Association Between Vertebral Artery Stiffness and Idiopathic Subjective Tinnitus: A Prospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
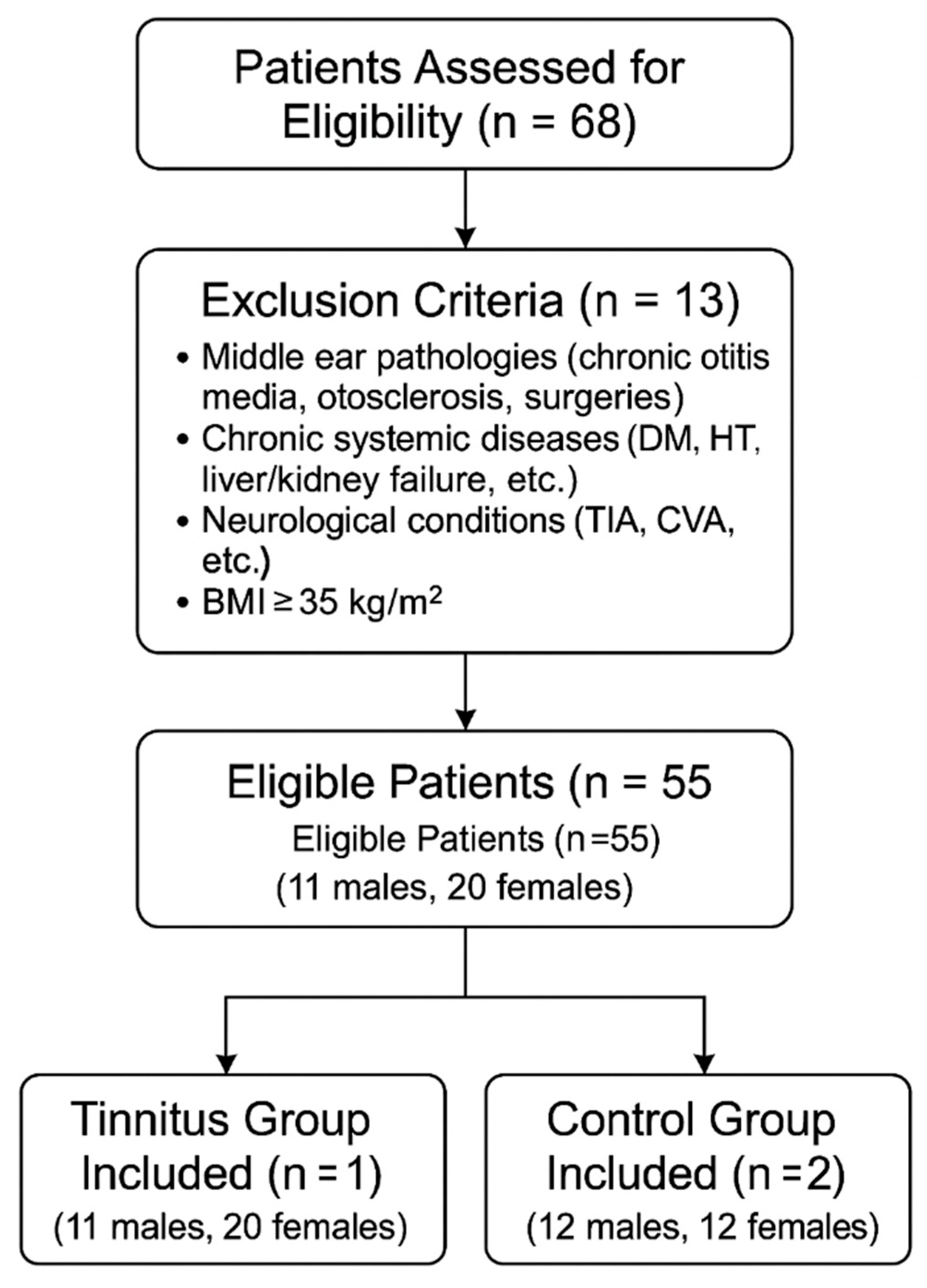
2.1. Study Design and Study Population
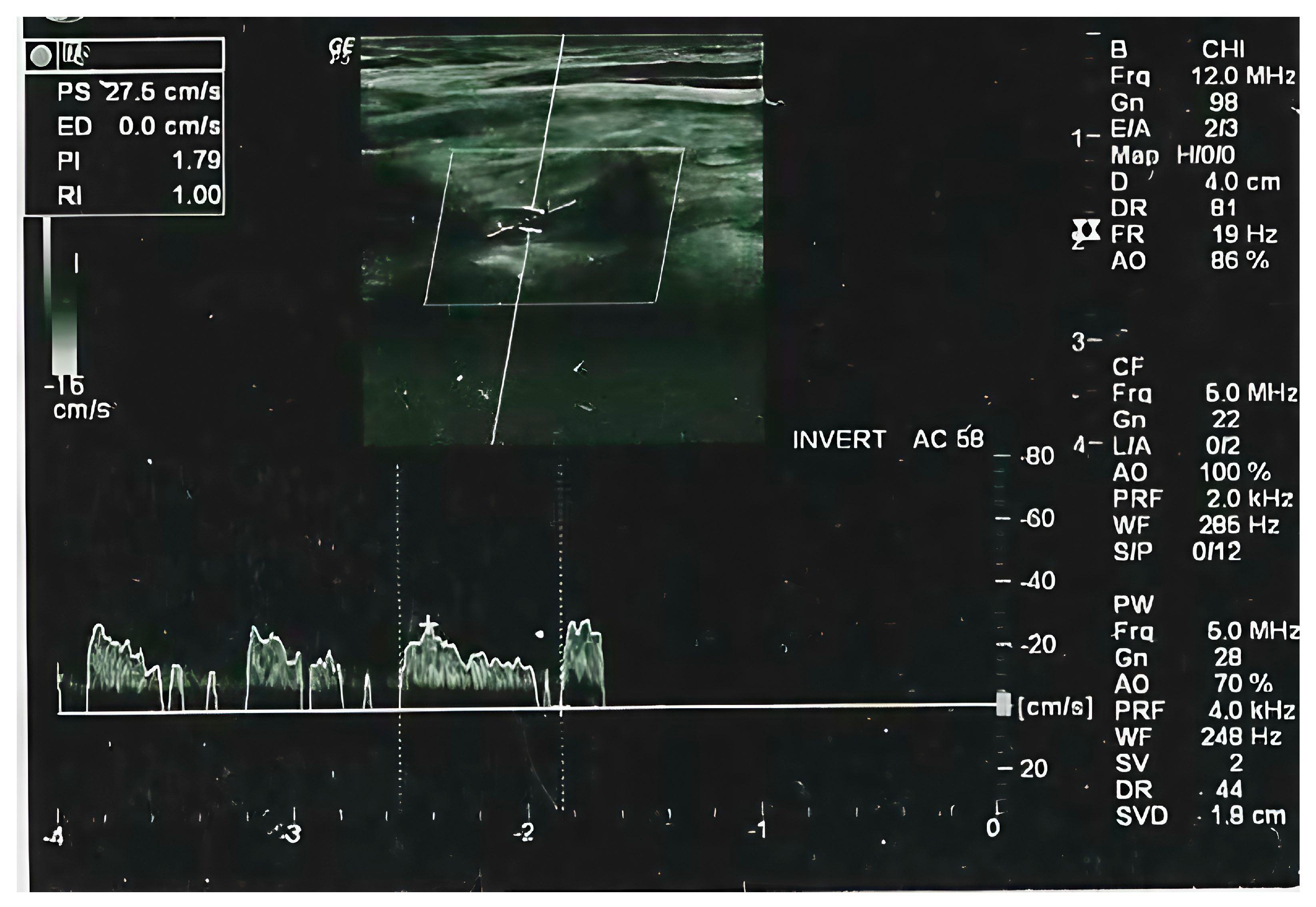
2.2. Radiological Evaluation
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2021 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global burden and strength of evidence for 88 risk factors in 204 countries and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2024, 403, 2162–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2021 Europe Life Expectancy Collaborators. Changing life expectancy in European countries 1990–2021: A subanalysis of causes and risk factors from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Public Health 2025, 10, e172–e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gruy, J.A.; Laurenzo, W.W.; Vu, T.H.; Paul, O.; Lee, C.; Spankovich, C. Prevalence and predictors of problematic tinnitus. Int. J. Audiol. 2025, 64, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batts, S.; Stankovic, K.M. Tinnitus prevalence, associated characteristics, and related healthcare use in the United States: A population-level analysis. Lancet Reg. Health Am. 2024, 29, 100659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, M.L.; Luo, J.; Zeng, F.G. Attention-Modulated Cortical Responses as a Biomarker for Tinnitus. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadekova, N.; Iulita, M.F.; Vallerand, D.; Muhire, G.; Bourmoum, M.; Claing, A.; Girouard, H. Arterial stiffness induced by carotid calcification leads to cerebral gliosis mediated by oxidative stress. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, K.A.; Cho, G.W.; Maharajan, N.; Jang, C.H. A Review on Peripheral Tinnitus, Causes, and Treatments from the Perspective of Autophagy. Exp. Neurobiol. 2022, 31, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, P.; Kotz, S.A.; Smit, J.V.; Janssen, M.L.F.; Schwartze, M. Auditory thalamus dysfunction and pathophysiology in tinnitus: A predictive network hypothesis. Brain Struct. Funct. 2021, 226, 1659–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, H.F.; Bojic, T.; Ribeiro, S.F.; Paco, J.; Hall, D.A.; Szczepek, A.J. Pathophysiology of Subjective Tinnitus: Triggers and Maintenance. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuzuki, N.; Wasano, K. Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A review focused on the contribution of vascular pathologies. Auris Nasus Larynx 2024, 51, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouelleil, M.; Aljiboori, K.; Lyons, L.; Restrepo, A.; Singer, J. Commentary: Venous Causes of Pulsatile Tinnitus: Clinical Presentation, Clinical and Radiographic Evaluation, Pathogenesis, and Endovascular Treatments: A Literature Review. Neurosurgery 2022, 90, e65–e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Xu, C.; Wang, H.; Shi, H.; Yu, D. Video head impulse test results suggest that different pathomechanisms underlie sudden sensorineural hearing loss with vertigo and vestibular neuritis: Our experience in fifty-two patients. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2018, 43, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Spira, A.P.; Reed, N.S.; Lin, F.R.; Deal, J.A. Sleep Characteristics and Hearing Loss in Older Adults: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005–2006. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2022, 77, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, C.; Xie, X.; Wu, Y.; Xu, L.; Guan, X.; Li, F.; Zhan, X.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Reference values of carotid intima-media thickness and arterial stiffness in Chinese adults based on ultrasound radio frequency signal: A nationwide, multicenter study. Chin. Med. J. 2024, 137, 1802–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutouyrie, P.; Chowienczyk, P.; Humphrey, J.D.; Mitchell, G.F. Arterial Stiffness and Cardiovascular Risk in Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 864–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, C.; Tasolar, S. Relationship between increased carotid artery stiffness and idiopathic subjective tinnitus. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 274, 2125–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gedikli, O.; Kemal, O.; Yildirim, U.; Cecen, A.B.; Karabulut, H.; Akcay, M.; Terzi, O. Is there an association between the parameters of arterial stiffness and tinnitus? Acta Otolaryngol. 2020, 140, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Vecchio, V.; Tricarico, L.; Pisani, A.; Serra, N.; D’Errico, D.; De Corso, E.; Rea, T.; Picciotti, P.M.; Laria, C.; Manna, G.; et al. Vascular Factors in Patients with Midlife Sensorineural Hearing Loss and the Progression to Mild Cognitive Impairment. Medicina 2023, 59, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, T.; Okada, M.; Hanari, T.; Takagi, T.; Fujiwara, T.; Hato, N. Association of the prognosis and severity of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss with cervical ultrasonographic findings. Auris Nasus Larynx 2021, 48, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badji, A.; Sabra, D.; Bherer, L.; Cohen-Adad, J.; Girouard, H.; Gauthier, C.J. Arterial stiffness and brain integrity: A review of MRI findings. Ageing Res. Rev. 2019, 53, 100907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeve, E.H.; Barnes, J.N.; Moir, M.E.; Walker, A.E. Impact of arterial stiffness on cerebrovascular function: A review of evidence from humans and preclincal models. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2024, 326, H689–H704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palombo, C.; Kozakova, M. Arterial stiffness, atherosclerosis and cardiovascular risk: Pathophysiologic mechanisms and emerging clinical indications. Vascul Pharmacol. 2016, 77, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.Y.; Shin, S.H.; Byun, S.W. Electrocochleography in Chronic Tinnitus: Correlations with Audiological Profiles and Psychological Distress. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2024, 45, 104477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aazh, H.; Najjari, A.; Moore, B.C.J. A Preliminary Analysis of the Clinical Effectiveness of Audiologist-Delivered Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Delivered via Video Calls for Rehabilitation of Misophonia, Hyperacusis, and Tinnitus. Am. J. Audiol. 2024, 33, 559–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal-Robledano, A.; Perez-Carpena, P.; Kikidis, D.; Mazurek, B.; Schoisswohl, S.; Staudinger, S.; Langguth, B.; Schlee, W.; Lopez-Escamez, J.A. Cognitive Screening and Hearing Assessment in Patients With Chronic Tinnitus. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2024, 17, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhavkar, N.; Goldrich, D.Y.; Roychowdhury, S.; Kwong, K. Laceration of Aberrant Internal Carotid Artery Following Myringotomy: A Case Report and Review of Literature. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2022, 131, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Ding, J.Y.; Ya, J.Y.; Pan, L.Q.; Yan, F.; Yang, Q.; Ding, Y.C.; Ji, X.M.; Meng, R. Understanding jugular venous outflow disturbance. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2018, 24, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T.; Kikumori, A.; Kimura, N.; Shiomi, M. Distribution of atherosclerotic lesions in various arteries of WHHLMI rabbits, an animal model of familial hypercholesterolemia. Exp. Anim. 2019, 68, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasani, M.; Aydin, A.L.; Aytan, N.; Yapicier, O.; Oktenoglu, T.; Ozer, N.K.; Ozer, A.F. Effect of a hypercholesterolemia as a starting factor on spinal degeneration in rabbits and role of Vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol). Surg. Neurol. Int. 2016, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.S.; Koo, M.; Chen, J.C.; Hwang, J.H. The association between tinnitus and the risk of ischemic cerebrovascular disease in young and middle-aged patients: A secondary case-control analysis of a nationwide, population-based health claims database. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, M.; Gavino, A.; Li, Y.; McLachlan, C.S. Comparison of Parameters for Assessment of Carotid Stiffness and Their Association with Carotid Atherosclerosis in Rural Australian Adults: A Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turk, M.; Zaletel, M.; Pretnar-Oblak, J. Ratio between carotid artery stiffness and blood flow—A new ultrasound index of ischemic leukoaraiosis. Clin. Interv. Aging 2016, 11, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Case (n = 31) | Control (n = 24) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 50 ± 9.64 | 46.6 ± 10.63 | 0.188 |
| Gender (Female/Male) | 20/11 | 12/12 | 0.279 |
| PTA (dB) Right | 22.16 ± 13.8 | 20.3 ± 7.3 | 0.585 |
| (dB) Left | 21.9 ± 9.4 | 20 ± 5.3 | 0.838 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 47.2 ± 11.6 | 49.3 ± 7 | 0.453 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 149.4 ± 37.9 | 106.1 ± 10.7 | <0.005 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 202.2 ± 83.5 | 148.6 ± 26.4 | <0.005 |
| Fasting Glucose (mg/dL) | 82.5 ± 7.4 | 80.5 ± 5.5 | 0.310 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 193.6 ± 47.28 | 167.5 ± 28.99 | 0.021 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 116.48 ± 8.28 | 112.56 ± 5.8 | 0.380 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 76.12 ± 3.58 | 75.15 ± 4.72 | 0.160 |
| Case (n = 31) | Control (n = 24) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
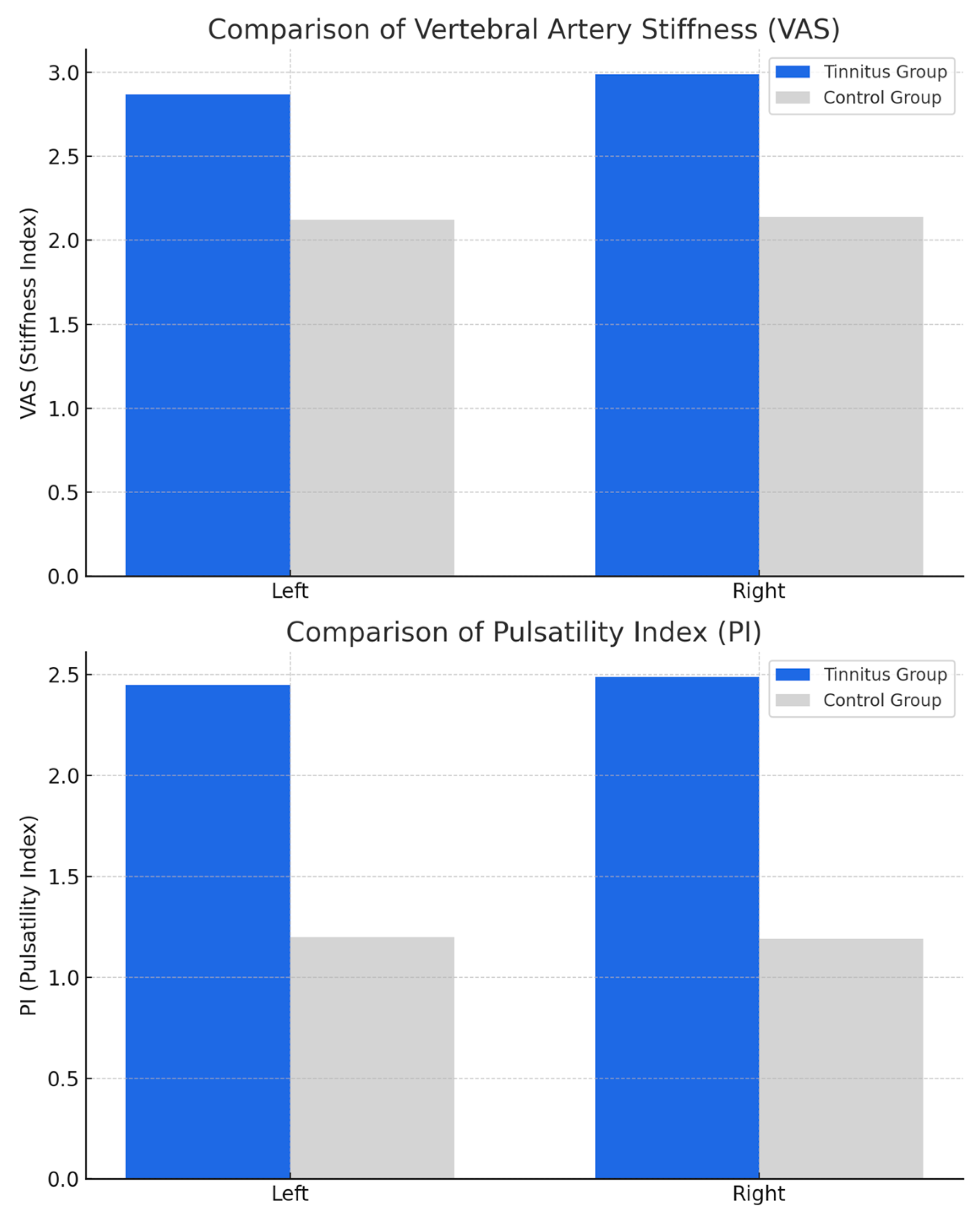
| Vertebral artery stiffness Left | 2.87 ± 0.72 | 2.12 ± 0.22 | <0.005 |
| Vertebral artery stiffness Right | 2.99 ± 0.77 | 2.14 ± 0.5 | <0.005 |
| Vertebral artery RI Left | 0.86 ± 0.32 | 0.94 ± 0.24 | 0.581 |
| Vertebral artery RI Right | 0.84 ± 0.31 | 0.91 ± 0.22 | 0.509 |
| Vertebral artery PI Left | 2.45 ± 1.2 | 1.2 ± 0.43 | <0.005 |
| Vertebral artery PI Right | 2.49 ± 1.02 | 1.19 ± 0.42 | <0.005 |
| Left | Right | Bilateral | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vert. Art. Stiff Left | 3.27 ± 0.79 | 2.57 ± 0.76 | 2.2 ± 0.45 | 0.058 |
| Vert. Art. Stiff Right | 2.7 ± 0.66 | 3.62 ± 0.87 | 2.76 ± 0.01 | 0.010 |
| Vert Art. RI Left | 0.93 ± 0.15 | 0.97 ± 0.29 | 0.64 ± 0.32 | 0.543 |
| Vert Art. RI Right | 0.84 ± 0.19 | 1.08 ± 0.19 | 0.69 ± 0.4 | 0.579 |
| Vert Art. PI Left | 2.74 ± 1.58 | 2.41 ± 1.34 | 2.2 ± 0.45 | 0.024 |
| Vert Art. PI Right | 2.6 ± 1.5 | 2.7 ± 0.95 | 2.21 ± 0.22 | 0.016 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aytac, I.; Yazici, A.; Tunc, O.; Gul, R.; Inanc, Y.; Tumuklu, K. Association Between Vertebral Artery Stiffness and Idiopathic Subjective Tinnitus: A Prospective Study. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7890. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147890
Aytac I, Yazici A, Tunc O, Gul R, Inanc Y, Tumuklu K. Association Between Vertebral Artery Stiffness and Idiopathic Subjective Tinnitus: A Prospective Study. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(14):7890. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147890
Chicago/Turabian StyleAytac, Ismail, Alper Yazici, Orhan Tunc, Rauf Gul, Yusuf Inanc, and Koray Tumuklu. 2025. "Association Between Vertebral Artery Stiffness and Idiopathic Subjective Tinnitus: A Prospective Study" Applied Sciences 15, no. 14: 7890. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147890
APA StyleAytac, I., Yazici, A., Tunc, O., Gul, R., Inanc, Y., & Tumuklu, K. (2025). Association Between Vertebral Artery Stiffness and Idiopathic Subjective Tinnitus: A Prospective Study. Applied Sciences, 15(14), 7890. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147890






