Sem-SLAM: Semantic-Integrated SLAM Approach for 3D Reconstruction
Abstract
1. Introduction
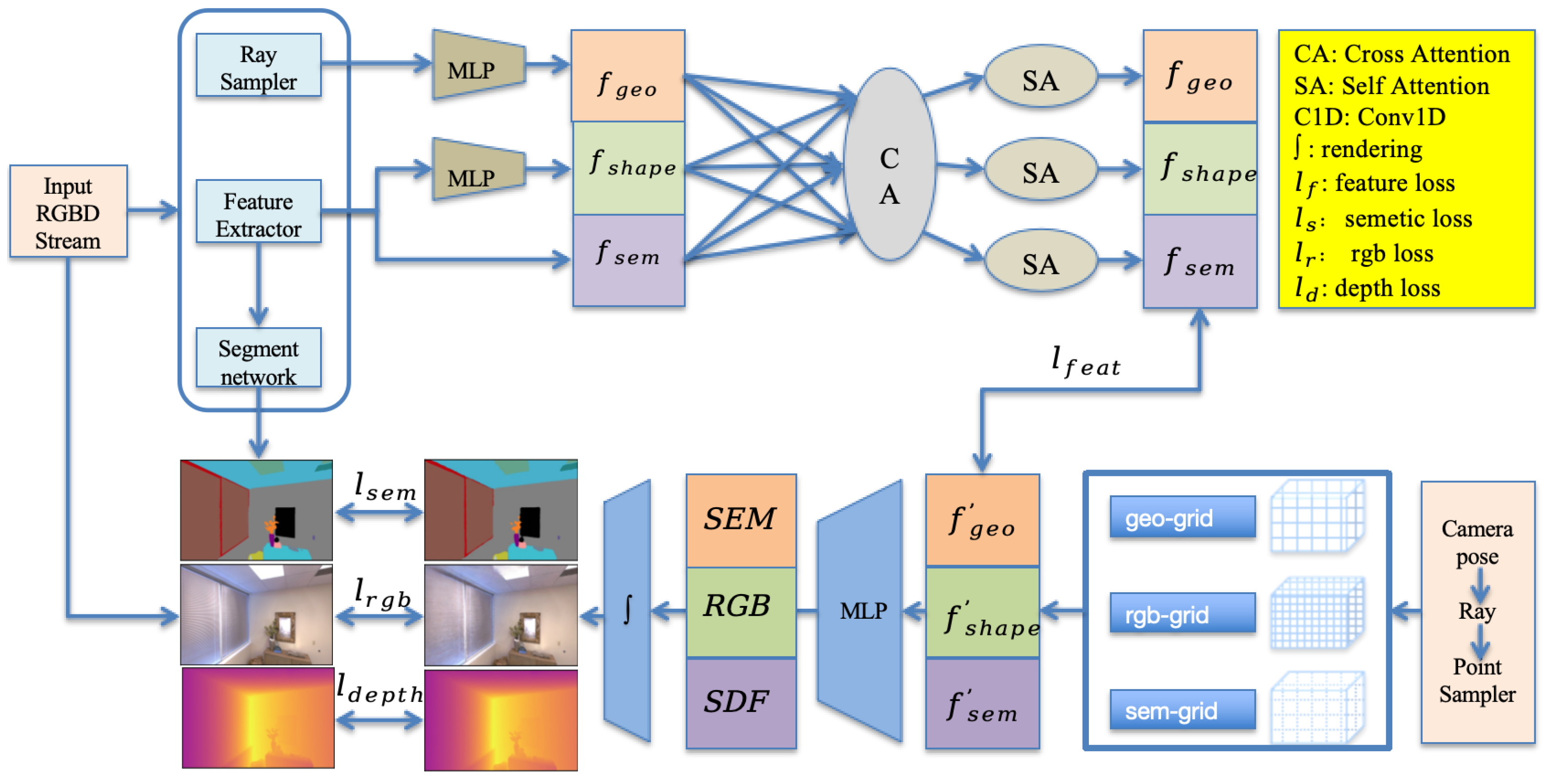
- We propose a NeRF-based visual semantic SLAM system. To accurately construct a semantic map for mapping, we introduce a multi-scale information extractor to extract both coarse-grained and fine-grained information from the camera pose. This enables a more comprehensive and detailed understanding of the spatial information related to the camera, laying a solid foundation for precise mapping.
- We implement a full-attention cross-modal feature fusion method to integrate geometric, shape, and semantic features based on cross-attention and self-attention. This innovative structure can fully utilize the functions of features at various levels. By effectively combining different types of features, it enhances the system’s ability to perceive and analyze the environment, resulting in more accurate and meaningful semantic representations.
- Additionally, we employ color loss, appearance loss, feature loss, and depth loss to guide the optimization of the network. These carefully designed loss functions play a crucial role in adjusting the network parameters, helping the system to converge towards better solutions. As a result, we can obtain more optimal results in terms of mapping accuracy, object recognition, and overall system performance.
- We conduct extensive evaluations on two challenging datasets, Replica [6] and ScanNet [7]. The experimental results clearly demonstrate that, compared with existing NeRF-based SLAM methods, our method exhibits state-of-the-art performance in mapping, tracking, and semantic segmentation. It not only shows higher accuracy in mapping the environment but also achieves more precise object tracking and semantic segmentation, highlighting the superiority and practical value of our proposed Sem-SLAM.
2. Related Work
3. Methodology
3.1. Forward Feature Fusion
3.2. Backward Semantic Mapping
3.3. Loss Function
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Settings
4.2. Qualitative Evaluations
4.3. Quantitative Results
4.4. Runtime Analysis
4.5. Ablation Study on Loss Function
4.6. Ablation Study on Segmentation Backbone Errors
4.7. Cross-Attention Weights Temporal Stability Experiment
4.8. Failure Cases
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, M.; Ma, Y.; Qiu, Q. SemanticSLAM: Learning based Semantic Map Construction and Robust Camera Localization. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), Orlando, FL, USA, 5–8 December 2023; pp. 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Y.; Zhu, S.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H. Towards Autonomous Indoor Parking: A Globally Consistent Semantic SLAM System and A Semantic Localization Subsystem. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.121692024. [Google Scholar]
- Mildenhall, B.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Tancik, M.; Barron, J.T.; Ramamoorthi, R.; Ng, R. Nerf: Representing scenes as neural radiance fields for view synthesis. Commun. ACM 2021, 65, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, R.; Liao, Y. NGEL-SLAM: Neural Implicit Representation-based Global Consistent Low-Latency SLAM System. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.09525. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Y.; Bhalgat, Y.; Fu, L.F.T.; Mattamala, M.; Chebrolu, N.; Fallon, M.F. SiLVR: Scalable Lidar-Visual Reconstruction with Neural Radiance Fields for Robotic Inspection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Yokohama, Japan, 13–17 May 2024; pp. 17983–17989. [Google Scholar]
- Straub, J.; Whelan, T.; Ma, L.; Chen, Y.; Wijmans, E.; Green, S.; Engel, J.J.; Mur-Artal, R.; Ren, C.; Verma, S.; et al. The Replica dataset: A digital replica of indoor spaces. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.05797. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, A.; Chang, A.X.; Savva, M.; Halber, M.; Funkhouser, T.; Nießner, M. Scannet: Richly-annotated 3d reconstructions of indoor scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5828–5839. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, Y.; Ye, W.; Calway, A. iDF-SLAM: End-to-End RGB-D SLAM with Neural Implicit Mapping and Deep Feature Tracking. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.07919. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Wang, Y.; Tan, L.; Li, M.; Shan, H.; Liao, P. DNIV-SLAM: Dynamic Neural Implicit Volumetric SLAM. In Proceedings of the Chinese Conference on Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision (PRCV), Singapore, 25–28 October 2025; pp. 33–47. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, Z.; Yue, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, C. HERO-SLAM: Hybrid Enhanced Robust Optimization of Neural SLAM. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Yokohama, Japan, 13–17 May 2024; pp. 8610–8616. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Gu, X.; Yuan, W.; Yang, L.; Dong, Z.; Tan, P. Dense RGB SLAM With Neural Implicit Maps. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Kigali, Rwanda, 1–5 May 2023; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Wang, J.; Deng, S.; Liu, J. DF-SLAM: Dictionary Factors Representation for High-Fidelity Neural Implicit Dense Visual SLAM System. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.17876. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Peng, S.; Larsson, V.; Xu, W.; Bao, H.; Cui, Z.; Oswald, M.R.; Pollefeys, M. Nice-slam: Neural implicit scalable encoding for slam. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 12786–12796. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Tosi, F.; Mattoccia, S.; Poggi, M. GO-SLAM: Global Optimization for Consistent 3D Instant Reconstruction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, D.; Yan, C.; Wang, D.; Yin, J.; Chen, Q.; Xu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Li, X. Implicit Event-RGBD Neural SLAM. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 19584–19594. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, G.; Deng, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. DDN-SLAM: Real-time Dense Dynamic Neural Implicit SLAM. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.01545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, G.; Blum, H.; Liu, J.; Song, L.; Pollefeys, M.; Wang, H. SNI-SLAM: Semantic Neural Implicit SLAM. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 21167–21177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Chen, Q.; Yan, Y.; Pu, J. EC-SLAM: Real-time Dense Neural RGB-D SLAM System with Effectively Constrained Global Bundle Adjustment. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.13346v1. [Google Scholar]
- Cartillier, V.; Schindler, G.; Essa, I. SLAIM: Robust Dense Neural SLAM for Online Tracking and Mapping. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 2862–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Chen, X.; Feng, B.; Li, G.; Yang, L.; Bao, H.; Zhang, G.; Cui, Z. Cg-slam: Efficient dense rgb-d slam in a consistent uncertainty-aware 3d gaussian field. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Zurich, Switzerland, 21–25 September 2025; pp. 93–112. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S. Automated fault diagnosis detection of air handling units using real operational labelled data and transformer-based methods at 24-hour operation hospital. Build. Environ. 2025, 282, 113257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oquab, M.; Darcet, T.; Moutakanni, T.; Vo, H.; Szafraniec, M.; Khalidov, V.; Fernandez, P.; Haziza, D.; Massa, F.; El-Nouby, A.; et al. Dinov2: Learning robust visual features without supervision. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.07193. [Google Scholar]
- Johari, M.M.; Carta, C.; Fleuret, F. Eslam: Efficient dense slam system based on hybrid representation of signed distance fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 17408–17419. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Li, H.; Zhai, H.; Ming, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G. Vox-Fusion: Dense tracking and mapping with voxel-based neural implicit representation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR), Singapore, 17–21 October 2022; pp. 499–507. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Theobalt, C.; Komura, T.; Wang, W. NeuS: Learning Neural Implicit Surfaces by Volume Rendering for Multi-view Reconstruction. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Online, 6–14 December 2021; Ranzato, M., Beygelzimer, A., Dauphin, Y., Liang, P., Vaughan, J.W., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 34, pp. 27171–27183. [Google Scholar]
- Haghighi, Y.; Kumar, S.; Thiran, J.P.; Gool, L.V. Neural Implicit Dense Semantic SLAM. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.14560. [Google Scholar]



| Methods | Replica | ScanNet | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Room 0 | Room 1 | Avg | 0000 | 0106 | Avg | |
| NIDS-SLAM | 60.23 | 30.51 | 54.64 | 70.78 | 63.46 | 10.16 |
| SNI-SLAM | 58.46 | 50.48 | 64.78 | 84.62 | 55.84 | 53.64 |
| Sem-SLAM | 88.56 | 90.26 | 81.45 | 86.21 | 78.96 | 80.47 |
| Methods | Replica | ScanNet | Confidence | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Room 0 | Room 1 | Avg | 0000 | 0106 | Avg | ||
| NIDS-SLAM | 9.5 | 12 | 10.8 | 12.2 | 7.70 | 9.55 | 89% |
| SNI-SLAM | 8.3 | 9.9 | 9.2 | 10.1 | 5.5 | 8.55 | 90% |
| Sem-SLAM | 8.0 | 9.0 | 8.1 | 8.6 | 7.8 | 8.0 | 92% |
| Methods | Param | Memory | Slam FPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| NIDS-SLAM | 12.5 M | 1.5 GB | 1.8 |
| SNI-SLAM | 6.3 M | 1.1 GB | 2.12 |
| Sem-SLAM | 8.2 M | 1.3 GB | 2.2 |
| Replica | ScanNet | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATE ↓ | mIOU ↑ | ATE ↓ | mIOU ↑ | |
| 20.59 | 60.51 | 22.54 | 63.24 | |
| 17.52 | 67.48 | 14.35 | 70.45 | |
| 9.47 | 78.25 | 8.53 | 80.56 | |
| Noise Type | Noise Level | Replica mIoU | ScanNet mIoU |
|---|---|---|---|
| No Noise | 0 | 78.25 | 80.56 |
| Gaussian | 0.1 | 75.32 | 77.43 |
| Gaussian | 0.3 | 68.74 | 70.21 |
| Salt-and-Pepper | 0.1 | 74.18 | 76.39 |
| Salt-and-Pepper | 0.3 | 66.57 | 68.42 |
| Different Weight Combinations | Replica | ScanNet | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mIoU ↑ | ATE ↓ | mIoU ↑ | ATE ↓ | |
| Balance (, , , ) | 70.23 | 12.45 | 72.15 | 13.67 |
| sem-prior (, , , ) | 73.45 | 10.89 | 75.32 | 11.23 |
| depth-prior (, , , ) | 78.22 | 9.45 | 82.41 | 8.56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Hou, J. Sem-SLAM: Semantic-Integrated SLAM Approach for 3D Reconstruction. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7881. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147881
Liu S, Zhuang Y, Zhang C, Li Q, Hou J. Sem-SLAM: Semantic-Integrated SLAM Approach for 3D Reconstruction. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(14):7881. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147881
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shuqi, Yufeng Zhuang, Chenxu Zhang, Qifei Li, and Jiayu Hou. 2025. "Sem-SLAM: Semantic-Integrated SLAM Approach for 3D Reconstruction" Applied Sciences 15, no. 14: 7881. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147881
APA StyleLiu, S., Zhuang, Y., Zhang, C., Li, Q., & Hou, J. (2025). Sem-SLAM: Semantic-Integrated SLAM Approach for 3D Reconstruction. Applied Sciences, 15(14), 7881. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147881







