Electrochemical and Electroless Deposition of High-Entropy Alloy Thin Films: A Review of Plating Conditions, Properties, and Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Electrodeposition
3.1. Electrolytes
3.2. Current/Potential Regimes
3.3. Properties Relevant to Applications
3.3.1. Corrosion Resistance
3.3.2. Catalytic Activity
3.3.3. Wettability
3.3.4. Magnetic Properties
3.3.5. Mechano-Structural Properties
3.4. Data-Driven Design of HEAs
4. Electroless Deposition
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HEA | High-entropy alloy |
| MEA | Medium-entropy alloy |
| FCC | Face-centered cubic |
| BCC | Body-centered cubic |
| GD | Galvanostatic deposition |
| DC | Direct current deposition |
| PD | Potentiostatic deposition |
| CV | Constant voltage deposition |
| PP | Pulsed potential deposition |
| PC | Pulsed current deposition |
| HER | Hydrogen evolution reaction |
| OER | Oxygen evolution reaction |
References
- Popov, K.I.; Djokić, S.S.; Nikolić, N.D.; Jović, V.D. Morphology and Electrochemically and Chemically Deposited Metals; Springer: Dordrecht, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger, M. Modern Electroplating; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shojaei, Z.; Khayati, G.R.; Darezereshki, E. Review of electrodeposition methods for the preparation of high-entropy alloys. Int. J. Min. Metall. Mater. 2022, 29, 1683–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechvoglod, O.; Moghaddam, A.O.; Pratskova, S.; Trofimova, S.; Samodurova, M.; Trofimov, E. A review on high-entropy alloys coatings fabricated by electrodeposition: The correlation between composition, properties and processing parameters. JOM 2025, 77, 1005–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeje, S.O.; Mpofu, P.; Malatji, N.; Kanyane, L.R.; Shongwe, M.B. Multi-principal element alloy coatings: A review of deposition techniques, applications, and future prospects. In Metals and Materials International; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liaw, P.K.; Zhang, Y. Science and technology in high-entropy alloys. Sci. China Mater. 2018, 61, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ubaidy, S.K.; Bouraoui, C. High-entropy alloys: Advantages and applications in challenging environments. Ann. Chim. 2024, 48, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yang, B.; Liaw, P.K. Corrosion-resistant high-entropy alloys: A review. Metals 2017, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumara, P.; Gupta, A.K.; Mishra, R.K.; Ahmad, M.S.; Shahi, R.R. A comprehensive review: Recent progress on magnetic high entropy alloys and oxides. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 554, 169142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Han, H.; Chen, L.; Feng, D.; Li, L.; Zhai, T.; Chen, Z.; Gao, R.; Wu, H.; Liu, S.; et al. Critical review of high-entropy alloys for catalysts: Design, synthesis, and applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 90, 885–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sun, X.; Huang, H. The concept of high entropy for rechargeable batteries. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2025, 148, 101382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, S.A.; Noble, N.; Radhika, N.; Saleh, B. A comprehensive review on advances in high entropy alloys: Fabrication and surface modification methods, properties, applications, and future prospects. J. Man. Proc. 2024, 109, 583–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragunath, S.; Radhika, N.; Saleh, B. Advancements and future prospects of additive manufacturing in high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 997, 174859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Zhang, Y. High-entropy alloy films. Coatings 2023, 13, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.Z.; Zhang, P.; Liu, M.; Li, G.R.; Ye, J.Q.; Liu, P.; Tong, Y.X. Electrochemical preparation and magnetic study of Bi-Fe-Co-Ni-Mn high entropy alloy. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 8359–8365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premlata; Singh, D.; Pandel, U.; Duchaniya, R.K. Graphene oxide reinforced high entropy alloy (CuNiFeCrMo-GO) nanocomposite coating deposited by electroless coating method on mild steel. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 28, 2411–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. Electrodeposition of multi-component alloys: Thermodynamics, kinetics and mechanism. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2023, 39, 101289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, A. Electrodeposition of Alloys: Principles and Practice; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1963; Volume I. [Google Scholar]
- Sopittakamol, N.; Sattawiitchayapit, S.; Sindhurattavej, N.; Pimcharoken, K.; Padama, A.A.B.; Shimizu, K.; Chookajorn, T. Data-driven design of multicomponent alloy electrodeposits: A machine learning-based analysis of Ni-Co anomalous co-deposition. Acta Mater. 2025, 290, 120593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, K.; Zheng, H.; Wen, M.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, G.; Xie, G.; Liu, X.; et al. Facile electrodeposition synthesis and super performance of nano-porous Ni-Fe-Cu-Co-W high entropy alloy electrocatalyst. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 459, 129407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroll, Z.L.; Haché, M.J.R.; Wang, B.; Chen, L.; Wu, S.; Erb, W.; Thorpe, S.; Zou, Y. Electrodeposited NiFeCoMoW high-entropy alloys with nanoscale amorphous structure as effective hydrogen evolution electrocatalysts. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2024, 7, 8414–8422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Liu, Z.; Chu, M.; Kang, N.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, J.; Xie, G.; Liu, X. Electrochemical self-construction to fabricate NiFeCoMnSn electrocatalysts: Enhanced lattice distortion effect induced by Sn incorporation for superior hydrogen evolution performance. Appl. Mater. Today 2024, 41, 102525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shen, J.; Lan, A.; Jin, X.; Han, L.; Qiao, J. High-entropy amorphous FeCoCrNi thin films with excellent electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1005, 176089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.J.; Ma, H.; Kang, N.; Jiang, X.; Chu, M.; Xie, G.; Liu, X.; Liu, X. Nanoscale raspberry-like Ni-Fe-Co-Mn-V high-entropy alloy electrocatalysts: A pathway to ultralow overpotential hydrogen evolution. Mater. Today Chem. 2024, 42, 102404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divya, V.; Kannan, R.; Sengodan, R. Electrodeposited FeNiWMoMn high-entropy alloys: Synthesis, characterization, and annealed. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2025, 36, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundotiya, B.M.; Shah, A.; Burdak, P.; Bairwa, S.K. Development and corrosion behavior of electrodeposited FeCoNiMoW and FeCoNiMoWCr high entropy alloy coatings. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1020, 179466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, M.; Guo, Z. Facile preparation of Fe-Co-Ni-Mo-W high entropy alloy coatings from an aqueous bath by direct current electrodeposition: Microstructure and performance. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2024, 171, 036504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Liu, P.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Tang, X.; He, M.; Liu, J. Microstructure and properties of FeCoNiCr and FeCoNiCrW high entropy alloy coatings by electro-deposition. Intermetallics 2024, 175, 108492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Zheng, C.; Lv, T.; Ju, H.; Ma, H.; Ju, D.; Zhang, J.; Gong, K.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; et al. Microstructures and properties of FeCoNiCr high-entropy alloy coatings prepared by electrodeposition. Corr. J. 2024, 80, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Peng, L.; Qiao, Q.; Xiao, J.; Guo, F.; Wang, R.; Yu, J. Electrochemical deposition and corrosion resistance characterization of FeCoNiCr high-entropy alloy coatings. Coatings 2023, 13, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, M.; Singh, S.; Pandel, U.; Kumar, K. Microstructural features, corrosion and wear behavior of the AlCrFeCoNiCu high-entropy alloy, electrodeposited coatings, and subsequent heat treatment. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczyk, T.; Donten, M. Comparative analysis of metal electrodeposition rates towards formation of high-entropy WFeCoNiCu alloy. Materials 2024, 17, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, G.F.N.; Gomes, W.S.; Souza, J.P.I.; Pinotti, C.N.; Passamani, E.C.; Montemor, M.F.; Della Noce, R. Direct electrodeposition of CoFeNiMoW high entropy alloy thin films from aqueous medium. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 309, 128438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haché, M.J.R.; Tam, J.; Erb, U.; Zou, Y. Electrodeposited NiFeCo-(Mo, W) high-entropy alloys with nanocrystalline and amorphous structures. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 952, 170026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huo, J.; Luan, X.; Sun, S.; Ma, G. Microstructure and electrochemical properties of FeCoNiCuZn high-entropy alloy films by DC electrodeposition. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2022, 113, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, A.M.; Dutta, P.; Singh, P.; Singh, A.K.; Prasad, B.L.V. Design and synthesis of PtPdNiCoMn high-entropy alloy electrocatalyst for enhanced alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction: A theoretically supported predictive design approach. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2418644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, A.M.J.; Branzoi, F.; Burada, M.; Moreno, J.C.; Anastasescu, M.; Anasiei, I.; Olaru, M.T.; Constantin, V. CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy thin films electrodeposited on aluminum support. Coatings 2023, 13, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serban, B.A.; Olaru, M.T.; Badea, I.C.; Mitrica, D.; Burada, M.; Anasiei, I.; Ghita, M.; Tudor, A.I.; Matei, C.A.; Popescu, A.M.J.; et al. Non-aqueous electrodeposition and characterization of AlCrCuFeNi high entropy alloy thin films. Materials 2022, 15, 6007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tian, G.; Yan, H.; Guo, R.; Niu, B. Anticorrosive superhydrophobic high-entropy alloy coating on 3D iron foam for efficient oil/water separation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 468, 129756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.S.K.J.; Chokkakula, L.P.P.; Dey, S.R. Compositional modulation through galvanic displacement in electrochemically deposited FeCoNiCuZn high entropy alloy thin films. Mater. Lett. 2023, 350, 134941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Zhao, X.; Dong, Q.; Li, B.; Lyu, X. Gradient composition design of FeCoCrMnNi high entropy alloys: An efficient and stable electrocatalyst for water splitting. J. Power Sources 2025, 627, 235804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavithra, C.L.P.; Janardhana, R.K.S.K.; Reddy, K.M.; Murpaka, C.; Joardar, J.; Sarada, B.V.; Tamboli, R.R.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. An advancement in the synthesis of unique soft magnetic CoCuFeNiZn high entropy alloy thin films. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Meng, H.; Ren, P. CoNiWReP high entropy alloy coatings prepared by pulse current electrodeposition from aqueous solution. Coll. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 648, 129404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehestani, M.; Shafari, S.; Khayati, G.R. The effect of pulse current density on the microstructure, magnetic, mechanical, and corrosion properties of high-entropy alloy coating Fe-Co-Ni-Mo-W, achieved through electro co-deposition. Intermetallics 2022, 147, 107610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, Z.; Khayati, G.R.; Darezereshki, E. Study of the effect of current density on the metallurgical properties of AlFeCrNiTi high entropy alloy coating produced by pulse plating. Met. Mater. Int. 2025, 31, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehestani, M.; Sharafi, S.; Khayati, R. Effect of pulse parameters on structure, magnetic, microhardness, and wear properties of electrodeposited FeCoNiMoW high-entropy alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2025, 56, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.S.K.J.; Chokkakula, L.P.P.; Dey, S.R. Strategies to engineer FeCoNiCuZn high entropy alloy composition through aqueous electrochemical deposition. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 453, 142350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoosefan, F.; Ashrafi, A.; Vaghefi, S.M.M.; Constantin, I. Synthesis of CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy thin films by pulse electrodeposition: Part 1: Effect of pulse electrodeposition parameters. Met. Mater. Int. 2020, 26, 1262–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoosefan, F.; Ashrafi, A.; Vaghefi, S.M.M.; Constantin, I. Synthesis of CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy thin films by pulse electrodeposition: Part 2: Effect of pulse electrodeposition parameters on the wettability and corrosion resistance. Met. Mater. Int. 2021, 27, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Niu, J.; Li, S.; Guo, C.; Qiu, Z.; Gao, S. Enhancement of electrocatalytic efficiency by rapid buble detachment at electrodeposited feather-like FeCoNiCuMn high-entropy alloy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 115, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, L.; Wu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q. Electrodeposition of FeNiCoCrMn high-entropy alloys on copper foam for enhanced hydrogen evolution reaction—influence of additives and deposition potential. Mat. Lett. 2024, 374, 137195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.Y.; Ahn, S.H. Empirical approach for configuring high-entropy catalysts in alkaline water electrolysis. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 9938–9947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.Q.; Cheng, C.C.; Cheng, P.Y.; Huang, C.L.; Lu, S.Y. Pulse electrodeposited FeCoNiMnW high entropy alloys as efficient and stable bifunctional electrocatalysts for acidic water splitting. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Dong, M.; You, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z. Microstructure and properties of FeCoNiCrX (X=Mn, Al) high-entropy alloy coatings. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 921, 166061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, A.M.J.; Branzoi, F.; Constantin, I.; Anastasescu, M.; Burada, M.; Mitrica, D.; Anasiei, I.; Olaru, M.T.; Constantin, V. Electrodeposition, characterization, and corrosion behavior of CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy thin films. Coatings 2021, 11, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadkhaniha, D.; Kreummling, J.; Zanella, C. Electrodeposition of high entropy alloy of Ni-Co-Cu-Mo-W from aqueous bath. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 082515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadkhaniha, D.; Ascani, D.; Fedel, M.; Zanella, C. Electrodeposition and properties of Ni-Co-W-(Mo-Cu) high/medium entropy alloy coatings deposited from an aqueous bath. Intermetallics 2025, 181, 108744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soare, V.; Burada, M.; Constantin, I.; Mitrica, D.; Badilita, V.; Caragea, A.; Tarcolea, M. Electrochemical deposition and microstructural characterization of AlCrFeMnNi and AlCrCuFeMnNi high entropy alloy thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 358, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Wang, C.; Zhao, S.; Han, G.; Xie, G.; Qi, P.; Liu, X.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, P. Preparation of highly efficient high-entropy alloy catalysts with electrodeposition and corrosion engineering for OER electrocatalysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 57, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Qi, P.; Xie, G.; Liu, X.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, P. HEA-NiFeCuCoCe/NF through ultra-fast electrochemical self-reconstruction with high catalytic activity and corrosion resistance for seawater electrolysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 477, 147286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, W.; Sun, B.; Xu, T.; Liu, S.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Ge, M.; et al. Growth modulation of high-entropy alloys for electrocatalytic methanol oxidation reaction. Inorg. Chem. 2024, 63, 20697–20704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Nam, H.N.; Zhou, J.; Kang, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, L.; Nandan, R.; Eguchi, M.; et al. Mesoporous high-entropy alloy films. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 27617–27629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Ma, C.; Shi, P.; Zhu, X.; Qu, K.; Zhu, L.; Lu, Q.; Wang, A.L. Self-supported FeCoNiCuP high-entropy alloy nanosheet arrays for efficient glycerol oxidation and hydrogen evolution in seawater electrolytes. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 10921–10928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, M.; Singh, S.; Kumar, K.; Pandel, U. Influence of heat treatment on microstructural, corrosion and tribological behaviour of electrodeposited AlCoFeMnNiCu high entropy alloy coatings. J. Inst. Eng. (India) Ser. D 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haché, M.J.R.; Ziu, Y.; Erb, U. Thermal stability of electrodeposited nanostructured high-entropy alloys. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 482, 130719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, P.; Peter, L.; Czigany, Z.; Chinh, N.Q.; Gubicza, J. Processing and characterization of an electrodeposited nanocrystalline Co-Fe-Ni-Zn multi-principal alloy film. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 467, 129740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, P.; Peter, L.; Kolonits, T.; Nagy, A.; Gubicza, J. Combinatorial design of an electroplated multi-principal element alloy: A case study in the Co-Fe-Ni-Zn system. Metals 2024, 14, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.M.; Zhang, J.Y.; Liaw, P.K.; Yang, T. Machine learning-based computational design methods for high-entropy alloys. High Entropy Alloys Mater. 2025, 3, 41–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. Amorphous and Nano Alloys Electroless Depositions; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Asgari, M.; Darband, G.B.; Monirvaghefi, M. Electroless deposition of Ni-W-Mo-Co-P films as a binder-free, efficient and durable electrode for electrochemical hydrogen evolution. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 446, 142001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unni, M.; Jothi, S. Ni-CoW-Zr(P) quinary-based medium entropy alloy achieved by an electrochemical route and its properties. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2025, 172, 012502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Wu, S.; Huang, X. Preparation process for high-entropy alloy coatings based on electroless plating and thermal diffusion. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 902, 163736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Huang, X.; Huang, W.; Chen, D.; Wang, Q.; Wu, S.; Chen, R. Formation mechanism of CuCoNiFe high-entropy alloy tube walls for microlattice ultralight materials. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1020, 179406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiorcea-Paquim, A.M.; Brett, C.M.A. Electrodeposition in deep eutectic solvents: Perspectives towards advanced corrosion protection. Appl. Mater. Today 2025, 44, 102746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, J.G.R.; Costa, J.M.; de Almeida Neto, A.F. Progress on electrodeposition of metals and alloys using ionic liquids as electrolytes. Metals 2022, 12, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Jiang, Y. Electrochemical additive manufacturing of micro/nano functional materials. Mater. Today Sustain. 2024, 27, 100793. [Google Scholar]
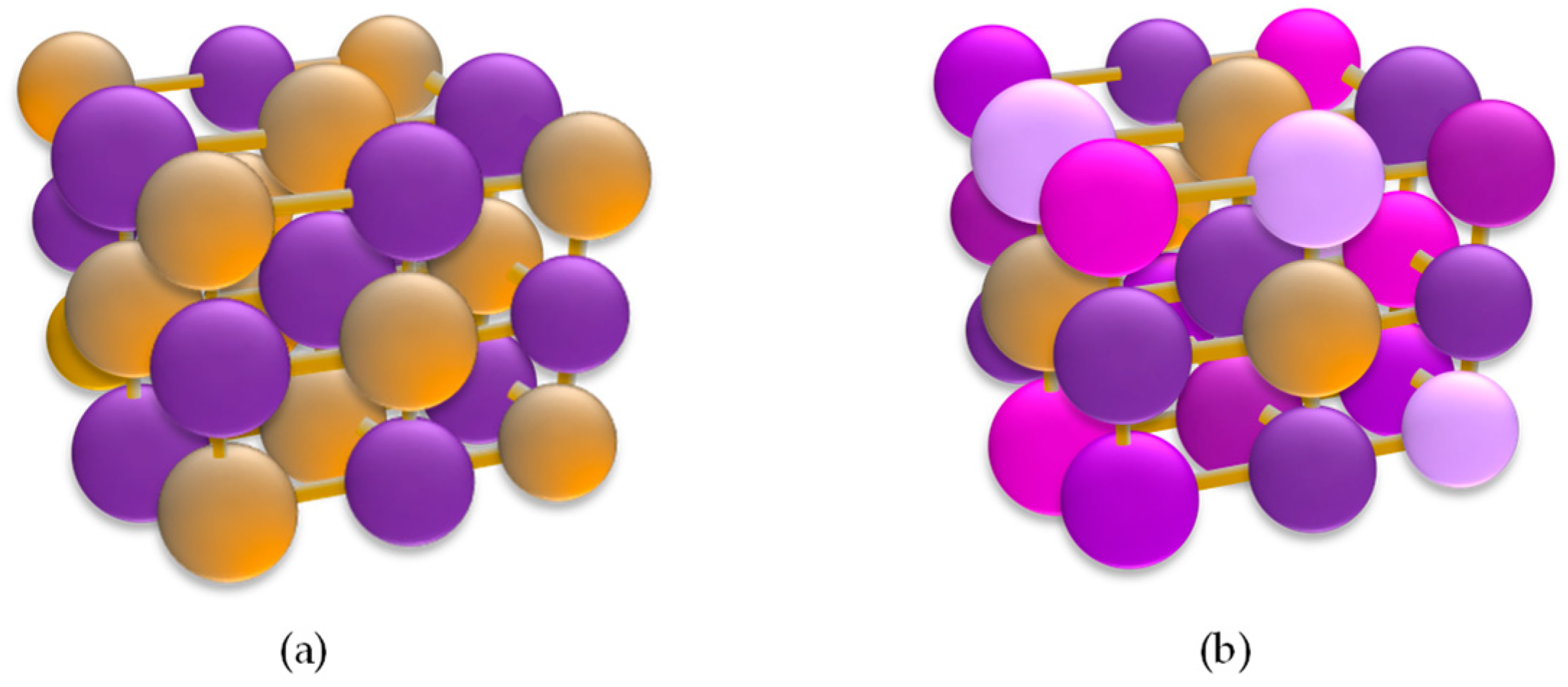
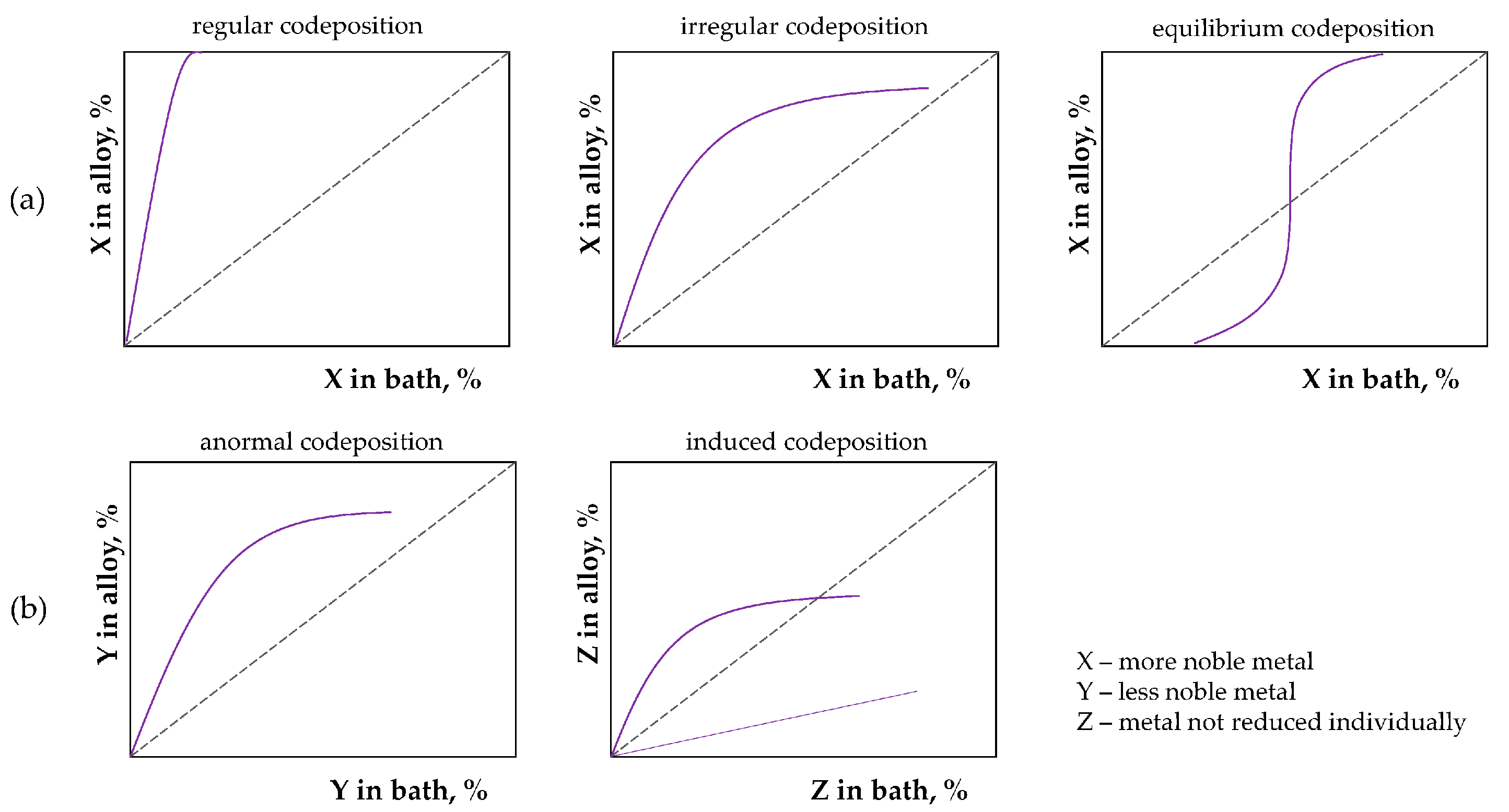
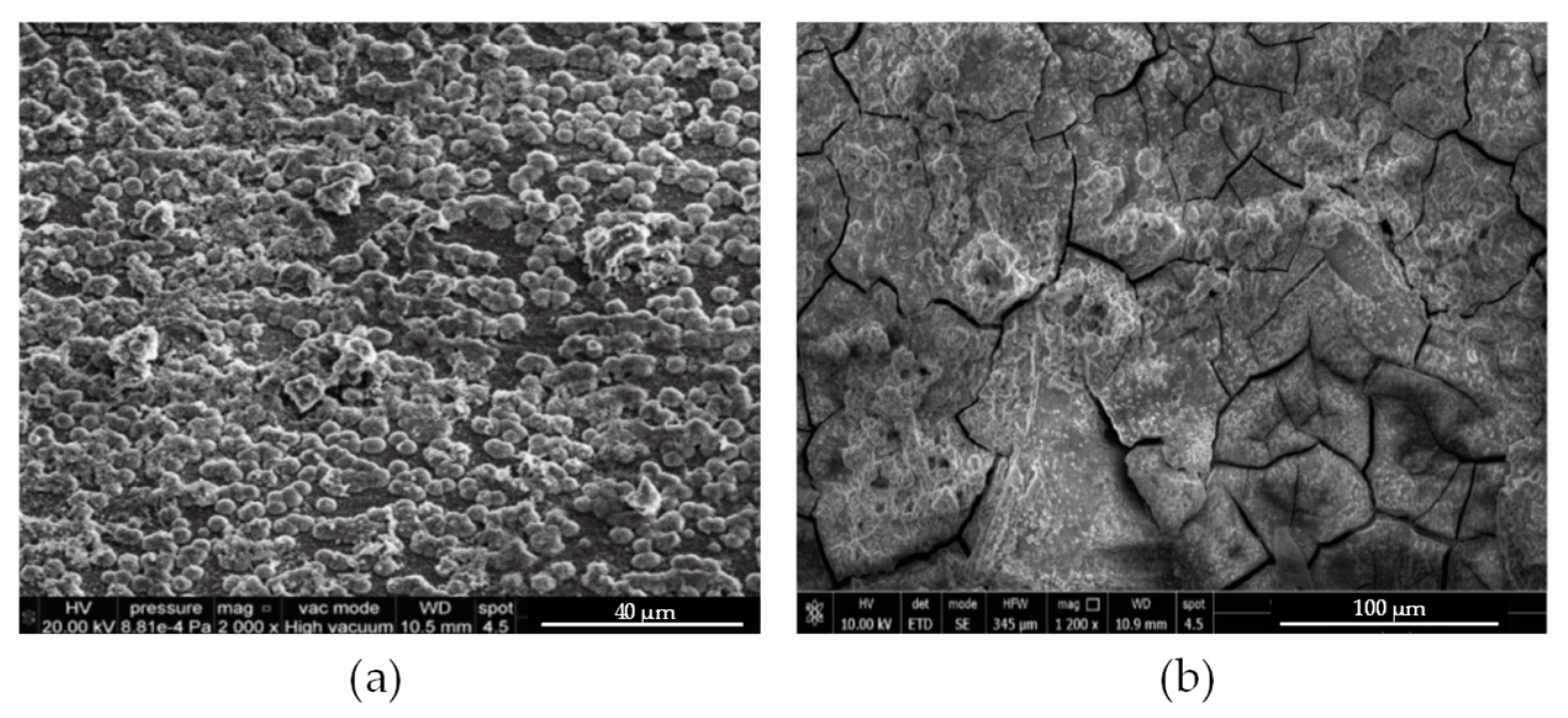
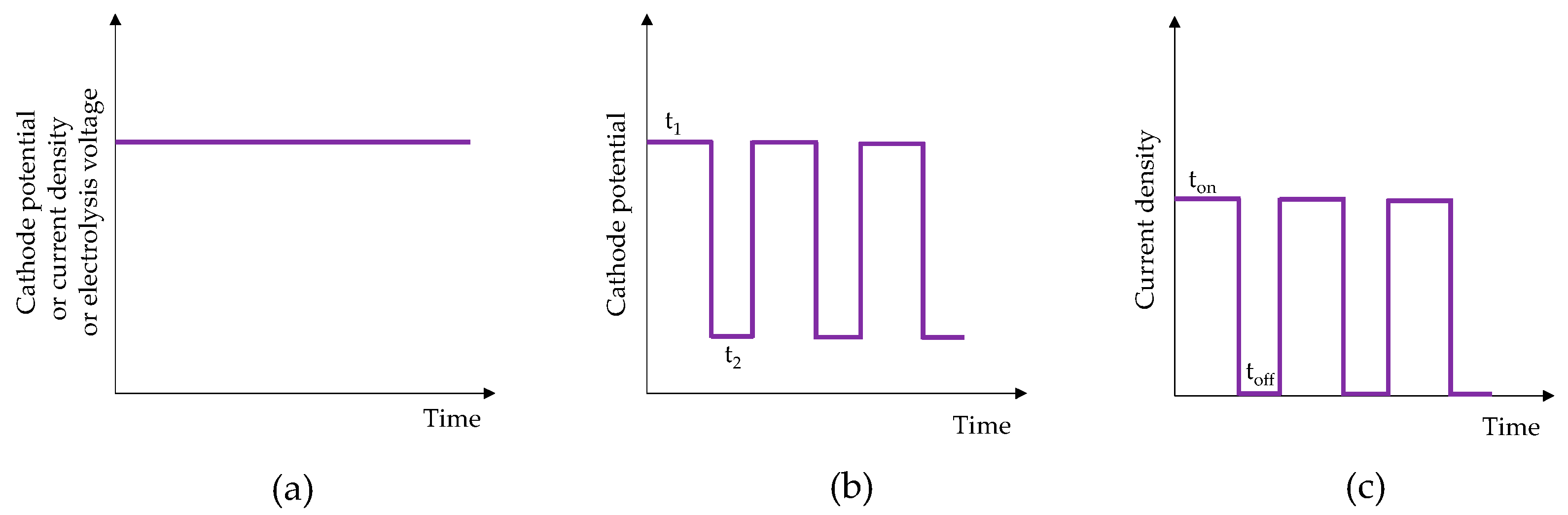
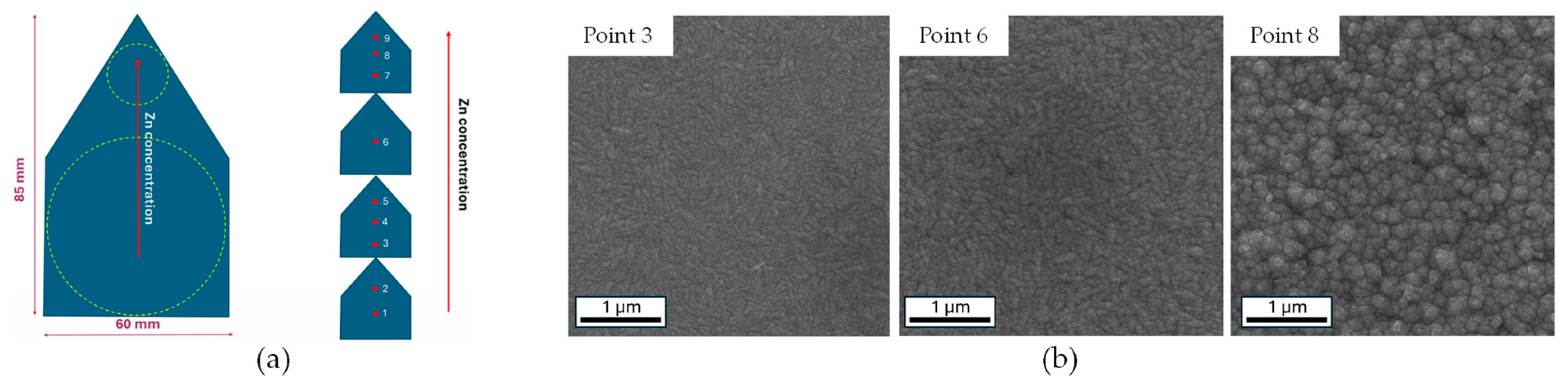
| Bath Type | Al | Bi | Cr | Co | Cu | Fe | Mn | Mo * | Ni | P | Pd | Pt | Re * | Ti | W * | V * | Zn | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aqueous Acidic Baths | ||||||||||||||||||
| sulfate–citrate–oxyanions * | [22,34,35] | |||||||||||||||||
| [53] | ||||||||||||||||||
| chloride–sulfate– citrate–oxyanions * | [28,45,47] | |||||||||||||||||
| [21] | ||||||||||||||||||
| [25] | ||||||||||||||||||
| [26] | ||||||||||||||||||
| chloride–sulfate–citrate | [36,41,43,48] | |||||||||||||||||
| [30,31] | ||||||||||||||||||
| [55] | ||||||||||||||||||
| [55] | ||||||||||||||||||
| sulfate–citrate | [51] | |||||||||||||||||
| [24] | ||||||||||||||||||
| chloride–citrate | [52] | |||||||||||||||||
| chloride–oxyanions * | [27] | |||||||||||||||||
| chloride | [46] | |||||||||||||||||
| [32,65] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Aqueous Alkaline Baths | ||||||||||||||||||
| sulfate–citrate–oxyanions * | [33] | |||||||||||||||||
| [44] | ||||||||||||||||||
| chloride–citrate–oxyanions * | [54] | |||||||||||||||||
| Organic Baths | ||||||||||||||||||
| chloride–DMF–AN | [38,42,49,50] | |||||||||||||||||
| [37] | ||||||||||||||||||
| [59] | ||||||||||||||||||
| [59] | ||||||||||||||||||
| chloride–nitrate(Bi)–DMF–AN | [16] | |||||||||||||||||
| chloride–nitrate(Co)–DMSO–AN | [56] | |||||||||||||||||
| chloride–glycerin | [40] | |||||||||||||||||
| Alloy | Structure | icorr, μA/cm2 | Ecorr, V | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe7Ni50W17Mo27Mn0.1 Fe7Ni48W17Mo27Mn0.1 (annealed 200 °C) | FCC | 40 | −0.40 | [26] |
| FCC | 17 | −0.16 | ||
| Fe(36–47)Co(23–25)Ni(3–8)Mo(7–13)W(16–20) | – | 92 | −0.95 | [28] |
| Fe18Co18Ni16Mo17W31 | FCC | 4.4 | −0.83 | [27] |
| Fe22Co13Ni8Mo12W22Cr21 | FCC | 3.5 | −0.34 | |
| Fe32Co24Ni27W7Cr10 | FCC | 2.9 | −0.65 | [29] |
| Fe18Co19Ni21Cr42 | FCC | 1.4 | −0.32 | [30] |
| Fe24Co28Ni25Cr23 | amorphous | 1.7 | −0.45 | [31] |
| 12 | −0.33 1 | |||
| 1.4 | −0.74 2 | |||
| Fe22Co19Ni30Cr29 | FCC | 33 | −0.51 | [55] |
| Fe23Co20Ni21Cr15Mn20 | FCC | 58 | −0.40 | |
| Fe23Co15Ni26Cr14Al20 | FCC | 18 | −0.39 | |
| Fe24Co26Ni14Cr9Mn27 | no data | 3.3 | −0.23 | [56] |
| Fe41Co27Ni4Cr27Mn0.3 | no data | 1.1 | −0.53 | [38] |
| Fe37Co27Ni10Cr25Mn0.6 | no data | 8.5 | −0.75 | |
| Al15Fe26Cr21Ni27Ti14 | FCC+BCC | 0.09 | −0.77 | [46] |
| Alloy | Structure | ηHER, mV/i, mA/cm2 | ηOER, mV/i, mA/cm2 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeCoCrNi | amorphous | – | 295/10 2 | [24] |
| NiFeCoMnSn | amorphous | 4/10 2 | – | [23] |
| FeMnCuCo | FCC+BCC | – | 226/10 2 | [60] |
| FeCoNiCuMn | FCC | 200/100 2 | 251/100 2 | [51] |
| FeNiCoCrMn | FCC | 168/10 2 | 231/10 2 | [42] |
| FeNiCoCrMn | FCC | 191/10 2 | – | [52] |
| NiFeCoMnV | FCC | 7/10 2 | – | [25] |
| FeCoNiMnW | FCC | 15/10 1 | 512/10 1 | [54] |
| NiFeCuCoW | FCC | – | 247/10 2 | [21] |
| NiFeCoMoW | amorphous | 171/10 2 | – | [22] |
| CuMoNiCoFe | no data | 12/10 2 | 290/10 2 | [53] |
| NiFeCuCoCe | FCC | – | 219/10 2 | [61] |
| PtPdNiCoMn | FCC | 23/10 2 | – | [37] |
| Alloy | Structure | Coercivity, Oe | Saturation Magnetization, emu/g | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi19Fe21Co19Ni22Mn19 | FCC | 20 °C: 0 | – | [15] |
| −268 °C: 100 | – | |||
| 20 °C: 658 1 | – | |||
| Fe7Ni48W17Mo27Mn0.1 | cubic | 20 °C: 121 | – | [26] |
| 20 °C: 103 2 | – | |||
| Co20Cu21Fe19Ni17Zn23 | FCC + BCC | 20 °C: 19 | 20 °C: 82 | [43] |
| AlCrFeNiTi | FCC + BCC | 20 °C: 0 | 20 °C: 83–106 | [46] |
| FeCoNiMoW | FCC + amorphous | 20 °C: 7–34 | 20 °C: 42–107 | [47] |
| Alloy | Deposition Conditions | Structure | Properties | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuNiFeCrMo-GO 1 | chloride–hypophosphite bath; pH 1–2; 80–85 °C, 1 h | FCC + BCC | hardness, wear | [17] |
| NiCoWZrP 1 | chloride–citrate–hypophosphite bath; pH 8–9; 85 °C, 1 h | FCC | corrosion, adhesion, wear | [72] |
| CuNiCo 2 | sulfate–complexing baths; room temperature; thermal diffusion 800 °C, 2–10 h | FCC | corrosion | [73] |
| CuCoNiFe 2 | sulfate–complexing baths; room temperature; substrate etching in NaOH; thermal diffusion 800/1000 °C, 8 h | two-phased | strength | [74] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rudnik, E. Electrochemical and Electroless Deposition of High-Entropy Alloy Thin Films: A Review of Plating Conditions, Properties, and Applications. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8009. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148009
Rudnik E. Electrochemical and Electroless Deposition of High-Entropy Alloy Thin Films: A Review of Plating Conditions, Properties, and Applications. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(14):8009. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148009
Chicago/Turabian StyleRudnik, Ewa. 2025. "Electrochemical and Electroless Deposition of High-Entropy Alloy Thin Films: A Review of Plating Conditions, Properties, and Applications" Applied Sciences 15, no. 14: 8009. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148009
APA StyleRudnik, E. (2025). Electrochemical and Electroless Deposition of High-Entropy Alloy Thin Films: A Review of Plating Conditions, Properties, and Applications. Applied Sciences, 15(14), 8009. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148009







