Analysis of Sushi Rice: Preparation Techniques, Physicochemical Properties and Quality Attributes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Initial Characterization of Sushi Rice
2.2. Investigating the Sushi Rice Production Process
2.2.1. Washing and Soaking Sushi Rice
2.2.2. Cooking, Seasoning and Rice Formation
2.3. Shelf-Life Examination of Cooked Sushi Rice
2.3.1. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
2.3.2. Sensory Evaluation
2.3.3. Microbiological Analysis
2.3.4. Colour Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
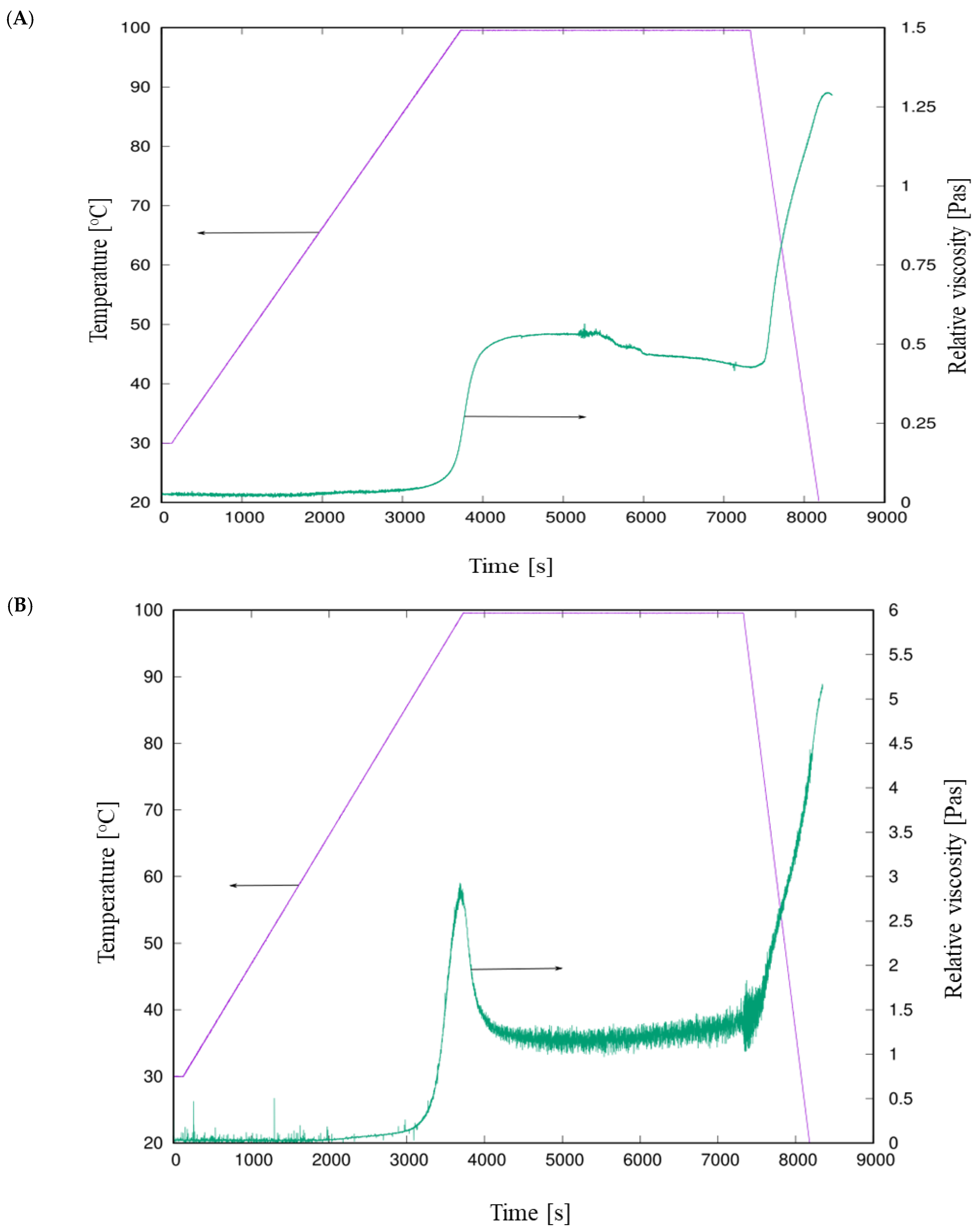
3.1. Initial Characterization of Sushi Rice
3.2. Investigating the Sushi Rice Production Process
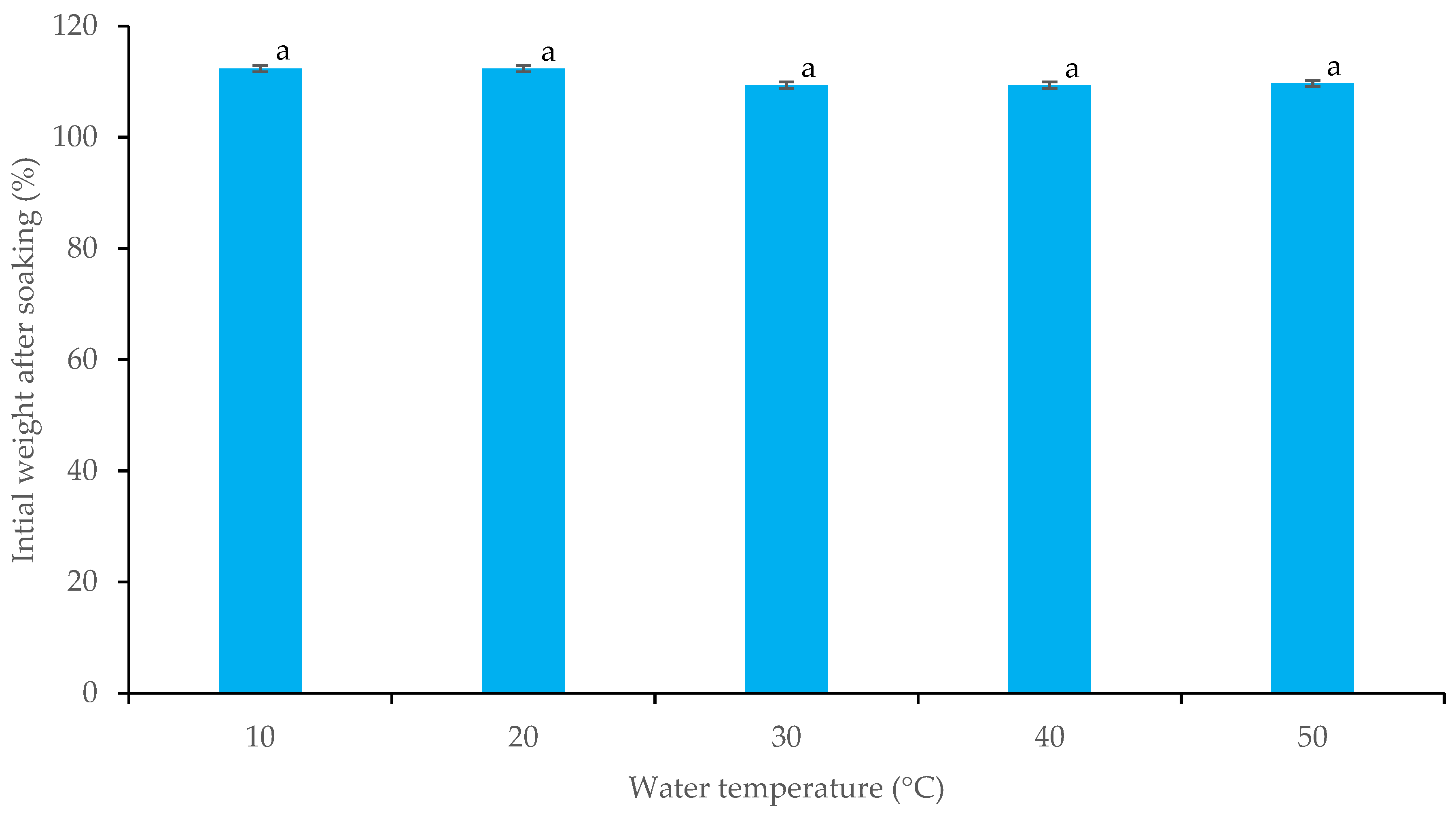
3.2.1. Washing and Soaking Sushi Rice
3.2.2. Seasoning
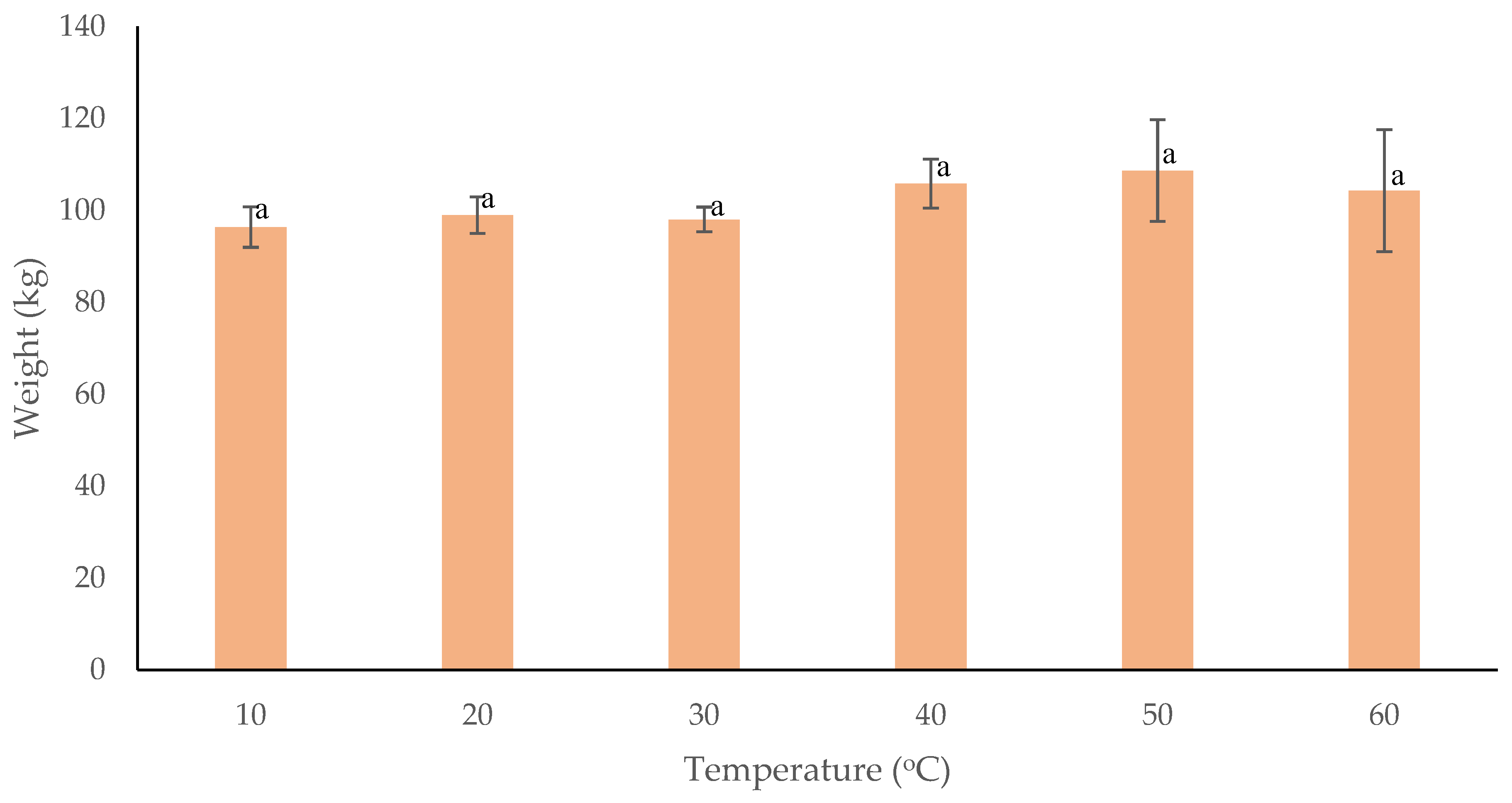
3.2.3. Nigiri Ball Weight at Different Temperatures
3.3. Shelf-Life Study of Cooked Sushi Rice
3.3.1. TPA
Different Washing Time on TPA
Different Water-to-Rice Ratio on TPA
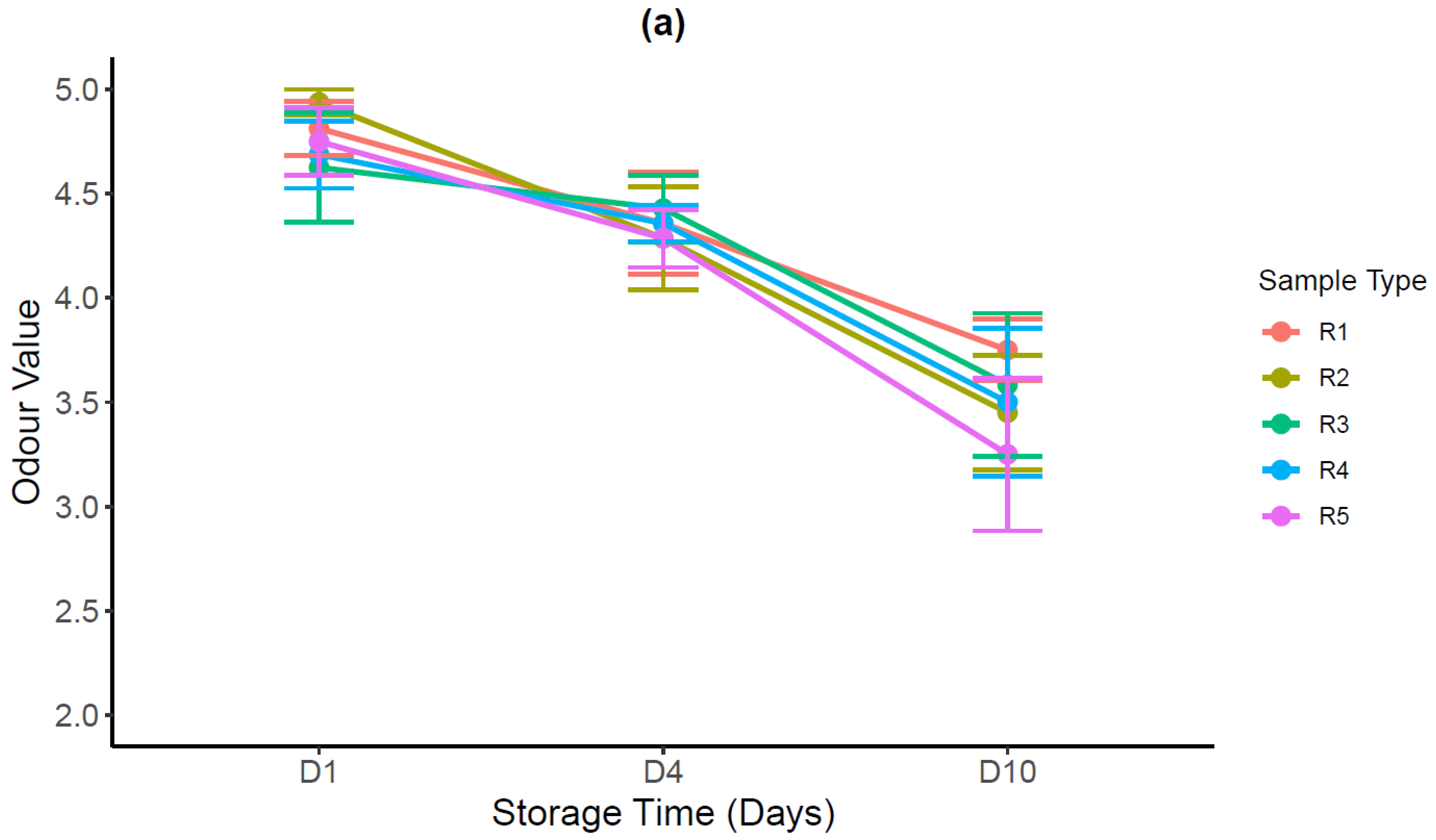
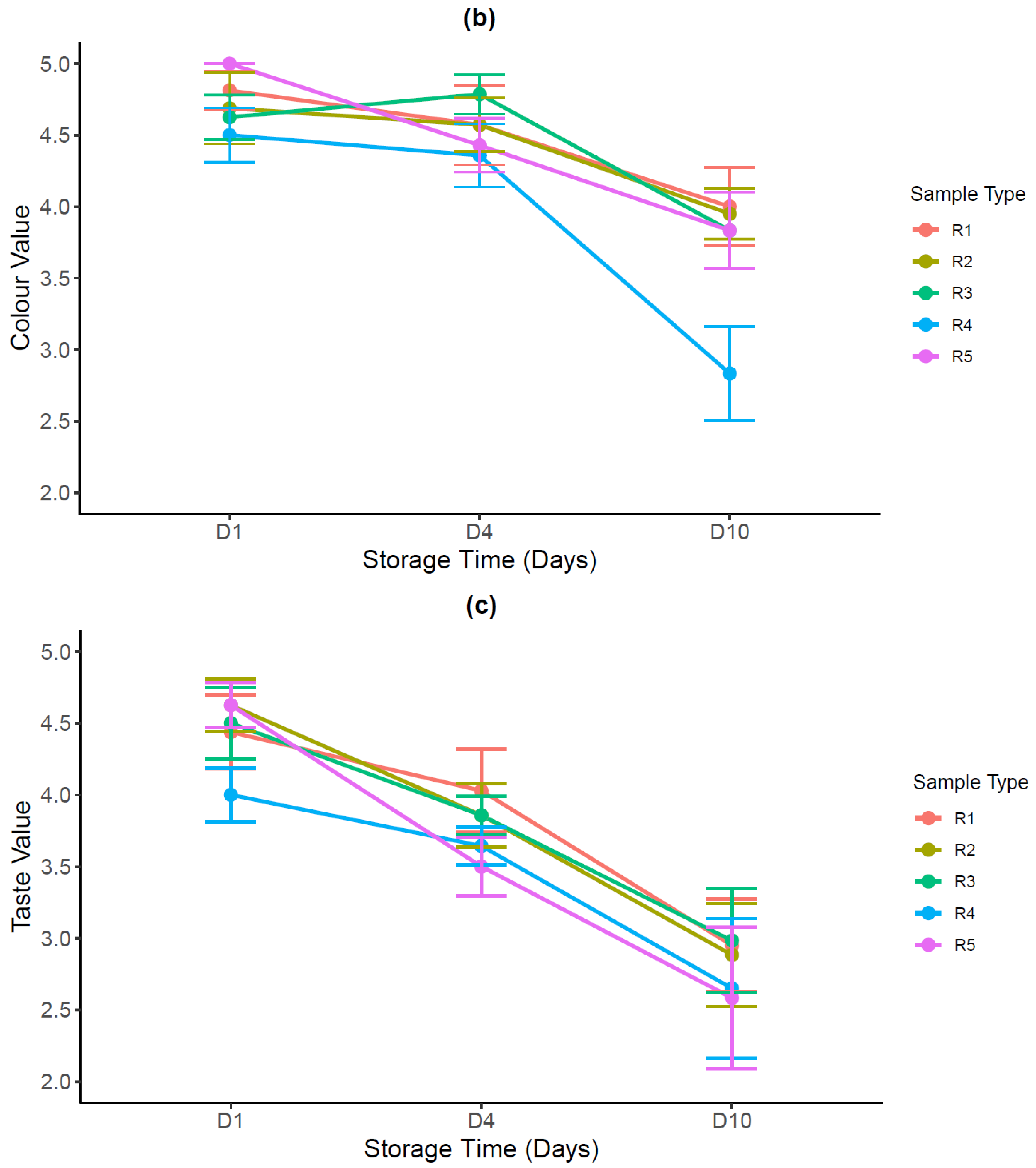
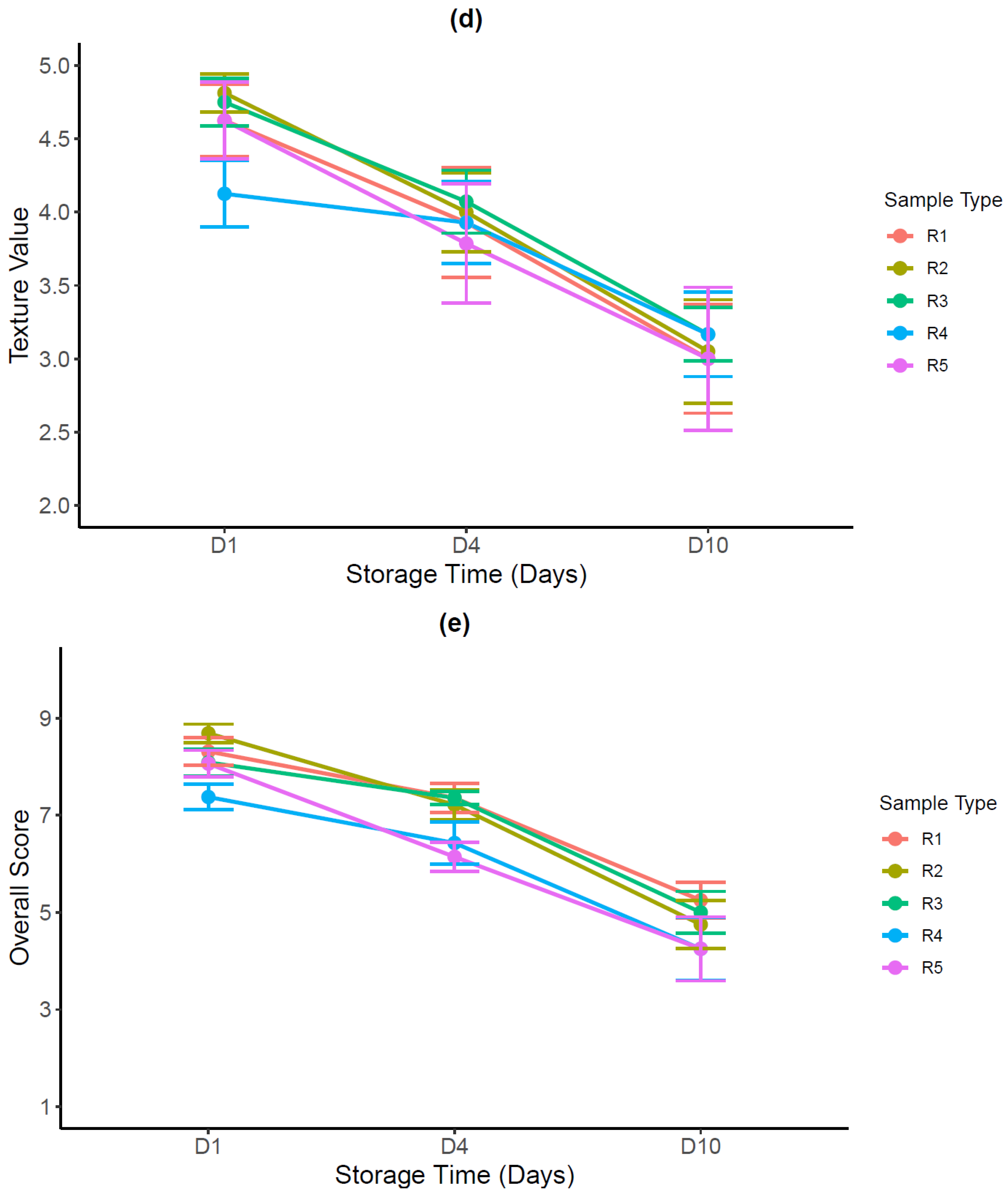
3.3.2. Sensory Evaluation
3.3.3. Microbiological and Colour Analysis
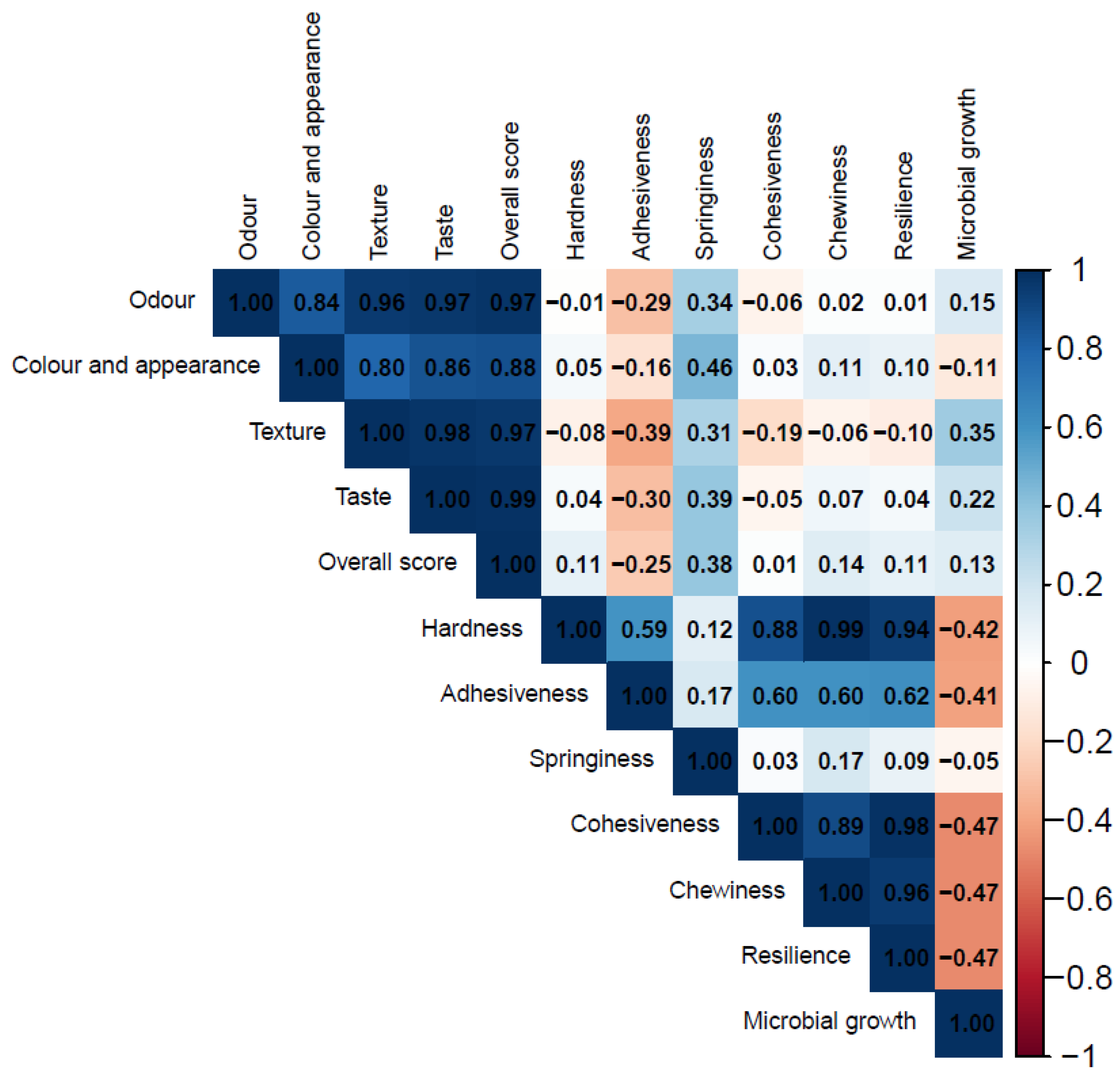
3.3.4. Pearson Correlation
4. Conclusions and Future Prospects of Sushi Rice Production
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altintzoglou, T.; Heide, M.; Wien, A.H.; Honkanen, P. Traditional sushi for modern consumers: A comparison between sushi consumption behavior in Japan and Norway. J. Food Prod. Mark. 2016, 22, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulawik, P.; Dordević, D. Sushi processing: Microbiological hazards and the use of emerging technologies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1270–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Lee, J.; Oh, S.; Yoon, M.; Choi, I.; Park, J.; Chung, H.; Cho, M.; Lee, J.; Kim, C. Quality characteristics of rice varieties suitable for sushi. Korean J. Crop Sci./Hanguk Jakmul Hakhoe Chi 2012, 57, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebishy, E.; Buchanan, D.; Rice, J.; Oyeyinka, S. Variation in amylose content in three rice variants predominantly influences sushi rice. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 4545–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.-Y.; Rico, C.W.; Lee, S.-C. Physicochemical properties of eight popular glutinous rice varieties in Korea. Plant Prod. Sci. 2010, 13, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadele, W.; Kulawik, P.; Szymkowiak, A.; Jambrak, A.R.; Ozogul, Y.; Ozogul, F. Cold-Storage Preservation of Cooked Rice Quality: Exploring Challenges and Strategies, Featuring Insights on Sushi Rice. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, C.J. Rice end-use quality analysis. In Rice: Chemistry and Technology; AACC International: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2019; pp. 273–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Prakash, S.; Nicholson, T.M.; Fitzgerald, M.A.; Gilbert, R.G. The importance of amylose and amylopectin fine structure for textural properties of cooked rice grains. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champagne, E.T.; Bett-Garber, K.L.; Fitzgerald, M.A.; Grimm, C.C.; Lea, J.; Ohtsubo, K.I.; Jongdee, S.; Xie, L.; Bassinello, P.Z.; Resurreccion, A.; et al. Important sensory properties differentiating premium rice varieties. Rice 2010, 3, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.P.; Kumar, D.; Dalbhagat, C.G.; Mishra, H.N. A Comprehensive Review on Instant rice: Preparation Methodology, Characterization, and Quality Attributes. Food Chem. Adv. 2024, 4, 100581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Turner, M.S.; Fitzgerald, M.; Stokes, J.R.; Witt, T. Review of the effects of different processing technologies on cooked and convenience rice quality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 59, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wu, G.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Qian, H.; Qi, X. Effect of soaking and cooking on structure formation of cooked rice through thermal properties, dynamic viscoelasticity, and enzyme activity. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xie, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Jin, Z. Effect of different pressure-soaking treatments on color, texture, morphology and retrogradation properties of cooked rice. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 55, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, D.; Bal, S. Cooking quality and instrumental textural attributes of cooked rice for different milling fractions. J. Food Eng. 2006, 73, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altheide, M.; Morawicki, R.; Hager, T. Impact of milling and water-to-rice ratio on cooked rice and wastewater properties. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2012, 18, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, M. Quantitative instrumental assessment of cooked rice stickiness. Food Eng. Rev. 2020, 12, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; OkAWA, Y.; Ninomiya, K.; Kumagai, H.; Kumagai, H. Evaluation and suppression of retrogradation of gelatinized rice starch. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2019, 65, S134–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Yu, W.; Prakash, S.; Gilbert, R.G. Investigating cooked rice textural properties by instrumental measurements. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2020, 9, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Ma, Y.; Sun, D.-W. Impact of amylose content on starch retrogradation and texture of cooked milled rice during storage. J. Cereal Sci. 2009, 50, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bett-Garber, K.L.; Champagne, E.T.; Ingram, D.A.; McClung, A.M. Influence of water-to-rice ratio on cooked rice flavor and texture. Cereal Chem. 2007, 84, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avaro, M.R.A.; Pan, Z.; Yoshida, T.; Wada, Y. Two alternative methods to predict amylose content of rice grain by using tristimulus CIE lab values and developing a specific color board of starch-iodine complex solution. Plant Prod. Sci. 2011, 14, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, R.; Holmes, W.; Orgeron, C.; McIntyre, C.; Hernandez, R.; Revellame, E.D. Rapid estimation of parameters for gelatinization of waxy corn starch. Foods 2019, 8, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Liu, C.; Jiang, S.; Cao, J.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. Functional properties of glutinous rice flour by dry-heat treatment. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 4833-1:2013; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Microorganisms—Part 1: Colony Count at 30 °C by the Pour Plate Technique. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- Kim, H.-S.; Patel, B.; BeMiller, J.N. Effects of the amylose–amylopectin ratio on starch–hydrocolloid interactions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 1438–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, E.-H.; Lee, S.-J.; Hong, J.-Y.; Chung, H.-J.; Lee, Y.-T.; Kang, B.-S.; Lim, S.-T. Correlation between physicochemical properties of japonica and indica rice starches. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, P.; Yu, J.; Guo, P.; Wang, S. Multi-scale structures and functional properties of starches from Indica hybrid, Japonica and waxy rice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Li, M.; Fang, C.; Yu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Shao, Y. Effects of storage on the starch fine structure and physicochemical properties of different rice variety types. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 300, 120273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Li, S.; Pan, D.; Wang, K.; Qiu, M.; Qiu, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J. The variation of rice quality and relevant starch structure during long-term storage. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varavinit, S.; Shobsngob, S.; Varanyanond, W.; Chinachoti, P.; Naivikul, O. Effect of amylose content on gelatinization, retrogradation and pasting properties of flours from different cultivars of Thai rice. Starch-Stärke 2003, 55, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, L.; Shao, K.; Gu, M.; Liu, Q. Toward underlying reasons for rice starches having low viscosity and high amylose: Physiochemical and structural characteristics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 1543–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashaninejad, M.; Maghsoudlou, Y.; Rafiee, S.; Khomeiri, M. Study of hydration kinetics and density changes of rice (Tarom Mahali) during hydrothermal processing. J. Food Eng. 2007, 79, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.; Oh, Y.-G.; Kwak, J.; Chun, A.; Kim, M.-J.; Hyun, W. Water-absorption characteristics and cooked rice texture of milled rice. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 53, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guo, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, F.; Chen, J. Effects of soaking treatment on water distribution of rice grains, starch characteristics and eating quality of wet rice noodles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Lu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, J. Kinetics of water absorption expansion of rice during soaking at different temperatures and correlation analysis upon the influential factors. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, C.N.; Garzón, R.; Rosell, C.M. Unraveling seasonings impact on cooked rice quality: Technological and nutritional implications for sushi. J. Cereal Sci. 2022, 104, 103442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadele, W.; Kulawik, P.; Stępień, A.; Zając, M.; Nowak, N.; Grzebieniarz, W.; Jasińska, J.M.; Vlcko, T.; Szymkowiak, A.; Milosavljević, V. Effects of multilayer Nano/Mini Furcellaran/Chitosan Emulsions with oregano essential oil and bioactive peptides on sensory, physicochemical properties and retrogradation in Sushi in cold storage conditions. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2024, 96, 103767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Lee, K.Y.; Lee, H.G. Effect of different pH conditions on the in vitro digestibility and physicochemical properties of citric acid-treated potato starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.; Li, B.; Tan, H.; Zhang, W.; Zang, Z.; Cui, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Meng, X. The effect of pH on the chemical and structural interactions between apple polyphenol and starch derived from rice and maize. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 5026–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, C.; Copeland, L.; Niu, Q.; Wang, S. Starch Retrogradation: A Comprehensive Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 568–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, R.; Inaguma, C.; Kawai, K. Effects of maltotriose syrup, water content, and pH on the retrogradation of cooked rice in chilled storage. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2022, 16, 2510–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestra, F. Empirical and Fundamental Mechanical Tests in the Evaluation of Dough and Bread Rheological Properties; Alma Mater Studiorum—Università di bologna: Bologna, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, J.; Gao, M.; Wang, J.; Sun, B. Washing rice before cooking has no large effect on the texture of cooked rice. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasert, W.; Suwannaporn, P. Optimization of instant jasmine rice process and its physicochemical properties. J. Food Eng. 2009, 95, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Yu, W.; Liu, H.; Li, C. Importance of both leached and residual starch molecular structures in determining cooked rice texture at different rice-to-water cooking ratios. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258, 129040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulawik, P.; Jamróz, E.; Zając, M.; Guzik, P.; Tkaczewska, J. The effect of furcellaran-gelatin edible coatings with green and pu-erh tea extracts on the microbiological, physicochemical and sensory changes of salmon sushi stored at 4 C. Food Control 2019, 100, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
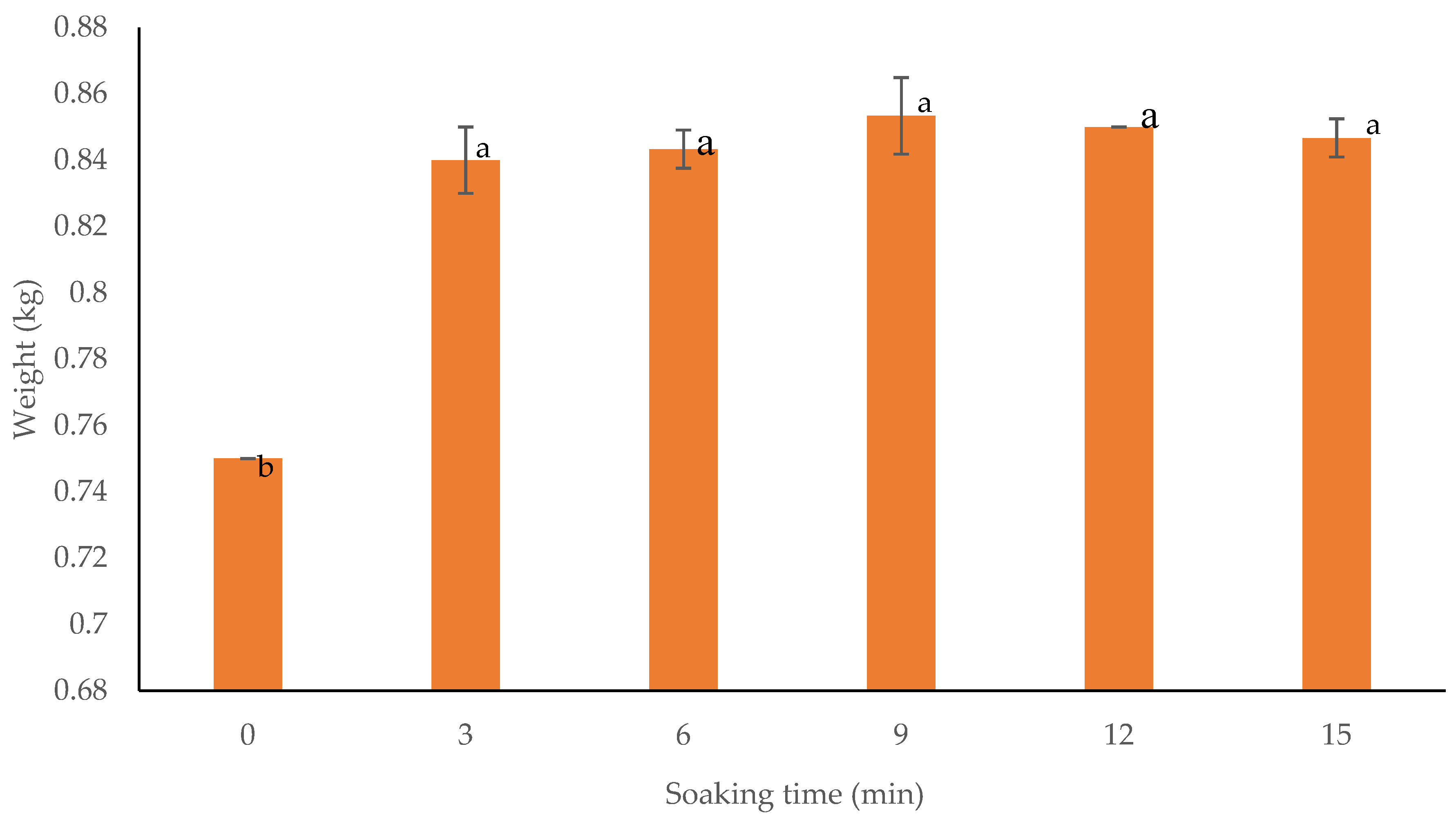
| Ingredient | Mix 1 | Mix 2 | Mix 3 | Mix 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice vinegar | 52 | 64 | 76 | 40 | |
| Sugar | 42 | 31 | 21 | 52 | |
| Salt | 6 | 5 | 3 | 8 | |
| Rice composition (2020 harvest) | |||||
| Protein | Fat | Carbohydrate | Ash | Dry weight | Amylose content |
| 6.8 | 0.7 | 78.3 | 0.8 | 13.4 | 20.2 ± 0.8 |
| Group | Washing Duration [s] | Initial Weight After Soaking (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 min | CV (%) | 30 min | CV (%) | 45 min | CV (%) | 60 min | CV (%) | 75 min | CV (%) | ||
| W1 | 200 | 112.50 a ± 0.71 | 0.63 | 112.50 a ± 0.71 | 0.63 | 113 a ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 112.50 a ± 0.71 | 0.63 | 112 a ± 0.00 | 0.38 |
| W2 | 230 | 112.50 a ± 0.71 | 0.63 | 113 a ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 112.5 a ± 0.71 | 0.63 | 112.50 a ± 0.71 | 0.63 | 110.50 a ± 2.12 | 0.76 |
| W3 | 260 | 114 b ± 1.41 | 1.24 | 116 c ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 115.5 c ± 0.71 | 0.61 | 115 bc ± 1.41 | 1.23 | 113 b ± 0.00 | 0.62 |
| W4 | 290 | 113.50 b ± 0.71 | 0.63 | 116 c ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 116.5 c ± 2.12 | 1.82 | 114.50 b ± 0.71 | 0.62 | 113.50 b ± 0.71 | 0.74 |
| W5 | 320 | 114 b ± 1.41 | 1.24 | 114.50 bc ± 2.12 | 1.85 | 114 b ± 1.41 | 1.24 | 114.50 b ± 2.12 | 1.85 | 112.50 a ± 0.71 | 1.36 |
| W6 | 350 | 114.50 b ± 2.12 | 1.85 | 116 c ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 116 c ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 114.50 b ± 2.12 | 1.85 | 113.50 b ± 0.71 | 0.86 |
| Amount (g/kg) | Seasoned Rice 1 | Seasoned Rice 2 | Seasoned Rice 3 | Seasoned Rice 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 120 | 4.28 ± 0.01 | 4.22 ± 0.01 | 4.18 ± 0.01 | 4.46 ± 0.10 |
| 180 | 4.16 ± 0.02 | 4.09 ± 0.01 | 4.08 ± 0.01 | 4.33 ± 0.02 |
| Storage Duration (d) | Group | Hardness (N) | CV (%) | Adhesiveness (N·S) | CV (%) | Springiness | CV (%) | Cohesiveness | CV (%) | Chewiness (N) | CV (%) | Resilience | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | W1 | 59.44 def ± 9.28 | 15.61 | −730.1 def ± 8.67 | 1.19 | 0.88 a ± 0.13 | 14.77 | 0.54 a ± 0.07 | 12.96 | 28.35 bcde ± 3.77 | 13.30 | 0.21 a ± 0.02 | 9.52 |
| 4 | 110.00 bc ± 12.56 | 11.42 | −164 bg ± 21.95 | 13.38 | 0.84 a ± 0.02 | 2.38 | 0.43 a ± 0.03 | 6.98 | 40.13 abcd ± 2.56 | 6.38 | 0.21 a ± 0.01 | 4.76 | |
| 6 | 132 ab ± 5.37 | 4.07 | −30.71 ab ± 1.50 | 4.88 | 0.85 a ± 0.09 | 10.58 | 0.51 a ± 0.08 | 15.69 | 50.72 ab ± 5.03 | 9.92 | 0.24 a ± 0.03 | 12.50 | |
| 1 | W2 | 13.96 g ± 0.35 | 2.51 | −658.5 cd ± 33.44 | 5.08 | 0.93 a ± 0.08 | 8.60 | 0.57 a ± 0.10 | 17.54 | 21.91 bcde ± 3.69 | 16.84 | 0.22 a ± 0.03 | 13.64 |
| 4 | 39.95 efg ± 5.66 | 14.17 | −51.05 cde ± 5.10 | 9.99 | 0.50 a ± 0.04 | 8.00 | 0.57 a ± 0.05 | 8.77 | 11.89 e ± 2.07 | 17.40 | 0.26 a ± 0.03 | 11.54 | |
| 6 | 129.50 ab ± 5.65 | 4.36 | −132.99 ef ± 15.67 | 11.78 | 0.81 a ± 0.04 | 4.94 | 0.51 a ± 0.10 | 19.61 | 50.23 abc ± 1.73 | 3.44 | 0.24 a ± 0.04 | 16.67 | |
| 1 | W3 | 31.65 fg ± 5.78 | 18.26 | −653.40 cd ± 20.91 | 3.20 | 0.85 a ± 0.02 | 2.35 | 0.53 a ± 0.08 | 15.09 | 16.19 e ± 2.13 | 13.15 | 0.20 a ± 0.03 | 15.00 |
| 4 | 59.48 def ± 9.32 | 15.67 | −134.10 ef ± 17.02 | 12.69 | 0.67 a ± 0.12 | 17.91 | 0.47 a ± 0.02 | 4.26 | 21.22 bcde ± 2.27 | 10.69 | 0.22 a ± 0.02 | 9.09 | |
| 6 | 166.20 a ± 13.56 | 8.16 | −77.94 c ± 7.96 | 10.21 | 0.86 a ± 0.14 | 16.28 | 0.44 a ± 0.03 | 6.82 | 46.73 abc ± 8.13 | 17.39 | 0.26 a ± 0.05 | 19.23 | |
| 1 | W4 | 54.35 def ± 6.02 | 11.07 | −645.32 cd ± 36.93 | 5.72 | 0.76 a ± 0.15 | 19.74 | 0.54 a ± 0.08 | 14.81 | 19.40 de ± 2.96 | 15.26 | 0.20 a ± 0.02 | 10.00 |
| 4 | 76.60 de ± 11.00 | 14.37 | −109.74 c ± 12.52 | 11.41 | 0.63 a ± 0.09 | 14.28 | 0.50 a ± 0.03 | 6.00 | 29.32 bcde ± 2.67 | 9.11 | 0.23 a ± 0.02 | 8.70 | |
| 6 | 146.10 ab ± 8.00 | 5.47 | −21.06 ab ± 3.73 | 17.71 | 0.83 a ± 0.04 | 4.82 | 0.53 a ± 0.09 | 16.98 | 55.11 ab ± 6.10 | 11.07 | 0.25 a ± 0.03 | 12.00 | |
| 1 | W5 | 35.54 fg ± 6.55 | 18.43 | −649.8 cd ± 25.50 | 3.92 | 0.85 a ± 0.11 | 12.94 | 0.56 a ± 0.09 | 16.07 | 12.09 e ± 1.51 | 12.48 | 0.21 a ± 0.02 | 9.52 |
| 4 | 69.50 def ± 12.80 | 18.42 | −94.62 c ± 8.42 | 8.89 | 0.64 a ± 0.07 | 10.94 | 0.49 a ± 0.04 | 8.16 | 20.19 bcde ± 3.40 | 16.84 | 0.23 a ± 0.02 | 8.70 | |
| 6 | 155.30 a ± 9.40 | 6.05 | −19.85 a ± 3.89 | 19.59 | 0.70 a ± 0.12 | 17.14 | 0.52 a ± 0.10 | 19.23 | 57.18 a ± 2.52 | 4.41 | 0.25 a ± 0.03 | 12.00 | |
| 1 | W6 | 72.48 cd ± 9.40 | 12.96 | −654.20 cd ± 41.48 | 1.19 | 0.93 a ± 0.06 | 6.45 | 0.48 a ± 0.05 | 10.42 | 23.93 cde ± 2.73 | 11.40 | 0.18 a ± 0.01 | 5.56 |
| 4 | 27.11 fg ± 4.90 | 18.07 | −54.11 cde ± 1.11 | 2.05 | 0.58 a ± 0.06 | 10.34 | 0.59 a ± 0.11 | 18.64 | 12.95 e ± 2.28 | 17.60 | 0.23 a ± 0.04 | 17.39 | |
| 6 | 139.90 ab ± 12.36 | 8.83 | −38.41 ab ± 3.78 | 9.84 | 0.93 a ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.54 a ± 0.08 | 14.81 | 57.62 a ± 4.01 | 6.96 | 0.24 a ± 0.04 | 16.67 |
| Storage Duration (d) | Group | Hardness (N) | CV (%) | Adhesiveness (N·S) | CV (%) | Springiness | CV (%) | Cohesiveness | CV (%) | Chewiness (N) | CV (%) | Resilience | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | R1 | 406.30 cd ± 15.13 | 3.72 | −369.30 a ± 70.25 | 19.03 | 0.99 a ± 0.02 | 2.02 | 0.27 ab ± 0.01 | 3.70 | 109.50 b ± 6.56 | 5.99 | 0.14 abcd ± 0.01 | 7.14 |
| 4 | 538.90 a ± 23.85 | 4.43 | −718.80 c ± 14.44 | 2.01 | 0.99 a ± 0.02 | 2.02 | 0.30 ab ± 0.02 | 6.67 | 155.40 a ± 14.19 | 9.13 | 0.16 ab ± 0.01 | 6.25 | |
| 10 | 538.10 a ± 27.73 | 5.16 | −532.10 b ± 73.50 | 13.81 | 1.00 a ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.29 ab ± 0.02 | 6.90 | 152.90 a ± 13.52 | 8.84 | 0.14 abcd ± 0.02 | 14.30 | |
| 1 | R2 | 411.30 c ± 19.49 | 4.74 | −1650 j ± 30.44 | 1.84 | 0.99 a ± 0.01 | 1.01 | 0.25 b ± 0.02 | 8.00 | 100.60 bc ± 10.67 | 10.61 | 0.12 abcd ± 0.01 | 8.33 |
| 4 | 265.40 b ± 19.55 | 7.37 | −913.10 d ± 58.51 | 6.41 | 1.00 a ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.29 ab ± 0.02 | 6.90 | 138.10 a ± 7.68 | 5.56 | 0.15 abc ± 0.01 | 6.25 | |
| 10 | 415.30 c ± 11.09 | 2.67 | −948.70 de ± 39.37 | 4.15 | 0.99 a ± 0.02 | 2.02 | 0.29 ab ± 0.05 | 17.24 | 117.20 b ± 10.20 | 8.71 | 0.14 abcd ± 0.02 | 14.30 | |
| 1 | R3 | 301.20 fg ± 11.18 | 3.71 | −1341 hi ± 27.12 | 2.02 | 0.99 a ± 0.02 | 2.02 | 0.22 b ± 0.01 | 4.55 | 63.88 ef ± 1.73 | 2.71 | 0.09 bcd ± 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 4 | 325.40 ef ± 29.41 | 9.04 | −1127 fg ± 5.16 | 0.46 | 1.00 a ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.23 b ± 0.01 | 4.35 | 74.76 de ± 5.53 | 7.40 | 0.11 bcd ± 0.01 | 9.10 | |
| 10 | 365 de ± 15.48 | 4.24 | −669.60 bc ± 27.26 | 4.07 | 1.00 a ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.23 b ± 0.02 | 8.70 | 85.32 cd ± 8.83 | 10.35 | 0.11 bcd ± 0.01 | 9.10 | |
| 1 | R4 | 225.60 h ± 19.14 | 8.48 | −1292 gh ± 39.87 | 3.09 | 1.03 a ± 0.06 | 5.83 | 0.22 b ± 0.02 | 9.09 | 50.07 fg ± 3.79 | 7.57 | 0.09 bcd ± 0.01 | 11.11 |
| 4 | 265.40 gh ± 15.71 | 5.92 | −1155 fg ± 25.10 | 2.17 | 1.00 a ± 0.01 | 1.00 | 0.20 b ± 0.01 | 5.00 | 51.85 f ± 4.21 | 8.12 | 0.08 bcd ± 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 10 | 276 g ± 17.29 | 6.26 | −1122 f ± 54.31 | 4.84 | 0.99 a ± 0.01 | 1.01 | 0.20 b ± 0.01 | 5.00 | 54.32 fg ± 4.10 | 7.55 | 0.08 bcd ± 0.01 | 12.50 | |
| 1 | R5 | 167.30 i ± 13.64 | 8.15 | −1474 i ± 11.18 | 0.76 | 0.99 a ± 0.02 | 2.02 | 0.20 b ± 0.01 | 5.00 | 32.36 gh ± 3.41 | 10.54 | 0.08 bcd ± 0.01 | 12.50 |
| 4 | 169.20 i ± 12.20 | 7.21 | −1117 ef ± 13.98 | 1.25 | 0.99 a ± 0.03 | 3.03 | 0.17 b ± 0.01 | 5.88 | 27.75 h ± 2.37 | 8.54 | 0.06 bcd ± 0.01 | 16.67 | |
| 10 | 161.60 i ± 12.82 | 7.93 | −1228 fgh ± 47.98 | 3.91 | 0.99 a ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.16 b ± 0.01 | 6.25 | 25.28 h ± 1.28 | 5.06 | 0.05 d ± 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Storage Time (d) | Group | Microbial Growth (log CFU/g) | CV (%) | L* | CV (%) | a* | CV (%) | b* | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | R1 | 1.20 ab ± 0.34 | 28.33 | 62.35 bcd ± 1.70 | 2.73 | −1.54 abc ± 0.12 | 7.79 | 1.64 abc ± 0.74 | 45.12 |
| 4 | 0.66 b ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 63.49 abc ± 1.40 | 2.21 | −1.56 abc ± 0.13 | 8.33 | 2.07 ab ± 0.61 | 29.47 | |
| 10 | 0.66 b ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 60.92 d ± 4.78 | 7.85 | −1.44 a ± 0.11 | 7.64 | 1.85 abc ± 0.69 | 37.30 | |
| 1 | R2 | 1.12 ab ± 0.41 | 36.61 | 63.38 abc ± 1.82 | 2.87 | −1.62 c ± 0.14 | 8.64 | 1.64 abc ± 0.5 | 30.49 |
| 4 | 0.92 ab ± 0.24 | 26.09 | 62.73 abcd ± 2.05 | 3.27 | −1.59 bc ± 0.16 | 10.06 | 2.12 ab ± 0.62 | 29.25 | |
| 10 | 0.92 ab ± 0.24 | 26.09 | 64.54 ab ± 0.89 | 1.38 | −1.47 ab ± 0.10 | 6.80 | 2.16 a ± 0.65 | 30.09 | |
| 1 | R3 | 1.24 ab ± 0.63 | 50.81 | 62.98 abcd ± 1.23 | 1.95 | −1.55 abc ± 0.12 | 7.74 | 1.24 c ± 0.44 | 35.48 |
| 4 | 0.66 b ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 63.64 abc ± 1.37 | 2.15 | −1.55 abc ± 0.07 | 4.52 | 1.83 abc ± 0.64 | 34.97 | |
| 10 | 0.9 ab ± 0.34 | 37.78 | 64.36 abc ± 1.47 | 2.28 | −1.47 ab ± 0.12 | 8.16 | 1.82 abc ± 0.47 | 25.82 | |
| 1 | R4 | 0.96 ab ± 0.43 | 44.79 | 62.73 abcd ± 1.09 | 1.74 | −1.53 abc ± 0.10 | 6.54 | 1.45 bc ± 0.32 | 22.07 |
| 4 | 1.33 ab ± 0.92 | 69.17 | 62.67 abcd ± 1.96 | 3.13 | −1.52 abc ± 0.17 | 11.18 | 1.76 abc ± 0.72 | 40.91 | |
| 10 | 1.52 ab ± 1.22 | 80.26 | 64.71 a ± 1.53 | 2.36 | −1.45 a ± 0.07 | 4.83 | 1.73 abc ± 0.48 | 27.75 | |
| 1 | R5 | 1.20 ab ± 0.76 | 63.33 | 62.17 cd ± 0.80 | 1.29 | −1.5 abc ± 0.10 | 6.67 | 1.84 abc ± 0.74 | 40.22 |
| 4 | 0.98 ab ± 0.55 | 56.12 | 63.48 abc ± 1.21 | 1.91 | −1.47 ab ± 0.07 | 4.76 | 1.74 abc ± 0.77 | 44.25 | |
| 10 | 1.13 ab ± 0.67 | 59.29 | 63.51 abc ± 2.58 | 4.06 | −1.46 a ± 0.07 | 4.79 | 1.71 abc ± 0.50 | 29.24 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wonbebo, W.T.; Kulawik, P.; Szymkowiak, A.; Tadesse, E.E. Analysis of Sushi Rice: Preparation Techniques, Physicochemical Properties and Quality Attributes. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6540. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126540
Wonbebo WT, Kulawik P, Szymkowiak A, Tadesse EE. Analysis of Sushi Rice: Preparation Techniques, Physicochemical Properties and Quality Attributes. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(12):6540. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126540
Chicago/Turabian StyleWonbebo, Wondyfraw Tadele, Piotr Kulawik, Andrzej Szymkowiak, and Eskindir Endalew Tadesse. 2025. "Analysis of Sushi Rice: Preparation Techniques, Physicochemical Properties and Quality Attributes" Applied Sciences 15, no. 12: 6540. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126540
APA StyleWonbebo, W. T., Kulawik, P., Szymkowiak, A., & Tadesse, E. E. (2025). Analysis of Sushi Rice: Preparation Techniques, Physicochemical Properties and Quality Attributes. Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6540. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126540







