Dual-Dimensional Gaussian Splatting Integrating 2D and 3D Gaussians for Surface Reconstruction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We propose DDGS, which integrates both 2D and 3D Gaussians to enable flexible and precise surface reconstruction by adaptively selecting the optimal Gaussian representation based on the characteristics of the object surfaces.
- We introduce gradient-based regularization terms to improve the alignment accuracy between rendered Gaussian normals and the underlying ground truth surfaces, thus enhancing geometric fidelity.
2. Related Work
2.1. Novel View Synthesis with 3D Gaussians
2.2. Surface Reconstruction with Gaussians
2.3. Hybrid Representation with 2D and 3D Gaussians
3. Methods
3.1. Background
3.2. Dual-Dimensional Gaussian Modeling
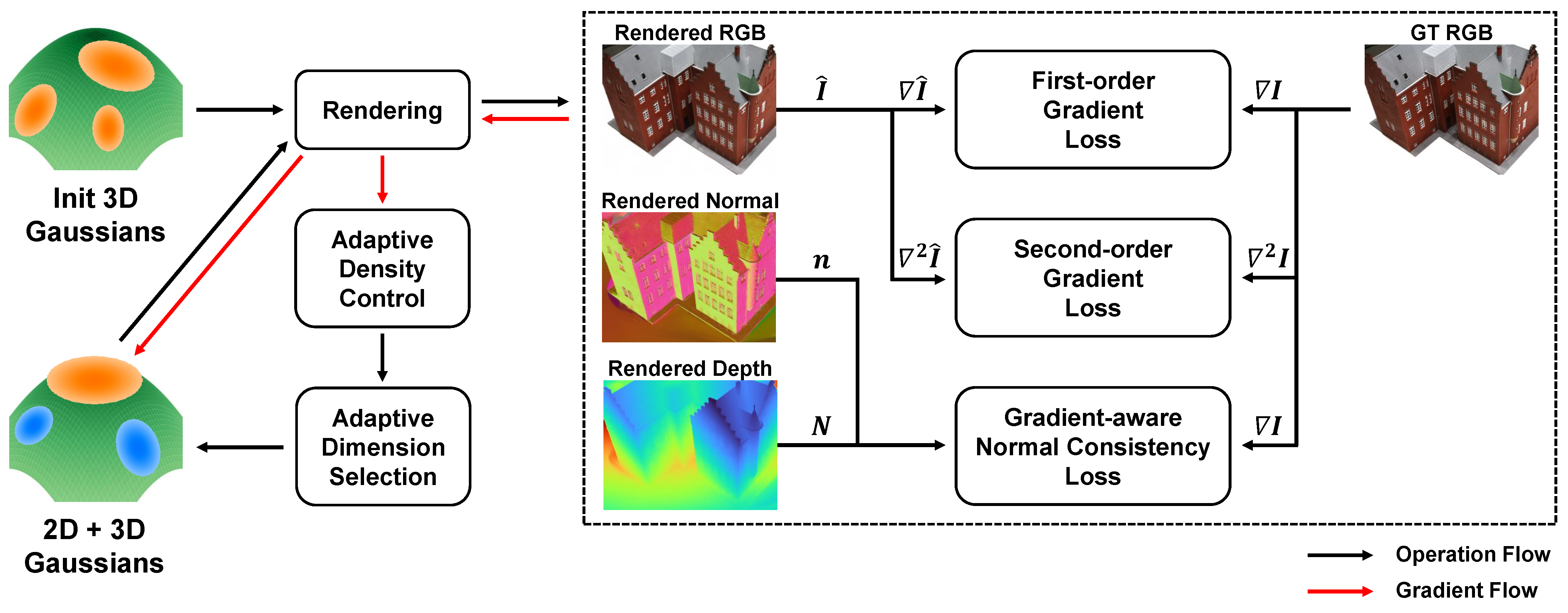
3.3. Adaptive Selection of 2D and 3D Gaussians
3.4. Gaussian Splatting
3.5. Optimization
4. Experiments and Discussion
4.1. Implementation Details
4.2. Evaluation and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3DGS | 3D Gaussian Splatting |
| 2DGS | 2D Gaussian Splatting |
| DDGS | Dual-Dimensional Gaussian Splatting |
| TnT | Tanks and Temples dataset |
| NVS | Novel view synthesis |
| TSDF | Truncated Signed Distance Fusion |
| MLP | Multi-layer perceptron |
| SLAM | Simultaneous localization and mapping |
| SuGaR | Surface-Aligned Gaussian Splatting |
| PSNR | Peak signal-to-noise ratio |
| SSIM | Structural similarity index measure |
| LPIPS | Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity |
| CD | Chamfer distance |
References
- Tang, J.; Ren, J.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, G. Dreamgaussian: Generative gaussian splatting for efficient 3D content creation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.16653. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Zeng, G.; Liu, Z. Lgm: Large multi-view gaussian model for high-resolution 3D content creation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September 29–4 October 2024; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Tonderski, A.; Lindström, C.; Hess, G.; Ljungbergh, W.; Svensson, L.; Petersson, C. Neurad: Neural rendering for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 14895–14904. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, P.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, H.; Yu, C.; Yu, B. SRNeRF: Super-Resolution Neural Radiance Fields for Autonomous Driving Scenario Reconstruction from Sparse Views. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; He, Z.; Ye, J.; Duinkharjav, B.; Chakravarthula, P.; Yang, X.; Sun, Q. Fov-nerf: Foveated neural radiance fields for virtual reality. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2022, 28, 3854–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, H.; Liu, K.; Cao, R.; Fei, Z.; Wen, X.; Chen, L. Integration of 3D Gaussian Splatting and Neural Radiance Fields in Virtual Reality Fire Fighting. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramov, N.; Lankegowda, H.; Liu, S.; Barazzetti, L.; Beltracchi, C.; Ruttico, P. Implementing Immersive Worlds for Metaverse-Based Participatory Design through Photogrammetry and Blockchain. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabra, L.; Solanes, J.E.; Muñoz, A.; Martí-Testón, A.; Alabau, A.; Gracia, L. Application of Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) for 3D model representation in the industrial metaverse. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerbl, B.; Kopanas, G.; Leimkühler, T.; Drettakis, G. 3D gaussian splatting for real-time radiance field rendering. ACM Trans. Graph. 2023, 42, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Yu, Z.; Chen, A.; Geiger, A.; Gao, S. 2d gaussian splatting for geometrically accurate radiance fields. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH 2024 Conference Papers, Denver, CO, USA, 27 July–1 August 2024; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.Y.; Park, J.; Koltun, V. Open3D: A modern library for 3D data processing. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.09847. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Yu, M.; Xu, L.; Xiangli, Y.; Wang, L.; Lin, D.; Dai, B. Scaffold-gs: Structured 3D gaussians for view-adaptive rendering. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 20654–20664. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Wang, K.; Wen, K.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, D.; Wang, Z. Lightgaussian: Unbounded 3D gaussian compression with 15x reduction and 200+ fps. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 140138–140158. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, S.; Wu, C.; Wan, Z.; Tong, S. High-Fold 3D Gaussian Splatting Model Pruning Method Assisted by Opacity. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Gao, C.; Bai, Y.; Lv, X. RD-SLAM: Real-Time Dense SLAM Using Gaussian Splatting. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, C.; Zhu, H.; Hu, X. DyGS-SLAM: Realistic Map Reconstruction in Dynamic Scenes Based on Double-Constrained Visual SLAM. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Song, C.; Ji, Y.; Zhong, S. Related Keyframe Optimization Gaussian–Simultaneous Localization and Mapping: A 3D Gaussian Splatting-Based Simultaneous Localization and Mapping with Related Keyframe Optimization. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Song, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, T.; Do, H. Click-gaussian: Interactive segmentation to any 3D gaussians. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; pp. 289–305. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.; Ding, L.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xue, T.; Xu, D. Interactive3d: Create what you want by interactive 3D generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 4999–5008. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, C.; Fan, L.; Wang, N.; Peng, J.; Zhang, Z. Citygaussian: Real-time high-quality large-scale scene rendering with gaussians. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; pp. 265–282. [Google Scholar]
- Shaheen, B.; Zane, M.D.; Bui, B.T.; Shubham; Huang, T.; Merello, M.; Scheelk, B.; Crooks, S.; Wu, M. ForestSplat: Proof-of-Concept for a Scalable and High-Fidelity Forestry Mapping Tool Using 3D Gaussian Splatting. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Zuo, X.; Guo, C.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Wu, X.; Xu, S.; Dai, P.; Yan, Y.; Cheng, L. Gsd: View-guided gaussian splatting diffusion for 3D reconstruction. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; pp. 55–72. [Google Scholar]
- Mithun, N.C.; Pham, T.; Wang, Q.; Southall, B.; Minhas, K.; Matei, B.; Mandt, S.; Samarasekera, S.; Kumar, R. Diffusion-Guided Gaussian Splatting for Large-Scale Unconstrained 3D Reconstruction and Novel View Synthesis. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.01960. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, H.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Geng, Y.; Chen, J.; Ma, W.; Li, C.; Wang, L.; Feng, H.; Shi, L.; et al. Robo-gs: A physics consistent spatial-temporal model for robotic arm with hybrid representation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.14873. [Google Scholar]
- Guédon, A.; Lepetit, V. Sugar: Surface-aligned gaussian splatting for efficient 3D mesh reconstruction and high-quality mesh rendering. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 5354–5363. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, B.; Li, H.; He, Y.; Cui, Z.; Bao, H.; Zhang, G. Splatloc: 3D gaussian splatting-based visual localization for augmented reality. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2025, 31, 3591–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, C.; Lee, G.H. Neusg: Neural implicit surface reconstruction with 3D gaussian splatting guidance. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.00846. [Google Scholar]
- Turkulainen, M.; Ren, X.; Melekhov, I.; Seiskari, O.; Rahtu, E.; Kannala, J. Dn-splatter: Depth and normal priors for gaussian splatting and meshing. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.17822. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Gu, J.; Fan, L.; Wu, B.; Lou, Y.; Chen, R.; Liu, L.; Ye, J. HybridGS: Decoupling Transients and Statics with 2D and 3D Gaussian Splatting. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.03844. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Wei, X.; Wuwu, Q.; Wang, X.; Xiao, X.; Lu, M. MixedGaussianAvatar: Realistically and Geometrically Accurate Head Avatar via Mixed 2D-3D Gaussian Splatting. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.04955. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Gong, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, J.; Luo, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, S.; Fei, B.; He, Y. MGSR: 2D/3D Mutual-boosted Gaussian Splatting for High-fidelity Surface Reconstruction under Various Light Conditions. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.05182. [Google Scholar]
- Zwicker, M.; Rasanen, J.; Botsch, M.; Dachsbacher, C.; Pauly, M. Perspective accurate splatting. In Proceedings of the Graphics Interface, London, ON, Canada, 17–19 May 2004; pp. 247–254. [Google Scholar]
- Hahlbohm, F.; Friederichs, F.; Weyrich, T.; Franke, L.; Kappel, M.; Castillo, S.; Stamminger, M.; Eisemann, M.; Magnor, M. Efficient Perspective-Correct 3D Gaussian Splatting Using Hybrid Transparency. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.08129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinn, J.F. A homogeneous formulation for lines in 3 space. In Proceedings of the 4th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, San Jose, CA, USA, 20–22 July 1977; pp. 237–241. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, R.; Dahl, A.; Vogiatzis, G.; Tola, E.; Aanæs, H. Large scale multi-view stereopsis evaluation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 406–413. [Google Scholar]
- Knapitsch, A.; Park, J.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Koltun, V. Tanks and temples: Benchmarking large-scale scene reconstruction. ACM Trans. Graph. 2017, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, J.T.; Mildenhall, B.; Verbin, D.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Hedman, P. Mip-nerf 360: Unbounded anti-aliased neural radiance fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5470–5479. [Google Scholar]



| Methods | DTU Scene ID | Mean | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 | 37 | 40 | 55 | 63 | 65 | 69 | 83 | 97 | 105 | 106 | 110 | 114 | 118 | 122 | CD↓ | Time↓ | |
| 3DGS | 2.54 | 1.35 | 2.03 | 1.77 | 3.07 | 2.61 | 1.79 | 2.20 | 2.15 | 1.87 | 2.05 | 2.38 | 1.89 | 1.65 | 1.72 | 2.07 | 6 min |
| SuGaR | 1.79 | 1.05 | 1.04 | 0.69 | 1.86 | 1.59 | 1.27 | 1.80 | 1.86 | 1.31 | 1.01 | 1.83 | 1.37 | 1.04 | 0.83 | 1.36 | 39 min |
| 2DGS | 0.50 | 0.81 | 0.34 | 0.43 | 0.94 | 0.85 | 0.82 | 1.28 | 1.21 | 0.64 | 0.69 | 1.37 | 0.42 | 0.67 | 0.48 | 0.76 | 11 min |
| Ours | 0.47 | 0.81 | 0.34 | 0.41 | 0.91 | 0.84 | 0.76 | 1.20 | 1.10 | 0.63 | 0.65 | 1.10 | 0.40 | 0.57 | 0.42 | 0.71 | 15 min |
| Methods | TnT Scene ID | Mean | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barn | Caterpillar | Courthouse | Ignatius | Meetingroom | Truck | F1-Score↑ | Time↓ | |
| 3DGS | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.20 | 0.12 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 14 min |
| SuGaR | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 50 min |
| 2DGS | 0.39 | 0.24 | 0.16 | 0.50 | 0.20 | 0.45 | 0.32 | 16 min |
| Ours | 0.38 | 0.23 | 0.16 | 0.51 | 0.20 | 0.54 | 0.34 | 23 min |
| Methods | Outdoor Scene (Mean) | Indoor Scene (Mean) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR ↑ | SSIM ↑ | LPIPS ↓ | Time ↓ | PSNR ↑ | SSIM ↑ | LPIPS ↓ | Time ↓ | |
| 3DGS | 24.60 | 0.726 | 0.240 | 29 min | 30.91 | 0.923 | 0.188 | 23 min |
| SuGaR | 22.94 | 0.647 | 0.312 | 66 min | 29.46 | 0.906 | 0.208 | 58 min |
| 2DGS | 24.16 | 0.702 | 0.288 | 33 min | 30.03 | 0.909 | 0.214 | 35 min |
| Ours | 24.24 | 0.713 | 0.267 | 40 min | 29.44 | 0.908 | 0.205 | 46 min |
| Ablation Setting | Mean CD ↓ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| w/o gradient-aware normal consistency weight | ✓ | ✓ | 0.7239 | |
| w/o first-order gradient loss | ✓ | ✓ | 0.7216 | |
| w/o second-order gradient loss | ✓ | ✓ | 0.7457 | |
| Full model | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 0.7074 |
| Ratio Threshold | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Chamfer Distance ↓ | 0.7248 | 0.7074 | 0.7159 | 0.7170 | 0.7144 | 0.7123 |
| Method | Image Rendering Speed ↑ (fps) | Mean Mesh Extraction Time ↓ (s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DTU | TnT | Mip-NeRF 360 | DTU | TnT | Mip-NeRF 360 | |
| 3DGS | 261.27 | 163.14 | 97.55 | 1.36 | 376.24 | 58.59 |
| SuGaR | 78.74 | 82.02 | 72.79 | 98.11 | 295.15 | 471.96 |
| 2DGS | 140.30 | 112.33 | 50.29 | 1.52 | 158.60 | 42.70 |
| Ours | 102.91 | 82.43 | 43.92 | 1.49 | 178.62 | 43.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.; Suh, J.-W.; Ban, Y. Dual-Dimensional Gaussian Splatting Integrating 2D and 3D Gaussians for Surface Reconstruction. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6769. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126769
Park J, Suh J-W, Ban Y. Dual-Dimensional Gaussian Splatting Integrating 2D and 3D Gaussians for Surface Reconstruction. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(12):6769. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126769
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jichan, Jae-Won Suh, and Yuseok Ban. 2025. "Dual-Dimensional Gaussian Splatting Integrating 2D and 3D Gaussians for Surface Reconstruction" Applied Sciences 15, no. 12: 6769. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126769
APA StylePark, J., Suh, J.-W., & Ban, Y. (2025). Dual-Dimensional Gaussian Splatting Integrating 2D and 3D Gaussians for Surface Reconstruction. Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6769. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126769






