Abstract
Multi-view data improve the effectiveness of clustering tasks, but they often encounter complex noise and corruption. The missing view of the multi-view samples leads to serious degradation of the clustering model’s performance. Current multi-view clustering methods always try to compensate for the missing information in the original domain, which is limited by the linear representation function. Even more, their clustering structures across views are not sufficiently considered, which leads to suboptimal results. To solve these problems, a tensioned multi-view subspace clustering algorithm is proposed based on sequential kernels to integrate complementary information in multi-source heterogeneous data. By superimposing the kernel matrix based on the sequential characteristics onto the third-order tensor, the robust low-rank representation for the missing is reconstructed by the matrix calculation of sequential kernel learning. Moreover, the tensor structure helps subspace learning to mine the high-order associations between different views. Tensioned Multi-view Ordered Kernel Subspace Clustering (TMOKSC) implements the ADMM framework. Compared with current representative multi-view clustering algorithms, the proposed TMOKSC algorithm is the best in many objective measures. In general, the robust sequential kernel represents the tensor fusion potential subspace structure.
1. Introduction
With the exponential growth of online data, clustering tasks enable people to get rid of the heavy workload of grouping, and automatically labeling samples becomes possible. Sparse Subspace Clustering algorithms can effectively capture the intrinsic geometric characteristics of data [1] to carry out effective data segmentation [2,3]. Nowadays, multi-view heterogeneous data have brought about various forms of expression online; as a result, multi-view subspace clustering has become mainstream. For example, when a visual object is caught by different cameras with different angles, the visual object can be presented with different views with diverse rotation views and distinct zoom compositions. In this way, multi-view data enriches the information of the samples. Naturally, multi-view subspace clustering mines complementary information from different perspectives, which is helpful for identifying potential low-dimensional subspace structures in high-dimensional datasets [4].
Current multi-view subspace clustering algorithms work well, relying on complete multi-view data. But in real life, the data of views are often missing seriously, so incomplete multi-view subspace clustering algorithms face great challenges, while normal multi-view methods have no effect [5,6,7] under these circumstances. For example, due to the different camera lights or angles, the obtained data often suffers from information loss in real scenarios. These reasons limit clustering tasks to acquire low-dimensional representations of data with incomplete feature descriptions. In text analysis, various language grammatical structures and expressions result in distinct semantic information. There is no doubt that data deficiency will disrupt the correlation between different views of the original data, and it can lead to different emotional orientations. In scenarios of treatment, the loss of sample data due to sensor failures is very common, and the legacy data is often accompanied by complex noise. Of course, the loss of samples may be random, regular, or even related to some variables. Therefore, in the big data era, it is extremely difficult to accurately identify these loss patterns, and multi-view subspace clustering algorithms are difficult to effectively handle these complex scenarios. So, incomplete multi-view subspace clustering has turned into a research hotspot with great challenges.
Incomplete data results in the loss of the effective information they contain. Mitra generated the probability distribution [8] for each sample of each view, attempting to learn the unified probability distribution of the sample in distinct views with the merging method, and such an integrated embedding was generated in the low-dimensional space to effectively preserve the neighbor relationship. Wang obtained the robust graph representation of each view through semi-non-negative matrix factorization and then used Laplacian regularization to perform fusion learning on the graph [9]. The discriminative Sparse Representation learning (DSRL) model measured the similarity of existing features and simultaneously integrates the sparse regularization term and the consistent regularization term to learn a discriminative dictionary [10] from the original samples. Jie Wen adopted a multi-view graph learning technique in spectral subspace incomplete clustering for the general representation and then used k-means for data partitioning [11]. The adversarial Incomplete Multi-view Subspace Clustering [12] framework combined element reconstruction and generative adversarial networks to seek common latent representations of multi-view data for inferring missing data. Another framework with Robust Matrix Completion [13] introduced low-rank constraints to estimate missing values. These shallow models above often ignore the clustering structure characteristics among multi-view data, thus failing to mine the dependencies between different views well. Guo [14] added the extracted matrix to the original matrix in tensor form, applying base-order limitations of the tensor to delve into higher-order correlations.
By applying low-order constraints of tensors based on sequential kernels, Tensioned Multi-view Ordered Kernel Subspace Clustering (TMOKSC) explores the higher-order correlations among different views. On the other hand, a sequential regularization method reflects the interrelation of each subspace. The merits of the proposed TMOKSC algorithm are manifested in:
- In the high-dimensional kernel feature space, the inner product of the vector is expanded by the sequential kernel function.
- The missing samples are completed with the sequential kernel matrix calculation so as to implicitly map the nonlinear samples to high-dimensional kernel features.
- The tensioned kernel representation not only realizes the linear transformation for the nonlinear data but also mines the high-order correlations among views with tensor transformation.
2. Incomplete Multi-View Subspace Clustering
In most cases, each view of data is updated independently. So, the missing effective information contained in each view will lead to clustering errors in the case of incomplete multi-view situations. Early multi-view learning models (as it is shown in Table 1) such as Weighted Multi-view spectral clustering based on spectral perturbation (WMSC), Affinity aggregation for spectral clustering (AASC) and Multi-view Clustering via Adaptively Weighted Procrustes (AWP) directly ignore non-existing information [5,6,7] and do not fill in the missing data. These model learning methods only use complete multi-view information. Naturally, they cannot handle incomplete multi-view data. These models are to continue to be used at the expense of sacrificing certain valuable information.

Table 1.
Some modern approaches for incomplete Multi-View clustering.
For incomplete clustering, a naive idea is to try to adopt the data completion method. Liang [15] selected the overlapping parts of views for alignment. Furthermore, he made full use of the feature transformation of the cross-views to complete the unobserved samples and carried out modeling. Li [16] proposed an algorithm to achieve incomplete kernel completion based on low-redundancy multi-kernel and then captured the approximate subspace representation. However, such data-filling methods are prone to producing noise, which gives rise to similar instances in the same view not being well grouped. Multi-kernel learning (MKL) relies on experience to integrate different kernel functions [17,18]. However, on this multi-view dataset with a missing sample, incomplete kernel inputs lead to difficulty in aligning multiple kernels, resulting in poor performance of kernel-based methods. DKLM utilizes a data-driven technique to retain the local manifold structure within each nonlinear subspace, thereby obtaining high-quality spectral clustering. Meanwhile, Deep Subspace Clustering Networks (DSCN) are also carried out through deep semantic mapping and are a popular modern approach [19].
Average value completion or the third subspace completion always adopts a shallow clustering structure, which cannot well handle the dependencies and differences among views. In fact, there are higher-order connections among views to construct the consensus matrix. Tensors are experts in expressing the senior-order correlation among multi-view samples in space clustering [20]. The secret lies in fully considering the clustering structure to improve the final performance.
This structural characteristic of the tensor pays more attention to the clustering structure of the multi-view data to uncover the latent information from the missing data. The Low-rAnk Tensor regularization viEws Recovery (LATER) [21] jointly reconstructed and utilized the missing views in a unified model. Moreover, it learned multi-layer graphs for comprehensive similarity discovery. The low-rank tensor Learning (LRTL) method [22] fused multi-view embedding matrices to form a three-norm tensor, which aimed to obtain consistent low-dimensional embedding characteristics. While in the tensor low-rank constrained learning model [23], the tensor Schatchen p norm served as a closer approximation for tensor rank in clustering, maintaining consistency and uniqueness. The above-mentioned methods performed particularly well when dealing with missing multi-view data. Therefore, the exploration of tensor Subspace Clustering in theory and practice has gradually become a research hotspot.
Xie adopts a new tensor low-rank regularizer for the rotating self-representation coefficient tensor [24]. However, in actual applications, data features usually exist in the nonlinear subspaces. The solution for extracting potential low-dimensional subspace structures is to apply kernel-induced mappings to ensure the separability of different view self-representation coefficients.
The Tensioned Incomplete Multi-View Kernel Space Clustering (TIMKSC) method combines kernel learning techniques into the incomplete subspace clustering framework [25] with the aim of maintaining global consistency among different views.
3. The Proposed TMOKSC Algorithm
3.1. Multi-View Ordered Kernel Subspace Clustering Based on Tensor
In the multimodal sparse subspace clustering model, the similarity kernel function of samples often appears in the form of pairwise inner products. The proposed TMOKSC algorithm considers the preservation of local sequential information coinciding with the fusion of global information, as shown in Figure 1. Its goal is to capture the overall structure of the clustering by matrix operations.

Figure 1.
Tensioned Multi-view Ordered Kernel Subspace Clustering.
Multi-view subspace clustering algorithms often assume that heterogeneous data are located in the union of the same linear subspaces. It often roughly learns association graphs from the original data containing noise and missing views. In extreme cases, it even damages the clustering structure, which is originally inseparable in a low-dimensional linear space. By analyzing the context of data across views, we can observe the sparsity of the original data and the sequential relationship among the inherence data. Suppose represent the specific norm of the noises matrix of We respectively explore the inherent consistent information to represent noise by integrating the sparse regularization term , meanwhile, we adopt the consistent regularization domain to modify the sequential complementary information. So its objective function is generally expressed as:
If we replace the noise term according to the norm of the difference between the sample and the reconstructed sample. Then the formula turns to:
At present, the dot product in the kernel function mainly reflects the included angle relationship of the samples. This rough similarity function may cause an inaccurate result. The spatial distance dissimilarity measure is timely added to reflect the distribution of the samples in the feature space.
From the perspective of sequence characteristics, the selection of kernel functions is detrimental to the performance of kernel learning. So, a good selection of kernel functions is necessary for the success of the kernel subspace clustering method. In the sample set X, the dot product is often used to initially describe the similarity of two vectors . In addition to reflecting the global relationship of the vector field, the sequential kernel function is proposed. Taking into account the sequential relationship among vector samples, the function is represented as follows:
Here, means the physical position of the sample. In the construction of this kernel function, the sequential function is defined in the spatiotemporal domain to reflect a new ordered feature. The sequential constraint kernel function can obey its following properties:
- (1)
- Non-negativity:
- (2)
- Symmetry:
This kernel matrix K induced by this kernel function also satisfies non-negativity and symmetry. Thus, the representation of order norm in the spatial domain is added to the feature space. Certainly, the idea of the neighborhood can be applied to the design of the optimization model.
To represent the incomplete data samples , the only change we need to make is to generate the optimal consensus kernel. indicates the multi-kernel matrix of this incomplete observation sample. The multiple base kernel functions set are weighted and fused into an optimal consensus kernel to handle the nonlinear structure of the data.
Correspondingly, our objective function becomes:
In the objective function, the item is presented as noise or outlier. Here, indicates the Frobenius norm, conducts an adaptive learning sequence structure, this penalty item forced the similarity samples between the sequence relationship and obtained the local correlation of the model. Here, R is defined as:
Finally, through the similarity between tensors, the global consensus clustering structure is propagated, emphasizing the complete similarity structure among all samples.
The emphasis on the order penalty term in the consensus kernel considers view-specific local information and global information fusion, replacing incomplete views for clustering. This adaptive learning sequence structure can alleviate the cognitive bias caused by insufficient information from the high-order linearly separable feature space.
The missing data of different views does not belong to the same sample. Therefore, the similarity matrix obtained from this can only restore the underlying local popular structure. We make up for this deficiency by learning the complete clustering index for each view.
The multi-view clustering method solves an affinity graph with a consensus representation, and the model optimization results mainly depend on the optimal consensus affinity graph. Conventional model optimization only lies in seeking the optimal consensus kernel matrix. We attempt to utilize the order kernel to enhance the consensus affinity graph. Furthermore, we reduce the interference of data noise on the learning of the target affinity graph all the time. Since different views share the same clustering structure, the optimal consensus affinity graph is constructed using a low-rank tensor to seek the high-order consensus relationship existing among different kernel matrices.
The tensor is composed of subspace representations stacking together, in the form of , which size is After rotating, its size can be turned into . Tension acts as an internal stress that resists deformation; in this rotation way, it is convenient to obtain high-order correlations between samples in the row direction, and it is easy to get high-order correlations between views in the column direction. We divide the original data into two different levels. The original principal components are deduced in the form of tensors, striving to achieve a certain consistency of the spectral block matrix in the feature space. However, directly converting feature tensors into matrices will lead to the loss of spatial structure information. Therefore, the TMOKSC algorithm emphasizes the sequential constraints with penalty terms , so as to retain the spatial information of tensors to improve clustering performance.
3.2. The Optimization Algorithm
The TMOKSC algorithm adopts an iterative optimization strategy to capture the complementary characteristics among different views. In general, its augmented Lagrange function is:
3.2.1. Solve
When the other parameters are fixed, we will obtain:
Let the derivative of this function be zero, we can obtain the solution:
3.2.2. Solve
When the other parameters are fixed, we will solve by:
In this problem, it can be solved by the transformation of tensors .
Here, the t-SVD [26] transformation can be performed on the tensor . The spectral norm corresponds to the sum of the singular values after the t-SVD decomposition of the tensor slice. As we know, the t-SVD models achieve the cyclic structure by t-product. So, the diagonal elements in the core tensor represent the “energy intensity” of the sample in a certain view. The larger singular values correspond to more significant subspace structures, which are manifested as the main components in the Fourier domain. The core tensor suppresses the weights of the noise perspective; at the same time, it also coordinates the contributions to clustering. However, since the tensor representation requires the same dimension for incomplete multi-views, the missing samples need to be restored.
3.2.3. Solve
During the process, we will show how to complete the missing samples.
We denote the incomplete data sample with , so symbolizes the multiple kernel mapping of this incomplete observation sample. While represents the multiple kernel of incomplete multi-view clustering, in order to better reflect kernel transformation of the incomplete data, we divide into two parts . indicates that the corresponding data sample is complete, the size of . Correspondingly, are missing parts, the size of is .
Let , by computing in blocks, we can reconstruct the missing part as , and finally we can obtain
With Algorithm 1, we find that the obtained kernel block matrices are highly correlated and exhibit a cooperative low-rank pattern. The TMOKSC algorithm can automatically learn the samples of missing data through the existing observational data.
| Algorithm 1 TMOKSC |
| Input: Incomplete multi-view data samples X, the balancing parameters Output: Incomplete Multi-view subspace clustering result Step 1: Preprocess the Incomplete multi-view data samples X by Equation (3), and calculate their multi-view kernels by Equation (6) Step 2: Initialize , multiply and give the maximum number of iterations Step 3: Solve the following with ADMM: While ( and ) 1. Setting others, solve using Equation (14) 2. Setting others, solve using Equation (16) 3. Setting others, solve using Equation (18) 4. Update multiples by the formula 5. Renew variables End while Step 4: Calculate the affinity matrix with weight Step 5: Get cluster result with N-cut |
In the first step, the TMOKSC algorithm approximately applies a time complexity of in calculating ordered kernel functions. The second step requires a constant amount of time complexity noted as for initialization work. In the main part of the optimization, if n represents all the samples, represents the samples we can observe, and represents the number of samples with losses; we spent to solve . Suppose the multi-view samples include V views, so it takes time of to solve . It also takes time of to solve , finally it takes to update the multiplier variable. Suppose the loop of optimization needs T times to converge, so the time complexity of the entire algorithm is approximately .
4. Experiments
We made comparisons with classical methods (WMSC, AASC and AWP), Deep Subspace Clustering Networks (DSCN) and Tensioned Incomplete Multi-View Kernel Space Clustering (TIMKSC) with the source code and parameters published by the author. Since the DSCN clustering method in [19] has dimension requirements for the sample size of 1024, we use the same dataset provided by the DSCN clustering method for missing information processing. To make the comparison, run it once with the pre-trained model as required by the source program.
4.1. Experiments of Multi-View Face Images Datasets
The TMOKSC model proposed in this paper has the best performance on the YALE [27] and ORL datasets [28] (seen from Table 2, Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5), verifying the design of multi-view subspace clustering optimized by applying sequential kernel tensor learning in this paper. Under the attacks of any missing rate, this TMOKSC model can keep a good clustering structure by means of mutual propagation among the clustering structure tensors. Thereby, the experiments show that The TMOKSC model compensates for the loss caused by the missing samples among different views and learns more accurate consistent clustering results.

Table 2.
The accuracy (%) scores over 20 runs by different approaches on the YALE dataset.

Table 3.
The NMI scores (%) over 20 runs by different approaches on the YALE dataset.

Table 4.
The accuracy (%) scores over 20 runs by different approaches on the ORL dataset.

Table 5.
The NMI scores (%) over 20 runs by different approaches on the ORL dataset.
4.2. Experiments on Multi-View News Datasets
We evaluate the performance of TMOKSC with other subspace clustering algorithms on Multi-View News Datasets [29]; each view has 2000 dimensions. The documents from Reuters are presented in English, Spanish, French, German and Italian. In our experiment, we randomly selected a subset of 1200 documents (seen from Table 6 and Table 7), which were divided into six categories, and the parameters in the formula were set as follows: , .

Table 6.
The accuracy (%) scores over 20 runs by different approaches on the Reuters dataset.

Table 7.
The NMI scores (%) over 20 runs by different approaches on the Reuters dataset.
The results of the experiment were evaluated both in NMI (%) and ACC (%) measures. The reason for the excellent performance of our TMOKSC method might be that it emphasized the inherent context characteristics of the data in document clustering. Therefore, the final affinity matrix could be strengthened with special weights made up for the characteristics of multi-view data. The sequential kernel representation of The TMOKSC algorithm can improve the subspace learning ability of local views by tensor fusion of multi-view information and enhance complementarities between different views.
4.3. Experiments on Multi-View Object Image Datasets
The COIL20 dataset [30] created by Columbia University consists of 1440 grayscale images of objects from different angles, which are classified into 20 categories of objects. In the experiment, we regarded the Intensity (1024), LBP (3304), and Gabor(6750) of all images as three views. It can be seen from the data in the Table 8 and Table 9 that when the dimension of each data sample in the COIL20 set of the WMSC, AASC and AWP clustering algorithms reaches as high as 11,078, it is difficult to tell the redundant information and effective information. As a result, the clustering performance does not get the optimal result. While TMOKSC and TIMKSC regard tensors as the clustering orientation, the clustering algorithms work well. Especially for the TMOKSC algorithm, the clustering performance of the algorithm remains stable, coinciding with the original losing rate increases.

Table 8.
The accuracy (%) scores over 20 runs by different approaches on the COIL 20 dataset.

Table 9.
The NMI scores (%) over 20 runs by different approaches on the dataset.
5. Discussion of Results
In this section, we observe that once the original instance of the Multi-View Datasets is lost, it is set to the zero vector, resulting in the failure of traditional methods. DSCN performs well relying on the pre-trained model when only a few instances in this dataset are unavailable. However, when the views are severely damaged, it cannot maintain consistent good performance. This indicates that the absence of views leads to severe information loss, exacerbating the information imbalance among different views. The tensor structure is conducive to the mining of consistent information to perform well. Especially the TMOKSC method that combines the tensor model with ordered kernel learning. The TMOKSC method demonstrates high efficiency on various datasets.
Then, we delve into the parameter effects on clustering performance. We take all samples as information monitoring information on ORL datasets. Furthermore, we change the value of alpha and beta, respectively, with the other parameters fixed; Figure 2 displays the average clustering ACC value, NMI value, F_score value and CR value of our proposed TMOKSC methods as the missing rate rise from 0.1 to 0.5.
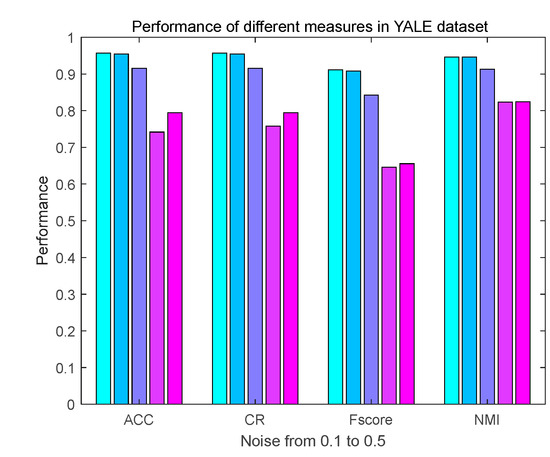
Figure 2.
Performance of different attacks from 0.1 to 0.5.
We can draw conclusions from the Figure 3 that the clustering performance of each data set is relatively steady in the test parameter range in , . In most cases, The TMOKSC algorithm will cluster with consistent results.
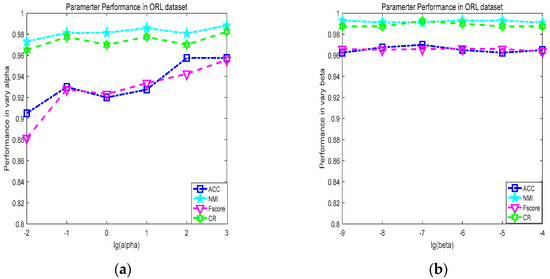
Figure 3.
Parameter Performance under varied alpha and beta (a) Parameter Performance under varied alpha; (b) Parameter Performance under varied beta.
A quantitative analysis was conducted on the stability of the TMOKSC’s clustering accuracy. When α changed, the mean of ACC was 0.9329, the standard variance of ACC was 0.0209, the mean NMI was 0.9818, and the standard variance of NMI was 0.0052, indicating that the overall accuracy rate of the model fluctuated less and had good stability. When β changed, the mean value of ACC was 0.964, and the mean value of NMI was 0.9925. Furthermore, the standard variance respectively decreased to 0.0169 and 0.0039, indicating that the accuracy stability of the model was stronger in these cases.
In this article, the convergence tests of TMOKSC are also carried out on Yale, COIL 20, ORL and Reuters data sets. As shown in Figure 4, we can observe that the value of the loss function decreases rapidly under the update rule. In the COIL 20, ORL and Reuters datasets, the value reaches the minimum at about 20 iterations, even in the worst case, the minimum is about 35 iterations in the Yale dataset. Ordered kernels explore the unique attributes of each view, and as a result, the feature complementarity among different perspectives can be enhanced. The fast convergence curves of TMOKSC show the effectiveness and convergence of the proposed method.
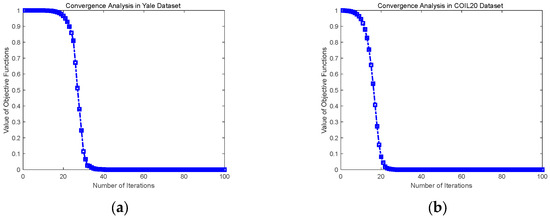
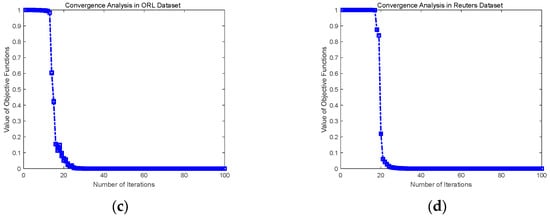
Figure 4.
Convergence Curves (a) Convergence Curve in Yale data set; (b) Convergence Curve in COIL 20 data set; (c) Convergence Curve in ORL data set; (d) Convergence Curve in Reuters data set.
6. Conclusions
The computer vision field and news linguistics field focus on the robust processing of nonlinear data. Incomplete views lead to severe information loss and exacerbate the information imbalance among different views. Therefore, the incomplete learning problem becomes a difficult issue in multi-view subspace clustering, and its research is of great significance for computer vision or linguistics applications. We propose a novel algorithm for incomplete multi-view clustering that combines order kernel learning and tensioned clustering. Ordered kernel functions of each view implicitly map to the high-dimensional feature space, with the aim of making the originally complex data structure linearly separable. However, each view is an independent update process without taking into account the higher-order connections between views. Therefore, by extending it and applying the tensor kernel norm, a good tensioned clustering structure maintains the mutual propagation to make up for the losses caused by the missing samples. When the views are severely damaged, current representative multi-view clustering algorithms cannot maintain good performance. While the TMOKSC works well, compared with current representative multi-view clustering algorithms, the average improvement of ACC is 4.64%, and the average improvement of NMI is 4.775%.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.C. and G.G.; methodology, L.C.; software, L.C.; validation, L.C. and G.G.; formal analysis, L.C.; investigation, L.C.; resources, L.C. and G.G.; data curation, L.C. and G.G.; writing—original draft preparation, L.C.; writing—review and editing, L.C.; visualization, L.C.; supervision, L.C.; project administration, L.C.; funding acquisition, L.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Fujian Province Natural Science Foundation, grant number 2023J01532.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data in the article are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| TMOKSC | Tensioned Multi-view Ordered Kernel Subspace Clustering |
| TIMKSC | Tensioned Incomplete Multi-View Kernel Space Clustering |
| WMSC | Weighted Multi-view spectral clustering based on spectral perturbation |
| AASC | Affinity aggregation for spectral clustering |
| AWP | Multi-view Clustering via Adaptively Weighted Procrustes |
| SSC | Sparse Subspace Clustering |
References
- Wei, L.; Li, K.; Zhou, R.; Liu, J. Purely Contrastive Multiview Subspace Clustering. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yesong, X.; Shuo, C.; Jun, L.; Yang, J. Metric Learning-Based Subspace Clustering. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2025, 36, 10491–10503. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Xiu, X.; Liu, W.; Yin, C. Robust and stochastic sparse subspace clustering. Neurocomputing 2025, 611, 128703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Cui, Z.; Wu, L.; Xu, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Fei, L. Salient and consensus representation learning based incomplete multiview clustering. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 2723–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Yu, H. Weighted Multiview spectral clustering based on spectral perturbation. In Proceeding of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; pp. 4621–4628. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.C.; Chuang, Y.Y.; Chen, C.S. Affinity aggregation for spectral clustering. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, F.; Tian, L.; Li, X. Multiview Clustering via Adaptively Weighted Procrustes. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, UK, 19–23 August 2018; pp. 1990–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Saha, S.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Multi-view clustering for multi-omics data using unified embedding. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, J.; Dai, Q. Incomplete multiview subspace clustering algorithm based on self-representation and consistent learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 4th International Conference on Computer Engineering and Application (ICCEA), Hangzhou, China, 7–9 April 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Yang, S.; Peng, X.; Peng, D.; Wang, Z. Augmented Sparse Representation for Incomplete Multiview Clustering. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 35, 4058–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, W.; Yong, X.; Hong, L. Incomplete Multiview Spectral Clustering with Adaptive Graph Learning. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 50, 1418–1429. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Liu, H.; Guan, Z.; Wu, X.; Tan, J.; Ling, B. Adversarial Incomplete Multiview Subspace Clustering Networks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 10490–10503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Zheng, X.; Lu, Y.; Chen, B. Incomplete multi-view subspace clustering based on robust matrix completion. Neurocomputing 2025, 621, 129240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Lu, G.-F. Comprehensive Consensus Representation Learn-Ing for Incomplete Multi-View Subspace Clustering. Inf. Sci. 2024, 678, 120935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, N.; Yang, Z.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Xie, S. Incomplete Multiview Clustering with Cross-View Feature Transformation. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2022, 3, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Wang, Z.; Xi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, H. Multiple Kernel Low-Redundant Representation Learning Based Incomplete Multiview Subspace Clustering. SSRN 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Chen, L.; Wang, S. A Multi-view Kernel Clustering framework for Categorical sequences. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 197, 116637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Chen, L.; Wang, S. Towards Robust Nonlinear Subspace Clustering: A Kernel Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.; Zhang, T.; Li, H.; Salzmann, M.; Reid, I. Deep Subspace Clustering Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1709.02508. ttps://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1709.02508. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.J. A Survey on Incomplete Multiview Clustering. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Systems 2023, 53 Pt 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Chen, C.; Jia, X.; Chen, C. Low-Rank Tensor Regularized Views Recovery for Incomplete Multiview Clustering. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 35, 9312–9324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Mao, H.; Peng, X. Low-Rank Tensor Learning for Incomplete Multiview Clustering. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2022, 35, 11556–11569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Yang, M. View-Consistency Learning for Incomplete Multiview Clustering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 4790–4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Liu, J.; Qu, Y.; Tao, D.; Zhang, W.; Dai, L.; Ma, L. Robust Kernelized Multiview Self-Representation for Subspace Clustering. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 868–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Y.; Huang, D.; Wang, C.D. Tensorized Incomplete Multi-view Kernel Subspace Clustering. Neural Netw. 2024, 179, 106529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilmer, M.E.; Martin, C.D. Factorization strategies for third-order tensors–ScienceDirect. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 2011, 435, 641–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Tu, W.; Wang, S.; Zhou, S.; Liang, W.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y. Self-representation subspace clustering for incomplete multi-view data. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Virtual, 20–24 October 2021; pp. 2726–2734. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; Sun, S. Incomplete multi-view clustering with cosine similarity. Pattern Recognit. J. Pattern Recognit. Soc. 2022, 123, 108371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Y.; Zhou, Y.R.; He, X.Y.; Wang, C.D.; Huang, D. One step kernel multi-view subspace clustering. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2019, 189, 105126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.W.; Huang, D.; Wang, C.D.; Yu, P.S. Multi-view graph learning by joint modeling of consistency and inconsistency. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 35, 2848–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).