Aspen Plus Simulation of a Sorption-Enhanced Steam Methane Reforming Process in a Fluidized Bed Reactor Using CaO as a Sorbent for CO2 Capture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modeling
3. Results
3.1. Comparison Between FluidBed and RGibbs Aspen Reactors
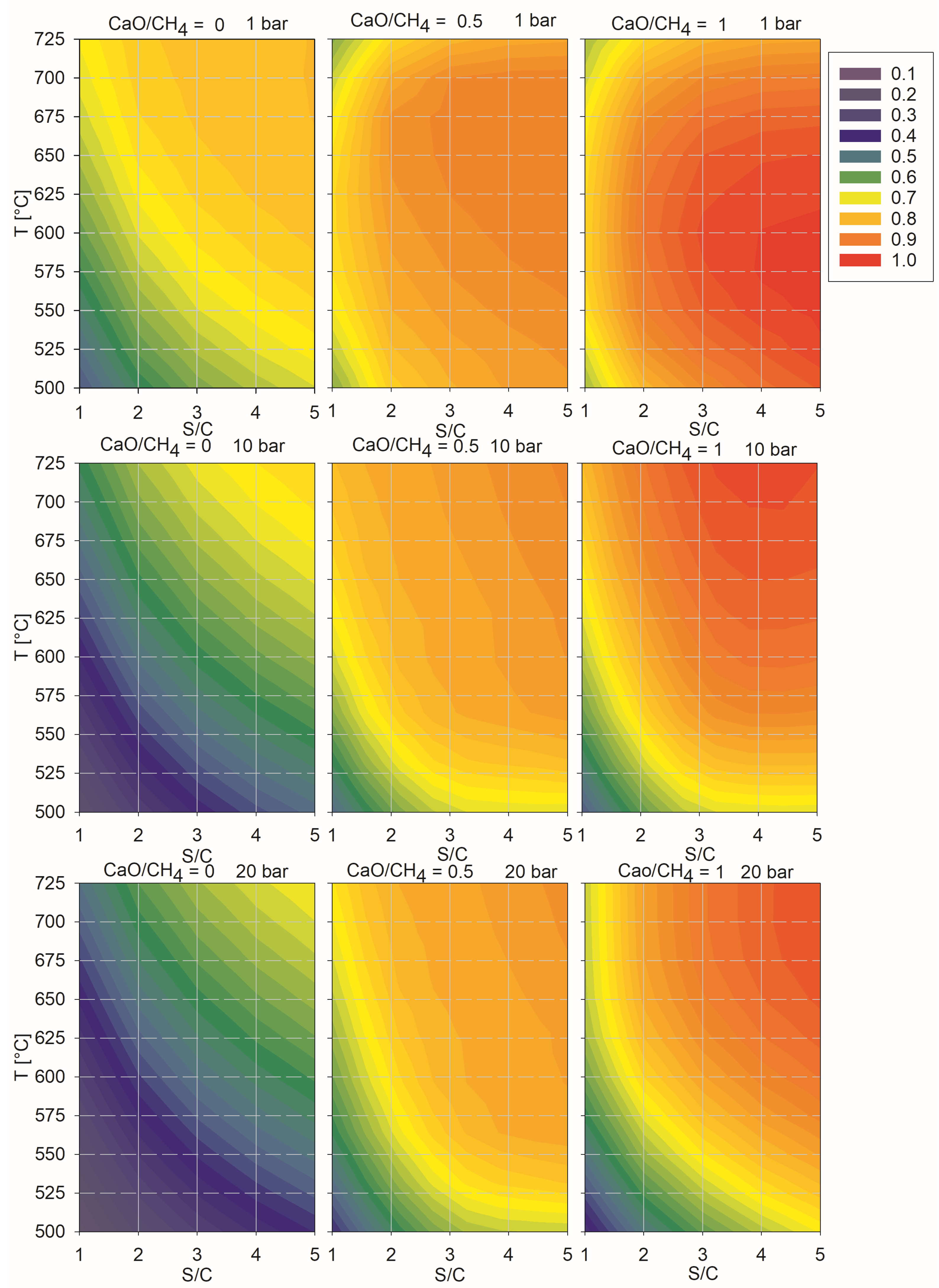
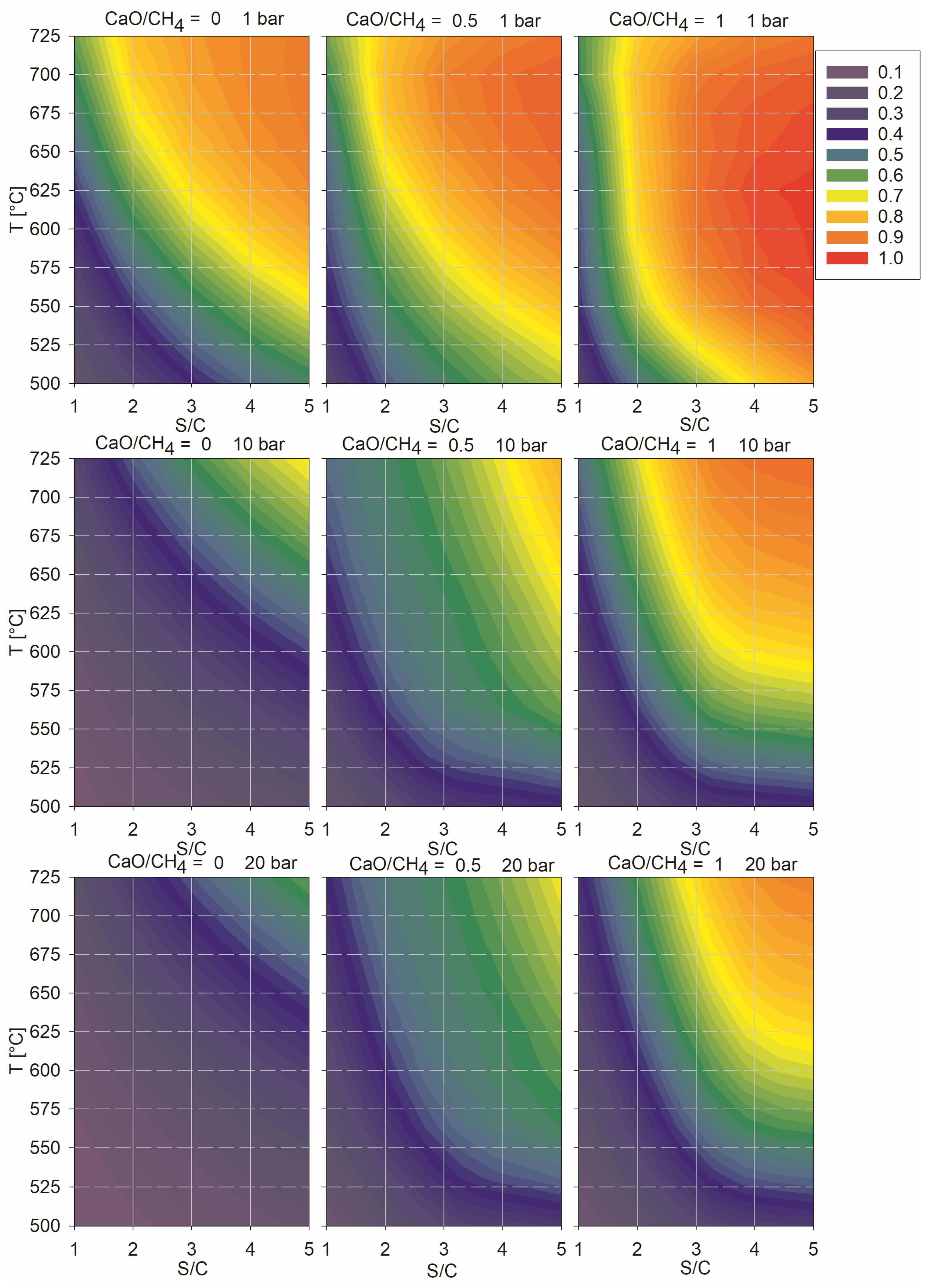
3.2. SMR vs. SE-SMR: Sensitivity Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soltani, S.M.; Lahiri, A.; Bahzadb, H.; Cloughd, P.; Gorbounova, M.; Yan, Y. Sorption-enhanced Steam Methane Reforming for Combined CO2 Capture and Hydrogen Production: A State-of-the-Art Review. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2021, 1, 100003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udemu, C.; Font-Palma, C. Modelling of sorption-enhanced steam reforming (SE-SR) process in fluidised bed reactors for low-carbon hydrogen production: A review. Fuel 2023, 340, 127588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdin, Z.; Zafaranloo, A.; Rafiee, A.; Mérida, W.; Lipiński, W.; Khalilpour, K.R. Hydrogen as an energy vector. Renew. Sust. Energy. Rev. 2020, 120, 109620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA-International Energy Agency. Global Hydrogen Review 2024-Analysis. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/global-hydrogen-review-2024 (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Patel, G.H.; Havukainen, J.; Horttanainen, M.; Soukka, R.; Tuomaala, M. Climate change performance of hydrogen production based on life cycle assessment. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 992–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katebah, M.; Al-Rawashdeh, M.; Linke, P. Analysis of hydrogen production costs in Steam-Methane Reforming considering integration with electrolysis and CO2 capture. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2022, 10, 100552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antzaras, A.N.; Lemonidou, A.A. Recent advances on materials and processes for intensified production of blue hydrogen. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2022, 155, 111917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluud, W.; Keller, K.; Schonfelder, R.; Klempt, W. Production of Hydrogen. U.S. Patent No. US1816523A, 28 July 1931. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Manovic, V.; Anthony, E.J.; Clough, P.T. Techno-economic analysis of low-carbon hydrogen production by sorption enhanced steam methane reforming (SE-SMR) processes. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 226, 113530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherbański, R.; Molga, E. Sorption-enhanced steam-methane reforming with simultaneous sequestration of CO2 on fly ashes—Proof of concept and simulations for gas-solid-solid trickle flow reactor. Chem. Eng. Process Process Intensif. 2018, 124, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Lario, A.L.; Grasa, G.S.; Murillo, R. Performance of a combined CaO-based sorbent and catalyst on H2 production, via sorption enhanced methane steam reforming. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloisi, I.; Di Giuliano, A.; Di Carlo, A.; Foscolo, P.U.; Courson, C.; Gallucci, K. Sorption enhanced catalytic Steam Methane Reforming: Experimental data and simulations describing the behaviour of bi-functional particles. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 314, 570–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arstad, B.; Prostak, J.; Blom, R. Continuous hydrogen production by sorption enhanced steam methane reforming (SE-SMR) in a circulating fluidized bed reactor: Sorbent to catalyst ratio dependencies. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 189, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildenbrand, N.; Readman, J.; Dahl, I.M.; Blom, R. Sorbent enhanced steam reforming (SESR) of methane using dolomite as internal carbon dioxide absorbent: Limitations due to Ca(OH)2 formation. Appl. Catal. A 2006, 303, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, K.; Ryu, H.J.; Grace, J.R.; Lim, C.J. Sorption-enhanced steam reforming of methane in a fluidized bed reactor with dolomite as CO2-acceptor. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazi, S.S.; Aranda, A.; Meyer, J.; Mastin, J. High performance CaO-based sorbents for pre- and postcombustion CO2 capture at high temperature. Energy Procedia 2014, 63, 2207–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, I.; Grasa, G.; Meyer, J.; Di Felice, L.; Kazi, S.; Sanz, C.; Maury, D.; Voisin, C. Performance and operating limits of a sorbent-catalyst system for sorption-enhanced reforming (SER) in a fluidized bed reactor. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 205, 94105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranfield University. Available online: https://www.cranfield.ac.uk/press/news-2024/69-million-boost-for-hydrogen-at-cranfield (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- IFE Hynor Hydrogen Technology Center. Available online: https://ife.no/en/laboratory/ife-hynor-hydrogen-technology-center-ife-hynor/ (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- OSTI.GOV U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific and Technical Information. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/biblio/2335475 (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Dou, B.; Wang, C.; Song, Y.; Chen, H.; Jiang, B.; Yang, M. Solid sorbents for in–situ CO2 removal during sorption–enhanced steam reforming process: A review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2016, 53, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancheshmeh, M.S.; Radfarnia, H.R.; Iliuta, M.C. High temperature CO2 sorbents and their application for hydrogen pro-duction by sorption enhanced steam reforming process. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 420–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giuliano, A.; Giancaterino, F.; Courson, C.; Foscolo, P.U.; Gallucci, K. Development of a Ni-CaO-mayenite combined sorbent-catalyst material for multicycle sorption enhanced steam methane reforming. Fuel 2018, 234, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Felice, L.; Kazi, S.S.; Sørby, M.H.; Martinez, I.; Grasa, G.; Maury, D. Combined sorbent and catalyst material for sorption enhanced reforming of methane under cyclic regeneration in presence of H2O and CO2. Fuel Process. Technol. 2019, 183, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Froment, G.F. Methane steam reforming, methanation and water-gas shift: I. Intrinsic kinetics. AIChE J. 1989, 35, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S.K.; Perlmutter, D.D. Effect of the product layer on the kinetics of the CO2-lime reaction. AIChE J. 1983, 29, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, E.H. 87. The calcium oxide–carbon dioxide system in the pressure range 1–300 atmospheres. J. Chem. Soc. 1962, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, D.; Abanades, J.C. Determination of the critical product layer thickness in the reaction of CaO with CO2. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 5608–5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasa, G.S.; Abanades, J.C. CO2 capture capacity of CaO in long series of carbonation/calcination cycles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 8846–8851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasa, G.S.; Abanades, J.C.; Alonso, M.; González, B. Reactivity of highly cycled particles of CaO in a carbonation/calcination loop. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 137, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, T. Evaluation of the Effect of CaO on Hydrogen Production by Sorption-Enhanced Steam Methane Reforming. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 5330–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carapellucci, R.; Giordano, L. Steam, dry and autothermal methane reforming for hydrogen production: A thermodynamic equilibrium analysis. J. Power Sources 2020, 469, 228391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| To ⇒ | SMR 10 bar | SMR 20 bar | SE-SMR 1 Bar CaO/CH4 = 0.5 | SE-SMR 1 Bar CaO/CH4 = 1 | SE-SMR 10 Bar CaO/CH4 = 0.5 | SE-SMR 10 Bar CaO/CH4 = 1 | SE-SMR 20 Bar CaO/CH4 = 0.5 | SE-SMR 20 Bar CaO/CH4 = 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| From ⇓ | |||||||||
| SMR 1 bar | yH2→−16% X→−44% η→−41% | yH2→−24% X→−56% η→−54% | yH2→+14% X→+2% η→+7% | yH2→+25% X→+8% η→+15% | yH2→+9% X→−31% η→−24% | yH2→+20% X→−14% η→−4% | yH2→+7% X→−38% η→−31% | yH2→+16% X→−24% η→−15% | |
| SMR 10 bar | yH2→−10% X→−23% η→−22% | yH2→+36% X→+85% η→+83% | yH2→+50% X→+91% η→+94% | yH2→+30% X→+24% η→+31% | yH2→+44% X→+54% η→+65% | yH2→+28% X→+11% η→+18% | yH2→+39% X→+38% η→+48% | ||
| SMR 20 bar | yH2→+51% X→+140% η→+136% | yH2→+67% X→+149% η→+150% | yH2→+44% X→+61% η→+68% | yH2→+60% X→+101% η→+112% | yH2→+42% X→+45% η→+52% | yH2→+54% X→+80% η→+90% | |||
| SE-SMR 1 bar CaO/CH4 = 0.5 | yH2→+9% X→+5% η→+10% | yH2→−4% X→−32% η→−28% | yH2→+6% X→−16% η→−10% | yH2→−6% X→−39% η→−35% | yH2→+2% X→−25% η→−20% | ||||
| SE-SMR 1 bar CaO/CH4 = 1 | yH2→−13% X→−36% η→−34% | yH2→−3% X→−20% η→−17% | yH2→−15% X→−43% η→−41% | yH2→−7% X→−28% η→−25% | |||||
| SE-SMR 10 bar CaO/CH4 = 0.5 | yH2→+10% X→+24% η→+25% | yH2→−2% X→−10% η→−9% | yH2→+6% X→+10% η→+12% | ||||||
| SE-SMR 10 bar CaO/CH4 = 1 | yH2→−11% X→−27% η→−27% | yH2→−4% X→−11% η→−11% | |||||||
| SE-SMR 20 bar CaO/CH4 = 0.5 | yH2→+8% X→+22% η→+23% | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Massa, F.; Scala, F.; Coppola, A. Aspen Plus Simulation of a Sorption-Enhanced Steam Methane Reforming Process in a Fluidized Bed Reactor Using CaO as a Sorbent for CO2 Capture. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6535. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126535
Massa F, Scala F, Coppola A. Aspen Plus Simulation of a Sorption-Enhanced Steam Methane Reforming Process in a Fluidized Bed Reactor Using CaO as a Sorbent for CO2 Capture. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(12):6535. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126535
Chicago/Turabian StyleMassa, Fiorella, Fabrizio Scala, and Antonio Coppola. 2025. "Aspen Plus Simulation of a Sorption-Enhanced Steam Methane Reforming Process in a Fluidized Bed Reactor Using CaO as a Sorbent for CO2 Capture" Applied Sciences 15, no. 12: 6535. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126535
APA StyleMassa, F., Scala, F., & Coppola, A. (2025). Aspen Plus Simulation of a Sorption-Enhanced Steam Methane Reforming Process in a Fluidized Bed Reactor Using CaO as a Sorbent for CO2 Capture. Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6535. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126535








