Responses of Corn Yield, Soil Microorganisms, and Labile Organic Carbon Fractions Under Integrated Straw Return and Tillage Practices in Black Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Analysis Methods
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Crop Yield
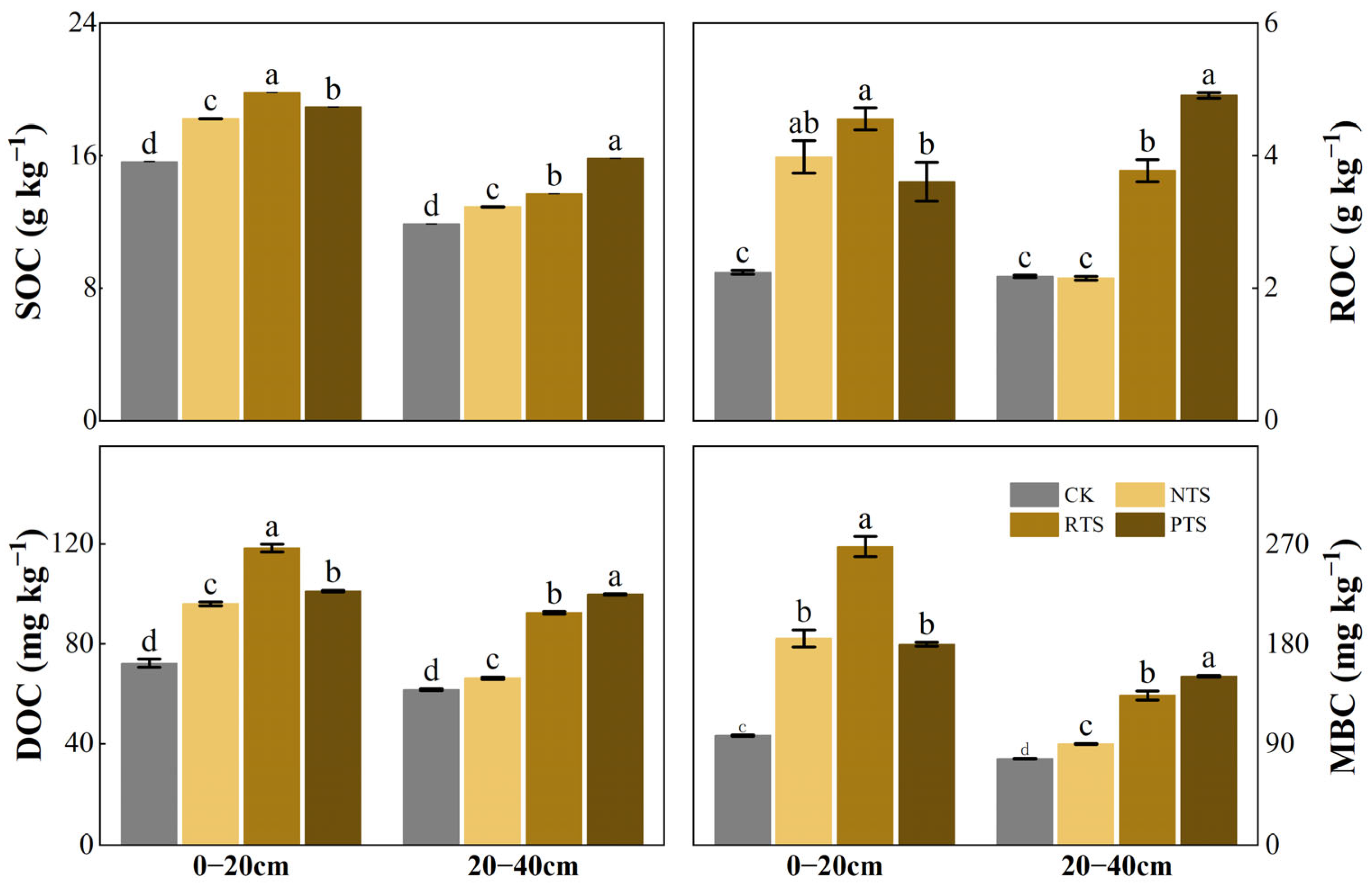
3.2. Soil Organic Carbon and Its Labile Fractions
3.3. Diversity of Microbial Bacterial and Fungal Communities
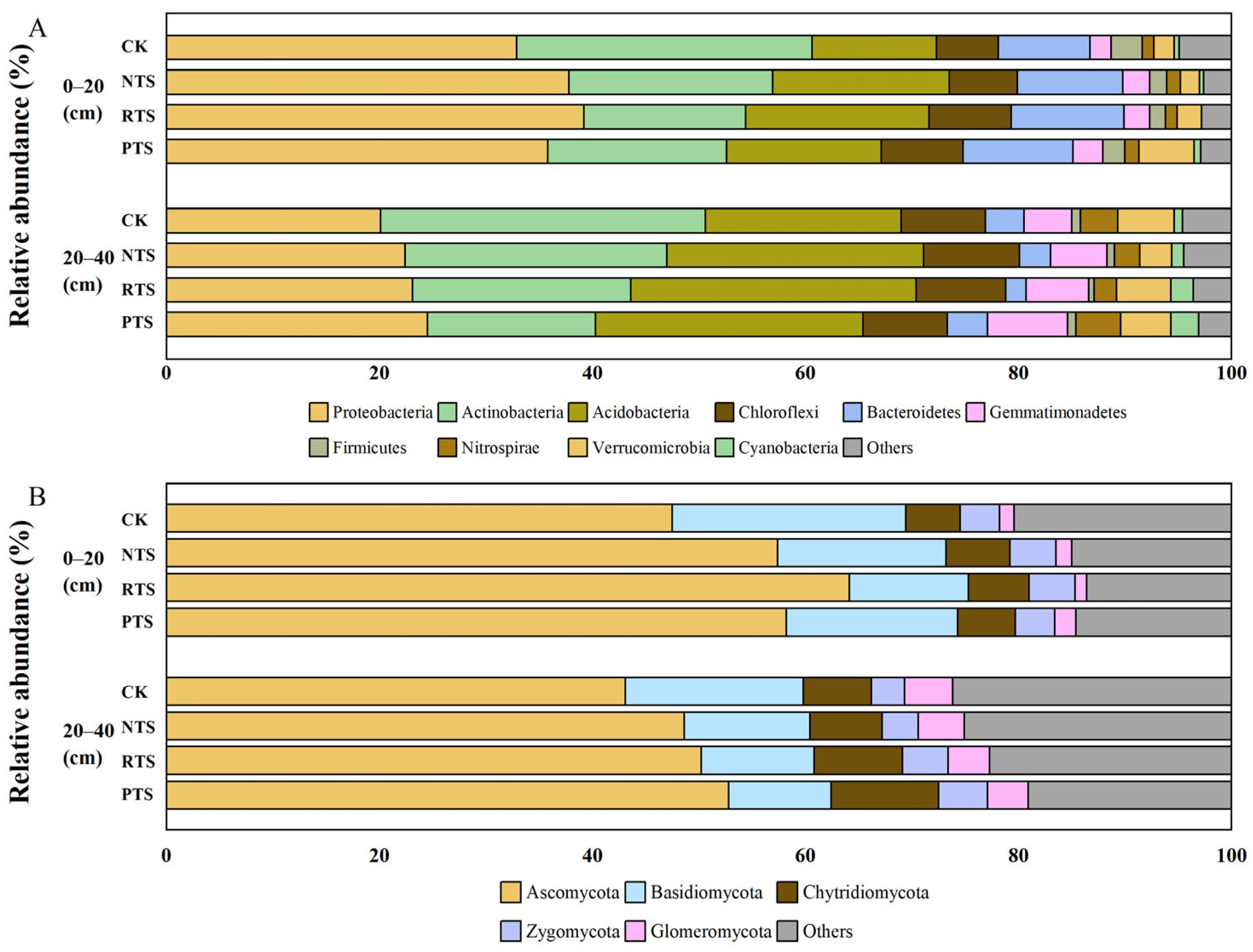
3.4. Composition of Bacterial and Fungal Communities at the Phylum Level
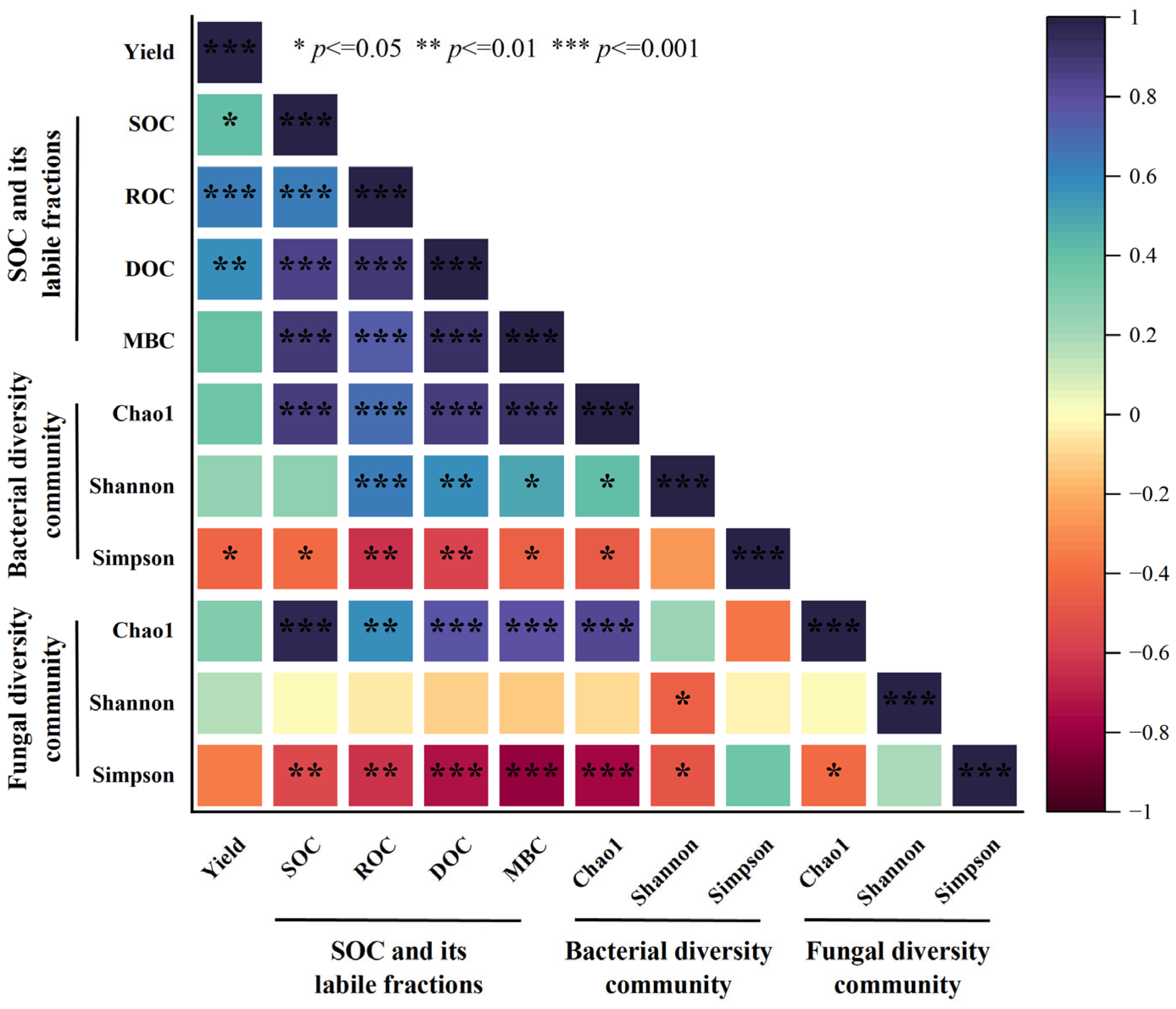
3.5. Correlation Analysis of Soil Microbial Community Composition, Organic Carbon Fractions and Crop Yield
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Integrated Straw Return and Tillage Practices on Soil Organic Carbon and Its Labile Fractions, and Microbial Communities
4.2. Responses of Corn Yield to Integrated Straw Return and Tillage Practices
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, X.C.; Sun, L.Y.; Song, F.B.; Liu, S.Q.; Liu, F.L.; Li, X.N. Soil microbial community and activity are affected by integrated agricultural practices in China. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 924–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; He, Z.C.; Yang, Y.H.; Jia, S.Q. Linking soil microbial community dynamics to straw-carbon distribution in soil organic carbon. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, F.X.; Li, Y.Y.; Chapman, S.J.; Khan, S.; Yao, H.Y. Microbial utilization of rice straw and its derived biochar in a paddy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 559, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, A.L.; Lee, D.H.; Koo, N. Liming Alters the Soil Microbial Community and Extracellular Enzymatic Activities in Temperate Coniferous Forests. Forests 2021, 12, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Q.; Ma, Y.; Wei, Z.; Wu, J.; Sun, C.; Yang, J.; Liu, L.; Liao, H. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi symbiosis on microbial diversity and enzyme activities in the rhizosphere soil of Artemisia annua. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2021, 85, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Zhang, L.; He, N.; Gong, D.; Gao, H.; Ma, Z.; Fu, L. Soil bacterial community as impacted by addition of rice straw and biochar. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, G.M.; Schmit, J.P. Fungal biodiversity: What do we know? What can we predict? Biodivers. Conserv. 2007, 16, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poeplau, C.; Dechow, R. The legacy of one hundred years of climate change for organic carbon stocks in global agricultural topsoils. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, A.R.G.; Salomon, M.; Lowe, A.; Cavagnaro, T. Microbial solutions to soil carbon sequestration. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 417, 137993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Z.; Chang, D.; Li, B.; Cao, W.; Lu, Y.; Pan, Z. Effects of planting and incorporation of Chinese Milk Vetch coupled with application of chemical fertilizer on active organic carbon and nitrogen in paddy soil. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2017, 54, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.X.; Luo, Y.; Chen, J.; Jin, M.; Li, Y. Straw return strategies to improve soil properties and crop productivity in a winter wheat-summer maize cropping system. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 133, 126436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikgwatlhe, S.B.; Chen, Z.-D.; Lal, R.; Zhang, H.-L.; Chen, F. Changes in soil organic carbon and nitrogen as affected by tillage and residue management under wheat-maize cropping system in the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 144, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.L.; Wu, J.; Ding, D.; Yang, Y.; Gao, C. Effects of tillage and straw mulching on the crop productivity and hydrothermal resource utilization in a winter wheat-summer maize rotation system. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 254, 106933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.W.; Fan, J.; Hao, M.; Chen, X. Effects of long-term tillage and mulching methods on properties of surface soil and maize yield in tableland region of the Loess Plateau. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2016, 22, 1558–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Li, J. Study of tillage patterns suitable for soil physicochemical properties and crop yields in wheat/maize fields. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2014, 20, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.D.; LI, j.; Jiao, X.; Jiang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. The fate and challenges of the main nutrients in returned straw: A basic review. Agronomy 2024, 14, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Li, Y.; Cong, P.; Wang, J.; Guo, W.; Pang, H. Depth of straw incorporation significantly alters crop yield, soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 205, 104772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.D.; Men, X.; Huang, W.; Yi, S.; Wang, W.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z. Effects of Exiguobacterium sp. DYS212, a saline-alkaline-tolerant P-solubilizing bacterium, on Suaeda salsa germination and growth. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Yan, J.; Han, X.; Zou, W.; Chen, X.; Lu, X. Labile organic carbon fractions drive soil microbial communities after long-term fertilization. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 32, e01867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.G.; Yu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y. Effects of tillage practices on grain yield formation of wheat and the physiological mechanism in rainfed areas. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 202, 104675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Shi, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, M. Effects of different management measures on the organic carbon of farmland soil profile in China based on Meta analysis. Soils 2021, 53, 1290–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.A.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, R.; Wei, C. The net and combined effects of minimum tillage and straw mulching on carbon accumulation in global croplands. Eur. J. Agron 2023, 143, 126719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busari, M.A.; Kukal, S.; Kaur, A.; Bhatt, R.; Dulazi, A. Conservation tillage impacts on soil, crop and the environment. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2015, 3, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essel, E. Long-Term Tillage Effects on Soil Microbial Diversity, CO2 Emission and the Underlying Mechanisms in Wheat-Pea Rotation Field in the Semi-Arid Loess Plateau, China. Ph.D. Thesis, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou, China, 2019; p. 16. [Google Scholar]
- Song, D.L.; Xie, W.S. A political economy analysis of the protection and utilization of the black soil in northeast China: Based on the Pear Tree Model. China Rev. Political Econ. 2021, 12, 47–62. [Google Scholar]
- Du, G.M.; Yao, X.; Zang, L.Z. Evolution of farming system and its influencing factors in the black soil region of Northeast China. Chin. J. Econ. Agric. 2025, 33, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.H.; Cai, H.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Liu, H.G. Analysis on the change of maize production spatial layout and its influencing factors. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2018, 39, 169–176. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.N.; Zeng, Q.P.; Tian, F.; Luo, H.B. Analysis on the changes of maize sown area and yield in China from 1997 to 2020. Crop Res. 2024, 38, 329–333. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.P.; Xie, R.; Luo, Y.; Sui, P.; Zheng, H.; Ming, B.; Wang, H. Effects of conservation tillage methods on maize growth and yields in a typical black soil region. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2024, 32, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xue, H.; Li, Z. Effects of saline-alkali stress on bacterial and fungal community diversity in Leymus chinensis rhizosphere soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 70000–700013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Miao, J.; Saleem, M.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y. Bacterial compatibility and immobilization with biochar improved tebuconazole degradation, soil microbiome composition and functioning. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, T.; Gao, S.; Jiang, S.; Kan, G.; Liu, P.; Wu, X.; AN, Y.; Yao, S. A method suitable for DNA extraction from humus-rich soil. Biotechnol. Lett. 2014, 36, 2223–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maguire, V.G.; Bordenave, C.; Nieva, A.; Llames, M.; Colavolpe, M. Soil bacterial and fungal community structure of a rice monoculture and rice-pasture rotation systems. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 151, 103535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R. Analytical Methods for Soil Agricultural Chemistry; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.Q.; Walker, S.; Huang, Q.; Cai, P. Adhesion of bacterial pathogens to soil colloidal particles: Influences of cell type, natural organic matter, and solution chemistry. Water Res. 2014, 53, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, G.J.; Lefroy, R.; Lise, L. Soil carbon fractions based on their degree of oxidation, and the development of a carbon management index for agricultural systems. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1995, 46, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.C.; Landman, A.; Pruden, G.; Jenjinson, D. Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: A rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1985, 17, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Yu, M.; Xi, H.; Lv, J.; Ma, Z.; Kou, C.; Shen, A. Soil microbial community shifts with long-term of different straw return in wheat-corn rotation system. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Gevers, D.; Westcott, S.L. Reducing the effects of PCR amplification and sequencing artifacts on 16S rRNA-based studies. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; Deng, S.; Zhang, J.; Hou, J.; Wang, C.; Fu, Z. Effect of different washing solutions on soil enzyme activity and microbial community in agricultural soil severely contaminated with cadmium. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 54641–54651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Y.; Han, P. Maize straw returning for three consecutive years: Effects on soil physical and chemical properties and crop yield. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2018, 34, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Chakraborty, D. Global meta-analysis suggests that no-tillage favourably changes soil structure and porosity. Geodema 2022, 45, 115443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Yang, N.; Lu, C.; Qin, X.; Siddique, K.H.M. Soil organic carbon, total nitrogen, available nutrients, and yield under different straw returning methods. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 214, 105171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Xu, C.; Dungait, J.A.J.; Bol, R.; Wang, X.; Wu, W. Straw incorporation increases crop yield and soil organic carbon sequestration but varies under different natural conditions and farming practices in China: A system analysis. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 1933–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, E.; Chi, F.; Su, Q.; Zhang, J.; Jin, L. Decomposition characteristics of maize straws under different returning methods. Maize Sci. 2012, 20, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, P.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ma, Q.; Sui, P. Effect of straw return methods on maize straw decomposition and soil nutrients contents. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2019, 27, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.H. Yield increasing and quality improving effects of smash-ridging method and its potential in benefiting the nation and the people. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2014, 15, 1767–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlon, M.S.; Lal, R.; Ann-Varughese, M. Twenty-two years of tillage and mulching impacts on soil physical characteristics and carbon sequestration in Central Ohio. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 126, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.T.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, P.; Wang, W.; Hou, X.; Yang, B. Effects of straw returning on soil labile organic carbon and enzyme activity in Semi-arid areas of Southern Ningxia, China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2011, 30, 522–528. [Google Scholar]
- Dhaliwal, S.S.; Naresh, R.; Gupta, R.; Panwar, A.; Mahajan, N. Effect of tillage and straw return on carbon footprints, soil organic carbon fractions and soil microbial community in different textured soils under rice–wheat rotation: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2020, 19, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, J.F.; Paul, L.; Finlay, R. Microbial interactions in the mycorrhizosphere and their significance for sustainable agriculture. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 48, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihara, J.; Martius, C.; Bationo, A.; Thuita, M.; Lesueur, D. Soil aggregation and total diversity of bacteria and fungi in various tillage systems of sub-humid and semi-arid Kenya. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2012, 58, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Hu, H.; Liu, Z.; Dong, Q. Shifts in microbial community and carbon sequestration in farmland soil under long-term conservation tillage and straw returning. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 136, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Xiao, S.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, W. Microbial biomass, metabolic functional diversity, and activity are affected differently by tillage disturbance and maize planting in a typical karst calcareous soil. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soong, J.L.; Castanha, C.; Hicks Pries, C.E.; Ofiti, N.; Porras, R.C. Five years of whole-soil warming led to loss of subsoil carbon stocks and increased CO2 efflux. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabd1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Q.; Li, D.; Ma, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, B. Effects of straw management and nitrogen application rate on soil organic matter fractions and microbial properties in North China Plain. J. Soil Sediment 2019, 19, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, E.B.; Acosta-Martinez, V. Cover cropping frequency is the main driver of soil microbial changes during six years of organic vegetable production. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 109, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Han, P.; Hao, J. Impact of soil disinfestation on fungal and bacterial communities in soil with cucumber cultivation. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 685111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.N.; Lin, X.; Guan, S.; Dou, S. Deep incorporation of corn straw benefits soil organic carbon and microbial community composition in a black soil of Northeast China. Soil Use Manag. 2022, 38, 1266–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yin, C.; Fan, X.; Ye, M.; Liang, Y. Effect of P availability on straw-induced priming effect was mainly regulated by fungi in croplands. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 9403–9418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Mark, A.; Robert, B. Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 2007, 88, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patkowska, E.; Blazewicz-Wozniak, M.; Konopinski, M. The effect of cover crops on the fungal and bacterial communities in the soil under carrot cultivation. Plant Soil Environ. 2016, 62, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Gu, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhao, H.; Hu, W. Short-term straw returning improves quality and bacteria community of black soil in Northeast China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 31, 1869–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsbrink, J.; Tuveng, T.; Pope, P.; Bulone, P.; Eijsink, V. Proteomic insights into mannan degradation and protein secretion by the forest floor bacterium Chitinophaga pinensis. J. Proteom. 2017, 56, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; Wu, J. Changes in soil fungal community on SOC and POM accumulation under different straw return modes in dryland farming. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2021, 7, 1935326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breulmann, M.; Masyutenko, N.; Kogut, B.; Schroll, R. Short-term bioavailability of carbon in soil organic matter fractions of different particle sizes and densities in grassland ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 497, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, H.; An, S.; Bhople, P.; Davlatbekov, F. Geographic distance and soil microbial biomass carbon drive biogeographical distribution of fungal communities in Chinese Loess Plateau soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.H.; Xu, C.; Yu, J.; Yan, W.; Sun, N.; Tan, G.; Zhao, H.; Li, F.; Meng, X.; Bian, S. Effects of straw returning on soil moisture, temperature and maize yield in semi humid area. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 35, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, C.F.; Tan, C.; Welacky, T.; Oloya, T.; Hamill, A. Red clover and tillage influence on soil temperature, water content, and corn emergence. Agron. J. 1999, 91, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, C.; Lv, X. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer input and rice season nitrogen fertilizer application on soil nutrients, carbon pool and yield in rape-rice rotation. Jiangsu J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 36, 896–904. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.S.; Hu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Shen, Z.; Meng, Y. Effects of Green Manure Returning on Soil Labile Organic Carbon in Paddy Field Under Smash Ridging. Soils 2021, 53, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Total Carbon | Total Nitrogen | Total Phosphorus | Total Potassium | Hemi Cellulose | Cellulose | Lignin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 41.78 ± 0.10 | 0.92 ± 0.04 | 0.15 ± 0.00 | 1.11 ± 0.01 | 23.45 ± 0.41 | 37.25 ± 0.23 | 2.85 ± 0.03 |
| OM (g kg−1) | TN (g kg−1) | AN (mg kg−1) | AP (mg kg−1) | AK (mg kg−1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20.10 ± 0.03 | 1.54 ± 0.01 | 121.84 ± 0.20 | 26.34 ± 0.04 | 134.24 ± 0.49 | 6.11 ± 0.02 |
| Depth | Treatment | Bacterial | Fungal | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chao1 | Shannon | Simpson | Chao1 | Shannon | Simpson | ||
| 0–20 cm | CK | 2991.33 ± 53.76 c | 8.53 ± 0.09 b | 0.998 ± 0.002 a | 475.55 ± 5.94 c | 3.29 ± 0.15 a | 0.871 ± 0.002 a |
| NTS | 3341.00 ± 39.0 b | 8.54 ± 0.10 b | 0.997 ± 0.001 a | 527.55 ± 4.89 a | 3.20 ± 0.17 a | 0.852 ± 0.001 b | |
| RTS | 3743.33 ± 46.25 a | 8.91 ± 0.06 a | 0.996 ± 0.002 a | 533.16 ± 6.46 a | 3.11 ± 0.10 a | 0.836 ± 0.001 c | |
| PTS | 3201.67 ± 60.89 b | 8.54 ± 0.11 b | 0.996 ± 0.001 a | 509.43 ± 4.06 b | 3.27 ± 0.19 a | 0.856 ± 0.002 b | |
| 20–40 cm | CK | 2581.33 ± 44.83 c | 8.49 ± 0.08 c | 0.999 ± 0.001 a | 329.19 ± 4.07 d | 3.22 ± 0.14 a | 0.865 ± 0.001 a |
| NTS | 2938.00 ± 52.29 c | 8.56 ± 0.08 bc | 0.998 ± 0.000 a | 366.10 ± 6.15 c | 3.15 ± 0.13 a | 0.853 ± 0.001 b | |
| RTS | 3027.33 ± 31.18 ab | 8.74 ± 0.08 ab | 0.996 ± 0.001 a | 388.45 ± 5.82 b | 3.17 ± 0.14 a | 0.854 ± 0.002 b | |
| PTS | 3103.33 ± 39.9 a | 8.88 ± 0.05 a | 0.996 ± 0.001 a | 448.22 ± 7.14 a | 3.24 ± 0.09 a | 0.856 ± 0.002 b | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, L.; Sun, Y.; Chen, G. Responses of Corn Yield, Soil Microorganisms, and Labile Organic Carbon Fractions Under Integrated Straw Return and Tillage Practices in Black Soil. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7129. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137129
Feng L, Sun Y, Chen G. Responses of Corn Yield, Soil Microorganisms, and Labile Organic Carbon Fractions Under Integrated Straw Return and Tillage Practices in Black Soil. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(13):7129. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137129
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Lei, Yunyun Sun, and Guifen Chen. 2025. "Responses of Corn Yield, Soil Microorganisms, and Labile Organic Carbon Fractions Under Integrated Straw Return and Tillage Practices in Black Soil" Applied Sciences 15, no. 13: 7129. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137129
APA StyleFeng, L., Sun, Y., & Chen, G. (2025). Responses of Corn Yield, Soil Microorganisms, and Labile Organic Carbon Fractions Under Integrated Straw Return and Tillage Practices in Black Soil. Applied Sciences, 15(13), 7129. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137129






