222Rn Exhalation Rate of Building Materials: Comparison of Standard Experimental Protocols and Radiological Health Hazard Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological Framework of the Investigated Samples
3. Materials and Methods
- -
- Standard room: 4 × 5 × 2.8 m.
- -
- Minimal ventilation rate: 0.2 h−1.
- -
- Uniform radon distribution.
- -
- No other sources of radon.
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
- utest values indicated good agreement between the two methods, supporting the validity of the shorter, more time-efficient method for estimating radon exhalation rates. Thus, the faster 24 h method has been validated for use in practical applications, offering time-efficient assessments for construction materials. This has implications for quick screening in construction and heritage preservation—areas where fast decision-making is crucial for worker and public safety and compliance with safety standards.
- The predicted indoor radon concentrations, for all samples, remained well below the regulatory limits set by Legislative Decree No. 101/2020, as well as the WHO recommended limit and the EPA action level, thereby excluding any significant health concerns under typical indoor conditions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNSCEAR. United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation, Vol. I, Annex B: Exposure of the Public and Workers from Various Sources of Radiation, United Nations, New York; UNSCEAR: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hendry, J.H.; Simon, S.L.; Wojcik, A.; Sohrabi, M.; Burkart, W.; Cardis, E.; Laurier, D.; Tirmarche, M.; Hayata, I. Human exposure to high natural background radiation: What can it teach us about radiation risks? J. Radiol. Prot. 2009, 29, A29–A42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation. Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation: Report to the General Assembly, with Scientific Annexes; UNSCEAR: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 92-1-142238-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, R.R.; Twedt, D.J.; Elliott, A.B. Comparison of Line Transects and Point Counts for Monitoring Spring Migration in Forested Wetlands. J. Field Ornithol. 2000, 71, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi-Gahrouei, D. Natural Background Radiation Dosimetry in the Highest Altitude Region of Iran. J. Radiat. Res. 2003, 44, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caridi, F.; Messina, M.; Faggio, G.; Santangelo, S.; Messina, G.; Belmusto, G. Radioactivity, radiological risk and metal pollution assessment in marine sediments from Calabrian selected areas, Southern Italy. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2018, 133, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontoriero, A.; Critelli, P.; Conti, A.; Cardali, S.; Angileri, F.F.; Germanò, A.; Lillo, S.; Carretta, A.; Brogna, A.; Santacaterina, A.; et al. The “Combo” radiotherapy treatment for high-risk grade 2 meningiomas: Dose escalation and initial safety and efficacy analysis. J. Neurooncol. 2023, 161, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iatì, G.; Parisi, S.; Santacaterina, A.; Pontoriero, A.; Cacciola, A.; Brogna, A.; Platania, A.; Palazzolo, C.; Cambareri, D.; Davì, V.; et al. Simultaneous Integrated Boost Radiotherapy in Unresectable Stage IV (M0) Head and Neck Squamous Cell Cancer Patients: Daily Clinical Practice. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2020, 25, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantarini, L.; Brogna, A.; Fioravanti, A.; Galeazzi, M. Henoch-Schönlein purpura associated with pidotimod therapy. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2008, 26, S152. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gupta, T. Radiation, Ionization, and Detection in Nuclear Medicine; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 135–185. ISBN 978-3-642-34075-8. [Google Scholar]
- Donya, M.; Radford, M.; Elguindy, A.; Firmin, D.; Yacoub, M. Radiation in medicine: Origins, risks and aspirations. Glob. Cardiol. Sci. Pract. 2014, 2014, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krumholz, H.; Wang, Y.; Ross, J.; Chen, J.; Ting, H.; Shah, N.; Nasir, K.; Einstein, A.; Nallamothu, B. Exposure to Low-Dose Ionizing Radiation from Medical Imaging Procedures. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, S.; Ferini, G.; Lillo, S.; Brogna, A.; Chillari, F.; Ferrantelli, G.; Settineri, N.; Santacaterina, A.; Platania, A.; Leotta, S.; et al. Stereotactic boost on residual disease after external-beam irradiation in clinical stage III non-small cell lung cancer: Mature results of stereotactic body radiation therapy post radiation therapy (SBRTpostRT) study. Radiol. Medica 2023, 128, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhauser, G.; Brandl, A.; Johnson, T.E. Comparison of the Chernobyl and Fukushima nuclear accidents: A review of the environmental impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 800–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar-Nazir, L.; Shi, X.; Moller, A.; Mousseau, T.; Byun, S.; Hancock, S.; Seymour, C.; Mothersill, C. Long-term effects of ionizing radiation after the Chernobyl accident: Possible contribution of historic dose. Environ. Res. 2018, 165, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moysich, K.B.; Menezes, R.J.; Michalek, A.M. Chernobyl-related ionising radiation exposure and cancer risk: An epidemiological review. Lancet Oncol. 2002, 3, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, A.; Tanigawa, K.; Ohtsuru, A.; Yabe, H.; Maeda, M.; Shigemura, J.; Ohira, T.; Tominaga, T.; Akashi, M.; Hirohashi, N.; et al. Health effects of radiation and other health problems in the aftermath of nuclear accidents, with an emphasis on Fukushima. Lancet 2015, 386, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bard, D.; Verger, P.; Hubert, P. Chernobyl, 10 Years After: Health Consequences. Epidemiol. Rev. 1997, 19, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wai, K.-M.; Krstic, D.; Nikezic, D.; Lin, T.-H.; Yu, P. External Cesium-137 doses to humans from soil influenced by the Fukushima and Chernobyl nuclear power plants accidents: A comparative study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caridi, F.; D’Agostino, M.; Belvedere, A.; Marguccio, S.; Belmusto, G. Radon radioactivity in groundwater from the Calabria region, south of Italy. J. Instrum. 2016, 11, P05012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caridi, F.; Belmusto, G. Assessment of the public effective dose due to the 222Rn radioactivity in drinking water: Results from the Calabria region, southern Italy. J. Instrum. 2021, 16, P02033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrisi, L.; Caridi, F.; Margarone, D.; Borrielli, A. Characterization of laser-generated silicon plasma. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 2090–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrisi, L.; Caridi, F.; Margarone, D.; Giuffrida, L. Nickel plasma produced by 532-nm and 1064-nm pulsed laser ablation. Plasma Phys. Rep. 2008, 34, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caridi, F.; Belmusto, G. Overview of the technologies for assessment of natural radioactivity in drinking water. J. Instrum. 2019, 14, T02002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, K. Drinking water and cancer. Cancer Causes Control 1997, 8, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa-Lorenzo, R.; Barros-Dios, J.M.; Ruano-Ravina, A. Radon and stomach cancer. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 767–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auvinen, A.; Salonen, L.; Pekkanen, J.; Pukkala, E.; Ilus, T.; Kurttio, P. Radon and other natural radionuclides in drinking water and risk of stomach cancer: A case-cohort study in Finland. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 114, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, W.A. Risk Assessment and Control Management of Radon in Drinking Water; Lewis Publishers, Inc.: Chelsea, MI, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Caridi, F.; Chiriu, D.; Pelo, S.D.; Faggio, G.; Guida, M.; Messina, G.; Ponte, M.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Majolino, D.; Venuti, V. Radon Exhalation Rate, Radioactivity Content, and Mineralogy Assessment of Significant Historical and Artistic Interest Construction Materials. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskaran, M. Radon: A Tracer for Geological, Geophysical and Geochemical Studies; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-21328-6. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi Aghdam, M.; Crowley, Q.; Rocha, C.; Dentoni, V.; Da Pelo, S.; Long, S.; Savatier, M. A Study of Natural Radioactivity Levels and Radon/Thoron Release Potential of Bedrock and Soil in Southeastern Ireland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coletti, C.; Ciotoli, G.; Benà, E.; Brattich, E.; Cinelli, G.; Galgaro, A.; Massironi, M.; Mazzoli, C.; Mostacci, D.; Morozzi, P.; et al. The assessment of local geological factors for the construction of a Geogenic Radon Potential map using regression kriging. A case study from the Euganean Hills volcanic district (Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Pelo, S.; Mousavi Aghdam, M.; Dentoni, V.; Loi, A.; Randaccio, P.; Crowley, Q. Assessment of natural radioactivity and radon release potential of silurian black shales. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2023, 215, 111347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Verde, G.; Raulo, A.; D’avino, V.; Paternoster, G.; Roca, V.; La Commara, M.; Pugliese, M. Pietra leccese and other natural stones in puglia region: A new category of building materials for radiation protection? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dentoni, V.; Da Pelo, S.; Mousavi Aghdam, M.; Randaccio, P.; Loi, A.; Careddu, N.; Bernardini, A. Natural radioactivity and radon exhalation rate of Sardinian dimension stones. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 247, 118377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, S.; Guida, M.; Cuomo, A.; Guida, D.; Ismail, A.H. Modelling of indoor radon activity concentration dynamics and its validation through in-situ measurements on regional scale. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, Cambridge, UK, 16–18 February 2018; Volume 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Bulut, H.A.; Şahin, R. Radon, Concrete, Buildings and Human Health—A Review Study. Buildings 2024, 14, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, J.; Yoon, S.; Lee, C. 222 rn exhalation rates from some granite and marble used in korea: Preliminary study. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Rahman, N.M.; Atiya, I.A. Radon exhalation from building materials for decorative use. J. Environ. Radioact. 2010, 101, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estokova, A.; Singovszka, E.; Vertal, M. Investigation of Building Materials’ Radioactivity in a Historical Building—A Case Study. Materials 2022, 15, 6876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. WHO Indoor Radon a Public Health Perspective; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; p. 110. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Qian, H. Biological effects of radiation on cancer cells. Mil. Med. Res. 2018, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisz, J.A.; Bansal, N.; Qian, J.; Zhao, W.; Furdui, C.M. Effects of ionizing radiation on biological molecules—Mechanisms of damage and emerging methods of detection. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 260–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darby, S.; Hill, D.; Auvinen, A.; Barros-Dios, J.M.; Baysson, H.; Bochicchio, F.; Deo, H.; Falk, R.; Forastiere, F.; Hakama, M.; et al. Radon in homes and risk of lung cancer: Collaborative analysis of individual data from 13 European case-control studies. BMJ 2005, 330, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legislation Italian D.Lgs. 101/20. 2020. Available online: https://www.normattiva.it/uri-res/N2Ls?urn:nir:stato:decreto.legislativo:2020-07-31;101 (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Zhang, L.; Lei, X.; Guo, Q.; Wang, S.; Ma, X.; Shi, Z. Accurate measurement of the radon exhalation rate of building materials using the closed chamber method. J. Radiol. Prot. 2012, 32, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuccimei, P.; Mollo, S.; Soligo, M.; Scarlato, P.; Castelluccio, M. Real-time setup to measure radon emission during rock deformation: Implications for geochemical surveillance. Geosci. Instrum. Methods Data Syst. Discuss. 2015, 4, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanchao, S.; Junlin, W.; Bing, S.; Hongxing, C.; Wu, Y. Study on a new charcoal closed chamber method for measuring radon exhalation rate of building materials. Radiat. Meas. 2020, 134, 106308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuccimei, P.; Castelluccio, M.; Soligo, M.; Moroni, M. Radon exhalation rates of building materials: Experimental, analytical protocol and classification criteria. In Building Materials: Properties, Performance and Applications; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 259–273. [Google Scholar]
- Bossio, A.; Mazzei, R.; Monteforti, B.; Salvatorini, G. Stratigrafia del neogene e quaternario del salento sud-orientale (con rilevamento geologico alla scala 1:25.000). Geol. Rom. 2005, 38, 31–60. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzei, R.; Margiotta, S.; Foresi, L.M.; Riforgiato, F.; Gianfranco, S. Mazzei Biostratigraphy and chronostratigraphy of the Miocene Pietra Leccese in the type area of Lecce (Apulia, southern Italy). Boll. Della Soc. Paleontol. Ital. 2009, 48, 129–145. [Google Scholar]
- Punturo, R.; Russo, L.; Giudice, A.; Mazzoleni, P.; Pezzino, A. Building stone employed in the historical monuments of Eastern Sicily (Italy). An example: The ancient city centre of Catania. Environ. Geol. 2006, 50, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Russa, M.F.; Belfiore, C.M.; Fichera, G.V.; Maniscalco, R.; Calabrò, C.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Pezzino, A. The behaviour to weathering of the Hyblean limestone in the Baroque architecture of the Val di Noto (SE Sicily): An experimental study on the “calcare a lumachella” stone. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 77, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forni, F.; Bachman, O.; Mollo, S.; De Astis, G. The origin of a zoned ignimbrite: Insights into the Campanian Ignimbrite magma chamber (Campi Flegrei, Italy). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2016, 449, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcaterra, D.; Cappelletti, P.; Langella, A.; Colella, A.; Gennaro, M. The ornamental stones of Caserta province: The Campanian Ignimbrite in the medieval architecture of Casertavecchia. J. Cult. Herit. 2004, 5, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffolo, S.A.; La Russa, M.F.; Ricca, M.; Belfiore, C.M.; Macchia, A.; Comite, V.; Pezzino, A.; Crisci, G.M. New insights on the consolidation of salt weathered limestone: The case study of Modica stone. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2017, 76, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivetti, V.; Cyr, A.J.; Molin, P.; Faccenna, C.; Granger, D.E. Uplift history of the Sila Massif, southern Italy, deciphered from cosmogenic 10Be erosion rates and river longitudinal profile analysis. Tectonics 2012, 31, TC3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forestieri, G.; Alvarez de Buergo, M. Relationships Between Petrophysical and Mechanical Properties of Certain Calcarenites Used in Building. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2021, 39, 5021–5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giampaolo, C.; Mengarelli, L.; Torracca, E.; Spencer, C. Zeolite characterization of “Vico red tuff with black scoria” ignimbrite flow: The extractive district of Civita Castellana (Viterbo, Italy). Nuovo Cim. B 2008, 123, 1459–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, F.; Taddeucci, J.; Freda, C.; Marzocchi, W.; Scarlato, P. Recurrence of volcanic activity along the Roman Comagmatic Province (Tyrrhenian margin of Italy) and its tectonic significance. Tectonics 2004, 23, TC4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorovic, N.; Nikolov, J.; Forkapic, S.; Bikit, I.; Mrdja, D.; Krmar, M.; Veskovic, M. Public exposure to radon in drinking water in Serbia. Appl. Radiat. Isot. Incl. Data Instrum. Methods Use Agric. Ind. Med. 2012, 70, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, A.; Subber, A.; Shaltakh, A. Measurement of Radon Concentration in Soil Gas using RAD7 in the Environs of Al-Najaf Al-Ashraf City-Iraq. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 2011, 2, 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Tuccimei, P.; Moroni, M.; Norcia, D. Simultaneous determination of 222Rn and 220Rn exhalation rates from building materials used in Central Italy with accumulation chambers and a continuous solid state alpha detector: Influence of particle size, humidity and precursors concentration. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2006, 64, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, W.; Dulai, H. Estimating the dynamics of groundwater input into the coastal zone via continuous radon-222 measurements. J. Environ. Radioact. 2003, 69, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petropoulos, N.; Anagnostakis, M.; Simopoulos, S. Building materials radon exhalation rate: ERRICCA intercomparison exercise results. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 272, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, H.B.; Whitney, D.R. On a Test of Whether one of Two Random Variables is Stochastically Larger than the Other. Ann. Math. Stat. 1947, 18, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markkanen, M. Radiation Dose Assessments for Materials with Elevated Natural Radioactivity; Finnish Centre for Radiation and Nuclear Safety: Helsinki, Finland, 1995; Volume 2, ISBN 9517120796.
- Righi, S.; Bruzzi, L. Natural radioactivity and radon exhalation in building materials used in Italian dwellings. J. Environ. Radioact. 2006, 88, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Environmental Protection Agency. Exposure Factors Handbook, 2011th ed.; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.



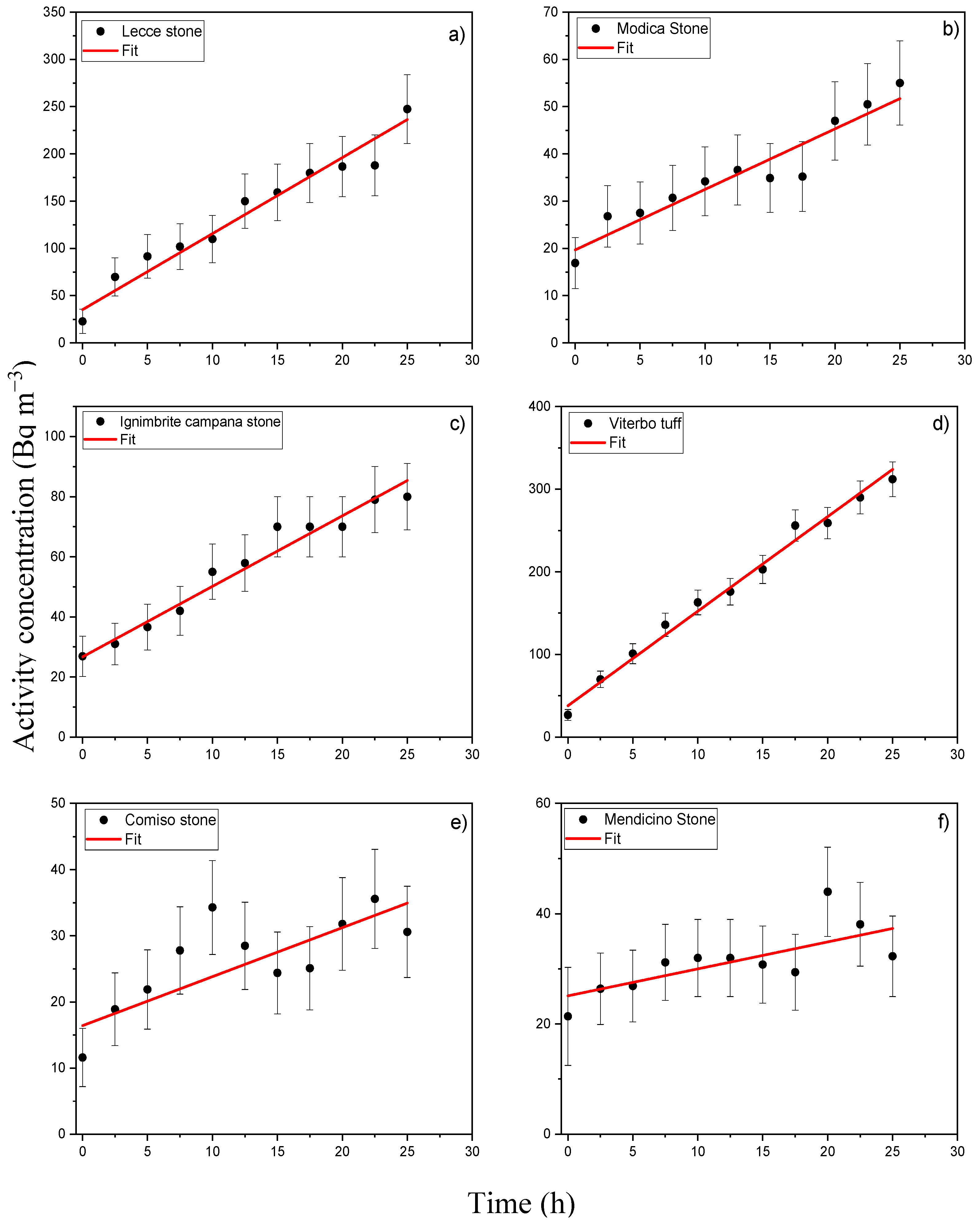
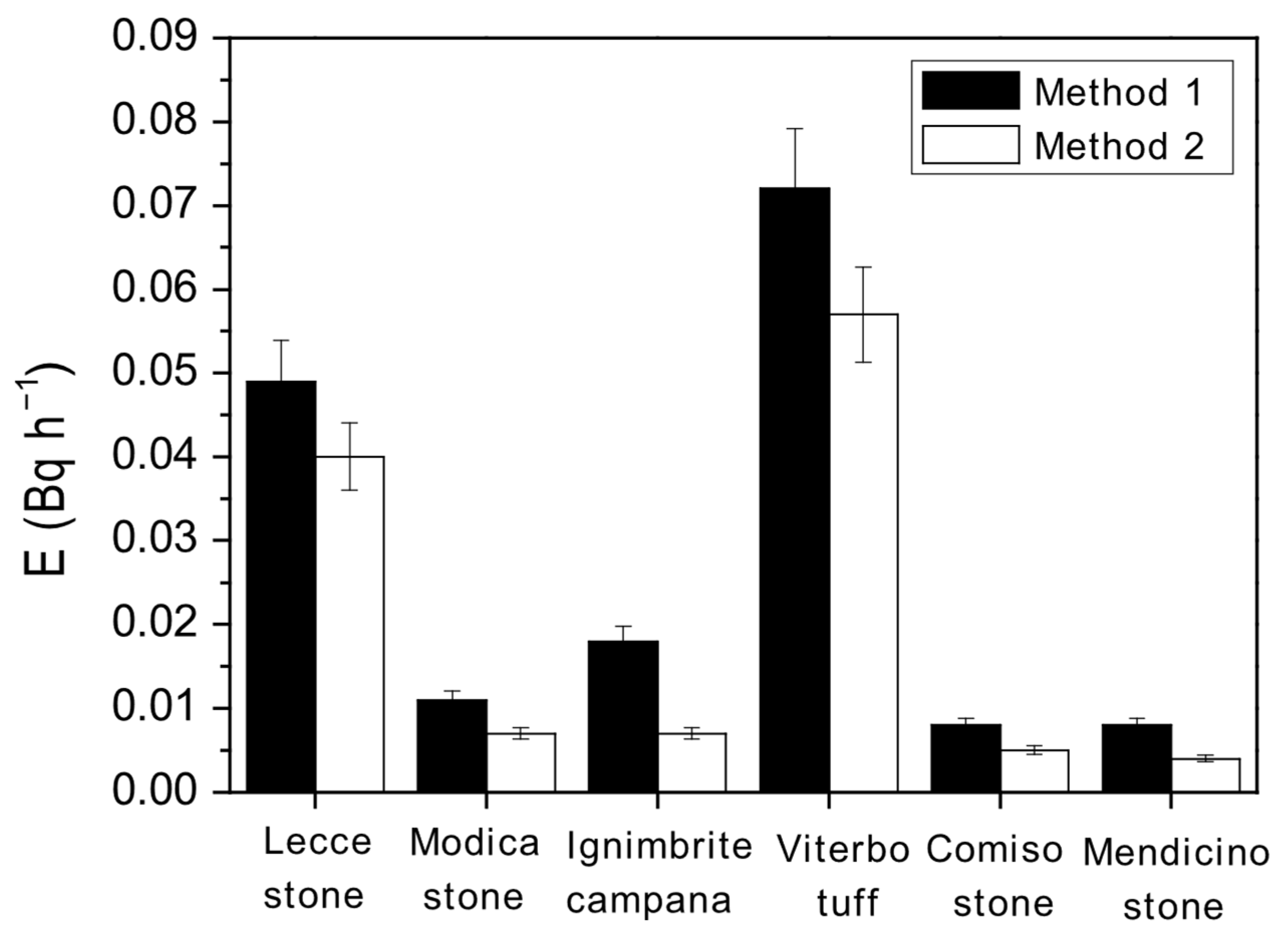
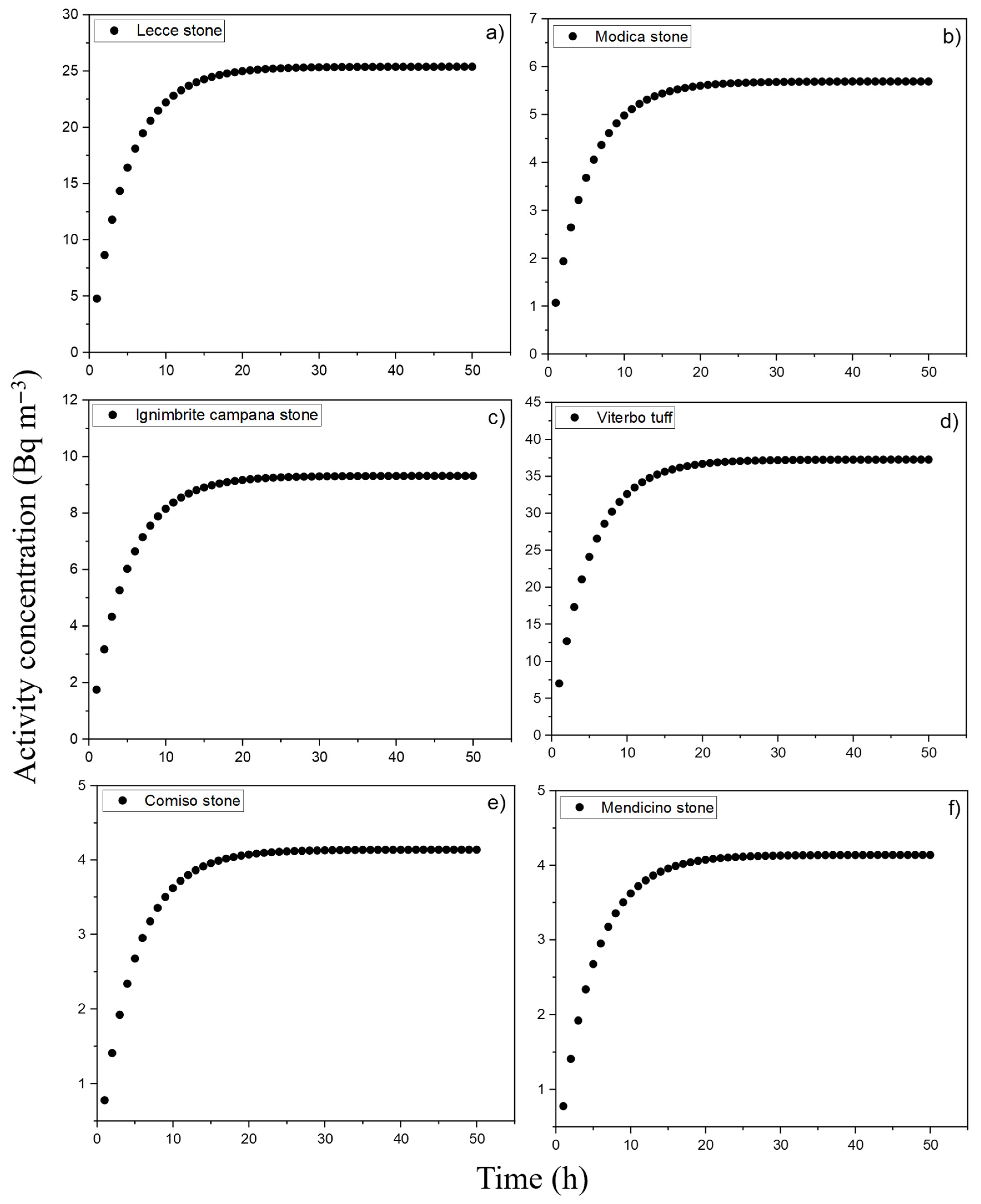
| Sample | λ (h−1) |
|---|---|
| Lecce stone | 0.023 ± 0.001 |
| Modica stone | 0.027 ± 0.001 |
| Ignimbrite Campana | 0.017 ± 0.001 |
| Comiso stone | 0.050 ± 0.004 |
| Mendicino stone | 0.081 ± 0.011 |
| Viterbo tuff | 0.018 ± 0.001 |
| Sample | E (Bq h−1) Method 1 | E (Bq h−1) Method 2 | u-Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lecce stone | 0.049 ± 0.012 | 0.040 ± 0.010 | 0.6 |
| Modica stone | 0.011 ± 0.003 | 0.007 ± 0.002 | 1.1 |
| Ignimbrite Campana | 0.018 ± 0.005 | 0.007 ± 0.002 | 2.0 |
| Viterbo tuff | 0.072 ± 0.018 | 0.057 ± 0.014 | 0.7 |
| Comiso stone | 0.008 ± 0.002 | 0.005 ± 0.001 | 1.3 |
| Mendicino stone | 0.008 ± 0.002 | 0.004 ± 0.001 | 1.8 |
| Sample | Simulated Activity Concentration (Bq m−3) |
|---|---|
| Lecce stone | 25.4 |
| Modica stone | 5.7 |
| Ignimbrite campana | 9.3 |
| Viterbo tuff | 37.3 |
| Comiso stone | 4.1 |
| Mendicino stone | 4.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caridi, F.; Pistorino, L.; Minissale, F.; Paladini, G.; Guida, M.; Mancini, S.; Majolino, D.; Venuti, V. 222Rn Exhalation Rate of Building Materials: Comparison of Standard Experimental Protocols and Radiological Health Hazard Assessment. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8015. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148015
Caridi F, Pistorino L, Minissale F, Paladini G, Guida M, Mancini S, Majolino D, Venuti V. 222Rn Exhalation Rate of Building Materials: Comparison of Standard Experimental Protocols and Radiological Health Hazard Assessment. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(14):8015. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148015
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaridi, Francesco, Lorenzo Pistorino, Federica Minissale, Giuseppe Paladini, Michele Guida, Simona Mancini, Domenico Majolino, and Valentina Venuti. 2025. "222Rn Exhalation Rate of Building Materials: Comparison of Standard Experimental Protocols and Radiological Health Hazard Assessment" Applied Sciences 15, no. 14: 8015. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148015
APA StyleCaridi, F., Pistorino, L., Minissale, F., Paladini, G., Guida, M., Mancini, S., Majolino, D., & Venuti, V. (2025). 222Rn Exhalation Rate of Building Materials: Comparison of Standard Experimental Protocols and Radiological Health Hazard Assessment. Applied Sciences, 15(14), 8015. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148015












