Multi-Level Feature Fusion Attention Generative Adversarial Network for Retinal Optical Coherence Tomography Image Denoising
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
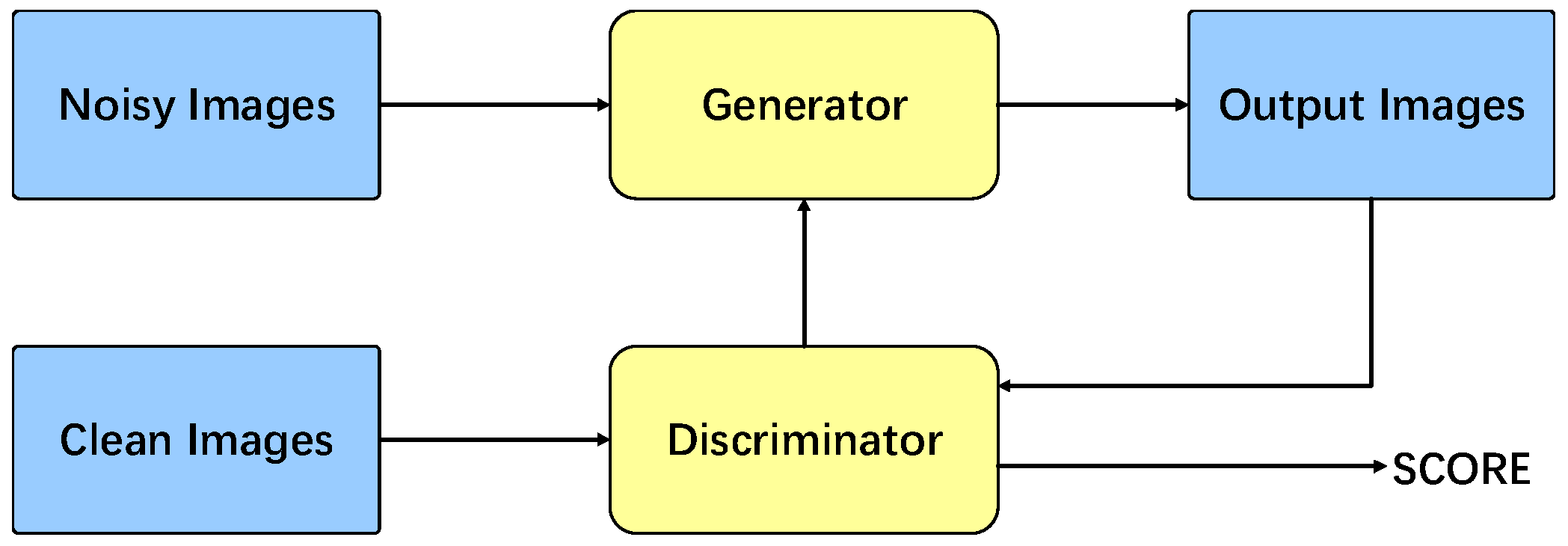
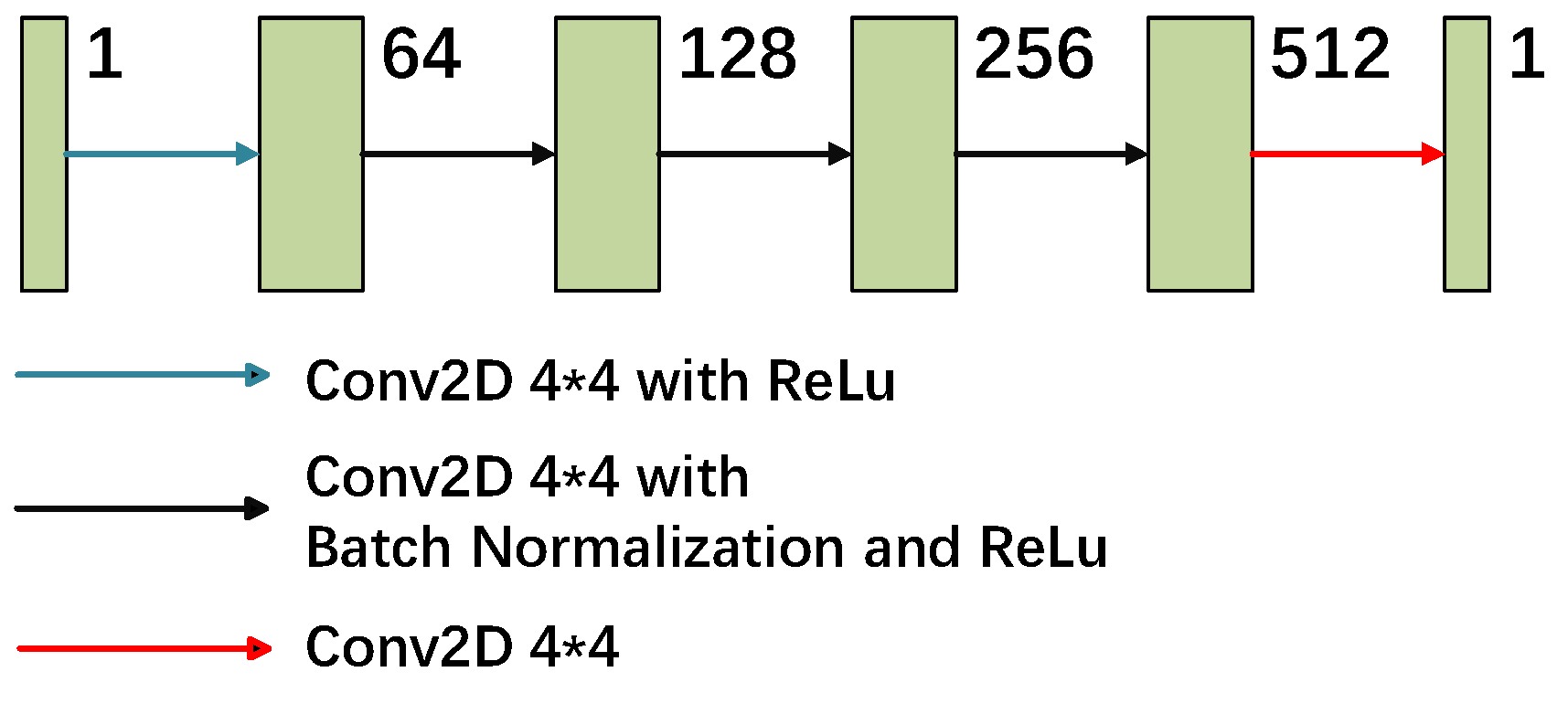
2.1. Generative Adversarial Networks
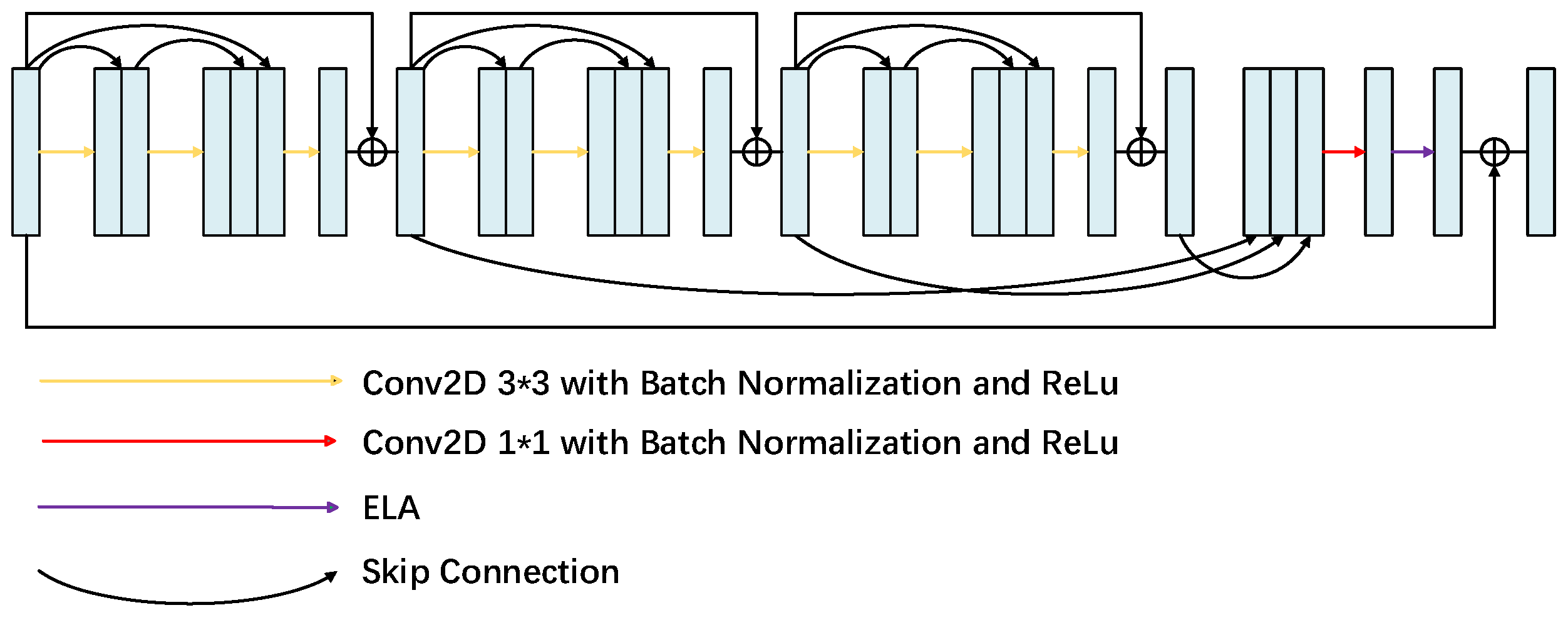
2.2. Total Model
2.2.1. Multi-Level Feature Fusion Attention Module
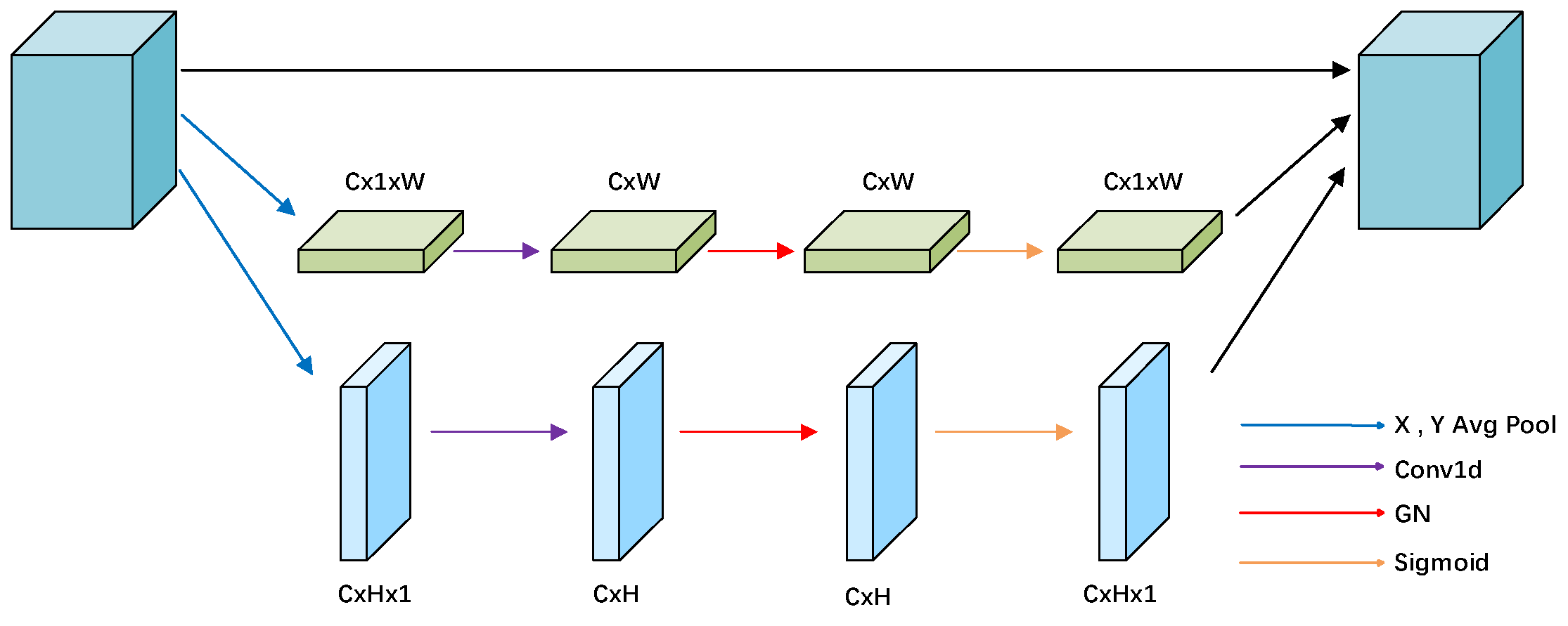
2.2.2. ELA Attention Module
2.3. Loss Function
3. Experiment
3.1. Data Used in the Experiment
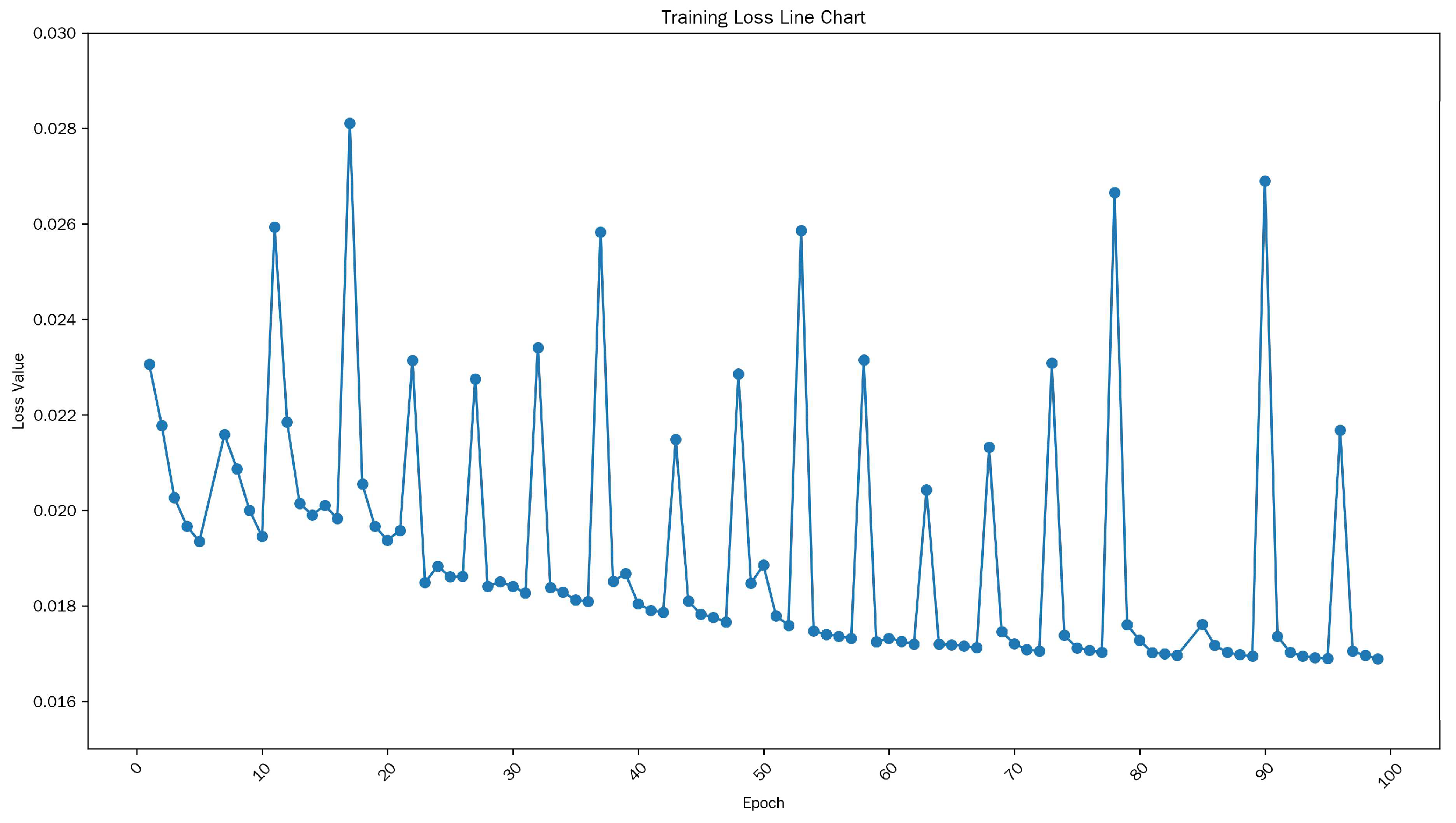
3.2. Experimental Parameter Settings
3.3. Result Descriptions of Performance Indicators
3.3.1. PSNR
3.3.2. SSIM
3.3.3. CNR
3.3.4. ENL
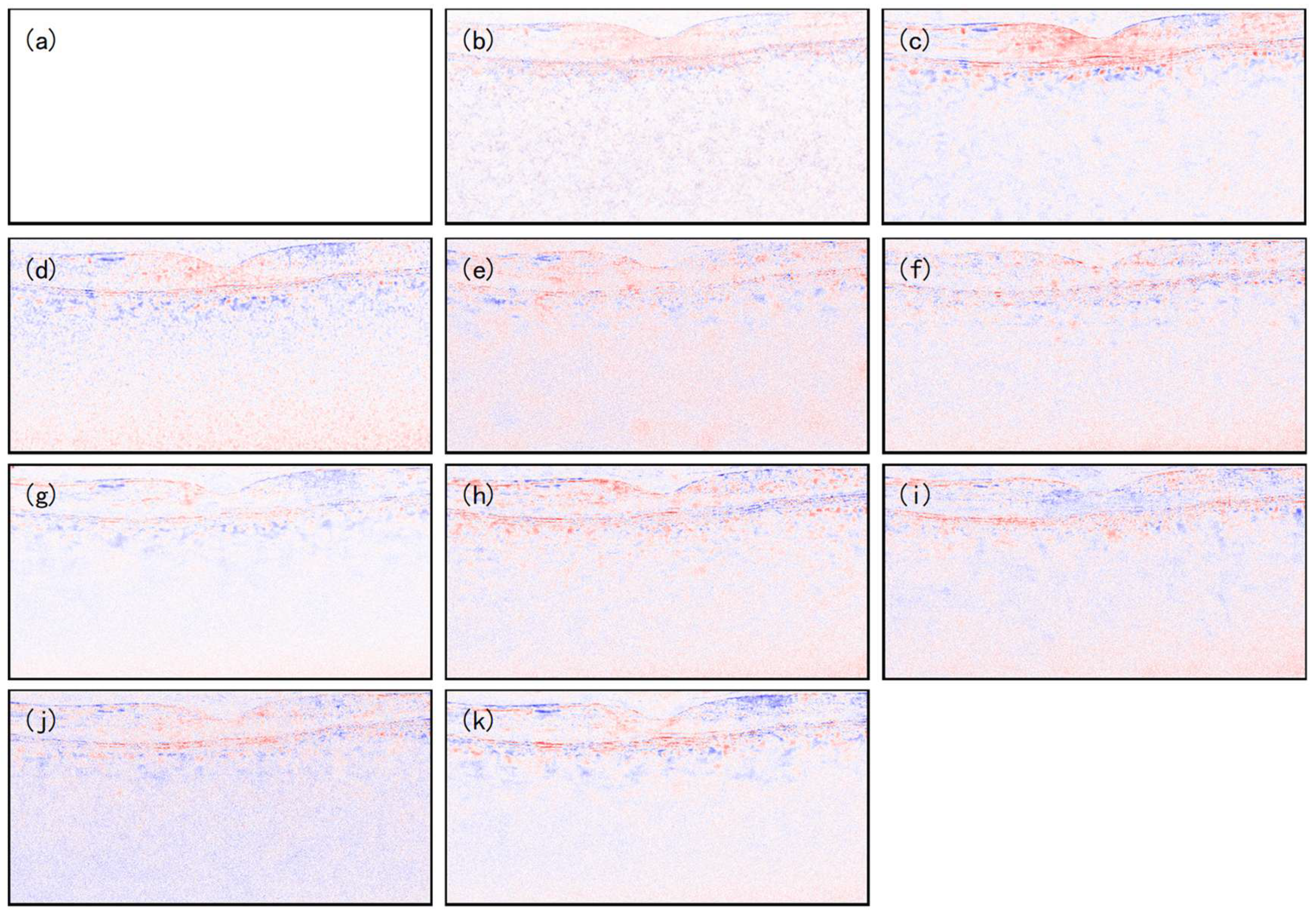
4. Results
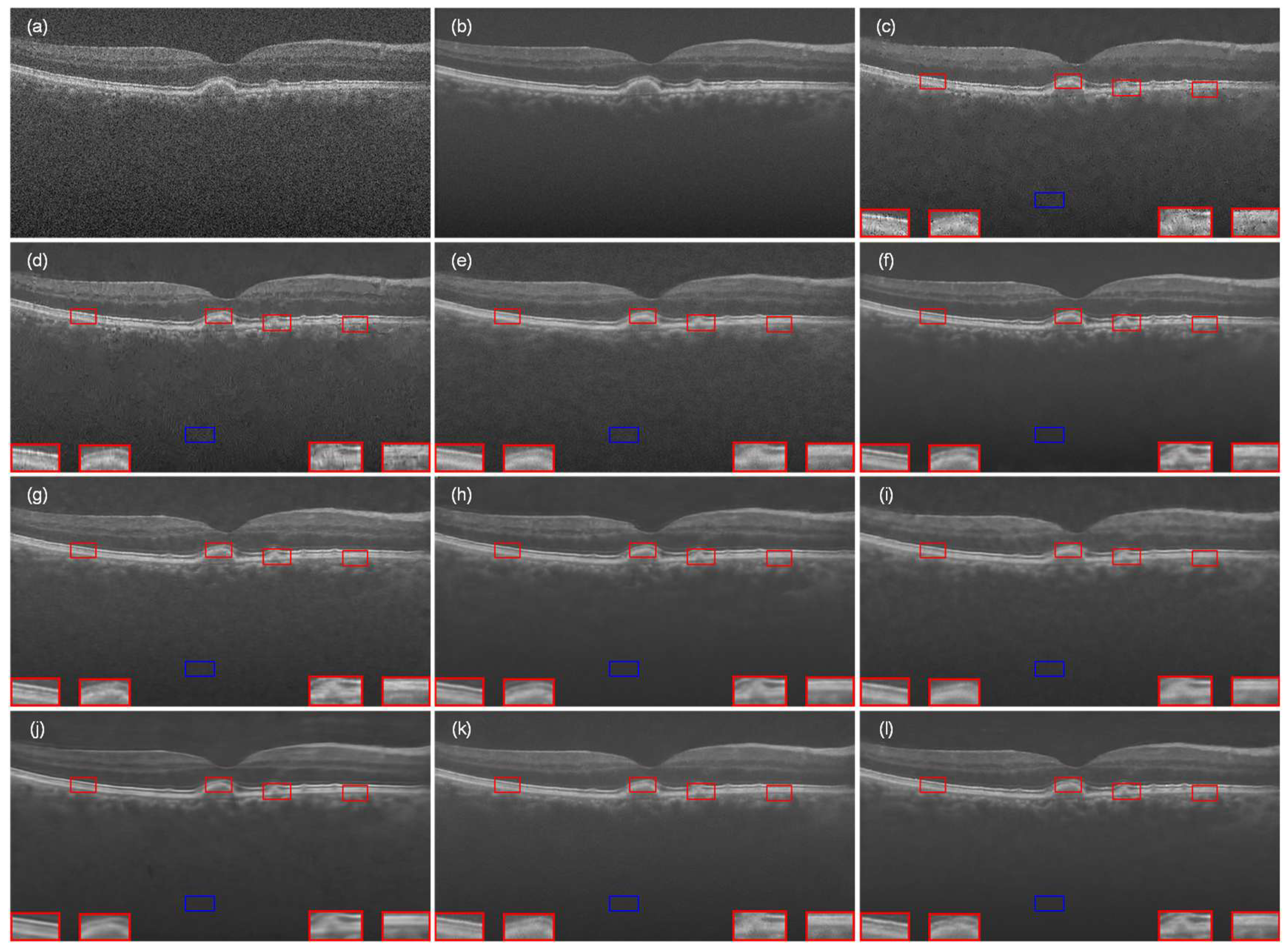
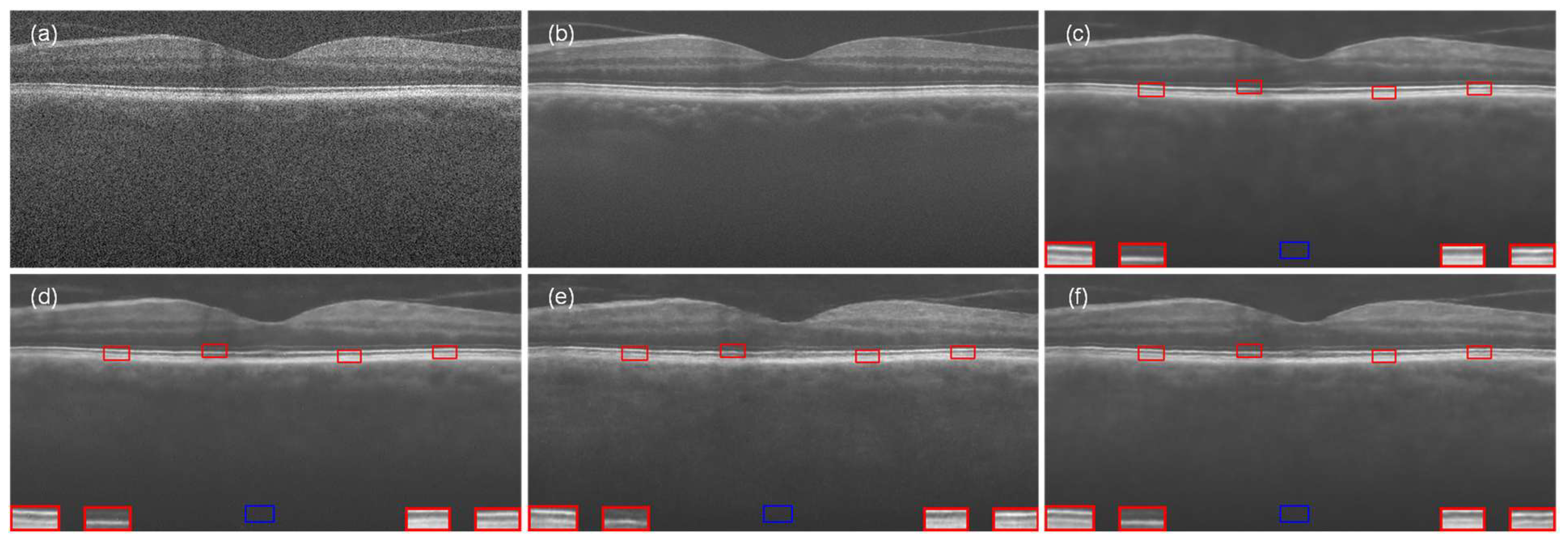
4.1. Experiment with Data-1
4.2. Experiment with Data-2
4.3. Experiment with the Data-3
4.4. Ablation Study
5. Discussion
5.1. Limitations
5.2. Ethical Considerations in Clinical Imaging
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, D.; Swanson, E.A.; Lin, C.P.; Schuman, J.S.; Stinson, W.G.; Chang, W.; Hee, M.R.; Flotte, T.; Gregory, K.; Puliafito, C.A.; et al. Optical coherence tomography. Science 1991, 254, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, L.M.; Sakata, V.; DeLeon-Ortega, J.; A Girkin, C. Optical coherence tomography of the retina and optic nerve—A review. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2009, 37, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hepburn, M.S.; Foo, K.Y.; Wijesinghe, P.; Munro, P.R.T.; Chin, L.; Kennedy, B.F. Speckle-dependent accuracy in phase-sensitive optical coherence tomography. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 16950–16968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Winetraub, Y.; Yuan, E.; Chan, W.H.; Aasi, S.Z.; Sarin, K.Y.; de la Zerda, A. Angular compounding for speckle reduction in optical coherence tomography using geometric image registration algorithm and digital focusing. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pircher, M.; Götzinger, E.; Leitgeb, R.A.; Fercher, A.F.; Hitzenberger, C.K. Speckle reduction in optical coherence tomography by frequency compounding. J. Biomed. Opt. 2003, 8, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Rollins, A.M. Speckle reduction in optical coherence tomography using angular compounding by B-scan Doppler-shift encoding. J. Biomed. Opt. 2009, 14, 030512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pircher, M.; Goetzinger, E.; Leitgeb, R.; Hitzenberger, C.K. Three dimensional polarization sensitive OCT of human skin in vivo. Opt. Express 2004, 12, 3236–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; Mishra, A.; Bizheva, K.; Clausi, D.A. General Bayesian estimation for speckle noise reduction in optical coherence tomography retinal imagery. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 8338–8352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aum, J.; Kim, J.-H.; Jeong, J. Effective speckle noise suppression in optical coherence tomography images using nonlocal means denoising filter with double Gaussian anisotropic kernels. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, D43–D50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, B.; Zhu, Y.-K. Speckle reduction in optical coherence tomography images of human finger skin by wavelet modified BM3D filter. Opt. Commun. 2013, 291, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, F.; Yang, W.; Peng, S.; Zhou, J. A survey of convolutional neural networks: Analysis, applications, and prospects. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 33, 6999–7019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Mancini, M.; Zhu, X.; Akata, Z. Semi-supervised and unsupervised deep visual learning: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 46, 1327–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisbert, G.; Dey, N.; Ishikawa, H.; Schuman, J.; Fishbaugh, J.; Gerig, G. Improved denoising of optical coherence tomography via repeated acquisitions and unsupervised deep learning. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, PB0035. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Hao, Q. Real-time noise reduction based on ground truth free deep learning for optical coherence tomography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 2027–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; He, W.; Eschweiler, D.; Dou, N.; Fan, Z.; Mi, S.; Walter, P.; Stegmaier, J. Retinal OCT Synthesis with Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models for Layer Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Athens, Greece, 27–30 May 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Azam, M.A.; Gunalan, A.; Mattos, L.S. One-Step Enhancer: Deblurring and Denoising of OCT Images. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Chen, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhang, L. Beyond a Gaussian Denoiser: Residual Learning of Deep CNN for Image Denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 3142–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Shao, Z.; Ran, M.; Zhou, J.; Fang, L.; Zhang, Y. Simultaneous denoising and super-resolution of optical coherence tomography images based on generative adversarial network. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 12289–12307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Xu, Y.; Zuo, W.; Du, B.; Lin, C.-W.; Zhang, D. Designing and training of a dual CNN for image denoising. Knowledge-Based Syst. 2021, 226, 106949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Ge, C.; Li, M.; Aziz, M.Z.; Mo, J.; Fan, Z. Multiscale denoising generative adversarial network for speckle reduction in optical coherence tomography images. J. Med. Imaging 2023, 10, 024006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, M.; Ge, C.; Shum, P.P.; Chen, J.; Liu, L. A generative adversarial network with multi-scale convolution and dilated convolution res-network for OCT retinal image despeckling. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 80, 104231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Liu, S.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, Y. Dual residual attention network for image denoising. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 149, 110291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Lv, G.; Duan, Y.; Liang, P.; Zhang, Y. Dual convolutional neural network with attention for image blind denoising. Multimedia Syst. 2024, 30, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintada, B.R.; Ruiz-Lopera, S.; Restrepo, R.; Bouma, B.E.; Villiger, M.; Uribe-Patarroyo, N. Probabilistic volumetric speckle suppression in OCT using deep learning. Biomed. Opt. Express 2024, 15, 4453–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wu, D.; Gao, W.; Xu, R.X.; Sun, M. Physics-Based Practical Speckle Noise Modeling for Optical Coherence Tomography Image Denoising. Photonics 2024, 11, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial networks. Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Chao, H.; Yang, M. Image Blind Denoising with Generative Adversarial Network Based Noise Modeling. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3155–3164. [Google Scholar]
- Xun, S.; Li, D.; Zhu, H.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; Wu, B.; Zhang, H.; Chai, X.; et al. Generative adversarial networks in medical image segmentation: A review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 140, 105063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Fang, L.; Rabbani, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z. Retinal optical coherence tomography image classification with label smoothing generative adversarial network. Neurocomputing 2020, 405, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszár, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.P.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Photo-Realistic Single Image Super-Resolution Using a Generative Adversarial Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1611.07004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Kong, Y.; Zhong, B.; Fu, Y. Residual dense network for image super-resolution. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.08797. [Google Scholar]
- Musunuri, Y.R.; Kwon, O.-S. Deep Residual Dense Network for Single Image Super-Resolution. Electronics 2021, 10, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbin, C.; Zhu, X.; Marques, O. Dropout vs. batch normalization: An empirical study of their impact to deep learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 12777–12815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubechies, I.; DeVore, R.; Foucart, S.; Hanin, B.; Petrova, G. Nonlinear approximation and (deep) ReLU networks. Constr. Approx. 2022, 55, 127–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yi, W. ELA: Efficient local attention for deep convolutional neural networks. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.01123. [Google Scholar]
- Shahdoosti, H.R.; Rahemi, Z. Edge-preserving image denoising using a deep convolutional neural network. Signal Process. 2019, 159, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, L.; Li, S.; Nie, Q.; Izatt, J.A.; Toth, C.A.; Farsiu, S. Sparsity based denoising of spectral domain optical coherence tomography images. Biomed. Opt. Express 2012, 3, 927–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Li, S.; McNabb, R.P.; Nie, Q.; Kuo, A.N.; Toth, C.A.; Izatt, J.A.; Farsiu, S. Fast Acquisition and Reconstruction of Optical Coherence Tomography Images via Sparse Representation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2013, 32, 2034–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, S.J.; Izatt, J.A.; O’Connell, R.V.; Winter, K.P.; Toth, C.A.; Farsiu, S. Validated Automatic Segmentation of AMD Pathology Including Drusen and Geographic Atrophy in SD-OCT Images. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| PSNR (↑) | SSIM (↑) | ENL (↑) | CNR (↑) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NLM | 25.452 | 0.428 | 27.300 | 1.929 |
| BM3D | 27.309 | 0.559 | 51.893 | 2.246 |
| DnCNN | 27.618 | 0.469 | 49.743 | 2.258 |
| SDSR-OCT | 29.859 | 0.642 | 137.385 | 2.638 |
| DudeNet | 29.647 | 0.706 | 285.529 | 2.885 |
| MDGAN | 28.912 | 0.713 | 594.706 | 3.286 |
| MDRGAN | 28.917 | 0.689 | 286.261 | 3.102 |
| DCANet | 29.208 | 0.726 | 907.062 | 3.375 |
| DRANet | 29.693 | 0.675 | 198.857 | 3.165 |
| MFFA-GAN | 30.107 | 0.727 | 529.161 | 3.927 |
| PSNR (↑) | SSIM (↑) | ENL (↑) | CNR (↑) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NLM | 25.151 | 0.422 | 25.689 | 2.413 |
| BM3D | 27.584 | 0.559 | 50.503 | 2.926 |
| DnCNN | 27.739 | 0.605 | 161.126 | 2.789 |
| SDSR-OCT | 28.310 | 0.608 | 152.350 | 3.619 |
| DudeNet | 28.612 | 0.658 | 535.944 | 3.625 |
| MDGAN | 28.697 | 0.676 | 489.783 | 3.651 |
| MDRGAN | 28.706 | 0.661 | 613.285 | 3.767 |
| DCANet | 28.434 | 0.688 | 379.336 | 3.761 |
| DRANet | 28.425 | 0.611 | 182.153 | 3.818 |
| MFFA-GAN | 29.117 | 0.679 | 629.303 | 4.137 |
| ENL (↑) | CNR (↑) | |
|---|---|---|
| NLM | 26.389 | 2.762 |
| BM3D | 54.281 | 3.401 |
| DnCNN | 378.078 | 4.799 |
| SDSR-OCT | 191.811 | 4.619 |
| DudeNet | 446.660 | 4.767 |
| MDGAN | 503.134 | 4.669 |
| MDRGAN | 343.154 | 4.623 |
| DCANet | 595.731 | 5.526 |
| DRANet | 222.046 | 5.141 |
| MFFA-GAN | 674.836 | 5.208 |
| PSNR (↑) | SSIM (↑) | ENL (↑) | CNR (↑) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without ELA + DRB | 28.741 | 0.669 | 751.870 | 4.112 |
| Without DRB | 28.508 | 0.628 | 223.460 | 3.923 |
| Without ELA | 28.752 | 0.654 | 763.653 | 4.269 |
| MFFA-GAN | 29.117 | 0.679 | 1234.055 | 4.425 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, Y.; Meng, Y. Multi-Level Feature Fusion Attention Generative Adversarial Network for Retinal Optical Coherence Tomography Image Denoising. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6697. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126697
Qian Y, Meng Y. Multi-Level Feature Fusion Attention Generative Adversarial Network for Retinal Optical Coherence Tomography Image Denoising. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(12):6697. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126697
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Yiming, and Yichao Meng. 2025. "Multi-Level Feature Fusion Attention Generative Adversarial Network for Retinal Optical Coherence Tomography Image Denoising" Applied Sciences 15, no. 12: 6697. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126697
APA StyleQian, Y., & Meng, Y. (2025). Multi-Level Feature Fusion Attention Generative Adversarial Network for Retinal Optical Coherence Tomography Image Denoising. Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6697. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126697





