Radiomics and Machine Learning Approaches for the Preoperative Classification of In Situ vs. Invasive Breast Cancer Using Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DCE–MRI)
Abstract
1. Introduction
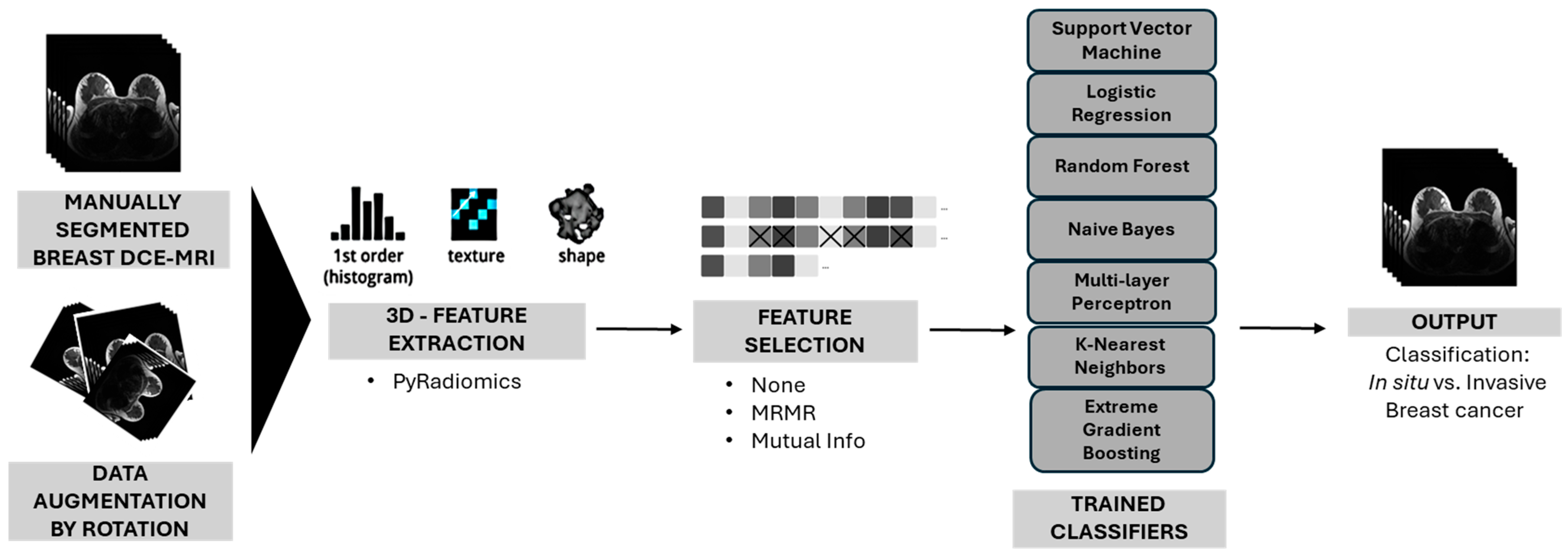
2. Methods
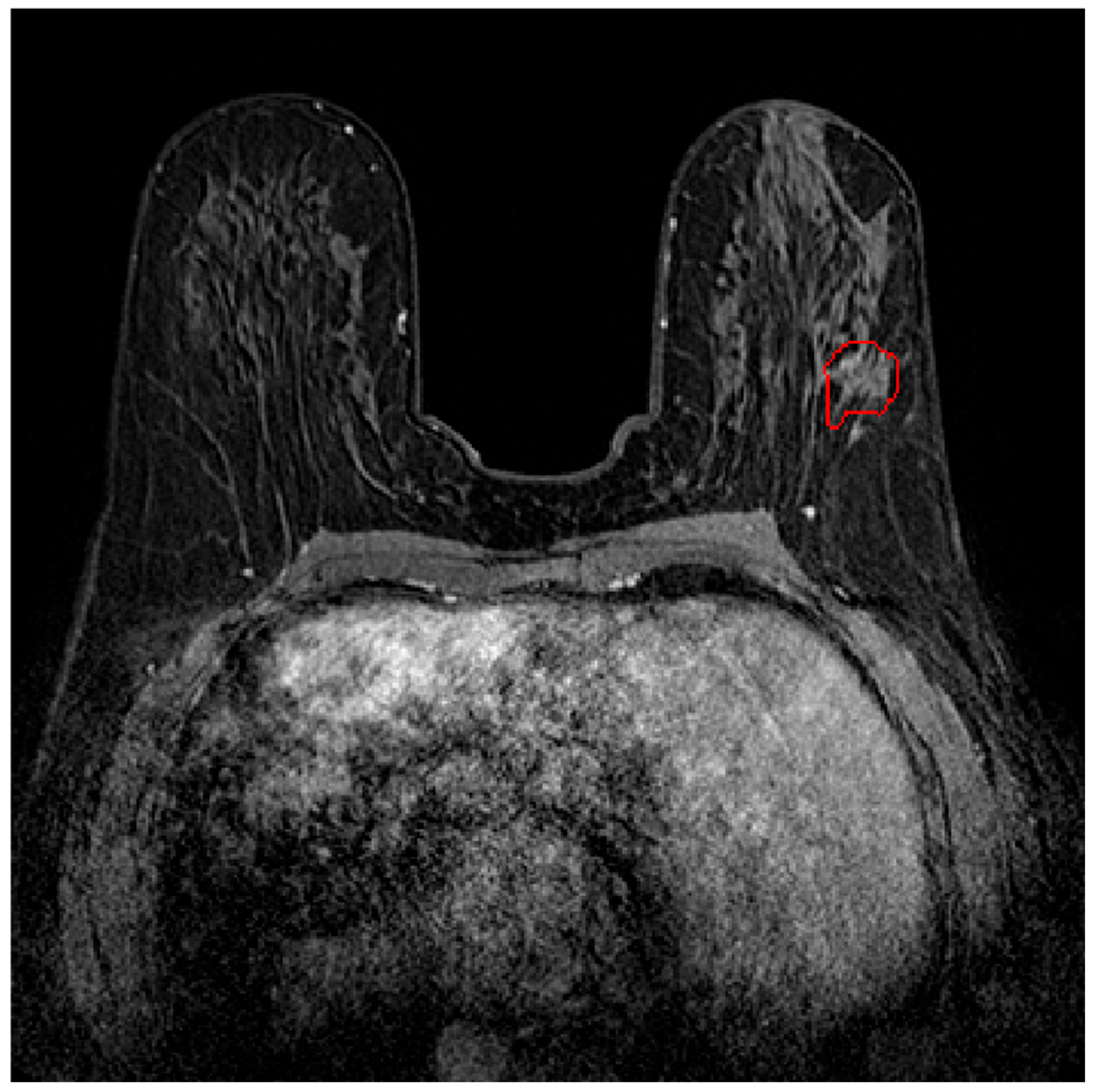
2.1. Dataset
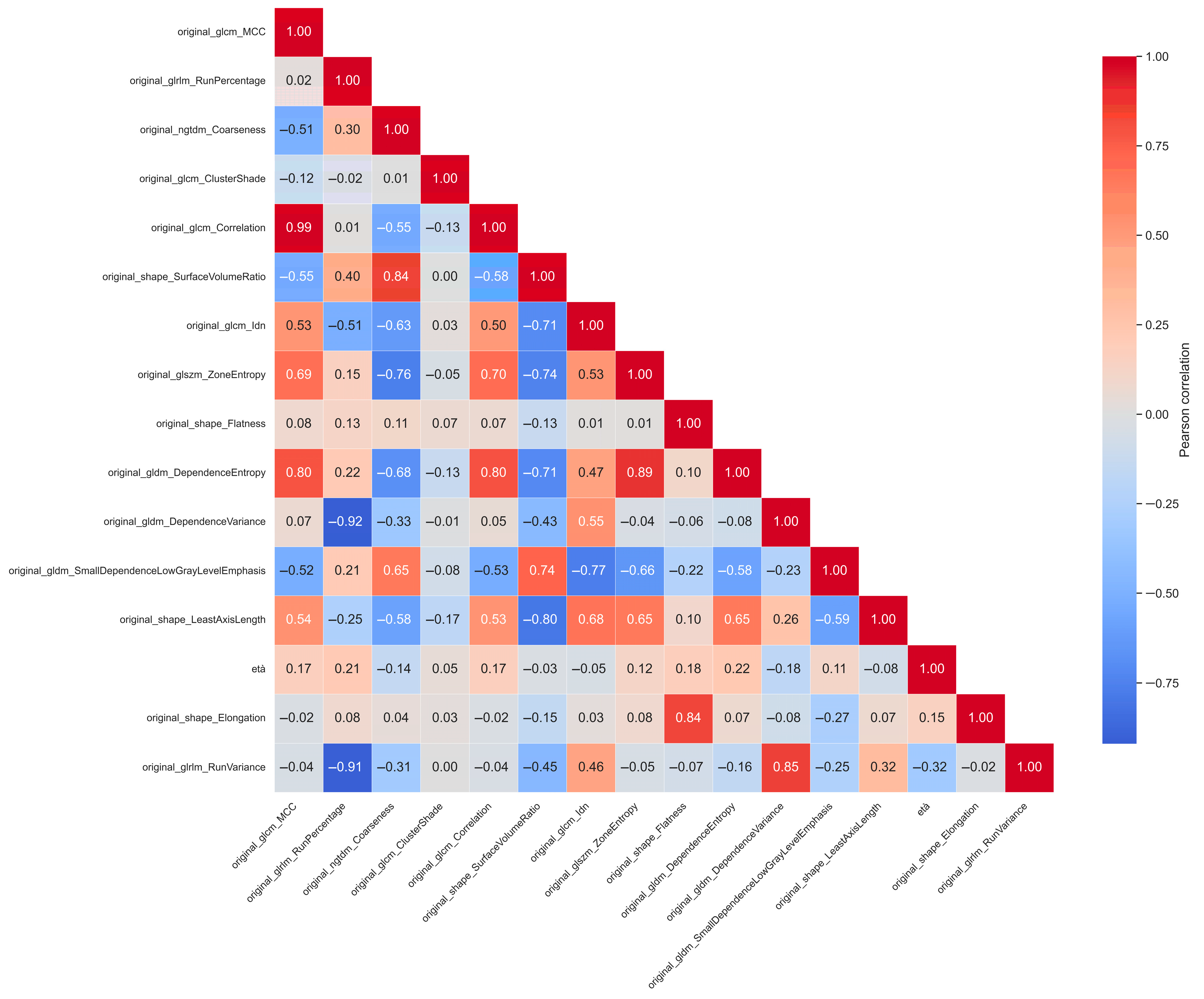
2.2. Feature Extraction
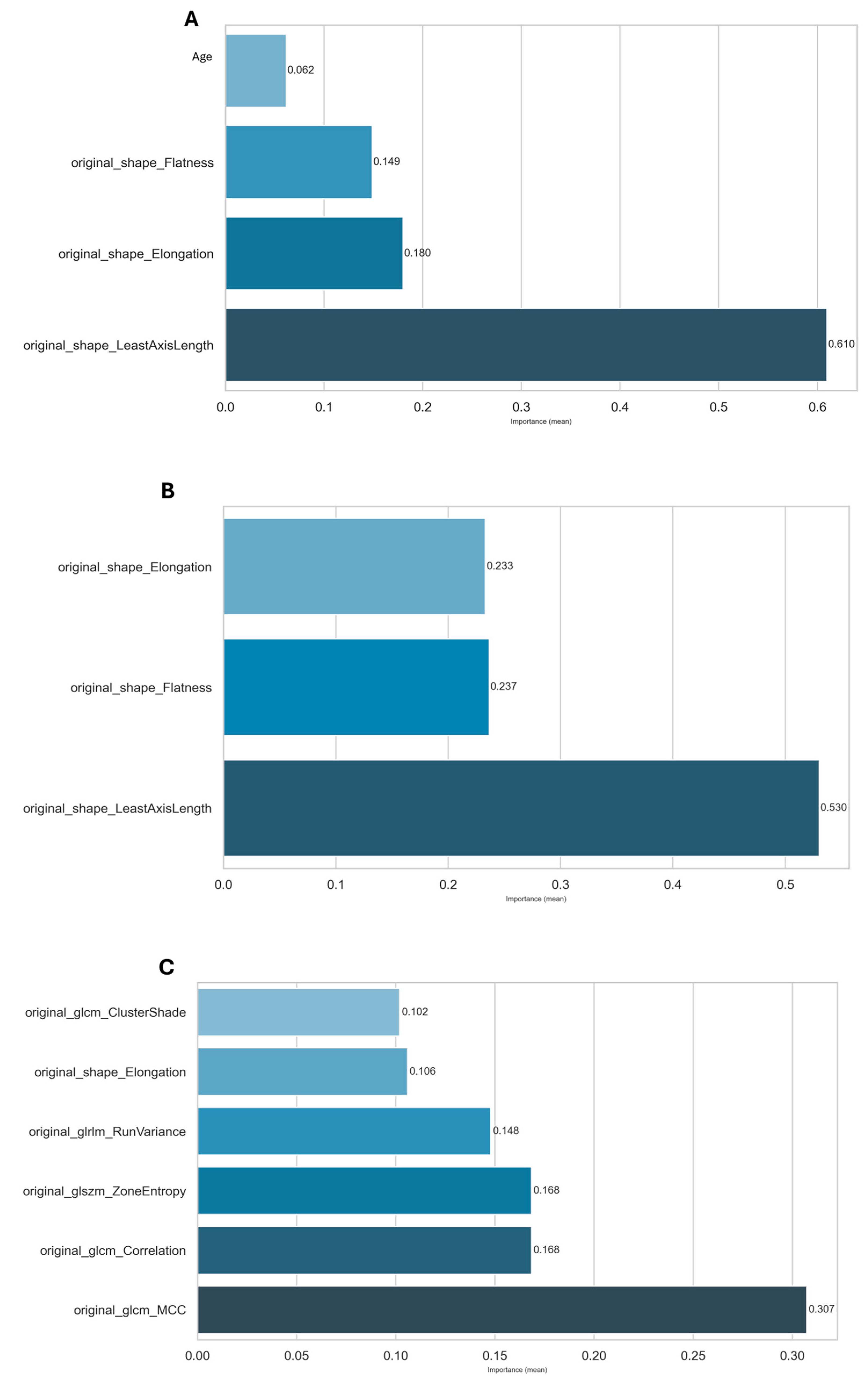
2.3. Feature Selection
2.4. Data Augmentation
2.5. Classification Algorithms
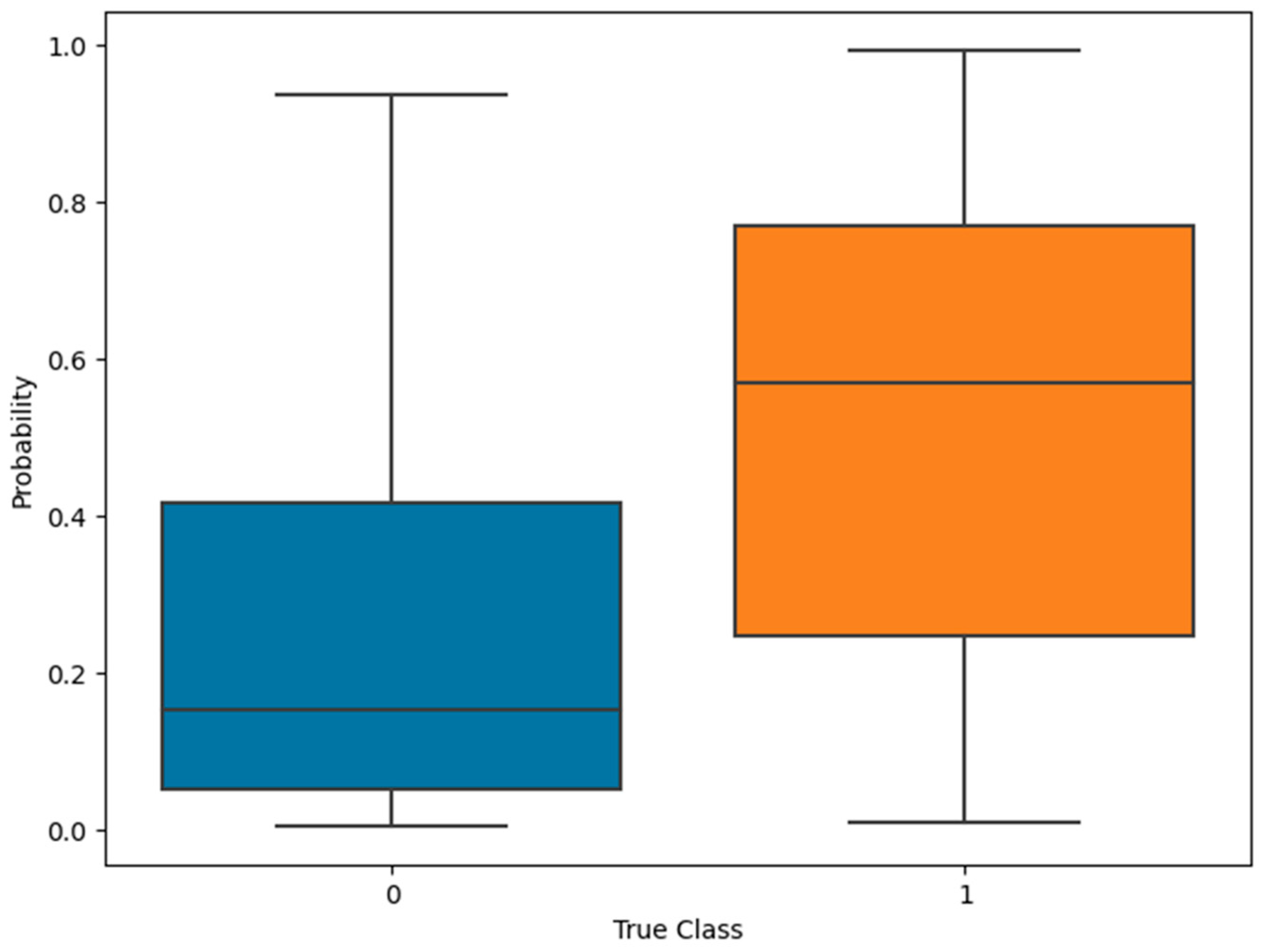
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- AIOM-AIRTUM-Siapec-Iap I Numeri Del Cancro in Italia 2024. Available online: https://www.aiom.it/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/2024_NDC_web-def.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Bijker, N.; Meijnen, P.; Peterse, J.L.; Bogaerts, J.; Van Hoorebeeck, I.; Julien, J.-P.; Gennaro, M.; Rouanet, P.; Avril, A.; Fentiman, I.S.; et al. Breast-Conserving Treatment with or without Radiotherapy in Ductal Carcinoma-in-Situ: Ten-Year Results of Randomized Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 3381–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernster, V.L. Detection of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ in Women Undergoing Screening Mammography. CancerSpectrum Knowl. Environ. 2002, 94, 1546–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Northridge, M.E.; Rhoads, G.G.; Wartenberg, D.; Koffman, D. The Importance of Histologic Type on Breast Cancer Survival. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1997, 50, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamel, J.W.; Meyer, J.S.; Feuer, E.; Miller, B.A. The Impact of Stage and Histology on the Long-Term Clinical Course of 163,808 Patients with Breast Carcinoma. Cancer 1996, 77, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, L.; De Nunzio, G.; Lupo, R.; Mieli, M.; Lezzi, A.; Vitale, E.; Carriero, M.C.; Calabrò, A.; Carvello, M.; Rubbi, I.; et al. Breast Cancer Prevention: The Key Role of Population Screening, Breast Self-Examination (BSE) and Technological Tools. Survey of Italian Women. J. Cancer Educ. 2023, 38, 1728–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, L.; Lupo, R.; Lezzi, A.; Paolo, V.; Rubbi, I.; Rizzo, E.; Carvello, M.; Calabrò, A.; Botti, S.; De Matteis, E.; et al. A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study Investigating Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet, Smoking, Alcohol and Work Habits, Hormonal Dynamics between Breast Cancer Cases and Healthy Subjects. Clin. Nutr. Open Sci. 2024, 55, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortesi, L.; Galli, G.R.; Domati, F.; Conte, L.; Manca, L.; Berio, M.A.; Toss, A.; Iannone, A.; Federico, M. Obesity in Postmenopausal Breast Cancer Patients: It Is Time to Improve Actions for a Healthier Lifestyle. The Results of a Comparison Between Two Italian Regions with Different “Presumed” Lifestyles. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 769683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, L.; Lupo, R.; Lezzi, A.; Sciolti, S.; Rubbi, I.; Carvello, M.; Calabrò, A.; Botti, S.; Fanizzi, A.; Massafra, R.; et al. Breast Cancer Prevention Practices and Knowledge in Italian and Chinese Women in Italy: Clinical Checkups, Free NHS Screening Adherence, and Breast Self-Examination (BSE). J. Cancer Educ. 2024, 40, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, L.; Lupo, R.; Sciolti, S.; Lezzi, A.; Rubbi, I.; Botti, S.; Carvello, M.; Fanizzi, A.; Massafra, R.; Vitale, E.; et al. Exploring the Landscape of Breast Cancer Prevention among Chinese Residents in Italy: An In-Depth Analysis of Screening Adherence, Breast Self-Examination (BSE) Practices, the Role of Technological Tools, and Misconceptions Surrounding Risk Factors and Symptoms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, R.M.; Cho, N.; Moy, L. Breast MRI: State of the Art. Radiology 2019, 292, 520–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhl, C.K.; Schild, H.H. Dynamic Image Interpretation of MRI of the Breast. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2000, 12, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhl, C.K.; Mielcareck, P.; Klaschik, S.; Leutner, C.; Wardelmann, E.; Gieseke, J.; Schild, H.H. Dynamic Breast MR Imaging: Are Signal Intensity Time Course Data Useful for Differential Diagnosis of Enhancing Lesions? Radiology 1999, 211, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnall, M.D. Breast MR Imaging. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2003, 41, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, E.A. Breast Cancer Imaging with MRI. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2002, 40, 443–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.S.; Goldin, J.G.; Rogers, S.; Kim, H.J.; Suh, R.D.; McNitt-Gray, M.F.; Shah, S.K.; Truong, D.; Brown, K.; Sayre, J.W.; et al. Computer-Aided Lung Nodule Detection in CT: Results of Large-Scale Observer Test. Acad. Radiol. 2005, 12, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peldschus, K.; Herzog, P.; Wood, S.A.; Cheema, J.I.; Costello, P.; Schoepf, U.J. Computer-Aided Diagnosis as a Second Reader: Spectrum of Findings in CT Studies of the Chest Interpreted as Normal. Chest 2005, 128, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalloul, R.; Chethan, H.K.; Alkhatib, R. A Review of Machine Learning Techniques for the Classification and Detection of Breast Cancer from Medical Images. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radak, M.; Lafta, H.Y.; Fallahi, H. Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques for Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Classification: A Comprehensive Review of Medical Imaging Studies. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 10473–10491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, L.; Rizzo, E.; Grassi, T.; Bagordo, F.; De Matteis, E.; De Nunzio, G. Artificial Intelligence Techniques and Pedigree Charts in Oncogenetics: Towards an Experimental Multioutput Software System for Digitization and Risk Prediction. Computation 2024, 12, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, R.; Dell’Aquila, K.; Hodges, L.; Maldjian, T.; Duong, T.Q. Deep Learning Applications to Breast Cancer Detection by Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Literature Review. Breast Cancer Res. 2023, 25, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Shao, X.; Shi, K.; Rominger, A.; Caobelli, F. AI in Breast Cancer Imaging: An Update and Future Trends. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2025, 55, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, L.; Tafuri, B.; Portaluri, M.; Galiano, A.; Maggiulli, E.; De Nunzio, G. Breast Cancer Mass Detection in DCE–MRI Using Deep-Learning Features Followed by Discrimination of Infiltrative vs. In Situ Carcinoma through a Machine-Learning Approach. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, L.; Rizzo, E.; Civino, E.; Tarantino, P.; De Nunzio, G.; De Matteis, E. Enhancing Breast Cancer Risk Prediction with Machine Learning: Integrating BMI, Smoking Habits, Hormonal Dynamics, and BRCA Gene Mutations—A Game-Changer Compared to Traditional Statistical Models? Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, L.-N.; Lee, H.-J.; Im, C.; Park, J.H.; Lim, H.S.; Park, I. Predicting Underestimation of Invasive Cancer in Patients with Core-Needle-Biopsy-Diagnosed Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Using Deep Learning Algorithms. Tomography 2022, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, C.; Grossmann, P.; Bussink, J.; Lambin, P.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Machine Learning Methods for Quantitative Radiomic Biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drukker, K.; Schram, J.; Burda, S.; Li, H.; Lan, L.; Giger, M. Radiomics Investigation in the Distinction between in Situ and Invasive Breast Cancers. Med. Phys. 2015, 42, 3602–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Song, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Ma, W.; Jiang, X.; Wu, Y.; Cai, H.; Li, L. Predicting Underestimation of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ: A Comparison between Radiomics and Conventional Approaches. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2019, 14, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinker, K.; Bickel, H.; Helbich, T.H.; Gruber, S.; Dubsky, P.; Pluschnig, U.; Rudas, M.; Bago-Horvath, Z.; Weber, M.; Trattnig, S.; et al. Combined Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance and Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Reading Adapted to the “Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System” for Multiparametric 3-T Imaging of Breast Lesions. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 1791–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spick, C.; Pinker-Domenig, K.; Rudas, M.; Helbich, T.H.; Baltzer, P.A. MRI-Only Lesions: Application of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Obviates Unnecessary MR-Guided Breast Biopsies. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickel, H.; Pinker-Domenig, K.; Bogner, W.; Spick, C.; Bagó-Horváth, Z.; Weber, M.; Helbich, T.; Baltzer, P. Quantitative Apparent Diffusion Coefficient as a Noninvasive Imaging Biomarker for the Differentiation of Invasive Breast Cancer and Ductal Carcinoma in Situ. Investig. Radiol. 2015, 50, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhooshan, N.; Giger, M.L.; Jansen, S.A.; Li, H.; Lan, L.; Newstead, G.M. Cancerous Breast Lesions on Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MR Images: Computerized Characterization for Image-Based Prognostic Markers. Radiology 2010, 254, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Harowicz, M.; Zhang, J.; Saha, A.; Grimm, L.J.; Hwang, E.S.; Mazurowski, M.A. Deep Learning Analysis of Breast MRIs for Prediction of Occult Invasive Disease in Ductal Carcinoma In Situ. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 115, 103498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
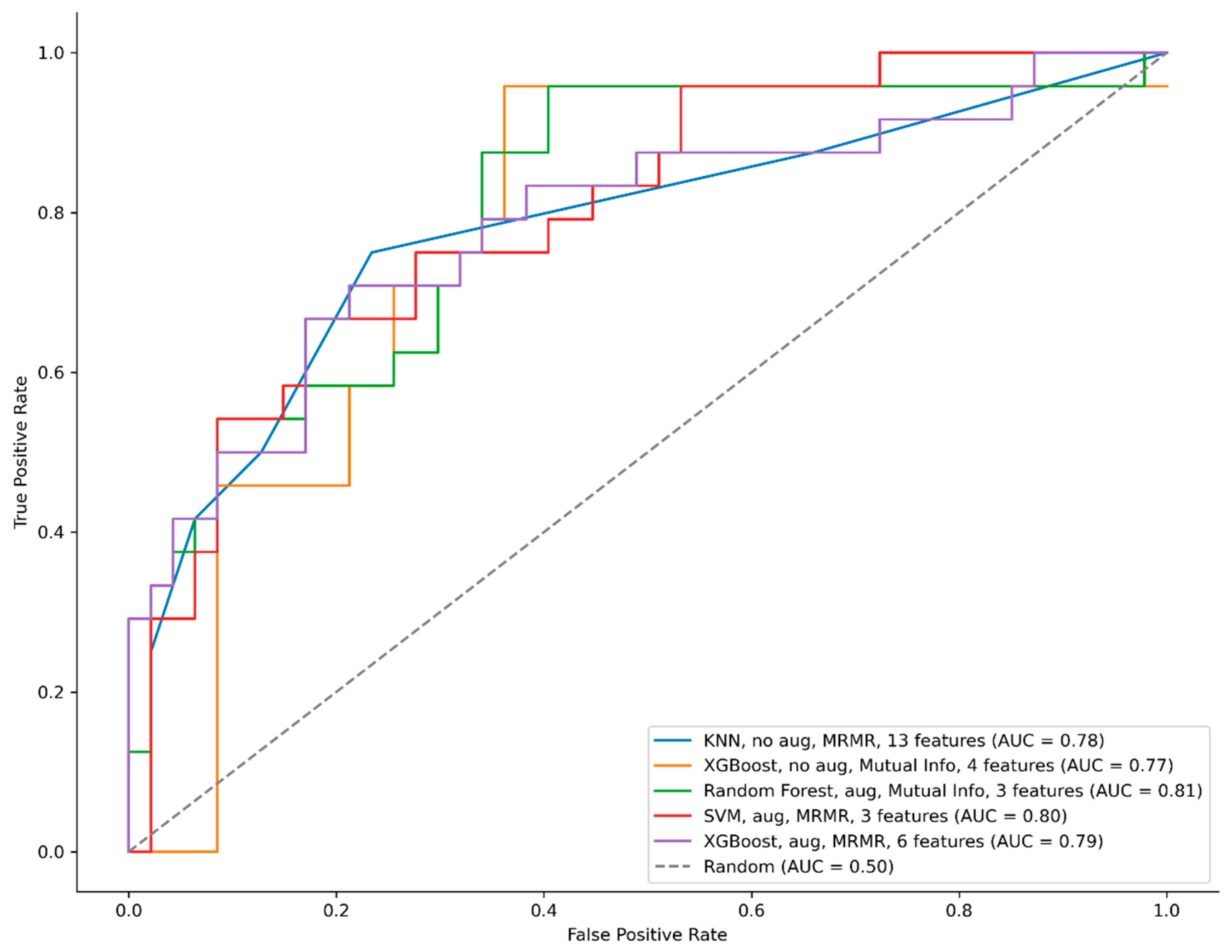
| Model | Hyper Parameters | Augmentation | Feature Selection | Number of Selected Features | AUC | Accuracy (%) | Threshold (Best-Accuracy Point) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | Confusion Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KNN | n_neighbors = 5 weights = uniform metric = cosine | No | MRMR | 13 | 0.78 | 0.76 | 0.80 | 0.77 | 0.42 | 0.54 | [44 3] [14 10] |
| XGBoost | objective = binary:logistic max_depth = 6 learning_rate = 0.01 n_estimators = 300 lambda = 0.5 alpha = 0.5 eval_metric = auc scale_pos_weight = 0.5435 | No | Mutual Info | 4 | 0.77 | 0.76 | 0.53 | 0.73 | 0.46 | 0.56 | [43 4] [16 8] |
| RF | n_estimators = 200 criterion = gini max_depth = 7 min_samples_split = 5 min_samples_leaf = 2 random_state = 42 | Yes | Mutual Info | 3 | 0.81 | 0.79 | 0.55 | 0.76 | 0.54 | 0.63 | [43 4] [11 13] |
| SVM | C = 5 kernel = rbf, gamma = scale shrinking = True probability = True class_weight = balanced random_state = 42 | Yes | MRMR | 3 | 0.80 | 0.79 | 0.80 | 0.76 | 0.54 | 0.63 | [43 4] [11 13] |
| XGBoost | objective = binary:logistic max_depth = 6 learning_rate = 0.01 n_estimators = 300 lambda = 0.5 alpha = 0.5 eval_metric = auc scale_pos_weight = 0.5435 | Yes | MRMR | 6 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.80 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.67 | [43 4] [12 12] |
| Model | Augmentation | Selection Method | Selected Features | Number of Selected Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KNN | No | MRMR | original_glcm_MCC, original_glrlm_RunPercentage, original_ngtdm_Coarseness, original_glcm_ClusterShade, original_glcm_Correlation, original_shape_SurfaceVolumeRatio, original_glcm_Idn, original_glszm_ZoneEntropy, original_shape_Flatness, original_gldm_DependenceEntropy, original_gldm_DependenceVariance, original_gldm_SmallDependenceLowGrayLevelEmphasis, original_shape_LeastAxisLength | 13 |
| XGBoost | No | Mutual Info | age, original_shape_Elongation, original_shape_Flatness, original_shape_LeastAxisLength | 4 |
| RF | Yes | Mutual Info | original_shape_Elongation, original_shape_Flatness, original_shape_LeastAxisLength | 3 |
| SVM | Yes | MRMR | original_glcm_Correlation, original_glrlm_RunVariance, original_shape_Elongation | 3 |
| XGBoost | Yes | MRMR | original_glcm_Correlation, original_glrlm_RunVariance, original_shape_Elongation, original_glszm_ZoneEntropy, original_glcm_ClusterShade, original_glcm_MCC | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Conte, L.; Rizzo, R.; Sallustio, A.; Maggiulli, E.; Capodieci, M.; Tramacere, F.; Castelluccia, A.; Raso, G.; De Giorgi, U.; Massafra, R.; et al. Radiomics and Machine Learning Approaches for the Preoperative Classification of In Situ vs. Invasive Breast Cancer Using Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DCE–MRI). Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7999. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147999
Conte L, Rizzo R, Sallustio A, Maggiulli E, Capodieci M, Tramacere F, Castelluccia A, Raso G, De Giorgi U, Massafra R, et al. Radiomics and Machine Learning Approaches for the Preoperative Classification of In Situ vs. Invasive Breast Cancer Using Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DCE–MRI). Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(14):7999. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147999
Chicago/Turabian StyleConte, Luana, Rocco Rizzo, Alessandra Sallustio, Eleonora Maggiulli, Mariangela Capodieci, Francesco Tramacere, Alessandra Castelluccia, Giuseppe Raso, Ugo De Giorgi, Raffaella Massafra, and et al. 2025. "Radiomics and Machine Learning Approaches for the Preoperative Classification of In Situ vs. Invasive Breast Cancer Using Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DCE–MRI)" Applied Sciences 15, no. 14: 7999. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147999
APA StyleConte, L., Rizzo, R., Sallustio, A., Maggiulli, E., Capodieci, M., Tramacere, F., Castelluccia, A., Raso, G., De Giorgi, U., Massafra, R., Portaluri, M., Cascio, D., & De Nunzio, G. (2025). Radiomics and Machine Learning Approaches for the Preoperative Classification of In Situ vs. Invasive Breast Cancer Using Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DCE–MRI). Applied Sciences, 15(14), 7999. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147999










