Time Series Prediction of Aerodynamic Noise Based on Variational Mode Decomposition and Echo State Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
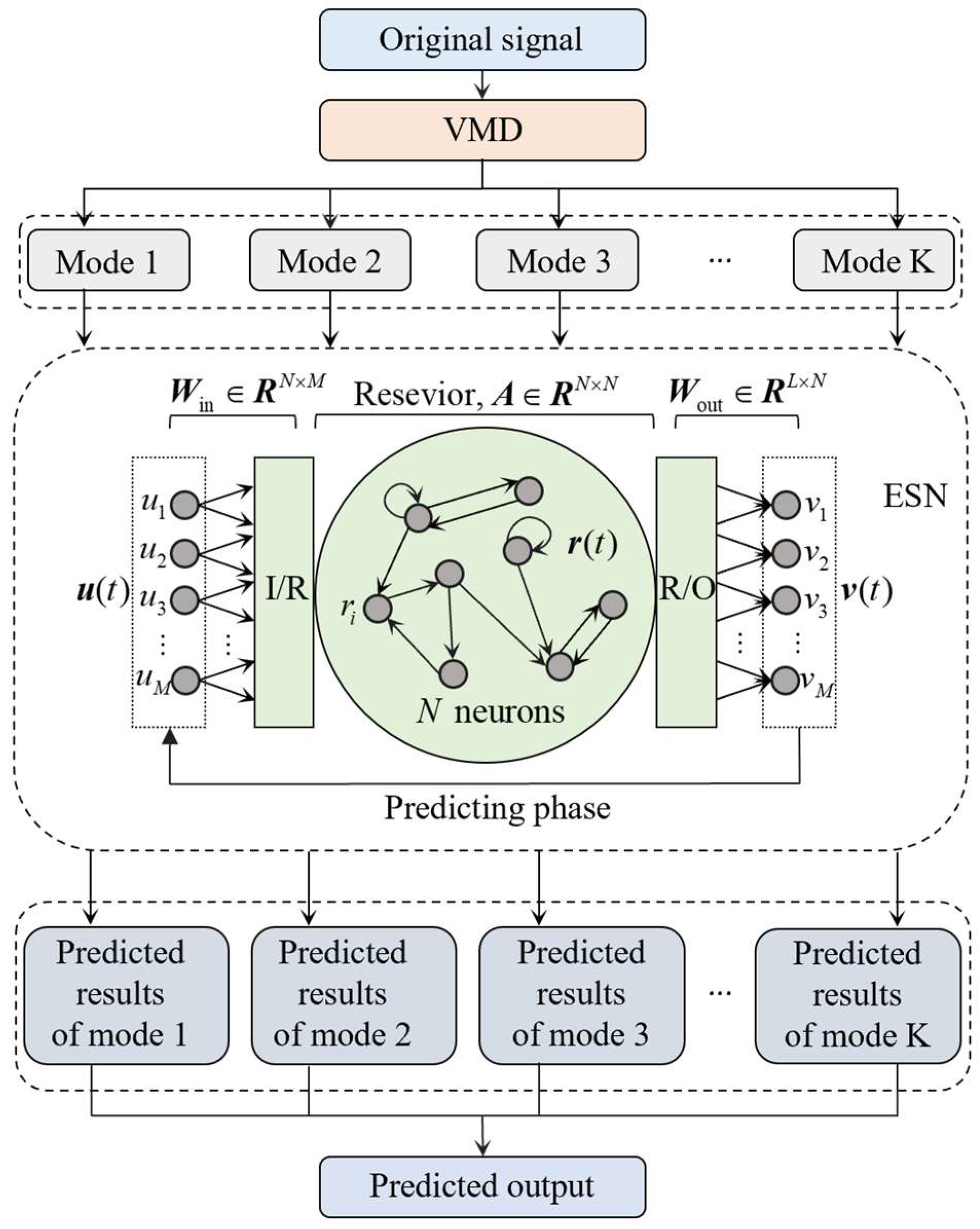
2. VMD-ESN Model
2.1. Variational Mode Decomposition
2.2. Echo State Network
2.3. Synthesis of Predicted Subseries in VMD-ESN Model
3. Time Series Prediction of Aerodynamic Noise
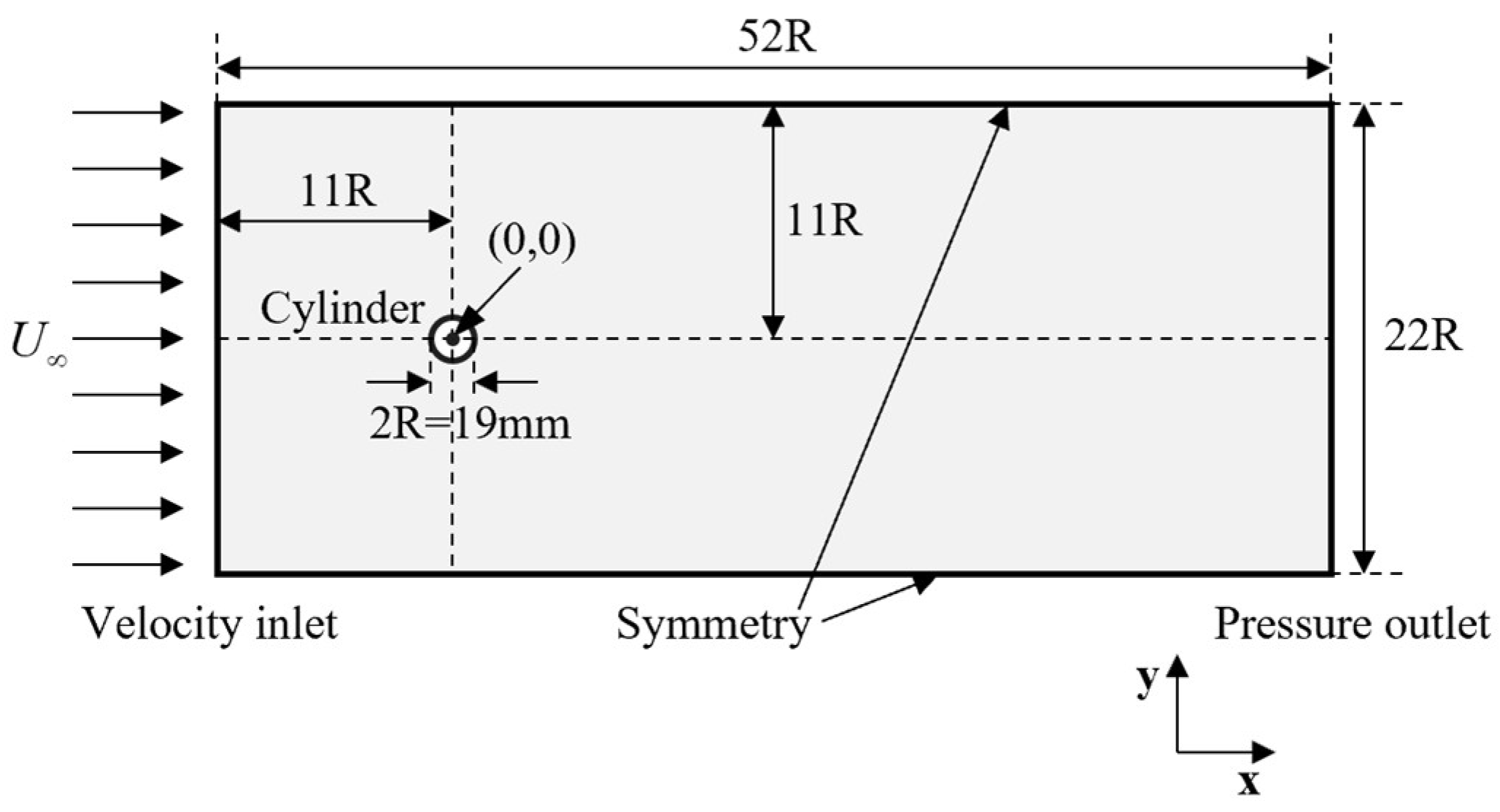
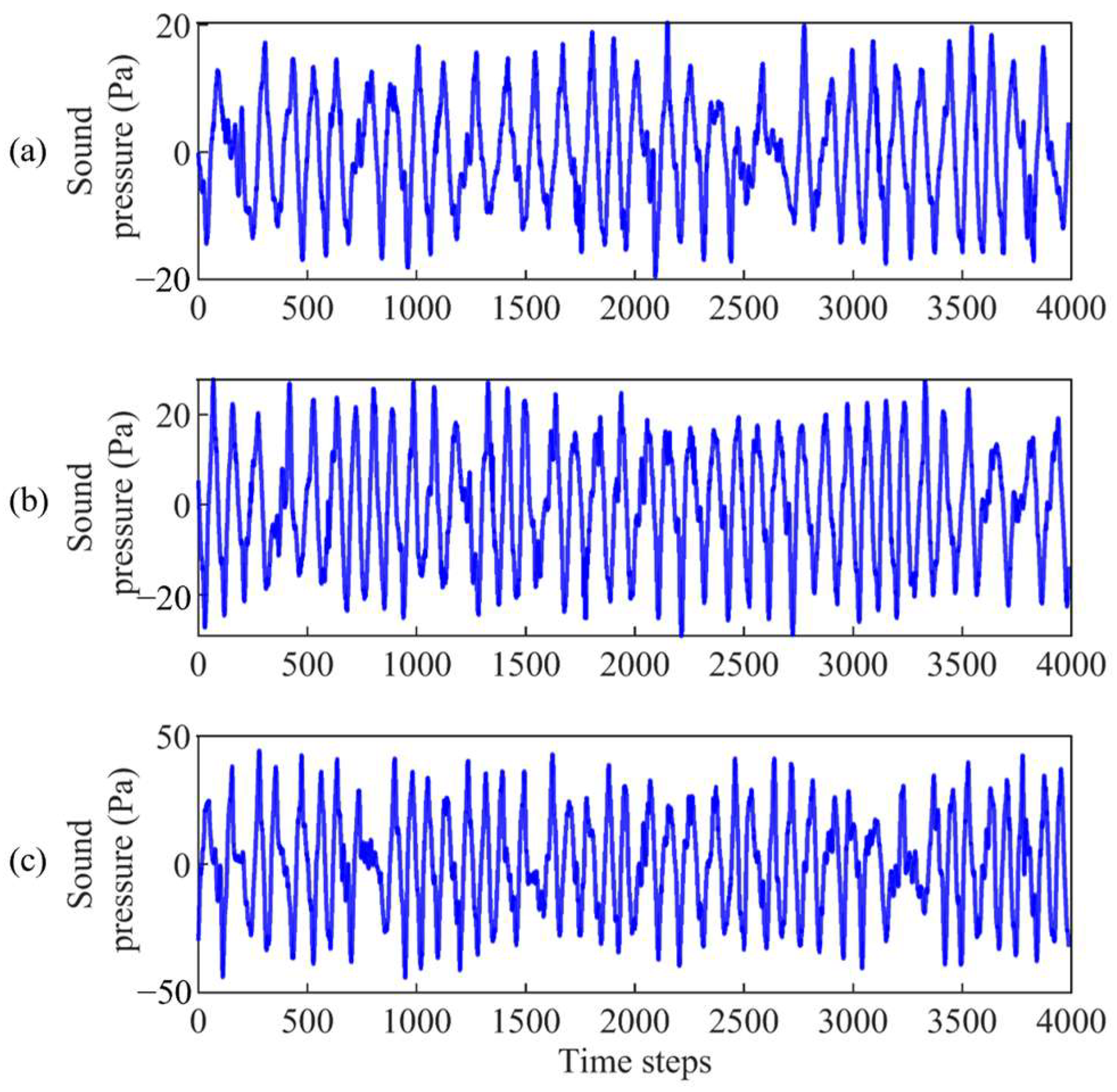
3.1. Data Preparation
3.2. Time Series Prediction Based on VMD-ESN Model
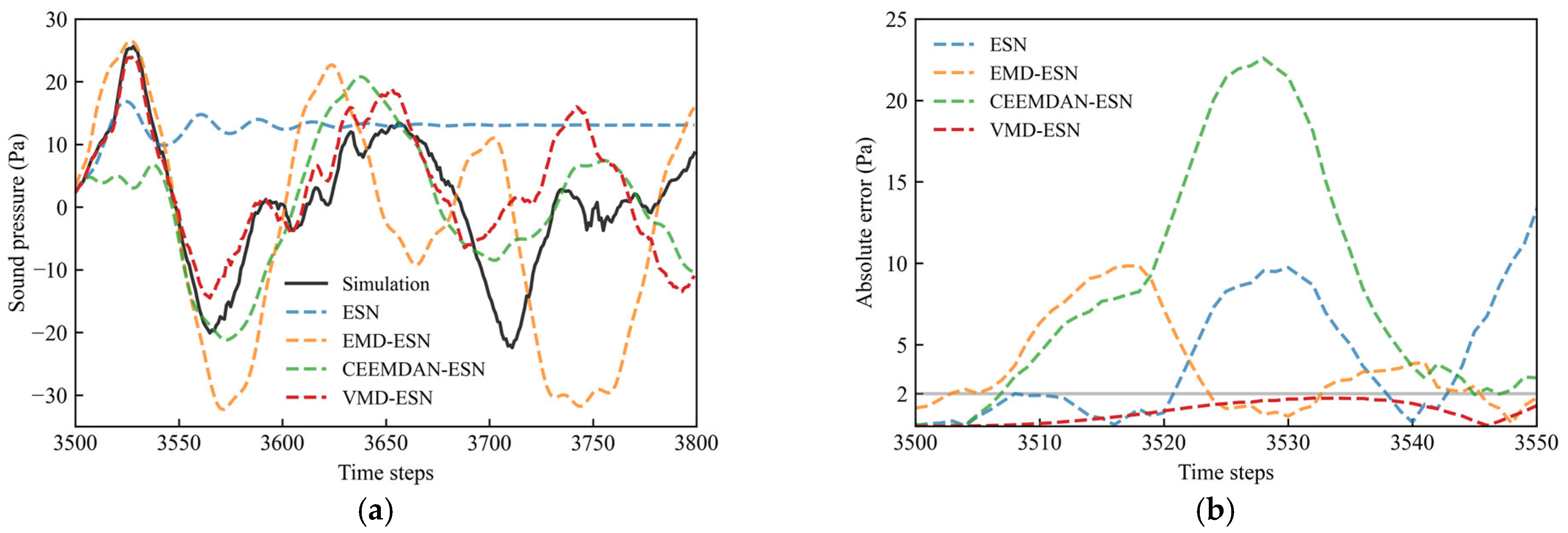
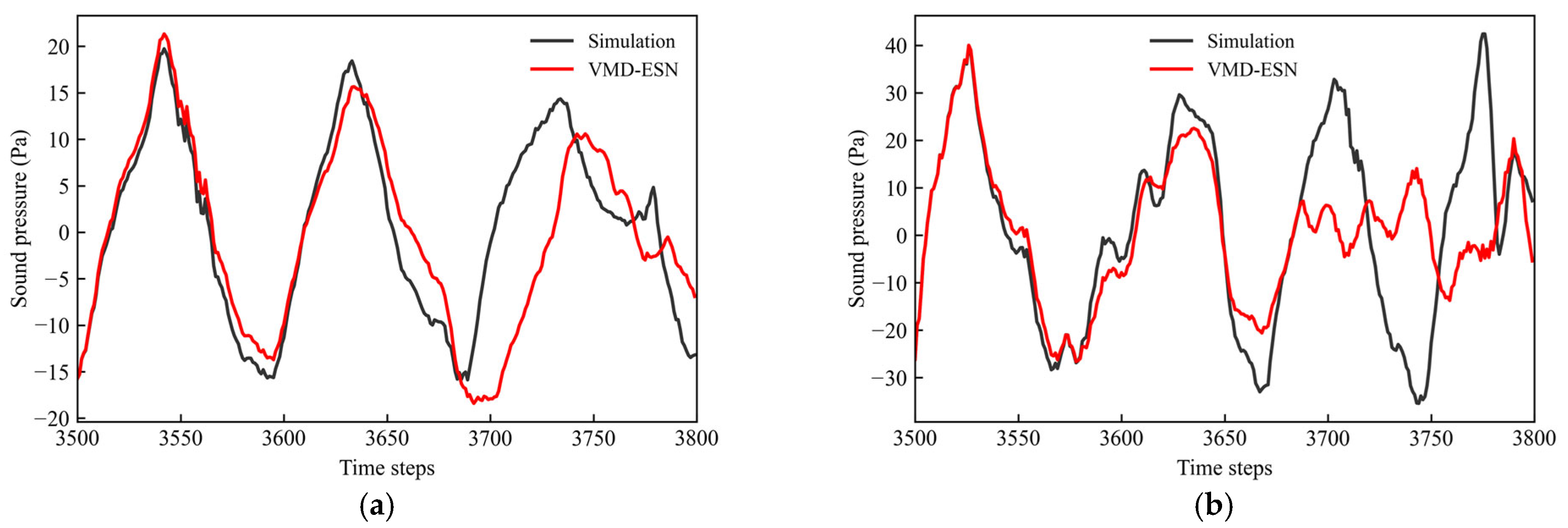
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VMD | Variational Mode Decomposition |
| ESN | Echo State Network |
| EMD | Empirical Mode Decomposition |
| CEEMDAN | Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise |
References
- Poinsot, T. Prediction and control of combustion instabilities in real engines. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2017, 36, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.C.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.K. Cause investigation of high-mode vortex-induced vibration in a long-span suspension bridge. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2020, 16, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, J. An experimental investigation of screech noise generation. J. Fluid Mech. 1999, 378, 71–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; He, Y.; Gui, L.; Wang, C.; Chen, L.; Li, Y. Aerodynamic noise prediction of a centrifugal fan considering the volute effect using IBEM. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 132, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, T.R.; Wolf, W.R.; Moffitt, N.J.; Kreitzman, J.R.; Bent, P. Numerical noise prediction and source identification of a realistic landing gear. J. Sound Vib. 2021, 496, 115933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Liu, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y. Effects and mechanisms of LES and DDES method on airfoil self-noise prediction at low to moderate Reynolds numbers. AIP Adv. 2021, 11, 025232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Hu, L.; Gong, J.; Wu, C.; Wang, S.; Zhu, X. Effects analysis on aerodynamic noise reduction of centrifugal compressor used for gasoline engine. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 180, 108104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polacsek, C.; Cader, A.; Buszyk, M.; Barrier, R.; Gea-Aguilera, F.; Posson, H. Aeroacoustic design and broadband noise predictions of a fan stage with serrated outlet guide vanes. Phys. Fluids 2020, 32, 107107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, B.S.; Ayton, L.J. Rapid noise prediction models for serrated leading and trailing edges. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 469, 115136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Liu, Q.; Zhong, S.Y.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, X. A study of the effect of serration shape and flexibility on trailing edge noise. Phys. Fluids 2020, 32, 127114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutz, J.N. Deep learning in fluid dynamics. J. Fluid Mech. 2017, 814, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.L.; Xiao, H.; Paterson, E. Physics-informed machine learning approach for augmenting turbulence models: A comprehensive framework. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2018, 3, 074602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, V.; Jiang, Q.H.; Shu, C.; Khoo, B.C. Fast flow field prediction over airfoils using deep learning approach. Phys. Fluids 2019, 31, 057103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Schumacher, J. Reservoir computing model of two-dimensional turbulent convection. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2020, 5, 113506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Choi, H. Toward neural-network-based large eddy simulation: Application to turbulent channel flow. J. Fluid Mech. 2021, 914, A16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.Y.; Xu, Z.X.; Yang, J.; Liang, B.; Cheng, J.C. Fast prediction of aerodynamic noise induced by the flow around a cylinder based on deep neural network. Chin. Phys. B 2022, 31, 064305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Z.X. The coupled deep neural networks for coupling of the Stokes and Darcy–Forchheimer problems. Chin. Phys. B 2023, 32, 010201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, M. Unsupervised data-driven response regime exploration and identification for dynamical systems. Chaos 2024, 34, 123122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rüttgers, M.; Lee, S.; Jeon, S.; You, D. Prediction of a typhoon track using a generative adversarial network and satellite images. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocquet, M.; Farchi, A.; Finn, T.S.; Durand, C.; Cheng, S.; Chen, Y.; Pasmans, I.; Carrassi, A. Accurate deep learning-based filtering for chaotic dynamics by identifying instabilities without an ensemble. Chaos 2024, 34, 091104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severson, K.A.; Attia, P.M.; Jin, N.; Perkins, N.; Jiang, B.; Yang, Z.; Chen, M.H.; Aykol, M.; Herring, P.K.; Fraggedakis, D.; et al. Data-driven prediction of battery cycle life before capacity degradation. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, E.A.; Unni, V.R.; Pavithran, I.; Sujith, R.I.; Saha, A. Convolutional neural networks to predict the onset of oscillatory instabilities in turbulent systems. Chaos 2021, 31, 093131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziletti, A.; Kumar, D.; Scheffler, M.; Ghiringhelli, L.M. Insightful classification of crystal structures using deep learning. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, W.K.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.B.; Chu, I.H.; Ong, S.P. Deep neural networks for accurate predictions of crystal stability. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Li, B.; Li, Q.Y.; Zhao, H.P.; Feng, X.Q. Deep neural network method for predicting the mechanical properties of composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 115, 161901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.X.; Gao, H.; Ding, Y.J.; Yang, J.; Liang, B.; Cheng, J.C. Topology-Optimized Omnidirectional Broadband Acoustic Ventilation Barrier. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2020, 14, 054016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.X.; Zheng, B.; Yang, J.; Liang, B.; Cheng, J.C. Machine-Learning-Assisted Acoustic Consecutive Fano Resonances: Application to a Tunable Broadband Low-Frequency Metasilencer. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2021, 16, 044020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.L.; Wang, L.; Tao, R. Wind speed forecasting based on variational mode decomposition and improved echo state network. Renew. Energy 2021, 164, 729–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godavarthi, V.; Unni, V.R.; Gopalakrishnan, E.A.; Sujith, R.I. Recurrence networks to study dynamical transitions in a turbulent combustor. Chaos 2017, 27, 063113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Gao, L.P.; Li, G.H. Underwater Acoustic Signal Prediction Based on MVMD and Optimized Kernel Extreme Learning Machine. Complexity 2020, 2020, 6947059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, H.L.; Fan, W.H.; Ma, P. A new chaotic time series hybrid prediction method of wind power based on EEMD-SE and full-parameters continued fraction. Energy 2017, 138, 977–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomiretskiy, K.; Zosso, D. Variational Mode Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process 2014, 62, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revell, J.D.; Prydz, R.A.; Hays, A.P. Experimental study of aerodynamic noise vs drag relationships for circular cylinders. AIAA J. 1978, 16, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Time Steps Ahead | Model | RMSE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | ESN | 5.1514 | −0.5559 |
| EMD-ESN | 4.6260 | 0.6395 | |
| CEEMDAN-ESN | 11.1393 | −1.0905 | |
| VMD-ESN | 1.0524 | 0.9813 | |
| 150 | ESN | 15.1145 | −30.7351 |
| EMD-ESN | 11.0795 | 0.0497 | |
| CEEMDAN-ESN | 9.3568 | 0.3223 | |
| VMD-ESN | 3.3225 | 0.9145 |
| Inflow Velocity | Time Steps Ahead | RMSE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 60 m/s | 50 | 1.7600 | 0.9878 |
| 150 | 3.9569 | 0.9544 | |
| 80 m/s | 50 | 1.2589 | 0.9854 |
| 150 | 1.9671 | 0.9678 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, Z.; Meng, H.; Yang, J.; Liang, B.; Cheng, J. Time Series Prediction of Aerodynamic Noise Based on Variational Mode Decomposition and Echo State Network. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7896. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147896
Lei Z, Meng H, Yang J, Liang B, Cheng J. Time Series Prediction of Aerodynamic Noise Based on Variational Mode Decomposition and Echo State Network. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(14):7896. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147896
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Zhoufanxing, Haiyang Meng, Jing Yang, Bin Liang, and Jianchun Cheng. 2025. "Time Series Prediction of Aerodynamic Noise Based on Variational Mode Decomposition and Echo State Network" Applied Sciences 15, no. 14: 7896. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147896
APA StyleLei, Z., Meng, H., Yang, J., Liang, B., & Cheng, J. (2025). Time Series Prediction of Aerodynamic Noise Based on Variational Mode Decomposition and Echo State Network. Applied Sciences, 15(14), 7896. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147896






