Readability Formulas for Elementary School Texts in Mexican Spanish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional Readability Formulas
2.2. Readability Models Produced by Machine Learning Algorithms
3. Methodology
3.1. Corpus Compilation
3.2. Design of the Point-Based Readability Scale
3.3. Readability Formula Based on Linear Regression
3.4. Automatic Generation of a Readability Formula Using GP
| Algorithm 1: Genetic Programming for Readability Formula Discovery |
 |
4. Experimental Study
4.1. Benchmark Indices
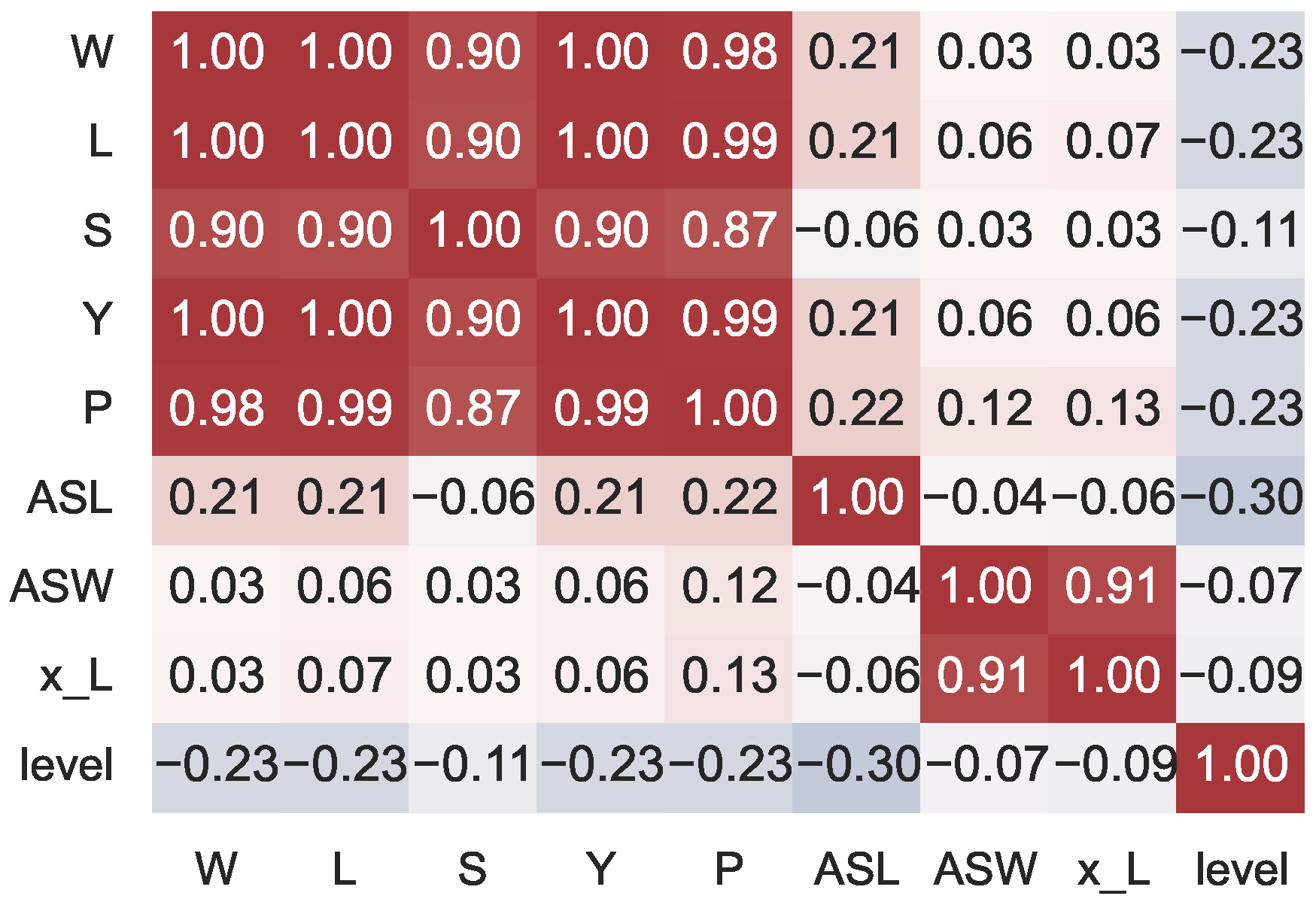
4.2. Statistical Analysis
4.3. Performance Metrics
4.4. Experimental Results
4.5. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GP | Genetic programming |
| NLP | Natural language processing |
| ML | Machine learning |
| NLTK | Natural Language Toolkit |
| MSE | Mean squared error |
| RMSE | Root mean squared error |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| HSD | Honestly significant differences |
References
- Fry, E.B. Elementary Reading Instruction; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- North, K.; Zampieri, M.; Shardlow, M. Lexical Complexity Prediction: An Overview. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, R.G. Reconstructing Readability: Recent Developments and Recommendations in the Analysis of Text Difficulty. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2012, 24, 63–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, E.A.; Gruba, P.; Velloso, E. The Relative Contribution of Language Complexity to Second Language Video Lectures Difficulty Assessment. Mod. Lang. J. 2022, 106, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaundinya, T.; El-Behaedi, S.; Choi, J.N. Readability of Online Patient Education Materials for Graft-Versus-Host Disease. J. Cancer Educ. 2023, 38, 1363–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajjala, S. Trends, Limitations and Open Challenges in Automatic Readability Assessment Research. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2105.00973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imperial, J.M. BERT Embeddings for Automatic Readability Assessment. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.07935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filighera, A.; Steuer, T.; Rensing, C. Automatic Text Difficulty Estimation Using Embeddings and Neural Networks. In Transforming Learning with Meaningful Technologies, Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Technology Enhanced Learning Delft, The Netherlands, 16–19 September 2019; Scheffel, M., Broisin, J., Pammer-Schindler, V., Ioannou, A., Schneider, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 335–348. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Gu, Q.; Yin, Y.; Chen, D. Enriching Word Embeddings with Domain Knowledge for Readability Assessment. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Santa Fe, NM, USA, 20–26 August 2018; pp. 366–378. [Google Scholar]
- Martinc, M.; Pollak, S.; Robnik-Šikonja, M. Supervised and Unsupervised Neural Approaches to Text Readability. Comput. Linguist. 2021, 47, 141–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancey, K.; Pintard, A.; Francois, T. Investigating readability of French as a foreign language with deep learning and cognitive and pedagogical features. Lingue Linguaggio Riv. Semest. 2021, 2, 229–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, F.; Ostendorf, M. Estimating Linguistic Complexity for Science Texts. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth Workshop on Innovative Use of NLP for Building Educational Applications, New Orleans, LA, USA, 5 June 2018; Tetreault, J., Burstein, J., Kochmar, E., Leacock, C., Yannakoudakis, H., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.W.; Jang, Y.S.; Lee, J.H.J. Pushing on Text Readability Assessment: A Transformer Meets Handcrafted Linguistic Features. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2109.12258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaparthi, V.S.; Pawar, A.A.; Suneera, C.M.; Prakash, J. Rating Ease of Readability using Transformers. In Proceedings of the 2022 14th International Conference on Computer and Automation Engineering (ICCAE), Brisbane, Australia, 25–27 March 2022; pp. 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flesch, R.F. Art of Readable Writing; MAcmilla Publishing: Sydney, Australia, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Huerta, J. Medidas sencillas de lecturabilidad. Consigna 1959, 214, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez de Polini, L.E. Investigación Sobre Lectura en Venezuela. Technical report. In Primeras Jornadas de Educación Primaria; Ministerio de Educación: Caracas, Venezuela, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Szigriszt-Pazos, F. Sistemas Predictivos de Legibilidad del Mensaje Escrito: Fórmula de Perspicuidad. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Facultad de Ciencias de la Información, Madrid, Spain, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Barrio Cantalejo, I.M. Legibilidad y Salud: Los métodos de Medición de la Legibilidad y su Aplicación al Diseño de Folletos Educativos Sobre Salud. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Madrid, Spain, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Baquedano, M.M. Legibilidad y variabilidad de los textos. Boletín Investig. Educ. Artículo Rev. 2006, 21, 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Crawford, A.N. A Spanish Language Fry-Type Readability Procedure: Elementary Level; Evaluation, Dissemination and Assessment Center, California State University: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1984; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Contreras, A.; García-Alonso, R.; Echenique, M.; Daye-Contreras, F. The SOL Formulas for Converting SMOG Readability Scores Between Health Education Materials Written in Spanish, English, and French. J. Health Commun. 1999, 4, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucisano, P.; Piemontese, M.E. Gulpease: Una formula per la predizione della difficolta dei testi in lingua italiana. Sc. Citta 1988, 3, 57–68. [Google Scholar]
- El-Haj, M.; Rayson, P. OSMAN—A Novel Arabic Readability Metric. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’16), Portorož, Slovenia, 23–28 May 2016; Calzolari, N., Choukri, K., Declerck, T., Goggi, S., Grobelnik, M., Maegaard, B., Mariani, J., Mazo, H., Moreno, A., Odijk, J., et al., Eds.; European Language Resources Association (ELRA): Paris, France, 2016; pp. 250–255. [Google Scholar]
- Pantula, M.; Kuppusamy, K.S. A Machine Learning-Based Model to Evaluate Readability and Assess Grade Level for the Web Pages. Comput. J. 2020, 65, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ji, M.; Lin, S.S.; Zhao, M.; Lyv, Z. Combining Readability Formulas and Machine Learning for Reader-oriented Evaluation of Online Health Resources. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 67610–67619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Anguita, R.; Montejo Ráez, A.; Martínez Santiago, F.; Díaz Galiano, M.C. Legibilidad del texto, métricas de complejidad y la importancia de las palabras. Proces. Leng. Nat. 2018, 61, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uçar, S.Ş.; Aldabe, I.; Aranberri, N.; Arruarte, A. Exploring Automatic Readability Assessment for Science Documents within a Multilingual Educational Context. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2024, 34, 1417–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morato, J.; Iglesias, A.; Campillo, A.; Sanchez-Cuadrado, S. Automated readability assessment for spanish e-government information. J. Inf. Syst. Eng. Manag. 2021, 6, em0137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, S.; Loper, E. NLTK: The Natural Language Toolkit. In Proceedings of the ACL Interactive Poster and Demonstration Sessions, Barcelona, Spain, 21–26 July 2004; pp. 214–217. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, D.M.; Yin, X. A faster algorithm for ridge regression of reduced rank data. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2002, 40, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koza, J.R. Genetic Programming: On the Programming of Computers by Means of Natural Selection; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Evett, M.; Fernandez, T. Numeric mutation improves the discovery of numeric constants in genetic programming. Genet. Program. 1998, 98, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Coayahuitl, L.; Morales-Reyes, A.; Escalante, H.J. TurboGP: A flexible and advanced python based GP library. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.00149. [Google Scholar]
- Stephens, T. Genetic Programming in Python with a Scikit-Learn Inspired API. Available online: https://gplearn.readthedocs.io/en/stable (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Fortin, F.A.; De Rainville, F.M.; Gardner, M.A.G.; Parizeau, M.; Gagné, C. DEAP: Evolutionary algorithms made easy. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2012, 13, 2171–2175. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M.B. An Analysis of Variance Test for Normality (Complete Samples). Biometrika 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukey, J.W. The Problem of Multiple Comparisons; Princeton University: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1953; Unpublished Manuscript. [Google Scholar]
- Devnath, L.; Kumer, S.; Nath, D.; Das, A.; Islam, R. Selection of wavelet and thresholding rule for denoising the ECG signals. Ann. Pure Appl. Math. 2015, 10, 65–73. [Google Scholar]




| Fernández-Huerta and | Gutiérrez de Polini (6th Grade) | Szigriszt-Pazos | Inflesz | Readability Levels |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 91–100 (4th grade) | >70 | 86–100 | 80–100 | Very easy |
| 81–90 (5th) | 61–70 | 76–85 | 65–80 | Easy |
| 71–80 (6th) | 51–60 | 66–75 | Relatively easy | |
| 61–70 (7th to 8th) | 41–50 | 51–65 | 55–65 | Standard |
| 51–60 (9th to 10th) | 34–40 | 36–50 | Relatively difficult | |
| 31–50 (11th to 12th) | 21–33 | 16–35 | 40–55 | Difficult |
| 0–30 (College) | ≤20 | 0–15 | 0–40 | Very difficult |
| Grade | 1st | 2nd | 3th | 4th | 5th | 6th |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avg. number of words | 83.37 | 205.68 | 226.94 | 302.28 | 295.37 | 299.63 |
| Avg. number of sentences | 8.83 | 19.52 | 21.49 | 18.96 | 20.71 | 19.83 |
| Avg. number of words per sentence | 9.41 | 11.01 | 12.52 | 17.80 | 14.63 | 15.51 |
| Avg. number of syllables per word | 1.76 | 1.78 | 1.80 | 1.80 | 1.77 | 1.81 |
| Avg. number of letters per word | 4.35 | 4.41 | 4.47 | 4.47 | 4.42 | 4.50 |
| Readability Scale | Mexican Elementary Grade Levels | Readability Levels |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 1st grade | Very easy |
| 80 | 2nd grade | Easy |
| 60 | 3rd grade | Relatively easy |
| 40 | 4th grade | Standard |
| 20 | 5th grade | Relatively difficult |
| 0 | 6th grade | Difficult |
| <0 | 7th grade or higher | Very difficult |
| Population size (N) | 5000 |
| Number of generations (G) | 50 |
| Maximum allowed tree depth | 2 |
| Selection method | Binary tournament |
| Protected crossover rate () | 0.30 |
| Protected mutation rate () | 0.30 |
| Protected numeric mutation rate () | 0.40 |
| Primitives | mean |
| Constants range | [−1, 1] |
| Formula | MSE | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fernández-Huerta | 516.60 | 22.73 | −0.771 |
| Gutiérrez-Polini | 1095.04 | 33.09 | 0.061 |
| Szigriszt-Pazos | 452.08 | 21.26 | −0.550 |
| 949.85 | 30.82 | −2.257 | |
| Linear-MX | 959.35 | 30.97 | 0.178 |
| GP-MX | 958.39 | 30.96 | 0.179 |
| Flesch | 5151.27 | 71.77 | −16.662 |
| Gulpease | 2029.19 | 45.05 | −5.957 |
| Osman | 2040.00 | 45.17 | −5.994 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fajardo-Delgado, D.; Rodriguez-Coayahuitl, L.; Sánchez-Cervantes, M.G.; Álvarez-Carmona, M.Á.; Rodríguez-González, A.Y. Readability Formulas for Elementary School Texts in Mexican Spanish. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7259. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137259
Fajardo-Delgado D, Rodriguez-Coayahuitl L, Sánchez-Cervantes MG, Álvarez-Carmona MÁ, Rodríguez-González AY. Readability Formulas for Elementary School Texts in Mexican Spanish. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(13):7259. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137259
Chicago/Turabian StyleFajardo-Delgado, Daniel, Lino Rodriguez-Coayahuitl, María Guadalupe Sánchez-Cervantes, Miguel Ángel Álvarez-Carmona, and Ansel Y. Rodríguez-González. 2025. "Readability Formulas for Elementary School Texts in Mexican Spanish" Applied Sciences 15, no. 13: 7259. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137259
APA StyleFajardo-Delgado, D., Rodriguez-Coayahuitl, L., Sánchez-Cervantes, M. G., Álvarez-Carmona, M. Á., & Rodríguez-González, A. Y. (2025). Readability Formulas for Elementary School Texts in Mexican Spanish. Applied Sciences, 15(13), 7259. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137259









