Featured Application
This study elucidates the distribution characteristics of depositional systems associated with coal-rich and organic mudstone facies in the Lower-Middle Jurassic of the Kuqa Depression, as well as their controlling factors, to guide future hydrocarbon exploration.
Abstract
The Lower–Middle Jurassic of the Kuqa Depression consists of terrestrial clastic deposits containing coal seams and thick lacustrine mudstones, and is of great significance for oil and gas exploration. Based on the comprehensive analysis of core, well-logging, outcrop, and seismic data, the sequence stratigraphy, depositional systems, and the controlling factors of the basin filling in the depression are systematically documented. Four primary depositional systems, including braided river delta, meandering river delta, lacustrine, and swamp deposits, are identified within the Ahe, Yangxia, and Kezilenuer Formations of the Lower–Middle Jurassic. The basin fills can be classified into two second-order and nine third-order sequences (SQ1–SQ9) confined by regional or local unconformities and their correlative conformities. This study shows that the sedimentary evolution has undergone the following three stages: Stage I (SQ1–SQ2) primarily developed braided river, braided river delta, and shallow lacustrine deposits; Stage II (SQ3–SQ5) primarily developed meandering river, meandering river delta, and extensive deep and semi-deep lacustrine deposits; Stage III (SQ6–SQ9) primarily developed swamp (SQ6–SQ7), meandering river delta, and shore–shallow lacustrine deposits (SQ8–SQ9). The uplift of the Tianshan Orogenic Belt in the Early Jurassic (Stage I) may have facilitated the development of braided fluvial–deltaic deposits. The subsequential expansion of the sedimentary area and the weakened sediment supply can be attributed to the planation of the source area and widespread basin subsidence, with the transition of the depositional environments from braided river delta deposits to meandering river delta and swamp deposits. The regional expansion or rise of the lake during Stage II was likely triggered by the hot and humid climate conditions, possibly associated with the Early Jurassic Toarcian Oceanic Anoxic Event. The thick swamp deposits formed during Stage III may be controlled by the interplay of rational accommodation, warm and humid climatic conditions, and limited sediment supply. Milankovitch cycles identified in Stage III further reveal that coal accumulation was primarily modulated by long-period eccentricity forcing.
1. Introduction
Terrestrial lacustrine basins constitute a significant category of sedimentary basins, which typically exhibit multistage evolutionary processes characterized by distinct sedimentary filling patterns [1,2,3,4]. These processes archive the complex interplay of tectonic activity, climatic variation, sediment supply, and lake-level fluctuations, serving as essential archives for studying sedimentary dynamics, sequence stratigraphy, and hydrocarbon accumulation [5,6,7]. Therefore, clarifying the evolutionary process of terrestrial lacustrine basins is often a fundamental research priority. Studies have shown that the evolution of terrestrial lacustrine basins is mainly controlled by the tectonic–climatic coupling dynamics [2,8,9]. These two dominant controls operate across divergent spatiotemporal scales [10,11]. When tectonism acts as the predominant control, intense tectonic activity governs basin geometry and accommodation development while augmenting sediment input, typically forming large-scale coarse-grained deposits such as alluvial fans and braided river depositional systems [1,3,9]. During tectonic quiescence, climatically driven lake-level changes assume dominance in governing the development of high-frequency sequence stratigraphic architecture, manifesting as cyclical patterns of accommodation and sediment partitioning within basin filling, which exhibit marked divergence from those developed during active tectonic phases [2,8,9]. The formation and development of organic carbon-rich accumulation, such as deep and semi-deep lacustrine and swamp depositional systems, exhibit a genetic linkage with multistage evolutionary processes in the lacustrine basin. Climatic perturbations potentially trigger distinctive depositional responses [12,13,14]. These perturbations, typically manifested through enhanced precipitation under hot–humid conditions, induce lake expansion and the formation of deep and semi-deep lacustrine deposits [15,16,17]. Under relatively stable tectonic conditions, warm and humid climates drive prolific vegetation growth, thus suppressing coarse clastic influx into the catchment while fostering the development of swamp deposits [16,17]. The linkage between Milankovitch-scale astronomical cycles and coal-bearing strata has gained substantial traction in sedimentological research, with climatic perturbations modulated by orbital eccentricity being recognized as primary controls on peat accumulation through precipitation-driven lacustrine level high-frequency oscillations [18,19].
The Tarim Basin represents a critical petroliferous basin located in northwestern China, where the Kuqa Depression serves as one of its most significant petroleum exploration areas. The Lower–Middle Jurassic in this depression contains extensively dis-tributed coal seams and dark-gray thick mudstones that constitute vital source rock intervals [20,21,22]. Consequently, elucidating the sedimentary filling patterns of the Lower–Middle Jurassic and clarifying the depositional systems distributions controlling coal-rich and organic mudstone-dominated facies is crucial for guiding hydrocarbon exploration in the future. Previous investigations have predominantly focused on depositional system identification, yet interpretations remain relatively generalized and subject to ongoing debate [5,23,24,25,26]. Meanwhile, there is no dissection regarding the spatial distribution of these depositional systems and detailed evolutionary processes of lacustrine basin staged filling. Comprehensive systematic analyses of the main controls on lacustrine basin evolution in the study area remain notably absent.
This study integrates outcrop, well-log, core, seismic, and geochemical data to resolve existing ambiguities and controversies regarding the sedimentary system types in the study area. It systematically delineates the types, distribution, and vertical evolution of the Lower–Middle Jurassic sedimentary systems under the sequence framework in the Kuqa Depression. Furthermore, by reconstructing the tectonic and climatic evolution, this study elucidates the controlling effects of tectonic activity and climatic conditions on sedimentary evolution, particularly on the development of coal-rich and organic-rich mudstone depositional systems.
2. Geological Setting
The Tarim Basin, the largest superimposed basin in China (Figure 1A), is primarily composed of a Paleozoic marine cratonic basin and Mesozoic–Cenozoic continental foreland basin [27,28]. It is divided into the following seven major tectonic units: the Kuqa Depression, Tabei Uplift, Northern Depression, Central Uplift, Southwest Depression, Southeast Uplift, and Southeast Depression (Figure 1B). The Kuqa Depression, trending NEE, is located in the northern part of the basin, bordered by the South Tianshan Mountains to the north and the Tabei Uplift to the south. This structurally complex region is rich in oil and gas resources, making it a focus of academic and industrial interest [29,30,31,32].
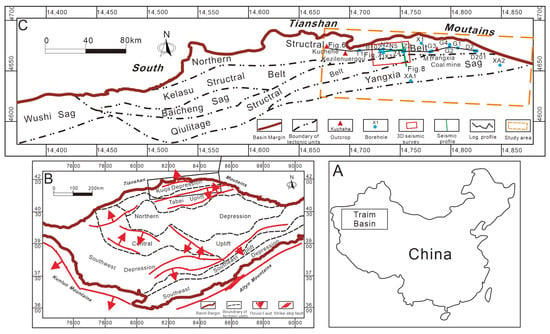
Figure 1.
(A) Diagram showing the location of the Tarim Basin; (B) Tectonic map of the Tarim Basin showing the location of the study area and tectonic features; (C) Map of structural units of Kuqa Depression showing data and figure location of the study area.
Thrust and strike-slip faults subdivide the Kuqa Depression into the following six secondary structural units: the Northern Structural Belt, Kelasu Structural Belt, Qiulitage Structural Belt, Yangxia Sag, Baicheng Sag, and Wushi Sag (Figure 1C). This study focuses on the Yangxia Sag and the eastern parts of the Northern Structural Belt and Qiulitage Structural Belt. The Jurassic in the Kuqa Depression is stratigraphically divided into, from bottom to top, the Lower Jurassic Ahe Formation and Yangxia Formation, the Middle Jurassic Kezilenuer Formation and Qiakemake Formation, and the Upper Jurassic Qigu Formation and Kalazha Formation (Figure 2) [27,33,34]. The Kalazha Formation is restricted to outcrops along the northern basin margin. This study targets the Ahe Formation, Yangxia Formation, and Kezilenuer Formation. The Ahe Formation, composed predominantly of conglomerates, pebbly sandstones, and medium-to-coarse-grained sandstones with minor mudstones and coal seams, is characterized by braided fluvial–delta depositional systems. The Yangxia Formation, comprising pebbly sandstones, medium-to-coarse-grained sandstones, coal seams, and dark-gray mudstones, primarily developed meandering river delta, lacustrine, and braid river delta systems. The Kizilenuer Formation, dominated by coal seams, pebbly sandstones, medium-to-fine-grained sandstones, gray mudstones, and carbonaceous mudstones, is interpreted as hosting swamp, meandering river delta, and shore–shallow lacustrine depositional systems.
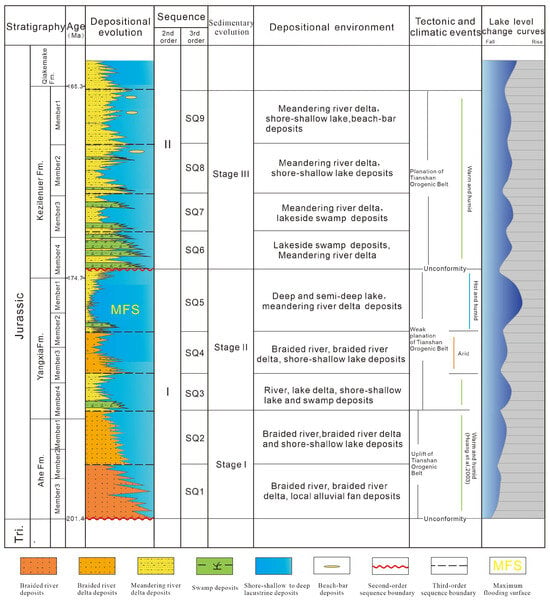
Figure 2.
Sequence classification and depositional evolution of the Jurassic in the Kuqa depression.
3. Data and Methods
The dataset used in this study comprises a 3D seismic survey covering 1100 km2 in the eastern Northern Structural Belt, supplemented by 2D seismic profiles, data from 24 boreholes, three outcrop sections (Kuchehe, Kezilenuergou, and Yangxia Coal Mine), and 507 m of cores. A total of 35 mudstone samples were collected from the Yangxia and Kezilenuer Formations at the Kuchehe outcrop. Comprehensive geochemical testing of these samples was performed by Beijing Craton Rock Innovation Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China), providing detailed major and trace element compositional data. Major elements were quantified using X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF), while trace elements were analyzed by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS).
Lithofacies classification is based on sedimentary structures, grain size, lithology, and color. Lithofacies associations and seismic facies were identified by analyzing core data, well-logging characteristics, and calibrated seismic data to elucidate features of the depositional systems. Seismic facies are also useful to explain the architecture and distribution of the depositional systems in the area without wells. Sequence stratigraphic analysis is based on sequence boundaries, including unconformities and sedimentary transition surfaces, derived from seismic, well-logging, and outcrop observations to delineate sequences. However, accurate identification of key sequence boundaries and their associated stratigraphic hierarchy, particularly for fourth-order and higher-resolution sequence units, remains challenging in conventional sequence stratigraphy [35,36]. Recent advancements in wavelet analysis of well logs have provided a quantitative approach to delineate sequence boundaries across multiple scales, effectively addressing the limitations of traditional methodologies [35,37]. Hierarchical correspondence between wavelet coefficient periodicities at varying scales and sequence orders provides a robust framework for stratigraphic subdivision, where low-frequency components correlate with prolonged geological cycles defining sequence stratigraphic frameworks [35,36], while high-frequency components align with Milankovitch band cycles, facilitating high-resolution cyclostratigraphic analysis [19,38]. Within an established framework, depositional systems’ temporal and spatial distribution is determined through integrated analysis of well-to-well cross-sections and well–seismic correlation sections. The Chemical Index of Alteration (CIA) and the logarithmic ratio of Al2O3/Na2O have been established as reliable indicators of paleoclimate conditions [39,40,41,42].
4. Results
4.1. Lithofacies Associations
Borehole and outcrop analyses reveal diverse lithofacies within the target strata, including sandstone, siltstone, mudstone, coal seams, and conglomerates. Based on sedimentary structures, fourteen distinct lithofacies (Table 1) and five lithofacies associations have been identified, representing four depositional systems.

Table 1.
Lithofacies of Lower–Middle Jurassic Ahe, Yangxia, and Kezilenuer Formations (facies codes are from Miall, 1978 [43]).
4.1.1. FA1: Delta Plain Deposits
Description:
FA1 exhibits a fining-upward succession comprising basal conglomerate/pebbly sandstone transitioning to coarse-grained sandstones, capped by fine-grained deposits (siltstone to coal; Figure 3 and Figure 4). Gamma-ray (GR) curves show box or bell-to-serrated compound morphologies. Two subtypes are distinguished by grain size, sand/mud ratio (SMR), and sedimentary scale: (1) FA1-1 (SMR ≫ 1), which contains a coarse interval (10–50 m) with conglomerate (Gm; 0.5–5 cm gravel; Figure 3B) succeeded by pebbly sandstone (Smg; Figure 5B), trough or planar cross-bedded sandstones (St, Sp; Figure 3C), and parallel bedded sandstone (Sh; Figure 3D). The fine interval (5–20 m) comprises interbedded mudstone (Fm; Figure 5A), rippled siltstone (Fr; Figure 3E and Figure 5A), carbonaceous mudstone (Mc; Figure 3F) with local coal (C; Figure 5A) and root clay (R; Figure 3G). (2) FA1-2 (SMR ≤ 1) has a finer coarse interval (5–20 m) of pebbly sandstone (Smg) over erosional surfaces transitioning to small-scale cross-bedded sandstones (St, Sp, Sh; Figure 4B and Figure 5G). Its thicker fine interval (10–30 m) shows distally thinning interbedded siltstone–mudstone wedges (Fl, Fm; Figure 4D and Figure 5F) overlain by thick bedded mudstone (Fm/Fl; Figure 5F), rippled siltstone (Fr; Figure 4E), carbonaceous mudstone (Mc), and medium-thick coal seams (C; Figure 4F).
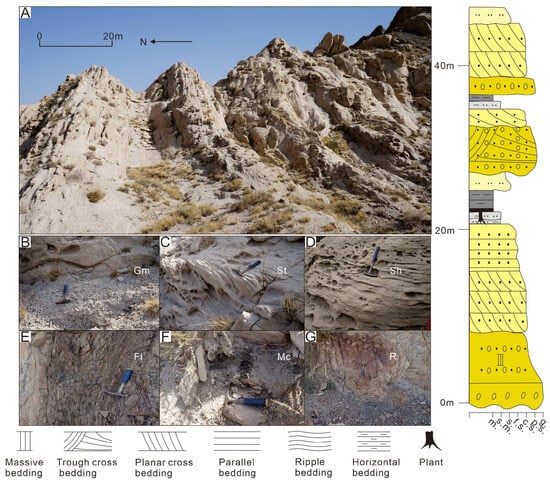
Figure 3.
Braided river delta plain depositional characteristics of the Jurassic Ahe Formation at the outcrop Kezilenuergou (outcrop location in Figure 1). (A) Macroscopic characteristics of braided river delta plain deposits; (B) lag deposits within braided channels; (C) pebbly sandstone with trough cross-bedding; (D) pebbly sandstone with high-energy parallel bedding; (E) horizontally bedded siltstone within floodplain; (F) carbonaceous mudstone; (G) root clay.
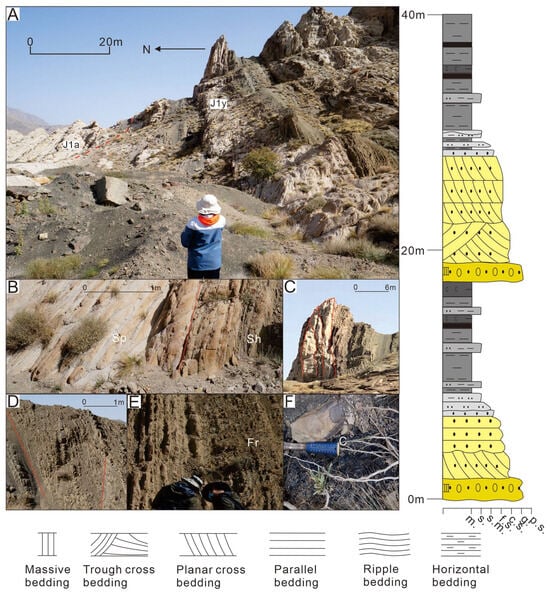
Figure 4.
Meandering river delta plain depositional characteristics of the Jurassic Yiangxia Formation in the outcrop Kezilenuergou (Outcrop location in Figure 1). (A) Macroscopic characteristics of meandering river delta plain deposits; (B) medium-fine sandstone with planar cross-bedding (left side of the red line) and parallel bedding (right side of the red line); (C) lateral migration of point bar; (D) continuous thin interbeds within wedge-shaped natural levee; (E) interbedded siltstone with ripple bedding and mudstone; (F) coal seams.
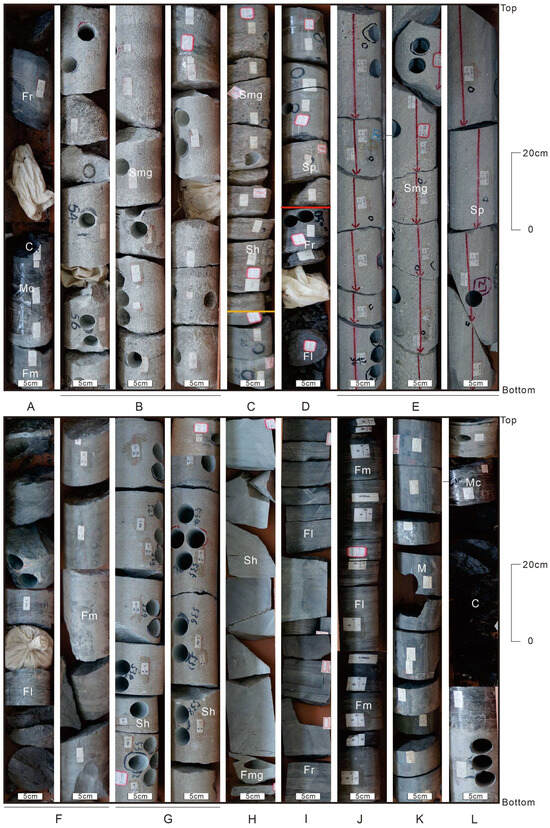

Figure 5.
Photographs of cores showing main lithofacies associations’ characteristics of the Lower–Middle Jurassic in the study area. (A) Muddy siltstone with horizontal and ripple bedding, massive carbonaceous mudstone and coal seams (Well M1, 603.06–608.96 m); (B) Pebbly sandstone with massive bedding, fining upward, with carbon fragments (Well M1, 603.06–608.96 m); (C,D) Superimposition of two sets of fining-upward deposits is observed above the red line: pebbly sandstone, medium-coarse sandstone with massive bedding and planar cross-bedding, scouring surfaces (Well N5, 4534.10–4539.50 m); below the red line: mudstone and muddy siltstone with horizontal bedding and ripple bedding (Well N5, 4534.10–4539.50 m); (E) Medium-to-pebbly sandstone with massive and cross-bedding, coarsening upward (T1, 2115.70–2120.40 m); (F) Interbedding of muddy siltstone and mudstone, marked by horizontal and massive bedding, with plant fossils, (Z2, 3515.90–3523.51 m); (G) Medium-to-fine sandstone with parallel bedding, scouring surfaces (Z2, 3515.90–3523.51 m); (H) Siltstone to fine sandstone with planar cross-bedding, containing black mud clasts, fining upward (N2, 4070.24–4072.36 m); (I) Muddy siltstone and mudstone with horizontal bedding and ripple bedding (N2, 4312.83–4321.33 m); (J) Muddy siltstone and mudstone interbedded, characterized by ripple and horizontal bedding (Z2, 4104.00–4110.50 m); (K) Mudstone, primarily with massive bedding and horizontal bedding (N2, 4400.26–4408.32 m); (L) Mudstone, carbonaceous mudstone and coal seams, with horizontal and massive bedding (M1, 417.09–422.69 m). Well location in Figure 1.
Interpretation:
FA1 is interpreted as delta plain deposits. The conglomerate or pebbly sandstone representing the coarsest sediments within the river channels indicate high-energy hydraulic conditions [44]. These thin deposits are lag deposits formed during major flood events [45]. Cross- and parallel-bedded pebbly sandstones or sandstones are indicative of high-energy fluvial channel deposits [46], whereas horizontally bedded mudstones and massive carbonaceous mudstones suggest low-energy floodplain deposits within shallow, stable water bodies [47]. The presence of coal seams and root clay (R) reflects a plant-rich, detritus-poor sedimentary setting, likely swamps within the floodplain [48,49]. FA1-1 and FA1-2 are interpreted as braided and meandering river delta plain deposits, respectively, with the former exhibiting higher sand/mud ratios and coarser-grained clastics. The thin layer of fine-grained sediments in FA1-1 suggests that the floodplain is often eroded by the instability and rapid migration of braided river channels [2,47]. The laterally migrating packages within FA1-2 coarse-grained intervals record point-bar lateral accretion processes diagnostic of meandering channels [50]. Distally thinning and fining wedges in FA1-2 fine-grained successions support natural levee deposition in meandering delta plains [51]. The wedge-shaped geometry reflects the diminishing energy of sheet flows during overbank flooding events, leading to a progressive decrease in grain size away from the channel edges [51].
4.1.2. FA2: Delta Front Deposits
Description:
FA2 exhibits a composite stratigraphic architecture characterized by superimposed coarsening-upward and fining-upward successions, resulting in “reverse-to-normal” grading patterns. GR curves show compound funnel-bell (or box)-to-serrated morphologies (Figure 6), though partial successions may occur. Two subtypes are distinguished by lithofacies, stratigraphic scales, and granulometry: (1) FA2-1 features a lower coarsening-upward succession (10–20 m) transitioning from parallel-bedded silt–fine sandstone to massive pebbly sandstone (Smg; Figure 5E). The middle fining-upward succession (5–30 m) grades from Smg (Figure 5C,D) through planar cross-bedded sandstone (Sp; Figure 5C,D) to parallel-bedded sandstone (Sh). The upper interval (5–20 m) comprises horizontally bedded (Fl; Figure 5D) and massive mudstone (Fm) with intercalated rippled mudstone (Fr; Figure 5D) and sporadic coal (C). (2) FA2-2 differs by its basal thin-bedded siltstone (Fl; 1–3 m) interbedded with mudstone, transitioning to parallel-bedded (Sh) and small-scale planar cross-bedded sandstone (Sp) in its lower coarsening-upward succession (3–10 m). The middle fining-upward succession (5–15 m) progresses from massive fine sandstone with black mud clasts (0.2–1 cm; Fmg) to Sh (Figure 5H). The upper interval (3–30 m) contains horizontally bedded (Fl; Figure 5I) and rippled silty mudstone (Fr; Figure 5I) with occasional coal (C).
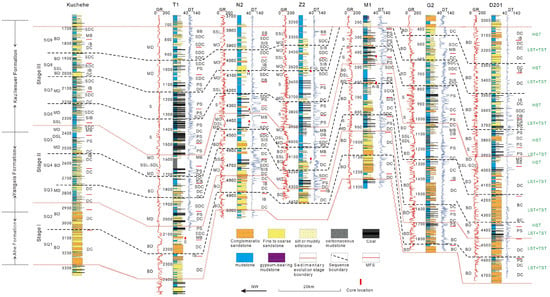
Figure 6.
Log-profile correlation of Lower–Middle Jurassic, showing sequence classification and depositional system in the study area (profile location in Figure 1). BB: Beach Bar; BD: Braided River Delta; DB: Distal Bar; DC: Distributary Channel; DSL: Deep and Semi-deep Lacustrine; IB: Interdistributary Bay; MB: Mouth Bar; MD: Meandering River Delta; PS: Peat Swamp; S: Swamp; SDC: Subaqueous Distributary Channel; SIB: Subaqueous Interdistributary Bay; SDL: Semi-deep Lacustrine; SSL: Shore–Shallow Lacustrine; LST: Lowstand Systems Tract; TST: Transgressive Systems Tract; HST: Highstand Systems Tract.
Interpretation:
FA2 is interpreted as delta front deposits. The lower lithofacies correspond to mouth bars overlying fine-grained deposits. Vertical reverse grading suggests an abrupt reduction in the hydrodynamic, likely caused by the rapid inflow of river water into a stable water body, a feature commonly observed in estuarine environments [52,53]. The middle lithofacies represent subaqueous distributary channels, characterized by finer grain sizes compared to the plain distributary channels [2]. Planar cross-bedding indicates strong hydrodynamic conditions [54]. The presence of mud clasts at the base likely results from the erosion and scouring of underlying muddy substrates by channelized flows [55]. The upper lithofacies represent a subaqueous interdistributary bay, characterized by horizontal and massive bedding. These features indicate weak hydraulic energy, with deposition primarily from settling suspended sediments [2,54,56]. FA2-1 and FA2-2 are interpreted as braided and meandering river delta front deposits, respectively. Key distinctions include the following: (1) the braided delta front (FA2-1) exhibits coarser-grained clastics and larger depositional scale, with pebbly coarse sandstone-dominated mouth bar deposits characterized by massive, indicative of rapid depositional regimes under high-energy conditions [57]; (2) the meandering delta front (FA2-2) displays finer-grained distal bar facies at its base, showing enhanced development of low-energy depositional elements compared to FA2-1.
4.1.3. FA3: Shore–Shallow Lacustrine Deposits
Description:
FA3 is characterized by gray silt–fine sandstone (Fl, Fr), silty mudstone, and mudstone (Fm, Figure 5J). The silt–fine sandstone forms sheet-like or lens-shaped bodies, typically 0.5 to 2 m thick, interbedded within thick mudstone. It commonly exhibits ripple and horizontal bedding, while the mudstone and silty mudstone are predominantly characterized by massive or horizontal bedding. The lithofacies association has an overall thickness ranging from 10 to 30 m, with the GR curve showing a relatively stable baseline with minor fluctuations (Figure 6).
Interpretation:
FA3 is interpreted as shore–shallow lacustrine deposits, dominated by fine-grained sediments. Ripple bedding indicates wave activity, while lens-shaped silt–fine sandstone interbedded within thick mudstone reflects beach–bar deposits influenced by wave action near the lake margin. Horizontal bedding in sandstone suggests low-energy traction currents entering the lacustrine environment [58]. Massive mudstones represent periods of stable lacustrine conditions, with suspended particles settling in low-energy environments [59]. Gray and black sediment predominance, with an absence of red-colored deposits, indicates humid climatic conditions [60].
4.1.4. FA4: Deep and Semi-Deep Lacustrine Deposits
Description:
FA4 is characterized by fine-grained lithofacies, predominantly medium-to-thick bedded massive mudstone (M), with occasional thin interbeds of silty mudstone (Fl and Fm) (Figure 5K). The deposits range from grayish-black to black and exhibit an overall thickness of approximately 30–50 m. Animal traces disappeared. The GR curve shows a stable baseline with relatively high values, peaking at 160 (Figure 6).
Interpretation:
FA4 is interpreted as deep and semi-deep lacustrine deposits, characterized by grayish-black massive mudstones indicative of deposition in stable, anoxic water conditions [61]. The absence of animal traces aligns with the low-energy, oxygen-deficient environment typical of deep lacustrine settings [62,63]. These deposits are typically concentrated in the central parts of the depression, with their spatial extent controlled by large-scale lake-level fluctuations.
4.1.5. FA5: Peat Swamp Deposits
Description:
FA5 primarily comprises fine-grained lithofacies, including gray thin-bedded argillaceous siltstone (Fr, Fm, Fl), gray–black medium-to-thick-bedded mudstone (M), gray–black thin-bedded carbonaceous mudstone (Mc), and coal (C), forming interbedded sequences of siltstone, mudstone, and coal seams (Figure 5L). Argillaceous siltstone typically exhibits ripple and horizontal bedding, while mudstone and carbonaceous mudstone predominantly display massive bedding, with occasional small-scale cross-bedding in siltstone or fine sandstone. Authigenic minerals, such as siderite, and plant fossils are abundant. Coal seams are well-developed, ranging from 1 to 10 m in thickness, with most classified as medium-thick seams (>1.5 m) and exhibiting good lateral continuity (Figure 6).
Interpretation:
FA5 is interpreted as swamp deposits, characterized by the widespread occurrence of coal seams and carbonaceous mudstone, indicative of a stable aquatic environment [64]. The presence of thick and multiple coal seams reflects prolonged periods of stable and humid climatic conditions with balanced rates of accommodation and peat accumulation [65]. The occasional occurrence of sand bodies suggests episodic deposition by coarse-grained traction currents.
4.2. Main Seismic Facies Types
Four main seismic facies were identified in the Jurassic of the study area based on seismic reflection structure, waveform, amplitude, frequency, continuity, and external morphology. The sedimentary facies were interpreted using calibration and comparative analysis of drilling and well-logging data (Table 2).

Table 2.
Main characteristics of major seismic facies of the Lower–Middle Jurassic in the Kuqa depression.
4.2.1. Seismic Facies SF1
Description:
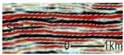
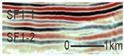
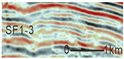
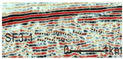
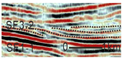
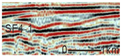
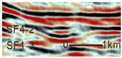
SF1 is characterized by parallel to sub-parallel seismic reflection configurations, which are further classified into the following three types based on their seismic reflection structures: (1) SF1-1 exhibits medium-to-high amplitude, low-to-medium frequency, and good continuity, predominantly observed in the lower-to-middle parts of the Kezilenuer Formation (Figure 7 and Figure 8). (2) SF1-2 displays medium-to-high amplitude, medium-to-high frequency, and good continuity, primarily observed at the top of the Yangxia Formation (Figure 7 and Figure 8). (3) SF1-3 exhibits low-to-medium amplitude, low-to-medium frequency, and fair-to-good continuity, identified within the Ahe and Yangxia Formations (Figure 7 and Figure 8).
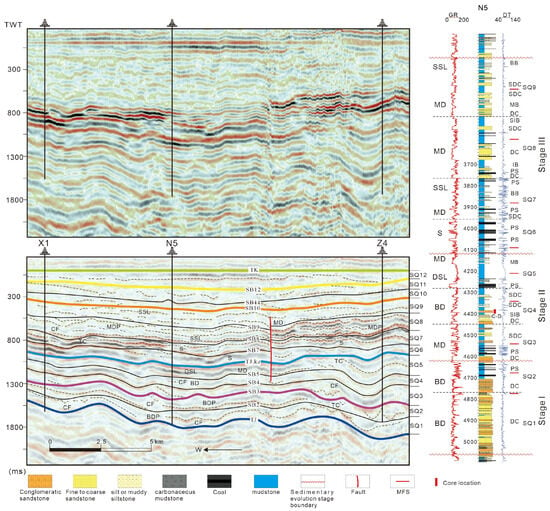
Figure 7.
Interpreted east–west seismic profiles calibrated to borehole N5 indicate depositional evolution within sequence stratigraphic framework of Jurassic in the study area (profile location in Figure 1). BD: Braided River Delta; BDP: Braided River Delta Plain; CF: Channel Filling; DSL: Deep and Semi-deep Lacustrine; MD: Meandering River Delta; MDP: Meandering River Delta Plain; MFS: Maximum Flooding Surface; S: Swamp; SB: Sequence Boundary; SSL: Shore–Shallow Lacustrine; TC: Truncation.
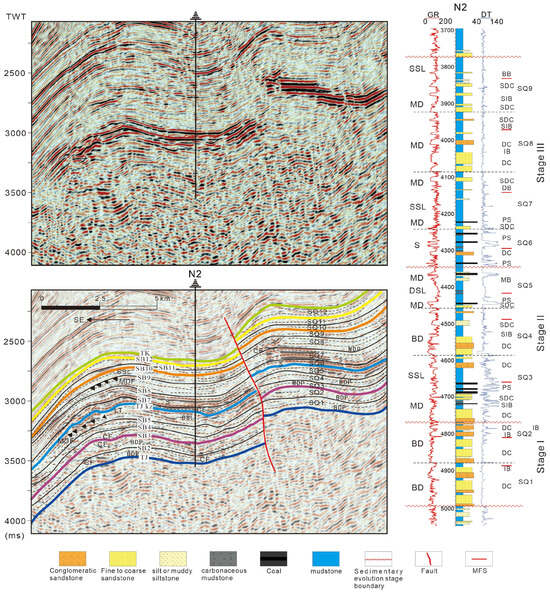
Figure 8.
Interpreted south–north seismic profiles calibrated to borehole N2 indicate depositional evolution within sequence stratigraphic framework of Jurassic in the study area (profile location in Figure 1). BDP: Braided River Delta Plain; CF: Channel Filling; DSL: Deep and Semi-deep Lacustrine; LT: Lake Transgression; MDP: Meandering River Delta Plain; MDF: Meandering River Delta Front; MFS: Maximum Flooding Surface; S: Swamp; SB: Sequence Boundary; SSL: Shore–Shallow Lacustrine.
Interpretation:
Drilling and well-logging data provide further insights into the depositional environments associated with these seismic facies: (1) SF1-1 is interpreted as swamp deposits (FA5), characterized by interbedded medium-to-thick coal seams, silty mudstone, medium-to-thick gray–black mudstone, and thin gray–black carbonaceous mudstone. These deposits are widely distributed across the study area, with a thickness of 200–300 m (Figure 6). (2) SF1-2 is interpreted as deep and semi-deep lacustrine deposits (FA4), dominated by thick black mudstone and carbonaceous mudstone. These deposits are extensively distributed across the study area, with a thickness of 30–50 m (Figure 6). (3) SF1-3 corresponds to braided river delta plain deposits (FA1-1), primarily comprising sandy conglomerates in distributary channels and mudstone in interdistributary bays. These deposits form fining-upward sequences (Figure 6) and are mainly developed along the northern margins of the depression.
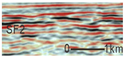
4.2.2. Seismic Facies SF2
Description:
SF2 is characterized by seismic reflection configurations that transitions from divergent to sub-parallel. It displays low-to-medium amplitude, medium frequency, and low-to-medium continuity, primarily observed within the Kezilenuer and Yangxia Formations (Figure 7 and Figure 8).
Interpretation:
Drilling and well-logging data reveal that SF2 comprises shore–shallow lacustrine deposits (FA3) and meandering river delta plain deposits (FA1-2), dominated by mudstone, siltstone, and minor fine sandstone (Figure 6). These deposits are primarily distributed in the transitional zone between the depression center and its margins.
4.2.3. Seismic Facies SF3
Description:
SF3 is characterized by progradational reflection configurations, commonly overlying SF1-3, and can be classified into the following two types: (1) SF3-1 exhibits imbricated progradational reflections, with medium amplitude, medium frequency, and low continuity. It primarily observed within the Ahe and Yangxia Formations (Figure 8). (2) SF3-2 features sigmoid–oblique progradational reflections, with medium amplitude, medium-to-high frequency, and medium continuity. This type is predominantly observed within the Kezilenuer Formation (Figure 8).
Interpretation:
Drilling and well-logging data provide further insights into these reflection types: (1) SF3-1 corresponds to braided river delta front deposits (FA2-1), comprising subaqueous interdistributary bays, mouth bars, and subaqueous distributary channels, forming a coarsening-upward depositional succession. These deposits are spatially restricted (Figure 8). (2) SF3-2 represents meandering river delta front deposits (FA2-2), including mouth bars and subaqueous distributary channels, also forming a coarsening-upward succession. Compared to SF3-1, the sediment grain size in SF3-2 is finer, and its spatial distribution is more extensive, reflecting more stable and continuous depositional conditions (Figure 8).
4.2.4. Seismic Facies SF4
Description:
SF4 is primarily developed near sequence boundaries and is characterized by medium-to-high amplitude, high frequency, and low-to-medium continuity in its seismic reflection structure. Based on reflection configurations, SF4 can be divided into the following two types: (1) SF4-1 displays distinctive internal blank reflections, often forming ‘W’-shaped or deep ‘U’-shaped geometries (Figure 7 and Figure 8). (2) SF4-2 exhibits a double onlap fill configuration with anomalous short-axis seismic facies, forming a lens-shaped geometry (Figure 7 and Figure 8).
Interpretation:
Drilling and well-logging data provide further insights into these reflection types: (1) These features of SF4-1 suggest large-scale channel incision with lateral migration. It is typically large in scale, serving as a critical indicator of sequence boundaries. It is also predominantly distributed along the depression margins, particularly in the eastern and northern regions. (2) This configuration of SF4-2 likely represents the fill of smaller channel sand bodies. In addition to occurring near sequence boundaries, it is frequently observed within delta plain deposits (SF1-3).
4.3. Sequence Framework
Sequence stratigraphy is a critical tool for establishing a chronostratigraphic framework, with the accurate identification and classification of sequence boundaries being essential for constructing a stratigraphic framework [66,67]. This study aims to develop a sequence stratigraphic framework and analyze the depositional system’s filling processes and evolution within this framework.
In the Kuqa Depression, two regional unconformities at the top and bottom of the Jurassic define a first-order sequence. Using integrated well-logging and seismic data from 3D seismic surveys and 2D seismic lines, the Jurassic is further classified based on angular unconformities, depositional transition surfaces, erosion-induced truncation surfaces, and transgressive–regressive cycles observed in well-logging data. This classification identifies two second-order sequences and twelve third-order sequences (SQ) (Figure 2). The second-order sequences correspond to long-term lake-level fluctuations, reflecting regional transgressive–regressive events that influenced the entire depression. This study focuses on nine third-order sequences (SQ1–SQ9) (Figure 2), encompassing two second-order sequence boundaries and eight third-order sequence boundaries.
4.3.1. Second-Order Sequence Boundaries
The second-order boundary TJ, separating Jurassic Ahe from Triassic Taliqike formations, constitutes a regional angular unconformity [68]. Seismic profiles show channel incisions characterized by SF4-1 seismic facies transitioning depression-ward to conformable contacts (Figure 7 and Figure 8), with prominent high-angle truncations in the Tabei Uplift and traceable regionally [68]. GR values decrease sharply above the boundary forming box-shaped curves, correlating with lithologic shifts from mudstone or coal to conglomeratic or coarse sandstone (Figure 6). Outcrops at Kuchehe and Yangxia Coal Mine exhibit Jurassic fluvial conglomeratic sandstone directly overlying Triassic mudstone or coal, manifesting as erosional (Figure 9A) and angular (Figure 9B) unconformities, respectively.

Figure 9.
Contact relationship of unconformity TJ in the study area. (A) Kuchehe outcrop; (B) Yangxia Coal Mine outcrop; J1a: Lower Jurassic Ahe Formation; T3t: Upper Triassic Taliqike Formation. Outcrops location in Figure 1.
The Jurassic intra-formational boundary TJ2kz (base Kezilenuer Fm), another second-order sequence boundary, marks a regional depositional transition. Overlying SF1-1 facies exhibit medium–high amplitude, low–medium frequency, and good continuity, while underlying SF1-2 facies (medium–high amplitude and frequency, and good continuity) show localized truncation (Figure 7 and Figure 8). Swamp mudstone and coal seams above the boundary differ from deltaic–lacustrine deposits below, indicating extensive depositional reorganization.
4.3.2. Third-Order Sequence Boundaries
The target layers comprise eight third-order sequence boundaries (SB2–SB5 and SB7–SB10). These boundaries are local unconformities at basin margins smaller in scale than second-order boundaries, and manifest as transgressive–regressive transition surfaces and incised channel truncation surfaces, which are inconspicuous on seismic profiles.
SB2 and SB4 represent incised erosional surfaces of braided channels with correlative conformity, exhibiting pronounced erosion. They are characterized by SF4-1 seismic facies with localized truncation against underlying layers (Figure 7 and Figure 8). Well-logging data reveal a sharp GR curve shift from baseline to a box or serrated box shape, correlating with lithologic transitions from mudstone, silty mudstone, or coal seams to conglomeratic or coarse sandstone (Figure 6).
SB3 and SB5 correspond to meandering channels incised surfaces with correlative conformity. Seismic signatures display low–medium amplitude, low-to-medium continuity with subtle truncations (Figure 7 and Figure 8). Well-logging data show a GR curve shift from baseline to a small box or bell shape, with lithological transitions from mudstone and silty mudstone to conglomeratic sandstone, sandstone, or siltstone (Figure 6).
SB7 denotes a regressive–transgressive transition surface within swamp deposits without significant exposure erosion. It displays medium-to-high amplitude and good continuity on seismic profiles, with SF1-1 seismic facies observed above and below the boundary (Figure 7 and Figure 8). GR baseline shifts to small box or bell shapes reflect lithologic transitions from mudstone or coal to sandstone or siltstone (Figure 6).
SB8–SB10 represent meandering channels incised surfaces with correlative conformity, showing stronger incision than SB3/SB5. SB8 marks the swamp-to-delta transition, displaying medium-to-high amplitude and good continuity on seismic profiles, with SF2 seismic facies above and SF1-1 seismic facies below the boundary (Figure 7 and Figure 8). SB9 and SB10 display low-to-medium amplitude and continuity on seismic profiles, with SF2 seismic facies above and below the boundaries and localized incision erosion features (SF4-2) (Figure 7 and Figure 8). All three boundaries show GR shifts to small box or bell shapes with mudstone-to-sandstone or siltstone transitions (Figure 6).
4.3.3. Cyclic Structure
This study employs wavelet transform analysis to quantitatively resolve depositional cyclicity using the GR curve from three representative wells (T1, N2, and Z2), validating the established sequence stratigraphic framework and characterizing cyclic depositional patterns.
Building on previous methodologies [35,36,69], Daubechies wavelet (db12) decomposition with 12 maximum decomposition levels optimally resolves hierarchical sequence units when calibrated with geological constraints. The d11 curve delineates two second-order sequence boundaries and the maximum flooding surface (MFS) of sequence I, defining one complete second-order sequence I and one incomplete sequence II (Figure 10). The d10 curve identifies ten third-order sequence boundaries partitioning nine third-order sequences (SQ1–SQ9), corroborating the proposed scheme of sequence stratigraphy (Figure 10). The d8 curve identifies forty-two fourth-order sequences in well T1.
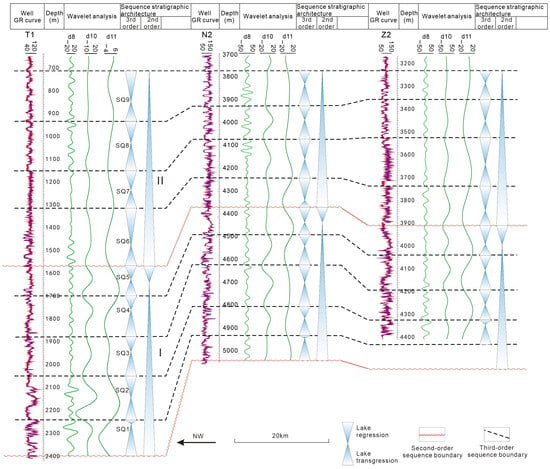
Figure 10.
Sequence classification and wavelet analysis of the Lower–Middle Jurassic in the Kuqa depression.
Sequence I comprises regional-scale transgressive hemicycles and rapid regressive hemicycles, with its MFS at the Yangxia Formation top marked by thick lacustrine mudstone (Figure 6 and Figure 10). The Kezilenuer Formation constitutes the partial transgressive hemicycles of sequence II. Five third-order sequences (SQ1–SQ5) occur within sequence I, and four (SQ6–SQ9) within sequence II, each subdivided into lowstand (LST), transgressive (TST), and highstand (HST) systems tracts via cycle inflection points and flooding surfaces.
4.4. Evolution of Depositional Systems
This study investigates the filling processes and evolution of the depositional system within an isochronal stratigraphic framework. The target interval has been subdivided into three evolutionary stages through the systematic analysis of depositional architectures and their genetic associations. (Figure 2).
4.4.1. Sedimentary Evolution Stage I
Stage I comprises SQ1 and SQ2. SQ1 primarily comprises multiple superimposed FA1-1 in LST, each exhibiting a fining-upward trend, ranging from 20 to 80 m (Figure 3 and Figure 6), showing characteristics of braided river delta plain deposits. Compared to SQ1, SQ2 shows a notable increase in the fine-grained deposit thicknesses, indicating more extensive floodplain deposits during SQ2 (Figure 6). Furthermore, FA2-1 develops in HST of SQ2 compared to SQ1, reflecting an increase in delta front deposits (Figure 6 and Figure 7). SQ1 and SQ2 appear as parallel seismic facies (SF1-3) on seismic profiles, characterized by low-to-medium amplitude, low-to-medium frequency, and moderate-to-good continuity (Table 2). Meanwhile, ‘W’- or ‘U’-shaped concave seismic facies (SF4-1) are often observed at boundaries, indicating braided river delta plain deposits (Figure 7 and Figure 8). Vertically, from SQ1 to SQ2, there is an increase in floodplain and delta front deposits in HST, reflecting lake expansion.
4.4.2. Sedimentary Evolution Stage II
SQ3 comprises two superimposed FA1-2 units at the Kezilenuergou outcrop, each exhibiting a fining-upward trend. These 20–40 m thick associations display muddy deposits often equal or exceed sandy thickness (Figure 4A), indicating meandering river delta plain deposits. In the depression, the lower part of FA1-2 (10–20 m) formed in LST is dominated by medium-to-fine-grained sandstone and pebbly sandstone channel deposits, while the upper part of FA1-2 (30–50 m) formed in TST features muddy and coal-rich interdistributary bay swamps (Figure 6), representing a key source rock interval. The FA2-2 (2–20 m) in HST shows coarsening-upward reverse grading mouth bars or fining-upward grading subaqueous channels, representing meandering delta front. However, these delta front deposits are below seismic resolution and challenging to identify on seismic profiles.
SQ4 transitions to braided delta deposits (Figure 6) with coarser sediments and larger channels than SQ3. This sequence contains well-developed LST + HST comprising coarse-grained braided delta plain deposits, while the limited HST primarily features mouth bars and subaqueous channels of braided delta front.
In the LST + TST of SQ5, outcrop areas are dominated by meandering river delta plain (FA1-2) and deep and semi-deep lacustrine deposits (FA4). Within the depression, the lower part of the LST + TST develops meandering river delta front deposits (FA2-2), transitioning rapidly upward to 30–50 m stable deep and semi-deep lacustrine deposits (FA4) representing the second source rock member (predominantly TST). These deposits, represented by a typical baseline GR curve, are widespread and mark the regional lake transgression, covering nearly the entire study area (Figure 6). LST + TST is seismically reflected by retrograding sigmoid–oblique progradation (SF3-1) converging to parallel facies (SF1-2) (Figure 8). The HST records rapid regression with extensive meandering river delta front deposits (FA2-2), featuring prominent mouth and distal bars (Figure 6).
4.4.3. Sedimentary Evolution Stage III
The most favorable period for swamp development is represented in SQ6–7 in the study area (Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8). In the depression, extensive swamp deposits (FA5) predominantly develop in the HST of SQ6 with a thickness of 80–100 m (Figure 6). These deposits are widely distributed, nearly resulting in the silting of the regional lacustrine basin. On seismic profiles, they are characterized by parallel seismic facies (SF1-1) with medium-to-high amplitude, low-to-medium frequency, and good continuity, features typical of coal seams (Figure 7 and Figure 8). During SQ7, swamp deposits (FA5) remain predominant. In the late TST, shore–shallow lacustrine deposits (FA3) developed locally, while minor meandering river delta front deposits (FA2-2), typically 20–50 m thick, formed during the HST (Figure 6). SQ7 continued to show parallel seismic facies (SF1-1) on seismic profiles. However, lens-shaped seismic facies (SF4-2) occasionally appear, indicating the presence of small subaqueous distributary channels. These sequences correspond to the third member of source rock development, representing the thickest organic matter accumulation in the study area. Characterized by low-amplitude transgressive–regressive cycles, they maintained stable accommodation that was favorable for preserving and developing thick coal seams.
In SQ8–9, swamp deposits significantly diminished. Deposition became dominated by meandering river delta deposits (FA1-2 and FA2-2) and shore–shallow lacustrine deposits (FA3). LST and TST develop seismic facies SF2, indicating shore–shallow lacustrine and meandering river delta plain deposits. A small occurrence of sigmoid–oblique progradational seismic facies (SF3-2) is observed in HST, representing meandering river delta front deposits (Figure 8). These deposits are primarily composed of mudstones, with medium-thin sandy intervals. East of Well G2, braided river delta deposits dominate (Figure 6).
5. Discussion
5.1. Tectonism
Detrital zircon U-Pb ages, heavy mineral assemblages, and paleocurrent data demonstrate that the Tianshan Orogenic Belt fundamentally governed sediment supply to the Kuqa Depression [5,70,71,72,73].
Early Early Jurassic (Stage I), the Kuqa Depression underwent significant sedimentation characterized by large-scale braided river plain deposits in the LST of SQ1 and SQ2 (Figure 6). This sedimentation reflects the intense uplift of the South Tianshan Mountains, which is manifested by pronounced basin elevation and enhanced sediment flux. This orogenic activity is further evidenced by large-scale incised surfaces and angular unconformities [74,75], consistent with Late Triassic–Early Jurassic collisional reactivation of Paleozoic structures along the Qiangtang–Eurasia margin [5,76,77,78,79,80] that directly drove the South Tianshan uplift [5,76,81].
Subsequent tectonic weakening initiated systematic depositional reorganization: Middle–Late Early Jurassic (Stage II) transitioned to meandering deltaic–lacustrine systems (SQ3–SQ5) under persistent fine-grained sedimentation (Figure 6), progressing to Middle Jurassic (Stage III) swamp (SQ6–SQ7) and deltaic deposits (SQ8–SQ9) within dominantly low-energy regimes. Critically, this evolution records post-Early Jurassic orogenic decay and diminished sediment flux [76,81] that controlled depositional system restructuring. Particularly significant in Stage III, subdued geomorphic gradients constrained erosional energy, suppressing proximal coarse input while optimizing organic accumulation. Quantifying this trend, zircon fission-track data [82] document declining South Tianshan uplift rates post-Early Jurassic, robustly substantiating the mechanism.
Progressive sediment maturity increases [70] further reflect northward sedimentary expansion and provenance retreat, thereby establishing tectonic pacing as the primary driver of foreland basin stratigraphic architecture, with direct implications for hydrocarbon resource distribution and basin evolution models.
5.2. Paleoclimate
Geochemistry plays a pivotal role in reconstructing paleoclimate. Soluble elements typically tend to be lost during intense chemical weathering, while refractory elements are retained. Based on this pattern, the chemical index of alteration (CIA) is widely used to evaluate weathering intensity and climate of fine-grained siliciclastic rocks [83,84,85,86,87]. The CIA is calculated as
where oxides are expressed in molar units, and CaO* represents CaO in silicate, corrected as CaO* = CaO − (10/3 × P2O5) [83,88]. CIA values provide insights into paleoclimate: 50–70 indicates cold and arid climates, 70–80 corresponds to warm and humid climates, and 80–100 reflects hot and humid climates [83,85,89,90].
CIA = 100 × Al2O3/(Al2O3 + CaO* + Na2O + K2O)
During Stage II, CIA values fluctuated significantly. SQ3 (78.48–81.03, mean 79.66) indicates warm and humid climates, SQ4 (64.12–81.03, mean 75.21) reflects a marked attenuation of warm and humid conditions and an ephemeral arid climatic perturbation, and SQ5 (77.59–84.78, mean 82.49) marks a shift to hot and humid climates (Figure 11). The Cyathidites–Cibotiumspora–Disacciatrileti spore–pollen assemblage identified in the Yangxia Formation (SQ3–5) exhibits a non-acme occurrence of Cyathidites minor, establishing biostratigraphic correlation with the Fuxian Formation of the Ordos Basin [91]. Previous palynological studies constrain the Fuxian Formation to the Early Jurassic Pliensbachian–Toarcian, with the Classopollis-dominated assemblage being stratigraphically associated with the Toarcian Oceanic Anoxic Event (T-OAE) [13]. This correlation suggests the Yangxia Formation spans equivalent Pliensbachian–Toarcian strata, where the abrupt proliferation of Classopollis and Klukisporites in SQ5 potentially records paleoclimatic perturbations linked to T-OAE [24,92,93,94]. In Stage III, CIA values stabilized: SQ6 (76.77–83.76, mean 81.10) reflects weakening hot and humid climates, while SQ7 (77.44–80.58, mean 78.99), SQ8 (79.04–79.29, mean 79.17), and SQ9 (77.93) indicate warm and humid climates with decreasing humidity (Figure 11).
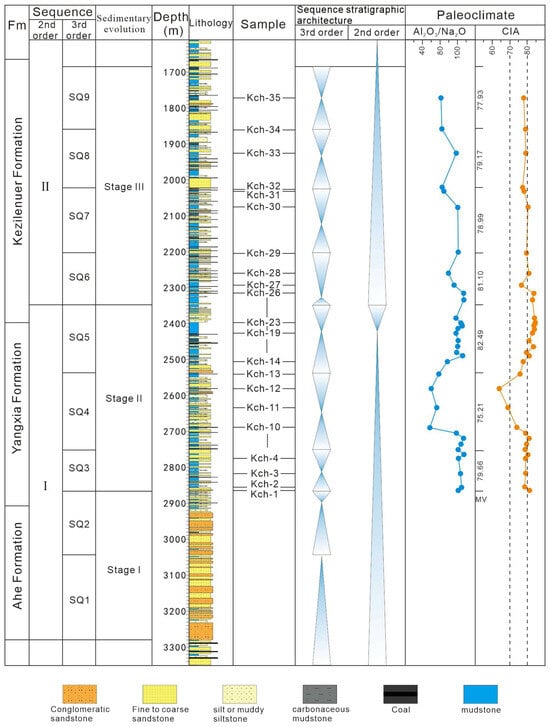
Figure 11.
Characteristics of paleoclimate indicators of Lower–Middle Jurassic of outcrop Kuchehe in the study area. CIA = 100 × Al2O3/(Al2O3 + CaO* + Na2O + K2O); CaO* represents CaO in silicate; CIA values indicate paleoclimate conditions: 50–70 reflects cold and arid climates, 70–80 corresponds to warm and humid climates, and 80–100 suggests hot and humid climates [12,83,85,90]. Ln (Al2O3/Na2O) is often used as a complementary weathering index for cross-validation [39,40,41,42]; High ln (Al2O3/Na2O) values indicate warm and humid climate with intense weathering, whereas low values reflect cold and arid condition with weak weathering [40,42]. MV = Mean Value.
Although CIA is extensively used to assess chemical weathering and paleoclimate in lacustrine catchments [83,84,85,86,87], uncertainties in CaO correction associated with phosphates and carbonates can affect its accuracy [39,40]. Therefore, ln (Al2O3/Na2O) is often used as a complementary weathering index for cross-validation [40,41,42]. High ln (Al2O3/Na2O) values indicate warm and humid climates with intense weathering, whereas low values reflect cold and arid climates with weak weathering [40,42]. The ln (Al2O3/Na2O) trend closely parallels the CIA curve (Figure 11), confirming the CIA’s reliability in reconstructing paleoclimate variations in the study area.
5.3. Sedimentary Responses to the Paleoclimate
Deposition in relatively stable lacustrine basins is critically modulated by climatic perturbations [3,9]. Notably, intensive Early Jurassic tectonic activity substantially attenuated during the Middle Jurassic, pivotally transitioning climatic controls to dominant regulators of depositional evolution post-Early Jurassic.
In Stage II, SQ3 coal-bearing meandering river delta and shore–shallow lacustrine successions diagnostically record sustained warm–humid climates (Figure 6) [3,61]. Elevated precipitation under this regime drove gradual lake transgression [3,61,95]. Subsequent SQ4 manifests climatic aridification through contracted shore–shallow lacustrine and braided river delta deposits with diminished coal seams (Figure 6 and Figure 8) [3,96,97]. This shift amplified mechanical weathering while suppressing fine-grained sedimentation, with vegetation degradation destabilizing riparian zones and promoting extensive braided channel development [96]. Critically, seismic facies in SQ5 reveal downlap configurations and condensed sections (Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8), diagnosing expansive deep and semi-deep lacustrine depositional systems [98]. Accelerated hydrological cycling under humid–tropical climatic conditions during this phase drove pronounced rainfall influx, driving rapid lacustrine transgression and expansion of profundal fine-grained deposits [18,19,20]. Paleoenvironmental proxies for climatic conditions provide robust validation for the depositional system characterization and paleoclimatic interpretations (Figure 8). This event aligns with Early Jurassic Toarcian Oceanic Anoxic Event (T-OAE) impacts, showing synchronicity across Tarim, Ordos, Sichuan, and Jinyang Basins [15,16,17]. Reduced coal accumulation substantiates swamp suppression induced by rapid transgression.
In Stage III, SQ6–SQ7 exhibits marked contraction of deep and semi-deep lacustrine facies compared to underlying SQ5, with laterally extensive swamp deposits prograding into basin centers, inducing the silting of the regional lacustrine basin (Figure 6 and Figure 8). This imentary reorganization records a climatic shift towards sustained warm and humid conditions, and rapid lacustrine base-level fall culminating in appropriate and stable accommodation through forced regression [65]. Enhanced floral colonization within estuarine and lakeshore wetlands under optimal climate and accommodation effectively trapped siliciclastic sediments, suppressing coarse-grained clastic influx while promoting vertically stacked swamp sequences [64,99,100,101]. SQ8–SQ9 exhibit extensive development of shore–shallow lacustrine and meandering river delta depositional systems during these two phases, yet with markedly reduced coal seams, indicating diminished warm–humid climatic intensity that deteriorated optimal swamp-forming conditions. This pattern within S6–SQ9 aligns with geochemical evidence of attenuated lake-level fluctuations and persistently warm and humid climates (Figure 8). Although depositional cyclicity exists in SQ6–SQ9, compared to SQ3–SQ5, relatively subdued climatic oscillations resulted in weakened cyclicity and indistinct depositional system evolution, manifested macroscopically by the absence of large-scale unconformities or depositional shift surfaces. Consequently, sequence boundaries are primarily characterized by minor meandering channel incisions, while wavelet transform analysis significantly enhances sequence boundary identification precision (Figure 10).
5.4. Coal Accumulation Patterns
The Kezilenuer Formation (Stage III) represents the most significant coal-forming episode in the Jurassic succession of the study area, characterized by the Cyathidites–Neoraistrickia–Disacciatrileti spore–pollen assemblage, where Cyathidites minor attains its acme abundance alongside diagnostic Neoraistrickia species [91,92], collectively indicating a Middle Jurassic age (Aalenian–Bathonian, ~9.4 Ma) through biostratigraphic correlation with continental lake basins in China [102,103]. This interval exhibits tectonically quiescent conditions, characterized by a limited clastic influx, a sustained warm–humid climate, and subdued lacustrine level fluctuations, which foster the deposition of multiple coal seams (1–22 m thick, predominantly thicker than 2 m)
In the coal-rich Well T1, the formation comprises 4 third-order sequences (SQ6–9) subdivided into 23 fourth-order sequences (Figure 10), demonstrating a ~406 kyr cyclicity that aligns with the Milankovitch long eccentricity cycle (405 kyr) [19,104]. Coal seams predominantly develop adjacent to fourth-order sequence boundaries, with thicker accumulations preferentially forming during transgressive hemicycles, followed by limited development in regressive hemicycles, while remaining essentially coal-barren near secondary flooding surfaces (Figure 10). This model suggests amplitude of the precession cycle modulated by eccentricity drove high-frequency climatic oscillations: minimum orbital eccentricity induces stable climatic conditions and sustains robust vegetation growth, and lower lacustrine levels facilitate peat preservation, representing the optimal coal-forming period, whereas maximal eccentricity induces enhanced climatic seasonality with increased precipitation, triggering lacustrine expansion and swamp inundation that terminated coal formation [18,19,104].
6. Conclusions
- Fourteen lithofacies, five lithofacies associations, and four major seismic facies have been identified within the Lower–Middle Jurassic Ahe, Yangxia, and Kezilenuer Formations, which represent the following four sedimentary systems: braided river delta, meandering river delta, lacustrine, and swamp deposits.
- The Lower–Middle Jurassic can be divided into two second-order and nine third-order sequences (SQ1–SQ9) based on regional and local unconformity and correlative conformity sequence boundaries, and this cyclic architecture was validated through wavelet transform analysis.
- Three stages of the sedimentary evolution during the Lower–Middle Jurassic are recognized: Stage I (SQ1–SQ2) is characterized by braided river delta and shore–shallow lacustrine deposits; Stage II (SQ3–SQ5) begins with a transition from meandering river delta deposits (SQ3) to braided river delta deposits (SQ4), followed by the development of deep and semi-deep lacustrine deposits in SQ5; Stage III (SQ6–SQ9) is marked by regional lacustrine siltation and swamp formation (SQ6–SQ7), eventually shifting to meandering river delta and shore–shallow lacustrine deposits in SQ8–SQ9.
- The Early Jurassic uplift of the Tianshan Orogenic Belt was a primary driver of widespread thick braided river delta deposits during Stage I. Therewith, the tectonic activity weakened with the source area planation and sediment supply decreased, facilitating the deposition of fine-grained meandering river delta and swamp deposits. Geochemical proxies record climatic shifts during Stages II and III. Meandering river delta systems predominantly develop under warm and humid climatic conditions, whereas braided river delta systems prevail during arid phases. Hot and humid conditions associated with the Early Jurassic Toarcian Oceanic Anoxic Event may trigger regional lacustrine transgression during the SQ5 of Stage II. Warm and humid climate with limited detrital input provided favorable conditions for widespread swamp development in Stage III. Minimum orbital eccentricity minima during this period facilitated coal accumulation, whereas maximal eccentricity corresponded to coal formation termination.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.L. and H.L.; Data curation, M.M. and H.L.; Investigation, M.M., J.L., and F.X.; Methodology, M.M. and C.L.; Resources, Y.L., W.Y., and C.S.; Software, Y.L. and W.Y.; Supervision, C.L. and M.Z.; Validation, C.L., J.L., and C.S.; Writing—original draft, M.M.; Writing—review and editing, C.L. and M.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42230816) and the National Key Basic Research Project (No. 2011CB201100-03).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank the Exploration and Development Research Institution of the Tarim Oilfield Company for their data donation and cooperative research.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Yongfu Liu, Wenfang Yuan, and Chaoqun Shi were employed by the company PetroChina Tarim Oilfield Company. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Vázquez-Urbez, M.; Arenas, C.; Pardo, G.; Pérez-Rivarés, J. The effect of drainage reorganization and climate on the sedimentologic evolution of intermontane lake systems: The final fill stage of the Tertiary Ebro Basin (Spain). J. Sediment. Res. 2013, 83, 562–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Lin, C.S.; Liu, Y.F.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhao, H.T.; Li, H.; Sun, Q.; Xia, H.; Ma, M.; Liang, Y. Lacustrine to fluvial depositional systems: The depositional evolution of an intracontinental depression and controlling factors, Lower Cretaceous, northern Tarim Basin, northwest China. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2021, 126, 104904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.J.; Li, Q.; Chen, H.H.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.P.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Z.H. Tectonic-geomorphological evolution and provenance-sedimentary response: Insights from the Middle Jurassic-Lower Cretaceous, Junggar Basin, China. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2023, 158, 106514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, M.; Naseem, A.A.; Saleem, M.; Rehman, J.U.; Kontakiotis, G.; Janjuhah, H.T.; Khan, E.U.; Antonarakou, A.; Khan, I.; Rehman, A.U.; et al. Sedimentary Facies, Architectural Elements, and Depositional Environments of the Maastrichtian Pab Formation in the Rakhi Gorge, Eastern Sulaiman Ranges, Pakistan. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, M.S.; Graham, S.A.; Carroll, A.R.; Sober, E.R.; Mcknight, C.L.; Shulein, B.J.; Wang, Z.X. Sedimentary record and climatic implication of recurrent deformation of the Tien Shan: Evidence from Mesozoic strata of the north Tarim, south Junggar and Turpan basins. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1992, 104, 53–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.R.L.; Friend, P.F. Deposition of Catskill facies, Appalachian Region: With some notes on some other Old Red sandstone Basins. In Late Palaeozoic and Mesozoic Continental Sedimentation, Northeastern North America; de Klein, G.V., Ed.; The Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1968; Volume 106, pp. 21–74. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Zhu, X.M.; Zhu, S.F.; McElroy, B. Impact of deep-time palaeoclimate on the sedimentary records and morphology of lacustrine shoal-water deltas, Upper Eocene Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Sedimentology 2021, 68, 3253–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wan, M.L.; Crowley, J.L.; Wang, J.; Luo, X.R.; Tabor, N.; Angielczyk, K.D.; Gastaldo, R.; Geissman, J.; Liu, F.; et al. Paleoenvironmental and paleoclimatic evolution and cyclo- and chrono-stratigraphy of upper Permian-Lower Triassic fluvial-lacustrine deposits in Bogda Mountains, NW China—Implications for diachronous plant evolution across the Permian-Triassic boundary. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 222, 103741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.F.; Liu, S.F.; Tian, C.; Zhuang, Q.T.; Li, R.W.; Tan, M.J.; Steel, R.J. Tectonic and climatic controls on the Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous stratigraphic architecture of the Xuanhua basin, North China. Basin Res. 2022, 34, 190–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pszonka, J.; Zecova, K.; Wendorff, M. Oligocene turbidite fans of the Dukla Basin: New age data from the calcareous nannofossils and paleoenvironmental conditions (Cergowa beds, Polish–Slovakian borderland). Geol. Carpathica 2019, 70, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pszonka, J.; Wendorff, M.; Godlewski, P. Sensitivity of marginal basins in recording global icehouse and regional tectonic controls on sedimentation. Example of the Cergowa Basin, (Oligocene) Outer Carpathians. Sediment. Geol. 2023, 444, 106326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.L.; Liu, B.; Ma, Y.S.; Song, X.M.; Wang, Y.J.; Xin, X.K.; Chen, Z.X. Controlling factors and dynamical formation models of lacustrine organic matter accumulation for the Jurassic Da’anzhai Member in the central Sichuan Basin, southwestern China. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2017, 86, 1391–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Shi, Z.; Baranyi, V.; Kemp, D.B.; Han, Z.; Luo, G.; Hu, J.; He, F.; Chen, L.; Preto, N. The Jenkyns Event (early Toarcian OAE) in the Ordos Basin, North China. Glob. Planet. Change 2020, 193, 103273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Sun, P.; Them II, T.R.; Li, Y.; Sun, S.; Gao, X.; Huang, X.; Tang, Y. Organic geochemistry of a lacustrine shale across the Toarcian Oceanic Anoxic Event (Early Jurassic) from NE China. Glob. Planet. Change 2020, 191, 103214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohacs, K.M.; Carroll, A.R.; Neal, J.E. Lessons from large lake systems-thresholds, nonlinearity, and strange attractions. In Extreme Depositional Environments: Mega End Members in Geological Time; Chan, M.A., Archer, A.W., Eds.; The Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2003; Volume 370, pp. 75–90. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.E.; Carroll, A.R.; Scott, J.J.; Singer, B.S. Early Eocene carbon isotope excursions and landscape destabilization at eccentricity minima: Green River Formation of Wyoming. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 403, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.Q.; Fan, M.J.; Lu, Y.C.; Liu, H.M.; Hao, Y.Q.; Xie, Z.H.; Peng, L.; Du, X.B.; Hu, H.Y. Middle Eocene paleohydrology of the Dongying Depression in eastern China from sedimentological and geochemical signatures of lacustrine mudstone. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2017, 479, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorbergen, L.J.; Abels, H.A.; Hilgen, F.J.; Robson, B.E.; de Jong, E.; Dekkers, M.J.; Krijgsman, W.; Smit, J.; Collinson, M.E.; Kuiper, K.F.; et al. Conceptual models for short-eccentricity-scale climate control on peat formation in a lower Palaeocene fluvial system, north-eastern Montana (USA). Sedimentology 2018, 65, 775–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, T.T.; Ramezani, J.; Lv, D.W.; Wang, C.S. Climate forcing of terrestrial carbon sink during the Middle Jurassic greenhouse climate: Chronostratigraphic analysis of the Yan’an Formation, Ordos Basin, North China. GSA Bull. 2021, 133, 1723–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.G.; Zhang, S.C.; Chen, J.P.; Wang, F.Y.; Wang, P.R. Organic geochemistry of oil and gas in the Kuqa depression, Tarim Basin, NW China. Org. Geochem. 2003, 34, 873–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.C.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, G.Y.; Wang, H.T.; Li, Z.X. Geochemical evidence for coal-derived hydrocarbons and their charge history in the Dabei Gas Field, Kuqa Thrust Belt, Tarim Basin, NW China. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2011, 28, 1364–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.Y.; Yang, S.C.; Hu, S.B. Thermal and maturation history of Jurassic source rocks in the Kuqa foreland depression of Tarim Basin, NW China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 89, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Guo, J.H.; Gao, Y.F. Jurassic sequence stratigraphy and sedimentary facies in Kuqa Depression of Tarim Basin. J. Jianghan Pet. Inst. 2002, 24, 110–113+120, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.D.; Lin, C.S.; Shen, Y.P.; Xie, X.J.; Xiao, J.X.; Liu, J.Y.; Shi, Y.L. Sequence Stratigraphy and Depositional Environments of the Kuche Depression. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2002, 20, 400–407, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Qin, M.K.; Huang, S.H.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.Y.; He, Z.B.; Guo, Q.; Song, J.Y. Sedimentary facies characteristics of early and middle Jurassic in northern monoclinal zone of western Kuqa Depression and uranium metallogenic conditions. Uranium Geol. 2019, 35, 129–136, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.H.; Yang, H.J.; Wei, H.X.; Yu, C.F.; Yang, Z.; Wu, J. The sandstone characteristics and hydrocarbon exploration signification of Lower Jurassic in middle-eastern section of northern tectonic belt in Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2019, 30, 1243–1252, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.H.; Xue, L.Q. Pattern and evolution of Mesozoic continental sequence stratigraphy in the Kuqa depression. Chin. J. Geol. 2002, 37 (Suppl. S1), 121–128, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.S.; Yu, B.S.; Liu, J.Y. Sequence Stratigraphy and Tectono-Geography of Superimposed Basins: Case study on the Tarim Basin in Northwest China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2011; pp. 200–260. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.S.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.M.; Xiao, J.X.; Chen, J.Q.; Ji, Y.L. Depositional architecture of the Tertiary tectonic sequences and their response to foreland tectonism in the Kuqa depression, the Tarim Basin. Sci. China Ser. D 2002, 45, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Shou, J.F.; Chen, Z.L.; Wang, S.Y.; Yang, X.N.; Pi, X.J.; Cai, Z.Z. Sedimentary Characteristics and Sandstone Body Distribution of the Lower Jurassic in Kuqa Depression. J. Palaeogeogr. 2002, 4, 47–58, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.Y.; Wang, Q.H.; Lin, C.S.; Zhang, L.J.; Lei, Y.P.; Hu, G.C.; Hu, B. Sequence and systems tract of Paleogene Kumugeliemu Group in Western Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2008, 35, 651–656, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.K.; Zeng, L.F.; Pan, C.C.; Xiao, Z.Y.; Zhang, H.Z.; Huang, Z.B.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, S.; Xu, H.; Chen, C.S.; et al. Petroleum generation potentials and kinetics of coaly source rocks in the Kuqa Depression of Tarim Basin, northwest China. Org. Geochem. 2019, 133, 32–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.Z.; Gu, J.Y.; Zhang, G.Y. Geological constraints of giant and medium-sized gas fields in Kuqa depression. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2002, 47 (Suppl. S1), 49–55. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.B.; Qi, J.F.; Yang, X.Z.; Liu, Q.Y.; Cao, S.J.; Fan, S.; Sun, T.; Yang, X.Y. Analysis of Mesozoic prototype basin in Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin. Xinjiang Petrol. Geol. 2016, 37, 644–653, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, C.M.; Qu, J.H.; Zhu, R.; Yuan, R.; Pan, J.; Tao, J.Y. A research on relative lacustrine level changes of the Lower Triassic Baikouquan Formation in Mahu Sag of Junggar Basin. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2018, 36, 684–694, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xia, H.; Lin, C.S.; Liu, Y.F.; Li, H.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, H.T.; Su, Z. A research on relative lacustrine level changes of Cretaceous Shushanhe Formation in the Yingmaili area of Tarim Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2019, 30, 1579–1589, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Prokoph, A.; Agterberg, F.P. Wavelet analysis of well-logging data from oil source rock, Egret Member, offshore eastern Canada. AAPG Bull. 2000, 84, 1617–1632. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.X.; Guo, Y.H.; Shen, Y.L.; Shao, Y.B. Study on sequence stratigraphic division by using Milankovitch cycles as constraints. Coal Sci. Technol. 2013, 41, 105–109, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- von Eynatten, H.; Barceló-Vidal, C.; Pawlowsky-Glahn, V. Modelling compositional change: The example of chemical weathering of granitoid rocks. Math. Geol. 2003, 35, 231–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Serrano, J.C.; Föllmi, K.B.; Adatte, T.; Spangenberg, J.E.; Tribovillard, N.; Fantasia, A.; Suan, G. Continental weathering and redox conditions during the early Toarcian oceanic anoxic event in the northwestern Tethys: Insight from the Posidonia shale section in the Swiss Jura Mountains. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2015, 429, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.C.; Guo, G.X.; Cai, X.M.; Thompson, J.A.; Xu, H.Y.; Zhong, N. Geochemical evidence of windblown origin of the late Cenozoic lacustrine sediments in Beijing and implications for weathering and climate change. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2016, 446, 342–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.Q.; Fan, M.J.; Lu, Y.C.; Liu, H.M.; Hao, Y.Q.; Xie, Z.H.; Liu, Z.H.; Peng, L.; Du, X.B.; Hu, H.Y. Climate-driven paleolimnological change controls lacustrine mudstone depositional process and organic matter accumulation: Constraints from lithofacies and geochemical studies in the Zhanhua Depression, eastern China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 167, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miall, A.D. Lithofacies types and vertical profile models in braided river deposits, a summary. In Fluvial Sedimentology; Miall, A.D., Ed.; Geological Survey of Canada: Calgary, AB, Canada, 1978; Volume 5, pp. 597–604. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.M.; Zeng, H.L.; Li, S.L.; Dong, Y.L.; Zhu, S.F.; Zhao, D.N.; Huang, W. Sedimentary characteristics and seismic geomorphologic responses of a shallow-water delta in the Qingshankou Formation from the Songliao Basin, China. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2017, 79, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miall, A.D. Architectural-element analysis: A new method of facies analysis applied to fluvial deposits. Earth-Sci. Rev. 1985, 22, 261–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miall, A.D. The Geology of Fluvial Deposits: Sedimentary Facies, Basin Analysis, and Petroleum Geology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996; pp. 57–98. [Google Scholar]
- Noda, A.; Takeuchi, M.; Adachi, M. Fan deltaic-to-fluvial sedimentation of the Middle Jurassic Murihiku Terrane, Southland, New Zealand. N. Z. J. Geol. Geophys. 2002, 45, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, V.P.; Marriott, S.B. The sequence stratigraphy of fluvial depositional systems: The role of floodplain sediment storage. Sediment. Geol. 1993, 86, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Fan, M.J. Depositional environment, sediment provenance and oxygen isotope paleoaltimetry of the early Paleogene greater Green River Basin, southwestern Wyoming, USA. Am. J. Sci. 2018, 318, 1018–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, E.M. Facies architecture and depositional environments of the Upper Cretaceous Kaiparowits Formation, southern Utah. Sediment. Geol. 2007, 197, 207–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridge, J.S. Fluvial facies models: Recent developments. In Facies Models Revisited; Posamentier, H., Walker, R.G., Eds.; SEPM Society for Sedimentary Geology: Claremore, OK, USA, 2006; Volume 84, pp. 85–170. [Google Scholar]
- Midwinter, D.; Hadlari, T.; Dewing, K. Lower Triassic river-dominated deltaic successions from the Sverdrup Basin, Canadian Arctic. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2017, 476, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, Q.Q.; Luo, S.S.; Fu, J.H.; Niu, X.B.; Xu, L.M.; Feng, S.B.; Li, S.X. Detailed study of lake fine grained deposition characteristics: A case study from Chang 7 of Yanhe section, Ordos Basin. Geoscience 2018, 32, 364–373, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, S.Y. Meandering river sand body architecture and heterogeneity: A case study of permian meandering river outcrop in palougou, baode, shanxi province. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2016, 43, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collinson, J.D. Alluvial sediments. In Sedimentary Environments: Processes, Facies and Stratigraphy; Reading, H.G., Ed.; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 1996; pp. 36–82. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.S.; Jiang, J.; Shi, H.S.; Zhang, Z.T.; Liu, J.Y.; Qin, C.G.; Li, H.; Ran, H.J.; Wei, A.; Tian, H.X.; et al. Sequence architecture and depositional evolution of the northern continental slope of the South China Sea: Responses to tectonic processes and changes in sea level. Basin Res. 2018, 30, 568–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.J.; Hu, M.Y.; Wu, Y.K.; Huang, M.Z.; Lu, K.N.; Cai, Q.S.; Hu, Z.G.; Du, J.B.; Yuan, L.; Qian, Z.T.; et al. Lacustrine to deltaic depositional systems: Sedimentary evolution and controlling factors of an Upper Cretaceous continental depression and implications for petroleum exploration. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2025, 173, 107234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazi, S.; Mountney, N.P. Facies and architectural element analysis of a meandering fluvial succession: The Permian Warchha Sandstone, Salt Range, Pakistan. Sediment. Geol. 2009, 221, 99–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tineo, D.E. Facies model of a sedimentary record for a Pantanal-like inland wetland. Sedimentology 2020, 67, 3683–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellwood, B.W. The genesis of some sideritic beds in the Yorkshire Lias (England). J. Sediment. Petrol. 1971, 41, 854–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.C.; Wang, H.Y.; Fan, T.L.; Zhang, H.A.; Yang, R.Z.; Li, Y.F.; Long, S.F. Rift-related sedimentary evolution and its response to tectonics and climate changes: A case study of the Guaizihu sag, Yingen-Ejinaqi Basin, China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2020, 195, 104370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.H.; Lu, Y.Z.; Fan, R.; Fang, L.H.; Li, X.; Liu, L. Structural controls on facies distribution in a small half-graben basin: Luanping Basin, Northeast China. Basin Res. 2010, 22, 33–44. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.W.; Su, X.; Jiang, Z.L. Sedimentary characteristics of large-scale lacustrine beach-bars and their formation in the Eocene Boxing sag of Bohai Bay Basin, east China. Sedimentology 2011, 58, 1087–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oesterlen, P.M.; Lepper, J. The Lower Karoo coal (k2-3) of the Mid-Zambezi basin, Zimbabwe: Depositional analysis, coal genesis and palaeogeographic implications. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2005, 61, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohacs, K.; Suter, J. Sequence stratigraphic distribution of coaly rocks: Fundamental controls and paralic examples. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull. 1997, 81, 1612–1639. [Google Scholar]
- Catuneanu, O.; Abreu, V.; Bhattacharya, J.P.; Blum, M.D.; Dalrymple, R.W.; Eriksson, P.G.; Fielding, C.R.; Fisher, W.L.; Galloway, W.E.; Gibling, M.R.; et al. Towards the standardization of sequence stratigraphy. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2009, 92, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.S. Sequence and depositional architecture of sedimentary basin and process responses. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2009, 27, 849–861, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.K.; Lin, C.S.; Yang, H.J.; Liu, J.Y.; Liu, Y.F.; Li, H.; Yang, X.Z.; Jiang, J.; He, Q.L.; Gao, D.K. Major unconformities in the Mesozoic sedimentary sequences in the Kuqa-Tabei region, Tarim Basin, NW China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 183, 103957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.X.; Hou, Z.J. A semiquantitative analytical method for base level changes of high resolution sequence and its application to study of member 4 of Lower Cretaceous Quantou Formation in Songliao Basin. J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. Sci. Technol. Ed. 2014, 41, 157–170, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, D.X.; Lin, W.; Wang, Q.C. Mesozoic-Cenozoic clastic composition in Kuqa depression, Northwest China: Implication for provenance types and tectonic attributes. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2004, 20, 655–666, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Peng, S.T. Detrital zircon geochronology and its provenance implications: Responses to Jurassic through Neogene basin-range interactions along northern margin of the Tarim Basin, Northwest China. Basin Res. 2010, 22, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, J.J.; Liu, K. Continuous denudation and pediplanation of the Chinese Western Tianshan orogen during Triassic to Middle Jurassic: Integrated evidence from detrital zircon age and heavy mineral chemical data. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 113, 310–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.Y.; Zhu, R.K.; Feng, J.R.; Li, X.P.; Zhao, X.S.; Guo, M.L. Jurassic-Neogene conglomerate characteristics in Kuqa Depression and their response to tectonic uplifting of Tianshan Mountains. Oil Gas Geol. 2015, 36, 534–544, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.X.; Qin, T.X.; Yang, Z.Y. Sedimentary facies of the Triassic-Jurassic strata in the Tarim Basin, Xinjiang. Sediment. Geol. Tethyan Geol. 2003, 23, 37–44, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.L.; Chen, Z.X.; Lei, Y.L.; Zhang, C.J. Structural geology correlation of foreland thrust-folded belts between the southern and northern edges of the Tianshan Mountain and some suggestions for hydrocarbon exploration. Acta Pet. Sin. 2011, 32, 395–403, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jolivet, M.; Dominguez, S.; Charreau, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.G.; Wang, Q.C. Mesozoic and Cenozoic tectonic history of the central Chinese Tian Shan: Reactivated tectonic structures and active deformation. Tectonics 2010, 29, 391–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.D.; Jolivet, M.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Cheng, F.; Bei, Z.; Guo, Z.J. Latest Paleozoic-early Mesozoic basin-range interactions in South Tian Shan (Northwest China) and their tectonic significance: Constraints from detrital zircon U-Pb ages. Tectonophysics 2013, 599, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.T.; Song, C.C.; He, S. Jurassic tectonostratigraphic evolution of the Junggar basin, NW China: A record of Mesozoic intraplate deformation in Central Asia. Tectonics 2015, 34, 86–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattak, S.A.; Khan, N.; Khan, W.; Dhas, S.S.J.; Kontakiotis, G.; Islam, I.; Janjuhah, H.T.; Antonarakou, A. Sedimentology and reservoir characterisation of Lower Jurassic clastic sedimentary rocks, Salt and Trans Indus Ranges, Pakistan: Evidence from petrography, scanning electron microscopy and petrophysics. Depos. Rec. 2025, 11, 698–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, K.A.; Rizwan, M.; Janjuhah, H.T.; Islam, I.; Kontakiotis, G.; Bilal, A.; Arif, M. An integrated petrographical and geochemical study of the Tredian Formation in the Salt and Trans-Indus Surghar ranges, North-West Pakistan: Implications for palaeoclimate. Depos. Rec. 2024, 10, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, J.; Jolivet, M.; Robin, C.; Heilbronn, G.; Barrier, L.; Bourquin, S.; Jia, Y.Y. Jurassic paleogeography of the Tian Shan: An evolution driven by far-field tectonics and climate. Earth Sci. Rev. 2018, 187, 286–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Qiu, N.S.; Li, C.X. Uplift and exhumation in the Tianshan, western China: New insights from detrital zircon morphology and thermochronology. Sci. Sin. Terrae 2022, 65, 449–461. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites. Nature 1982, 299, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedo, C.M.; Grant, G.M.; Nesbitt, H.W. Paleoclimatic control on the composition of the Paleoproterozoic Serpent formation, Huronian Supergroup, Canada: A greenhouse to icehouse transition. Precambrian Res. 1997, 86, 201–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.T.; Chen, D.Z.; Wang, Q.C.; Wang, J.G. Large-scale climatic fluctuations in the latest Ordovician on the Yangtze block, south China. Geology 2010, 38, 599–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Du, Y.S.; Yu, W.C.; Algeo, T.J.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, Y.; Qi, L.; Yuan, L.J.; Pan, W. The chemical index of alteration (CIA) as a proxy for climate change during glacial-interglacial transitions in Earth history. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 201, 103032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Guo, S.B. Sedimentary response and restoration of paleoshoreline of Taiyuan-Shanxi Formations in North China basin. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2023, 152, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLennan, S.M.; Hemming, S.; McDaniel, D.K.; Hanson, G.N. Geochemical approaches to sedimentation, provenance, and tectonics. In Processes Controlling the Composition of Clastic Sediments; Johnsson, M.J., Basu, A., Eds.; The Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1993; Volume 284, pp. 21–40. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Ruhl, M.; Jenkyns, H.C.; Hesselbo, S.P.; Riding, J.B.; Selby, D.; Naafs, B.D.A.; Weijers, J.W.H.; Pancost, R.D.; Tegelaar, E.W.; et al. Carbon sequestration in an expanded lake system during the Toarcian oceanic anoxic event. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wu, S.H.; Xia, D.L.; You, X.L.; Zhang, H.M.; Lu, H. Major and trace element geochemistry of the lacustrine organic-rich shales from the Upper Triassic Chang 7 Member in the southwestern Ordos Basin, China: Implications for paleoenvironment and organic matter accumulation. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2020, 111, 852–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.S. Jurassic palynological assemblages from the northern margin in the Tarim Basin of Xinjiang, NW China. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sin. 1998, 15, 144–165, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.N.; Zhan, J.Z.; Zou, Y.S.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, C.M.; Xiao, J.N. Sedimentary environments and palaeoclimate of the Triassic and Jurassic in Kuqa river area, Xinjiang. J. Palaeogeogr. 2003, 5, 197–208, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Joral, F.G.; Gómez, J.J.; Goy, A. Mass extinction and recovery of the Early Toarcian (Early Jurassic) brachiopods linked to climate change in northern and Central Spain. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2011, 302, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Them, T.R.; Gill, B.C.; Selby, D.; Gröcke, D.R.; Friedman, R.M.; Owens, J.D. Evidence for rapid weathering response to climatic warming during the Toarcian Oceanic Anoxic Event. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhou, D.; Yang, B.; Tong, J.S.; Luo, S.; Chen, Y.H.; He, N.X.; Liu, H.L.; Luo, P. The depositional evolution and controlling factors of the Lower Triassic Baikouquan Formation, Northern Mahu Slope, Junggar Basin, NW China. Geol. J. 2021, 56, 2720–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.H.; Zhu, R.; Tang, Z.H.; Liu, Z.G.; Zhao, X.F.; Chen, Z.C. Sedimentary environments of the Cangfanggou Group in Junggar Basin, Xinjiang, in response to climate and tectonic regime. Acta Geol. Sin. Engling Ed. 2000, 74, 795–806. [Google Scholar]
- Min, W.W.; Deng, H.W.; Xia, S.Q.; Ye, D.Q. The transition from meandering river delta to braided river delta: Depositional characteristics and controlling factors from the second member of Shanxi Formation to the eighth member of Lower Shihezi Formation in Southeastern Ordos Basin transition from meandering river delta to braided river delta. Geol. J. 2020, 55, 8122–8140. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.L.; Zou, C.N.; Qiu, Z.; Pan, S.Q.; Zhang, W.Z.; Jing, Z.H.; Hao, J.H.; Yin, S.; Wu, S.T.; Li, S.X.; et al. Sedimentary enrichment factors of extraordinarily high organic matter in the sub-member 3 of Member 7 of Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2022, 43, 1520–1541, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Flores, R.M.; Sykes, R. Depositional controls on coal distribution and quality in the Eocene Brunner Coal Measures, Buller Coalfield, South Island, New Zealand. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1996, 29, 291–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einsele, G.; Hinderer, M. Quantifying denudation and sediment–accumulation systems (open and closed lakes): Basic concepts and first results. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1998, 140, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Q.; Wang, M.; Wang, D.D.; Cao, Y.P.; Yan, Z.M. Composition characteristics and genetic mechanism of ultra thick coal seams: A case study of the Middle Jurassic in the Yuqia area, northern Qaidam Basin. Coal Sci. Technol. 2024, 52, 176–190, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Deng, S.H.; Lu, Y.Z.; Fan, R.; Fang, L.H.; Li, X.; Liu, L. Toarcian (Early Jurassic) Oceanic Anoxic Event and the Responses in Terrestrial Ecological System. Earth Sci. J. China Univ. Geosci. 2012, 37 (Suppl. S2), 23–38, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Da, X.J.; Zhu, Z.X.; Xu, G.W.; Mao, W.C.; Huang, W.K.; Xia, F.; Yang, P.L.; Luo, Y.H.; Liao, X.J. Response to carbon cycle perturbation during the Toarcian oceanic anoxic event in terrestrial strata of China. J. Palaeogeogr. 2025, 27, 528–540, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.Q.; Zhang, D.W.; Zhou, Y.X.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wu, K.Y.; Zhang, P.C.; Han, Q.C.; Li, F.J.; Ma, C. Astronomical forcing in the coal-bearing Middle Jurassic Dameigou Formation, Qaidam Basin, northwestern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 161, 105663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).