Computational Pharmacology Analysis of Lycopene to Identify Its Targets and Biological Effects in Humans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identifying Targets of Lycopene
2.2. Assessing the Targetability Potential of Lycopene Targets
2.3. Evaluating Protein–Protein Interactions Between Lycopene Targets
2.4. Analysing Tissue-Specific Protein Expression of Lycopene Targets in Humans
3. Results
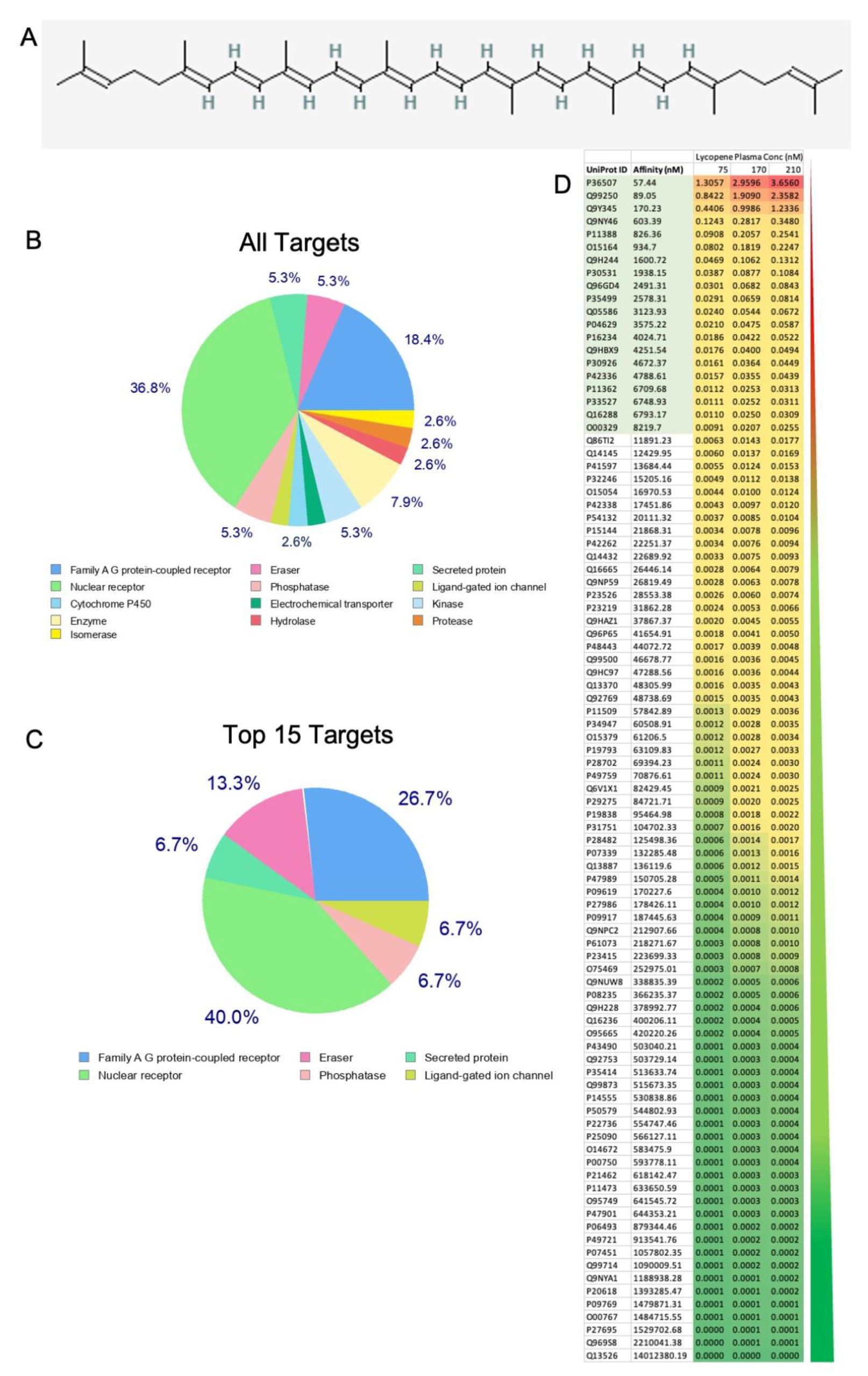
3.1. Categories and Specific Targets of Lycopene in Humans
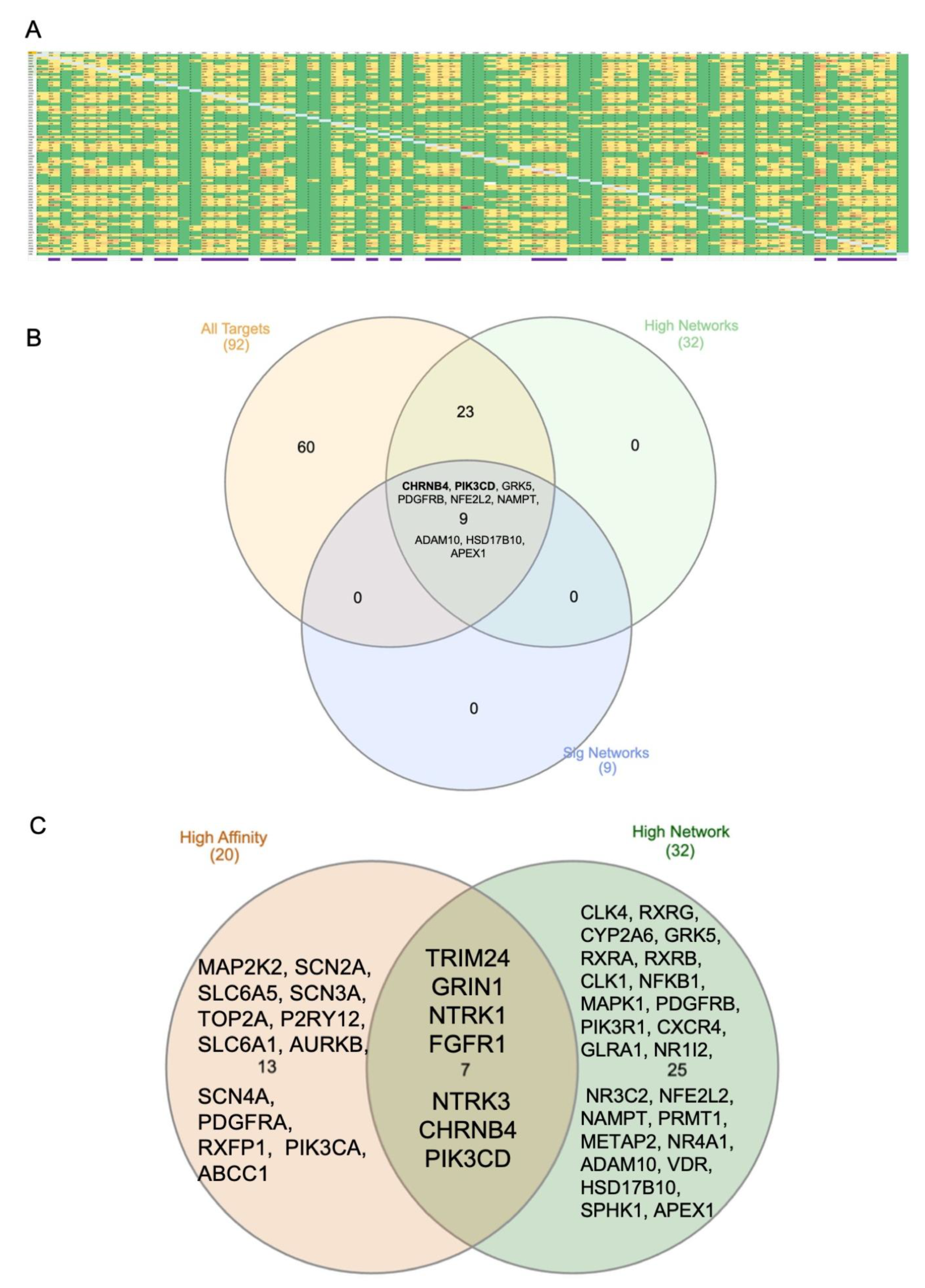
3.2. Computational Analysis of Lycopene Targets
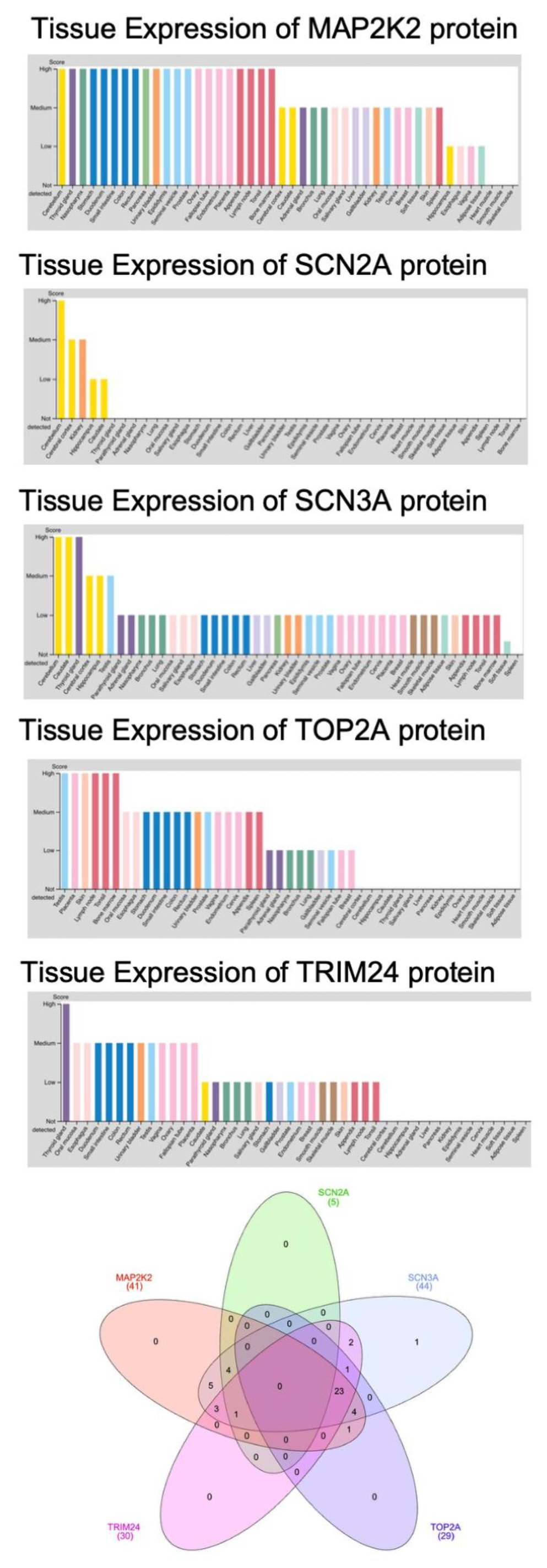
3.3. Expression Pattern of Lycopene Targets in Human Tissues
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giovannucci, E.; Rimm, E.B.; Liu, Y.; Stampfer, M.J.; Willett, W.C. A Prospective Study of Tomato Products, Lycopene, and Prostate Cancer Risk. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Waseem, Z.; Agarwal, S. Lycopene content of tomatoes and tomato products and their contribution to dietary lycopene. Food Res. Int. 1998, 31, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerster, H. The potential role of lycopene for human health. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1997, 16, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, E.; Mishra, P.; Singh, P.; Mishra, N. Evidence and prospects of lycopene as powerful red superfood: Modern approach to food science. Curr. Tradit. Med. 2024, 10, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, S.; Riaz, M.; Shabbir, A.; Zia-Ul-Haq, M.; Alwakeel, S.S.; Bin-Jumah, M. Commercialization and Marketing Potential of Carotenoids. In Carotenoids: Structure and Function in the Human Body; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 799–826. [Google Scholar]
- Kulawik, A.; Cielecka-Piontek, J.; Czerny, B.; Kamiński, A.; Zalewski, P. The Relationship Between Lycopene and Metabolic Diseases. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przybylska, S.; Tokarczyk, G. Lycopene in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartsen, F. Beitrage zur Organischen Chemie. Chem. Zentra 1873, 4, 204–207. [Google Scholar]
- Camara Hurtado, R.M.; Cáceres, J.O.; Cámara Hurtado, M.; Manzoor, S.; Fernández Ruiz, V.; Sánchez Mata, M.C. New Developments in Lycopene Analysis by Spectroscopic and Chromatographic Techniques, Accompanied by Mathematical Modelling. In Proceedings of the XIII International Symposium on Processing Tomato, Sirmione, Italy, 8–11 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bergougnoux, V. The history of tomato: From domestication to biopharming. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 170–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Maguer, M.L. Lycopene in tomatoes: Chemical and physical properties affected by food processing. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2000, 40, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinton, S.K. Lycopene: Chemistry, biology, and implications for human health and disease. Nutr. Rev. 1998, 56, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Srivastava, A.K. Lycopene; chemistry, biosynthesis, metabolism and degradation under various abiotic parameters. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valacchi, G.; Pecorelli, A. Role of Scavenger Receptor B1 (SR-B1) in Improving Food Benefits for Human Health. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 16, 403–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussa, M.; Landrier, J.-F.; Reboul, E.; Ghiringhelli, O.; Coméra, C.; Collet, X.; Fröhlich, K.; Böhm, V.; Borel, P. Lycopene absorption in human intestinal cells and in mice involves scavenger receptor class B type I but not Niemann-Pick C1-like 1. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1432–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arballo, J.; Amengual, J.; Erdman, J.W., Jr. Lycopene: A critical review of digestion, absorption, metabolism, and excretion. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botham, K.M.; Bravo, E. Lycopene and Chylomicrons. In Lycopene; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 159–182. [Google Scholar]
- Gustin, D.M.; Rodvold, K.A.; Sosman, J.A.; Diwadkar-Navsariwala, V.; Stacewicz-Sapuntzakis, M.; Viana, M.; Crowell, J.A.; Murray, J.; Tiller, P.; Bowen, P.E. Single-dose pharmacokinetic study of lycopene delivered in a well-defined food-based lycopene delivery system (tomato paste-oil mixture) in healthy adult male subjects. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2004, 13, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, S.; Sharma, S.; Goyal, P.K. Updates on the Anticancer Profile of Lycopene and its Probable Mechanism Against Breast and Gynecological Cancer. Nat. Prod. J. 2025, 24, e22103155331365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, G.; Günal-Köroğlu, D.; Karadag, A.; Capanoglu, E.; Cardoso, S.M.; Al-Omari, B.; Calina, D.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Cho, W.C. A mechanistic updated overview on lycopene as potential anticancer agent. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.M.; Sevindik, M.; Zarrabi, A.; Nami, M.; Ozdemir, B.; Kaplan, D.N.; Selamoglu, Z.; Hasan, M.; Kumar, M.; Alshehri, M.M. Lycopene: Food sources, biological activities, and human health benefits. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 2713511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heber, D.; Lu, Q.-Y. Overview of mechanisms of action of lycopene. Exp. Biol. Med. 2002, 227, 920–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozos, I.; Stoian, D.; Caraba, A.; Malainer, C.; Horbańczuk, J.O.; Atanasov, A.G. Lycopene and vascular health. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Ku, S.-K.; Bae, J.W.; Bae, J.-S. Inhibitory effects of lycopene on HMGB1-mediated pro-inflammatory responses in both cellular and animal models. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 1826–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prema, A.; Janakiraman, U.; Manivasagam, T.; Thenmozhi, A.J. Neuroprotective effect of lycopene against MPTP induced experimental Parkinson’s disease in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 599, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Chauhan, S.; Sandhir, R. Protective effect of lycopene on oxidative stress and cognitive decline in rotenone induced model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem. Res. 2011, 36, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palozza, P.; Simone, R.; Catalano, A.; Parrone, N.; Monego, G.; Ranelletti, F.O. Lycopene regulation of cholesterol synthesis and efflux in human macrophages. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2011, 22, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özmen, Ö.; Şahïn, M.; Topsakal, Ş.; Taşan, Ş.; Şahïn, U. Lycopene ameliorates diabetes-induced pancreatic, hepatic, and renal damage by modulating the JAK/STAT/SOCS signaling pathway in rats. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2025, 28, 461. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Dai, X.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Shi, H.; Yin, J.; Xu, T.; Zhu, R. Lycopene ameliorates islet function and down-regulates the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway in diabetic mice and Min6 cells. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 5090–5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, A.K.; Das, R.; Ray, A.K.; Mishra, S.K.; Anand, S. Recent insights on pharmacological potential of lycopene and its nanoformulations: An emerging paradigm towards improvement of human health. Phytochem. Rev. 2024, 24, 1091–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Ou, S.; Wu, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, H.; Jiang, M.; Xu, J.; Guo, K. Lycopene alleviates oxidative stress via the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2pathway in a cell model of Alzheimer’s disease. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assar, E.A.; Vidalle, M.C.; Chopra, M.; Hafizi, S. Lycopene acts through inhibition of IκB kinase to suppress NF-κB signaling in human prostate and breast cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 9375–9385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albadrani, G.M.; Altyar, A.E.; Kensara, O.A.; Haridy, M.A.; Sayed, A.A.; Mohammedsaleh, Z.M.; Al-Ghadi, M.Q.; Saleem, R.M.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Lycopene alleviates 5-fluorouracil-induced nephrotoxicity by modulating PPAR-γ, Nrf2/HO-1, and NF-κB/TNF-α/IL-6 signals. Ren. Fail. 2024, 46, 2423843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zhu, R.; Peng, J.; Liu, H.; Pan, W.; Jin, Y.; Pei, J.; Zhang, L. Molecular mechanisms and potential targets of lycopene for alleviating renal ischemia-reperfusion injury revealed by network pharmacology and animal experiments. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 143, 113421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzocco, S.; Singla, R.K.; Capasso, A. Multifaceted effects of lycopene: A boulevard to the multitarget-based treatment for cancer. Molecules 2021, 26, 5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. Lycopene inhibits activation of epidermal growth factor receptor and expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in gastric cancer cells. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.H. Network Proteins of Human Sortilin1, Its Expression and Targetability Using Lycopene. Life 2024, 14, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravi, Z.; Kumar, A.H. Analysing the role of SERPINE1 network in the pathogenesis of human glioblastoma. J. Cancer Res. 2023, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Friend, J.; Kumar, A.H.S. A Network Pharmacology Approach to Assess the Comparative Pharmacodynamics of Pharmaceutical Excipient Trehalose in Human, Mouse, and Rat. Nat. Cell Sci. 2023, 1, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.H. Pharmacological targets of Asundexian relevant to its therapeutic efficacy in treating cardiovascular diseases. Biol. Eng. Med. Sci. Rep. 2022, 8, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.K.; Dhanasekaran, M.; Kumar, A.H.S. Pharmacology of Berberine and Its Metabolites, Is It the Natures Ozempic or Imatinib? Arch. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 5, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrier, J.-F.; Breniere, T.; Sani, L.; Desmarchelier, C.; Mounien, L.; Borel, P. Effect of tomato, tomato-derived products and lycopene on metabolic inflammation: From epidemiological data to molecular mechanisms. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2023, 38, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puah, B.-P.; Jalil, J.; Attiq, A.; Kamisah, Y. New insights into molecular mechanism behind anti-cancer activities of lycopene. Molecules 2021, 26, 3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, T.; Bader Ul Ain, H.; Noreen, S.; Ikram, A.; Arshad, M.T.; Abdullahi, M.A. Nutritional benefits of lycopene and beta-carotene: A comprehensive overview. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 8715–8741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafe, M.O.; Gumede, N.M.; Nyakudya, T.T.; Chivandi, E. Lycopene: A Potent Antioxidant with Multiple Health Benefits. J. Nutr. Metab. 2024, 2024, 6252426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Chen, R.; Chen, J.; Yang, N.; Li, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R. Study of the anti-inflammatory mechanism of β-carotene based on network pharmacology. Molecules 2023, 28, 7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Yun, J.W. β-Carotene stimulates browning of 3T3-L1 white adipocytes by enhancing thermogenesis via the β3-AR/p38 MAPK/SIRT signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2022, 96, 153857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, N.E.; Thomas-Ahner, J.M.; Smith, J.W.; Silva, C.; Hason, N.A.; Erdman Jr, J.W.; Clinton, S.K. β-Carotene oxygenase 2 genotype modulates the impact of dietary lycopene on gene expression during early TRAMP prostate carcinogenesis. J. Nutr. 2022, 152, 950–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Wang, F.; Hu, J.; Duan, X.; Bai, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Su, Y.; Hu, J. Inhibitory interaction of flavonoids with organic cation transporter 2 and their structure–activity relationships for predicting nephroprotective effects. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2023, 43, 1421–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Sawarkar, S.; Doshi, G.; Pimple, P.; Shah, J.; Bana, T. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of nutraceuticals. Ind. Appl. Funct. Foods Ingred. Nutraceuticals 2023, 12, 725–783. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, D.; Koul, A.; Kaul, S.; Dhar, M.K. Tissue-specific transcriptional regulation and metabolite accumulation in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Protoplasma 2020, 257, 1093–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadou, E.C.; Antoniou, C.; Majak, I.; Goulas, V.; Filippou, P.; Smolińska, B.; Leszczyńska, J.; Fotopoulos, V. Tissue-specific elucidation of lycopene metabolism in commercial tomato fruit cultivars during ripening. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 284, 110144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves-Silva, S.; Xavier-de-Britto, I.; Gomes-da-Silva, N.C.; França, Á.R.S.; Pedrochi, F.; Queiroz, M.N.; Moura-Silva, J.; Majerowicz, D.; Ricci-Junior, E.; Ferreira, T.P.T. Enhancing therapeutic efficacy: In vivo mechanisms and biochemical effects of lycopene encapsulated in nanomicelles for acute inflammation and lipid metabolism. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2025, 207, 114585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Báo, S.N.; Machado, M.; Da Silva, A.L.; Melo, A.; Cunha, S.; Sousa, S.S.; Malheiro, A.R.; Fernandes, R.; Leite, J.R.S.; Vasconcelos, A.G. Potential biological properties of lycopene in a self-emulsifying drug delivery system. Molecules 2023, 28, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binsuwaidan, R.; Sultan, A.A.; Negm, W.A.; Attallah, N.G.; Alqahtani, M.J.; Hussein, I.A.; Shaldam, M.A.; El-Sherbeni, S.A.; Elekhnawy, E. Bilosomes as nanoplatform for oral delivery and modulated in vivo antimicrobial activity of lycopene. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y. Mechanisms of carotenoid intestinal absorption and the regulation of dietary lipids: Lipid transporter-mediated transintestinal epithelial pathways. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 1791–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhan, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Shang, X. Lycopene alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced testicular injury in rats by activating the PPAR signaling pathway to integrate lipid metabolism and the inflammatory response. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2023, 12, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrageiro, G.; Haylett, W.; Seedat, S.; Kuivaniemi, H.; Bardien, S. A review of genome-wide transcriptomics studies in Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018, 47, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, E.; Chmielecki, J.; Tang, C.-M.; Wang, K.; Heinrich, M.C.; Kang, G.; Corless, C.L.; Hong, D.; Fero, K.E.; Murphy, J.D. FGFR1 and NTRK3 actionable alterations in “Wild-Type” gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatu, A.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Siena, S. NTRK gene fusions as novel targets of cancer therapy across multiple tumour types. ESMO Open 2016, 1, e000023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appikonda, S.; Thakkar, K.N.; Barton, M.C. Regulation of gene expression in human cancers by TRIM24. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2016, 19, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambon, M.; Orsetti, B.; Berthe, M.-L.; Bascoul-Mollevi, C.; Rodriguez, C.; Duong, V.; Gleizes, M.; Thénot, S.; Bibeau, F.; Theillet, C. Prognostic significance of TRIM24/TIF-1α gene expression in breast cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, S.; Binko, M.A.; Mielnik, C.A.; Ramsey, A.J.; Lambe, E.K. Deficits in integrative NMDA receptors caused by Grin1 disruption can be rescued in adulthood. Neuropsychopharmacology 2023, 48, 1742–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Song, R.; Chen, W.; Strong, K.; Shrey, D.; Gedela, S.; Traynelis, S.F.; Zhang, G.; Yuan, H. Recurrent seizure-related GRIN1 variant: Molecular mechanism and targeted therapy. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2021, 8, 1480–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, R.; Ghiasi, M.; Mehdizadeh, S.; Mohammadi, J.; Mohammad Ganji, S. A comprehensive bioinformatic evaluation of the NTRK family’s potential as prognostic biomarkers in breast cancer. Bioinform. Adv. 2025, 5, vbaf030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stravodimou, A.; Voutsadakis, I.A. Neurotrophic receptor tyrosine kinase family members in secretory and non-secretory breast carcinomas. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 13, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becchetti, A.; Grandi, L.C.; Cerina, M.; Amadeo, A. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and epilepsy. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 189, 106698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, M.; Shimizu, D.; Nakamura, S.; Sawaki, K.; Umeda, S.; Miwa, T.; Tanaka, H.; Inokawa, Y.; Hattori, N.; Hayashi, M. Blockade of CHRNB2 signaling with a therapeutic monoclonal antibody attenuates the aggressiveness of gastric cancer cells. Oncogene 2021, 40, 5495–5504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labate, A.; Mumoli, L.; Fratto, A.; Quattrone, A.; Gambardella, A. Hippocampal sclerosis worsens autosomal dominant nocturnal frontal lobe epilepsy (ADNFLE) phenotype related to CHRNB2 mutation. Eur. J. Neurol. 2013, 20, 591–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, H.; Wen, J.; Li, D. PIK3CD correlates with prognosis, epithelial–mesenchymal transition and tumor immune infiltration in breast carcinoma. Discov. Oncol. 2023, 14, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.-R.; Lin, Q.-Y.; Adu, M.; Huang, H.-L.; Yan, Z.-H.; Shao, F.; Zhong, G.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Sang, Z.-P.; Cao, L. The sources, properties, extraction, biosynthesis, pharmacology, and application of lycopene. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 9974–9998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, A.W.K.; Choudhary, N.; Tewari, D.; El-Demerdash, A.; Tomczyk, M.; Das, N.; Pirgozliev, V.; Lucarini, M.; Durazzo, A.; Souto, E.B. Lycopene: Total-scale literature landscape analysis of a valuable nutraceutical with numerous potential applications in the promotion of human and animal health. Anim. Sci. Pap. Rep. 2022, 40, 119–134. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wei, M.; Shi, Q.; Yang, F. Integrated transcriptomics and metabolomics analyses reveal the molecular mechanisms of red-light on carotenoids biosynthesis in tomato fruit. Food Qual. Saf. 2022, 6, fyac009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Meng, Q.; Bai, Y.; Cao, C.; Li, J.; Cheng, B.; Shi, B.; Shan, A. Lycopene improves maternal reproductive performance by modulating milk composition and placental antioxidative and immune status. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 12448–12467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, M.; Barcelos, D.; Carapeto, F.C.L.; Cardili, L.; Comodo, A.N.; Mazloum, S.F.; Marins, M.M.; Mendes, A.R.; Pesquero, J.B.; Landman, G. Evaluation of Heterogeneity in the Coding Region of BRAF, MAP2K1, and MAP2K2 Genes in Primary and Metastatic Melanomas. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, S.; Ikegami, M.; Koyama, T.; Sunami, K.; Ogata, D.; Kage, H.; Yanagaki, M.; Ikeuchi, H.; Ueno, T.; Tanikawa, M. High-throughput functional evaluation of MAP2K1 variants in cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2023, 22, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzialla, C.; Arossa, A.; Mannarino, S.; Orcesi, S.; Veggiotti, P.; Fiandrino, G.; Zuffardi, O.; Errichiello, E. SCN2A and arrhythmia: A potential correlation? A case report and literature review. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2022, 65, 104639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadollahi, R.; Delvendahl, I.; Muff, R.; Tan, G.; Rodríguez, D.G.; Turan, S.; Russo, M.; Oneda, B.; Joset, P.; Boonsawat, P. Pathogenic SCN2A variants cause early-stage dysfunction in patient-derived neurons. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2023, 32, 2192–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunklaus, A.; Brünger, T.; Feng, T.; Fons, C.; Lehikoinen, A.; Panagiotakaki, E.; Vintan, M.-A.; Symonds, J.; Andrew, J.; Arzimanoglou, A. The gain of function SCN1A disorder spectrum: Novel epilepsy phenotypes and therapeutic implications. Brain 2022, 145, 3816–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, A.; Pour Abbasi, M.; Khorrami, S.; Khodamoradi, S.; Mohammadi Goldar, Z.; Ebrahimzadeh, F. The TRIM proteins in cancer: From expression to emerging regulatory mechanisms. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 24, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyson, S.P.; Gao, C.; Quinn, K.; Boyd, J.; Paculova, H.; Frietze, S.; Glass, K.C. Functional roles of bromodomain proteins in cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulawik, A.; Cielecka-Piontek, J.; Zalewski, P. The importance of antioxidant activity for the health-promoting effect of lycopene. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rao, A.; Kumar, A.H.S. Computational Pharmacology Analysis of Lycopene to Identify Its Targets and Biological Effects in Humans. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7815. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147815
Rao A, Kumar AHS. Computational Pharmacology Analysis of Lycopene to Identify Its Targets and Biological Effects in Humans. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(14):7815. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147815
Chicago/Turabian StyleRao, Abhinand, and Arun H. S. Kumar. 2025. "Computational Pharmacology Analysis of Lycopene to Identify Its Targets and Biological Effects in Humans" Applied Sciences 15, no. 14: 7815. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147815
APA StyleRao, A., & Kumar, A. H. S. (2025). Computational Pharmacology Analysis of Lycopene to Identify Its Targets and Biological Effects in Humans. Applied Sciences, 15(14), 7815. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147815






