High-Temperature Mechanical and Wear Behavior of Hypoeutectic Al–Si–(Cu)–Mg Alloys with Hardening Mechanisms Dictated by Varying Cu:Mg Ratios
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Preparation
2.2. Microstructural Characterization Preperation
2.3. Mechanical Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructural Characterization
3.1.1. Phase Identification via X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
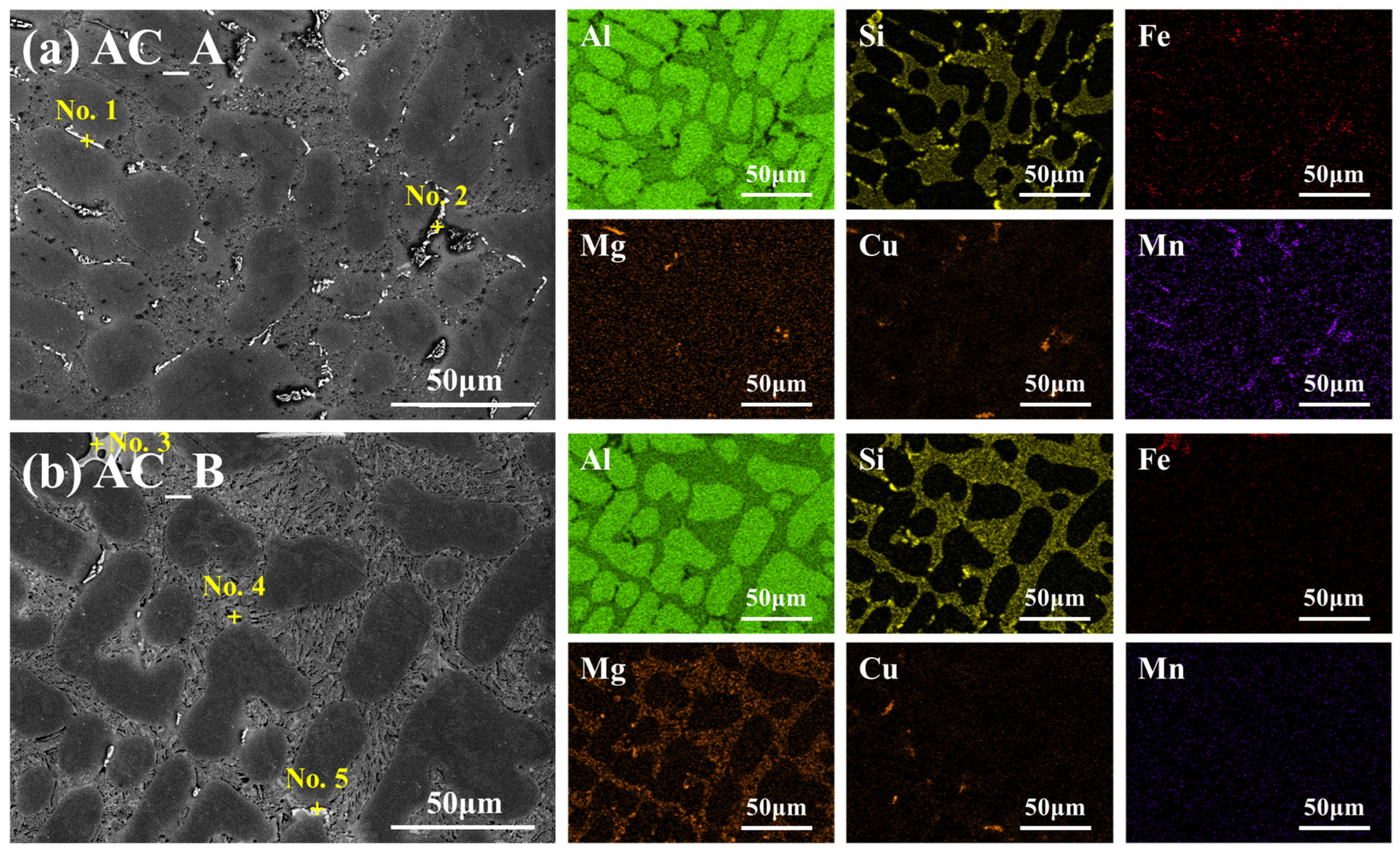
3.1.2. Microstructural Features in the As-Cast Condition
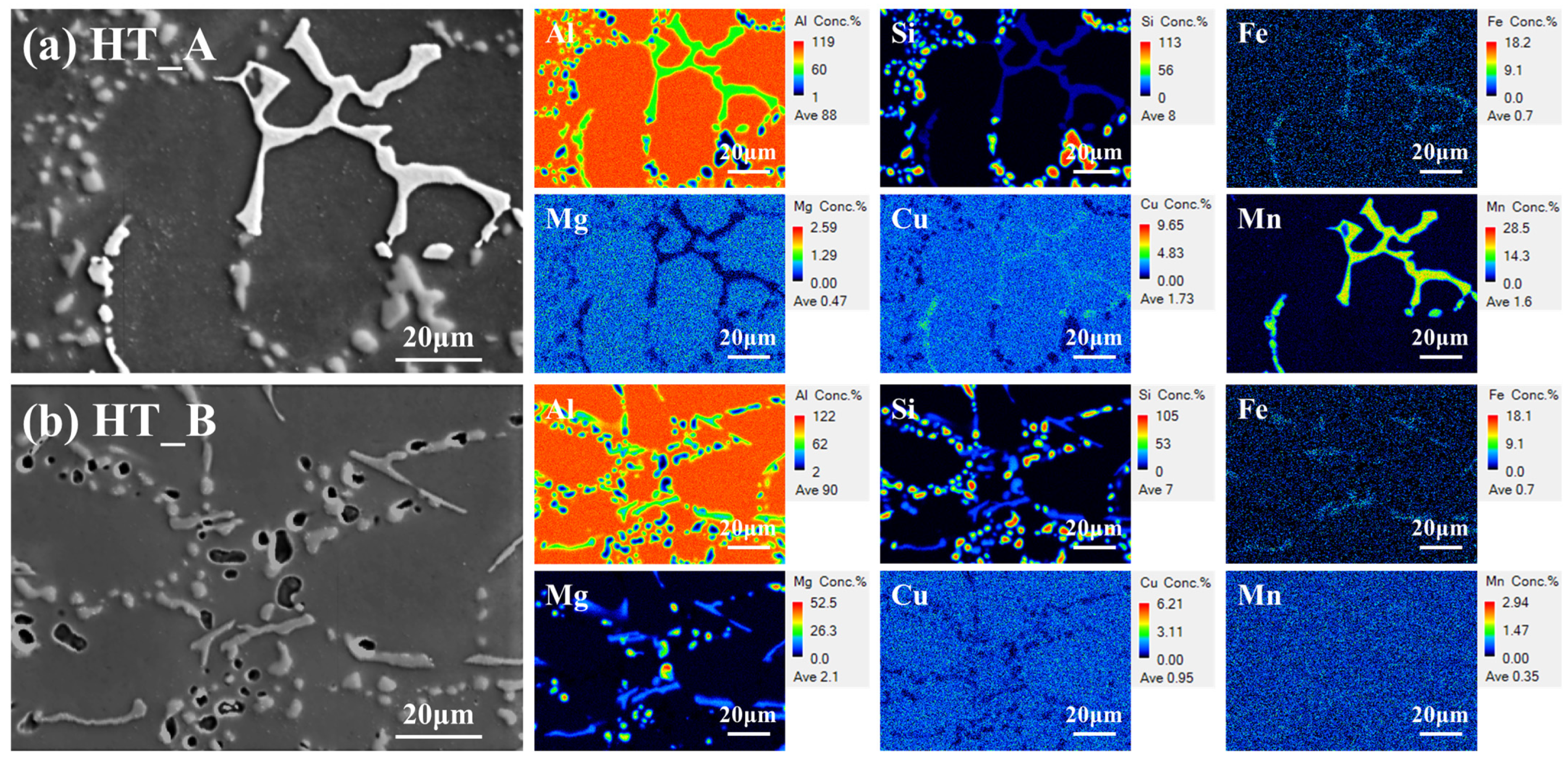
3.1.3. Microstructural Evolution After T6 Heat Treatment
3.2. Mechanical Behavior
3.2.1. Hardness Evolution at Elevated Temperatures
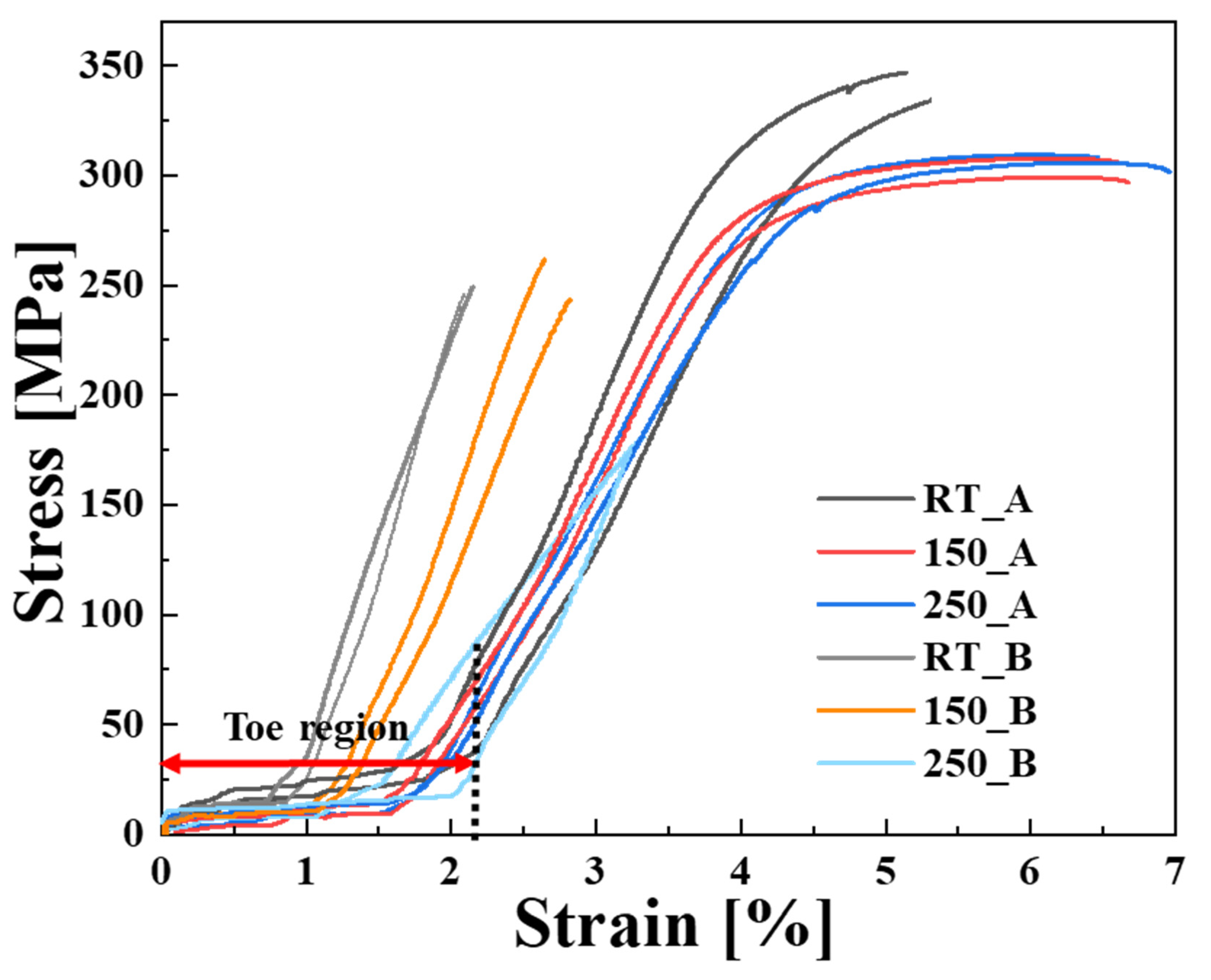
3.2.2. Elevated Temperature Tensile Behavior
3.2.3. Fractographic Analysis
3.3. Tribological Properties
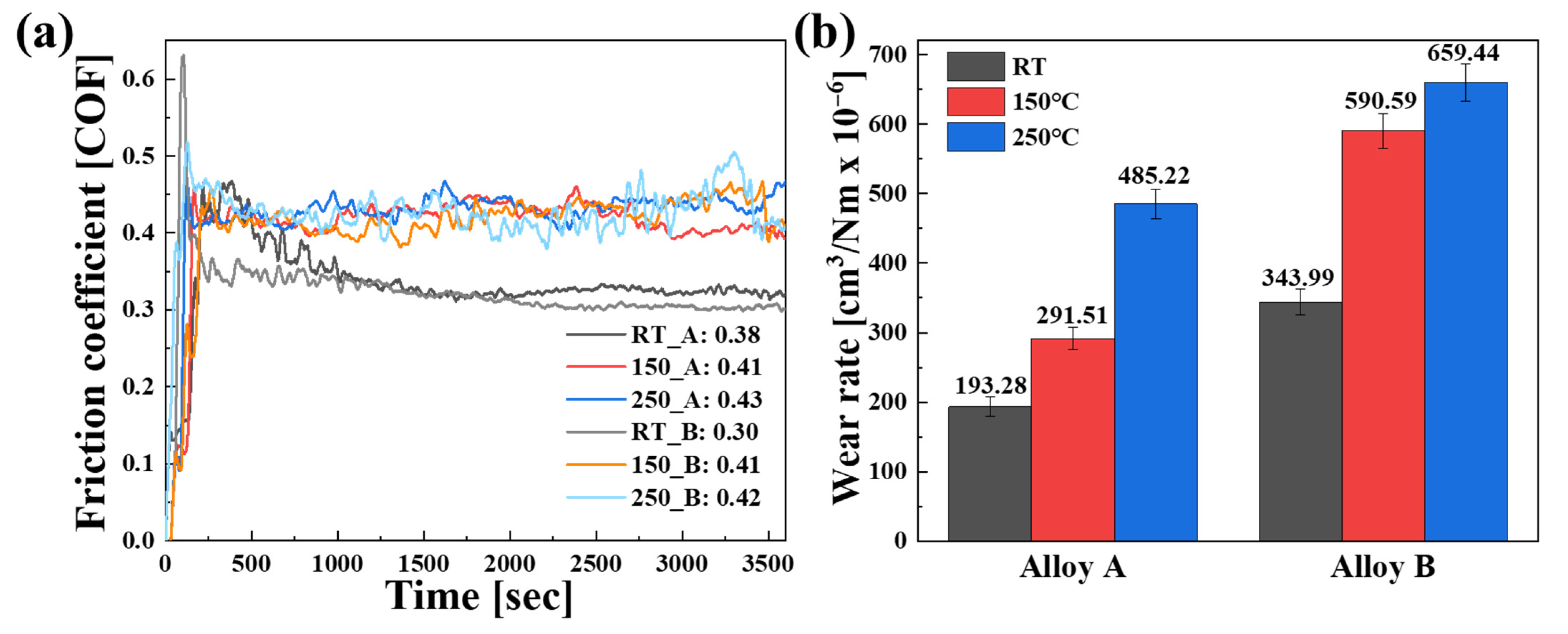
3.3.1. Friction Coefficient and Wear Rate
3.3.2. Wear Track Morphology
3.3.3. Surface Wear Mechanism Evolution with Temperature
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, F.; Chen, S.; Dong, Q.; Qin, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, B.; Nagaumi, H. Tailoring Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al-Mg-Si-Cu Alloy with Varying Mn and/or Cr Additions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 892, 146053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, T.; Zhou, L.; Hu, H.; Gao, W.; Sun, Y.; Zou, G.; Zu, Q.; Chen, H.; Wang, P.; Peng, Q. Nano-Twinned Silicon in Al-Si Alloys for High Wear-Resistance. Wear 2024, 558–559, 205559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, Y.; Pradhan, S.K.; Park, J.-S.; Oh, M.-S. Corrosion behavior of Zn, Zn-Mg-Al, and Al-Si alloy coated steel sheet in a simulated marine environment. J. Adv. Mar. Eng. Technol. 2024, 48, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.-L.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Li, B.; Xue, H.-S.; Yang, D.-Z. Effects of Mg Content on Primary Mg2si Phase in Hypereutectic Al–Si Alloys. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 3197–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Pan, L.; Chen, X.G. Elevated-Temperature Performances of Al-Si-Cu Casting Alloys for Cylinder Head Applications. Mater. Charact. 2024, 218, 114484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, N.; Lim, Y.; Heo, S.; Jeon, C.; Jo, I. Effect of Aging Temperature on Microstructure, Mechanical, and Wear Properties of 18ni-300 Maraging Steel Produced by Powder Bed Fusion. Metals 2024, 14, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, A.; Stegman, B.; Choy, K.; Niu, T.; Shen, C.; Shang, Z.; Sheng, X.; Lopez, J.; Hoppenrath, L.; Zhang, B.P.; et al. Additive Manufacturing of an Ultrastrong, Deformable Al Alloy with Nanoscale Intermetallics. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, M.; Seifeddine, S.; Jarfors, A.E.W. High Temperature Tensile Deformation Behavior and Failure Mechanisms of an Al–Si–Cu–Mg Cast Alloy—The Microstructural Scale Effect. Mater. Des. 2015, 86, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, D.; Nagaumi, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, P.; Wu, F.; Zhang, B. Achieving Excellent Strength-Ductility in Al–Si–Cu–Mg Cast Alloy Via Effective Work Hardening. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 889, 145840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Tang, J.; Lu, F.; Ma, L.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhan, X.; Xu, P. Study on Precipitation and Corrosion Behavior of Al-1.0mg-0.6si(-0.3cu) Alloys by Sn Addition Modification. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1024, 180120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yan, B.; Han, Y.; Sun, J.; Jiang, M.; Zu, G.; Zhu, W.; Ran, X. “High-Temperature Tensile Properties of Cu-Modified Alsi10mg Alloy Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1001, 175190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, M.H.; Elgallad, E.M.; Doty, H.W.; Samuel, F.H. Strengthening Precipitates and Mechanical Performance of Al–Si–Cu–Mg Cast Alloys Containing Transition Elements. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 820, 141497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Cao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, N. Effects of Mg Content on Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Fracture Behavior of Wrought Al–8si–(<0.01–1.32)Mg Alloy Sheets in T6 Temper. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 960, 170818. [Google Scholar]
- Alshammari, T.T.; Ijaz, M.F.; Alharbi, H.F.; Soliman, M.S. Effect of the Cu/Mg Ratio on Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Resistance of Wrought Al–Cu–Mg–Ag Alloy. Crystals 2023, 13, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tian, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, J. Research Progress on Multi-Component Alloying and Heat Treatment of High Strength and Toughness Al-Si-Cu-Mg Cast Aluminum Alloys. Materials 2023, 16, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM E384-22; Standard Test Method for Microindentation Hardness of Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- ASTM E8/E8M-22; Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016.
- ASTM G99-17; Standard Test Method for Wear Testing with a Pin-on-Disk Apparatus. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- Wei, Z.; Fang, N.; Zou, C.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Hu, K. Enhancing Mechanical Performances by Unconventional Si Precipitates Obtained in Pressure-Induced Al-Si-Cu-(Mg) Solid Solutions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 877, 145123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Yan, P.; Yan, B. Solidification Mechanism of Microstructure of Al-Si-Cu-Ni Alloy Manuf. by Laser Powder Bed Fusion and Mechanical Properties Effect. Metals 2024, 14, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, J.B.; Lopez, H.; Cho, K.; Kim, C.-S. Temperature Effects on the Tensile Properties of Precipitation-Hardened Al-Mg-Cu-Si Alloys. Metals 2016, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.M.; Arribas, M.; Galarraga, H.; de Cortazar, M.G.; Ellero, M.; Girot, F. Effects of Mn Addittion, Cooling Rate and Holding Temperature on the Modification and Purification of Iron-Rich Compounds in Alsi10mnmg(Fe) Alloy. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Si | Cu | Mg | Fe | Mn | Bal. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alloy A | 8.8 | 1.6 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.5 | Al |
| Alloy B | 9 | 0.8 | 2.5 | 0.2 | 0.5 | Al |
| Material | Temperature | Counter Body | Counter Body Diameter | Load | Sliding Radius | Rotational Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alloy A, B | RT 150 °C 250 °C | Al2O3 | 12.7 mm | 30 N | 11.5 mm | 100 rpm |
| No. | Compositions (wt.%) | Intermetallic Phase | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | Si | Fe | Mg | Cu | Mn | ||
| 1 | 66.84 | 22.16 | 4.13 | 6.87 | α-AlFeMnSi | ||
| 2 | 54.31 | 19.21 | 26.48 | AlCuFe | |||
| 3 | 62.88 | 16.38 | 20.74 | β-Al5FeSi | |||
| 4 | 4.21 | 36.27 | 59.52 | Mg2Si | |||
| 5 | 67.03 | 32.97 | Al2Cu | ||||
| Alloy A | Alloy B | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Condition | Temperature (℃) | Hardness (HV) | Condition | Temperature (℃) | Hardness (HV) |
| As-cast | RT | 97.63 ± 2.81 | As cast | RT | 86.88 ± 4.91 |
| T6 heat treatment | RT | 139.97 ± 5.96 | T6 heat treatment | RT | 128.54 ± 6.54 |
| 150 °C | 120.51 ± 5.09 | 150 °C | 104.29 ± 6.40 | ||
| 250 °C | 93.88 ± 7.91 | 250 °C | 82.26 ± 5.39 | ||
| Alloy A | Alloy B | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (℃) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Temperature (℃) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
| RT | 347.01 ± 7.56 | 227.74 ± 3.12 | 5.03 ± 0.16 | RT | 277.85 ± 4.26 | 123.98 ± 2.55 | 2.12 ± 0.11 |
| 150 °C | 343.27 ± 5.28 | 227.62 ± 2.87 | 4.26 ± 0.21 | 150 °C | 249.45 ± 7.81 | 112.27 ± 3.21 | 3.12 ± 0. 12 |
| 250 °C | 306.68 ± 4.45 | 176.87 ± 3.41 | 6.55 ± 0.20 | 250 °C | 229.92 ± 4.98 | 106.30 ± 2.71 | 3.43 ± 0.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bang, J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, E. High-Temperature Mechanical and Wear Behavior of Hypoeutectic Al–Si–(Cu)–Mg Alloys with Hardening Mechanisms Dictated by Varying Cu:Mg Ratios. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8047. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148047
Bang J, Kim Y, Lee E. High-Temperature Mechanical and Wear Behavior of Hypoeutectic Al–Si–(Cu)–Mg Alloys with Hardening Mechanisms Dictated by Varying Cu:Mg Ratios. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(14):8047. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148047
Chicago/Turabian StyleBang, Jaehui, Yeontae Kim, and Eunkyung Lee. 2025. "High-Temperature Mechanical and Wear Behavior of Hypoeutectic Al–Si–(Cu)–Mg Alloys with Hardening Mechanisms Dictated by Varying Cu:Mg Ratios" Applied Sciences 15, no. 14: 8047. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148047
APA StyleBang, J., Kim, Y., & Lee, E. (2025). High-Temperature Mechanical and Wear Behavior of Hypoeutectic Al–Si–(Cu)–Mg Alloys with Hardening Mechanisms Dictated by Varying Cu:Mg Ratios. Applied Sciences, 15(14), 8047. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148047







