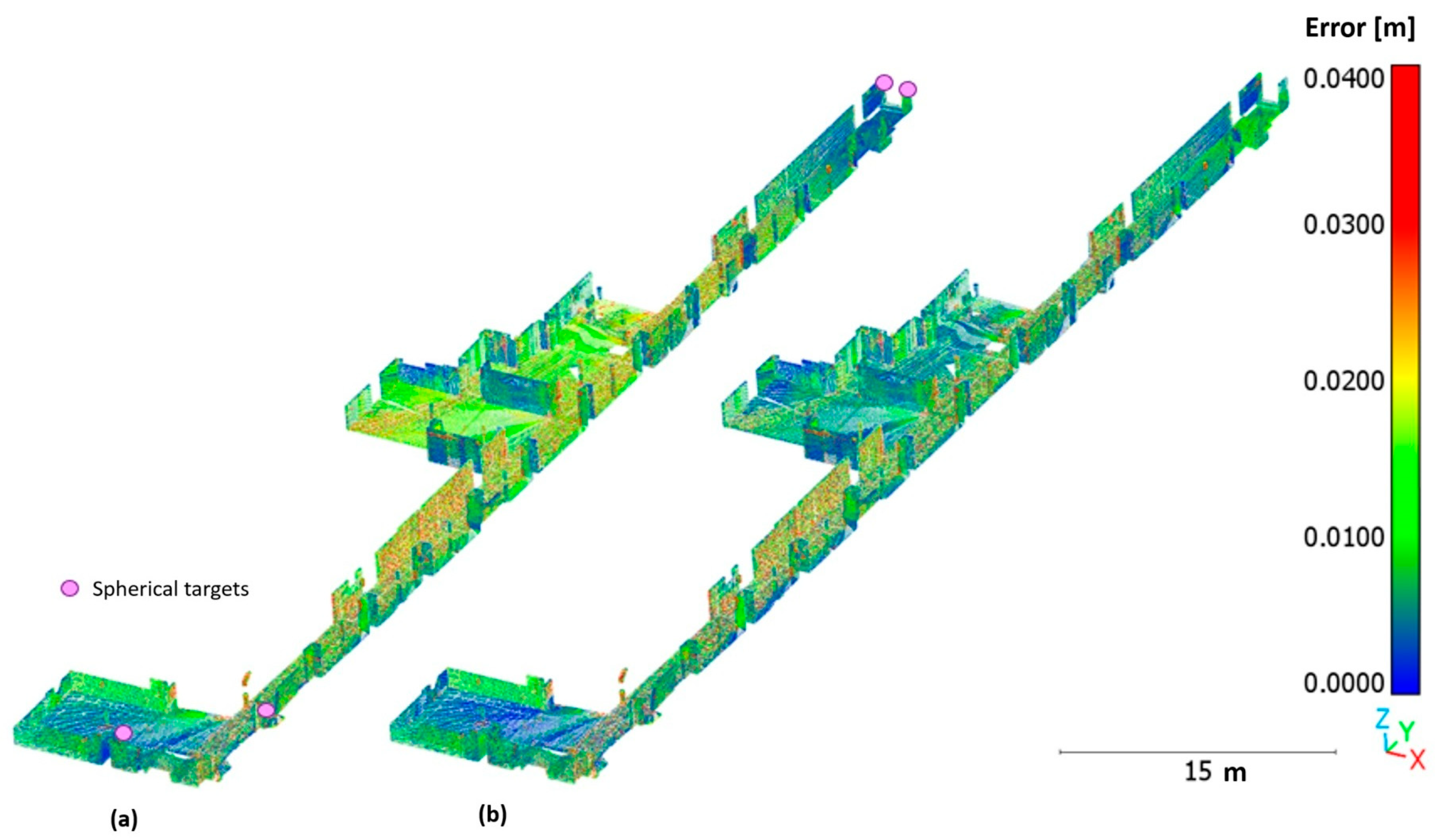
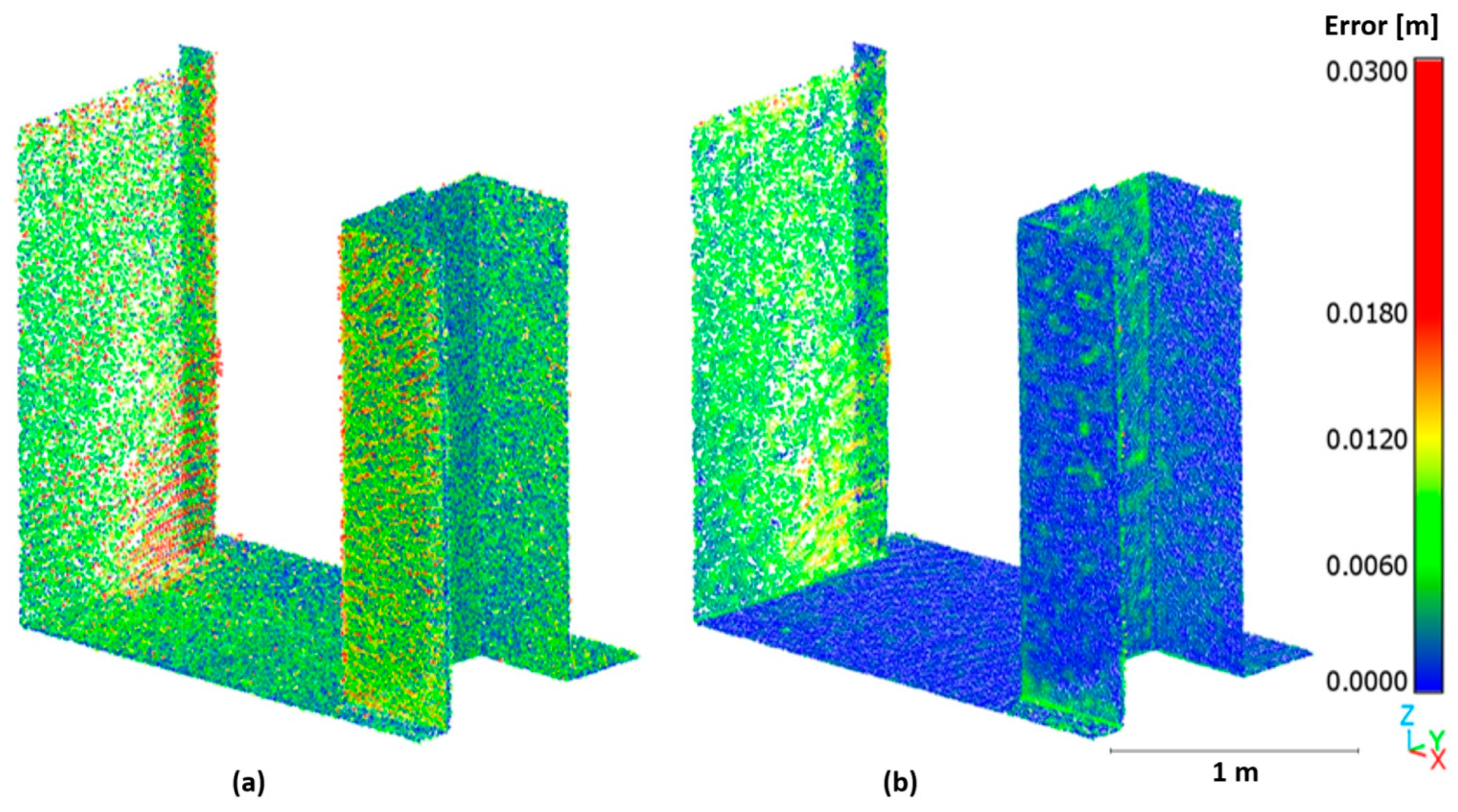
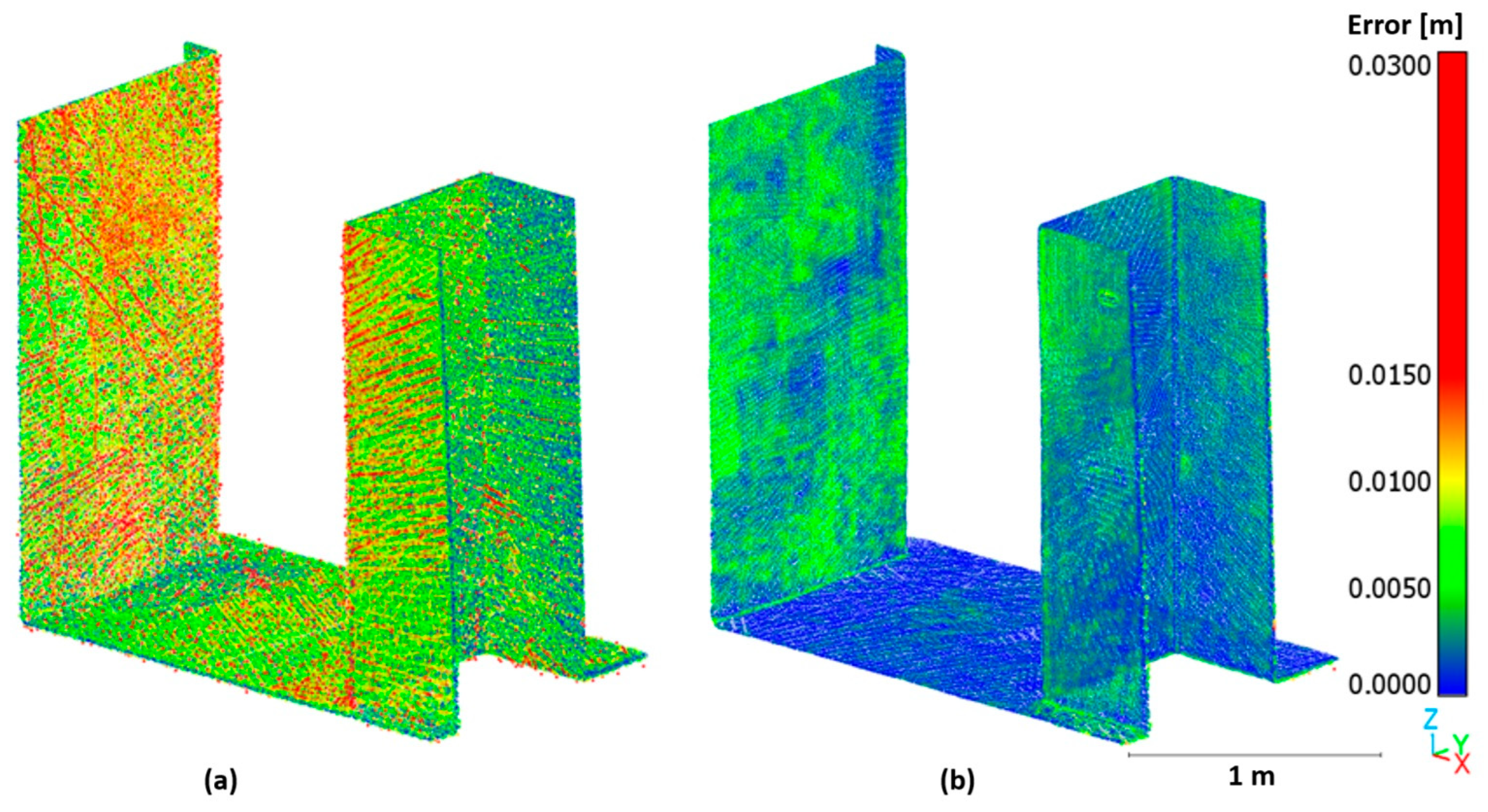
3.2. Visual Quality of the Point Clouds
3.3. Accuracies of Clouds Transformed to Spherical Targets
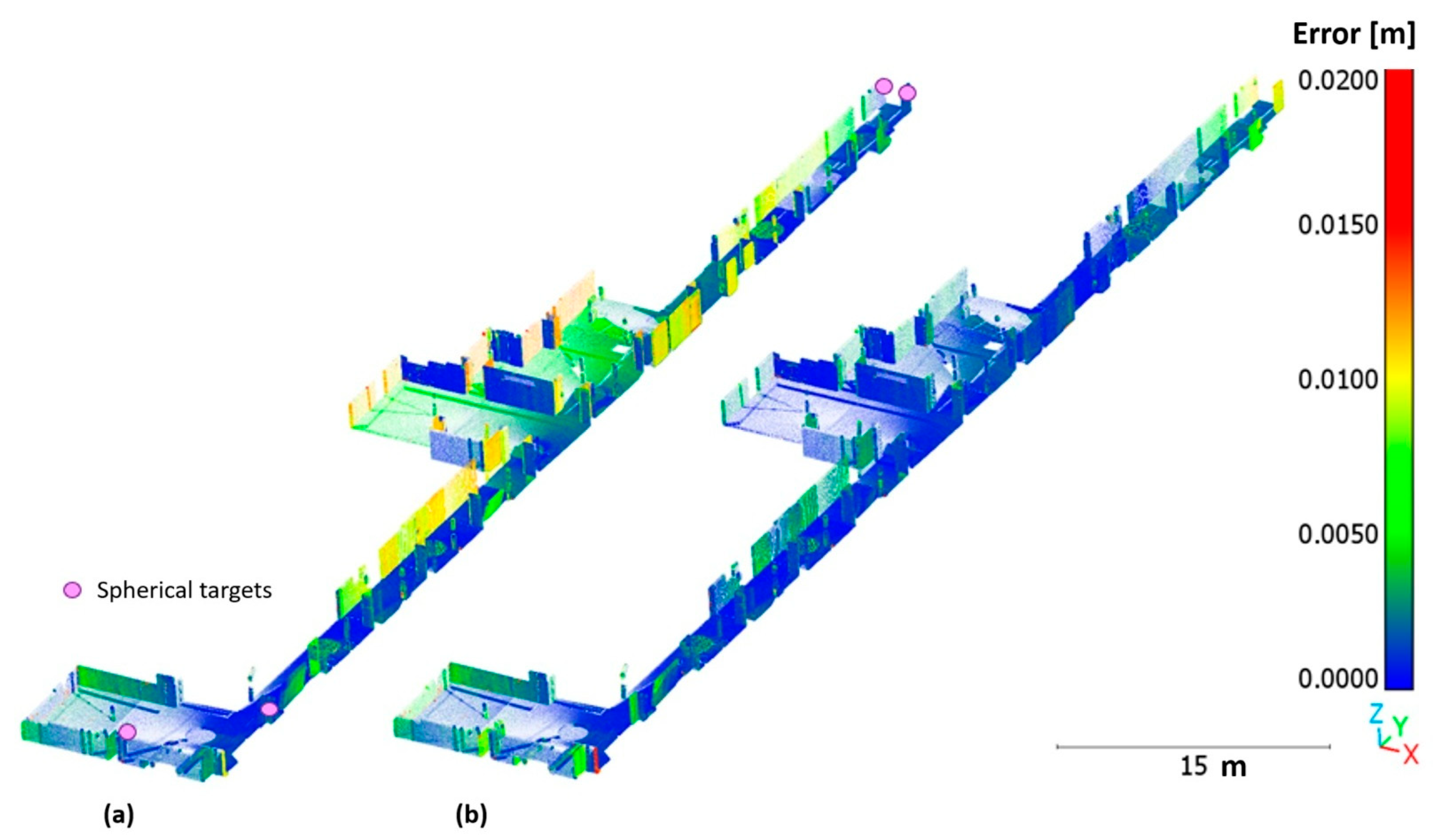
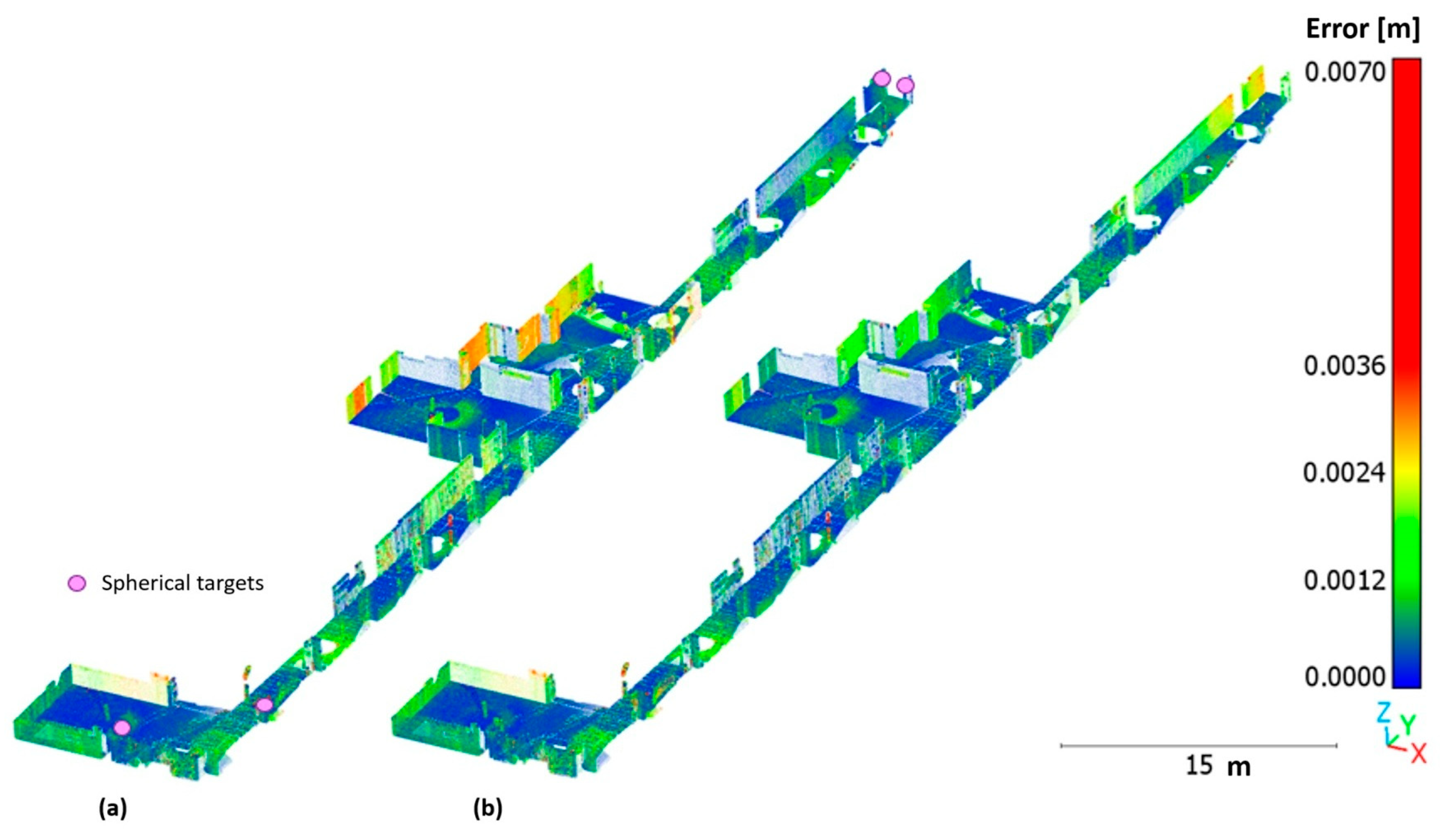
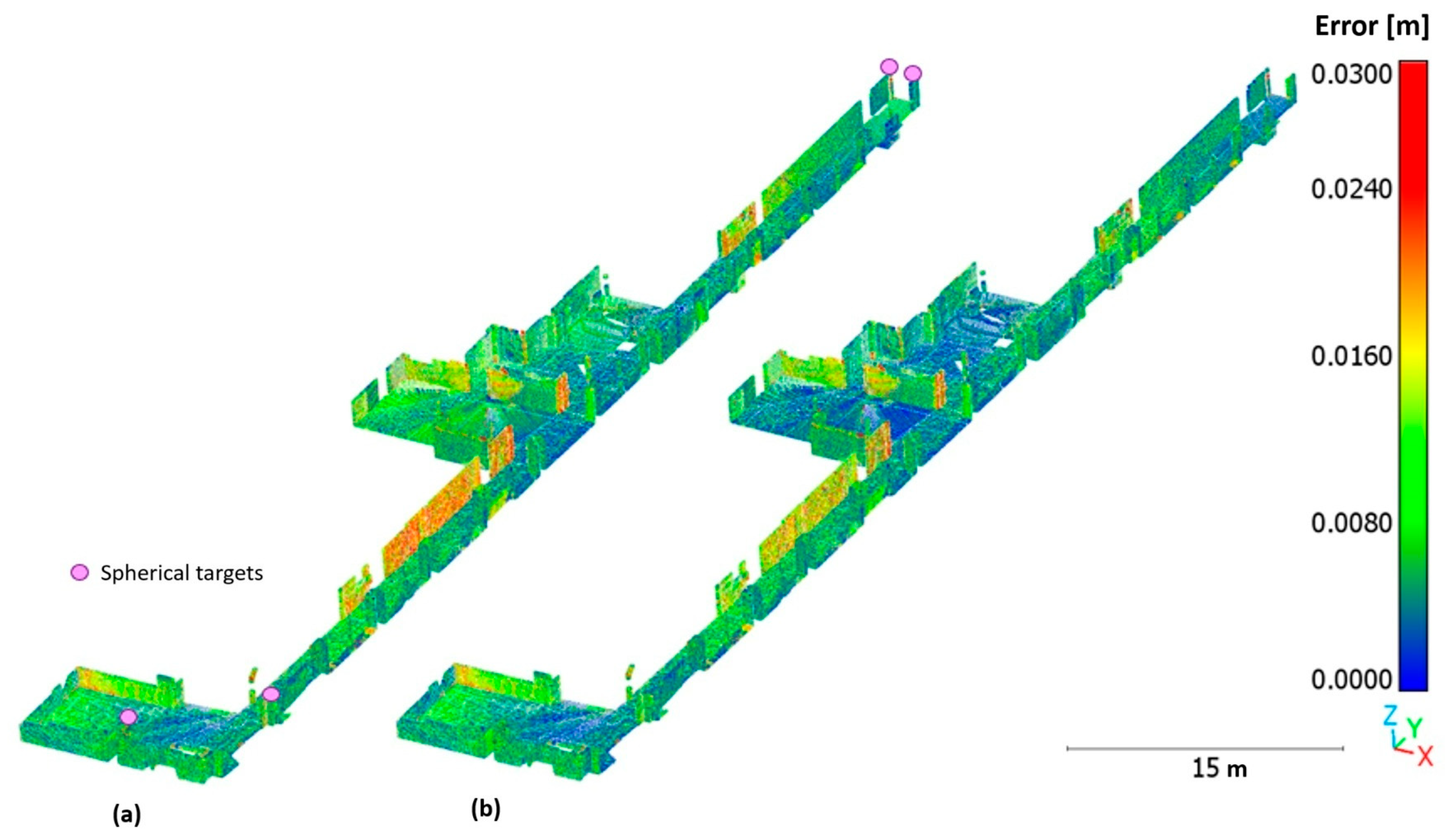
3.4. Global Point Cloud Accuracies After Icp Transformation
3.5. Visual Comparison of the Clouds
3.6. Local Accuracies in the Profiles
3.7. Comparison of the Scanners
3.8. Comparison of Scanners from the Perspective of Noise
Visual Comparison
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Azhar, S.; Willkens, D.; Li, B. Static Terrestrial Laser Scanning (TLS) for Heritage Building Information Modeling (HBIM): A Systematic Review. Virtual Worlds 2023, 2, 90–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, L.; Li, C.; Zheng, D. A Survey of Mobile Laser Scanning Applications and Key Techniques over Urban Areas. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolkas, D.; Guthrie, K.; Durrutya, L. sUAS LiDAR and Photogrammetry Evaluation in Various Surfaces for Surveying and Mapping. J. Surv. Eng. 2024, 150, 04023021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vílchez-Lara, M.d.C.; Molinero-Sánchez, J.G.; Rodríguez-Moreno, C.; Gómez-Blanco, A.J.; Reinoso-Gordo, J.F. High Resolution 3D Model of Heritage Landscapes Using UAS LiDAR: The Tajos de Alhama de Granada, Spain. Land 2024, 13, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, N. UAV-Based Investigation of Earthquake-Induced Deformation and Landscape Changes: A Case Study of the February 6, 2023 Earthquakes in Hatay, Türkiye. Earth Sci. Inform. 2023, 16, 3765–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartmiński, P.; Siłuch, M.; Kociuba, W. The Effectiveness of a UAV-Based LiDAR Survey to Develop Digital Terrain Models and Topographic Texture Analyses. Sensors 2023, 23, 6415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovanič, Ľ.; Peťovský, P.; Topitzer, B.; Blišťan, P. Complex Methodology for Spatial Documentation of Geomorphological Changes and Geohazards in the Alpine Environment. Land 2024, 13, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, J.; Lagner, O.; Klouček, T. UAV Leaf-on, Leaf-off and ALS-Aided Tree Height: A Case Study on the Trees in the Vicinity of Roads. Urban For. Urban Green. 2024, 93, 128229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štroner, M.; Urban, R.; Křemen, T.; Braun, J. UAV DTM Acquisition in a Forested Area—Comparison of Low-Cost Photogrammetry (DJI Zenmuse P1) and LiDAR Solutions (DJI Zenmuse L1). Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2023, 56, 2179942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fareed, N.; Flores, J.P.; Das, A.K. Analysis of UAS-LiDAR Ground Points Classification in Agricultural Fields Using Traditional Algorithms and PointCNN. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moudrý, V.; Cord, A.F.; Gábor, L.; Laurin, G.V.; Barták, V.; Gdulová, K.; Malavasi, M.; Rocchini, D.; Stereńczak, K.; Prošek, J.; et al. Vegetation Structure Derived from Airborne Laser Scanning to Assess Species Distribution and Habitat Suitability: The Way Forward. Divers. Distrib. 2022, 29, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinpin, L.; Wenge, Q.; Yunjian, C.; Feng, L. Application of 3D Laser Scanning in Underground Station Cavity Clusters. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 8896363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybansky, M. Determination of Forest Structure from Remote Sensing Data for Modeling the Navigation of Rescue Vehicles. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, S.H.; Haakonsen, T.A.; Dahle, H.; Fan, H. Assessing the Measurement Quality of UAV-Borne Laser Scanning in Steep and Snow-Covered Areas. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2023, XLVIII-1/W2-2023, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, G.; Mateus, L.; Ferreira, V. Historical Heritage Maintenance via Scan-to-BIM Approaches: A Case Study of the Lisbon Agricultural Exhibition Pavilion. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Kim, M.; Kim, G.; Kim, S.; Park, S.-C.; Lee, S. 3D Scanning Technique for Obtaining Road Surface and Its Applications. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2017, 18, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riveiro, B.; Morer, P.; Arias, P.; de Arteaga, I. Terrestrial Laser Scanning and Limit Analysis of Masonry Arch Bridges. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 1726–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenda, G.; Marmol, U. Integration of High-Precision UAV Laser Scanning and Terrestrial Scanning Measurements for Determining the Shape of a Water Tower. Measurement 2023, 218, 113178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenda, G.; Kudrys, J.; Fryc, D. Sub-Centimetre Integration of Scanning Measurements: UAV and Terrestrial-Based, for Determining the Shape of a Shell Structure. Measurement 2023, 221, 113516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keitaanniemi, A.; Rönnholm, P.; Kukko, A.; Vaaja, M.T. Drift Analysis and Sectional Post-Processing of Indoor Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM)-Based Laser Scanning Data. Autom. Constr. 2023, 147, 104700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-I.; Park, J.; Kim, K.-S. Fast and Accurate Desnowing Algorithm for LiDAR Point Clouds. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 160202–160212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhou, C.; Shang, G.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Xu, C.; Hu, K. SLAM Overview: From Single Sensor to Heterogeneous Fusion. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, H.; Xia, Z.C. SLAM; Definition and Evolution. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 97, 104032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Singh, S.; Pratap Banerjee, B.; Raval, S. A Review of Laser Scanning for Geological and Geotechnical Applications in Underground Mining. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2023, 33, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharineiat, Z.; Tarsha Kurdi, F.; Henny, K.; Gray, H.; Jamieson, A.; Reeves, N. Assessment of NavVis VLX and BLK2GO SLAM Scanner Accuracy for Outdoor and Indoor Surveying Tasks. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keitaanniemi, A.; Kukko, A.; Virtanen, J.-P.; Vaaja, M.T. Measurement Strategies for Street-Level SLAM Laser Scanning of Urban Environments. Photogramm. J. Finl. 2020, 27, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC 60825-1; Safety of Laser Products—Part 1: Equipment Classification and Requirements. International Electrotechnical Commision: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Akpınar, B. Performance of Different SLAM Algorithms for Indoor and Outdoor Mapping Applications. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2021, 4, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiozzo Fasiolo, D.; Scalera, L.; Maset, E. Comparing LiDAR and IMU-Based SLAM Approaches for 3D Robotic Mapping. Robotica 2023, 41, 2588–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajs, J.; Kasza, D.; Zagożdżon, P.P.; Zagożdżon, K.D. 3D Modeling of Underground Objects with the Use of SLAM Technology on the Example of Historical Mine in Ciechanowice (Ołowiane Range, The Sudetes). E3S Web Conf. 2018, 29, 00024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahle, L.; Holley, E.A.; Walton, G.; Petruska, A.J.; Brune, J.F. Analysis of SLAM-Based Lidar Data Quality Metrics for Geotechnical Underground Monitoring. Min. Metall. Explor. 2022, 39, 1939–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Křemen, T.; Michal, O.; Jiřikovský, T.; Kuric, I. Long-distance SLAM scanning of mine tunnel—Testing of precision and accuracy of Emesent Hovermap ST-X. Acta Monstanistica Slovaca 2024, 29, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, F.; Torresani, A.; Farella, E.M.; Pierdicca, R.; Menna, F.; Remondino, F. 3D Surveying of Underground Built Heritage: Opportunities and Challenges of Mobile Technologies. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štroner, M.; Urban, R.; Křemen, T.; Braun, J.; Michal, O.; Jiřikovský, T. Scanning the underground: Comparison of the accuracies of SLAM and static laser scanners in a mine tunnel. Measurement 2025, 242, 115875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammartano, G.; Spanò, A. Point Clouds by SLAM-Based Mobile Mapping Systems: Accuracy and Geometric Content Validation in Multisensor Survey and Stand-Alone Acquisition. Appl. Geomat. 2018, 10, 317–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, R.; Štroner, M.; Braun, J.; Suk, T.; Kovanič, Ľ.; Blistan, P. Determination of Accuracy and Usability of a SLAM Scanner GeoSLAM ZEB Horizon: A Bridge Structure Case Study. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keitaanniemi, A.; Virtanen, J.-P.; Rönnholm, P.; Kukko, A.; Rantanen, T.; Vaaja, M.T. The Combined Use of SLAM Laser Scanning and TLS for the 3D Indoor Mapping. Buildings 2021, 11, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Scanner | Trimble X7 | Leica RTC 360 | Emesent Hovermap ST-X | GeoSLAM ZEB Horizon RT | FARO Orbis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSESPHER [mm] for individual measurements | 2.0 | 1.5 | 4.4/5.5/4.8 | 17.5/15.9/17.9 | 6.6/8.0/3.9 |
| RMSESPHERÆ [mm] (StDev) | 2.0 | 1.5 | 4.9 (0.6) | 17.1 (1.1) | 6.4 (2.1) |
| Scanner | Trimble X7 | Leica RTC 360 | Emesent Hovermap ST-X | GeoSLAM ZEB Horizon RT | FARO Orbis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSESPHER [mm] for individual measurements | 5.4 | 1.2 | 5.9/6.6/9.1 | 31.5/35.3/41.2 | 9.0/8.2/9.3 |
| RMSESPHERÆ [mm] (StDev) | 5.4 | 1.2 | 7.3 (1.7) | 36.2 (4.9) | 8.8 (0.6) |
| Scanner | Trimble X7 | Leica RTC 360 | Emesent Hovermap ST-X | GeoSLAM ZEB Horizon RT | FARO Orbis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSESPHER [mm] for individual measurements | 2.5 | 1.0 | 5.6/5.4/6.5 | 20.6/21.9/27.8 | 6.3/6.0/5.9 |
| RMSESPHERÆ [mm] (StDev) | 2.5 | 1.0 | 5.8 (0.6) | 23.6 (3.8) | 6.1 (0.2) |
| Scanner | RMSE∅X (StDev) [mm] | RMSE∅Y (StDev) [mm] | RMSE∅Z (StDev) [mm] | RMSEMIN/MAX [mm] (Axis) | RMSEICP-PROFILE (StDev) [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trimble X7 | 8.8 (1.8) | 0.6 (0.5) | 1.2 (0.5) | 10.0 (X) | 1.2 (0.2) |
| Leica RTC 360 | 0.9 (0.5) | 0.2 (0.3) | 0.5 (0.6) | 1.2 (X) | 0.6 (0.1) |
| Emesent Hovermap ST-X | 9.8 (5.6) | 2.2 (2.2) | 2.3 (2.3) | −18.2 (X) | 5.5 (0.6) |
| GeoSLAM ZEB Horizon RT | 71.1 (14.4) | 10.7 (7.8) | 4.2 (4.4) | −96.4 (X) | 12.1 (0.7) |
| FARO Orbis | 11.2 (5.7) | 2.9 (2.7) | 6.4 (2.9) | −18.0 (X) | 5.2 (0.2) |
| Scanner | RMSEICP-local (StDev) [mm] | RMSEICP-local smoothed (StDev) [mm] | RMSEnoise (StDev) [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trimble X7 | 1.2 (0.2) | 0.9 (0.1) | 0.9 (0.2) |
| Leica RTC 360 | 0.6 (0.1) | 0.7 (0.1) | - |
| Emesent Hovermap ST-X | 5.5 (0.6) | 2.2 (0.5) | 5.0 (0.5) |
| GeoSLAM ZEB Horizon RT | 12.1 (0.7) | 7.6 (1.1) | 9.3 (0.3) |
| FARO Orbis | 5.2 (0.2) | 2.1 (0.4) | 4.7 (0.2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chrbolková, A.; Štroner, M.; Urban, R.; Michal, O.; Křemen, T.; Braun, J. A Comparative Study of Indoor Accuracies Between SLAM and Static Scanners. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8053. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148053
Chrbolková A, Štroner M, Urban R, Michal O, Křemen T, Braun J. A Comparative Study of Indoor Accuracies Between SLAM and Static Scanners. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(14):8053. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148053
Chicago/Turabian StyleChrbolková, Anna, Martin Štroner, Rudolf Urban, Ondřej Michal, Tomáš Křemen, and Jaroslav Braun. 2025. "A Comparative Study of Indoor Accuracies Between SLAM and Static Scanners" Applied Sciences 15, no. 14: 8053. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148053
APA StyleChrbolková, A., Štroner, M., Urban, R., Michal, O., Křemen, T., & Braun, J. (2025). A Comparative Study of Indoor Accuracies Between SLAM and Static Scanners. Applied Sciences, 15(14), 8053. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148053






