Reusing an Expired Drug as a Sustainable Corrosion Inhibitor for Bronze in 3.5% NaCl and Simulated Acid Rain Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrochemical Methods
2.3. SEM-EDX Investigations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
3.2. Potentiodynamic Polarization Measurements
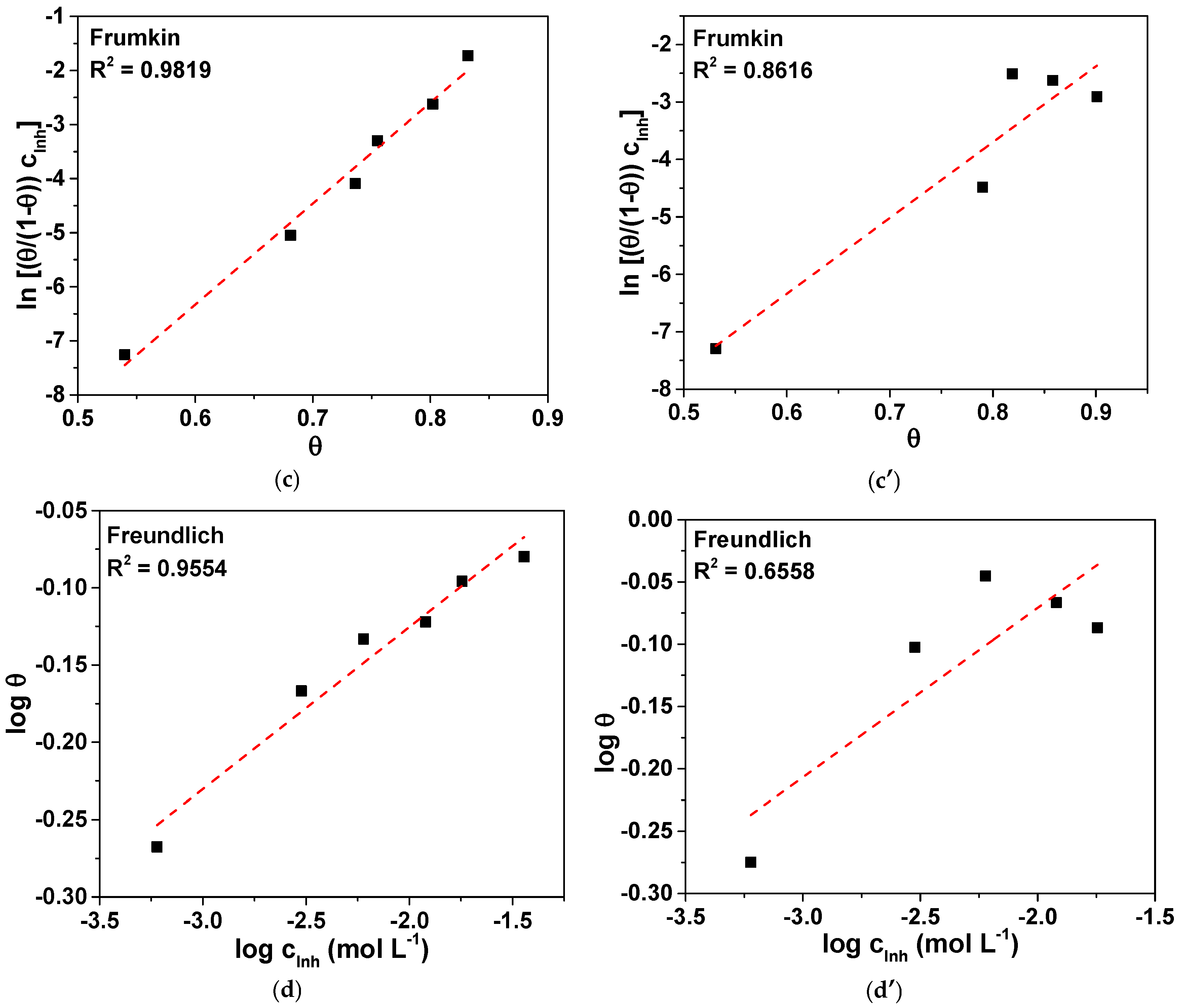
3.3. Adsorption Mechanism
3.4. SEM-EDX Analysis
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The drug acted as a good cathodic inhibitor of bronze corrosion in both tested electrolytes; the maximum values of the inhibition efficiency were 86.7% in the presence of 36 mM NAC in the saline solution and 90.2% obtained by the addition of 6 mM NAC in simulated acid rain. Generally, the inhibition performance of the drug was higher in the simulated acid rain solution than in the saline environment.
- (2)
- EIS results showed that the adsorption of NAC on bronze surface hindered the charge transfer reaction and impeded the formation of corrosion products, which became less prone to participate in redox reactions.
- (3)
- The inhibition mechanism was attributed to the spontaneous adsorption of NAC on the bronze surface via physical and chemical interactions. In both tested electrolytes, the adsorption process followed the Langmuir isotherm.
- (4)
- SEM and EDX analysis confirmed that the drug was able to effectively suppress corrosion product formation on the bronze surface exposed to both corrosive environments.
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EIS | Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy |
| NAC | N-acetylcysteine |
References
- Picciochi, R.; Ramos, A.C.; Mendonça, M.H.; Fonseca, I.T.E. Influence of the environment on the atmospheric corrosion of bronze. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2004, 34, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, F.J.R.; Lago, D.C.B.; Senna, L.F.; de Miranda, L.R.M.; D’Elia, E. Study of patina formation on bronze specimens. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 115, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostan, R.; Varvara, S.; Găină, L.; Petrisor, T., Jr.; Mureşan, L.M. Protective effect of inhibitor-containing nitrocellulose lacquer on artificially patinated bronze. Prog. Org. Coat. 2016, 111, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidblad, J.; Kucera, V.; Sherwood, S. Corrosion. In The Effects of Air Pollution on Cultural Heritage; Hamilton, R., Kucera, V., Tidblad, J., Watt, J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 53–103. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi, E.; Chiavari, C.; Lenza, B.; Martini, C.; Morselli, L.; Ospitali, F.; Robbiola, L. The atmospheric corrosion of quaternary bronzes: The leaching action of acid rain. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticelli, C. Corrosion Inhibitors. In Encyclopedia of Interfacial Chemistry; Wandelt, K., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 164–171. [Google Scholar]
- Tasić, Ž.Z.; Petrović Mihajlović, M.B.; Radovanović, M.B.; Antonijević, M.M. New trends in corrosion protection of copper. Chem. Pap. 2019, 73, 2103–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Kumar, S.; Bahadur, I.; Verma, C.; Ebenso, E.E. Organic corrosion inhibitors for industrial cleaning of ferrous and non-ferrous metals in acidic solutions: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 256, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillard, D.A.; Cornell, J.S.; DuFresne, D.L.; Hernandez, M.T. Toxicity of benzotriazole and benzotriazole derivatives to three aquatic species. Water Res. 2001, 35, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvara, S.; Rotaru, I.; Popa, M.; Mureşan, L.M. Inhibition of bronze corrosion in aerated acidic solution using amino acids as environmentally friendly inhibitors. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2011, 56, 793–801. [Google Scholar]
- El Ibrahimi, B.; Jmiai, A.; Bazzi, L.; El Issami, S. Amino acids and their derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for metals and alloys. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 740–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosev, I.; Pavlinac, J.; Hodoscek, M.; Lesar, A. Amino acids as corrosion inhibitors for copper in acidic medium: Experimental and theoretical study. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2013, 78, 2069–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaubey, N.; Savita; Qurashi, A.; Chauhan, D.S.; Quraishi, M.A. Frontiers and advances in green and sustainable inhibitors for corrosion applications: A critical review. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 321, 114385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Ebenso, E.E.; Bahadur, I.; Quraishi, M.A. An overview on plant extracts as environmental sustainable and green corrosion inhibitors for metals and alloys in aggressive corrosive media. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 266, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, M. Natural polymers as corrosion inhibitors. In Organic Corrosion Inhibitors: Synthesis, Characterization, Mechanism, and Applications; Chandrabhan, V., Hussain, C.M., Ebenso, E.E., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 411–434. [Google Scholar]
- Zunita, M.; Kevin, Y.J. Ionic liquids as corrosion inhibitor: From research and development to commercialization. Results Eng. 2022, 15, 0562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, A.K.; Dewangan, S.; Vaidya, N. Carbohydrates and derivatives as green corrosion inhibitors. In Computational Modelling and Simulations for Designing of Corrosion Inhibitors: Fundamentals and Realistic Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 435–460. [Google Scholar]
- Gece, G. Drugs: A review of promising novel corrosion inhibitors. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 3873–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaszilcsin, N.; Ordodi, V.; Borza, A. Corrosion inhibitors from expired drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 431, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Shukla, M.; Mishra, R.; Gupta, C.; Tiwari, K.S.; Nigam, R.S. Drugs: On sustainable and green solution for the prevention of metallic corrosion. J. Bio- Tribo-Corros. 2023, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.A.; Kahissay, M.H.; Hailu, A.D. Pharmaceuticals wastage and pharmaceuticals waste management in public health facilities of Dessie town, North East Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, J.; Söderström, H.; Lindberg, R.H.; Phan, C.; Tysklind, M.; Larsson, D.G.J. Contamination of surface, ground, and drinking water from pharmaceutical production. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 2522–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, K.; Mahapatra, S.; Hibzur Ali, M. Pharmaceutical wastewater as emerging contaminants (EC): Treatment technologies, impact on environment and human health. Energy Nexus 2022, 6, 100076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupoi, T.; Leroux, Y.R.; Feier, B.; Cristea, C.; Geneste, F. Electrochemical and Photoelectrochemical Aptasensors for the Detection of Environmental Pharmaceutical Pollutants. Electrochim. Acta 2025, 530, 146396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Jaiswal, R.; Ahmad, S.; Ali, A.; Jaiswal, R.; Yadav, R.; Yadav, R.; Ahsan, R.; Dwivedi, T.; Sonali, S. Pharmaceutical Waste Management Using Functional Materials for Environmental Remediation. Sustain. Chem. One World 2025, 6, 100068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Ashique, S.; Zaheen Hassan, M.; Afzal, O.; Asiri, Y.I.; Kumar, P.; Dua, K.; Webster, T.J.; Altamimi, A.S.A.; Altamimi, M.A. Pharmaceutical Contaminants in Aquatic Systems, Conventional and Green Strategies, Recent Updates, Challenges and Policies, and Potential Outcomes. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 389, 122905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Chen, C.; Lai, R.W.S.; Xu, S.; Adedipe, D.T.; Zhou, G.J.; Boxall, A.B.A.; Brooks, B.W.; Leung, K.M.Y. A Robust Method to Quantify Pharmaceuticals for the United Nations Endorsed Global Estuaries Monitoring (GEM) Programme. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 215, 117860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarnieri, T.; Nascimento, J.R.; Leonan, M.; Brandão, P.R.; Seabra Pereira, C.D.; Choueri, R.B.; Hardt, E.; Moraes, M.L.L.; Calixto, L.A.; Pereira, V.J.; et al. Pharmaceuticals in the Environment: A Strategy for Prioritizing Molecules of Environmental Concern. Chemosphere 2024, 368, 143778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.L.; Boxall, A.B.A.; Kolpin, D.W.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Lai, R.W.S.; Galbán-Malagón, C.; Adell, A.D.; Mondon, J.; Mondon, J.; Marchant, R.A.; et al. Pharmaceutical pollution of the world’s rivers. Environ. Sci. 2022, 119, e2113947119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodin, T.; Fick, J.; Jonsson, M.; Klaminder, J. Dilute Concentrations of a Psychiatric Drug Alter Behavior of Fish from Natural Populations. Science 2013, 339, 814–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Saini, M.; Singh, S.D.; Prakash, V.; Das, A.; Bharathi Dasan, R.; Pandey, S.; Bohara, D.; Galligan, T.H.; Green, R.E.; et al. Diclofenac Is Toxic to the Steppe Eagle Aquila Nipalensis: Widening the Diversity of Raptors Threatened by NSAID Misuse in South Asia. Bird Conserv. Int. 2014, 24, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oaks, J.L.; Gilbert, M.; Virani, M.Z.; Watson, R.T.; Meteyer, C.U.; Rideout, B.A.; Shivaprasad, H.L.; Ahmed, S.; Chaudhry, M.J.I.; Arshad, M.; et al. Diclofenac Residues as the Cause of Vulture Population Decline in Pakistan. Nature 2004, 427, 630–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paut Kusturica, M.; Jevtic, M.; Ristovski, J.T. Minimizing the Environmental Impact of Unused Pharmaceuticals: Review Focused on Prevention. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1077974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvara, S.; Damian, G.; Bostan, R.; Popa, M. Inhibition effect of Tantum Rosa drug on the corrosion of copper in 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2022, 17, 220958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Ganjoo, R.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, A. Evaluation of drugs as corrosion inhibitors for metals: A brief review. In Advances in Chemical, Bio and Environmental Engineering; Bhavanam, A., Pandhare, N.N., Sahu, D., Kumar Ratan, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2022; pp. 1071–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Vaszilcsin, N.; Duca, D.A.; Flueraş, A.; Dan, M.L. Expired drugs as inhibitors in electrochemical processes—A mini-review. Stud. Univ. Babes-Bolyai Chem. 2019, 64, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanwer, S.; Shukla, S.K. Recent advances in the applicability of drugs as corrosion inhibitor on metal surface: A review. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 5, 100227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour-Ali, S.; Hejazi, S. Tiazofurin drug as a new and non-toxic corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in HCl solution: Experimental and quantum chemical investigations. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 354, 118886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, S.T.; Li, W.P.; Hu, G.; Li, X. Experimental and computational studies of two antibacterial drugs as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in acid media. Mater. Corros. 2014, 65, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minagalavar, R.L.; Rajappa, S.K.; Rathod, M.R.; Sajjan, A.M. Investigation of corrosion inhibition performance of expired fluconazole drug on mild steel in 0.5M H2SO4 medium. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 391, 12329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbar, J.C.; Swetha, G.A.; Rangappa, R.; Priyadarshini, D.; Patil, Y.; Megalamani, M.; Nagaraju, G.; Choudhuri, J.R. Unlocking the corrosion inhibition potential of expired chlorzoxazone on mild steel in acidic media: A synergistic approach with electrochemical, surface and computational insights. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 45, 112409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunach, A.K.; Rani, G.; Rajiv; Kumar, H.; Singh, G.; Bhawna, S. Exploring expired ciprofloxacin: A theoretical and experimental investigation of corrosion prevention for mild steel in acidic environments. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2025, 176, 114288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhawsar, J.; Jani, M.; Jain, P. Evaluating the corrosion inhibition potential of expired ivermectin drug on mild steel: A comprehensive multi-method investigation. Corros. Commun. 2025, 18, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.H.; Sharifi, R.; Javidparvar, A.A.; Nwanonenyi, S.C.; Oguzie, E.E.; Manfo, T.A. Repurposing expired Remdesivir as a sustainable anti-corrosion agent for plain steel in hcl medium: Insights from electrochemical and molecular dynamics studies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamedien, H.A.; Kamal, S.M.; Taha, M.; EL-Deeb, M.M.; El-Deen, A.G. Experimental and computational evaluations of cefotaxime sodium drug as an efficient and green corrosion inhibitor for aluminum in NaOH solution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 290, 126546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghaban, A.M.H.; Abdullah, H.A.; Anaee, R.A.; Naser, S.A.; Khadom, A.A. Expired butamirate drug as eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for aluminum in seawater: Experimental and theoretical studies. J. Eng. Res. 2024, 12, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, K.H.; Khadom, A.A.; Abbas, S.H.; Al-azawi, K.F.; Mahood, H.B. Optimization studies of expired mouthwash drugs on the corrosion of aluminum 7475 in 1 M hydrochloric acid: Gravimetrical, electrochemical, morphological and theoretical investigations. Results Surf. Interfaces 2023, 13, 100165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Haddad, M.N. Inhibitive action and adsorption behavior of cefotaxime drug at copper/hydrochloric acid interface: Electrochemical, surface and quantum chemical studies. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 57844–57853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvara, S.; Bostan, R.; Popa, M.; Gaina, L.; Popa, F. Doxepin as corrosion inhibitor for copper in 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution. Stud. Univ. Babes-Bolyai Chem. 2020, 65, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinović, I.; Pilić, Z.; Zlatić, G.; Soldo, V.; Šego, M. N-acetyl cysteine and D-Penicillamine as green corrosion inhibitors for copper in 3% NaCl. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2023, 18, 100238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.H.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Feng, M.T.; He, J.H.; Xu, Y.Q.; Liao, B.K. Unraveling the inhibitive performance and adsorption behavior of expired compound glycyrrhizin tablets as an eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for copper in acidic medium. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2025, 168, 105913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oubahou, M.; El aloua, A.; Benzbiria, N.; El Harrari, S.; Takky, D.; Naimi, Y.; Zeroual, A.; Wang, S.; Syed, A.; Belghiti, M.E. Electrochemical, thermodynamic and computational investigation of the use of an expired drug as a sustainable corrosion inhibitor for copper in 0.5 M H2SO4. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 323, 129642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaser, A.A.; El-Mahdy, M.S.; Mahmoud, E.E.E.; Fouda, A.S. Recycling of expired ciprofloxacin in synthetic acid rain (SAR) solution as a green corrosion inhibitor for copper: A theoretical and experimental evaluation. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2024, 54, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, M.M.; Abdou, S.N.; Anwar, Z.M.; Sherif, M.A.; Mostafa, N.Y. Reusing the expired ceftazidime drug as an inhibiting agent for zinc metal corrosion in HCl medium. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 8506–8522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swetha, G.A.; Sachin, H.P. A Study on use of telmisartan drug for corrosion inhibition of zinc in 0.1M hydrochloric acid: Surface characterization and quantum studies. Chem. Data Collect. 2021, 32, 100668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbar, J.C.; Swetha, G.A.; Sachin, H.P. Impact of an expired hemorheologic drug on the mitigation of zinc corrosion in acidic environment: Insights from chemical, electrochemical, and surface evaluation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 650, 129518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotaru, I.; Varvara, S.; Gaina, L.; Muresan, L.M. Antibacterial drugs as corrosion inhibitors for bronze surfaces in acidic solutions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 321, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, G.A.; Soliman, M.M.; Nasr, Z.A.; Hyba, A.M. Comprehensive investigation of sustainable corrosion inhibitors on Cu–Zn alloy in simulated cooling water: Electrochemical explorations, SEM/EDX analysis, and DFT/molecular simulations utilizing expired Bepotastine-B as a green inhibitor. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2024, 37, 101340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, V.; Afsharian, P.; Shahhoseini, M.; Kalantar, S.M.; Moini, A. A review on various uses of N-acetyl cysteine. Cell J. 2017, 19, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Tenório, M.C.D.S.; Graciliano, N.G.; Moura, F.A.; de Oliveira, A.C.M.; Goulart, M.O.F. N-Acetylcysteine (NAC): Impacts on human health. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazary, A.E.; Awwad, N.S.; Ibrahium, H.A.; Shati, A.A.; Alfaifi, M.Y.; Ju, Y.H. Protonation equilibria of N-acetylcysteine. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 9598–19605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ituen, E.B.; Akaranta, O.; Umoren, S.A. N-acetylcysteine based corrosion inhibitor formulations for steel protection in 15% HCl solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 246, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samide, A.; Dobriţescu, A.; Tigae, C.; Spînu, C.I.; Oprea, B. Experimental and computational study on inhibitory effect and adsorption properties of N-acetylcysteine amino acid in acid environment. Molecules 2023, 28, 6799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hafeza, G.M.; Badawy, W.A. The use of cysteine, N-acetyl cysteine and methionine as environmentally friendly corrosion inhibitors for Cu-10Al-5Ni alloy in neutral chloride solutions. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 108, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikić, D.; Otmačić Ćurković, H.; Hosseinpour, S. Bronze corrosion protection by long-chain phosphonic acids. Corros. Sci. 2022, 205, 110445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: www.smpharma.co.th/pdf/moredetails2.pdf?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Varvara, S.; Bostan, R.; Gainə, L.; Muresan, L.M. Thiadiazole derivatives as inhibitors for acidic media corrosion of artificially patinated bronze. Mater. Corros. 2014, 65, 1202–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marušić, K.; Ćurković, H.O.; Takenouti, H. Inhibiting effect of 4-methyl-1-p-tolylimidazole to the corrosion of bronze patinated in sulphate medium. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 7491–7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raistrick, I.D.; Franceschetti, D.R.; Macdonald, J.R. The electrical analogs of physical and chemical processes. In Impedance Spectroscopy Emphasizing Solid Materials and Systems; MacDonald, J.R., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Li, W.; Cao, K.; Hou, B. Potent inhibition of copper corrosion in neutral chloride media by novel non-toxic thiadiazole derivatives. Corros. Sci. 2013, 73, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epelboin, I.; Gabrielli, C.; Keddam, M.; Takenouti, H. Alternating-Current impedance measurements applied to corrosion studies and corrosion-rate determination. In Electrochemical Corrosion Testing; Mansfeld, F., Bertocci, U., Eds.; ASTM International: Pennsylvania, PA, USA, 1981; Vol. STP 727. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Fan, B.; Zhao, J.; Yang, B.; Zheng, X. Benzothiazole derivatives-based supramolecular assemblies as efficient corrosion inhibitors for copper in artificial seawater: Formation, interfacial release and protective mechanisms. Corros. Sci. 2023, 212, 110957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Tegus, O. The corrosion properties of bronze alloys in NaCl solutions. Materials 2023, 16, 5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Odnevall Wallinder, I.; Leygraf, C. Mechanistic studies of corrosion product flaking on copper and copper-based alloys in marine environments. Corros. Sci. 2014, 85, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odnevall Wallinder, I.; Zhang, X.; Goidanich, S.; Le Bozec, N.; Herting, G.; Leygraf, C. Corrosion and runoff rates of cu and three Cu-alloys in marine environments with increasing chloride deposition rate. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.; Maltseva, A.; Volovitch, P.; Odnevall Wallinder, I.; Leygraf, C. A mechanistic study of stratified patina evolution on Sn-bronze in chloride-rich atmospheres. Corros. Sci. 2020, 166, 108477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zheng, H.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, X.; Yan, Z.; Sun, Y.; Li, X. Insight into the anti–corrosion behavior of Reineckia Carnea leaves extract as an eco–friendly and high–efficiency corrosion inhibitor. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 188, 115640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Guo, X. The Relationship between the inhibition performances of three benzo derivatives and their structures on the corrosion of copper in 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 598, 124809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvara, S.; Gaina, L.; Bostan, R.; Popa, F.; Grozav, A. Some phenothiazinyl-thiazolyl-hydrazine derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for carbon steel in 1.0 M HCl: Electrochemical, SEM-EDX and DFT investigations. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 8338–8364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, M.B.; Radovanović, M.B.; Simonović, A.T.; Milić, S.M.; Antonijević, M.M. The effect of cysteine on the behaviour of copper in neutral and alkaline sulphate solutions. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 9043–9057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanila, A.; Marcu, A.; Rusu, D.; Rusu, M.; David, L. Spectroscopic studies of some copper(II) complexes with amino acids. J. Mol. Struct. 2007, 834–836, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, J.G.; McClure, J.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Synthesis and structural analysis of copper(II) cysteine complexes. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2009, 36, 395–401. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacevic, N.; Milosev, I.; Kokalj, A. The roles of mercapto, benzene, and methyl groups in the corrosion inhibition of imidazoles on copper: II. Inhibitor–copper bonding. Corr. Sci. 2015, 98, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.A. Copper and Bronze in Art: Corrosion, Colorants, Conservation; Getty Conservation Institute: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-0-89236-638-5. [Google Scholar]
- Gyöngyösi, S.; Szabó, G.; Barkóczy, P.; Cseh, J. Metallographic investigation of the bronze sword from Vértesszőlős. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 2023, 12, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, A.S.; Figueiredo, E.; Águas, H.; Silva, R.J.C. Characterisation of archaeological high-tin bronze corrosion structures. Stud. Conserv. 2020, 67, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
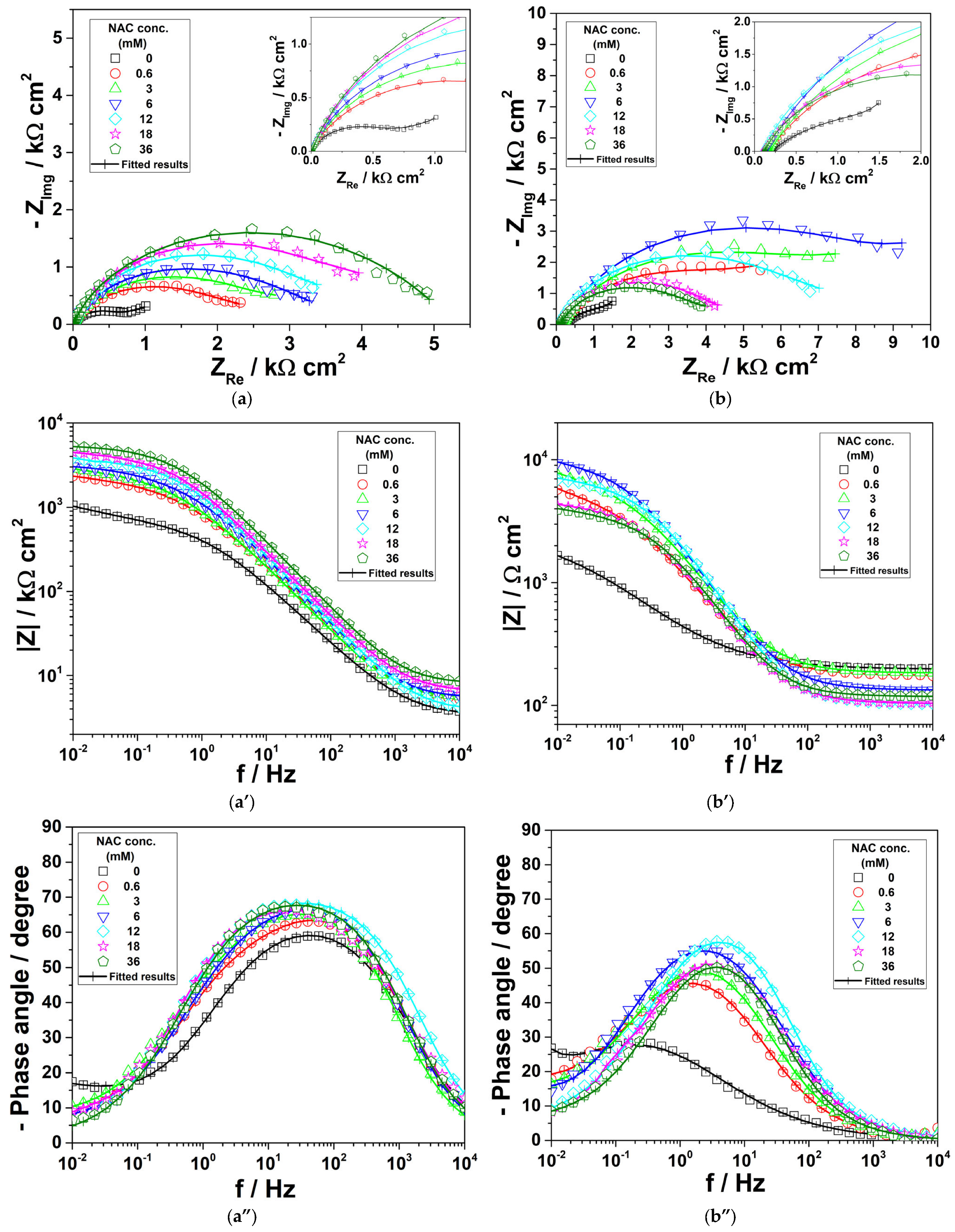
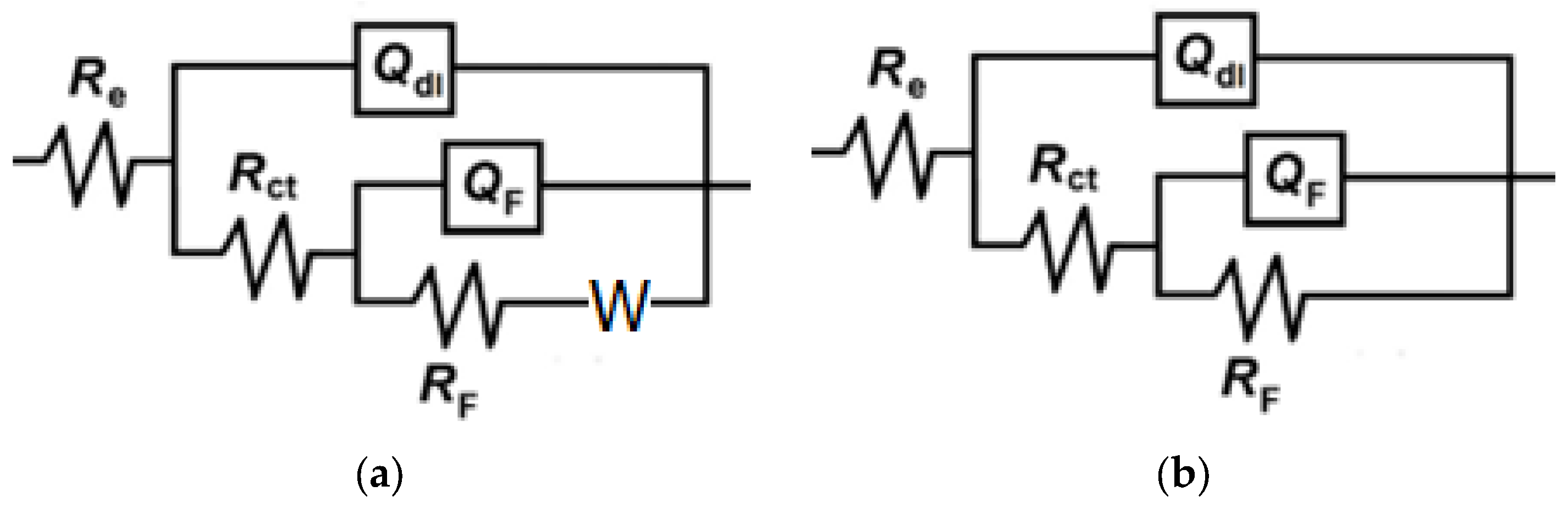

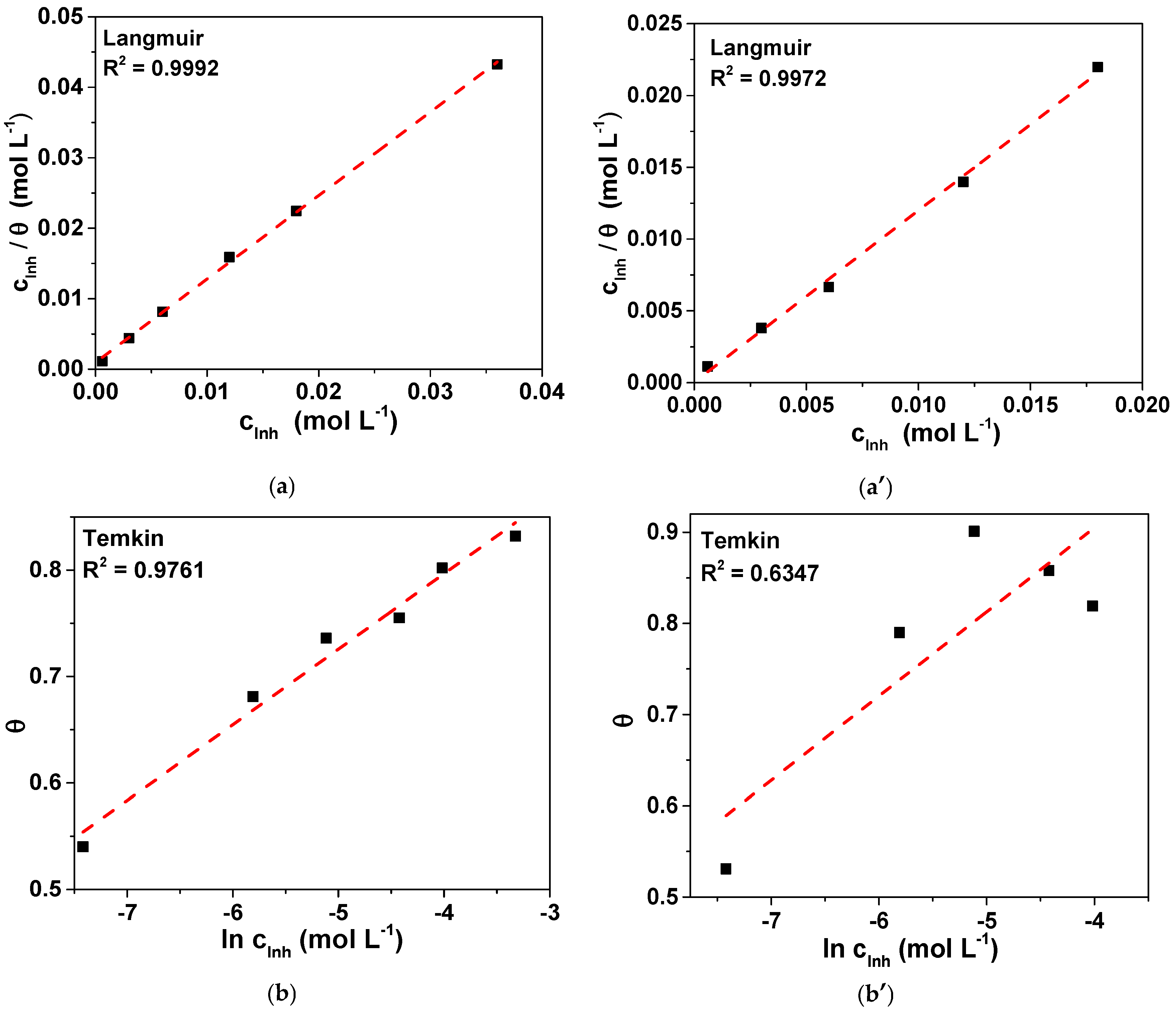
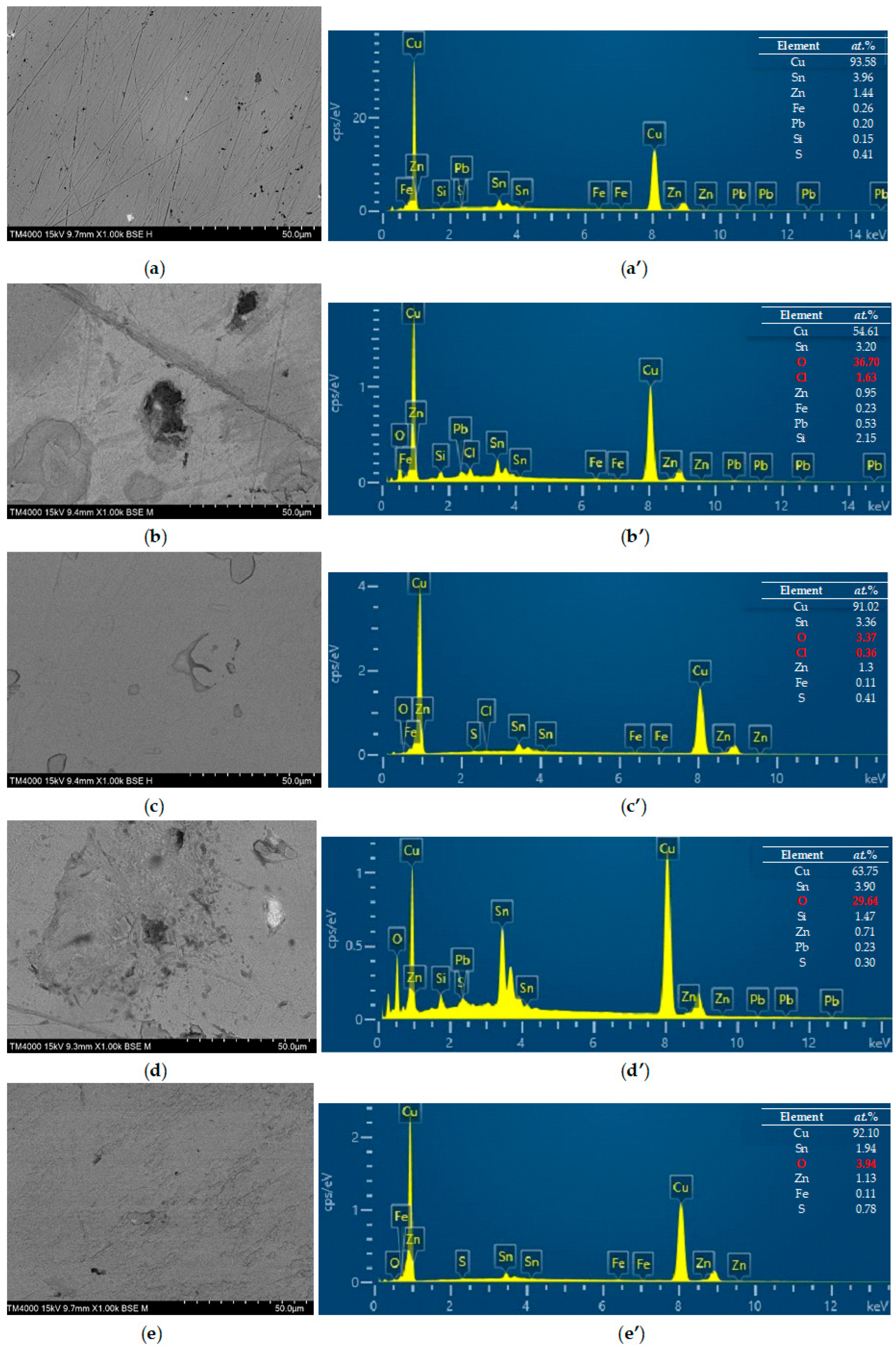
| Cu | Sn | Pb | Zn | Fe | S | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 93.58 | 3.96 | 0.20 | 1.44 | 0.26 | 0.41 | 0.15 |
| NAC conc. (mM) | Re (kΩ cm2) | Rct (kΩ cm2) | Qdl (μF sn−1cm−2) | ndl | Cdl (μF cm−2) | RF (kΩ cm2) | QF (mF sn−1cm−2) | nF | CF (mF cm−2) | Rp (kΩ cm2) | W (S s1/2 cm−2) | ηimp (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.5% NaCl solution | ||||||||||||
| 0 | 3.4 | 0.51 | 326.9 | 0.755 | 182.6 | 0.27 | 1.38 | 0.676 | 0.86 | 0.78 | 0.0095 | - |
| 0.6 | 3.5 | 1.08 | 182.5 | 0.781 | 115.6 | 1.58 | 0.66 | 0.500 | 0.68 | 2.66 | 70.7 | |
| 3 | 4.8 | 1.37 | 178.1 | 0.797 | 124.4 | 1.77 | 0.62 | 0.526 | 0.60 | 3.14 | 75.2 | |
| 6 | 5.3 | 1.51 | 134.0 | 0.809 | 91.9 | 1.81 | 0.51 | 0.500 | 0.46 | 3.32 | 76.5 | |
| 12 | 4.7 | 1.96 | 140.4 | 0.791 | 99.8 | 1.90 | 0.64 | 0.500 | 0.77 | 3.86 | 79.8 | |
| 18 | 6.5 | 2.93 | 119.2 | 0.796 | 91.1 | 2.06 | 0.52 | 0.500 | 0.57 | 4.99 | 84.4 | |
| 36 | 8.0 | 3.49 | 86.2 | 0.810 | 65.0 | 2.39 | 0.41 | 0.500 | 0.39 | 5.88 | 86.7 | |
| 0.2 g L−1 NaHCO3 + 0.2 g L−1 Na2SO4 + 0.2 g L−1 NaNO3, pH = 3.4 solution | ||||||||||||
| 0 | 0.2 | 0.22 | 653.1 | 0.600 | 178.2 | 1.01 | 5.51 | 0.738 | 10.2 | 1.23 | 0.0043 | - |
| 0.6 | 1.8 | 4.64 | 220.4 | 0.705 | 222.5 | 1.52 | 1.85 | 0.650 | 3.24 | 6.16 | 80.0 | |
| 3 | 1.8 | 7.09 | 156.4 | 0.716 | 162.9 | 3.08 | 4.49 | 0.928 | 5.51 | 10.17 | 87.9 | |
| 6 | 1.3 | 9.20 | 95.9 | 0.744 | 91.8 | 3.35 | 1.30 | 0.959 | 1.39 | 12.55 | 90.2 | |
| 12 | 1.0 | 5.38 | 113.8 | 0.794 | 100.2 | 3.29 | 0.94 | 0.500 | 2.89 | 8.67 | 85.8 | |
| 18 | 1.1 | 3.87 | 176.0 | 0.740 | 153.8 | 1.19 | 3.30 | 0.65 | 6.87 | 5.06 | 77.9 | |
| 36 | 1.2 | 3.02 | 148.4 | 0.771 | 116.8 | 1.61 | 1.59 | 0.500 | 4.04 | 4.63 | 75.8 | |
| NAC (mM) | Ecorr (mV vs. ESC) | icorr (μA cm−2) | |βc| (mV dec−1) | βa (mV dec−1) | ηpol (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution | |||||
| 0 | −229.4 | 221.3 | 70.0 | 67.4 | - |
| 0.6 | −279.8 | 101.9 | 186.9 | 129.5 | 54.0 |
| 3 | −293.8 | 69.5 | 142.9 | 70.6 | 68.1 |
| 6 | −286.8 | 58.5 | 143.0 | 73.2 | 73.6 |
| 12 | −300.7 | 54.3 | 131.9 | 78.5 | 75.5 |
| 18 | −291.8 | 43.8 | 156.1 | 95.4 | 80.2 |
| 36 | −328.7 | 34.6 | 202.3 | 121.7 | 83.2 |
| 0.2 g L−1 NaHCO3 + 0.2 g L−1 Na2SO4 + 0.2 g L−1 NaNO3, pH = 3.4 solution | |||||
| 0 | −52.2 | 24.3 | 83.9 | 46.9 | - |
| 0.6 | −88.8 | 11.4 | 82.1 | 58.2 | 53.1 |
| 3 | −145.8 | 4.4 | 74.5 | 92.3 | 81.9 |
| 6 | −185.5 | 2.4 | 118.0 | 93.9 | 90.1 |
| 12 | −214.1 | 3.8 | 157.7 | 80.8 | 85.8 |
| 18 | −249.4 | 4.4 | 223.3 | 139.6 | 81.9 |
| Electrolyte | Slope | K (L mol−1) | (kJ mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.5 wt. % NaCl | 1.18 | 1044.9 | −27.2 |
| 0.2 g L−1 NaHCO3 + 0.2 g L−1 Na2SO4 + 0.2 g L−1 NaNO3, pH = 3.4 | 1.19 | 25,839.8 | −35.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varvara, S. Reusing an Expired Drug as a Sustainable Corrosion Inhibitor for Bronze in 3.5% NaCl and Simulated Acid Rain Solutions. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6637. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126637
Varvara S. Reusing an Expired Drug as a Sustainable Corrosion Inhibitor for Bronze in 3.5% NaCl and Simulated Acid Rain Solutions. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(12):6637. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126637
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarvara, Simona. 2025. "Reusing an Expired Drug as a Sustainable Corrosion Inhibitor for Bronze in 3.5% NaCl and Simulated Acid Rain Solutions" Applied Sciences 15, no. 12: 6637. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126637
APA StyleVarvara, S. (2025). Reusing an Expired Drug as a Sustainable Corrosion Inhibitor for Bronze in 3.5% NaCl and Simulated Acid Rain Solutions. Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6637. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126637






