Non-Vertical Well Trajectory Design Based on Multi-Objective Optimization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Non-Vertical Well Trajectory Classification and Characteristics Analysis
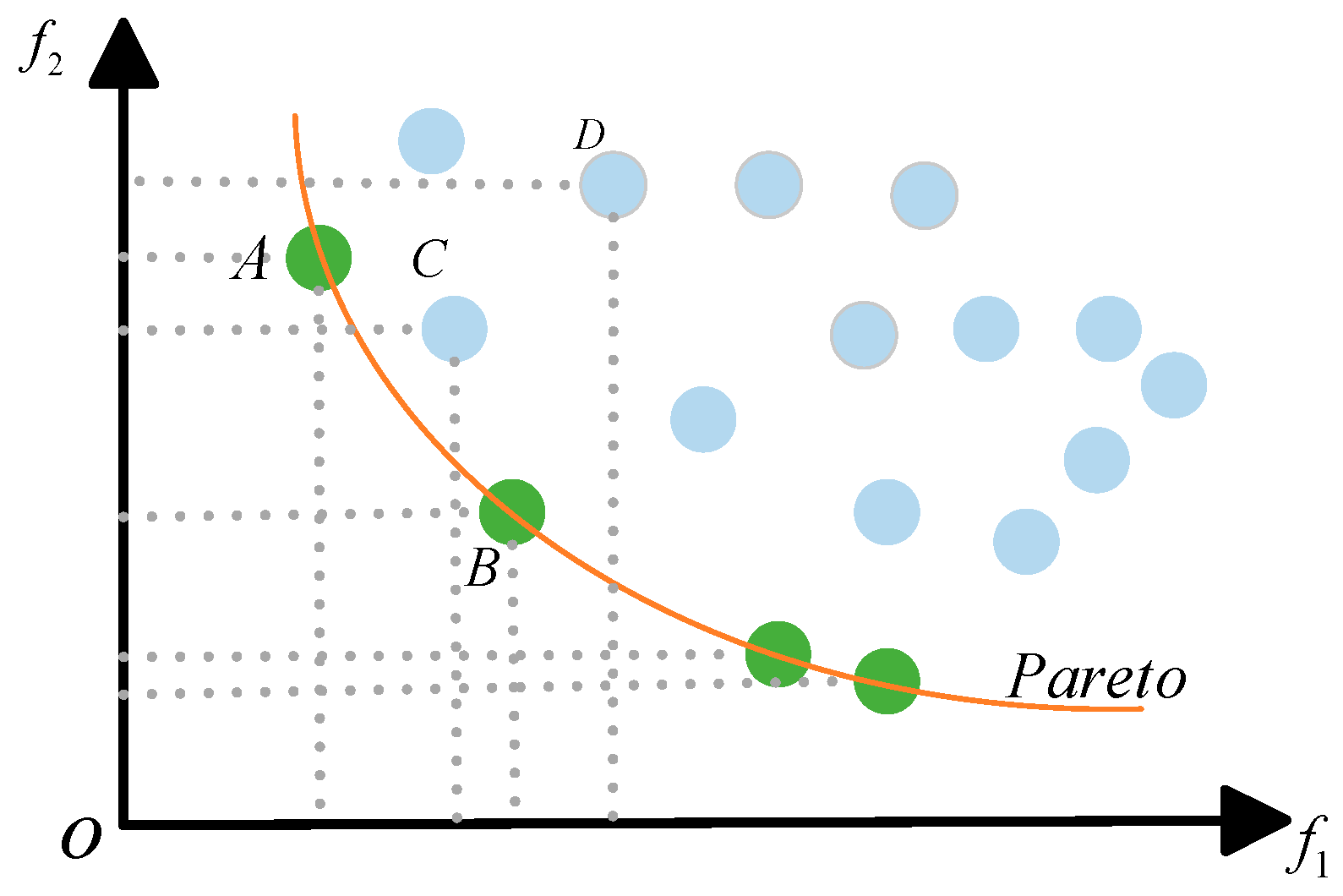
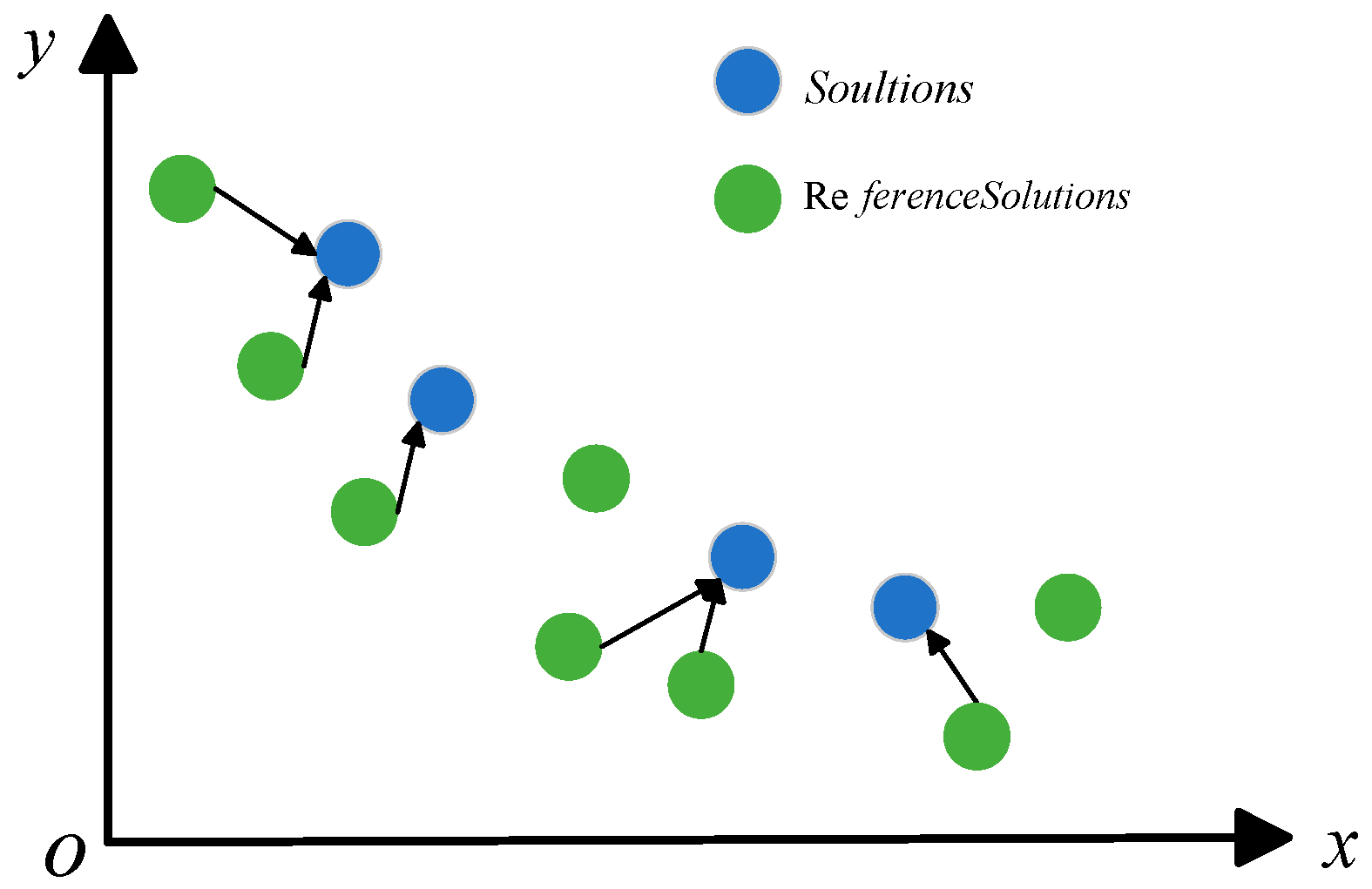
2.2. Theoretical Basis of Multi-Objective Optimization
3. Establishment of Optimization Model
3.1. Selection of Optimization Index
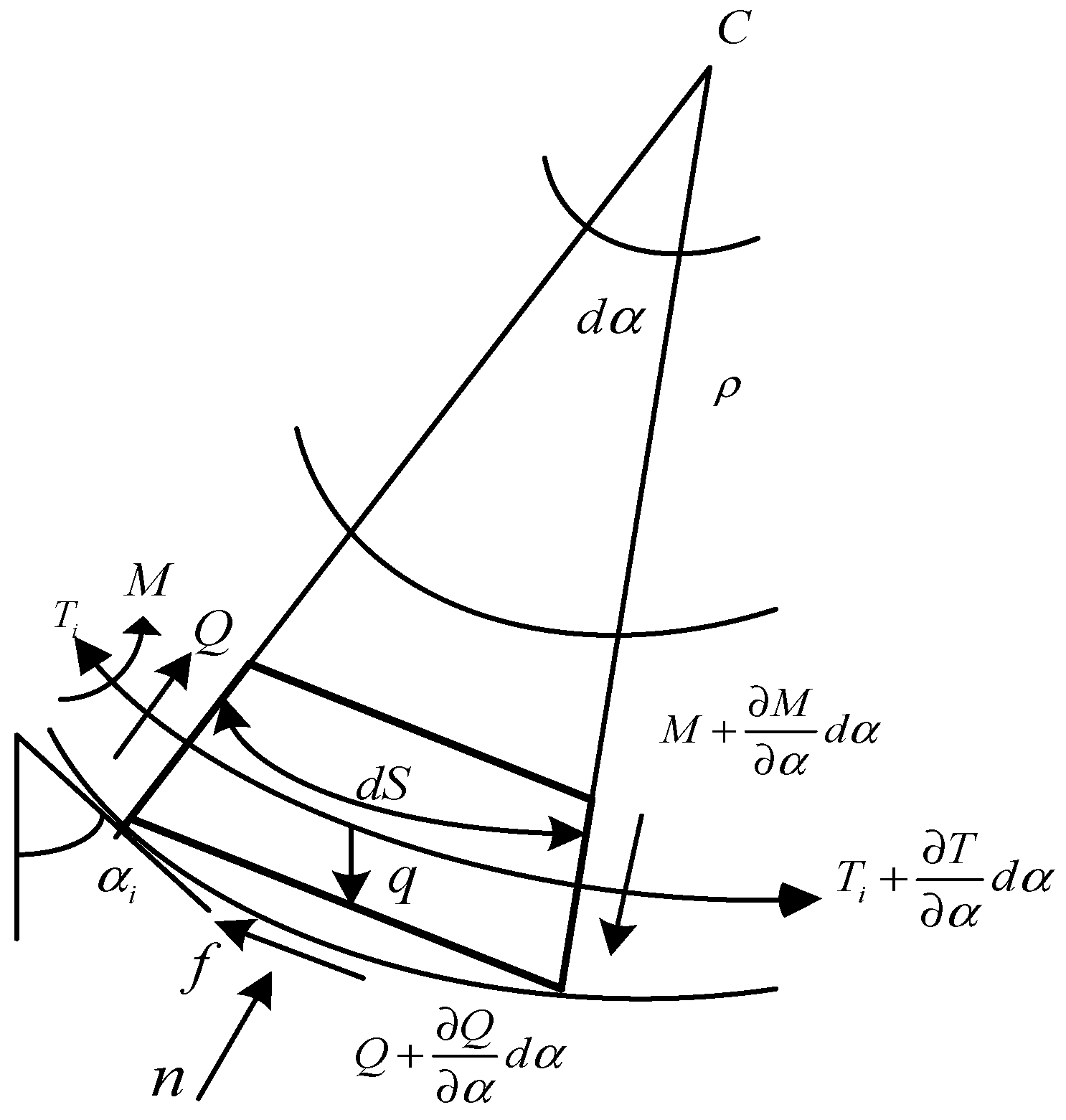
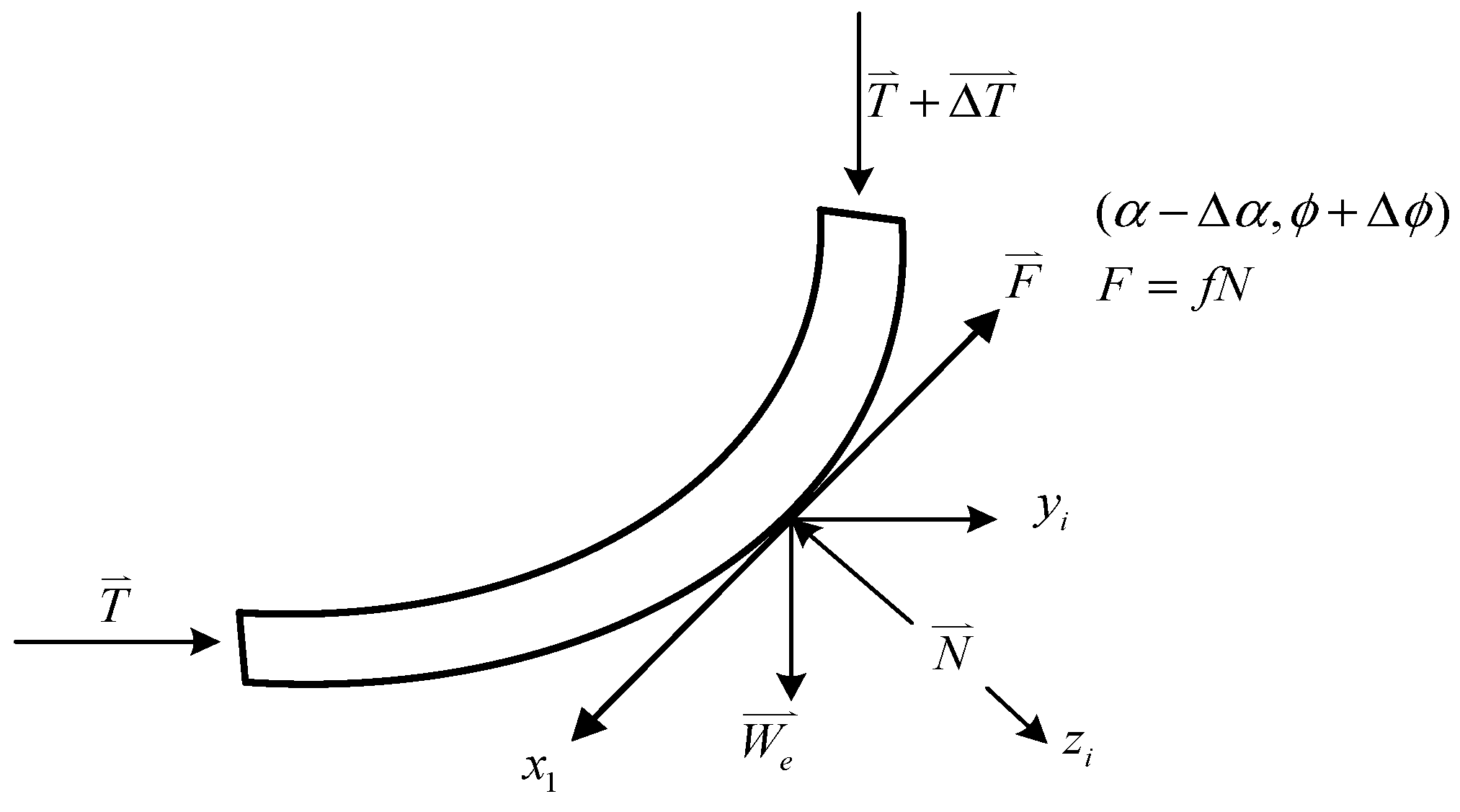
3.2. Objective Function Design
3.3. Constraint Conditions
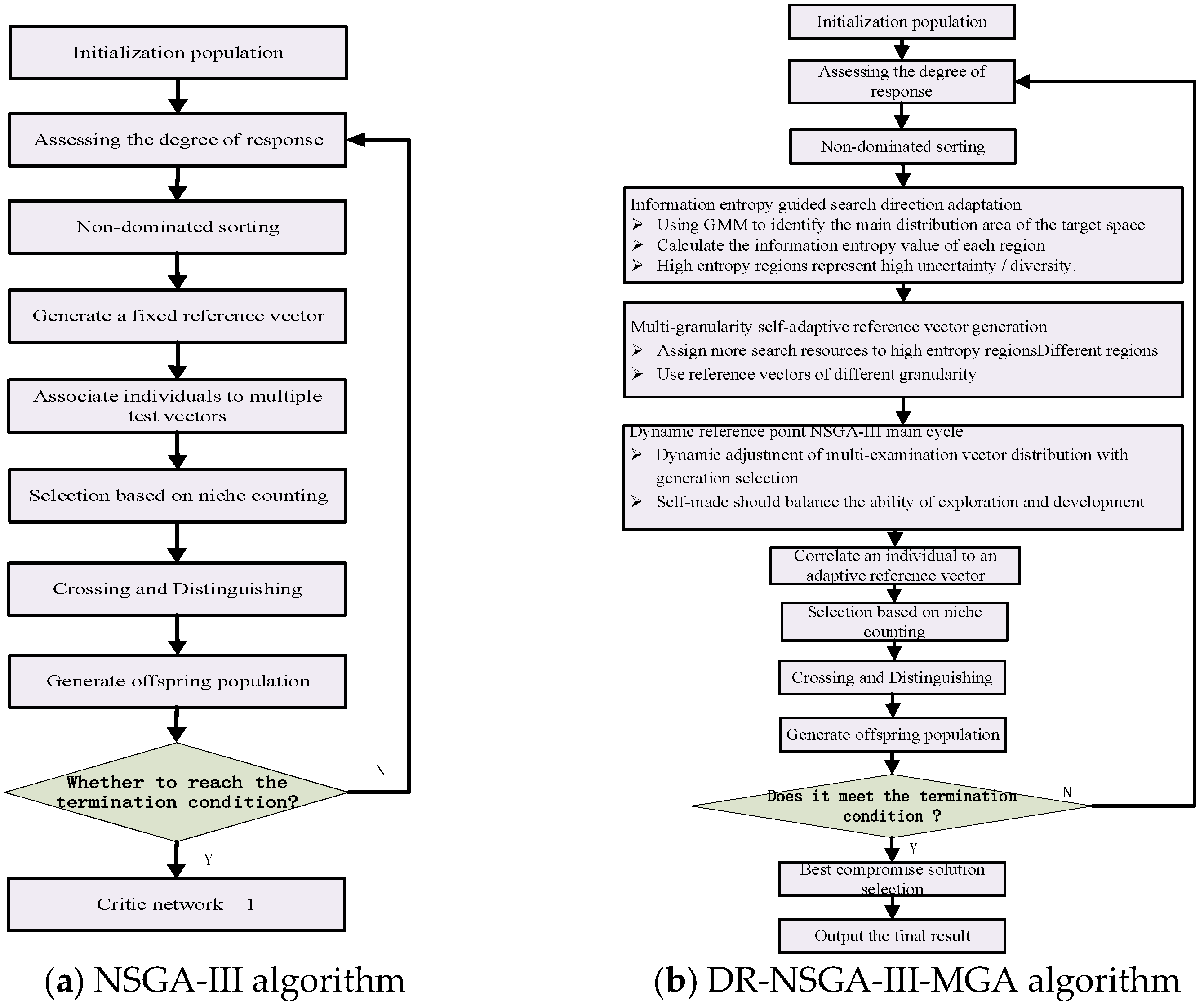
4. Information Entropy Guided Multi-Reference Vector NSGA-III Optimization Algorithm
4.1. Multi-Granularity Adaptive Reference Vector Generation
4.2. Dynamic Reference Point NSGA-III Main Cycle
4.3. Information Entropy Guided Search Direction Adaptation
5. Analysis of the Results
5.1. Experimental Results
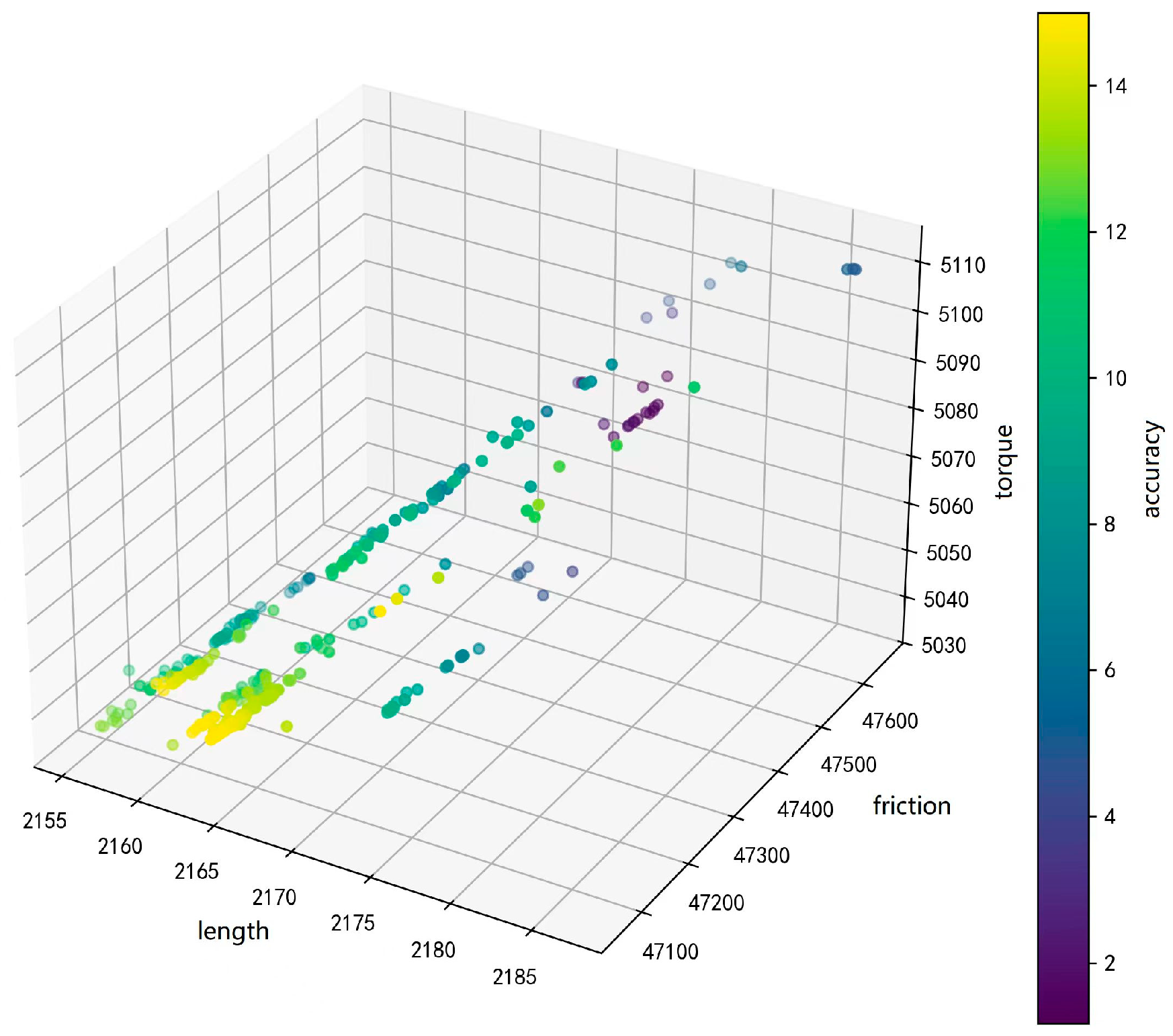
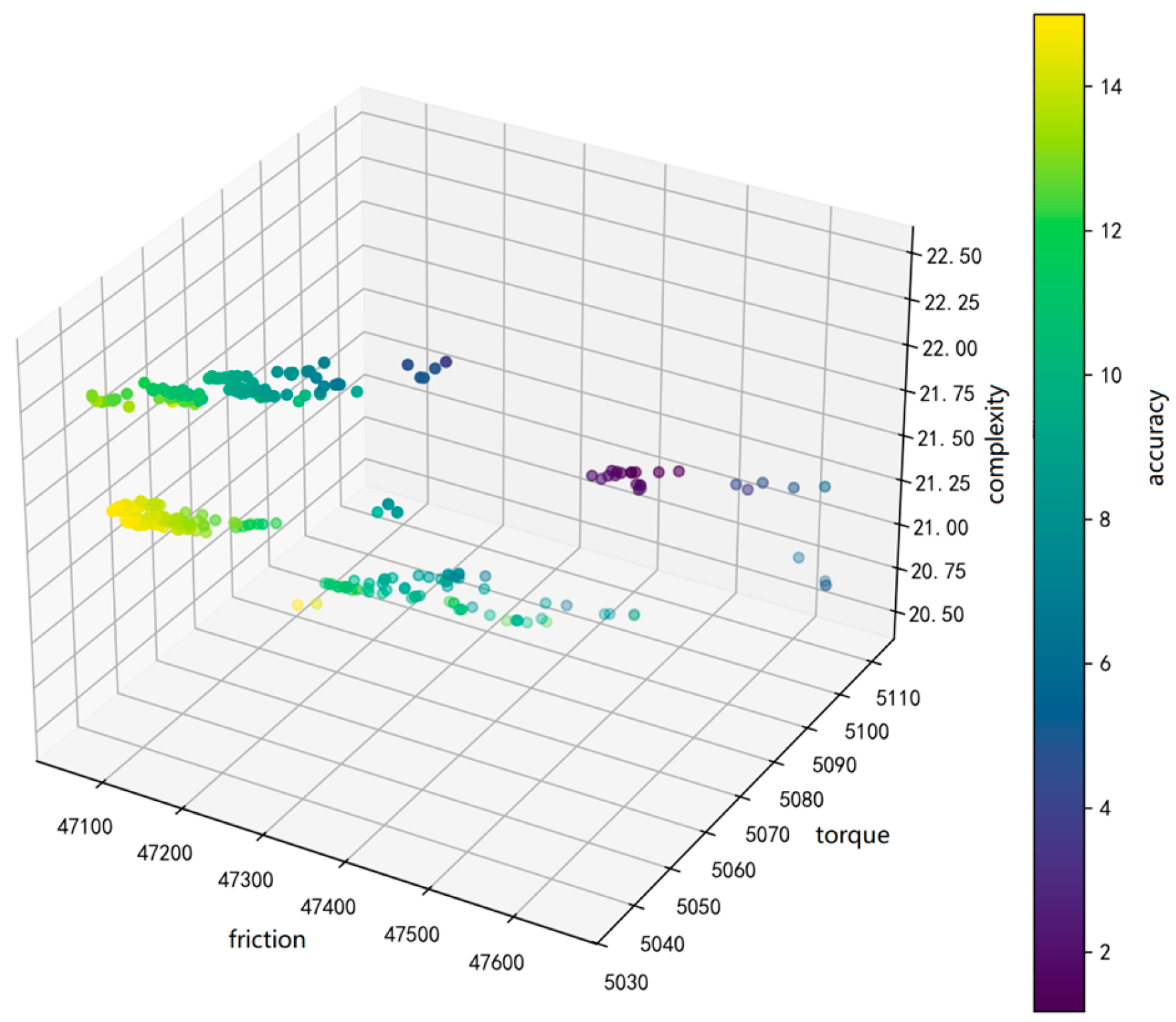
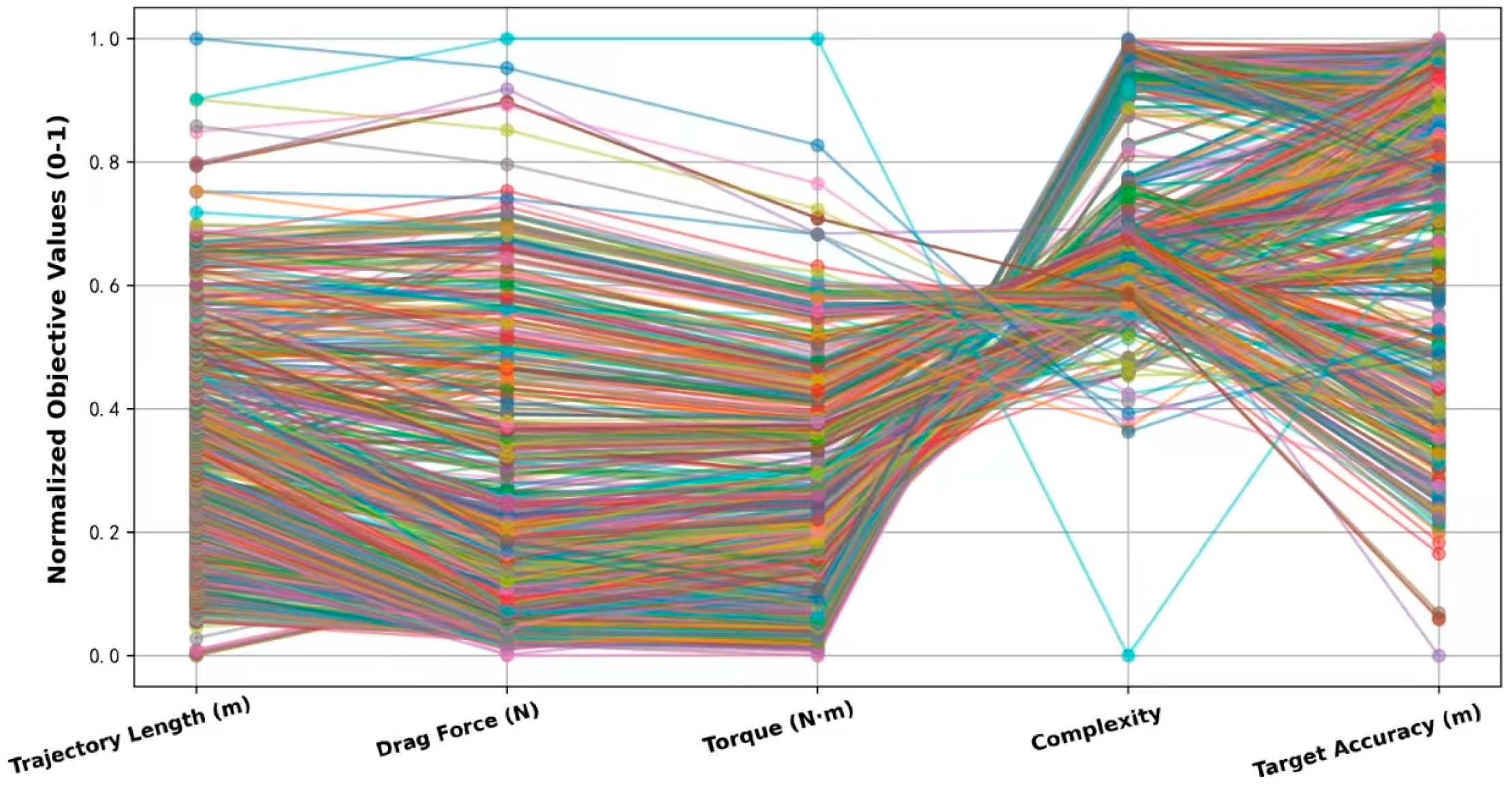
5.2. Pareto Front Visualization Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. List of Abbreviation
| Sign | Implication | Unit |
| Trajectory length equivalent function | ||
| , | The north coordinate increment of the inclined section and the stable section | |
| , | The east coordinate increment of the inclined section and the stable section | |
| , | The vertical depth increment of the inclined section and the stable section | |
| , , | Total friction, deflecting section friction, stabilizing section friction | |
| , , | Total torque, bit torque, deflection section, or deflection section micro segment torque | |
| coefficient of friction | ||
| Weight per unit length of drill string in mud | ||
| String diameter | ||
| Target N coordinate | ||
| Target E coordinate | ||
| Target D coordinate | ||
| shaft position | ||
| The north-south coordinate increment, east-west coordinate increment and vertical depth increment of the curve segment | ||
| The length of the ith curve segment | ||
| The minimum and maximum allowable length of the curve segment | ||
| Inclination starting end | ||
| kop depth | ||
| Deflecting end | ||
| Borehole curvature of in curve section | ||
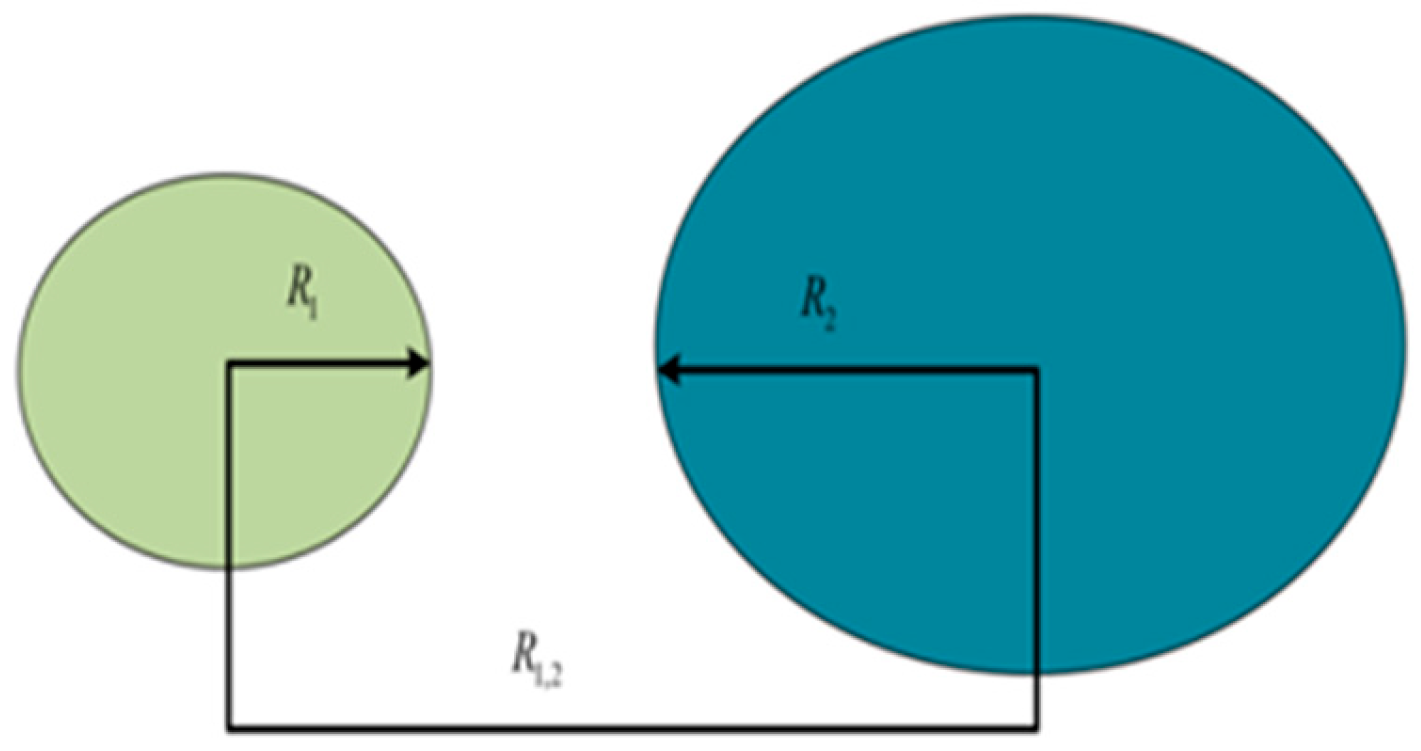
| Minimum separation coefficient value | ||
| The radius of curvature of the wellbore at the right end of the curve section | ||
| Length of stable inclined section | ||
| The deviation angle at the end of the deviation at the right end of the curve segment | ||
| The azimuth angle of the end of the deflection at the right end of the curve segment | ||
| Upper and lower limits of borehole curvature | ||
| The upper and lower limits of the depth of the oblique point | ||
| Upper and lower limits of well deviation angle | ||
| The upper and lower limits of azimuth angle | ||
| The upper and lower limits of the length of the inclined section | ||
| Upper and lower limits of borehole angle change rate | ||
| Track complexity | ||
| target accuracy |
Appendix B
| Algorithm A1: EISDA-NSGA-III |
| Input: Objective function f(x) Constraints g(x) Population size N Maximum generation G_maxOutput: Pareto optimal solution set ABegin // Step 1: Initialization 1. Set M = 5 // Objectives: length, friction, torque, complexity, accuracy 2. Initialize population P(0) = {x_1, x_2,…, x_N} 3. Initialize dynamic reference vector generator EISDA 4. Initialize non-dominated archive A = ∅ // Step 2: Evaluate initial population For each individual x_i in P(0): Evaluate objective values: f(x_i) If constraints g(x_i) violated: Apply penalty to f(x_i) // Step 3: Main loop For g = 1 to G_max: // a: Dynamic reference vector generation R_g = EISDA.generate_vectors(P(g−1), g, G_max) // b: Generate offspring Q(g) = Variation(P(g−1)) // Selection, Crossover, Mutation // c: Evaluate offspring For each individual q_i in Q(g): Evaluate objective values: f(q_i) If constraints g(q_i) violated: Apply penalty to f(q_i) // d: Combine populations C(g) = P(g − 1) ∪ Q(g) // e: Environmental selection P(g) = Select(C(g), R_g) // Reference-vector-based non-dominated sorting // f: Update non-dominated archive A = update_non_dominated(A, P(g)) // g: Record statisticsEnd For // Step 4: Post-processing Best_solution = TOPSIS(A) Visualize Pareto_front(A) Plot trajectory(Best_solution) // Step5: Save results Return A End Algorithm |
References
- Liu, Y.; Lian, P.; Tong, D.; Tian, J. Horizontal section length optimization design for horizontal wells using genetic algorithms. Acta Pet. Sin. 2008, 29, 296–299. [Google Scholar]
- Almedallah, M.K.; Al Mudhafar, A.A.; Clark, S.; Walsh, S.D. Vector-based three-dimensional (3D) well-path optimization assisted by geological modelling and borehole-log extraction. Upstream Oil Gas Technol. 2021, 7, 100053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, L.X.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Li, L.; Qiu, S. Complex Wellbore Trajectory Optimization Method Based on Fast Adaptive Quantum Genetic Algorithm. CN Patent 201710132117, 6 November 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, L.; Pan, Z. FSQGA-based 3D complexity wellbore trajectory optimization. Oil Gas Sci. Technol.-Rev. d’IFP Energ. Nouv. 2018, 73, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein, Y.; Jafar, Q.; Sigve, B.A.; Khosravanian, R. Selection of optimal well trajectory using multi-objective genetic algorithm and TOPSIS method. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 16831–16855. [Google Scholar]
- Davudov, D.; Odi, U.; Gupta, A.; Singh, G.; Dindoruk, B.; Venkatraman, A.; Osei, K. Hybrid machine learning framework for multi-well trajectory optimization in an unconventional field. Gas Sci. Eng. 2024, 131, 205443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95—International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H. Research on Optimization Design and Decision-Making Analysis of Nonlinear Well Trajectory. Master’s Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Atashnezhad, A.; Wood, D.A.; Fereidounpour, A.; Khosravanian, R. Designing and optimizing deviated wellbore trajectories using novel particle swarm algorithms. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2014, 21, 1184–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.F.; Yuan, Y. Borehole trajectory prediction and 3D visualization system development. Microcomput. Appl. 2017, 33, 65–67+71. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Mang, H.; Sun, T.; Song, Z.; Gao, D. Method for designing the optimal trajectory for drilling a horizontal well based on particle swarm optimization (PSO) and analytic hierarchy process (AHP). Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2019, 55, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, K.; Vasant, P.M.; Vintaned, J.A.G.; Watada, J. Cellular automata-based multi-objective hybrid Grey Wolf Optimization and particle swarm optimization algorithm for wellbore trajectory optimization. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2021, 85, 103695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefzadeh, R.; Sharifi, M.; Karkevandi-Talkhooncheh, A.; Ahmadi, H.; Farasat, A.; Ahmadi, M. Application of fast marching method and quality map to well trajectory optimization with a novel well parametrization. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 231, 212301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, M.; Maniezzo, V.; Colorni, A. Ant system: Optimization by a colony of cooperating agents. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B (Cybern.) 1996, 26, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.H.; Li, G.; Yuan, S.C. Chaos-based ant colony hybrid optimization method. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2011, 47, 42–45+102. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.J.; Huang, B.C.; Zhang, M. Function optimization with hybrid and improved ant colony algorithm. CAAI Trans. Intell. Syst. 2012, 7, 370–376. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Wu, X.J. Research on the application of ant colony optimization algorithm in WSN routing. Comput. Eng. Sci. 2015, 37, 740–746. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.Y. Research on the Application of Ant Colony Algorithm in Wellbore Trajectory Planning. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an Shiyou University, Xi’an, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mansouri, V.; Khosravanian, R.; Wood, D.A.; Aadnoy, B.S. 3D well path design using a multi-objective genetic algorithm. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 27, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guria, C.; Goli, K.K.; Pathak, A.K. Multi-objective optimization of oil well drilling using elitist non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm. Pet. Sci. 2014, 11, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.D.; Wu, M.; Cheng, J.; Chen, X.; Cao, W.; Hu, Y.; Gao, H. Multi-objective drilling trajectory optimization based on NSGA-II. In Proceedings of the 2017 11th Asian Control Conference (ASCC), Gold Coast, QLD, Australia, 17–20 December 2017; IEEE: Gold Coast, QLD, Australia, 2017; pp. 1234–1239. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Lu, C.; Gao, L. Multi-objective cellular particle swarm optimization for wellbore trajectory design. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 77, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.H.; Wen, G.J.; He, X. Application of adaptive grid-based multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm for directional drilling trajectory design. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 222, 211431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, L.X.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, Q.Z. Complex Wellbore Trajectory Optimization Method Based on Improved Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. CN Patent 201910410779.7, 17 August 2019. Available online: https://www.xjishu.com/zhuanli/54/201910410779.html (accessed on 8 July 2025).
- Yin, H.U.; Fan, T.; Zhao, X.; Li, Q. Multi-objective intelligent dynamic optimization design for well trajectory while drilling in horizontal wells. Res. Sq. 2024, preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Z.; Chen, T.; Liao, H. Theory and Technology of Drilling Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.F. Research on Intelligent Design and Optimization Method of Wellbore Trajectory; Yangtze University: Jingzhou, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Collette, Y.; Siarry, P. Multiobjective Optimization: Principles and Case Studies; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gunantara, N. A review of multi-objective optimization: Methods and its applications. Cogent Eng. 2018, 5, 1502242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, K. Nonlinear Multiobjective Optimization; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bezerra, L.C.T.; López-Ibáñez, M.; Stützle, T. An empirical assessment of the properties of inverted generational distance on multi-and many-objective optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Evolutionary Multi-criterion Optimization, Münster, Germany, 19–22 March 2017; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 31–45. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, H.Q.; Huang, G.L. Friction and torque prediction and analysis of Kendong 405-Ping 1 extended-reach well. Pet. Drill. Tech. 2007, 35, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Riegert, R.; Bagheri, M.; Krosche, M.; Kueck, N.; Ma, D. Multiple-objective optimization applied to well path design under geological uncertainty. In Proceedings of the SPE Reservoir Simulation Symposium. Society of Petroleum Engineers, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 21–23 February 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Samuel, G.R. Ultra-extended-reach drilling (u-ERD: Tunnel in the Earth)—A new well-path design. In Proceedings of the SPE/IADC Drilling Conference and Exhibition, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 17–19 March 2009; SPE: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2009. SPE-119459-MS. [Google Scholar]



| Serial Number | North | East | Height | Serial Number | North | East | Height |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 319.99 | 262.92 | 776.75 |
| 2 | 1.38 | 1.14 | 412.66 | 19 | 375.20 | 308.29 | 778.73 |
| 3 | 5.52 | 4.54 | 450.19 | 20 | 430.42 | 353.65 | 780.72 |
| 4 | 12.37 | 10.17 | 487.05 | 21 | 485.63 | 399.02 | 782.70 |
| 5 | 21.89 | 17.98 | 522.91 | 22 | 540.84 | 444.39 | 784.68 |
| 6 | 33.97 | 27.91 | 557.45 | 23 | 596.06 | 489.76 | 786.66 |
| 7 | 48.51 | 39.86 | 590.36 | 24 | 651.27 | 535.12 | 788.64 |
| 8 | 65.39 | 53.73 | 621.35 | 25 | 706.49 | 580.49 | 790.63 |
| 9 | 84.45 | 69.39 | 650.13 | 26 | 761.70 | 625.86 | 792.61 |
| 10 | 105.53 | 86.71 | 676.46 | 27 | 816.92 | 671.22 | 794.59 |
| 11 | 128.43 | 105.52 | 700.11 | 28 | 872.13 | 716.59 | 796.57 |
| 12 | 152.95 | 125.67 | 720.85 | 29 | 927.35 | 761.96 | 798.55 |
| 13 | 178.87 | 146.97 | 738.50 | 30 | 982.56 | 807.33 | 800.54 |
| 14 | 205.97 | 169.24 | 752.91 | 31 | 1037.77 | 852.69 | 801.52 |
| 15 | 233.99 | 192.26 | 763.95 | 32 | 1092.99 | 898.06 | 802.50 |
| 16 | 262.70 | 215.85 | 771.51 | 33 | 1148.20 | 943.43 | 803.48 |
| 17 | 291.82 | 239.78 | 775.54 | 34 | 1203.42 | 988.79 | 804.46 |
| Parameters | KOP(m) | Deviation Angle | Azimuth | Build Angle Rate | Length of Stable Inclined Section | Total Length of Wellbore Trajectory |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimization results | 374.79 ± 2.15 | 88.41 ± 0.32 | 39.41 ± 0.27 | 4.28 ± 0.15 | 1167.66 ± 8.42 | 2161.93 ± 5.27 |
| Algorithm | IGD | HV | Spacing |
|---|---|---|---|
| DR-NSGA-III-MGA | 0.082 ± 0.005 | 0.891 ± 0.012 | 0.063 ± 0.004 |
| MOEA/D | 0.115 ± 0.008 | 0.823 ± 0.015 | 0.087 ± 0.006 |
| SPEA2 | 0.103 ± 0.007 | 0.856 ± 0.013 | 0.079 ± 0.005 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hou, Z.; Gu, H. Non-Vertical Well Trajectory Design Based on Multi-Objective Optimization. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7862. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147862
Li X, Li Y, Wu Y, Hou Z, Gu H. Non-Vertical Well Trajectory Design Based on Multi-Objective Optimization. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(14):7862. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147862
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaowei, Yu Li, Yang Wu, Zhaokai Hou, and Haipeng Gu. 2025. "Non-Vertical Well Trajectory Design Based on Multi-Objective Optimization" Applied Sciences 15, no. 14: 7862. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147862
APA StyleLi, X., Li, Y., Wu, Y., Hou, Z., & Gu, H. (2025). Non-Vertical Well Trajectory Design Based on Multi-Objective Optimization. Applied Sciences, 15(14), 7862. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147862






