Heat-Resistant Behavior of PLA/PMMA Transparent Blends Induced by Nucleating Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the PLA/PMMA Blends
2.2.1. Melt Blending
2.2.2. Compression Molding
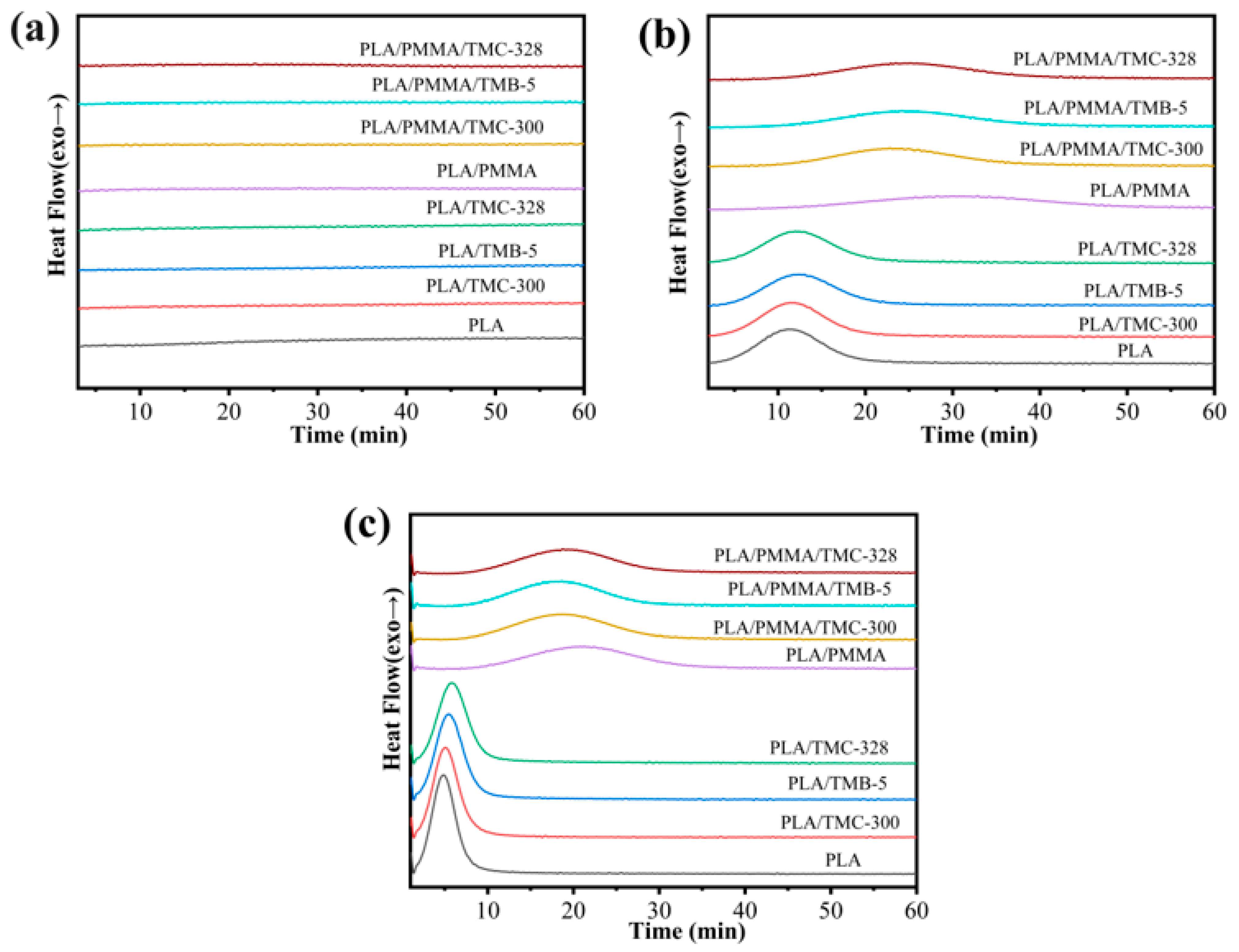
2.2.3. Isothermal Crystallization Treatment
2.3. Measurements
2.3.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.3.2. Wide-Angle X-Ray Diffraction Analysis (WAXD)
2.3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.4. Heat Resistance Property Measurements
2.3.5. Light Transmission Property Measurements
2.3.6. Mechanical Property Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
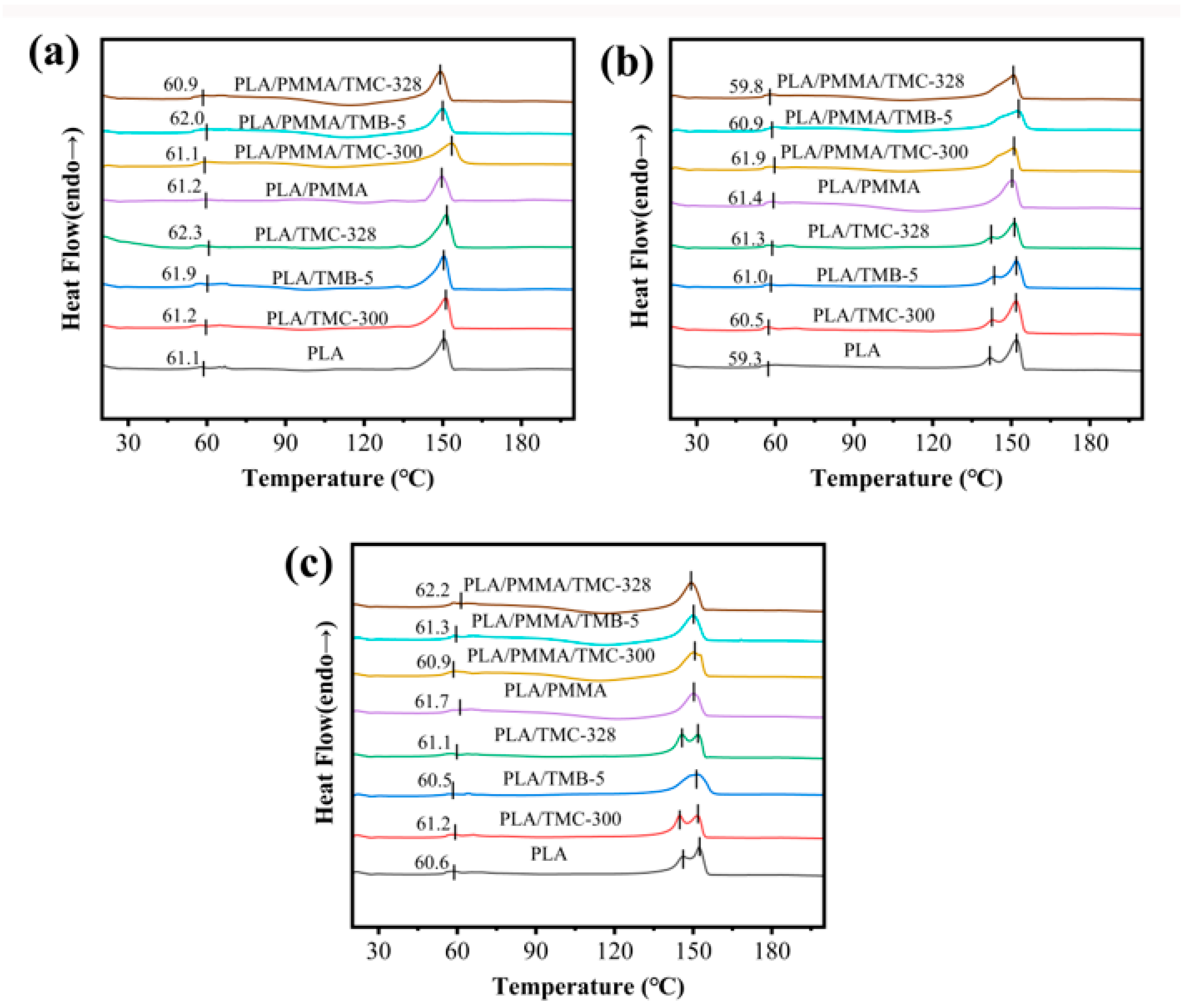
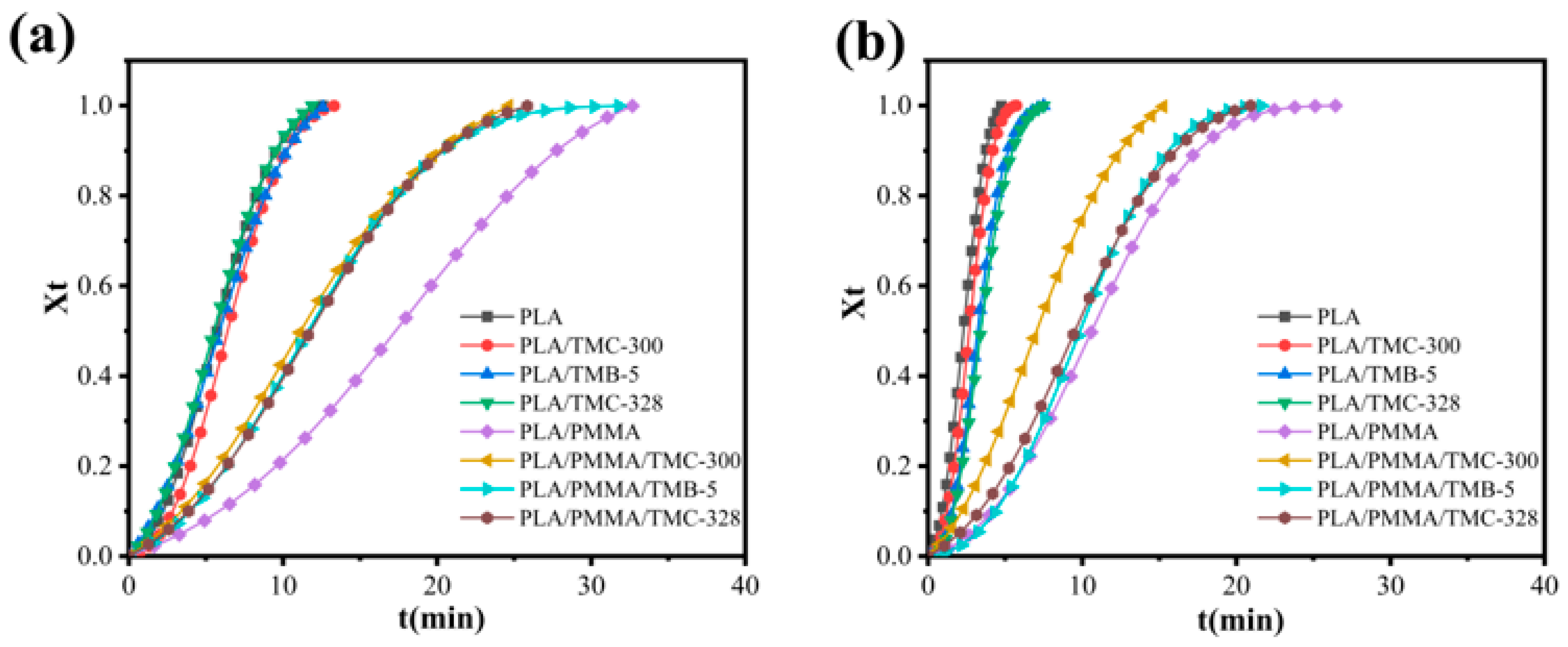
3.1. Melting and Crystallization Behavior
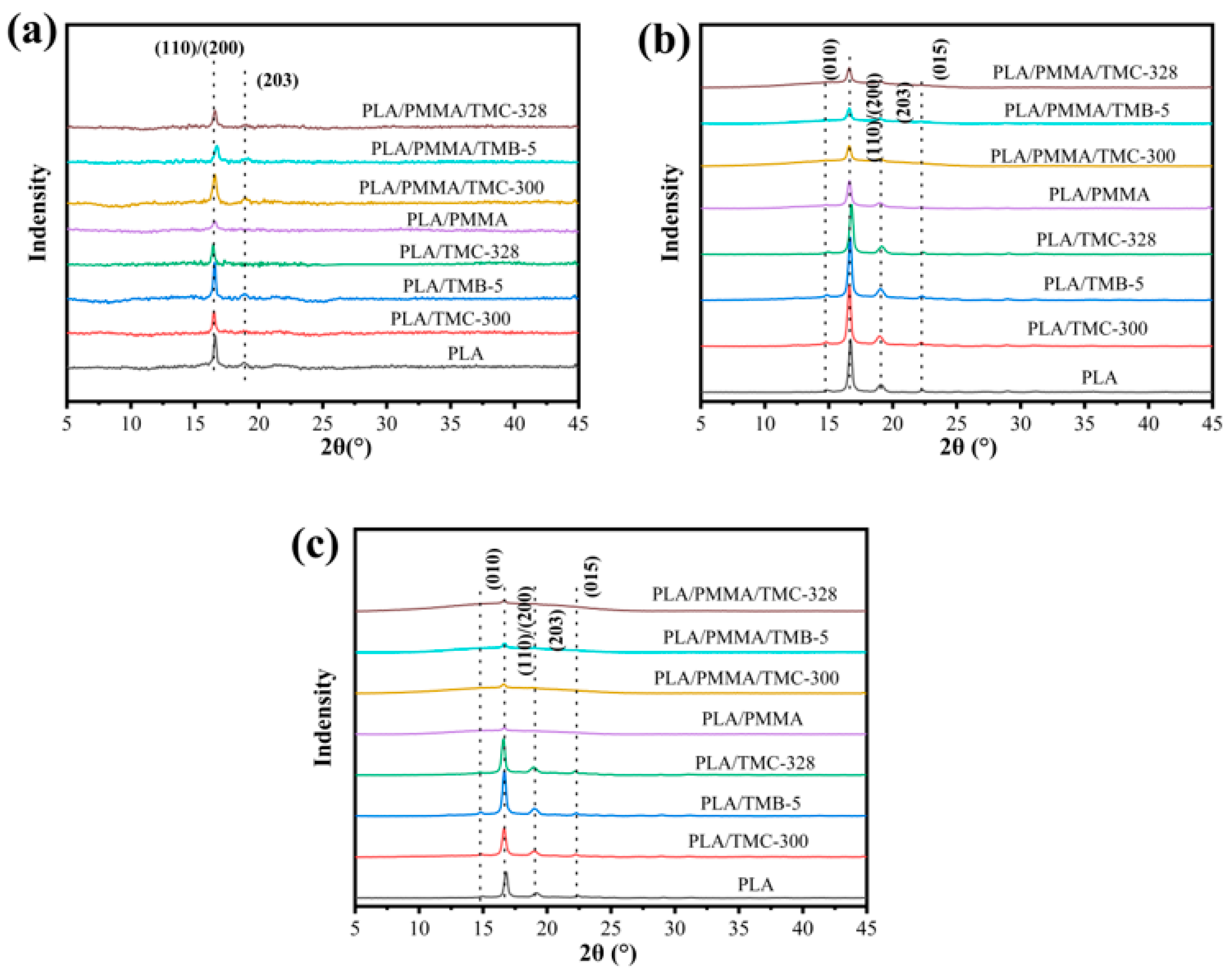
3.2. Crystal Structure
3.3. Morphology Analysis
3.4. Heat Resistance
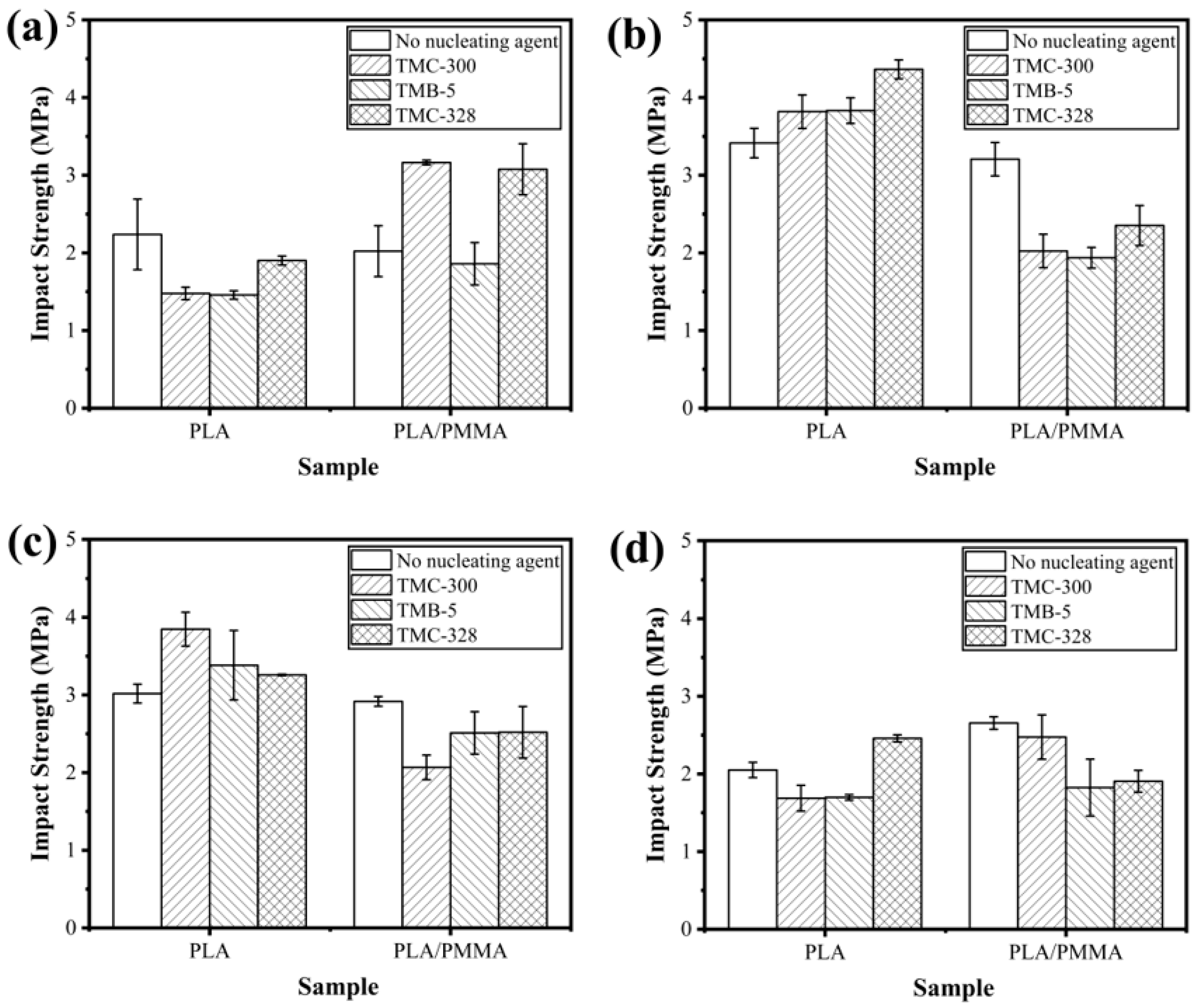
3.5. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, L.T.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M. Processing technologies for poly (lactic acid). Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 820–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Deng, C.; Lin, G.P.; Wang, Y.Z. Super toughened and high heat-resistant poly (lactic acid) (PLA)-based blends by enhancing interfacial bonding and PLA phase crystallization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 54, 5643–5655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.P.; Liu, J.C.; Li, J.C.; Liang, X.Y.; Zhou, W.; Peng, S. Strategies and techniques for improving heat resistance and mechanical performances of poly (lactic acid) (PLA) biodegradable materials. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 218, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, B.; Fan, B.; Sun, H.; Zhang, H. Enhanced nonisothermal crystallization and heat resistance of poly (L-lactic acid) by d-sorbitol as a homogeneous nucleating agent. ACS Macro Lett. 2021, 10, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.N.; Huang, Z.G.; Weng, Y.X. Heat resistance, crystallization behavior, and mechanical properties of polylactide/nucleating agent composites. Mater. Des. 2015, 66, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulinski, Z.; Piorkowska, E. Crystallization structure and properties of plasticized poly (lactide). Polymer 2005, 46, 10290–10300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauricio, G.G.; Shant, S.; Michel, A.H. Properties and phase structure of melt processed PLA/PMMA blends. Polym. Res. 2018, 25, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, M.; Yuryev, Y.; Mohanty, A.K. Novel durable bio-composites from biobased PC/PLA blend matrix system. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 130, 158–166. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, C.H.; Wang, C.H.; Lin, C.I.; Lee, Y.D. Synthesis and characterization of TPO/PLA copolymer and its behavior as compatibilizer for PLA/TPO blends. Polymer 2008, 49, 3902–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.B.; Lee, Y.K.; Choi, G.D.; Na, S.W.; Park, T.S.; Kim, W.N. Compatibilizing effects for improving mechanical properties of bio-degradable poly (lactic acid) and polycarbonate blends. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anakabe, J.; Zaldua, A.M.H.; Eceiza, A. Melt blending of polylactide and poly (methyl methacrylate): Thermal and mechanical properties and phase morphology characterization. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.Y.; Yin, J.B.; Fan, Y.Q.; Cai, Y.H.; Yan, S.F. Preparation and properties of transparent heat-resistant polylactic acid blends. Funct. Mater. 2011, 42, 842–845. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.H.; Woo, E.M. Effects of chain configuration on UCST behavior in blends of poly (L-lactic acid) with tactic poly (methyl methacrylate) s. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2008, 46, 2355–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, L.; Cinelli, P.; Coltelli, M.B.; Righetti, M.C.; Gazzano, M.; Lazzeri, A. Effect of nucleating agents on crystallinity and properties of poly (lactic acid). PLA Eur. Polym. 2017, 93, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.Q.; Kaschta, J.; Liu, X.H.; Pan, Y.M.; Schubert, D.W. Entanglement network formed in miscible PLA/PMMA blends and its role in rheological and thermo-mechanical properties of the blends. Polymer 2015, 80, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.X.; Zhang, M.; Li, Q.M.; Liu, W.L.; Shen, S.Y.; Dong, H.F. Overview of biodegradable plastics standards at home and abroad. Stand. Sci. 2016, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.W.; Sterzel, H.J.; Wegner, G. Investigation of the structure of solution grown crystals of lactide copolymers by means of chemical reactions. Kolloid Z. Z. Polym. 1973, 251, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, M.; Hasegawa, S.; Ohshima, M. Crystallization kinetics of poly(L-lactide) incontact with pressurized CO2. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2004, 44, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 1040.1-2018; Determination of Tensile Properties of Plastics-Part 1: General Principles. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- GB/T 1043.1-2008; Plastics—Determination of Charpy Impact Properties-Part 1: General Principles. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Avrami, M. Transformation-time relations for random distribution of nuclei kinetics of phase change II. Chem. Phys. 1940, 8, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Wang, Y.M.; Han, Q.; He, D.; Li, Q.; Shen, C. Nonisothermal crystallization kinetics of poly (lactic acid) nucleated with a multiamide nucleating agent. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2014, 53, 1680–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornes, T.D.; Paul, D.R. Crystallization behavior of nylon 6 nanocomposites. Polymer 2003, 44, 3945–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.L.; Masilamani, D.; Bui, L.K.; Khanna, Y.P.; Bray, R.G.; Hammond, W.B.; Curran, S.; Belles, J.J.J.; Binder-Castelli, S. The mechanism of action of sugar acetals as nucleating agents for polypropylene. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 3147–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.F.; Xia, C.; Jin, M.; Du, H.N.; Zhang, J. Effect of nucleating agent TMB-5 on crystallization properties of PLA. Synth. Resins Plast. 2015, 32, 4–7. [Google Scholar]

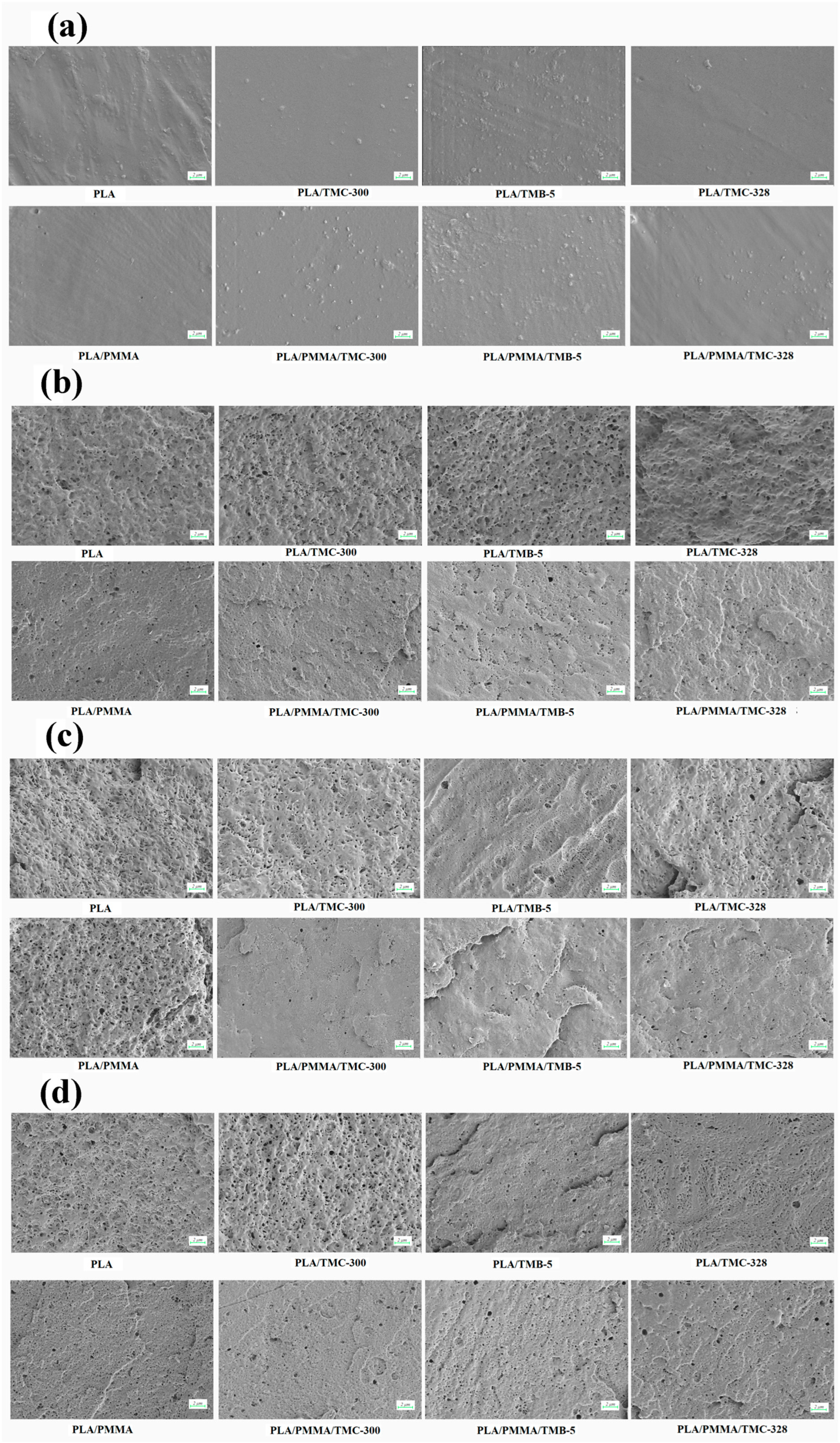
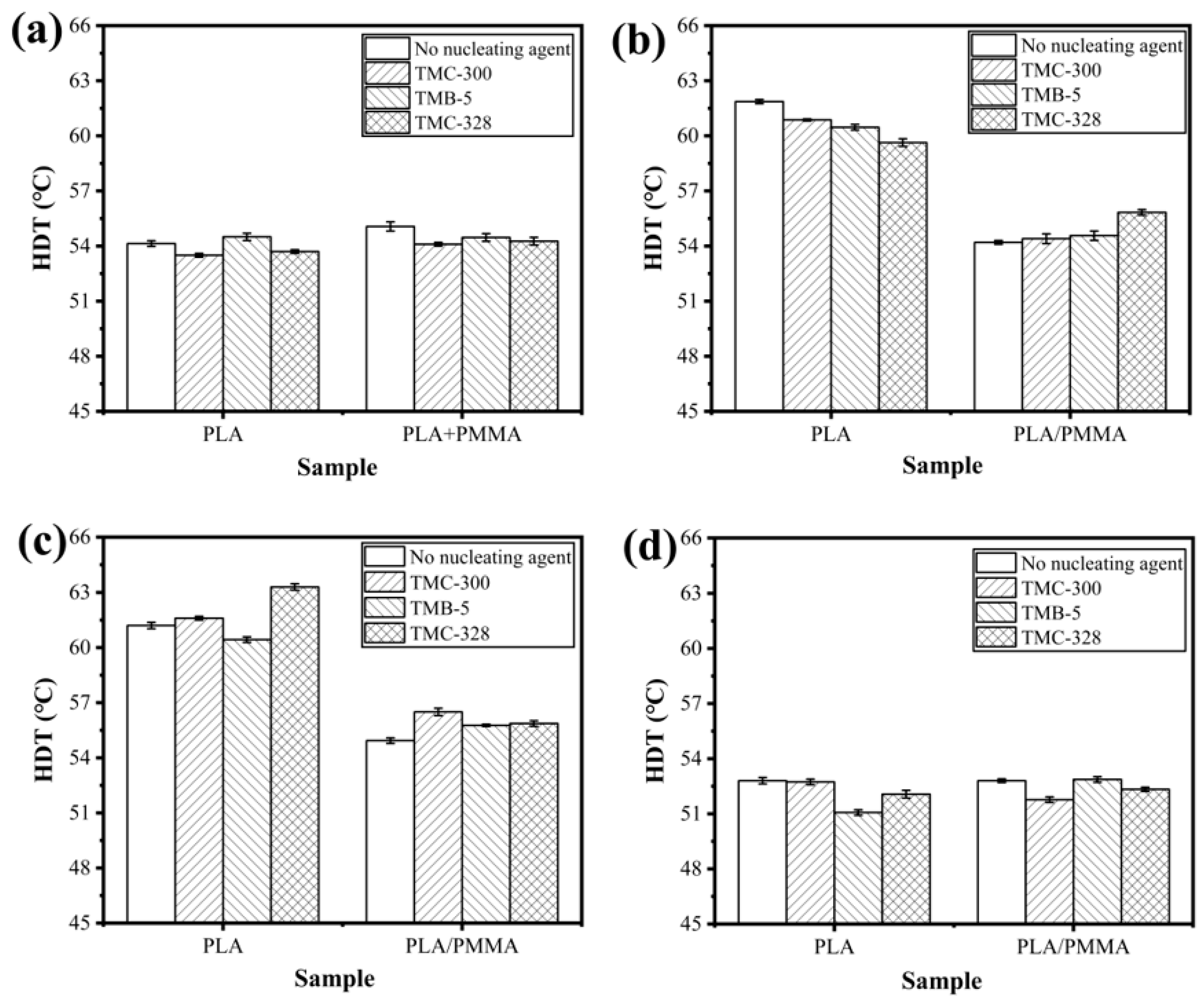
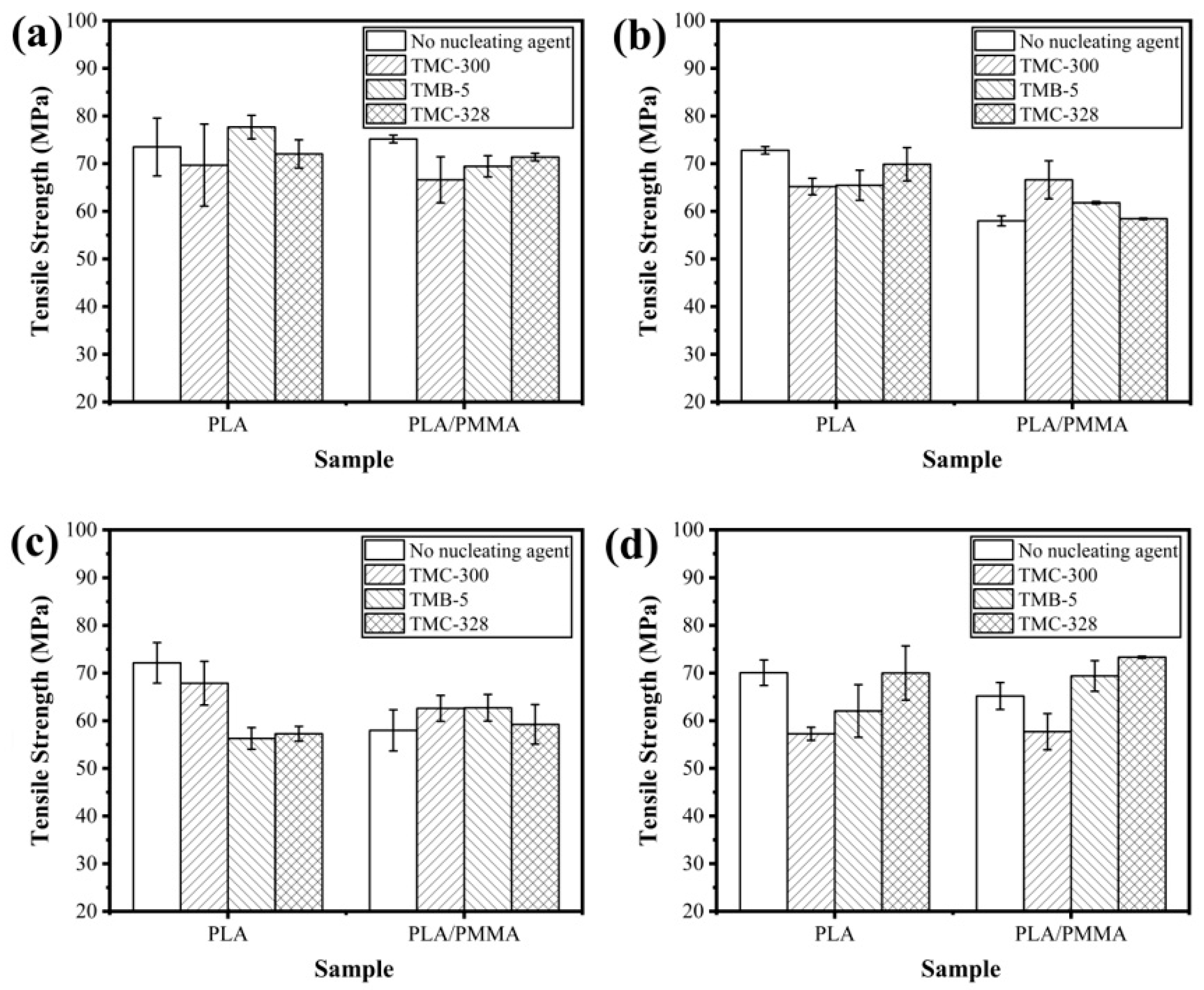
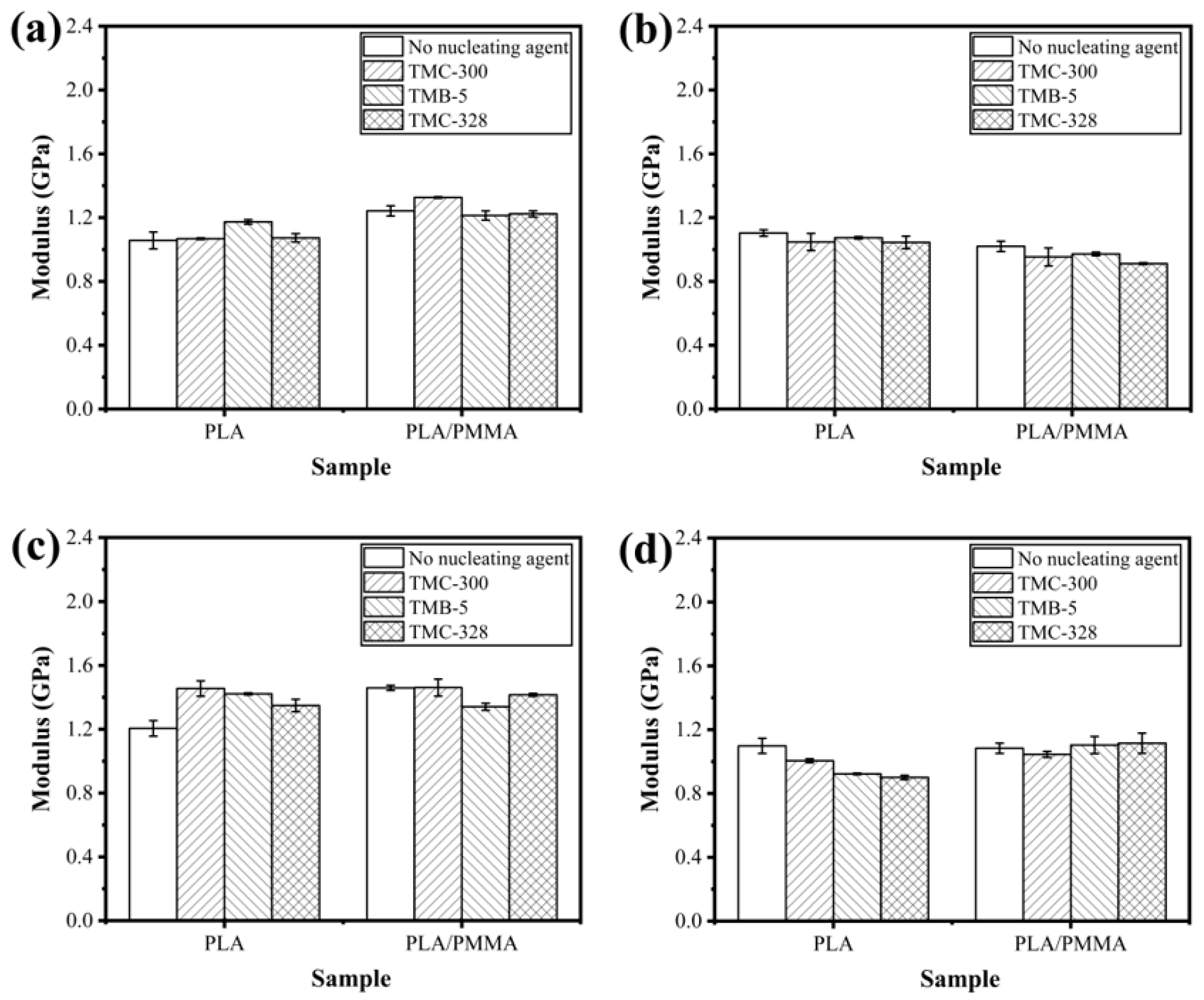
| Samples | PLLA (g) | PMMA (g) | TMC-300 (g) | TMB-5 (g) | TMC-328 (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLLA | 100 | ||||
| PLLA/PMMA | 90 | 10 | |||
| PLLA/TMC-300 | 100 | 0.3 | |||
| PLLA/TMB-5 | 100 | 0.3 | |||
| PLLA/TMC-328 | 100 | 0.3 | |||
| PLLA/PMMA/TMC-300 | 90 | 10 | 0.3 | ||
| PLLA/PMMA/TMB-5 | 90 | 10 | 0.3 | ||
| PLLA/PMMA/TMC-328 | 90 | 10 | 0.3 |
| Samples | Tg (°C) | Tm (°C) | Xc (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 °C | 90 °C | 100 °C | 80 °C | 90 °C | 100 °C | 80 °C | 90 °C | 100 °C | |
| PLA | 61.1 | 59.3 | 60.6 | 150.4 | 141.6/151.9 | 145.8/152.2 | 31.9 | 33.0 | 35.5 |
| PLA/TMC-300 | 61.2 | 60.5 | 61.2 | 151.2 | 142.5/151.8 | 144.6/151.8 | 31.3 | 38.2 | 34.6 |
| PLA/TMB-5 | 61.9 | 61.0 | 60.5 | 150.5 | 143.2/151.8 | 151.8 | 32.4 | 32.2 | 34.6 |
| PLA/TMC-328 | 62.3 | 61.3 | 61.1 | 151.6 | 142.0/151.2 | 145.5/151.8 | 33.1 | 32.2 | 35.6 |
| PLA/PMMA | 61.2 | 61.4 | 61.7 | 149.6 | 150.4 | 150.3 | 26.2 | 28.4 | 22.3 |
| PLA/PMMA/TMC-300 | 61.1 | 61.9 | 60.9 | 153.4 | 151.1 | 150.4 | 28.9 | 29.1 | 29.7 |
| PLA/PMMA/TMB-5 | 62.0 | 60.9 | 61.3 | 150.1 | 152.4 | 149.9 | 23.2 | 29.0 | 27.3 |
| PLA/PMMA/TMC-328 | 60.9 | 59.8 | 62.2 | 149.1 | 150.9 | 149.1 | 28.1 | 29.6 | 28.2 |
| Samples | n | k | t1/2 (min) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90 °C | 100 °C | 90 °C | 100 °C | 90 °C | 100 °C | |
| PLA | 2.2 | 2.2 | 1.64 × 10−2 | 1.18 × 10−1 | 5.48 | 2.24 |
| PLA/TMC-300 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 7.30 × 10−3 | 5.78 × 10−2 | 6.18 | 2.70 |
| PLA/TMB-5 | 1.8 | 2.6 | 2.99 × 10−2 | 3.40 × 10−2 | 5.73 | 3.19 |
| PLA/TMC-328 | 2.0 | 2.6 | 2.55 × 10−2 | 2.90 × 10−2 | 5.22 | 3.39 |
| PLA/PMMA | 2.0 | 2.2 | 2.29 × 10−3 | 3.70 × 10−3 | 17.40 | 10.79 |
| PLA/PMMA/TMC-300 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.02 × 10−2 | 2.26 × 10−2 | 10.45 | 6.70 |
| PLA/PMMA/TMB-5 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 5.68 × 10−3 | 2.48 × 10−3 | 11.04 | 9.52 |
| PLA/PMMA/TMC-328 | 2.0 | 2.1 | 5.80 × 10−3 | 7.15 × 10−3 | 10.93 | 8.83 |
| Samples | 80 °C (96 min) | 90 °C (29 min) | 100 °C (5 min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | 343 | 274 | 268 |
| PLA/TMC-300 | 344 | 270 | 246 |
| PLA/TMB-5 | 319 | 264 | 264 |
| PLA/TMC-328 | 350 | 260 | 272 |
| PLA/PMMA | 223 | 242 | 206 |
| PLA/PMMA/TMC-300 | 216 | 242 | 231 |
| PLA/PMMA/TMB-5 | 186 | 245 | 217 |
| PLA/PMMA/TMC-328 | 227 | 233 | 190 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Feng, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Z. Heat-Resistant Behavior of PLA/PMMA Transparent Blends Induced by Nucleating Agents. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6738. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126738
Li J, Feng Y, Yang J, Li Z, Zhao Z. Heat-Resistant Behavior of PLA/PMMA Transparent Blends Induced by Nucleating Agents. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(12):6738. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126738
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jiafeng, Yanjun Feng, Jianwei Yang, Zhengqiu Li, and Zhixin Zhao. 2025. "Heat-Resistant Behavior of PLA/PMMA Transparent Blends Induced by Nucleating Agents" Applied Sciences 15, no. 12: 6738. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126738
APA StyleLi, J., Feng, Y., Yang, J., Li, Z., & Zhao, Z. (2025). Heat-Resistant Behavior of PLA/PMMA Transparent Blends Induced by Nucleating Agents. Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6738. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126738






