Abstract
Obesity and low back pain (LBP) are major contributors to global disability and healthcare burden in both adults and children. Although a growing body of research supports a bidirectional relationship between these conditions, the underlying mechanisms remain poorly integrated in the current literature. While mechanical overload has traditionally been viewed as the principal link, emerging evidence points to additional roles for metabolic dysregulation, chronic low-grade inflammation, and adipokine activity in the development and persistence of LBP. This review addresses the need for a comprehensive synthesis of how obesity affects spinal structures, including the intervertebral discs, paraspinal muscles, facet joints, and epidural fat, through both biomechanical and systemic biological pathways. We specifically highlight key mechanisms such as oxidative stress, adipokine signalling, and neuroinflammation that may accelerate spinal degeneration and promote chronic pain. In doing so, we aim to bridge gaps between anatomical, biochemical, and clinical perspectives. Additionally, we assess current clinical evidence on weight loss as a potential strategy for alleviating LBP symptoms. By consolidating diverse lines of evidence, this review provides a clearer framework for understanding obesity-related spinal pathology and outlines priorities for future research and targeted interventions.
1. Introduction
Obesity and low back pain (LBP) are among the most prevalent global health issues, posing substantial socioeconomic challenges and significantly impacting quality of life [1,2,3]. While traditionally considered separate conditions, growing evidence suggests that obesity and LBP are closely interconnected, creating a vicious cycle of chronic pain, reduced mobility, and further weight gain (Figure 1) [4].
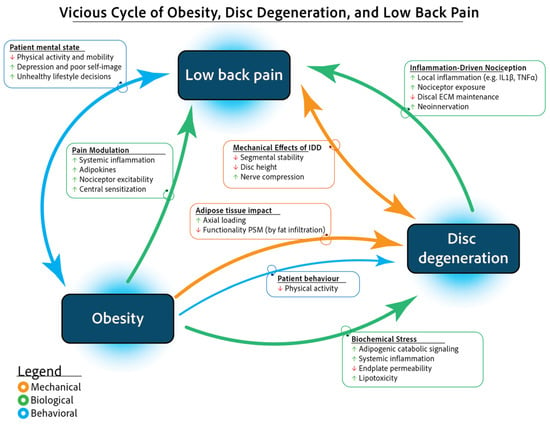
Figure 1.
Vicious cycle of obesity, IDD, and low back pain. Abbreviations: ECM (extracellular matrix); IDD (intervertebral disc degeneration); IL-1 (interleukin-1); PSM (paraspinal muscle); TNF- (tumour necrosis factor-).
Obesity, recognized as a chronic and systemic disorder, contributes to the progression of intervertebral disc (IVD) degeneration (IDD) and LBP [4,5,6]. Research indicates that individuals with obesity have a 1.4 to 1.7 times higher risk of developing chronic LBP [7,8]. Obesity contributes to LBP through both mechanical stress on the spine and biochemical effects, including systemic inflammation and adipokine-induced extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation by disc cells [4]. Additionally, LBP often leads to reduced physical activity, negatively affecting mental well-being, dietary habits, and social interactions, further perpetuating obesity and musculoskeletal decline.
This review aims to elucidate the mechanisms underlying the interplay between obesity and LBP by synthesizing anatomical, biochemical, and biomechanical evidence. Additionally, we highlight gaps in current knowledge and discuss potential strategies to disrupt the vicious obesity and LBP cycle.
2. Obesity
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), obesity is defined as a chronic and complex disorder characterized by excessive fat accumulation with multisystemic involvement. Recent estimates indicate that approximately 2.5 billion adults are overweight, with nearly 900 million living with obesity [9]. Although fat accumulation is often the result of an imbalance between calorie intake and energy expenditure, obesity is a multifactorial disease caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychosocial factors [10].
Being overweight or obese is associated with substantial health risks. In 2019, it was estimated that a higher-than-optimal body mass index (BMI), typically above 25 kg/m2, contributed to approximately 5 million deaths from noncommunicable diseases worldwide [11]. Obesity significantly increases the risk of developing a range of serious conditions, including type 2 diabetes, hypertension, chronic kidney disease, liver cirrhosis, cancer, chronic respiratory disorders, and retinopathy, posing a major socioeconomic burden on healthcare systems [12]. In fact, the global medical costs associated with obesity accounted for up to 2.5% of the global Gross Domestic Product in 2020, a figure projected to reach as high as 3% over the next decade [13]. It is important to note that although BMI is commonly used as a proxy for obesity, it fails to differentiate between fat and lean mass, or account for fat distribution, key factors that more accurately predict obesity-related health risks [14,15]. Obesity is not simply excess fat, but a complex pathological state marked by dysfunctional adipose tissue and systemic metabolic disruption. Nonetheless, this distinction is often overlooked in the literature due to practical limitations in clinical and epidemiological assessments. In order to comprehend obesity beyond BMI, it is essential to examine the underlying biological mechanisms that drive its pathophysiology.
The pathophysiology of obesity and associated comorbidities is complex and involves several genetic, epigenetic, environmental, hormonal, and immune mechanisms. Although rare forms of genetic obesity can be attributed to specific mutations [16], most cases are prompted by excessive food intake and unhealthy diet coupled with a sedentary lifestyle, ultimately leading to a caloric energy surplus and fat accumulation [17]. That said, new emerging evidence suggests that exposure to microplastics and their associated chemical burden may also contribute to obesity by inducing alterations in endocrine function and disrupting metabolic processes [18,19,20]. Increased and dysfunctional white adipose tissue deposits are metabolically active and secrete a wide array of adipokines and pro-inflammatory cytokines, which disrupt nutrient metabolism, alter hormone release (e.g., glucagon-like peptide [GLP]-1, oxyntomodulin, peptide tyrosine-tyrosine, cholecystokinin [CCK], etc.), and modulate food consumption behaviours, eventually establishing a chronic, systemic, low-grade inflammatory state [17]. In addition, disruptions in hormone regulation, including thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and cortisol, may predispose individuals to conditions such as hypothyroidism, Cushing’s syndrome, and polycystic ovary syndrome [21]. Nonetheless, systemic inflammation also leads to accelerated atherosclerosis and resulting macro- and microangiopathy, which may result in increased risks of ischemic heart disease, stroke, peripheral artery disease, etc. [17]. In short, obesity is a complex, multifactorial disorder that affects nearly all organs and physiological systems, significantly reducing both life expectancy and quality of life.
3. Low Back Pain
LBP is the most prevalent musculoskeletal condition worldwide, impacting nearly 570 million people and representing the leading cause of disability across all age groups [2]. Notably, symptoms can begin as early as childhood, with cases reported in children as young as 10 years old [22,23], and seemingly is on the rise in this young cohort [24]. LBP affects all populations, but certain risk factors are associated with a higher incidence and severity. These include age, genetic predisposition, obesity, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle [25,26]. Among workers, LBP is a leading cause of absenteeism and reduced productivity, imposing a significant economic burden on healthcare systems worldwide [2,27].
LBP can arise from various sources, including muscular strain, ligament injuries, facet joint degeneration, and IDD [28,29]. IDD is particularly common and often necessitates medical intervention or, in severe cases, surgical intervention. The IVDs, located between the vertebrae, are essential for spinal mobility, flexibility, and load distribution. Each IVD consists of a collagen-fibre-rich annulus fibrosus (AF) that surrounds the gel-like nucleus pulposus (NP) at its centre. These two tissues are separated from the vertebral bodies via interposition of two cartilaginous layers, namely the cartilaginous endplates (CEPs), which are essential for IVD integrity and IVD nourishment. Over time, age-related factors, mechanical stress, and metabolic changes can compromise IVD integrity, leading to IDD [28,30]. This process is characterized by a loss of NP hydration, reduced proteoglycan and collagen content, and the formation of fissures within the AF. IDD impairs the shock absorption and force distribution capacities of the IVD, stressing NP and AF cells. This promotes IVD cells to release a plethora of enzymes, such as matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), that facilitate ECM breakdown, leading to acceleration of disc dehydration, disc height loss, and mechanical instability [31]. Additionally, structural degeneration of the AF diminishes its ability to contain the swelling of the NP, potentially resulting in disc bulging, AF rupture, or disc herniation [30,32]. Furthermore, pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., interleukin [IL]-1β, tumour necrosis factor [TNF]-α) released by disc cells may exacerbate this cycle, by causing increased catabolic enzyme activity, oxidative stress, and cellular apoptosis [28,33,34,35]. These cytokines may also sensitize nerve endings [36,37,38] and promote the influx of immunogenic cells into the otherwise largely immune-compromised IVD [39,40,41], further contributing to LBP.
The treatment for LBP, especially discogenic LBP related to IDD, generally encompasses conservative intervention, and for most cases the condition will only present temporarily [42]. Here, conservative management typically includes physical therapy, pharmacological interventions (e.g., nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [NSAIDs], corticosteroids, etc.), and lifestyle modifications [43]. For patients with persistent pain who do not respond to conservative measures, surgical interventions, such as discectomy or spinal fusion, may be considered [44]. However, these surgical procedures often fail to restore full disc function and may lead to long-term complications, including reduced range of motion (ROM) and adjacent segment degeneration [45]. Moreover, long-term pain and disability benefits remain disputed [46,47]. While current therapies aim to relieve symptoms and stabilize the spine, they do not reverse or repair the degenerative changes within the disc [48]. This lack of restoration has driven interest in regenerative medicine as a promising approach to treat IDD and LBP [49]. Regenerative strategies, including cell-based therapies [50,51,52], biomaterial scaffolds [53,54,55], and extracellular vesicle injections [56,57,58] are designed to regenerate the IVD tissue, restore disc hydration, and bring back its mechanical function, thereby potentially delaying, halting, or even reversing IDD. However, these strategies remain in their initial stages of clinical development and encounter substantial translational hurdles [59,60,61,62].
4. Spinal Changes Related to Obesity
Epidemiological studies have consistently shown a strong correlation between elevated BMI and the prevalence of LBP (Figure 2). Sheng et al. found higher LBP and IDD risk in overweight and obese individuals, but no significant link with spondylosis or cervical disorders [63]. Additional factors, such as waist circumference, body fat percentage, and fat-free mass (i.e., all non-fat components of the body), were causally linked to increased risks of IDD and sciatica. Adjusting for BMI, whole-body fat-free mass maintained a significant association with the risk of IDD [64].
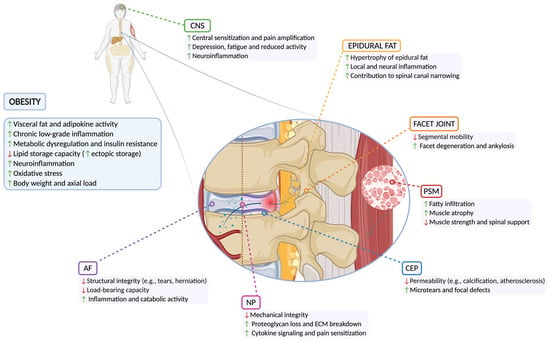
Figure 2.
Detrimental effects of obesity on spine structures. Abbreviations: AF (annulus fibrosus); CEP (cartilaginous endplate); CNS (central nervous system); ECM (extracellular matrix); NP (nucleus pulposus); PSM (paraspinal muscle).
A systematic review of twin studies by Dario et al. [65] examined the relationship between obesity, LBP, and lumbar IDD, highlighting that while obesity correlates with these conditions, genetic and early environmental factors also play a significant role. Similarly, a prospective study by Segar et al. [66] assessed the relationship between BMI and spinal pathologies, including IDD, disc herniation, and spinal stenosis. Their findings showed BMI modestly predicted IDD but was more strongly linked to disc herniation and spinal stenosis, especially in the upper lumbar spine. Obesity-related LBP involves mechanical stress, systemic inflammation, and metabolic disturbances, contributing to degeneration of the IVD, facet joints, paraspinal muscles (PSMs), and epidural fat, which are further discussed below (Table 1).

Table 1.
Overview of obesity-related changes associated with IDD and LBP.
4.1. Intervertebral Disc
Within the IVD, the NP and AF are particularly vulnerable to the metabolic stress associated with obesity. Obesity triggers chronic low-grade inflammation marked by elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines, which promote ECM degradation through increased matrix-degrading enzymes and cellular stress, while apoptosis and senescence reduce ECM-producing cells [33]. Here, the primary endocrine and paracrine mediators of this obesity-induced metabolic dysfunction are likely adipokines [91], whose role is described in detail below.
The connection between obesity and IDD has been well documented in preclinical animal models. Experimental mouse models subjected to high-fat diets (HFD), which result in elevated systemic lipid levels, exhibit altered IVD metabolism characterized by increased apoptosis and ECM degradation [67,68,92]. Similar degenerative changes are observed in other cartilage tissues, such as knee joints [67]. These ECM changes are accompanied by a loss of disc height, reduced hydration, and a significant increase in inflammatory factors such as TNF-α, Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein (MCP)-1, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and IL-1β [67,68]. Since obesity is often accompanied by diabetes, it is noteworthy that hyperglycemia can directly impair IVD integrity in murine models. While hyperglycemia can increase the glycosaminoglycan and collagen content of the disc, it also promotes the accumulation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs), leading to disorganized AF lamellae and reduced mechanical strength and elasticity [70]. In a mouse model, excessive dietary AGE intake resulted in increased collagen cross-linking and AF damage, ultimately leading to higher IVD compressive stiffness, torque range, and failure torque, particularly in female animals [71]. Additionally, glucose may dose-dependently upregulate a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs (ADAMTS)-4 and -5 through activation of the CREB-binding protein (CBP)-PPARγ coactivator 1α (PGC1α)-Runx2 complex, further contributing to IVD ECM breakdown [69].
Like the NP and AF, the CEP is also vulnerable to obesity-induced mechanical, metabolic, and inflammatory stressors, which heighten the risk of microfractures and structural damage. Additionally, elevated lipid levels and associated atherosclerosis in endplate vasculature are exhibited [4,93], while metabolic and inflammatory changes promote CEP thinning and calcification [72,73], thereby reducing CEP permeability and hindering essential nutrient and waste transport required for IVD homeostasis [94]. Specifically, Apolipoprotein E (ApoE), a crucial lipid metabolism regulator, has been shown to worsen CEP degeneration when deficient, largely via adipokine-mediated signalling pathways [95]. Elevated adipokine levels, such as leptin and resistin, accelerate CEP thinning and calcification while promoting chondrocyte and osteocyte senescence and apoptosis [74]. However, the clinical relevance of these findings remains uncertain. While some studies suggest that high BMI predisposes individuals to CEP defects, others have reported conflicting evidence [64,75,76]. Retrospective studies have found a higher prevalence of CEP alterations, including Schmorl’s nodes and Modic changes, in both obese children [77] and adults [78,79]. Collectively, these findings indicate that obesity-induced metabolic and inflammatory stressors compromise all IVD components (including the NP, AF, and CEP), consequently impacting homeostasis of other disc tissues, and thereby driving a multifaceted degenerative cascade (Figure 2). Critically, however, further clinical studies are needed to better clarify these associations in the human spinal tissues.
4.2. Facet Joints
Obesity exacerbates facet joint osteoarthritis primarily through mechanical overload and systemic inflammation, accelerating cartilage degradation, subchondral bone remodelling, and osteophyte formation, which collectively may contribute to pain and restricted mobility [80]. Inflammatory pathways also play a critical role, as elevated cytokine levels in obesity amplify catabolic activity within joint tissues, promoting ECM degradation and impairing cartilage repair. This imbalance weakens the subchondral bone supporting the facet joints, making it more prone to degeneration and microfractures (Figure 2). Additionally, lipid abnormalities further contribute by enhancing osteoclast activity and inhibiting osteoblast differentiation, resulting in a compromised bone microenvironment [96]. Interestingly, despite similar prevalence rates of facet joint-related LBP in obese and non-obese individuals based on BMI [81], obese patients have been reported to experience less pain relief following radiofrequency ablation treatments [82]. Moreover, another study found an association between increased outer abdominal fat thickness and higher rates of facet joint osteoarthritis, suggesting that fat distribution, rather than BMI alone, may influence facet joint degeneration [80].
4.3. Paraspinal Muscles
Excessive body weight significantly impacts PSMs, leading to fatigue, reduced strength, and an increased risk of strain injuries. Obesity is strongly associated with greater fatty infiltration in these muscles, particularly in women, compromising muscle quality and spinal stability [83]. As muscle fibres are replaced by adipose tissue, functional muscle mass and strength decline, resulting in a condition known as sarcopenic obesity [97]. Fatty degeneration of the PSMs is often classified using Kalichman’s scoring system (in short defined as the following: grade 1, indicating normal muscle with fatty infiltration up to 10% of the muscle’s cross-sectional area; grade 2, moderate degeneration with 10–50% fatty infiltration; and grade 3, severe degeneration with over 50% fatty infiltration) [98]. These changes reduce the functional capacity of PSMs, increase mechanical stress on the spine, and accelerate spinal degeneration, contributing to the chronicity of LBP in individuals with obesity [85]. Fat infiltration increases with both BMI and age, as demonstrated by Peng et al. [99], who reported that the combined fat infiltration ratio of the multifidus and erector spinae muscles rises from 9.7% ± 5.0% in individuals aged 40–49 years to 25.8% ± 7.6% in those aged 70–79 years. Concurrently, multifidus and external oblique muscle thickness decreases with increasing BMI, particularly in LBP patients [84]. Notably, reduced muscle quality at the upper lumbar levels increases mechanical stress on the lower lumbar segments, accelerating spinal degeneration and exacerbating chronic pain [85]. This redistribution of load and reduced stability further perpetuate the cycle of obesity, inactivity, and spinal dysfunction, emphasizing the critical role of maintaining muscle integrity to mitigate LBP in obese individuals (Figure 2). Here, strengthening the PSM through targeted exercise may enhance spinal stability, reduce mechanical strain, and serve as a protective factor against the development and progression of LBP [100].
4.4. Epidural Fat
Epidural fat is adipose tissue within the spinal canal that surrounds the dura mater, cushioning the spinal cord and nerve roots. In certain cases, excessive epidural fat accumulation (particularly in obesity) can lead to spinal stenosis by compressing neural structures, resulting in pain, numbness, and weakness in the lower extremities, a condition known as epidural lipomatosis [86]. A recent longitudinal study demonstrated a linear relationship between BMI and epidural fat volume, with each 1 kg/m2 increase in BMI corresponding to an additional 45 mm3 of epidural fat [87]. Similarly, Cushnie et al. reported greater epidural fat volume in obese patients undergoing urgent decompression for cauda equina syndrome, suggesting that epidural lipomatosis may increase the risk of this condition in obese individuals [88]. This association was further supported by a recent meta-analysis, which identified increased BMI as the primary risk factor for epidural lipomatosis and suggested that weight loss could mitigate symptom severity and surgical complications [89]. Beyond its mechanical effects, epidural fat accumulation has been recognized as a marker of metabolic syndrome (Figure 2). Studies have shown that its volume correlates not only with BMI but also with abdominal circumference, visceral fat area, and hypertension. From this perspective, epidural lipomatosis may represent a form of ectopic fat deposition, similar to that seen in the pancreas, heart, and liver in patients with metabolic syndrome [90]. Adipocytes from overweight patients undergoing decompression surgery for epidural lipomatosis were found to be hypertrophic and exhibited increased expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-1β [101]. However, further mechanistic studies are needed to validate these findings.
4.5. Nervous System
Interestingly, the promotion of degenerative and catabolic changes consequential to obesity not only changes the ECM and biochemistry of the affected tissues but also seems able to directly impact pain and behavioural changes. For example, in the work of Kerr et al. [67], the authors highlighted that both their HFD and “western diet” fed mice showed significant enhancements in the mechanical sensitivity and lower rates of mobility that preceded structural joint deterioration. More directly, HFDs have been shown to alter nerve and brain activity in rats by inducing neuroinflammation and disrupting metabolic signalling, which may sensitize pain pathways and exacerbate nociceptive responses [102]. This could partially explain the heightened perception of pain and increased susceptibility to IDD and LBP observed in obese patients, however this direct link requires more extensive investigation, especially in humans (Figure 2).
In a similar vein, the enhanced circulation of adipokines such as leptin and lipocalin-2 (LCN2) may further modulate neuroinflammatory processes involved in pain and mood regulation [103,104]. They are able to amplify the neuroinflammatory triad and contribute to central sensitization, a key feature of chronic pain states. Leptin, in particular, has been shown to enhance nociceptive signalling within the spinal cord and brain, while also influencing mood-related circuits [105,106]. These observations suggest that obesity-associated alterations in adipokine profiles not only drive inflammation and degeneration but also play a direct role in amplifying pain perception and emotional dysregulation stemming from both metabolic disorders and spinal degenerative changes.
5. The Biomechanical Impact of Obesity on the Spine
Overweight and obesity have long been recognized as major contributors to IDD and discogenic LBP, primarily due to the biomechanical overloading they place on the IVDs and spinal structures, particularly in the lumbar spine [3,6]. Studies indicate that individuals with excess weight have a significantly higher risk of developing chronic LBP, surpassing the influence of age and sex [107]. Furthermore, obesity increases the likelihood of developing IDD by up to 1.8 times [108], and raises the risk of lumbar disc herniations that may require surgical intervention [30]. Notably, weight loss after bariatric surgery has been suggested to improve LBP intensity and related disability [109], as well as L4-L5 disc height [110].
The biomechanical factors associated with increased IDD in overweight and obese individuals are related to a combination of the following factors: (1) overloading that exceeds the strength threshold of IVD tissues, (2) spinal joint instability caused by hypermobility under increased loads, and (3) cyclic loading under repetitive conditions exceeding the inherent tissue healing capacity [111]. Importantly, not only BMI, but also body shape and fat distribution may differentially affect spinal loading. Central obesity, characterized by accumulation of abdominal fat and a higher waist-to-hip ratio, is particularly associated with greater spinal forces, possibly causing damage to the IVDs and vertebrae [111]. These observations were confirmed by a recent meta-analysis, which showed that waist circumference and waist-to-hip ratio were associated with an increased risk of chronic LBP [112].
Obesity-related postural changes also affect spinal biomechanics. A recent study by Bayartai et al. [113] demonstrated that adults with obesity are characterized by increased thoracic kyphosis and decreased thoracic and lumbar flexion-extension ROM, a pattern previously noted in obese children and adolescents with and without idiopathic scoliosis [114]. On the other hand, reduced spine mobility in obese individuals may be attributed to several factors, including the increased soft tissue mass and more severe osteoarthritic changes. In a cadaveric study, Rodriguez-Martinez and coauthors [115] found that L4-L5 specimens from obese subjects exhibited greater facet joint degeneration and a higher prevalence of disc herniations. Additionally, a negative correlation between BMI and both flexion–extension ROM and axial compressive stiffness was noted, although significant only in female specimens [115]. Apart from postural features, overweight status has been shown to also impact dynamic activities. A finite-element study demonstrated that obese individuals experience around 40% higher compression and shear stress at the L5-S1 level during lifting activities, independent of hand position [116]. This finding implies that even postural adjustments (e.g., use of braces) may not effectively counterbalance the increased spinal loads in obese individuals [116]. Increased segmental overloading in distal lumbar segments has also been confirmed in vivo. In a recent study, Coppock et al. [117] compared lumbar IVD deformation before and after treadmill walking. Intriguingly, the authors demonstrated that post-exercise magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed that increasing BMI was associated with significantly higher strain in the L5-S1 disc.
Increased IDD in overweight and obese individuals may also be partly attributed to poor PSM quality due to fatty infiltration, as mentioned above. In physiological conditions, PSMs are essential for a balanced load distribution across the spine and proper postural control. Therefore, muscle imbalances and/or a reduction in functional muscle mass (e.g., loss of fibres due to atrophy or fatty substitution) diminish the net capacity of the muscle tissues to stabilize the spine and resist displacement forces [118]. It has been previously shown that patients with LBP have thinner core muscles and fewer type 1 fibres in the multifidus muscles, which are crucial for maintaining muscle tone and endurance [119]. In line with these findings, Ozcan-Eksi and colleagues [85] recently found that obese patients exhibit more severe IDD, a higher prevalence of Modic changes at lower lumbar levels, and increased fatty infiltration in the upper lumbar spine. Similarly, Ucar et al. [84] demonstrated that individuals with nonspecific LBP and high BMI had reduced thickness and increased fatty infiltration of abdominal and PSMs, which were linked to higher disability scores according to the Oswestry Disability Index (ODI). Collectively, these findings highlight how excess body weight compromises spinal biomechanics, amplifies mechanical stress, alters muscle adaptability, and ultimately accelerates degenerative changes across all spinal tissues (Figure 2).
6. The Biochemical Impact of Obesity on the Spine
Obesity-related biochemical disruptions—including systemic inflammation, lipid dysregulation, and metabolic imbalances—create a catabolic, pro-inflammatory microenvironment enriched with cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6 [120,121]. Oxidative stress further aggravates this state by inducing apoptosis, senescence, and mitochondrial dysfunction, further weakening disc biology [122]. Impaired nutrient diffusion to the avascular IVD compounds these effects, accelerating degeneration and linking obesity to IDD and LBP [74,123]. The following sections examine key biochemical drivers of obesity-related IDD and their roles in spinal degeneration.
6.1. Lipid Dysregulation
Lipid dysregulation refers to imbalances in lipid metabolism and transport, often marked by elevated levels of circulating fatty acids that disrupt cellular homeostasis and promote inflammation [124]. Obesity is associated with profound alterations in lipid metabolism [92], including dysregulated lipid profiles, characterized by elevated free fatty acids, triglycerides, and cholesterol, thus contributing to both systemic and local inflammation [125]. For the spine, excessive lipid deposition in vertebral marrow adipose tissue (MAT) correlates with impaired disc hydration, reduced cell viability, and increased production of MMP and ADAMTS enzymes [83]. Lipotoxicity from excess saturated fatty acids, such as palmitic acid, impairs mitochondrial function, triggering lipid accumulation, oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, and intrinsic apoptosis [126]. This promotes a senescent phenotype in disc cells, worsening spinal degeneration and underscoring the importance of lipid regulation in obesity-related IDD [127]. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein (LDL) increases mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and triggers apoptosis [128], while oxidative stress-induced ferroptosis in AF and NP cells further aggravates degeneration [129]. Inflammatory and metabolic disturbances also induce ER stress, which disrupts ECM protein regulation and lipid metabolism, impacting adipocyte differentiation, which consequentially alters fatty acid synthesis and triglyceride secretion [130]. These changes collectively accelerate ECM degradation, thereby driving IDD progression [131]. Altogether, these lipid-driven disturbances in obesity contribute significantly to spinal tissue degeneration, emphasizing the need to further elucidate the underlying mechanisms of lipid homeostasis in IVD health.
6.2. Metabolic Alterations
A range of metabolic disturbances are commonly observed in obesity, including insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, and impaired cellular energy regulation [68]. Due to the avascular nature of the IVD [72], disc cells reside in a hypoxic, low-glucose environment and have adapted to survive under limited nutrient conditions [94,95,132,133]. However, systemic metabolic dysfunctions can overwhelm these adaptations and adversely affect disc cell viability and function. For instance, hyperglycemia has been shown to promote the accumulation of AGEs, which stiffen ECM components, within the IVD [134]. AGEs also activate the receptor for AGEs (RAGE), triggering inflammatory pathways that upregulate matrix-degrading enzymes such as MMPs and ADAMTS, while also inducing apoptosis [135]. This cascade reduces proteoglycan content and undermines ECM integrity, contributing to IDD, pain, and dysfunction. Additionally, insulin resistance and mitochondrial impairments in obesity disrupt disc cell energy homeostasis, leading to reduced adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production and increased apoptosis [136]. Together, these metabolic alterations impair disc homeostasis, accelerating IDD and reinforcing the link between obesity and LBP.
6.3. The Adipokine Cascade
Adipokines are bioactive signalling molecules secreted by adipose tissue that regulate immune responses, inflammation, and tissue remodelling. In obesity, adipose tissue enters a chronic low-grade inflammatory state, characterized by elevated levels of pro-inflammatory adipokines, such as leptin, resistin, and LCN2, and decreased levels of anti-inflammatory molecules like adiponectin [137] (Table 2). This imbalance perpetuates systemic inflammation and metabolic dysfunction, contributing to the pathogenesis of IDD. Dysregulated adipokine signalling promotes ECM degradation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in IVD cells, primarily via Toll-like receptor (TLR)-mediated pathways [138,139]. In particular, pro-inflammatory adipokines like leptin as well as immune mediators secreted by vertebral MAT have been shown to exacerbate IDD [140]. Leptin and resistin, both elevated in obesity, enhance ECM breakdown, upregulate inflammatory cytokines, and induce IVD cell apoptosis [136,141]. Conversely, adiponectin, typically anti-inflammatory, is reduced in obesity. However, its role in IDD appears to be context-dependent, with evidence suggesting it may still activate inflammatory signalling under certain conditions [142]. Additional adipokines, such as LCN2 and visfatin, further drive degeneration, i.e., LCN2 activates NF-κB and increases MMP9 activity, while visfatin promotes IL-6 production and mediates IL-1β-induced apoptosis in NP cells [138,143,144]. Together, these alterations in adipokine secretion (Table 2) foster a pro-inflammatory, catabolic microenvironment within the disc (as well as other spinal tissues), accelerating degeneration and reinforcing the mechanistic link between obesity and IDD.

Table 2.
Overview of obesity-related dysregulated adipokines and their association with IDD.
Adipokines also influence pain pathways, potentially amplifying pain perception in obesity-related LBP. Leptin and resistin, for instance, can promote IL-1 synthesis, sensitizing nociceptors and enhancing central pain processing [183,184]. Leptin, along with its receptor (LepR), is expressed in dorsal root ganglion neurons and contributes to neuropathic pain by upregulating N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) subunits, increasing neuronal nitric oxide synthase, and intensifying pain signalling. These effects link systemic inflammation to heightened pain severity [185]. Neuromodulation therapies, such as spinal cord stimulation, have demonstrated the potential to modulate adipokine levels, suggesting a link between metabolic regulation and pain management [111]. Similarly, LCN2 exacerbates neuroinflammation by promoting microglial activation [186], increasing pro-inflammatory cytokine release, and enhancing neuronal sensitivity, all of which contribute to pain hypersensitivity in obesity-related LBP [186,187]. Despite growing insights into the biochemical interplay between obesity, IDD, and pain, key knowledge gaps remain. Future studies should investigate how adipokines interact, their regulatory networks in disc cells, and their roles in IDD progression and pain severity. Longitudinal and mechanistic research could support the development of adipokine-targeting therapies to modulate inflammation, disc metabolism, and nociception. Additionally, stratifying patients by adipokine profiles may help enable personalized treatment approaches [188,189].
6.4. Gut Microbiome and Metabolic Inflammation
The gut microbiome, a complex community of microorganisms residing in the gastrointestinal tract, plays a crucial role in maintaining metabolic homeostasis, immune regulation, and inflammation control. Dysbiosis [190], an imbalance in microbial composition, can disrupt these processes, leading to increased intestinal permeability, systemic inflammation, and metabolic dysfunction. Emerging evidence suggests that obesity is associated with gut microbiome alterations, characterized by reduced microbial diversity, an increased Firmicutes-to-Bacteroidetes ratio, and an enrichment of pro-inflammatory species [191,192,193]. This dysbiotic state contributes to systemic inflammation and metabolic dysfunction, ultimately promoting IDD [194]. Specifically, the altered gut microbiota composition promotes intestinal permeability, facilitating endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide; LPS) translocation into circulation, which generally triggers chronic low-grade inflammation via TLR-4 signalling, systematically affecting local tissues [195]. Furthermore, the microbiome-driven inflammation exacerbates insulin resistance, oxidative stress, and cytokine production, all of which have shown to be linked to ECM degradation and cell apoptosis within the disc [196]. Although the gut–spine axis offers a promising target for therapeutic intervention in obesity-related IDD, inconsistencies across studies currently limit its clinical application [191,197]. Methodological consistency and continued research are crucial to clarify the underlying mechanisms and confirm the therapeutic potential of the gut–spine axis.
6.5. Hypoxia and Angiogenesis
Due to its avascularity, the IVD relies on CEP-mediated diffusion for oxygen and nutrients. In obesity, metabolic stress and inflammation raise oxygen demand while hindering diffusion, causing systemic and local hypoxia [198]. Adipose tissue hypoxia, driven by obesity-related adenine nucleotide translocase 2 (ANT2)-mediated mitochondrial uncoupling, increases oxygen use, activates hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α, and promotes chronic inflammation [199]. These pathophysiological changes parallel those in the IVD, where obesity-induced CEP sclerosis restricts oxygen diffusion, and adipokine-mediated endothelial dysfunction impairs vascular homeostasis [200]. In response to hypoxia, HIF signalling is activated to promote cellular adaptation; however, prolonged HIF-1α activation also upregulates VEGF, contributing to pathological angiogenesis [201,202]. This hypoxia-driven neovascularization is a recognized feature of IDD and may reflect similar mechanisms observed in other degenerative tissues [38,72]. Obesity contributes to IDD and LBP through a dual mechanism: aggravating hypoxia and promoting pathological vascularization. Elevated systemic and local hypoxia intensifies catabolic activity in the NP, accelerating degeneration [203,204,205]. Simultaneously, obesity-driven neovascularization may compromise the IVD’s immune-privileged status [40], facilitating nociceptor sensitization, inflammatory cell infiltration into the IVD, and a spread of systemic obesity-related inflammation into the IVD-environment (Figure 1) [28,36]. This interplay between hypoxia, angiogenesis, and chronic inflammation reinforces a cycle of progressive IDD and pain and warrants more careful study.
In short, obesity profoundly impacts spinal health by inducing systemic and local inflammation, oxidative stress, lipid dysregulation, and metabolic disturbances, all of which accelerate IDD and LBP. Dysregulated adipokines, gut microbiome alterations, and hypoxia-driven angiogenesis create a pro-inflammatory, catabolic microenvironment that disrupts disc homeostasis. Future research should prioritize mechanistic studies and clinical investigations to harness these insights for the development of targeted, personalized interventions of LBP in obese and overweight individuals.
7. Therapeutic Strategies Targeting the Obesity–LBP Connection
7.1. Addressing Obesity as a Pathway to Alleviate LBP
Weight loss, improved dietary habits, and increased physical activity are associated with numerous health benefits [206,207]. Given the established connections between obesity, back pain, and IDD, these interventions hold promise as strategies for prevention and relief. Moreover, for LBP specifically, exercise has been shown to be therapeutic and preventative [208,209,210,211], and direct links have been made with enhanced muscle strength and reduced LBP risk [212]. The high prevalence of physical inactivity among individuals with obesity (often influenced by both physical limitations and motivational challenges) may thus further compound their risk of developing LBP [213,214]. Moreover, although speculative, by reducing mechanical stress on the spine and enhancing spinal stability, weight loss may alleviate pressure and strain on IVDs and vertebral structures [5], while also mitigating systemic and local inflammation—factors implicated in both obesity and IDD [4]. Moreover, the psychological benefits, such as improved mental well-being and self-esteem [215,216], can foster a more active lifestyle conducive to spinal health. Moreover, a poor mental state, such a depression, has been associated with the worsening of pain symptoms [217,218]. Thus, this multifaceted condition underscores a likely beneficial role of lifestyle modifications in managing back pain and promoting spinal health.
Given the established link between high BMI and increased risk of LBP, it seems logical to consider body weight control as a strategy for managing or alleviating LBP. However, despite this connection, research on weight control strategies for LBP relief is limited and often lacks quality. The overall evidence supporting weight loss as a method to alleviate chronic LBP remains inconclusive. For example, the 2023 WHO guideline for non-surgical management of chronic primary LBP [43] does not specifically recommend weight loss as a therapy for LBP and even advises against pharmacological weight management, both due to very low certainty of evidence. This recommendation reflects the very weak evidence base linking weight loss to improved pain or function, despite obesity’s well-established association with LBP severity. Similarly, a recent systematic review by Chen et al. [219] on weight loss programmes and interventions to alleviate LBP was only able to include 11 trials spanning 689 participants. They similarly concluded “there is only very low-quality evidence that some weight loss interventions lead to improvements in LBP and disability” [219]. If we consider the literature, three specific methods to promote weight or fat loss can be distinguished: (1) lifestyle, i.e., changes to calorie and macro-nutrient intake as well as promoting exercise, (2) surgical, e.g., gastric bypass operations, and (3) pharmacological, e.g., Ozempic. (Table 3).
Our literature review focusing on human trials that assess the alleviation of back pain or reduction in the proportion of LBP patients through weight loss primarily identified studies involving surgical interventions. (Table 3) These trials typically involved either bariatric surgery, leading to fat loss through reduced food intake, or abdominoplasty, resulting in an immediate reduction in body weight and fat proportion. Both types of surgical interventions generally showed significant BMI changes in their follow-ups. These BMI changes were often associated with a reduced proportion of LBP patients or clinically significant improvements in LBP scores. Notably, the participants often involved severely obese individuals.
Contrarily, trials that promote lifestyle changes, as in requesting participants to adhere to diets, exercise regimes, and/or counselling studies, were often unable to engender significant desirable changes in patients’ weight, making assessment of back pain less valuable. Nevertheless, it is interesting to see that the lack of BMI changes did correspond with the general maintenance of pain scores and the proportion of LBP patients. There was only one study by Silişteanu et al. [220] that was able to directly report a significant correlation between the rate of BMI loss and the alleviation of pain. The direct results are not presented in Table 3, as their findings were reported separately for males and females, and rural- and urban-habituated individuals. The overall lack of BMI changes can likely be explained by two critical features: (i) the general shorter follow-up and intervention duration and (ii) the difficulty of participants to adhere and their compliance to their allocated regimes [219]. As highlighted in the interesting work of Robson et al. [221], adherence to dietary restrictions and other regimes is challenging, in particular through tele-com counselling. Given that obesity often involves complex psychological factors, including an unhealthy relationship with food and self-image, the challenges in adherence are understandable and underscore the need for compassionate and tailored interventions.
Additionally, we sought to identify clinical trials investigating the use of pharmacological interventions for managing discogenic LBP in the context of obesity; however, no studies were found testing such approaches directly. There is a rising popularity of agents like Ozempic® (i.e., semaglutide), which have shown robust efficacy in promoting weight loss [222]. Semaglutide is a GLP-1 receptor agonist that stimulates insulin secretion, suppresses appetite, and slows gastric emptying. In a randomized controlled trial involving patients with knee osteoarthritis and obesity, once-weekly semaglutide significantly promoted weight loss and led to marked reductions in pain severity [223]. In addition to its metabolic effects, GLP-1 receptor activation has been shown to modulate inflammation and pain pathways by reducing pro-inflammatory cytokine expression, enhancing β-endorphin release, and inhibiting nociceptive signalling within the central nervous system [223,224]. However, in this trial [223], as with the relationship between obesity and LBP, the interplay between obesity and knee osteoarthritis [225] makes it difficult to fully disentangle weight-dependent effects from direct anti-inflammatory or mental-sate effects. These findings nonetheless suggest that GLP-1 receptor agonists may represent a promising dual-action therapy for obesity-related musculoskeletal pain. In conclusion, it is important to note that the current trials and studies identified are highly heterogeneous and do not uniformly investigate their impact on LBP. Furthermore, the specific sources of back pain were not consistently identified. Only one study, by Lidar et al. [110], examined spinal imaging features and reported a significant improvement in disc height with a decrease in overall BMI, suggesting that weight loss can reduce strain on the lumbar region. Additionally, most studies focused solely on recording BMI or weight changes, which can include loss of tissues other than fat. For instance, muscle loss should be avoided, as muscle strength is crucial for maintaining spinal health through supporting the spine and overall posture. We hope that more clinicians and researchers will explore this promising area further, as targeting fat loss represents potentially low-hanging fruit for developing cost-effective methods to alleviate LBP in a significant portion of the LBP patient population. Whether to recommend weight loss for LBP patients remains controversial [43,219]. While weight loss is generally safe and beneficial for overall health, though its effectiveness in treating LBP remains uncertain.

Table 3.
General literature review on the effectiveness of low back pain treatment by targeting weight or fat loss.
Table 3.
General literature review on the effectiveness of low back pain treatment by targeting weight or fat loss.
| Type | Author (Year) | Design | Intervention | N | Age (Years) Mean (±SD) | BMI (Baseline) Mean (±SD) | T2DM n (%) | LBP Rate (Baseline) n/N (%) | LBP Score (Baseline) Mean (±SD) | FU (Months) | BMI (Final FU) Mean (±SD) | LBP Rate (Final FU) n/N (%) | LBP Score (Final FU) Mean (±SD) | Imaging Findings | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical | McGoey (1990) [226] | Prospective single-arm | Banding | 104 | 33.4 | unspecified | unspecified | 65/104 (62.5%) | - | 22 (average) | unspecified | 11/104 (10.6%) | - | NA | Two patients that lost weight and then regained it, had matching LBP relief and reoccurrence. |
| Melissas (2003) [227] | Prospective two-arm | Banding | 50 | 37.5 (±10.2) | 46.7 (±7.7) | unspecified | 29/50 (58.0%) | - | 24 | 33.6 (±5.6) | 10/50 (20.0%) | - | NA | - | |
| Melissas (2005) [228] | unspecified | Banding | 29 | 37.5 (±11.2) | 47.2 (±8.8) | unspecified | NA | 5.5 (±2.0) * | 24 | 32.9 (±6.3) | NA | 2.1 (±1.9) * | NA | - | |
| Khoueir (2009) [229] | Prospective single-arm | Bypass or sleeve | 38 | 48.4 (±10.1) | 52.3 (±12.6) | unspecified | NA | 5.2 (±3.4) | 12 | 38.3 (±9.7) | NA | 2.9 (±3.1) | NA | - | |
| Vincent (2012) [230] | Prospective two arm | Bypass or banding | 25 | 41 (±11) | 47 (±7) | unspecified | 6/25 (25.0%) | 5.2 | 3 | 39.1 | 15/25 (61.1%) | 2.4 | NA | Follow-up too short and lack of BMI change. | |
| Lidar (2012) [110] | Prospective single arm | Bypass, sleeve, or banding | 30 | 49 (±10.4) | 42.8 (±4.8) | unspecified | 26/30 (86.7%) | 5.7 (±3.1) | 12 | 29.7 (±3.4) | unspecified | 1.3 (±2.1) | Sign. increase L4/5-disc height (from 6.8 (±1) to 8.8 (±1) mm) | - | |
| Çakır (2015) [231] | Prospective single arm | Sleeve | 39 | 37.7 (±11.3) | 46.5 | unspecified | unspecified | 6.7 (±2.7) | 6 | 32.3 | unspecified | 1.97 (±2.2) | NA | Work does not focus specifically on back pain patients | |
| Taylor (2018) [232] | Prospective single arm | Abdominoplasty | 214 | 42.1 (±8.7) | 26.3 (±4.3) | unspecified | 195/214 (91.2%) | unspecified | 6 | unspecified | unspecified | unspecified | NA | Significant improvement in ODI disability scores related to LBP. | |
| Bhandari (2019) [233] | Prospective single arm | Bypass or Sleeve | 45 | 54.7 (±8.5) | 54.2 (±8.6) | 23 (51.1%) | 34/45 (75.5%) | 7.3 (±1.4) | 12 | unspecified | 25/45 (55.6%) | 2.3 (±1.4) | NA | - | |
| Soteropulos (2020) [234] | Retrospective | Abdominoplasty | 143 | 48 | unspecified | unspecified | 51/143 (35.7%) | NA | 120 | unspecified | unspecified | NA | NA | Improvement in ODI and SF36 scores for patients with LBP pre-operation. | |
| Patel (2023) [235] | Prospective single arm | Abdominoplasty | 30 | 48.4 (±14.3) | 27.8 (±4.2) | 3 (10%) | 21/30 (70%) | 3.95 | 6 | unspecified | unspecified | 0.53 | NA | - | |
| Lifestyle/programme | Roffey (2011) [236] | Prospective single arm | Diet, exercise, and counselling | 46 | 50.1 (±12.9) | 44.7 (±7.6) | unspecified | NA | 3.3 (±2.2) | 12 | 39.6 (±8.2) | NA | 2.6 (±2.5) | NA | - |
| Silişteanu (2015) [220] | Prospective two arm | Diet (+physio, NSAID, analgesics, etc.) | 90 | unclear | unclear | unspecified | unclear | unclear | unclear | unclear | unclear | unclear | NA | Significant correlation BMI loss and VAS improvement. | |
| Williams (2018) [237] | RCT | Diet and exercise | 79 | 56.0 (±13.3) | 32.4 (±3.5) | unspecified | NA | 6.7 (±1.8) | 6 | 32.7 (±4.3) | NA | 5.8 (±2.7) | NA | Diet was not effective in reducing BMI. | |
| Dunlevy (2018) [238] | Retrospective | Diet, exercise, and counselling | 476 | 45.1 (±12.0) | 50.8 (±8.1) | 66 (29.3%) | 281/476 (59.0%) | 5.9 (±3.8) | 6 | 47.6 (±8.0) | 236/476 (49.6%) | 4.5 (±3.7) | NA | - | |
| Safari (2020) [239] | RCT | Diet (+NSAIDs) | 48 | 39.7 (±10.7) | 28.4 (±3.5) | unspecified | NA | 2.2 (±0.5) | 2 | unspecified | NA | 1.0 (±1.0) | NA | Follow-up too short. Diet unable to result in relevant BMI loss. | |
| Ward (2024) [240] | Prospective single arm | Diet | 136 | 47.7 (±10.7) | 30.7 (±2.3) | Excluded | 43/136 (31.8%) | unclear | 3 | unclear | 18/136 (13.6%) | unclear | NA | - | |
| Pharmaco- logical | None identified | ||||||||||||||
* Worst pain score. Abbreviations: BMI (body mass index); LBP (low back pain); NA (not assessed/applicable); ODI ((Oswestry disability index)—a patient-reported outcome measuring the impact of disability); RCT (randomized clinical trial); sd (standard deviation); SF36 ((short form 36)—a quality-of-life patient-reported outcome survey), Sign. (significant).
However, being too stringent about weight loss may discourage patients and set unrealistic expectations, particularly for those already struggling with their weight [241,242]. More research is needed to find the appropriate balance in this area.
7.2. Modulating Adipokine Signalling to Alleviate Obesity-Linked Discogenic Pain
As previously discussed, adipokines exert both systemic and local effects on spinal tissues, contributing to IDD potentially facilitating the onset or exacerbation of LBP. While targeting adipokine signalling is unlikely to resolve obesity or fully interrupt the pathological cycle described in this review, such interventions may offer benefit by dampening pain perception or reducing the catabolic effects of these factors on spinal tissues. Therapeutic strategies may include antagonizing pro-inflammatory and degradative adipokines, enhancing anti-inflammatory or protective adipokines, or modulating downstream pathways through neuro-immune or endocrine mechanisms [169]. However, given the widespread physiological roles of adipokines, such interventions require careful evaluation to avoid unintended systemic effects. Importantly, while numerous adipokine-targeting drugs are currently under investigation, a comprehensive review is beyond the scope of this review, we refer interested readers to the excellent review by Würfel et al. [243] on this specific topic.
7.3. Limitations and Considerations
This review provides a broad overview of the mechanistic connections between obesity and LBP; however, several limitations should be noted. As a scoping review, it does not aim to be exhaustive, and some relevant studies or mechanistic pathways may have been omitted. The topics and mechanisms discussed were selected based on the authors’ expertise in the field. In Section 7.1, Table 3 was reviewed as a semi-systematic search performed to identify relevant studies, involving search terms including “weight loss” and “low back pain”. Nonetheless, this should not be considered a full systematic review. Additionally, although age and sex are known to influence both obesity-related physiology and pain presentation [244,245,246,247,248,249], stratification by these factors was not feasible here due to inconsistent reporting across studies. Their role should be more carefully considered in future investigations, and we implore more work, including meta-analyses, on this topic. Finally, a common limitation in the literature is the lack of clear identification of the pain source in studies of LBP. In many cases, it remains uncertain whether the pain originates from disc, joint, musculature, or other structures, which complicates mechanistic interpretation [250]. In a similar vein, obesity severity was typically assessed using BMI alone; however, as previously mentioned, other metrics (though less practical) may offer more accurate insights. These limitations should be taken into account when interpreting the findings of this review.
8. Conclusions
Obesity significantly contributes to IDD and LBP through systemic inflammation, oxidative stress, lipid dysregulation, and metabolic disturbances, creating a catabolic environment that accelerates ECM degradation and tissue dysfunction. While the link between obesity and IDD is increasingly recognized, significant gaps in the literature persist. Most studies fail to isolate discogenic LBP, lack imaging evidence to connect fat loss with structural improvements, and overly focus on weight loss rather than fat loss. Emerging factors such as the role of plastic chemical exposure in hormone dysregulation and the influence of mental health on outcomes remain underexplored. A unified model integrating all impacted tissues, IVDs, CEPs, vertebral MAT, facet joints, and PSMs [203] is essential to fully understand this relationship. Moreover, the association between obesity, IDD, and mental health requires further study, as such psychological factors significantly influence pain perception and may impact spinal health. Strikingly, few studies have explored fat or weight loss as strategies to alleviate LBP. Future research must focus on targeted interventions, imaging-based evaluations, and the long-term effects of fat loss on IDD and LBP to guide effective, individualized treatments. Addressing these gaps is critical to mitigating the burden of obesity-related spinal disorders.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.A., J.S. and C.R.-F.; data curation, L.A., J.S. and C.R.-F.; writing—original draft preparation, L.A., J.S. and C.R.-F.; writing—review and editing, L.A., J.S., C.R.-F. and D.S.; visualization, L.A., J.S. and C.R.-F.; supervision, D.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
ADAMTS (A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase with Thrombospondin Motifs); AGE (Advanced Glycation End-Products); CBP (CREB-Binding Protein); CCK (Cholecystokinin); ECM (Extracellular Matrix); ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum); HFD (High-Fat Diet); HIF (Hypoxia-Inducible Factor); IDD (Intervertebral Disc Degeneration); IL (Interleukin); IVD (Intervertebral Disc); LBP (Low Back Pain); LCN2 (Lipocalin-2); LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein); MAT (Marrow Adipose Tissue); MMP (Matrix Metalloproteinase); MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging); NSAID (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug); ODI (Oswestry Disability Index); PGC1α (CBP-PPARγ Co-activator 1α); PSM (Paraspinal Muscle); RAGE (Receptor for Advanced Glycation End-Products); ROM (Range of Motion); ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species); TLR (Toll-Like Receptor); TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone); TNF (Tumour Necrosis Factor); VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor); WHO (World Health Organization).
References
- GBD 2021 Other Musculoskeletal Disorders Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of other musculoskeletal disorders, 1990–2020, and projections to 2050: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023, 5, e670–e682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2021 Low Back Pain Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of low back pain, 1990–2020, its attributable risk factors, and projections to 2050: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023, 5, e316–e329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosio, L.; Mazzuca, G.; Maguolo, A.; Russo, F.; Cannata, F.; Vadala, G.; Maffeis, C.; Papalia, R.; Denaro, V. The burden of low back pain in children and adolescents with overweight and obesity: From pathophysiology to prevention and treatment strategies. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2023, 15, 1759720X231188831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Fernandez, C.; Francisco, V.; Pino, J.; Mera, A.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Gomez, R.; Lago, F.; Gualillo, O. Molecular Relationships among Obesity, Inflammation and Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Are Adipokines the Common Link? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.K.; Singh, N.K.; Verma, R.; Diwan, A.D. Validation and Estimation of Obesity-Induced Intervertebral Disc Degeneration through Subject-Specific Finite Element Modelling of Functional Spinal Units. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannata, F.; Vadala, G.; Ambrosio, L.; Fallucca, S.; Napoli, N.; Papalia, R.; Pozzilli, P.; Denaro, V. Intervertebral disc degeneration: A focus on obesity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2019, 10, e3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiri, R.; Karppinen, J.; Leino-Arjas, P.; Solovieva, S.; Viikari-Juntura, E. The association between obesity and low back pain: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 171, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucha-Lopez, M.O.; Hidalgo-Garcia, C.; Monti-Ballano, S.; Marquez-Gonzalvo, S.; Ferrandez-Laliena, L.; Muller-Thyssen-Uriarte, J.; Lucha-Lopez, A.C. Body Mass Index and Its Influence on Chronic Low Back Pain in the Spanish Population: A Secondary Analysis from the European Health Survey (2020). Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Freisling, H.; Viallon, V.; Lennon, H.; Bagnardi, V.; Ricci, C.; Butterworth, A.S.; Sweeting, M.; Muller, D.; Romieu, I.; Bazelle, P.; et al. Lifestyle factors and risk of multimorbidity of cancer and cardiometabolic diseases: A multinational cohort study. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborators, G.B.D.R.F. Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1223–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh-Manoux, A.; Fayosse, A.; Sabia, S.; Tabak, A.; Shipley, M.; Dugravot, A.; Kivimaki, M. Clinical, socioeconomic, and behavioural factors at age 50 years and risk of cardiometabolic multimorbidity and mortality: A cohort study. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahase, E. Global cost of overweight and obesity will hit $4.32tn a year by 2035, report warns. BMJ 2023, 380, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Corral, A.; Somers, V.K.; Sierra-Johnson, J.; Thomas, R.J.; Collazo-Clavell, M.L.; Korinek, J.; Allison, T.G.; Batsis, J.A.; Sert-Kuniyoshi, F.H.; Lopez-Jimenez, F. Accuracy of body mass index in diagnosing obesity in the adult general population. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweatt, K.; Garvey, W.T.; Martins, C. Strengths and Limitations of BMI in the Diagnosis of Obesity: What is the Path Forward? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2024, 13, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaker, V.V. Genetic and Epigenetic Causes of Obesity. Adolesc. Med. State Art. Rev. 2017, 28, 379–405. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Li, H. Obesity: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Therapeutics. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 706978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heindel, J.J.; Howard, S.; Agay-Shay, K.; Arrebola, J.P.; Audouze, K.; Babin, P.J.; Barouki, R.; Bansal, A.; Blanc, E.; Cave, M.C.; et al. Obesity II: Establishing causal links between chemical exposures and obesity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 199, 115015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimentidis, Y.C.; Beasley, T.M.; Lin, H.Y.; Murati, G.; Glass, G.E.; Guyton, M.; Newton, W.; Jorgensen, M.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Kemnitz, J.; et al. Canaries in the coal mine: A cross-species analysis of the plurality of obesity epidemics. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2011, 278, 1626–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, C.M.; Beserra, B.T.S.; Silva, N.G.; Lima, C.L.; Rocha, P.R.S.; Coelho, M.S.; Neves, F.A.R.; Amato, A.A. Exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals and anthropometric measures of obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e033509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apovian, C.M. Obesity: Definition, comorbidities, causes, and burden. Am. J. Manag. Care 2016, 22, s176–s185. [Google Scholar]
- Minana-Signes, V.; Monfort-Panego, M.; Bosh-Bivia, A.H.; Noll, M. Prevalence of Low Back Pain among Primary School Students from the City of Valencia (Spain). Healthcare 2021, 9, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunzburg, R.; Balague, F.; Nordin, M.; Szpalski, M.; Duyck, D.; Bull, D.; Melot, C. Low back pain in a population of school children. Eur. Spine J. 1999, 8, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.; Louie, P.K.; Phillips, F.M.; An, H.S.; Samartzis, D. Low back pain in children: A rising concern. Eur. Spine J. 2019, 28, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parreira, P.; Maher, C.G.; Steffens, D.; Hancock, M.J.; Ferreira, M.L. Risk factors for low back pain and sciatica: An umbrella review. Spine J. Off. J. North Am. Spine Soc. 2018, 18, 1715–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Matsudaira, K. Prevalence of low back pain and factors associated with chronic disabling back pain in Japan. Eur. Spine J. 2013, 22, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevan, S.; Quadrello, T.; McGee, R.; Mahdon, M.; Vavrovsky, A.; Barham, L. Fit for Work? Musculoskeletal Disorders in the European Workforce; The Work Foundation: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Diwan, A.D.; Melrose, J. Intervertebral disc degeneration and how it leads to low back pain. JOR Spine 2023, 6, e1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, V.; Verdaguer, C.; Daste, C.; Bisseriex, H.; Lapeyre, E.; Lefevre-Colau, M.M.; Rannou, F.; Roren, A.; Facione, J.; Nguyen, C. Chronic Low Back Pain: A Narrative Review of Recent International Guidelines for Diagnosis and Conservative Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Theologis, A.A.; O’Connell, G.D. Understanding the etiopathogenesis of lumbar intervertebral disc herniation: From clinical evidence to basic scientific research. JOR Spine 2023, 7, e1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustenburg, C.M.E.; Emanuel, K.S.; Peeters, M.; Lems, W.F.; Vergroesen, P.A.; Smit, T.H. Osteoarthritis and intervertebral disc degeneration: Quite different, quite similar. JOR Spine 2018, 1, e1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schol, J.; Ambrosio, L.; Tamagawa, S.; Joyce, K.; Ruiz-Fernandez, C.; Nomura, A.; Sakai, D. Enzymatic chemonucleolysis for lumbar disc herniation-an assessment of historical and contemporary efficacy and safety: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamagawa, S.; Sakai, D.; Nojiri, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Warita, T.; Matsushita, E.; Schol, J.; Soma, H.; Ogasawara, S.; Munesada, D.; et al. SOD2 orchestrates redox homeostasis in intervertebral discs: A novel insight into oxidative stress-mediated degeneration and therapeutic potential. Redox Biology 2024, 71, 103091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stover, J.D.; Trone, M.A.R.; Weston, J.; Lewis, C.; Levis, H.; Philippi, M.; Zeidan, M.; Lawrence, B.; Bowles, R.D. Therapeutic TNF-alpha Delivery After CRISPR Receptor Modulation in the Intervertebral Disc. Biorxiv 2023, 32, 3955–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, G.; Fan, P.; Huang, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, C. Distinctive roles of tumor necrosis factor receptor type 1 and type 2 in a mouse disc degeneration model. J. Orthop. Transl. 2021, 31, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, B.; Liu, W.; Wang, P.; Lv, X.; Chen, S.; Shao, Z. The role of structure and function changes of sensory nervous system in intervertebral disc-related low back pain. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2021, 29, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Stefanoska, D.; Stone, L.S.; Hildebrand, M.; van Donkelaar, C.C.; Zou, X.; Basoli, V.; Grad, S.; Alini, M.; Peroglio, M. Hypoxic stress enhances extension and branching of dorsal root ganglion neuronal outgrowth. JOR Spine 2020, 3, e1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lama, P.; Le Maitre, C.L.; Harding, I.J.; Dolan, P.; Adams, M.A. Nerves and blood vessels in degenerated intervertebral discs are confined to physically disrupted tissue. J. Anat. 2018, 233, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Cai, W.; Liu, F.; Cheng, K.; Guo, D.; Liu, Z. An in-depth analysis of the immunomodulatory mechanisms of intervertebral disc degeneration. JOR Spine 2022, 5, e1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Lyu, F.J.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Z. The involvement of immune system in intervertebral disc herniation and degeneration. JOR Spine 2022, 5, e1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimann, M.K.; Thompson, K.; Gunsch, G.; Tang, S.N.; Klamer, B.; Corps, K.; Walter, B.A.; Moore, S.A.; Purmessur, D. Characterization and modulation of the pro-inflammatory effects of immune cells in the canine intervertebral disk. JOR Spine 2024, 7, e1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, D.; Schol, J.; Watanabe, M. Clinical Development of Regenerative Medicine Targeted for Intervertebral Disc Disease. Medicina 2022, 58, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Guidelines Approved by the Guidelines Review Committee. In WHO Guideline for Non-Surgical Management of Chronic Primary Low Back Pain in Adults in Primary and Community Care Settings; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- Haro, H.; Ebata, S.; Inoue, G.; Kaito, T.; Komori, H.; Ohba, T.; Sakai, D.; Sakai, T.; Seki, S.; Shiga, Y.; et al. Japanese Orthopaedic Association (JOA) clinical practice guidelines on the management of lumbar disc herniation, third edition–secondary publication. J. Orthop. Sci. Off. J. Jpn. Orthop. Assoc. 2022, 27, 31–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannion, A.F.; Leivseth, G.; Brox, J.I.; Fritzell, P.; Hagg, O.; Fairbank, J.C. ISSLS Prize winner: Long-term follow-up suggests spinal fusion is associated with increased adjacent segment disc degeneration but without influence on clinical outcome: Results of a combined follow-up from 4 randomized controlled trials. Spine 2014, 39, 1373–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannion, A.F.; Brox, J.I.; Fairbank, J.C. Consensus at last! Long-term results of all randomized controlled trials show that fusion is no better than non-operative care in improving pain and disability in chronic low back pain. Spine J. Off. J. North Am. Spine Soc. 2016, 16, 588–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannion, A.F.; Brox, J.I.; Fairbank, J.C. Comparison of spinal fusion and nonoperative treatment in patients with chronic low back pain: Long-term follow-up of three randomized controlled trials. Spine J. Off. J. North Am. Spine Soc. 2013, 13, 1438–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härtl, R.; Bonassar, L.; Bonassar, L.J. Biological Approaches to Spinal Disc Repair and Regeneration for Clinicians; Thieme Medical Publishers, Incorporated: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rudnik-Jansen, I.; van Kruining Kodele, S.; Creemers, L.; Joosten, B. Biomolecular therapies for chronic discogenic low back pain: A narrative review. JOR Spine 2024, 7, e1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schol, J.; Tamagawa, S.; Volleman, T.N.E.; Ishijima, M.; Sakai, D. A comprehensive review of cell transplantation and platelet-rich plasma therapy for the treatment of disc degeneration-related back and neck pain: A systematic evidence-based analysis. JOR Spine 2024, 7, e1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schol, J.; Sakai, D.; Warita, T.; Nukaga, T.; Sako, K.; Wangler, S.; Tamagawa, S.; Zeiter, S.; Alini, M.; Grad, S. Homing of vertebral-delivered mesenchymal stromal cells for degenerative intervertebral discs repair–an in vivo proof-of-concept study. JOR Spine 2023, 6, e1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schol, J.; Sakai, D. Comprehensive narrative review on the analysis of outcomes from cell transplantation clinical trials for discogenic low back pain. North Am. Spine Soc. J. 2023, 13, 100195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, M.D.; Ramos, D.M.; Nithyadevi, D.; Bordett, R.; Rudraiah, S.; Nukavarapu, S.P.; Moss, I.L.; Kumbar, S.G. Growing a backbone–functional biomaterials and structures for intervertebral disc (IVD) repair and regeneration: Challenges, innovations, and future directions. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 1216–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Iwasaki, N.; Sudo, H. Biomaterials and Cell-Based Regenerative Therapies for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration with a Focus on Biological and Biomechanical Functional Repair: Targeting Treatments for Disc Herniation. Cells 2022, 11, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogasawara, S.; Schol, J.; Sakai, D.; Warita, T.; Susumu, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Sako, K.; Tamagawa, S.; Matsushita, E.; Soma, H.; et al. Alginate vs. Hyaluronic Acid as Carriers for Nucleus Pulposus Cells: A Study on Regenerative Outcomes in Disc Degeneration. Cells 2024, 13, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosio, L.; Schol, J.; Ruiz-Fernandez, C.; Tamagawa, S.; Soma, H.; Tilotta, V.; Di Giacomo, G.; Cicione, C.; Nakayama, S.; Kamiya, K.; et al. ISSLS PRIZE in Basic Science 2024: Superiority of nucleus pulposus cell- versus mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles in attenuating disc degeneration and alleviating pain. Eur. Spine J. 2024, 33, 1713–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiStefano, T.J.; Vaso, K.; Danias, G.; Chionuma, H.N.; Weiser, J.R.; Iatridis, J.C. Extracellular Vesicles as an Emerging Treatment Option for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Therapeutic Potential, Translational Pathways, and Regulatory Considerations. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, e2100596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosio, L.; Schol, J.; Tilotta, V.; Di Giacomo, G.; Cicione, C.; Russo, F.; Sakai, D.; Vadalà, G.; Denaro, V. Extracellular vesicles for intervertebral disc regeneration. In Extracellular Vesicles for Therapeutic and Diagnostic Applications; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2025; pp. 347–395. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrosio, L.; Petrucci, G.; Russo, F.; Cicione, C.; Papalia, R.; Vadala, G.; Denaro, V. Why clinical trials in disc regeneration strive to achieve completion: Insights from publication status and funding sources. JOR Spine 2024, 7, e1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Donahue, R.P.; Nordberg, R.C.; Hu, J.C.; Currall, S.C.; Athanasiou, K.A. Commercialization of regenerative-medicine therapies. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2023, 1, 906–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, D.; Schol, J.; Foldager, C.B.; Sato, M.; Watanabe, M. Regenerative technologies to bed side: Evolving the regulatory framework. J. Orthop. Transl. 2017, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binch, A.L.A.; Fitzgerald, J.C.; Growney, E.A.; Barry, F. Cell-based strategies for IVD repair: Clinical progress and translational obstacles. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, B.; Feng, C.; Zhang, D.; Spitler, H.; Shi, L. Associations between Obesity and Spinal Diseases: A Medical Expenditure Panel Study Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2017, 14, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Mi, J.; Peng, Y.; Han, H.; Liu, Z. Causal Associations of Obesity with the Intervertebral Degeneration, Low Back Pain, and Sciatica: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 740200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dario, A.B.; Ferreira, M.L.; Refshauge, K.M.; Lima, T.S.; Ordonana, J.R.; Ferreira, P.H. The relationship between obesity, low back pain, and lumbar disc degeneration when genetics and the environment are considered: A systematic review of twin studies. Spine J. Off. J. North Am. Spine Soc. 2015, 15, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segar, A.H.; Baroncini, A.; Urban, J.P.G.; Fairbank, J.; Judge, A.; McCall, I. Obesity increases the odds of intervertebral disc herniation and spinal stenosis; an MRI study of 1634 low back pain patients. Eur. Spine J. 2024, 33, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, G.J.; To, B.; White, I.; Millecamps, M.; Beier, F.; Grol, M.W.; Stone, L.S.; Seguin, C.A. Diet-induced obesity leads to behavioral indicators of pain preceding structural joint damage in wild-type mice. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Huang, B.; Wang, J.; Shan, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Fan, S.; Zhao, F. Obesity Mediates Apoptosis and Extracellular Matrix Metabolic Imbalances via MAPK Pathway Activation in Intervertebral Disk Degeneration. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.; Han, Y.; Lv, Z.; Song, Q.; Wang, K.; Shen, H.; Chen, Z. Glucose-stimulated PGC-1α couples with CBP and Runx2 to mediate intervertebral disc degeneration through transactivation of ADAMTS4/5 in diet-induced obesity mice. Bone 2023, 167, 116617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lintz, M.; Walk, R.E.; Tang, S.Y.; Bonassar, L.J. The degenerative impact of hyperglycemia on the structure and mechanics of developing murine intervertebral discs. JOR Spine 2022, 5, e1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, D.; Hoy, R.C.; Natelson, D.M.; Torre, O.M.; Laudier, D.M.; Iatridis, J.C.; Illien-Jünger, S. Dietary advanced glycation end-product consumption leads to mechanical stiffening of murine intervertebral discs. Dis. Models Mech. 2018, 11, dmm036012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, D.E.; Kiser, P.K.; Shoemaker, J.K.; Battie, M.C.; Seguin, C.A. Vascularization of the human intervertebral disc: A scoping review. JOR Spine 2020, 3, e1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, K.B.; Alminnawi, A.; Bermudez-Lekerika, P.; Compte, R.; Gualdi, F.; McSweeney, T.; Munoz-Moya, E.; Nuesch, A.; Geris, L.; Dudli, S.; et al. Cartilaginous endplates: A comprehensive review on a neglected structure in intervertebral disc research. JOR Spine 2023, 6, e1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.C.; Ma, B.; Guo, S.; Yang, M.; Li, L.J.; Wang, S.J.; Tan, J. Leptin regulates disc cartilage endplate degeneration and ossification through activation of the MAPK-ERK signalling pathway in vivo and in vitro. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 2098–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videman, T.; Gibbons, L.E.; Kaprio, J.; Battie, M.C. Challenging the cumulative injury model: Positive effects of greater body mass on disc degeneration. Spine J. Off. J. North Am. Spine Soc. 2010, 10, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rade, M.; Maatta, J.H.; Freidin, M.B.; Airaksinen, O.; Karppinen, J.; Williams, F.M.K. Vertebral Endplate Defect as Initiating Factor in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Strong Association Between Endplate Defect and Disc Degeneration in the General Population. Spine 2018, 43, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudisill, S.S.; Hornung, A.L.; Kia, C.; Mallow, G.M.; Aboushaala, K.; Lim, P.; Martin, J.; Wong, A.Y.L.; Toro, S.; Kozaki, T.; et al. Obesity in children with low back pain: Implications with imaging phenotypes and opioid use. Spine J. 2023, 23, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, T.S.; Kjaer, P.; Korsholm, L.; Bendix, T.; Sorensen, J.S.; Manniche, C.; Leboeuf-Yde, C. Predictors of new vertebral endplate signal (Modic) changes in the general population. Eur. Spine J. 2009, 19, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Kuang, M.-J.; Ma, J.-X.; Ma, X.-L. Prevalence of Modic changes in the lumbar vertebrae and their associations with workload, smoking and weight in northern China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jentzsch, T.; Geiger, J.; Slankamenac, K.; Werner, C.M. Obesity measured by outer abdominal fat may cause facet joint arthritis at the lumbar spine. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2015, 28, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchikanti, L.; Pampati, V.; Singh, V.; Beyer, C.; Damron, K.; Fellows, B. Evaluation of the role of facet joints in persistent low back pain in obesity: A controlled, prospective, comparative evaluation. Pain Physician 2001, 4, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searcy, S.; Mora, J.; Meroney, M.; Jafari, A.; Henson, C.; Jenkins, K.; Mallett, B.; Shibu, V.; Ogbemudia, B.; Vasilopoulos, T.; et al. Retrospective Review of the Efficacy of Lumbar Radiofrequency Ablation for Lumbar Facet Arthropathy: The Influence of Gender and Obesity. Pain Physician 2023, 26, E695–E701. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Han, S.; Hu, X.; Ye, L.; Li, Y.; Gao, J. Advances in research on fat infiltration and lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1067373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uçar, İ.; Karartı, C.; Cüce, İ.; Veziroğlu, E.; Özüdoğru, A.; Koçak, F.A.; Dadalı, Y. The relationship between muscle size, obesity, body fat ratio, pain and disability in individuals with and without nonspecific low back pain. Clin. Anat. 2021, 34, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan-Ekşi, E.E.; Turgut, V.U.; Küçüksüleymanoğlu, D.; Ekşi, M.Ş. Obesity could be associated with poor paraspinal muscle quality at upper lumbar levels and degenerated spine at lower lumbar levels: Is this a domino effect? J. Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 94, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.B.; Sark, C.; Brennan, G.; Smith, T.; Sherman, W.F.; Kaye, A.D. Spinal Epidural Lipomatosis: A Comprehensive Review. Orthop. Rev. 2021, 13, 25571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigsby, R.K.; Barnes, S.; Sabaté, J.; Oyoyo, U.; Chowdhury, S.; Peters, E.M. Correlation of spinal epidural fat volume with body mass index: A longitudinal study. Clin. Imaging 2023, 98, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushnie, D.; Urquhart, J.C.; Gurr, K.R.; Siddiqi, F.; Bailey, C.S. Obesity and spinal epidural lipomatosis in cauda equina syndrome. Spine J. 2018, 18, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Yuan, H.; Hu, L.; Saad, M. Obesity is a risk factor for epidural lipomatosis: A meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. 2021, 29, 23094990211027391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, S.; Fujita, N.; Azuma, K.; Michikawa, T.; Yagi, M.; Tsuji, T.; Takayama, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Nakamura, M.; Matsumoto, M.; et al. Spinal epidural lipomatosis is a previously unrecognized manifestation of metabolic syndrome. Spine J. 2019, 19, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannata, F.; Vadala, G.; Ambrosio, L.; Napoli, N.; Papalia, R.; Denaro, V.; Pozzilli, P. Osteoarthritis and type 2 diabetes: From pathogenetic factors to therapeutic intervention. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2020, 36, e3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, J.; Niu, S.; Ji, G.; Zheng, T. Lipid metabolism disorder promotes the development of intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 166, 115401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.T.; Zhong, X.X.; Mo, L.; Huang, R.Z.; Lin, Q.; Liu, C.J.; Zhang, S.C. Evaluating the causal effect of atherosclerosis on the risk of intervertebral disc degeneration. JOR Spine 2024, 7, e1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, E.E.; Buckley, C.T. Consolidating and re-evaluating the human disc nutrient microenvironment. JOR Spine 2022, 5, e1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, J.; Wilkinson, K.J.; Otsuru, S. Nutrient metabolism of the nucleus pulposus: A literature review. North Am. Spine Soc. J. 2023, 13, 100191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.H.; Guo, L.J.; Yuan, L.Q.; Xie, H.; Zhou, H.D.; Wu, X.P.; Liao, E.Y. Adiponectin stimulates human osteoblasts proliferation and differentiation via the MAPK signaling pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2005, 309, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyani, R.R.; Corriere, M.; Ferrucci, L. Age-related and disease-related muscle loss: The effect of diabetes, obesity, and other diseases. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalichman, L.; Klindukhov, A.; Li, L.; Linov, L. Indices of Paraspinal Muscles Degeneration: Reliability and Association with Facet Joint Osteoarthritis: Feasibility Study. Clin. Spine Surg. 2016, 29, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L.; Cai, W.; Yang, S.; Liao, W.; Cheng, X. Age-related fatty infiltration of lumbar paraspinal muscles: A normative reference database study in 516 Chinese females. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2020, 10, 1590–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, J.; Bruce-Low, S.; Smith, D. A review of the clinical value of isolated lumbar extension resistance training for chronic low back pain. PM R. J. Inj. Funct. Rehabil. 2015, 7, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, N.; Hosogane, N.; Hikata, T.; Iwanami, A.; Watanabe, K.; Shiono, Y.; Okada, E.; Ishikawa, M.; Tsuji, T.; Shimoda, M.; et al. Potential Involvement of Obesity-Associated Chronic Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Spinal Epidural Lipomatosis. Spine 2016, 41, E1402–E1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Briceño, W.; Velásquez, V.B.; Silva-Olivares, F.; Ceballo, K.; Céspedes, R.; Jorquera, G.; Cruz, G.; Martínez-Pinto, J.; Bonansco, C.; Sotomayor-Zárate, R. Chronic Exposure to High Fat Diet Affects the Synaptic Transmission That Regulates the Dopamine Release in the Nucleus Accumbens of Adolescent Male Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragano, N.R.; Haddad-Tovolli, R.; Velloso, L.A. Leptin, Neuroinflammation and Obesity. Front. Horm. Res. 2017, 48, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Kim, O. Perspectives in Lipocalin-2: Emerging Biomarker for Medical Diagnosis and Prognosis for Alzheimer’s Disease. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2018, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Nie, L.; Hou, X.; Wu, W.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Y. Leptin Contributes to Neuropathic Pain via Extrasynaptic NMDAR-nNOS Activation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Huang, T.-Y.; Garza, J.C.; Chua, S.C.; Lu, X.-Y. Selective deletion of leptin receptors in adult hippocampus induces depression-related behaviours. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 16, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Li, X.; Wu, W. Association Between Overweight or Obesity and Lumbar Disk Diseases: A Meta-Analysis. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2015, 28, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samartzis, D.; Karppinen, J.; Chan, D.; Luk, K.D.; Cheung, K.M. The association of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration on magnetic resonance imaging with body mass index in overweight and obese adults: A population-based study. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 1488–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergin, A.; Ergin, E.; Atasever, A.; Çiyiltepe, H.; Fersahoğlu, M.M.; Esen Bulut, N.; Taşdelen, İ.; Güneş, Y.; Teke, E.; Yılmaz, C.; et al. Investigatıon of the effect of weight loss after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy on cobb angle, waist and back pain: A prospective study. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2023, 19, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidar, Z.; Behrbalk, E.; Regev, G.J.; Salame, K.; Keynan, O.; Schweiger, C.; Appelbaum, L.; Levy, Y.; Keidar, A. Intervertebral disc height changes after weight reduction in morbidly obese patients and its effect on quality of life and radicular and low back pain. Spine 2012, 37, 1947–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezelbash, F.; Shirazi-Adl, A.; Plamondon, A.; Arjmand, N.; Parnianpour, M. Obesity and Obesity Shape Markedly Influence Spine Biomechanics: A Subject-Specific Risk Assessment Model. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 45, 2373–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Li, D.; Wang, T.; Wang, S.; Cao, S. Waist circumference, waist-hip ratio, body fat rate, total body fat mass and risk of low back pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Spine J. 2021, 31, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayartai, M.-E.; Luomajoki, H.; Tringali, G.; De Micheli, R.; Abbruzzese, L.; Sartorio, A. Differences in spinal posture and mobility between adults with obesity and normal weight individuals. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdovino, A.G.; Bastrom, T.P.; Reighard, F.G.; Cross, M.; Bartley, C.E.; Shah, S.A.; Yaszay, B.; Newton, P.O.; Upasani, V.V. Obesity Is Associated with Increased Thoracic Kyphosis in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Patients and Nonscoliotic Adolescents. Spine Deform. 2019, 7, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Martinez, N.G.; Perez-Orribo, L.; Kalb, S.; Reyes, P.M.; Newcomb, A.G.; Hughes, J.; Theodore, N.; Crawford, N.R. The role of obesity in the biomechanics and radiological changes of the spine: An in vitro study. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2016, 24, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahramian, M.; Arjmand, N.; El-Rich, M.; Parnianpour, M. Effect of obesity on spinal loads during load-reaching activities: A subject- and kinematics-specific musculoskeletal modeling approach. J. Biomech. 2023, 161, 111770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppock, J.A.; Danyluk, S.T.; Englander, Z.A.; Spritzer, C.E.; Goode, A.P.; DeFrate, L.E. Increasing BMI increases lumbar intervertebral disc deformation following a treadmill walking stress test. J. Biomech. 2021, 121, 110392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthukrishnan, R.; Shenoy, S.D.; Jaspal, S.S.; Nellikunja, S.; Fernandes, S. The differential effects of core stabilization exercise regime and conventional physiotherapy regime on postural control parameters during perturbation in patients with movement and control impairment chronic low back pain. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanti, C.; Conti, C.; Faresin, F.; Ferrari, S.; Piccarreta, R. The Relationship Between Clinical Instability and Endurance Tests, Pain, and Disability in Nonspecific Low Back Pain. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2016, 39, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unamuno, X.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodriguez, A.; Becerril, S.; Fruhbeck, G.; Catalan, V. Adipokine dysregulation and adipose tissue inflammation in human obesity. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risbud, M.V.; Shapiro, I.M. Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: Pain and disc content. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014, 10, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, L.; Hottiger, M.; Boos, N.; Wuertz, K. Peroxynitrite induces gene expression in intervertebral disc cells. Spine 2009, 34, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauppila, L.I. Atherosclerosis and disc degeneration/low-back pain—A systematic review. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2009, 37, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakal, T.C.; Xiao, F.; Bhusal, C.K.; Sabapathy, P.C.; Segal, R.; Chen, J.; Bai, X. Lipids dysregulation in diseases: Core concepts, targets and treatment strategies. Lipids Health Dis. 2025, 24, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curic, G. Intervertebral Disc and Adipokine Leptin—Loves Me, Loves Me Not. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.; Dong, Y.; Li, C.; Jiang, M.; Duan, L.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X. Phosphatidylcholine Ameliorates Palmitic Acid-Induced Lipotoxicity by Facilitating Endoplasmic Reticulum and Mitochondria Contacts in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. JOR Spine 2025, 8, e70062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, V.; Ait Eldjoudi, D.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, M.; Ruiz-Fernandez, C.; Cordero-Barreal, A.; Marques, P.; Sanz, M.J.; Real, J.T.; Lago, F.; Pino, J.; et al. Metabolomic signature and molecular profile of normal and degenerated human intervertebral disc cells. Spine J. Off. J. North Am. Spine Soc. 2023, 23, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Jing, D.; Huang, X.; Yang, W.; Shao, Z. Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission is involved in oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced AF cella poptosis. J. Orthop. Res. 2021, 39, 1496–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.Z.; Xu, W.N.; Zheng, H.L.; Zheng, X.F.; Li, B.; Jiang, L.S.; Jiang, S.D. Involvement of oxidative stress-induced annulus fibrosus cell and nucleus pulposus cell ferroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration pathogenesis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 2725–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Park, S.; Lee, D.; Ginting, R.P.; Lee, M.R.; Lee, M.W.; Han, J. Reduction in endoplasmic reticulum stress activates beige adipocytes differentiation and alleviates high fat diet-induced metabolic phenotypes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 166099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Ren, Q.; Luo, L.; Ji, G.; Zheng, T. Endoplasmic reticulum stress associates with the development of intervertebral disc degeneration. Front Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1094394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Ni, B.; Zhang, F.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, J. High Glucose-Induced Oxidative Stress Mediates Apoptosis and Extracellular Matrix Metabolic Imbalances Possibly via p38 MAPK Activation in Rat Nucleus Pulposus Cells. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 3765173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.M.; Knowles, R.; Tyler, J.; Mobasheri, A.; Hoyland, J.A. Expression of glucose transporters GLUT-1, GLUT-3, GLUT-9 and HIF-1alpha in normal and degenerate human intervertebral disc. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 129, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhu, D.; Wang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Huang, L.; Kang, X.; Ma, B. Role of Advanced Glycation End Products in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Mechanism and Therapeutic Potential. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 7299005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassara, H.; Striker, G.E. AGE restriction in diabetes mellitus: A paradigm shift. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Park, S.; Cho, H.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, H. Adipokine human Resistin promotes obesity-associated inflammatory intervertebral disc degeneration via pro-inflammatory cytokine cascade activation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, N.; Parker, J.L.; Lugus, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A. The Role of Adipokines in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Med. Sci 2018, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, V.; Pino, J.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Lago, F.; Karppinen, J.; Tervonen, O.; Mobasheri, A.; Gualillo, O. A new immunometabolic perspective of intervertebral disc degeneration. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C375–C391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segar, A.H.; Fairbank, J.C.T.; Urban, J. Leptin and the intervertebral disc: A biochemical link exists between obesity, intervertebral disc degeneration and low back pain-an in vitro study in a bovine model. Eur. Spine J. 2019, 28, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Huang, L.; Yan, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, B.; Ma, Y.; Luo, Z. Adiponectin Downregulates TNF-alpha Expression in Degenerated Intervertebral Discs. Spine 2018, 43, E381–E389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Wang, W.; Yu, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, W.; Ji, Z.; He, W.; Hua, D.; Wang, W.; Yao, L.; et al. M1 macrophage-derived exosomes promote intervertebral disc degeneration by enhancing nucleus pulposus cell senescence through LCN2/NF-kappaB signaling axis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Du, X.; Liu, C.; Chen, S.; Cui, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Zheng, Z. Visfatin promotes intervertebral disc degeneration by inducing IL-6 expression through the ERK/JNK/p38 signalling pathways. Adipocyte 2021, 10, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Chen, X.; Wu, W.; Lin, H.; Qing, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, B.; Xiao, Y.; Shao, Z.; Peng, Y. Nucleus pulposus cells regulate macrophages in degenerated intervertebral discs via the integrated stress response-mediated CCL2/7-CCR2 signaling pathway. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Qin, J.; Wang, R.; Wang, S.; Fu, W.; Niu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; et al. Osteopontin deficiency promotes cartilaginous endplate degeneration by enhancing the NF-kappaB signaling to recruit macrophages and activate the NLRP3 inflammasome. Bone Res. 2024, 12, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Cao, S.; Zhu, M.D.; Liu, J.Q.; Chen, J.J.; Gao, Y.J. Contribution of chemokine CCL2/CCR2 signaling in the dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord to the maintenance of neuropathic pain in a rat model of lumbar disc herniation. J. Pain 2014, 15, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakawaki, M.; Uchida, K.; Miyagi, M.; Inoue, G.; Kawakubo, A.; Kuroda, A.; Satoh, M.; Takaso, M. Sequential CCL2 Expression Profile After Disc Injury in Mice. J. Orthop. Res. 2020, 38, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, H.E.; Hoelscher, G.L.; Ingram, J.A.; Bethea, S.; Cox, M.; Hanley, E.N., Jr. Proinflammatory cytokines modulate the chemokine CCL2 (MCP-1) in human annulus cells in vitro: CCL2 expression and production. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2015, 98, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Jang, S.H.; Suzuki-Narita, M.; Gregoire, S.; Millecamps, M.; Stone, L.S. Voluntary running attenuates behavioural signs of low back pain: Dimorphic regulation of intervertebral disc inflammation in male and female SPARC-null mice. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2022, 30, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboushaala, K.; Chee, A.V.; Toro, S.J.; Vucicevic, R.; Yuh, C.; Dourdourekas, J.; Patel, I.K.; Espinoza-Orias, A.; Oh, C.; Al-Harthi, L.; et al. Discovery of circulating blood biomarkers in patients with and without Modic changes of the lumbar spine: A preliminary analysis. Eur. Spine J. 2024, 33, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krock, E.; Millecamps, M.; Anderson, K.M.; Srivastava, A.; Reihsen, T.E.; Hari, P.; Sun, Y.R.; Jang, S.H.; Wilcox, G.L.; Belani, K.G.; et al. Interleukin-8 as a therapeutic target for chronic low back pain: Upregulation in human cerebrospinal fluid and pre-clinical validation with chronic reparixin in the SPARC-null mouse model. EBioMedicine 2019, 43, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.P.; Tian, Q.Y.; Liu, B.; Cuellar, J.; Richbourgh, B.; Jia, T.H.; Liu, C.J. Progranulin knockout accelerates intervertebral disc degeneration in aging mice. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wei, J.; Fan, Y.; Ding, H.; Tian, H.; Zhou, X.; Cheng, L. Progranulin Is Positively Associated with Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Interaction with IL-10 and IL-17 Through TNF Pathways. Inflammation 2018, 41, 1852–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Wei, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Cheng, L. Progranulin derived engineered protein Atsttrin suppresses TNF-α-mediated inflammation in intervertebral disc degenerative disease. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 109692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Ilalov, K.; Carlson, C.S.; Feng, J.Q.; Di Cesare, P.E.; Liu, C.J. Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein associates with granulin-epithelin precursor (GEP) and potentiates GEP-stimulated chondrocyte proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 11347–11355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Chen, L.; Mamun, A.A.; Zhao, N.; Cai, J.; Lou, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, J. Chemerin facilitates intervertebral disc degeneration via TLR4 and CMKLR1 and activation of NF-kB signaling pathway. Aging 2020, 12, 11732–11753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, M.; Hirose, N.; Sumi, C.; Yanoshita, M.; Nishiyama, S.; Onishi, A.; Asakawa, Y.; Tanimoto, K. ANGPTL2 Promotes Inflammation via Integrin alpha5beta1 in Chondrocytes. Cartilage 2021, 13, 885S–897S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Wei, H.; Li, Z.M.; Dong, X.B.; Wang, P.Y. TGF-beta1 aggravates degenerative nucleus pulposus cells inflammation and fibrosis through the upregulation of angiopoietin-like protein 2 expression. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 12025–12033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyland, J.A.; Le Maitre, C.; Freemont, A.J. Investigation of the role of IL-1 and TNF in matrix degradation in the intervertebral disc. Rheumatol. 2008, 47, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrselja, Z.; Curic, G. Vertebral marrow adipose tissue adipokines as a possible cause of intervertebral disc inflammation. Jt. Bone Spine 2018, 85, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.A.; Shen, E.; Cui, A.; Zhou, F.; Zhuang, Y. Assessing the causal relationship between CRP, IL-1alpha, IL-1beta, and IL-6 levels and intervertebral disc degeneration: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.T.; Alipui, D.O.; Sison, C.P.; Bloom, O.; Quraishi, S.; Overby, M.C.; Levine, M.; Chahine, N.O. Serum levels of the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 vary based on diagnoses in individuals with lumbar intervertebral disc diseases. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Gao, L.; Wang, H.X.; Ye, L.; Shi, Y.Y.; Yang, W.Y.; Li, Y.N.; Li, Y. Interleukin-18 Inhibition Protects Against Intervertebral Disc Degeneration via the Inactivation of Caspase-3/9 Dependent Apoptotic Pathways. Immunol. Investig. 2022, 51, 1895–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Ju, B.; Wang, H.; Lee, K.B. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 provokes interleukin-18-induced human intervertebral disc degeneration. Bone Jt. Res. 2016, 5, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landy, E.; Carol, H.; Ring, A.; Canna, S. Biological and clinical roles of IL-18 in inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2024, 20, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.K.; Nie, L.; Zhao, Y.P.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.S.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Cheng, L. IL-17 mediates inflammatory reactions via p38/c-Fos and JNK/c-Jun activation in an AP-1-dependent manner in human nucleus pulposus cells. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veras, M.A.; McCann, M.R.; Tenn, N.A.; Seguin, C.A. Transcriptional profiling of the murine intervertebral disc and age-associated changes in the nucleus pulposus. Connect. Tissue Res. 2020, 61, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recinella, L.; Orlando, G.; Ferrante, C.; Chiavaroli, A.; Brunetti, L.; Leone, S. Adipokines: New Potential Therapeutic Target for Obesity and Metabolic, Rheumatic, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 578966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natelson, D.M.; Lai, A.; Krishnamoorthy, D.; Hoy, R.C.; Iatridis, J.C.; Illien-Junger, S. Leptin signaling and the intervertebral disc: Sex dependent effects of leptin receptor deficiency and Western diet on the spine in a type 2 diabetes mouse model. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liang, J.; Wu, W.K.; Yu, X.; Yu, J.; Weng, X.; Shen, J. Leptin activates RhoA/ROCK pathway to induce cytoskeleton remodeling in nucleus pulposus cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 1176–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.Q.; Liu, D.; Li, H.; Jiang, L.S.; Dai, L.Y. Expression of leptin and its functional receptor on disc cells: Contribution to cell proliferation. Spine 2008, 33, E858–E864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Cao, F.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Z.; Yu, B.; Feng, H.; Ba, Z.; Liu, T.; et al. Intervertebral disc degeneration in mice with type II diabetes induced by leptin receptor deficiency. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020, 21, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yurube, T.; Takeoka, Y.; Kanda, Y.; Tsujimoto, R.; Miyazaki, K.; Matsuo, T.; Ryu, M.; Kumagai, N.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Adiponectin Receptor Agonist AdipoRon against Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terashima, Y.; Kakutani, K.; Yurube, T.; Takada, T.; Maeno, K.; Hirata, H.; Miyazaki, S.; Ito, M.; Kakiuchi, Y.; Takeoka, Y.; et al. Expression of adiponectin receptors in human and rat intervertebral disc cells and changes in receptor expression during disc degeneration using a rat tail temporary static compression model. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2016, 11, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khabour, O.F.; Abu-Rumeh, L.; Al-Jarrah, M.; Jamous, M.; Alhashimi, F. Association of adiponectin protein and ADIPOQ gene variants with lumbar disc degeneration. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 8, 1340–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrion, M.; Frommer, K.W.; Perez-Garcia, S.; Muller-Ladner, U.; Gomariz, R.P.; Neumann, E. The Adipokine Network in Rheumatic Joint Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giardullo, L.; Corrado, A.; Maruotti, N.; Cici, D.; Mansueto, N.; Cantatore, F.P. Adipokine role in physiopathology of inflammatory and degenerative musculoskeletal diseases. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2021, 35, 20587384211015034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Pan, H.; Yang, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, J. Resistin promotes CCL4 expression through toll-like receptor-4 and activation of the p38-MAPK and NF-kappaB signaling pathways: Implications for intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2017, 25, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, H.; Gao, F.; Li, X.; An, Y.; Wang, J.; Jin, A. Resistin Promotes Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Upregulation of ADAMTS-5 Through p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway. Spine 2016, 41, 1414–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, X.; Qu, R.; Wang, W.; Chen, X.; Cheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, C. Ghrelin protects against nucleus pulposus degeneration through inhibition of NF-kappaB signaling pathway and activation of Akt signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 91887–91901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, V.L.F.; Wang, F.; Peng, X.; Gao, J.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, R.; Bao, J.; Wu, X. Omentin-1 promoted proliferation and ameliorated inflammation, apoptosis, and degeneration in human nucleus pulposus cells. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2022, 102, 104748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y.; Yamashita, T. The Effects of Leptin on Glial Cells in Neurological Diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinfe, T.M.; Buchfelder, M.; Chaudhry, S.R.; Chakravarthy, K.V.; Deer, T.R.; Russo, M.; Georgius, P.; Hurlemann, R.; Rasheed, M.; Muhammad, S.; et al. Leptin and Associated Mediators of Immunometabolic Signaling: Novel Molecular Outcome Measures for Neurostimulation to Treat Chronic Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuertz, K.; Haglund, L. Inflammatory mediators in intervertebral disk degeneration and discogenic pain. Glob. Spine J. 2013, 3, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.J.; Jin, Z.; An, H.S.; Park, G.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Jang, H.M.; Jeong, E.A.; Kim, K.E.; Lee, J.; et al. Lipocalin-2 Deficiency Reduces Hepatic and Hippocampal Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells-2 Expressions in High-Fat Diet/Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, T.H.; Peng, Y.J.; Salter, D.M.; Lee, H.S. Nerve growth factor increases MMP9 activity in annulus fibrosus cells by upregulating lipocalin 2 expression. Eur. Spine J. 2015, 24, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boisson, M.; Borderie, D.; Henrotin, Y.; Teboul-Core, S.; Lefevre-Colau, M.M.; Rannou, F.; Nguyen, C. Serum biomarkers in people with chronic low back pain and Modic 1 changes: A case-control study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.N.; Jacobsen, H.E.; Khan, J.; Filippi, C.G.; Levine, M.; Lehman, R.A., Jr.; Riew, K.D.; Lenke, L.G.; Chahine, N.O. Inflammatory biomarkers of low back pain and disc degeneration: A review. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1410, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.; Kolodziejczyk, A.A.; Thaiss, C.A.; Elinav, E. Dysbiosis and the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, S.; Vasudevan, G.; Tangavel, C.; Ramachandran, K.; Nayagam, S.M.; Muthurajan, R.; Gopalakrishnan, C.; Anand, S.V.; Shetty, A.P.; Kanna, R.M. Does the gut microbiome influence disc health and disease? The interplay between dysbiosis, pathobionts, and disc inflammation: A pilot study. Spine J. Off. J. North Am. Spine Soc. 2024, 24, 1952–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboushaala, K.; Chee, A.V.; Adnan, D.; Toro, S.J.; Singh, H.; Savoia, A.; Dhillon, E.S.; Yuh, C.; Dourdourekas, J.; Patel, I.K.; et al. Gut microbiome dysbiosis is associated with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis in symptomatic patients. JOR Spine 2024, 7, e70005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Li, Z.; Duan, J.; Liu, E.; Sun, F.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.; Yang, S. Unveiling the Gut-Disc Axis: How Microbiome Dysbiosis Accelerates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 8271–8280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, B.; Chisari, E.; Parvizi, J. Osteoarthritis Can Also Start in the Gut: The Gut-Joint Axis. Indian. J. Orthop. 2022, 56, 1150–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, C.G.; Radjabzadeh, D.; Medina-Gomez, C.; Garmaeva, S.; Schiphof, D.; Arp, P.; Koet, T.; Kurilshikov, A.; Fu, J.; Ikram, M.A.; et al. Intestinal microbiome composition and its relation to joint pain and inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersoug, L.G.; Moller, P.; Loft, S. Role of microbiota-derived lipopolysaccharide in adipose tissue inflammation, adipocyte size and pyroptosis during obesity. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2018, 31, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Kakiuchi, T.; Esaki, M.; Tsukamoto, M.; Yoshihara, T.; Hirata, H.; Yabuki, S.; Mawatari, M. Gut-spine axis: A possible correlation between gut microbiota and spinal degenerative diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1290858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lempesis, I.G.; van Meijel, R.L.J.; Manolopoulos, K.N.; Goossens, G.H. Oxygenation of adipose tissue: A human perspective. Acta Physiol. 2020, 228, e13298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Kim, J.W.; Osborne, O.; Oh, D.Y.; Sasik, R.; Schenk, S.; Chen, A.; Chung, H.; Murphy, A.; Watkins, S.M.; et al. Increased adipocyte O2 consumption triggers HIF-1alpha, causing inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity. Cell 2014, 157, 1339–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, S.; Lin, J.; Wang, L.; Jiang, S.; Sun, Z.; Li, W. Cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying obesity in degenerative spine and joint diseases. Bone Res. 2024, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Pan, D.; Xu, B.; Xing, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, S.; Ning, G.; Feng, S. The potential role and trend of HIF-1alpha in intervertebral disc degeneration: Friend or foe? (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, C.M.; Shapiro, I.M.; Risbud, M.V. Molecular regulation of CCN2 in the intervertebral disc: Lessons learned from other connective tissues. Matrix Biol. J. Int. Soc. Matrix Biol. 2013, 32, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainor, M.; Orozco, B.S.; Muir, V.G.; Mahindroo, S.; Gupta, S.; Mauck, R.L.; Burdick, J.A.; Smith, H.E.; Gullbrand, S.E. Mechanical crosstalk between the intervertebral disc, facet joints, and vertebral endplate following acute disc injury in a rabbit model. JOR Spine 2023, 6, e1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalash, W.; Ahrens, S.R.; Bardonova, L.A.; Byvaltsev, V.A.; Giers, M.B. Patient-specific apparent diffusion maps used to model nutrient availability in degenerated intervertebral discs. JOR Spine 2021, 4, e1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpinar, V.E.; Rand, S.D.; Klein, A.P.; Maiman, D.J.; Muftuler, L.T. Changes in perfusion and diffusion in the endplate regions of degenerating intervertebral discs: A DCE-MRI study. Eur. Spine J. 2015, 24, 2458–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, D.H.; Yockey, S.R. Weight Loss and Improvement in Comorbidity: Differences at 5%, 10%, 15%, and Over. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2017, 6, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, C.L.; Lopes, S.; Olsen, A.H.; Satylganova, A.; Schnecke, V.; McEwan, P. Weight loss and risk reduction of obesity-related outcomes in 0.5 million people: Evidence from a UK primary care database. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffens, D.; Maher, C.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Stevens, M.L.; Oliveira, V.C.; Chapple, M.; Teixeira-Salmela, L.F.; Hancock, M.J. Prevention of Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2016, 176, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Campos, T.F.; Maher, C.G.; Fuller, J.T.; Steffens, D.; Attwell, S.; Hancock, M.J. Prevention strategies to reduce future impact of low back pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2021, 55, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, H.J.; Correa, L.; Brown, B.T.; Ferreira, G.E.; Nim, C.; Aspinall, S.L.; Wareham, D.; Choi, J.; Maher, C.G.; Hancock, M.J. Long-term effectiveness of non-surgical interventions for chronic low back pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Rheumatol. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadalà, G.; Di Giacomo, G.; Ambrosio, L.; Cicione, C.; Tilotta, V.; Russo, F.; Papalia, R.; Denaro, V. The Effect of Irisin on Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells: New Insights into the Biological Crosstalk between the Muscle and Intervertebral Disc. Spine 2023, 48, 468–475, publish ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Lu, X.; Wen, M.; Li, X.; Gao, Q.; Qin, R. Association between muscle strength and low back pain among middle-aged and older adults: A cross-sectional study. BMC Public. Health 2025, 25, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friend, D.M.; Devarakonda, K.; O’Neal, T.J.; Skirzewski, M.; Papazoglou, I.; Kaplan, A.R.; Liow, J.S.; Guo, J.; Rane, S.G.; Rubinstein, M.; et al. Basal Ganglia Dysfunction Contributes to Physical Inactivity in Obesity. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, F.; Davis, M.E.; Murphy, K.; Tersigni, N.; King, A.; Ngo, N.; O’Donoghue, G. Correlates of physical activity and sedentary behavior in adults living with overweight and obesity: A systematic review. Obes. Rev. 2023, 24, e13615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Chang, S.H. Self-esteem and weight status of young adults: Findings from a pilot study. J. Educ. Health Promot. 2022, 11, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei-Assibey, G.; Kyrou, I.; Kumar, S.; Saravanan, P.; Matyka, K.A. Self-Reported Psychosocial Health in Obese Patients before and after Weight Loss. J. Obes. 2010, 2010, 372463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lazaridou, A.; Paschali, M.; Zgierska, A.E.; Garland, E.L.; Edwards, R.R. Exploring the Relationship Between Endogenous Pain Modulation, Pain Intensity, and Depression in Patients Using Opioids for Chronic Low Back Pain. Clin. J. Pain 2022, 38, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codella, R.; Chirico, A. Physical Inactivity and Depression: The Gloomy Dual with Rising Costs in a Large-Scale Emergency. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2023, 20, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.H.; Weber, K.; Mehrabkhani, S.; Baskaran, S.; Abbass, T.; Macedo, L.G. The effectiveness of weight loss programs for low back pain: A systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silisteanu, S.; Covasa, M. Reduction of body weight through nutrition intervention reduces chronic low back pain. In Proceedings of the 2015 E-Health and Bioengineering Conference (EHB), Iasi, Romania, 19 November 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Robson, E.; Kamper, S.J.; Lee, H.; Palazzi, K.; O’Brien, K.M.; Williams, A.; Hodder, R.K.; Williams, C.M. Compliance with telephone-based lifestyle weight loss programs improves low back pain but not knee pain outcomes: Complier average causal effects analyses of 2 randomised trials. Pain 2022, 163, e862–e868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiz, A.; Levett, J.Y.; Filion, K.B.; Peri, K.; Reynier, P.; Eisenberg, M.J. Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Once-Weekly Semaglutide for Weight Loss in Patients Without Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am. J. Cardiol. 2024, 222, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliddal, H.; Bays, H.; Czernichow, S.; Hemmingsson, J.U.; Hjelmesæth, J.; Morville, T.H.; Koroleva, A.; Neergaard, J.S.; Sánchez, P.V.; Wharton, S.; et al. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Persons with Obesity and Knee Osteoarthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 1573–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhang, M.; Chen, D.; Wu, S.; Gao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Kuang, J.; Fang, Q. Advances in GLP-1 receptor agonists for pain treatment and their future potential. J. Headache Pain 2025, 26, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumnalieva, R.; Kotov, G.; Monov, S. Obesity-Related Knee Osteoarthritis—Current Concepts. Life 2023, 13, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGoey, B.V.; Deitel, M.; Saplys, R.J.; Kliman, M.E. Effect of weight loss on musculoskeletal pain in the morbidly obese. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 1990, 72, 322–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melissas, J.; Volakakis, E.; Hadjipavlou, A. Low-back pain in morbidly obese patients and the effect of weight loss following surgery. Obes. Surg. 2003, 13, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melissas, J.; Kontakis, G.; Volakakis, E.; Tsepetis, T.; Alegakis, A.; Hadjipavlou, A. The effect of surgical weight reduction on functional status in morbidly obese patients with low back pain. Obes. Surg. 2005, 15, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoueir, P.; Black, M.H.; Crookes, P.F.; Kaufman, H.S.; Katkhouda, N.; Wang, M.Y. Prospective assessment of axial back pain symptoms before and after bariatric weight reduction surgery. Spine J. Off. J. North Am. Spine Soc. 2009, 9, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, H.K.; Ben-David, K.; Conrad, B.P.; Lamb, K.M.; Seay, A.N.; Vincent, K.R. Rapid changes in gait, musculoskeletal pain, and quality of life after bariatric surgery. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2012, 8, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakir, T.; Oruc, M.T.; Aslaner, A.; Duygun, F.; Yardimci, E.C.; Mayir, B.; Bulbuller, N. The effects of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy on head, neck, shoulder, low back and knee pain of female patients. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 2668–2673. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, D.A.; Merten, S.L.; Sandercoe, G.D.; Gahankari, D.; Ingram, S.B.; Moncrieff, N.J.; Ho, K.; Sellars, G.D.; Magnusson, M.R. Abdominoplasty Improves Low Back Pain and Urinary Incontinence. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 141, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, M.; Mathur, W.; Kosta, S.; Salvi, P.; Fobi, M. Assessment of functional ability of nonambulatory patients with obesity: After and before bariatric surgery. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2019, 15, 2087–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soteropulos, C.E.; Edinger, K.M.; Leibl, K.E.; Siebert, J.W. Improvement in Back Pain Following Abdominoplasty: Results of a 10-Year, Single-Surgeon Series. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2020, 40, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.D.; Joo, A.; Xu, J.; Palic, A.; Wood, J.J.; Sirls, E.R.; Tomczyk, E.G.; Rothkopf, D.M. Back Pain According to Roland-Morris Low Back Pain Scale After Abdominoplasty with Plication: A Prospective Case Series. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2023, 90, S704–S706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roffey, D.M.; Ashdown, L.C.; Dornan, H.D.; Creech, M.J.; Dagenais, S.; Dent, R.M.; Wai, E.K. Pilot evaluation of a multidisciplinary, medically supervised, nonsurgical weight loss program on the severity of low back pain in obese adults. Spine J. Off. J. North Am. Spine Soc. 2011, 11, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.; Wiggers, J.; O’Brien, K.M.; Wolfenden, L.; Yoong, S.L.; Hodder, R.K.; Lee, H.; Robson, E.K.; McAuley, J.H.; Haskins, R.; et al. Effectiveness of a healthy lifestyle intervention for chronic low back pain: A randomised controlled trial. Pain 2018, 159, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunlevy, C.; MacLellan, G.A.; O’Malley, E.; Blake, C.; Breen, C.; Gaynor, K.; Wallace, N.; Yoder, R.; Casey, D.; Mehegan, J.; et al. Does changing weight change pain? Retrospective data analysis from a national multidisciplinary weight management service. Eur. J. Pain 2019, 23, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safari, M.B.; Nozad, A.; Ghaffari, F.; Ghavamzadeh, S.; Alijaniha, F.; Naseri, M. Efficacy of a Short-Term Low-Calorie Diet in Overweight and Obese Patients with Chronic Sciatica: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2020, 26, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, S.J.; Coates, A.M.; Carter, S.; Baldock, K.L.; Berryman, C.; Stanton, T.R.; Yandell, C.; Buckley, J.D.; Tan, S.Y.; Rogers, G.B.; et al. Effects of weight loss through dietary intervention on pain characteristics, functional mobility, and inflammation in adults with elevated adiposity. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1274356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed Mohamed, W.J.; Joseph, L.; Canby, G.; Paungmali, A.; Sitilertpisan, P.; Pirunsan, U. Are patient expectations associated with treatment outcomes in individuals with chronic low back pain? A systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2020, 74, e13680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, A.; De Carvalho, D.; Page, I.; Wong, A.; Johansson, M.S.; Pohlman, K.A.; Hartvigsen, J.; Swain, M. Expectations influence treatment outcomes in patients with low back pain. A secondary analysis of data from a randomized clinical trial. Eur. J. Pain 2019, 23, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Würfel, M.; Blüher, M.; Stumvoll, M.; Ebert, T.; Kovacs, P.; Tönjes, A.; Breitfeld, J. Adipokines as Clinically Relevant Therapeutic Targets in Obesity. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenawy, H.M.; Nunez, M.I.; Morales, X.; Lisiewski, L.E.; Burt, K.G.; Kim, M.K.M.; Campos, L.; Kiridly, N.; Hung, C.T.; Chahine, N.O. Sex differences in the biomechanical and biochemical responses of caudal rat intervertebral discs to injury. JOR Spine 2023, 6, e1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnheim, N.B.; Lazar, A.A.; Kumar, A.; Akkaya, Z.; Zhou, J.; Guo, X.; O’Neill, C.; Link, T.M.; Lotz, J.C.; Krug, R.; et al. ISSLS Prize in Bioengineering Science 2023: Age- and sex-related differences in lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration between patients with chronic low back pain and asymptomatic controls. Eur. Spine J. 2023, 32, 1517–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosley, G.E.; Wang, M.; Nasser, P.; Lai, A.; Charen, D.A.; Zhang, B.; Iatridis, J.C. Males and females exhibit distinct relationships between intervertebral disc degeneration and pain in a rat model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosley, G.E.; Hoy, R.C.; Nasser, P.; Kaseta, T.; Lai, A.; Evashwick-Rogler, T.W.; Lee, M.; Iatridis, J.C. Sex Differences in Rat Intervertebral Disc Structure and Function Following Annular Puncture Injury. Spine 2019, 44, 1257–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.X.; Yu, Y.J.; Li, X.F.; Liu, Z.D.; Yu, B.W.; Guo, Z. Estrogen receptor expression in lumbar intervertebral disc of the elderly: Gender- and degeneration degree-related variations. Jt. Bone Spine 2014, 81, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otani, Y.; Schol, J.; Sakai, D.; Nakamura, Y.; Sako, K.; Warita, T.; Tamagawa, S.; Ambrosio, L.; Munesada, D.; Ogasawara, S.; et al. Assessment of Tie2-Rejuvenated Nucleus Pulposus Cell Transplants from Young and Old Patient Sources Demonstrates That Age Still Matters. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, N.V.; Piva, S.R.; Patterson, C.G.; McKernan, G.P.; Zhou, L.; Bell, K.M.; Anderst, W.; Greco, C.M.; Schneider, M.J.; Delitto, A.; et al. Toward the Identification of Distinct Phenotypes: Research Protocol for the Low Back Pain Biological, Biomechanical, and Behavioral (LB3P) Cohort Study and the BACPAC Mechanistic Research Center at the University of Pittsburgh. Pain Med. 2023, 24, S36–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).