Personality Emulation Utilizing Large Language Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
Ethical Implications of Fake Identities and LLMs
2. Literature Review
2.1. Psychometric Personality Models
2.2. Determining Big Five Characteristics from Online Data
2.3. LLM Model Comparison
2.4. Personality Emulation and LLMs
2.5. Fake Identities and the Use & Abuse Project
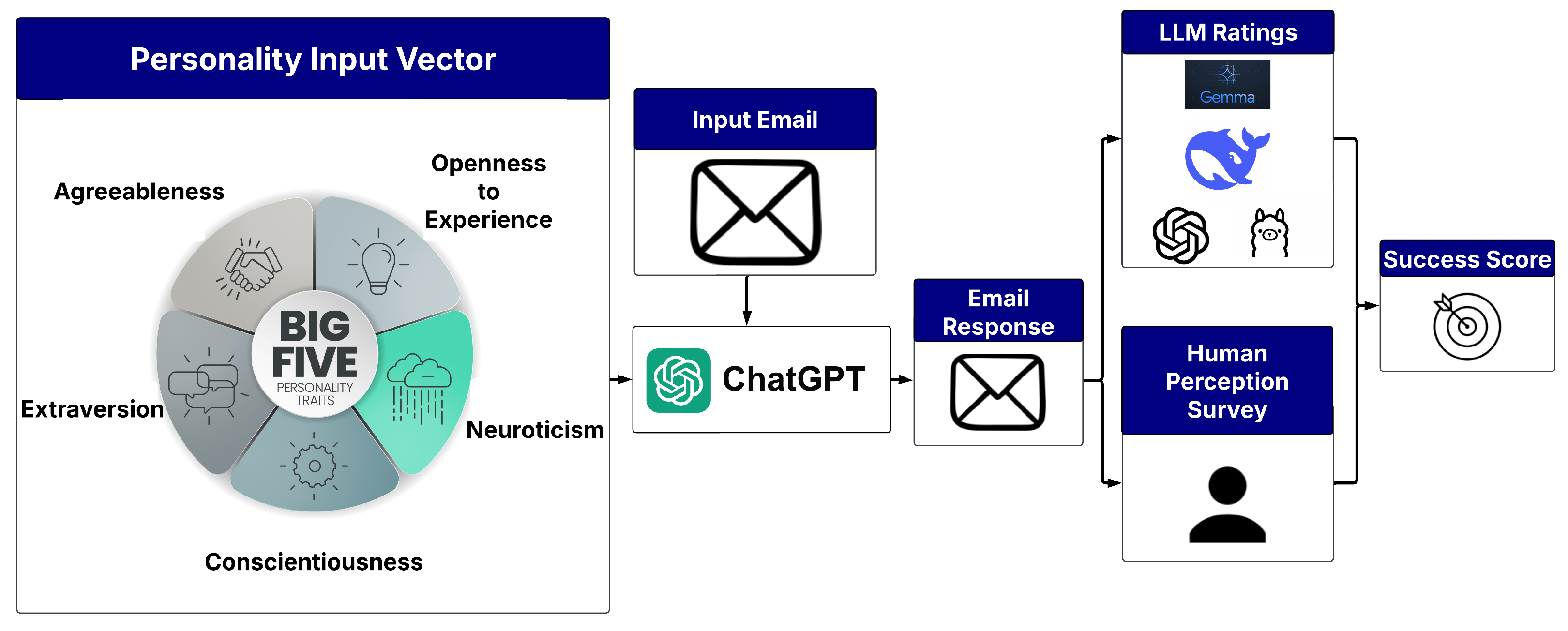
3. Methodology
3.1. Personality Profile Creation
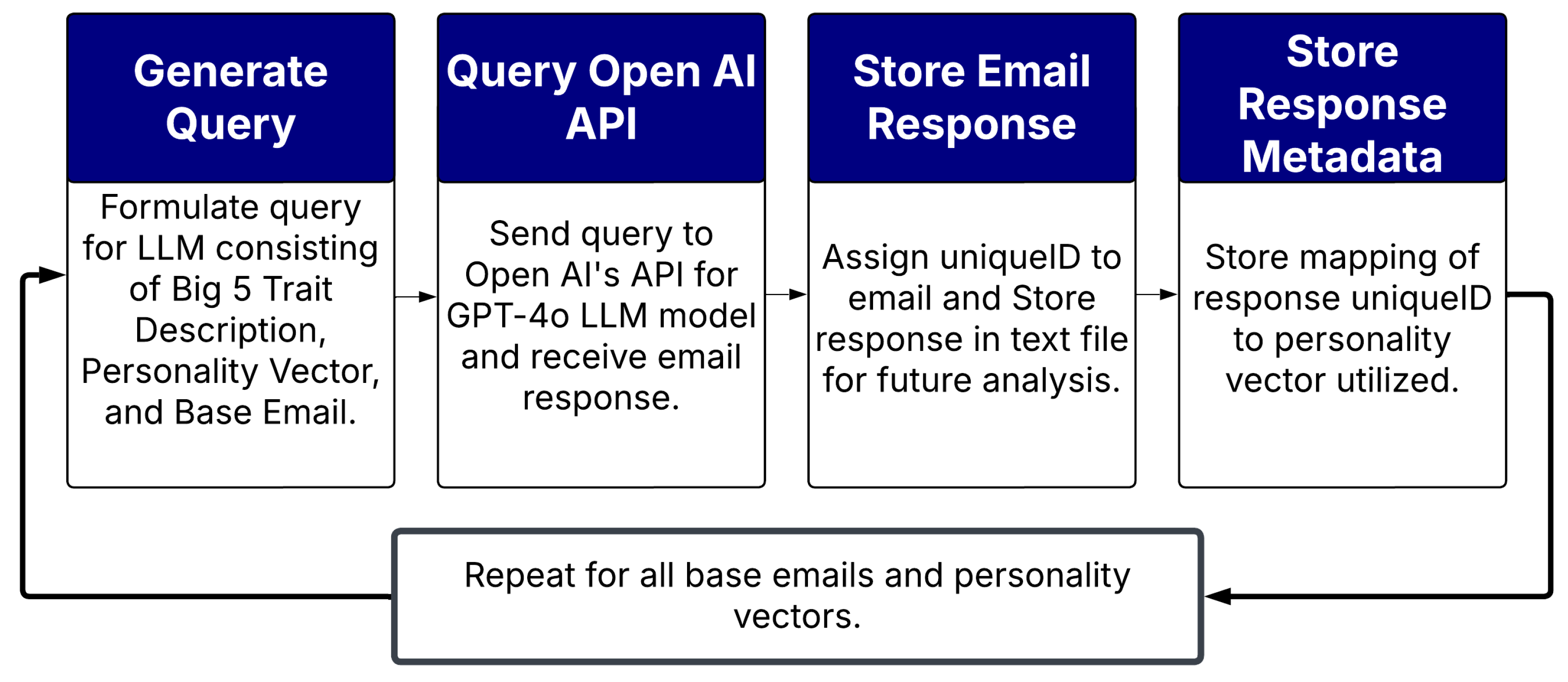
3.2. Email Creation and Response Generation
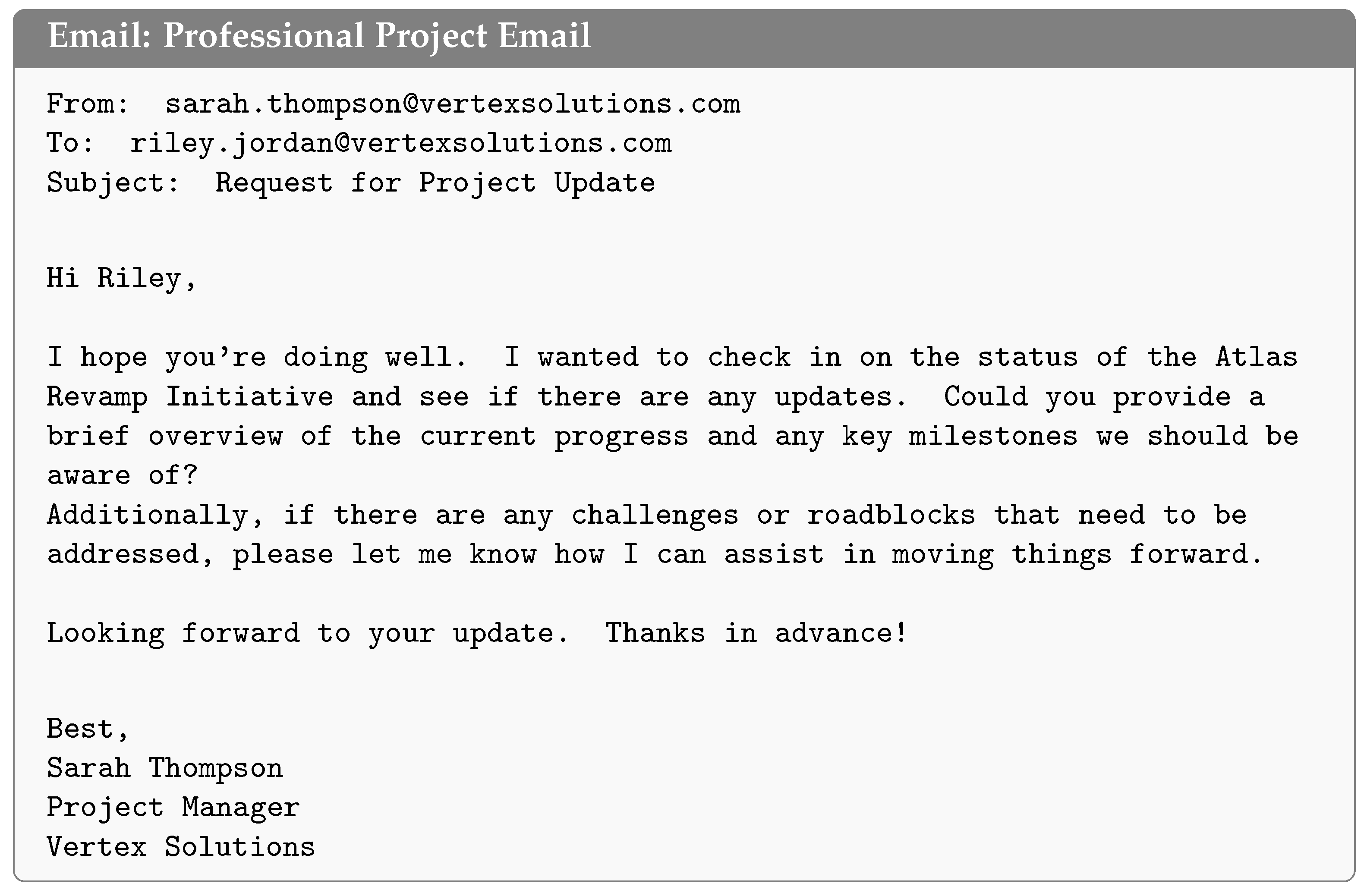
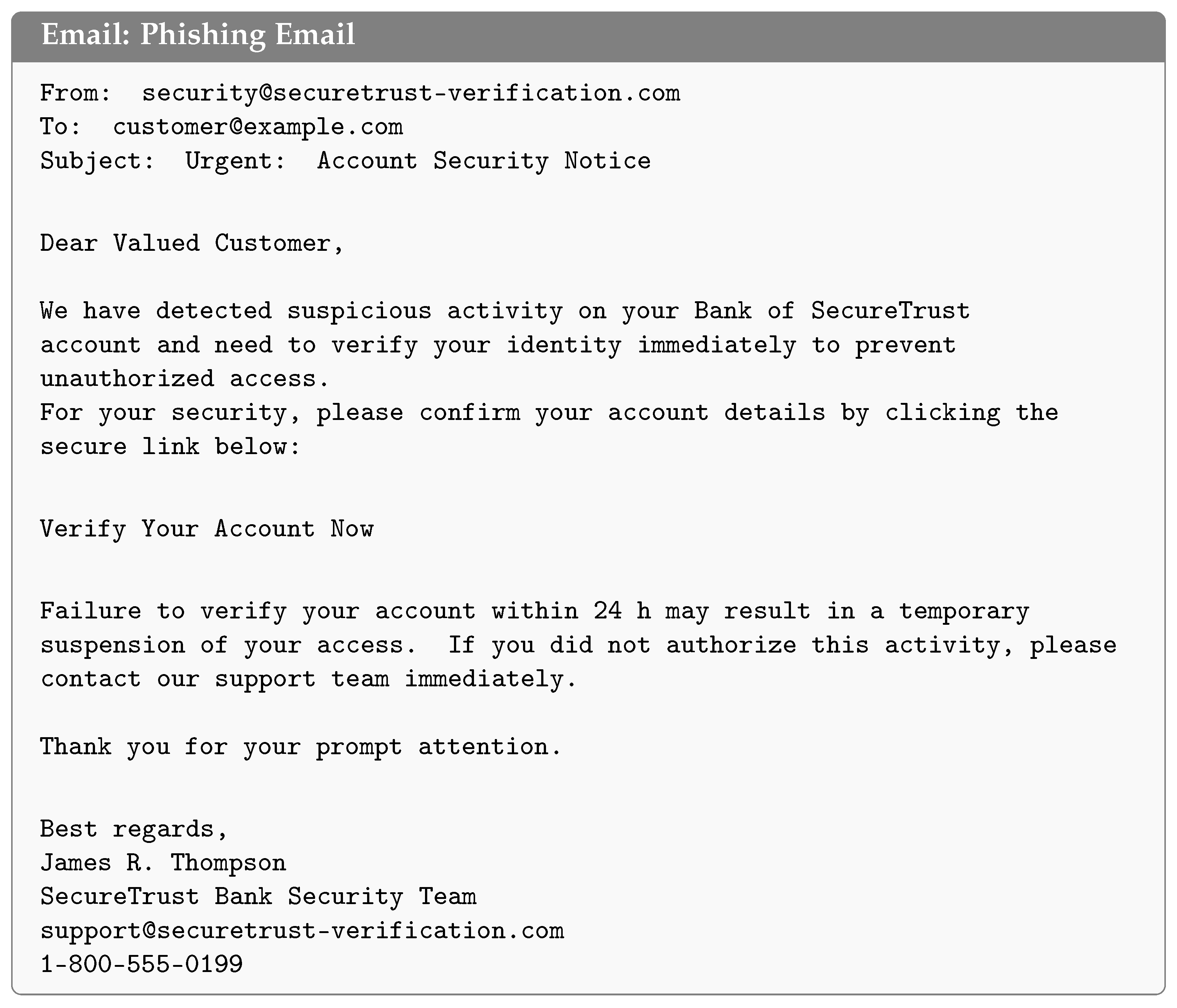
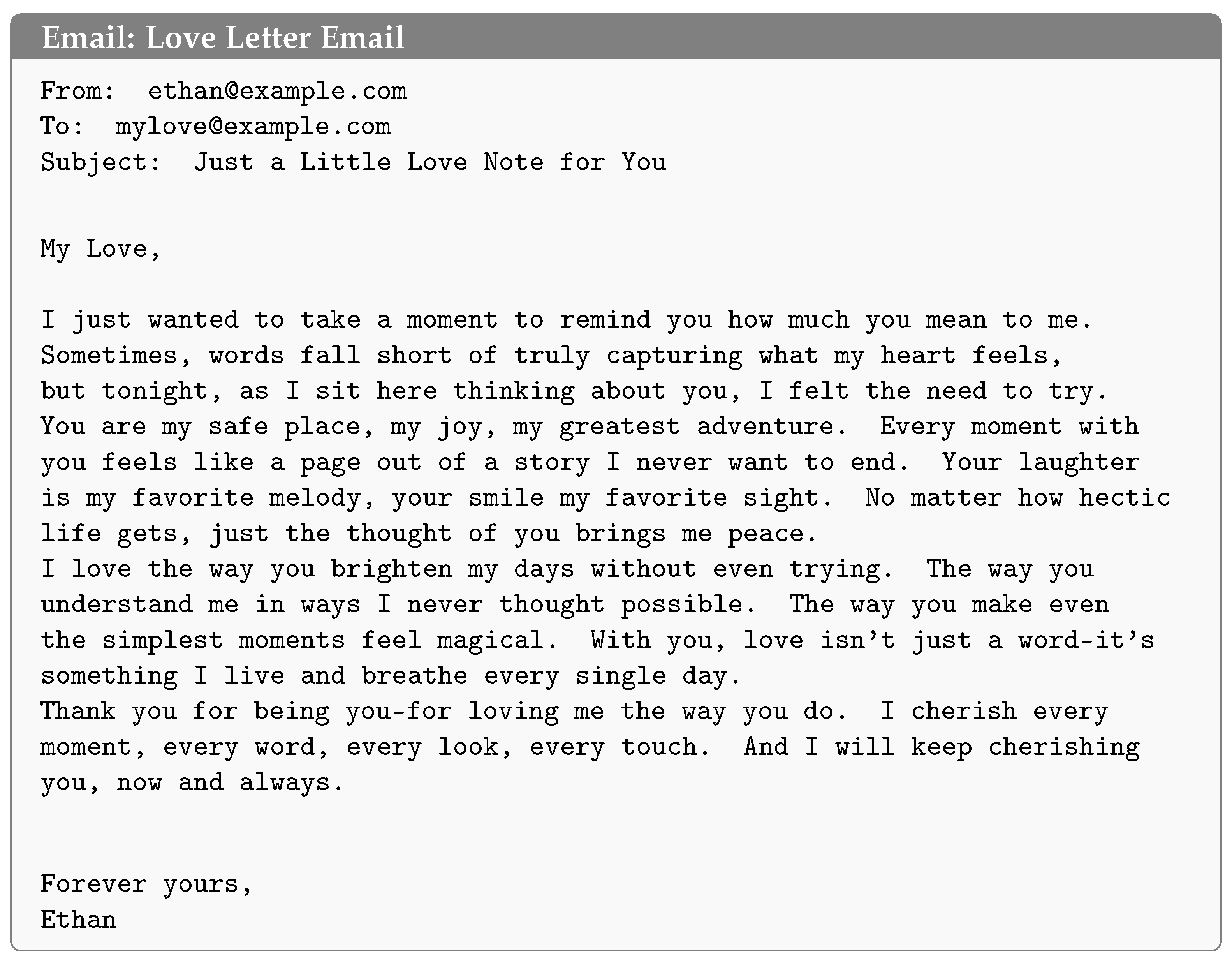
3.2.1. Email Base Set Creation
3.2.2. Response Generation and Collection
3.3. LLM Personality Ratings
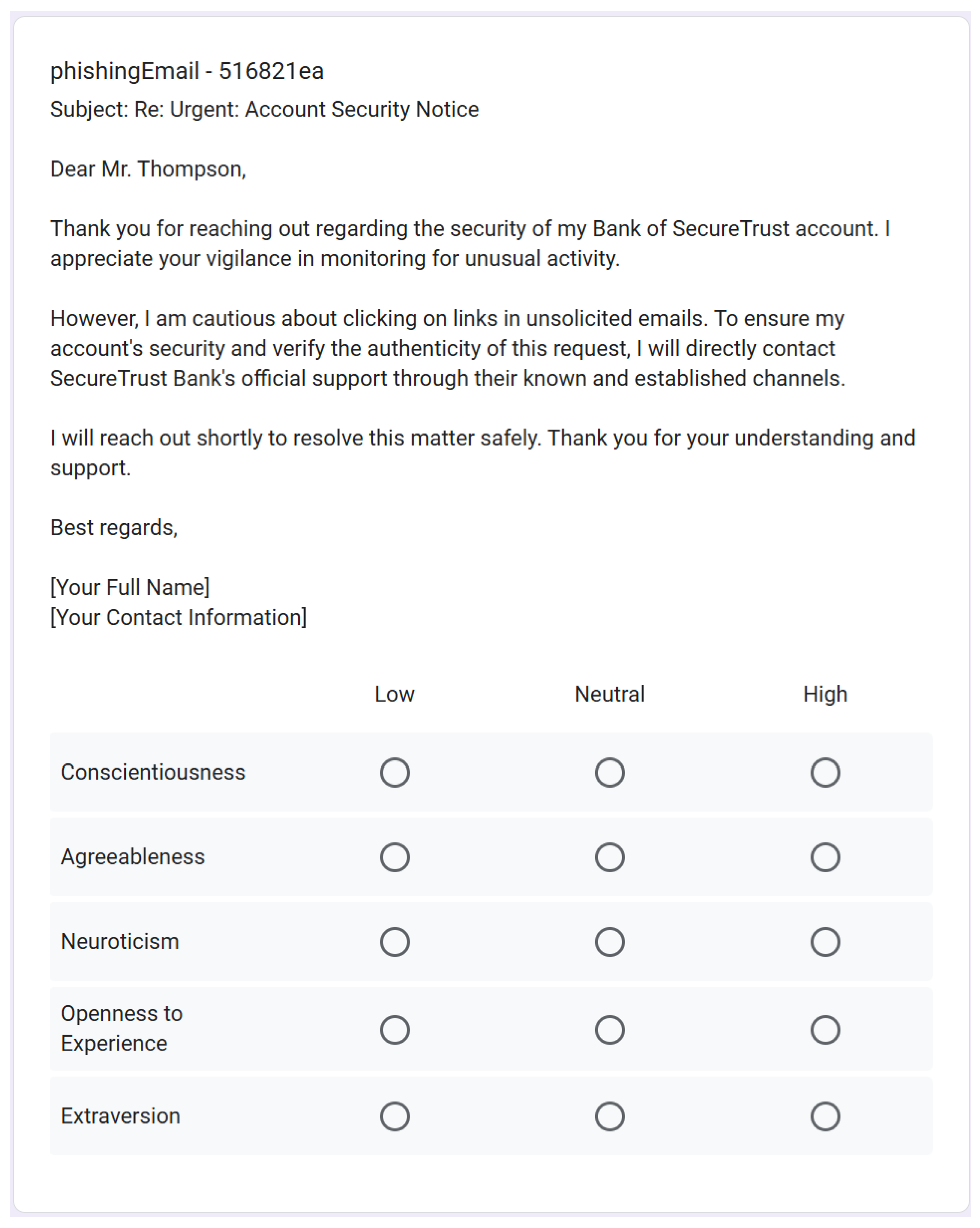
3.4. Human Perception Survey
4. Results
4.1. LLM Validation Results
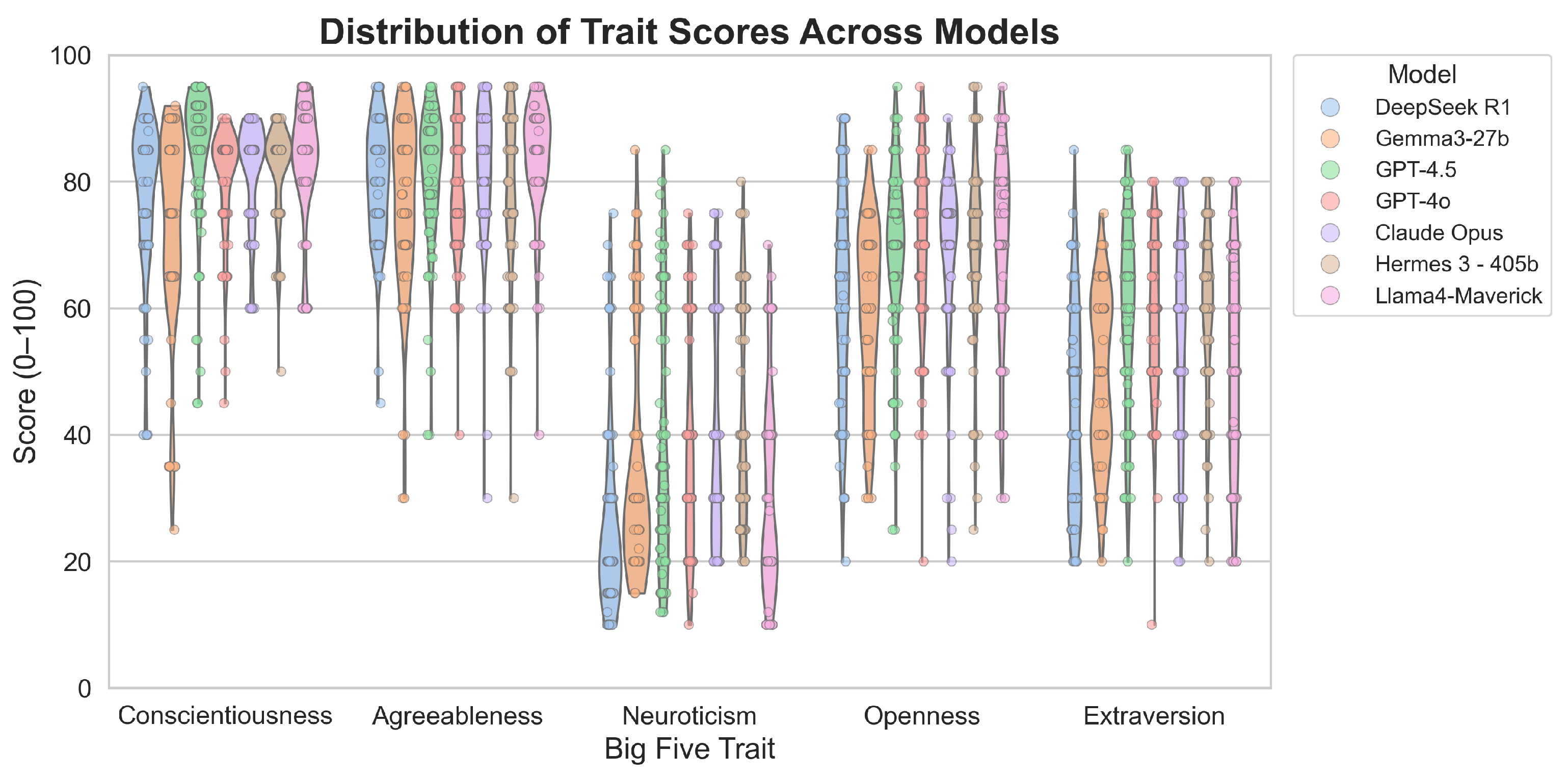
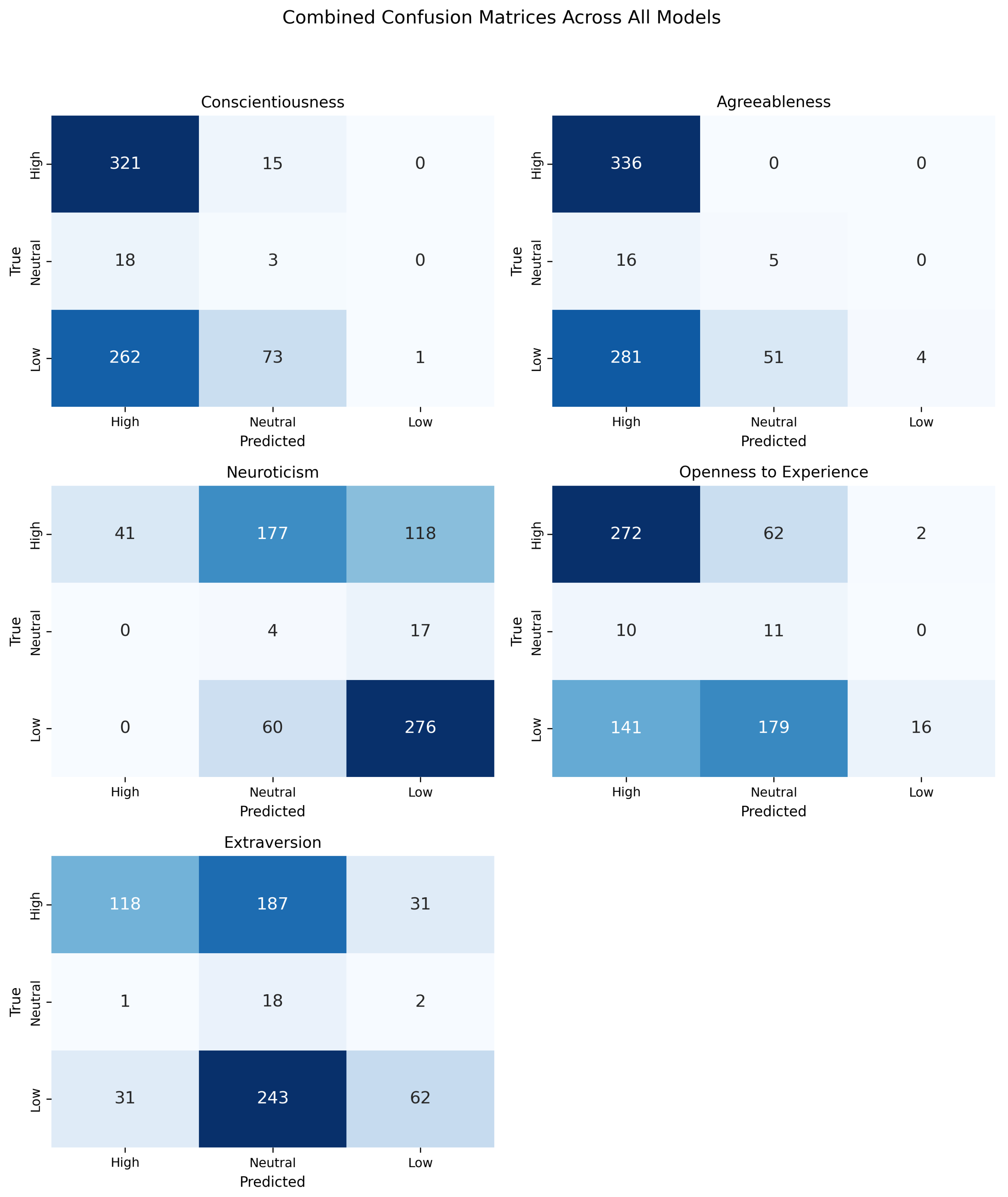
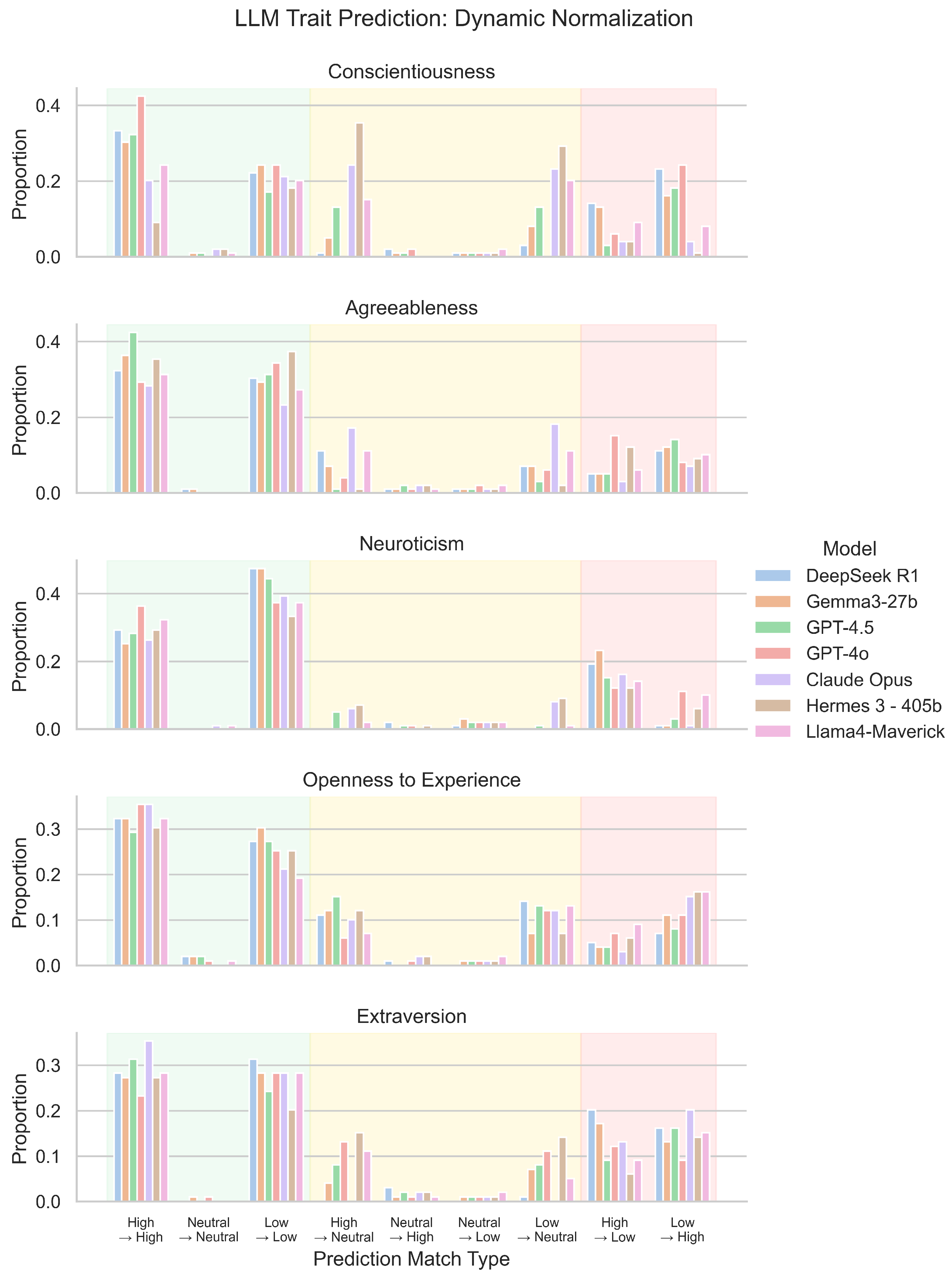
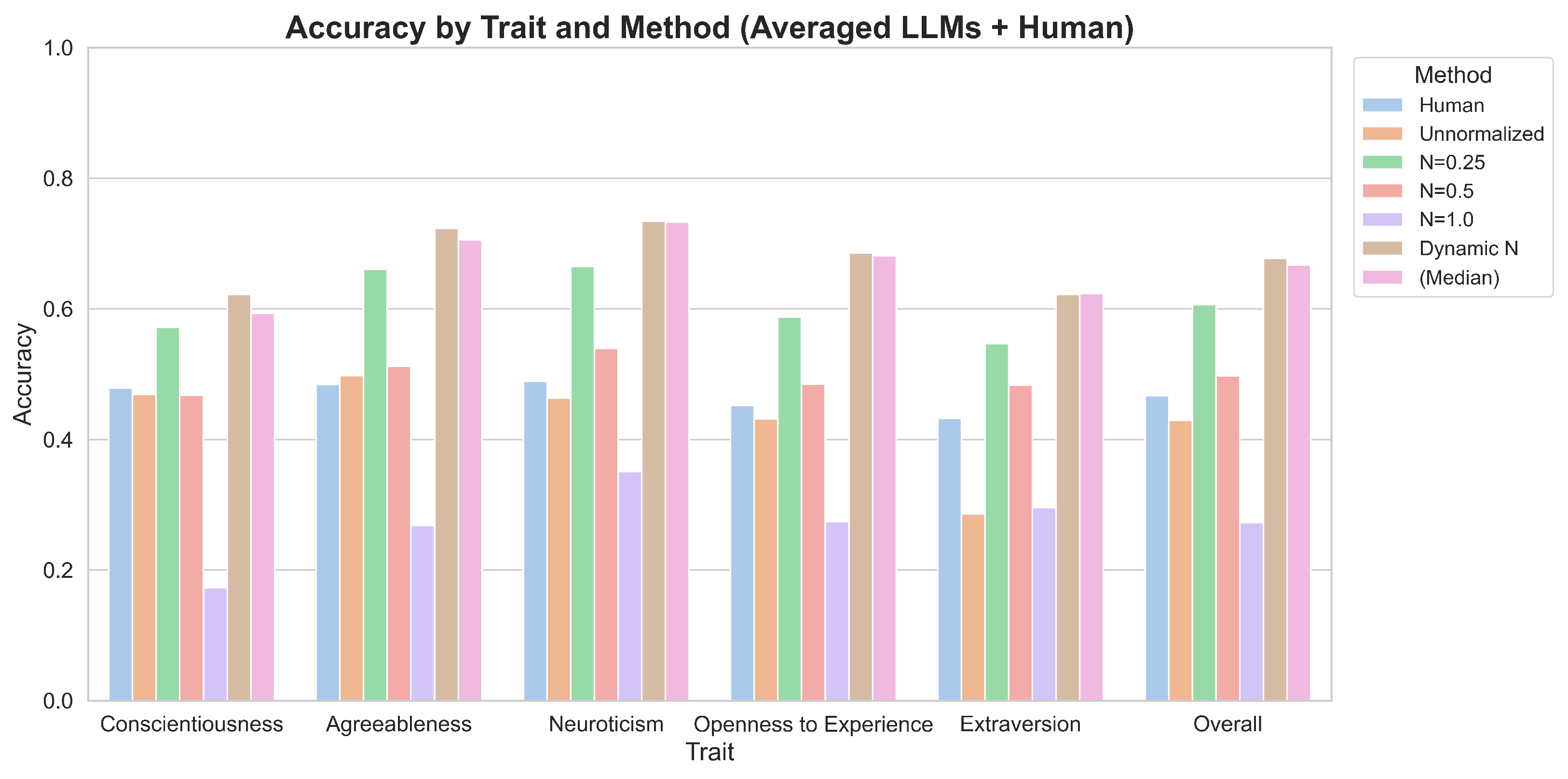
4.1.1. Non-Normalized LLM Data
4.1.2. Normalization with Standard Deviation
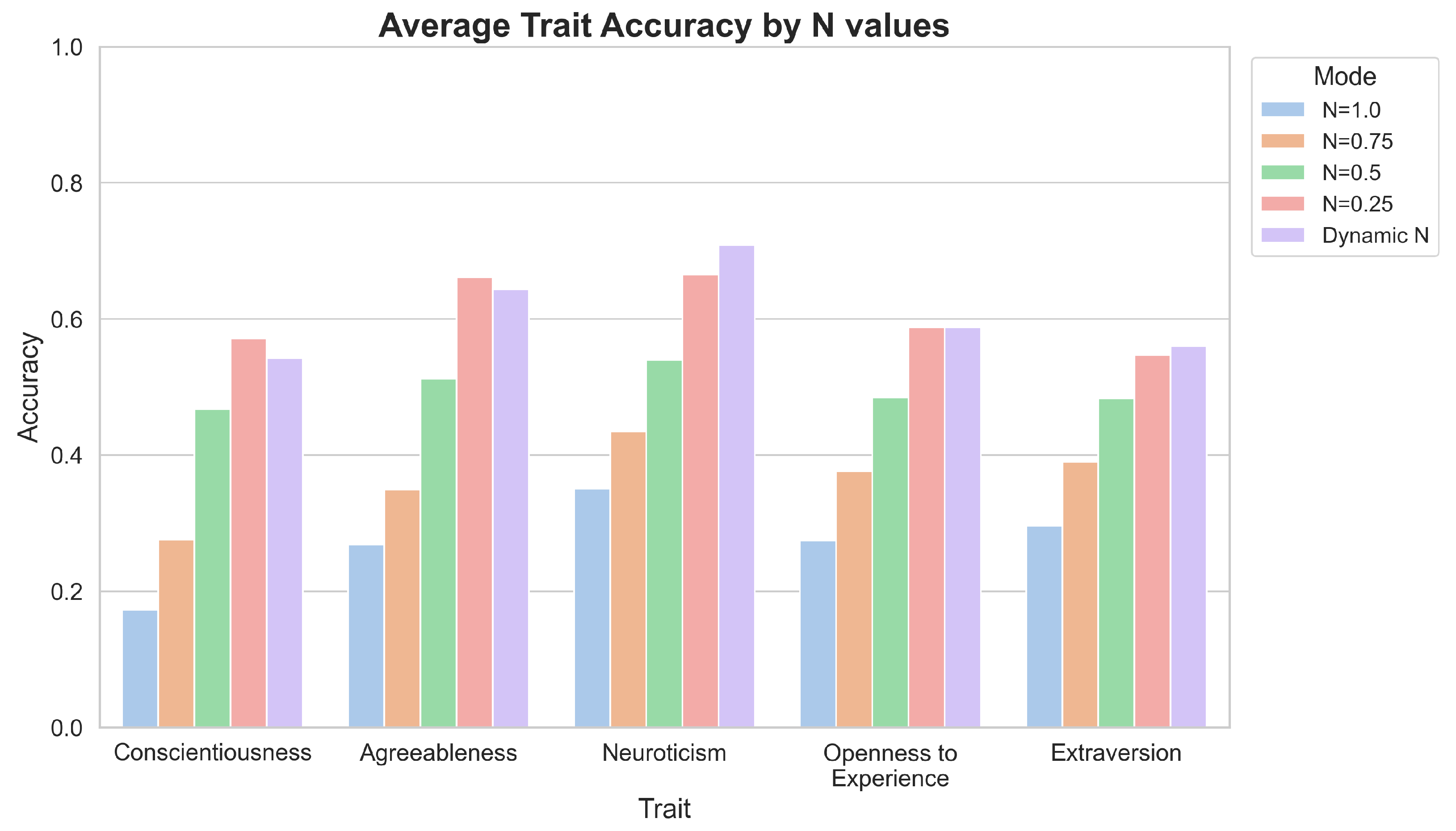
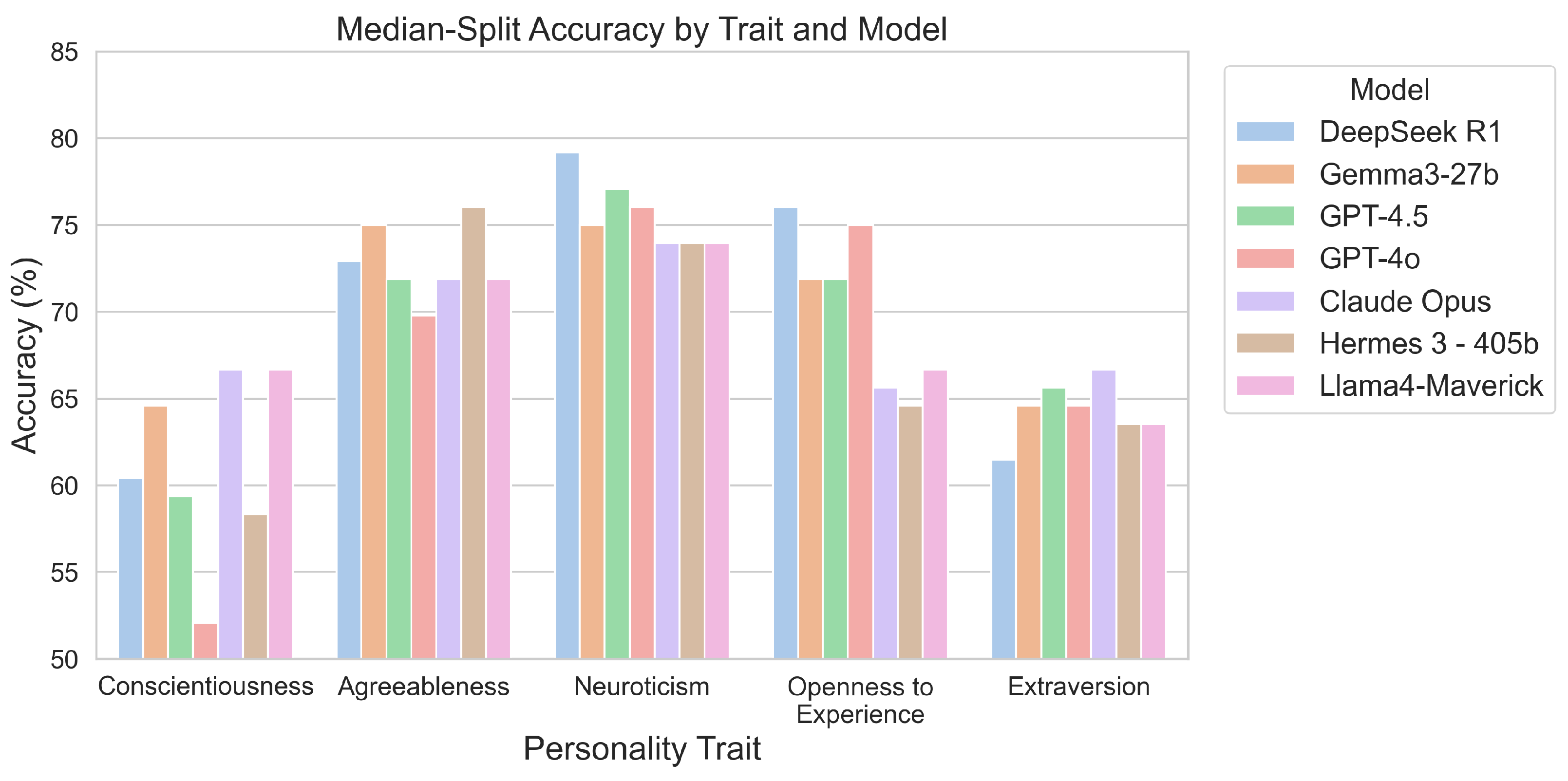
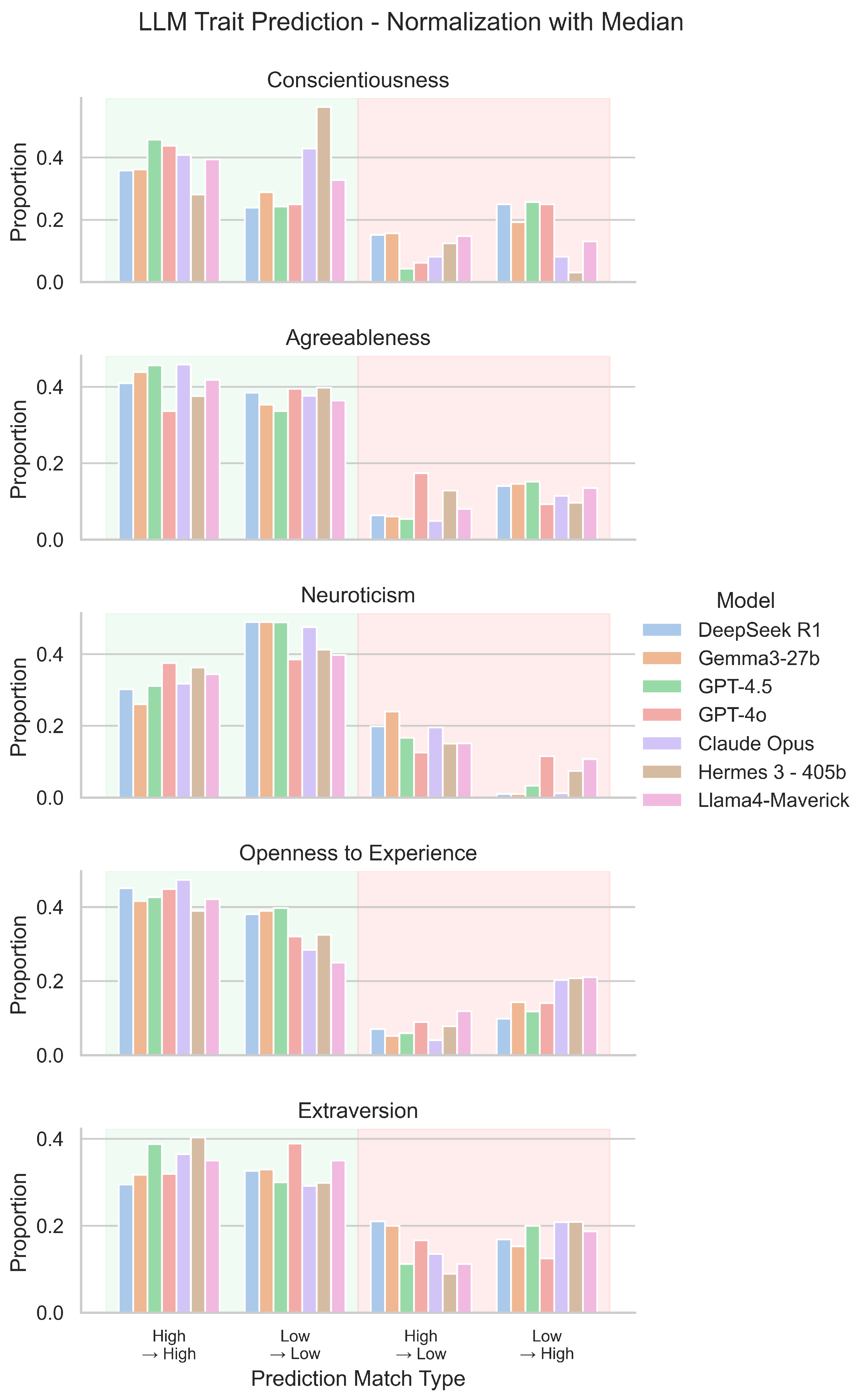
4.1.3. Normalization Utilizing Median
4.2. Human Perception Validation Results
4.3. Overall Validation Results
5. Conclusions
6. Future Work
- Investigation and formulation of the ethical model for fake identity OSINT and LLM applications
- Analysis of alternative personality models
- Analysis of alternative LLM Models
- Investigation of LLM capability in extended conversations and alternative communication contexts
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elovici, Y.; Fire, M.; Herzberg, A.; Shulman, H. Ethical Considerations when Employing Fake Identities in Online Social Networks for Research. Sci. Eng. Ethics 2014, 20, 1027–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolenbrander, J.; Husmann, E.; Henshaw, C.; Rheault, E.; Boswell, M.; Michaels, A.J. Use & Abuse of Personal Information, Part II: Robust Generation of Fake IDs for Privacy Experimentation. J. Cybersecur. Priv. 2024, 4, 546–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheault, E.; Nerayo, M.; Leonard, J.; Kolenbrander, J.; Henshaw, C.; Boswell, M.; Michaels, A.J. Use and Abuse of Personal Information, Part I: Design of a Scalable OSINT Collection Engine. J. Cybersecur. Priv. 2024, 4, 572–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurajala, S.; White, J.S.; Hudson, B.; Matthews, J.N. Fake Twitter Accounts: Profile Characteristics Obtained Using an Activity-Based Pattern Detection Approach. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Social Media & Society, Toronto, ON, Canada, 27–29 July 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, S.; El-Tazi, N.; Mokhtar, H.M.O. Detecting Fake Accounts on Social Media. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Seattle, WA, USA, 10–13 December 2018; pp. 3672–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyusufi, Y.; Elyusufi, Z.; Kbir, M.A. Social Networks Fake Profiles Detection Based on Account Setting and Activity. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Smart City Applications, Casablanca, Morocco, 2–4 October 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y. Large Language Model and Text Generation. In Natural Language Processing in Biomedicine: A Practical Guide; Xu, H., Demner Fushman, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 265–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Qin, H.; Dong, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Li, Z. Large Language Model (LLM) AI text generation detection based on transformer deep learning algorithm. arxiv 2024, arXiv:2405.06652. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, A.; Coenen, A.; Reif, E.; Ippolito, D. Wordcraft: Story Writing With Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, Helsinki, Finland, 22–25 March 2022; pp. 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallwork, A. Using Large Language Models to Improve, Correct and Generate Your Emails. In English for Academic Research: Grammar Exercises; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiergart, J.; Huber, S.; Übellacker, T. Understanding Emails and Drafting Responses—An Approach Using GPT-3. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.03062. [Google Scholar]
- Ait Baha, T.; El Hajji, M.; Es-Saady, Y.; Fadili, H. The Power of Personalization: A Systematic Review of Personality-Adaptive Chatbots. SN Comput. Sci. 2023, 4, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrae, R.R.; John, O.P. An Introduction to the Five-Factor Model and Its Applications. J. Pers. 1992, 60, 175–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foundation, M.B. Myers-Briggs Overview. 2023. Available online: https://www.myersbriggs.org/my-mbti-personality-type/myers-briggs-overview/ (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- The VIA Institute. VIA Character Strengths Survey & Character Reports: Via Institute. Available online: https://www.viacharacter.org/ (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Sutcliffe, R. A Survey of Personality, Persona, and Profile in Conversational Agents and Chatbots. arxiv 2023, arXiv:2401.00609. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Kim, J. Personality of AI. In Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing; Rutkowski, L., Scherer, R., Korytkowski, M., Pedrycz, W., Tadeusiewicz, R., Zurada, J.M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 244–252. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Yan, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Li, J. Neuronal Correlates of Individual Differences in the Big Five Personality Traits: Evidences from Cortical Morphology and Functional Homogeneity. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Woude, M.; Dodds, T.; Torres, G. The ethics of open source investigations: Navigating privacy challenges in a gray zone information landscape. Journalism 2024, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hribar, G.; Podbregar, I.; Ivanuša, T. OSINT: A “Grey Zone”? Int. J. Intell. Counterintell. 2014, 27, 529–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S. The Art of Open Source Intelligence (OSINT): Addressing Cybercrime, Opportunities, and Challenges. 2025. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=5281845 (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Desai, S.; Dubiel, M.; Zargham, N.; Mildner, T.; Spillner, L. Personas Evolved: Designing Ethical LLM-Based Conversational Agent Personalities. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.20513. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.; Zhan, X.; Such, J. Building Better AI Agents: A Provocation on the Utilisation of Persona in LLM-based Conversational Agents. In Proceedings of the 6th ACM Conference on Conversational User Interfaces, Luxembourg, 8–10 July 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapania, S.; Wang, R.; Li, T.J.J.; Li, T.; Shen, H. ’I’m Categorizing LLM as a Productivity Tool’: Examining Ethics of LLM Use in HCI Research Practices. Proc. ACM Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2025, 9, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Tao, M.; Fang, R.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Y.E.; Zhou, W. AI PERSONA: Towards Life-long Personalization of LLMs. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.13103. [Google Scholar]
- The Enneagram Institute. 2024. Available online: https://www.enneagraminstitute.com/ (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- Bai, S.; Zhu, T.; Cheng, L. Big-Five Personality Prediction Based on User Behaviors at Social Network Sites. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1204.4809. [Google Scholar]
- Sitaraman, G.; Cock, M.d. Inferring Big 5 Personality from Online Social Networks. Master’s Thesis, University of Washington Libraries, Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, K.; Singh, V.K.; Chakraborty, P.; Sidhardhan, S.K.; Krishna, B.S.; Dash, C. Analyzing Big-Five Personality Traits of Indian Celebrities Using Online Social Media. Psychol. Stud. 2017, 62, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanatsiou, D.; Sermpezis, P.; Gruda, D.; Kafetsios, K.; Dimitriadis, I.; Vakali, A. My Tweets Bring All the Traits to the Yard: Predicting Personality and Relational Traits in Online Social Networks. ACM Trans. Web 2022, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, T.; Penchev, V. AI Benchmarks and Datasets for LLM Evaluation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.01020. [Google Scholar]
- Vardhan, H. Top 10 LLM Models. 2024. Available online: https://medium.com/@harsh.vardhan7695/top-10-llms-model-e4d8c2c440bd (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Hendrycks, D.; Burns, C.; Basart, S.; Zou, A.; Mazeika, M.; Song, D.; Steinhardt, J. Measuring Massive Multitask Language Understanding. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2009.03300. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, P.; Mai, Y.; Somerville, J.; Kaiyom, F.; Lee, T.; Bommasani, R. Helm Lite V1.0.0: Lightweight and Broad Capabilities Evaluation. 2023. Available online: https://crfm.stanford.edu/2023/12/19/helm-lite.html (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Wu, Y.; Mei, J.; Yan, M.; Li, C.; Lai, S.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, M.; Jin, Q.; et al. WritingBench: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Generative Writing. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.05244. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhang, G.; Ni, Y.; Chandra, A.; Guo, S.; Ren, W.; Arulraj, A.; He, X.; Jiang, Z.; et al. MMLU-Pro: A More Robust and Challenging Multi-Task Language Understanding Benchmark. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.01574. [Google Scholar]
- Stanford. A Holistic Framework for Evaluating Foundation Models. Holistic Evaluation of Language Models (HELM), Center for Research on Foundation Models. 2024. Available online: https://crfm.stanford.edu/helm/lite/latest/ (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Sorokovikova, A.; Fedorova, N.; Rezagholi, S.; Yamshchikov, I.P. LLMs Simulate Big Five Personality Traits: Further Evidence. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.01765. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, I.; Giulianelli, M. LLM Agents in Interaction: Measuring Personality Consistency and Linguistic Alignment in Interacting Populations of Large Language Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.02896. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, J.Y.; Xu, T.; Chatterjee, I.; Passarella-Ward, K.; Kulshrestha, A.; Shin, D. Steerable Chatbots: Personalizing LLMs with Preference-Based Activation Steering. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.04260. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, R.; Li, X.; Akella, A.; Konstan, J.A. Multi-Prompting Scenario-based Movie Recommendation with Large Language Models: Real User Case Study. In Proceedings of the Extended Abstracts of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Yokohama, Japan, 26 April–1 May 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Z.Y.; Pandey, S.; Schrum, M.L.; Dragan, A. Context Steering: Controllable Personalization at Inference Time. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2405.01768. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, K.; Zeng, Y. Do LLMs Possess a Personality? Making the MBTI Test an Amazing Evaluation for Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.16180. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, X.; Cao, X.; Breazeal, C.; Roy, D.; Kabbara, J. PersonaLLM: Investigating the Ability of Large Language Models to Express Personality Traits. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: NAACL 2024, Mexico City, Mexico, 16–21 June 2024; pp. 3605–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinkert, L.J.; Buongiorno, S.; Clark, C. Evaluating the Efficacy of LLMs to Emulate Realistic Human Personalities. In Proceedings of the Twentieth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Interactive Digital Entertainment, Lexington, KY, USA, 18–22 November 2024; Volume 20, pp. 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Cava, L.; Tagarelli, A. Open Models, Closed Minds? On Agents Capabilities in Mimicking Human Personalities through Open Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, 25 February–4 March 2025; Volume 39, pp. 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenAI. Hello gpt-4o. 2024. Available online: https://openai.com/index/hello-gpt-4o (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- OpenAI. API Platform. 2025. Available online: https://openai.com/api (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- DeepSeek. DeepSeek. 2025. Available online: https://www.deepseek.com/ (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- NOUS RESEARCH. Hermes 3. 2024. Available online: https://nousresearch.com/hermes3/ (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Farabet, C. Introducing Gemma 3: The Most Capable Model You Can Run on a Single GPU or TPU. 2025. Available online: https://blog.google/technology/developers/gemma-3/ (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Ollama. Llama 3.3. 2025. Available online: https://ollama.com/library/llama3.3 (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Anthropic. Meet Claude: Anthropic. 2025. Available online: https://www.anthropic.com/claude (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Lambda. Lambda Cloud API Documentation. 2025. Available online: https://cloud.lambda.ai/api/v1/docs#overview–response-types-and-formats (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Ollama. Python & JavaScript Libraries · Ollama Blog. 2024. Available online: https://ollama.com/blog/python-javascript-libraries (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Anthropic. Getting Started. 2025. Available online: https://docs.anthropic.com/en/api/getting-started (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Tao, Y.; Viberg, O.; Baker, R.S.; Kizilcec, R.F. Cultural bias and cultural alignment of large language models. PNAS Nexus 2024, 3, pgae346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helt, A. What’s Your Writing Personality Type? 2018. Available online: https://rootedinwriting.com/writing-personality/ (accessed on 15 May 2025).

| Model | Parameters | MMLU Pro [36] | HELM [37] | Writing Bench [35] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-4.5 | N/A | 0.861 | Unscored | Unscored |
| GPT-4o | N/A | 87.2 | 0.779 | 8.16 |
| DeepSeek R1 | 671B | 0.84 | Unscored | 8.55 |
| Gemma 3 | 27B | 0.675 | Unscored | Unscored |
| Hermes 3 | 405B | Unscored | Unscored | Unscored |
| Llama 4 | 400B | 0.6592 | 0.812 | 7.01 |
| Claude 3 Opus | N/A | 0.6845 | 0.683 | Unscored |
| Big Five Trait | Vector 1 | Vector 2 | Vector 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conscientiousness | High | High | Neutral |
| Agreeableness | High | Low | Neutral |
| Neuroticism | Low | High | Neutral |
| Extraversion | Low | Low | Neutral |
| Openness to Experience | Low | High | Neutral |
| Model | Query Method |
|---|---|
| GPT-4.5 | OpenAI API |
| GPT-4o | OpenAI API |
| DeepSeek R1 | Lambda API |
| Gemma 3 | Ollama Python Library |
| Hermes 3 | Lambda API |
| Llama 3 | Ollama Python Library |
| Claude 3 Opus | Anthropic API |
| Model | C | A | N | O | E | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepSeek R1 | 46.46 | 48.48 | 50.51 | 37.37 | 31.31 | 42.83 |
| Gemma 3-27b | 37.37 | 51.52 | 54.55 | 35.35 | 18.18 | 39.39 |
| GPT-4.5 | 49.49 | 49.49 | 49.49 | 47.47 | 33.33 | 45.86 |
| GPT-4o | 48.48 | 49.49 | 44.44 | 43.43 | 24.24 | 42.02 |
| Claude 3 Opus | 48.48 | 50.51 | 50.51 | 50.51 | 33.33 | 46.67 |
| Hermes Hermes 3-405b | 49.49 | 50.51 | 35.35 | 45.45 | 23.23 | 40.81 |
| Llama 4-Maverick | 48.48 | 48.48 | 39.39 | 42.42 | 36.36 | 43.03 |
| Average by Trait | 47.18 | 49.78 | 46.61 | 43.14 | 29.72 | 42.94 |
| Model | Parameter Count | Overall Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| DeepSeek R1 | 671B | 42.83 |
| Gemma 3 | 27B | 39.39 |
| GPT-4.5 | Proprietary | 45.86 |
| GPT-4o | Proprietary | 42.02 |
| Claude 3 Opus | Proprietary | 46.67 |
| Hermes 3 | 405B | 40.81 |
| Llama 4-Maverick | 400B | 43.03 |
| Model | Conscient. | Agreeab. | Neurotic. | Openness | Extrav. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | |
| DeepSeek R1 | 40 | 95 | 45 | 95 | 10 | 75 | 20 | 90 | 20 | 85 |
| Gemma 3-27b | 25 | 92 | 30 | 95 | 15 | 85 | 30 | 85 | 20 | 75 |
| GPT-4.5 | 45 | 95 | 40 | 95 | 12 | 85 | 25 | 95 | 20 | 85 |
| GPT-4o | 45 | 90 | 40 | 95 | 10 | 75 | 20 | 95 | 10 | 80 |
| Claude Opus | 60 | 90 | 30 | 95 | 20 | 75 | 20 | 90 | 20 | 80 |
| Hermes 3-405b | 50 | 90 | 30 | 95 | 20 | 80 | 25 | 95 | 20 | 80 |
| Llama 4-Maverick | 35 | 85 | 40 | 90 | 25 | 70 | 30 | 90 | 35 | 90 |
| Trait | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| Conscientiousness | 0.479115 |
| Agreeableness | 0.484029 |
| Neuroticism | 0.488943 |
| Openness to Experience | 0.452088 |
| Extraversion | 0.432432 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kolenbrander, J.; Michaels, A.J. Personality Emulation Utilizing Large Language Models. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6636. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126636
Kolenbrander J, Michaels AJ. Personality Emulation Utilizing Large Language Models. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(12):6636. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126636
Chicago/Turabian StyleKolenbrander, Jack, and Alan J. Michaels. 2025. "Personality Emulation Utilizing Large Language Models" Applied Sciences 15, no. 12: 6636. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126636
APA StyleKolenbrander, J., & Michaels, A. J. (2025). Personality Emulation Utilizing Large Language Models. Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6636. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126636







