Phenotypic Characterization and Whole-Genome Analysis Revealing the Promising Metabolic Potential of a Newly Isolated Streptomyces sp. CH6
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation of Actinomycetes and Screening for Their Antibacterial Activity
2.2. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
2.3. Growth Curve Assay
2.4. Antioxidant Assays
2.5. Cytotoxic Activity
2.6. Phenotypic Characterization
2.7. Genomic DNA Extraction, Whole-Genome Sequencing, and Assembly
2.8. Annotation and Comparative Genome Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Preliminary Screening of Antibacterial Metabolites Extracted from Actinomycete Cultures
3.2. Antibacterial Activity of the CH6 Crude Extract
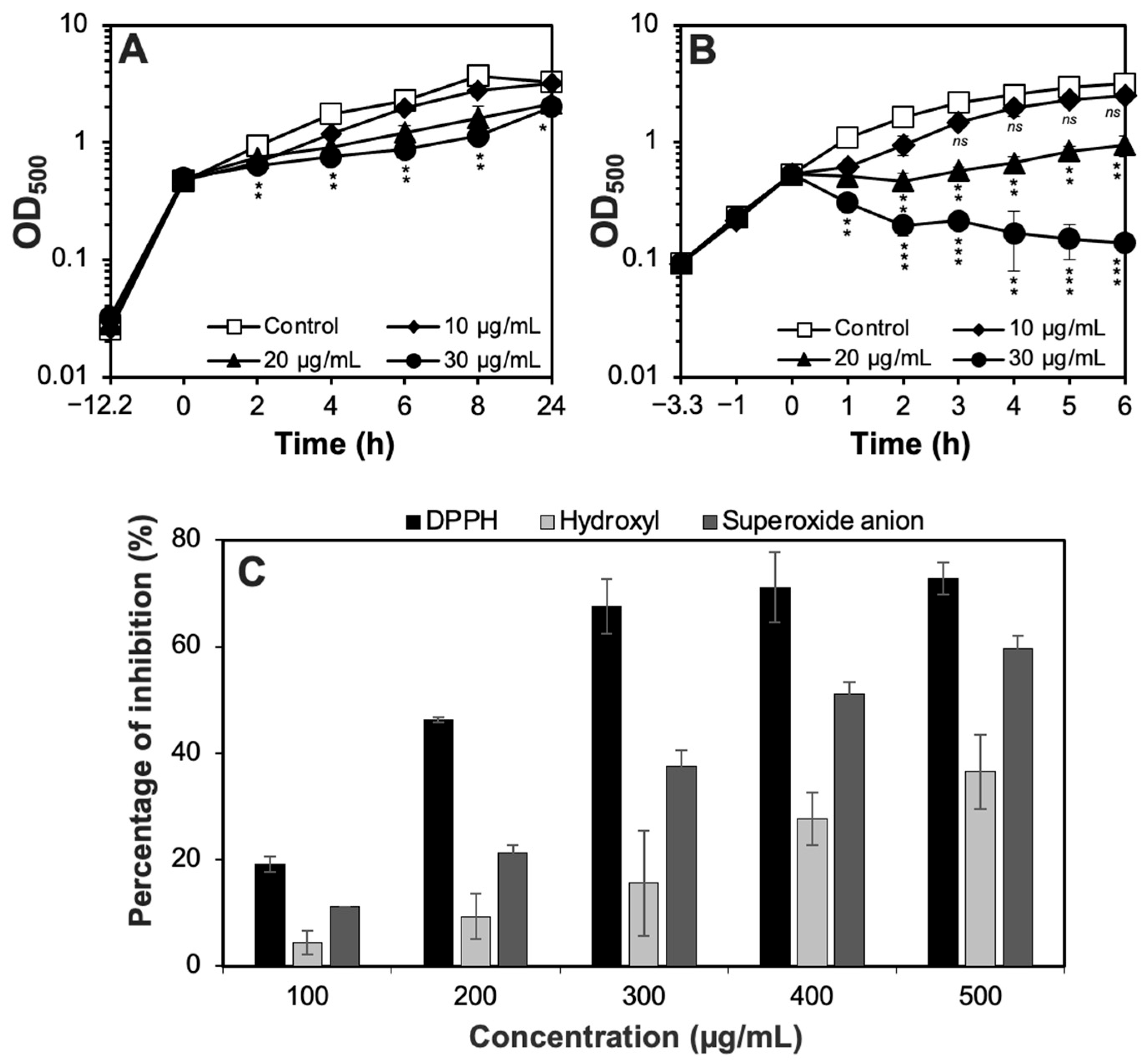
3.3. Antioxidant Potential of the CH6 Extract
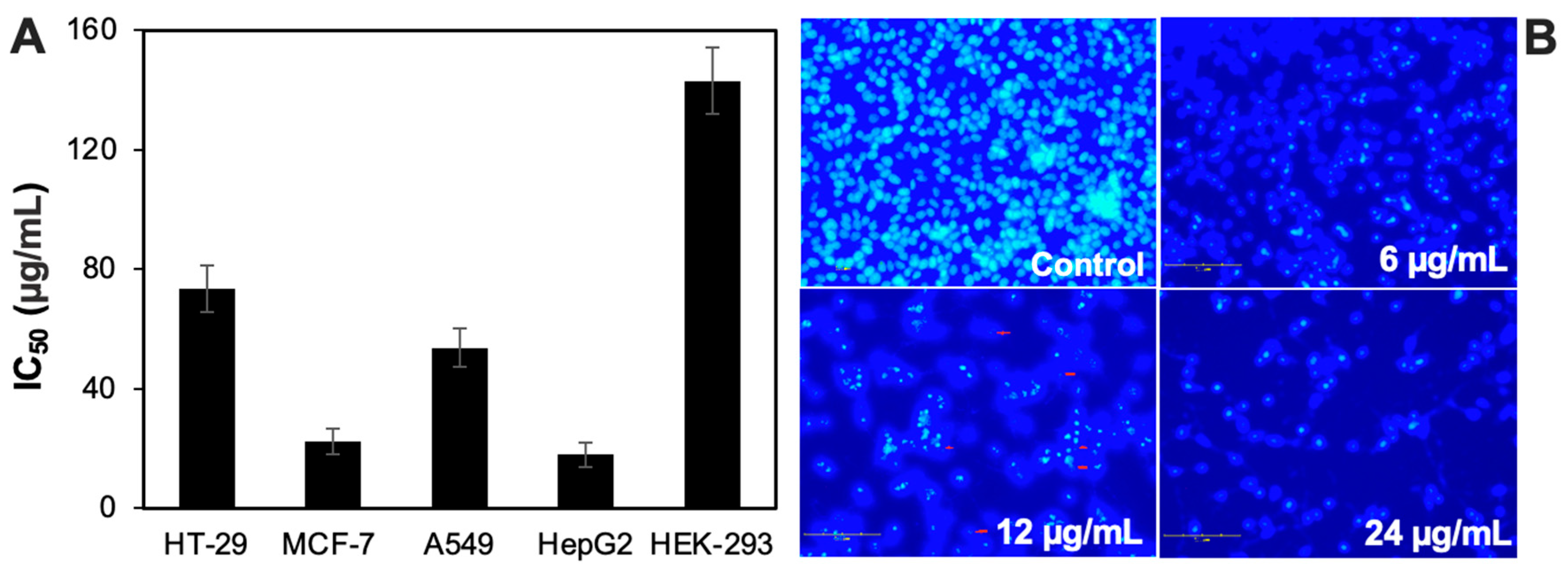
3.4. Anticancer Potential of the CH6 Extract
3.5. Phenotypic Analysis of the CH6 Isolate
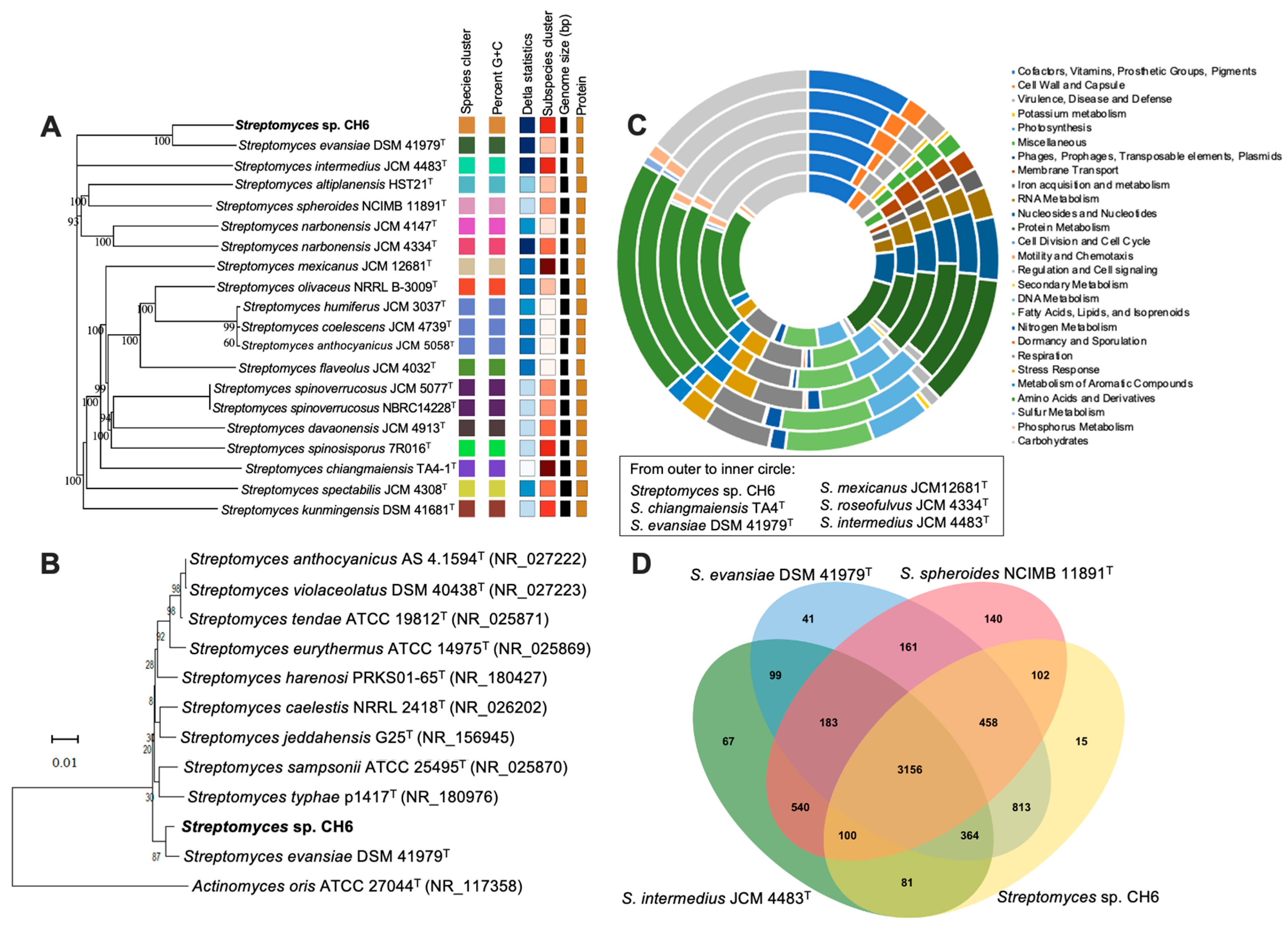
3.6. Genomic Features and Taxonomy Study
3.7. Functional Annotation and Comparative Genomes
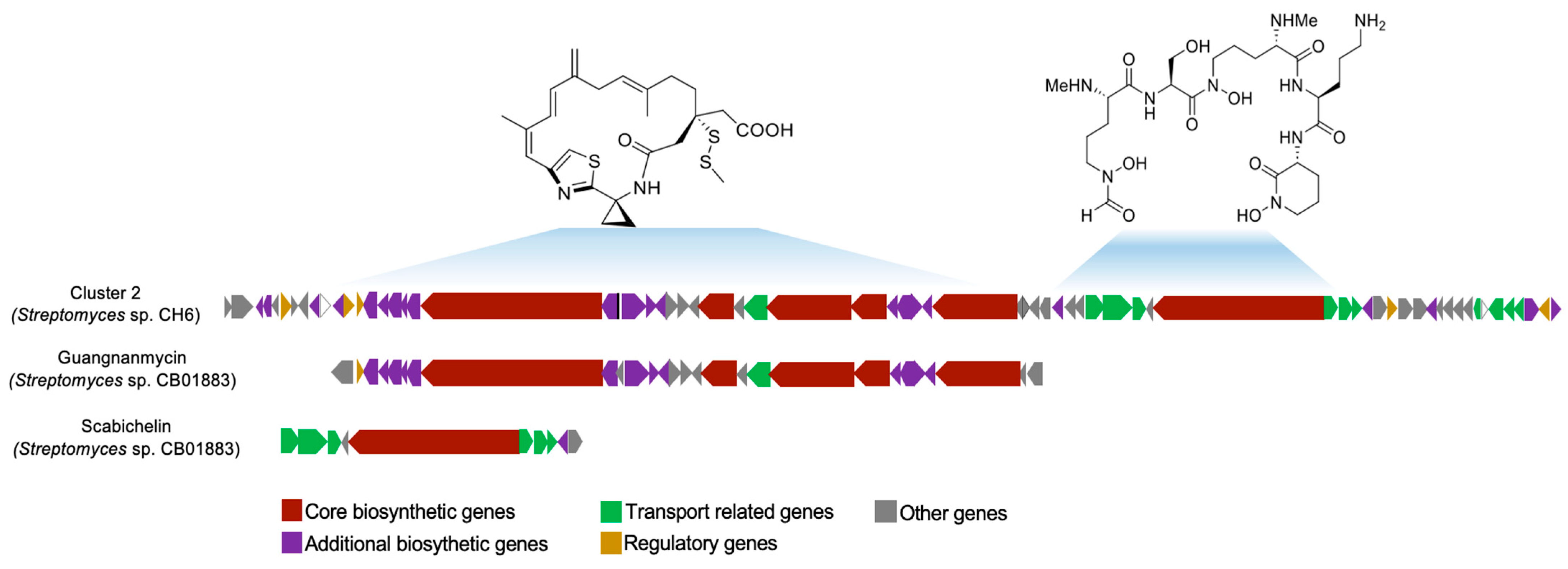
3.8. Identification of Secondary Metabolite-Biosynthetic Gene Clusters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DPPH | 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl |
| MIC | Minimum inhibitory concentration |
| dDDH | digital DNA–DNA hybridization |
| ANI | Average nucleotide identity |
| BGCs | Biosynthetic gene clusters |
| IC50 | Half-maximal inhibitory concentration |
| CDSs | Protein-coding sequences |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
References
- Demain, A.L. Importance of microbial natural products and the need to revitalize their discovery. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 41, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, J.V.; Yilma, M.A.; Feliz, A.; Majid, M.T.; Maffetone, N.; Walker, J.R.; Kim, E.; Cho, H.J.; Reynolds, J.M.; Song, M.C.; et al. A review of the microbial production of bioactive natural products and biologics. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.-Q.; Wang, J.-F.; Hao, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y. Recent advances in the discovery and development of marine microbial natural products. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 700–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quach, N.T.; Nguyen, Q.H.; Vu, T.H.N.; Le, T.T.H.; Ta, T.T.T.; Nguyen, T.D.; Van Doan, T.; Van Nguyen, T.; Dang, T.T.; Nguyen, X.C.; et al. Plant-derived bioactive compounds produced by Streptomyces variabilis LCP18 associated with Litsea cubeba (Lour.) Pers as potential target to combat human pathogenic bacteria and human cancer cell lines. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parte, A.C.; Sardà Carbasse, J.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Reimer, L.C.; Göker, M. List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) moves to the DSMZ. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 5607–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prole, J.R.; Allenby, N.; Manning, D.A.C.; Goodfellow, M. Identification of four novel Streptomyces isolated from machair grassland soil using a culture-based bioprospecting strategy: Streptomyces caledonius sp. nov., Streptomyces machairae sp. nov., Streptomyces pratisoli sp. nov. and Streptomyces achmelvichensis sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2025, 75, 006736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quach, N.T.; Vu, T.H.N.; Nguyen, T.T.A.; Le, P.C.; Do, H.G.; Nguyen, T.D.; Thao, P.T.H.; Nguyen, T.T.L.; Chu, H.H.; Phi, Q.-T. Metabolic and genomic analysis deciphering biocontrol potential of endophytic Streptomyces albus RC2 against crop pathogenic fungi. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2023, 54, 2617–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mast, Y.; Stegmann, E. Actinomycetes: The antibiotics producers. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-F.; Wu, Q.-X.; Wu, H.; Li, Y.; Peng, Q.; Han, R.-H.; Zhang, D.-H.; Yu, W.-D.; Xu, R.; Wang, J.; et al. Complete genome sequence of Streptomyces sp. HP-A2021, a promising bacterium for natural product discovery. Biochem. Genet. 2023, 61, 2042–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Xu, Z.; Guo, Z.; Hindra; Ma, M.; Yang, D.; Zhou, H.; Gansemans, Y.; Zhu, X.; Huang, Y.; et al. Discovery of the leinamycin family of natural products by mining actinobacterial genomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E11131–E11140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahata, K.; Furstner, A. Total Synthesis of the Guangnanmycin A Alcohol. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2024, 63, e202319070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodska, B.; Holoubek, A. Generation of reactive oxygen species during apoptosis induced by DNA-damaging agents and/or histone deacetylase inhibitors. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2011, 2011, 253529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, S.; Steele, A.D.; Yan, W.; Pan, G.; Kalkreuter, E.; Liu, Y.-C.; Xu, Z.; Shen, B. Thiocysteine lyases as polyketide synthase domains installing hydropersulfide into natural products and a hydropersulfide methyltransferase. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofiani, R.; Ardiningsih, P.; Rizky; Putri, C.D.; Rikayati, R.; Elfahmi; Syamsurizal; Sukito, A.; Juanssilfero, A.B.; Siregar, J.E.; et al. Complete genome sequence, biological activities, and metabolomic profiles of mangrove-derived Streptomyces sp. SM1P. Curr. Microbiol. 2025, 82, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaidis, M.; Hesketh, A.; Frangou, N.; Mossialos, D.; Van de Peer, Y.; Oliver, S.G.; Amoutzias, G.D. A panoramic view of the genomic landscape of the genus Streptomyces. Microb. Genom. 2023, 9, mgen001028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quach, N.T.; Vu, T.H.N.; Bui, T.L.; Le, T.T.X.; Nguyen, T.T.A.; Ngo, C.C.; Phi, Q.-T. Genomic and physiological traits provide insights into ecological niche adaptations of mangrove endophytic Streptomyces parvulus VCCM 22513. Ann. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Vijayakumar, S.; Shintre, N.; Tamhane, V.; Deshpande, N.; Joshi, T.; Mathpal, S.; Anbarasu, A.; Ramaiah, S. In silico exploration of biosynthetic gene clusters in marine Streptomyces sp. and Nocardiopsis sp. from the western coast of India: Genome-based profiling using whole genome sequencing. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2025, 23, 100483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Molloy, B.; Braña, A.F.; Zabala, D.; Olano, C.; Cortés, J.; Morís, F.; Salas, J.A.; Méndez, C. Identification by genome mining of a type I polyketide gene cluster from Streptomyces argillaceus involved in the biosynthesis of pyridine and piperidine alkaloids argimycins P. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balouiri, M.; Sadiki, M.; Ibnsouda, S.K. Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: A review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Esmail, G.A.; Ghilan, A.M.; Arasu, M.V.; Duraipandiyan, V.; Ponmurugan, K. Chemical constituents of Streptomyces sp. strain Al-Dhabi-97 isolated from the marine region of Saudi Arabia with antibacterial and anticancer properties. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, Q.N.; Busche, T.; Van Loi, V.; Kalinowski, J.; Antelmann, H. The redox-sensing MarR-type repressor HypS controls hypochlorite and antimicrobial resistance in Mycobacterium smegmatis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 147, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loi, V.V.; Huyen, N.T.T.; Busche, T.; Tung, Q.N.; Gruhlke, M.C.H.; Kalinowski, J.; Bernhardt, J.; Slusarenko, A.J.; Antelmann, H. Staphylococcus aureus responds to allicin by global S-thioallylation-Role of the Brx/BSH/YpdA pathway and the disulfide reductase MerA to overcome allicin stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 139, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quach, N.T.; Vu, T.H.N.; Nguyen, T.T.A.; Ha, H.; Ho, P.H.; Chu-Ky, S.; Nguyen, L.H.; Van Nguyen, H.; Thanh, T.T.T.; Nguyen, N.A.; et al. Structural and genetic insights into a poly-γ-glutamic acid with in vitro antioxidant activity of Bacillus velezensis VCN56. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, T.H.N.; Pham, N.S.; Le, P.C.; Pham, Q.A.; Quach, N.T.; Nguyen, V.T.; Do, T.T.; Chu, H.H.; Phi, Q.T. Distribution, cytotoxicity, and antioxidant activity of fungal endophytes isolated from Tsuga chinensis (Franch.) Pritz. in Ha Giang province, Vietnam. Ann. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods. 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid Annotations using Subsystems Technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatusova, T.; DiCuccio, M.; Badretdin, A.; Chetvernin, V.; Nawrocki, E.P.; Zaslavsky, L.; Lomsadze, A.; Pruitt, K.D.; Borodovsky, M.; Ostell, J. NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6614–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antipov, D.; Hartwick, N.; Shen, M.; Raiko, M.; Lapidus, A.; Pevzner, P.A. plasmidSPAdes: Assembling plasmids from whole genome sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3380–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Göker, M. TYGS is an automated high-throughput platform for state-of-the-art genome-based taxonomy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.; Ouk Kim, Y.; Park, S.C.; Chun, J. OrthoANI: An improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1100–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Vader, L.; Szenei, J.; Reitz, Z.L.; Augustijn, H.E.; Cediel-Becerra, J.D.D.; Crécy-Lagard, V.D.; Koetsier, R.A.; Williams, S.E.; et al. antiSMASH 8.0: Extended gene cluster detection capabilities and analyses of chemistry, enzymology, and regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, M.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Xie, B.; Sun, Z. Potential TSPO ligand and photooxidation quencher isorenieratene from Arctic Ocean Rhodococcus sp. B7740. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Huang, H.; Liang, J.; Wang, M.; Lu, L.; Shao, Z.; Cobb, R.E.; Zhao, H. Activation and characterization of a cryptic polycyclic tetramate macrolactam biosynthetic gene cluster. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, K.A.; Wu, X.; Patel, D.; Liang, H.; Yalowich, J.C.; Chen, N.; Goodfellow, V.; Adedayo, O.; Dmitrienko, G.I.; Hasinoff, B.B. Mechanism of the cytotoxicity of the diazoparaquinone antitumor antibiotic kinamycin F. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 1132–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Quach, N.T.; Loan, T.T.; Nguyen, T.T.A.; Nguyen Vu, T.H.; Pham, Q.A.; Chu, H.H.; Phi, Q.-T.; Thuoc, D.V. Phenotypic and genomic characterization provide new insights into adaptation to environmental stressors and biotechnological relevance of mangrove Alcaligenes faecalis D334. Res. Microbiol. 2023, 174, 103994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Ding, W.; Sun, C.; Ji, X.; Ling, C.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Ju, J. Julichrome monomers from marine Gastropod Mollusk-associated Streptomyces and stereochemical revision of julichromes Q(3 ⋅ 5) and Q(3 ⋅ 3). Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e2000057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Alam, K.; Zhao, Y.; Hao, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Li, A. Mining and biosynthesis of bioactive lanthipeptides from microorganisms. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 692466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Aguilar, G.R.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barka, E.A.; Vatsa, P.; Sanchez, L.; Gaveau-Vaillant, N.; Jacquard, C.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Klenk, H.P.; Clement, C.; Ouhdouch, Y.; van Wezel, G.P. Taxonomy, Physiology, and Natural Products of Actinobacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadipanah, F.; Wink, J. Actinobacteria from Arid and Desert Habitats: Diversity and Biological Activity. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, J.; Oren, A.; Ventosa, A.; Christensen, H.; Arahal, D.R.; da Costa, M.S.; Rooney, A.P.; Yi, H.; Xu, X.W.; De Meyer, S.; et al. Proposed minimal standards for the use of genome data for the taxonomy of prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Flores, M.; Forteza, I.; Henriksen, N.M.; Concepcion, G.P.; Rosenberg, G.; Haygood, M.G.; Olivera, B.M.; Light, A.R.; Cheatham, T.E., 3rd; et al. Totopotensamides, polyketide-cyclic peptide hybrids from a mollusk-associated bacterium Streptomyces sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Munoz, J.C.; Selem-Mojica, N.; Mullowney, M.W.; Kautsar, S.A.; Tryon, J.H.; Parkinson, E.I.; De Los Santos, E.L.C.; Yeong, M.; Cruz-Morales, P.; Abubucker, S.; et al. A computational framework to explore large-scale biosynthetic diversity. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, T.; Patel, K. Carotenoids: Potent to Prevent Diseases Review. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2020, 10, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, J.M.; Salvador, M.; Argandona, M.; Bernal, V.; Reina-Bueno, M.; Csonka, L.N.; Iborra, J.L.; Vargas, C.; Nieto, J.J.; Canovas, M. Ectoines in cell stress protection: Uses and biotechnological production. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 782–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Lohman, J.R.; Liu, T.; Shen, B. C-S bond cleavage by a polyketide synthase domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 10359–10364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Tested Pathogen | MIC (µg/mL) |
|---|---|
| S. Typhimurium ATCC 14028 | 32 |
| E. coli ATCC 11105 | 32 |
| M. smegmatis MC2 155 | 64 |
| P. aeruginosa ATCC 9027 | 16 |
| S. aureus ATCC 29213 | 8 |
| E. aerogenes ATCC 13048 | 32 |
| B. cereus ATCC 11778 | 16 |
| C. albicans ATCC 10231 | 128 |
| Attribute | Streptomyces sp. CH6 | S. evansiae DSM 41979T | S. chiangmaiensis TA4-1T | S. mexicanus JCM 12681T | S. spheroides NCIMB 11891T |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genome size (bp) | 6,936,977 | 7,502,396 | 9,707,984 | 8,193,100 | 8,727,323 |
| GC content (%) | 73.0 | 73.3 | 69.7 | 72.5 | 70.5 |
| rRNA genes | 3 | 33 | 3 | 18 | 20 |
| tRNA genes | 65 | 65 | 40 | 67 | 66 |
| ncRNA genes | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| CDSs | 5831 | 6577 | 9330 | 7436 | 7799 |
| Predicted genes | 5902 | 6678 | 9376 | 7524 | 7886 |
| GenBank accession | JBNOXK000000000 | JAVRET000000000 | JAYWVC000000000 | JBHTGD000000000 | AWQW00000000 |
| Cluster | Type | Length (bp) | Most Similar Known Cluster | Similarity (%) | Potential Activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NRPS-like, NRPS, nucleoside | 114,856 | Detoxin S1 | 19.8 | - |
| 2 | TransAT-PKS, NRPS, NRP-metallophore | 133,857 | Guangnanmycin | 76.0 | Anticancer [13] |
| 3 | Terpene | 21,104 | Detoxin S1 | 30.6 | - |
| 4 | Lanthipeptide-class-iii | 22,655 | AmfS | 61.0 | - |
| 5 | HglE-KS, terpene | 55,247 | Isorenieratene | 56.7 | Antioxidant, anti-UVB radiation [34] |
| 6 | Terpene | 26,704 | Hopene | 53.9 | - |
| 7 | NRPS, T1PKS | 49,405 | SGR PTMs | 71.0 | Antifungal, antibiotic, antioxidant [35] |
| 8 | NI-siderophore | 33,324 | Kinamycin | 13.2 | Antibacterial, anticancer [36] |
| 9 | Ectoine | 10,399 | Ectoine | 80.7 | Antioxidant [37] |
| 10 | NRPS, T1PKS, T3PKS, NRPS-like | 57,731 | Totopotensamide | 54.1 | - |
| 11 | Terpene | 21,173 | Julichrome Q3-3 | 16.5 | Antibacterial, anticancer [38] |
| 12 | Terpene | 22,436 | Geosmin | 57.3 | - |
| 13 | NRPS, lanthipeptide-class-ii | 32,791 | Birimositide | 73.0 | Antibacterial [39] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, C.T.; Nguyen, H.T.; Dao, V.T.H.; Do, K.P.; Ta, T.T.T. Phenotypic Characterization and Whole-Genome Analysis Revealing the Promising Metabolic Potential of a Newly Isolated Streptomyces sp. CH6. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7126. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137126
Nguyen CT, Nguyen HT, Dao VTH, Do KP, Ta TTT. Phenotypic Characterization and Whole-Genome Analysis Revealing the Promising Metabolic Potential of a Newly Isolated Streptomyces sp. CH6. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(13):7126. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137126
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Chung Thanh, Huong Thi Nguyen, Van Thi Hong Dao, Khanh Phuong Do, and Thuy Thi Thu Ta. 2025. "Phenotypic Characterization and Whole-Genome Analysis Revealing the Promising Metabolic Potential of a Newly Isolated Streptomyces sp. CH6" Applied Sciences 15, no. 13: 7126. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137126
APA StyleNguyen, C. T., Nguyen, H. T., Dao, V. T. H., Do, K. P., & Ta, T. T. T. (2025). Phenotypic Characterization and Whole-Genome Analysis Revealing the Promising Metabolic Potential of a Newly Isolated Streptomyces sp. CH6. Applied Sciences, 15(13), 7126. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137126